Tetrafluoroboric Acid Digestion for Accurate Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Fly Ash by ICP-MS Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method Development and Materials
2.1. Field Sites and Samples
2.2. Preparation of Tetrafluoroboric Acid (HBF4) Solution
2.3. Microwave Acid Digestion
2.4. ICP-MS Instrumentation for REE Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Recovery of REE Concentrations in Standard Reference Materials
3.2. REE Concentrations of Coal and Fly Ash from SW USA
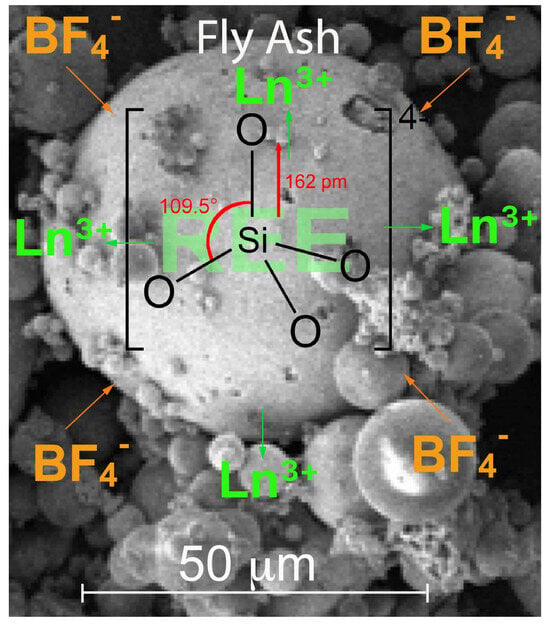
3.3. Supply of Fluoride through BF4− for Dissolution of Silicates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, K.R.; Van Gosen, B.S.; Foley, N.K.; Cordier, D. The Principal Rare Earth Elements Deposits of theUnited States—A Summary of Domestic Deposits and a Global Perspective, in U.S. Geological Survey, reston, Virginia, Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5220; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Orris, G.J.; Grauch, R.I. Rare Earth Element Mines, Deposits, Occurrences; US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey: Burlington, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-H. Analysis of Rare Earth Elements in Water and Sediments, in Encyclopedia of Water: Science, Technology, Society P. Maurice, Editor; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Franus; Wiatros-Motyka, M.M.; Widowin, M. Coal fly ash as a source for rare earth elements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.S.; Dennen, K.O. The National Coal Resource Assessment Overview, in USGS Professional Paper 1625-F; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009; p. 402.
- Bryan, R.C.; Richers, D.; Andersen, H.T. Assessment of Rare Earth Elemental Contents in Select United States Coal Basins; Leonardo Technologies: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Folkedahl, B.; Nyberg, C.; Biswas, S.; Zheng, X. Round-Robin Interlaboratory Study on Rare-Earth Elements in U.S.-Based Geologic Materials. Minerals 2023, 13, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Kenneth N. Characteristics of Precipitation of Rare Earth Elements with Various Precipitants. Minerals 2020, 10, 178.
- Tarnopolskaia, M.E.; Bychkov, A.Y.; Shvarov, Y.V.; Popova, Y.A. Experimental Study of Fluorite Solubility in Acidic Solutions as a Method for Boron Fluoride Complexes Studying. Geochem. Int. 2017, 55, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Makishima, A.; Nakamura, E. Formation and suppression of AlF3 during HF digestion of rock samples in Teflon bomb for precise trace element analyses by ICP-MS and ID-TIMS. Proc. Jpn. Acad. 2001, 77, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, R.K.; Hower, J.C.; Dwyer, G.S.; Hsu-Kim, H. Trends in the Rare Earth Element Content of U. S.-Based Coal Combustion Fly Ashes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lichte, F.E.; Meier, A.L.; Grock, J.G. Determination of the Rare-Earth Elements in Geological Materials by Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1987, 59, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Hower, J.C.; Zhang, W.; Luo, G.; Hu, H.; Yao, H. A review of rare earth elements and yttrium in coal ash: Content, modes of occurrences, combustion behavior, extraction methods. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 88, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, ASTM UOP407-09: Trace Metals in Organics by Dry Ashing—ICP-OES. Available online: https://www.astm.org/uop407-09.html (accessed on 1 July 2009).
- Akinyele, I.; Shokunbi, O. Comparative analysis of dry ashing and wet digestion methods for the determination of trace and heavy metals in food samples. Food Chem. 2014, 173, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, T.; Roth, E.; Tinker, P.; Granite, E. Analysis of Rare Earth Elements in Geologic Samples using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry; U.S. Department of Energy: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016; p. 10.
- Javed, M.B.; Grant-Weaver, I.; Shotyk, W. An optimized HNO3 and HBF4 digestion method for multielemental soil and sediment analysis using inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 100, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, A.; Krachler, M.; Scholz, C.; Cheburkin, A.K.; Shotyk, W. Analytical procedures for the determination of selected major (Al, Ca, Fe, K, Mg, Na, Ti) and trace (Li, Mn, Sr, Zn) elements in peat and plant samples using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 540, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; Mohl, C.; Emons, H.; Shotyk, W. Analytical procedures for the determination of selected trace elements in peat and plant samples by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2002, 57, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachler, M.; MOhl, C.; Emons, H.; Shotyk, W. Influence of digestion procedures on the determination of rare earth elements in peat and plant samples by USN-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2002, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, F.J. Descriptions and Analyses of Eight New USGS Rock Standards. In Geological Survey Professional Paper 840; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, G.K. Uses of Fly Ash from New Mexico Coals. New Mex. Geol. 2000, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RPB. Not All “Fluoro” Is the Same. Available online: https://rbpchemical.com/2023/01/not-all-fluoro-is-the-same/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Watkins, R.T.; Ridley, M.K.; Pougnet, M.; Willis, J.P. Determination of rare-earth elements in coal using microwave digestion and gradient ion chromatography. Chem. Geol. 1995, 121, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-X.; Zhu, Z.-W.; Yin, X.-F.; Han, B.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.-T.; Wang, X.-R. Analysis of Contents and Distribution Patterns of Rare Earth Elements in the Surface Sediments of the South Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Fast preconcentration of trace rare earth elements from environmental samples by di(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid grafted magnetic nanoparticles followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2017, 136, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telgmann, L.; Lindner, U.; Lingott, J.; Jakubowski, N. Analysis and Speciation of Lanthanoides by ICP-MS, in Fundamentals of ICP-MS; Alfred, G., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH: Berlin/Boston, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Longerich, H.; Fryer, B.; Strong, D.; Kantipuly, C. Effects of operating conditions on the determination of the rare earth elements by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Spectrochim. Acta 1987, 42, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, N.M.; Huang, L.-S.; Lin, K.-C.; Aggarwal, S.K. Uncertainty propagation through correction methodology for the determination of rare earth elements by quadrupole based inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 530, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seredin, V.V.; Dai, S.; Sun, Y.; Chekryzhov, I.Y. Coal deposits as promising sources of rare metals for alternative power and energy-efficient technologies. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamser, C.A. Hydrolysis of Fluoboric Acid in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1948, 70, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, O.; Sasahira, A.; Kani, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Aoi, M.; Kawamura, F. Solubility of Lanthanide Fluorides in Nitric Acid Solution in the Dissolution Process of FLUOREX Reprocessing System. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2004, 41, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Symbol | Standard Reference Materials, REE Concentration in PPM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIST 1632e, Coal | NIST 1633c, Fly Ash | USGS Agv-1, Andesite | |||
| LREE | Lanthanum | La | 7 * | 87 | 38 |
| Cerium | Ce | 12.24 | 180 * | 67 | |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 1.5 * | - | 7.6 | |
| Neodymium | Nd | 6 * | 87 * | 33 | |
| Samarium | Sm | 1 * | 19 * | 5.9 | |
| Europium | Eu | 0.2457 | 4.67 | 1.64 | |
| HREE | Gadlinium | Gd | 1 * | - | 5 |
| Terbium | Tb | 0.2 * | 3.12 | 0.7 | |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 1 * | 18.7 | 3.6 | |
| Holmium | Ho | 0.2 * | - | 0.67 | |
| Erbium | Er | 0.7 * | - | 1.7 | |
| Thulium | Tm | 0.1 * | - | 0.34 | |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 0.6 * | 7.7 * | 1.72 | |
| Lutetium | Lu | 0.1 * | 1.32 | 0.27 | |
| Site | Sample ID | Material | Location | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SJ-780501 | Coal | San Juan coal mine | 36.801° N, 108.431° W |
| 2 | FC-1 SRMG | Coal | Four corner, Salt River Material Group | 36.686° N, 108.481° W |
| 2 | PFA78480 | Fly ash | San Juan Generating Station | 36.802° N 108.439° W |
| 3 | Escalante E-2 | Bottom ash | Escalante, Plains Electric Generating and Transmission Coop | 35.416° N, 108.083° W |
| 5 | EL Sequndo E-1 | Coal | EL Sequndo mine, owned by Peabody Energy | 35.10° N, 107.51° W |
| 6 | K3-Raton | Coal | Coal mine, Raton, NM | 36.903° N, 104.439° W |
| 6 | ORP R6 | Coal | Coal mine, Raton, NM | 36.903° N, 104.439° W |
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (bar) | Ramp Time (min) | Hold Time (min) | Microwave Power % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 30 | 8 | 10 | 50 |
| 190 | 30 | 8 | 15 | 50 |
| 220 | 30 | 8 | 15 | 50 |
| 50 | 30 | 1 | 5 | 0 |
| 20 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| REEs | Suitable Isotopes | Interference (MO+, MOH+) * | Isobaric Overlap (M+) | Correction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La | 139La (99.91%) | - | - | - | |
| Ce | 140Ce (88.45%) | - | - | - | |
| Pr | 141Pr (100%) | - | Monoisotope | - | |
| Nd | 143Nd (12.18%) | - | - | - | |
| 144Nd (23.8%) | - | 144Sm (3.07%) | −0.204803 * 147Sm | ||
| 146Nd (17.2%) | 130BaO | - | |||
| Sm | 147Sm (14.99%) | 130BaOH | - | - | |
| 152Sm (26.75%) | 136CeO, 136BaO, 135BaOH | 152Gd (0.2%) | −0.012780 * 157Gd | ||
| Eu | 151Eu (47.81%) | 135BaO, 134BaOH | - | ||
| Gd | 157Gd (15.65%) | 141PrO | |||
| 160Gd (21.86%) | 144SmO, 144NdO | 160Dy (2.34%) | −0.093976 * 163Dy | ||
| Tb | 159Tb (100%) | 143NdO | Monoisotope | ||
| Dy | 163Dy (24.90%) | 147SmO | - | ||
| 164Dy (28.18%) | 148SmO, 148NdO | 164Er (1.61%) | −0.047902 * 166Er | ||
| Ho | 165Ho (100%) | 149SmO | Monoisotope | ||
| Er | 166Er (33.61%) | 150SmO, 150NdO | - | ||
| 167Er (22.93%) | 151EuO | - | |||
| 168Er (26.78%) | 152SmO, 152GdO | 168Yb (0.13%) | −0.005955 * 172Yb | ||
| Tm | 169Tm (100%) | 153EuO | Monoisotope | ||
| Yb | 171Yb (14.28%) | 155GdO | |||
| 173Yb (16.13%) | 157GdO | ||||
| 174Yb (31.83%) | 158DyO, 158GdO | 174Hf(0.16%) | −0.192815 * 178Hf | ||
| Lu | 175Lu (97.40%) | 159TbO | - | ||
| Parameters | Conditions |
|---|---|
| RF power, W | 1600 |
| Plasma gas flow (L/min) | 18 |
| Nebulizer gas flow (L/min) | 0.89 |
| Auxiliary gas flow (L/min) | 1.2 |
| Replicates per sample | 3 |
| Mode of Operation | Collision/KED (He gas) |
| REE Calibration Standard (ppb) | 0, 1, 2, 5, 10 |
| Ce2+/Ce (70/140) | ≤0.03 |
| CeO/Ce (156/140) | ≤0.025 |
| Internal standard | Indium |
| Sample Id | Material | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1632e | Coal | This study | 6.59 | 13.41 | 1.57 | 5.87 | 1.22 | 0.29 | 1.37 | 0.20 | 1.21 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.19 | 0.64 | 0.14 |
| NIST | 7.00 | 12.24 | 1.50 | 6.00 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.70 | 0.10 | 0.60 | 0.10 | ||
| 1633c | Fly ash | This study | 79.22 | 177.34 | 21.21 | 87.18 | 19.67 | 4.39 | 21.15 | 3.12 | 17.45 | 3.51 | 10.38 | 1.37 | 8.26 | 1.20 |
| NIST | 87.00 | 180.00 | - | 87.00 | 19.00 | 4.67 | - | 3.12 | 18.70 | - | - | - | 7.70 | 1.32 | ||
| agv-1 | Andesite | This study | 41.01 | 73.15 | 8.74 | 32.97 | 6.33 | 1.83 | 5.77 | 0.92 | 3.86 | 0.71 | 2.08 | 0.27 | 1.84 | 0.26 |
| USGS | 38.00 | 67.00 | 7.60 | 33.00 | 5.90 | 1.64 | 5.00 | 0.70 | 3.60 | 0.67 | 1.70 | 0.34 | 1.72 | 0.27 |
| Sample ID | Material | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFA 78480 | Fly ash | 64.08 | 126.08 | 15.30 | 57.27 | 9.54 | 1.85 | 8.69 | 1.22 | 7.44 | 1.46 | 4.37 | 0.65 | 5.02 | 0.60 |
| Escalante E-2 | Bottom ash | 41.89 | 83.41 | 9.20 | 34.01 | 6.44 | 1.43 | 6.09 | 0.91 | 5.48 | 1.09 | 3.26 | 0.46 | 2.86 | 0.42 |
| K3-Raton | Coal | 22.89 | 47.52 | 4.93 | 17.02 | 3.14 | 0.77 | 2.85 | 0.41 | 2.46 | 0.45 | 1.22 | 0.18 | 1.07 | 0.18 |
| ORP R6 | Coal | 29.52 | 34.80 | 3.08 | 11.27 | 1.67 | 0.47 | 2.37 | 0.36 | 2.50 | 0.62 | 1.95 | 0.28 | 1.73 | 0.27 |
| SJ-780501 | Coal | 15.11 | 28.81 | 3.21 | 11.47 | 2.05 | 0.42 | 1.96 | 0.28 | 1.73 | 0.34 | 1.03 | 0.16 | 1.04 | 0.16 |
| FC-1 SRMG | Coal | 13.99 | 25.97 | 2.83 | 10.50 | 1.89 | 0.39 | 1.81 | 0.25 | 1.58 | 0.32 | 0.98 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.14 |
| El Segundo E-1 | Coal | 10.35 | 21.71 | 2.20 | 8.13 | 1.50 | 0.33 | 1.51 | 0.27 | 1.24 | 0.25 | 0.81 | 0.13 | 1.79 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.-H.; WoldeGabriel, G.; Marina, O. Tetrafluoroboric Acid Digestion for Accurate Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Fly Ash by ICP-MS Analysis. Minerals 2024, 14, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010072
Li Z-H, WoldeGabriel G, Marina O. Tetrafluoroboric Acid Digestion for Accurate Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Fly Ash by ICP-MS Analysis. Minerals. 2024; 14(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zheng-Hua, Giday WoldeGabriel, and Oana Marina. 2024. "Tetrafluoroboric Acid Digestion for Accurate Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Fly Ash by ICP-MS Analysis" Minerals 14, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010072
APA StyleLi, Z.-H., WoldeGabriel, G., & Marina, O. (2024). Tetrafluoroboric Acid Digestion for Accurate Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Coal and Fly Ash by ICP-MS Analysis. Minerals, 14(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14010072