Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Lidocaine by Non-Fibrous Raw Mg-Clays: The Role of Composition and Texture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Mg-Clays
Structural and Physicochemical Characterization of Raw Mg-Clays
2.2. Adsorbates
2.3. Adsorption Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
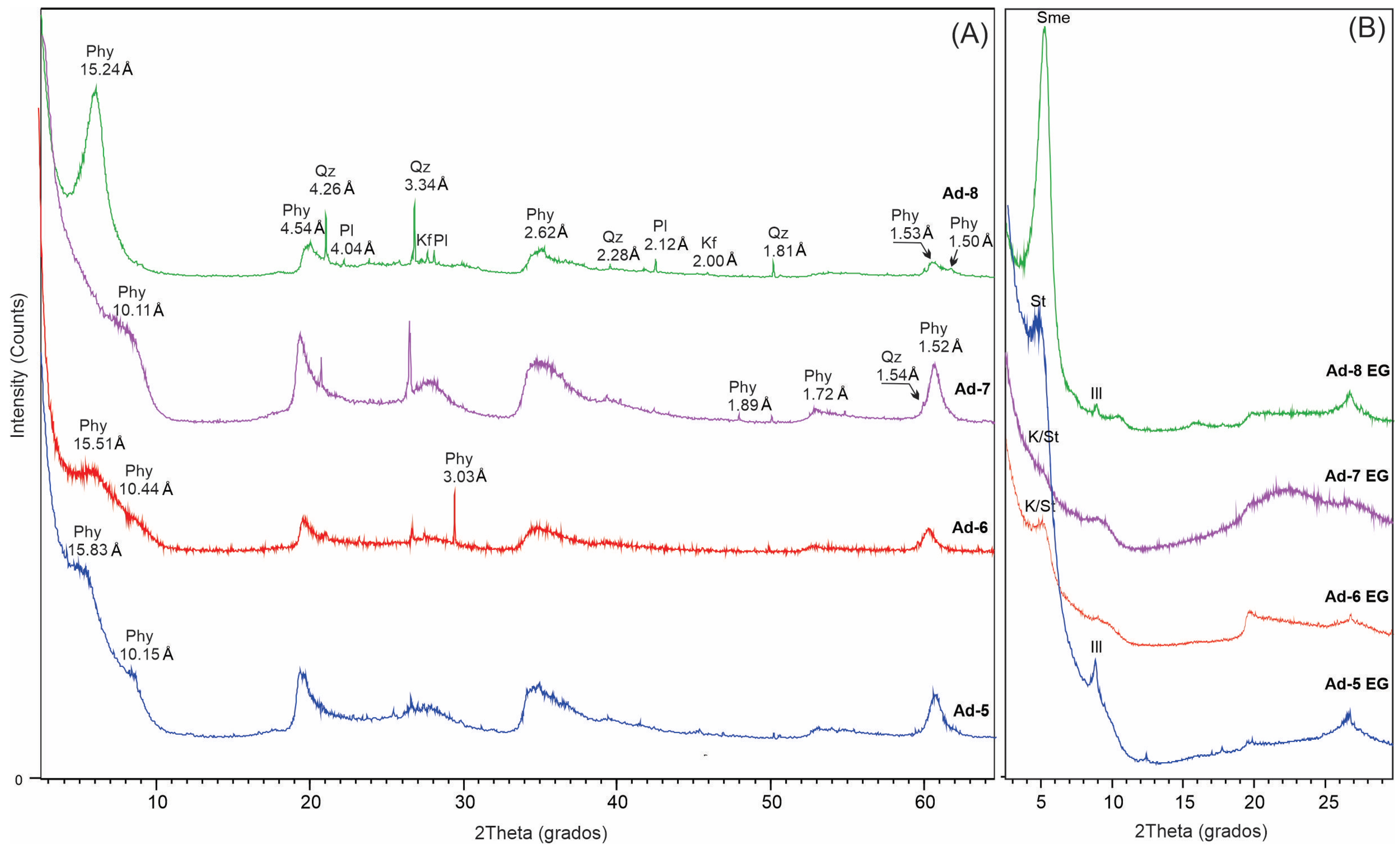
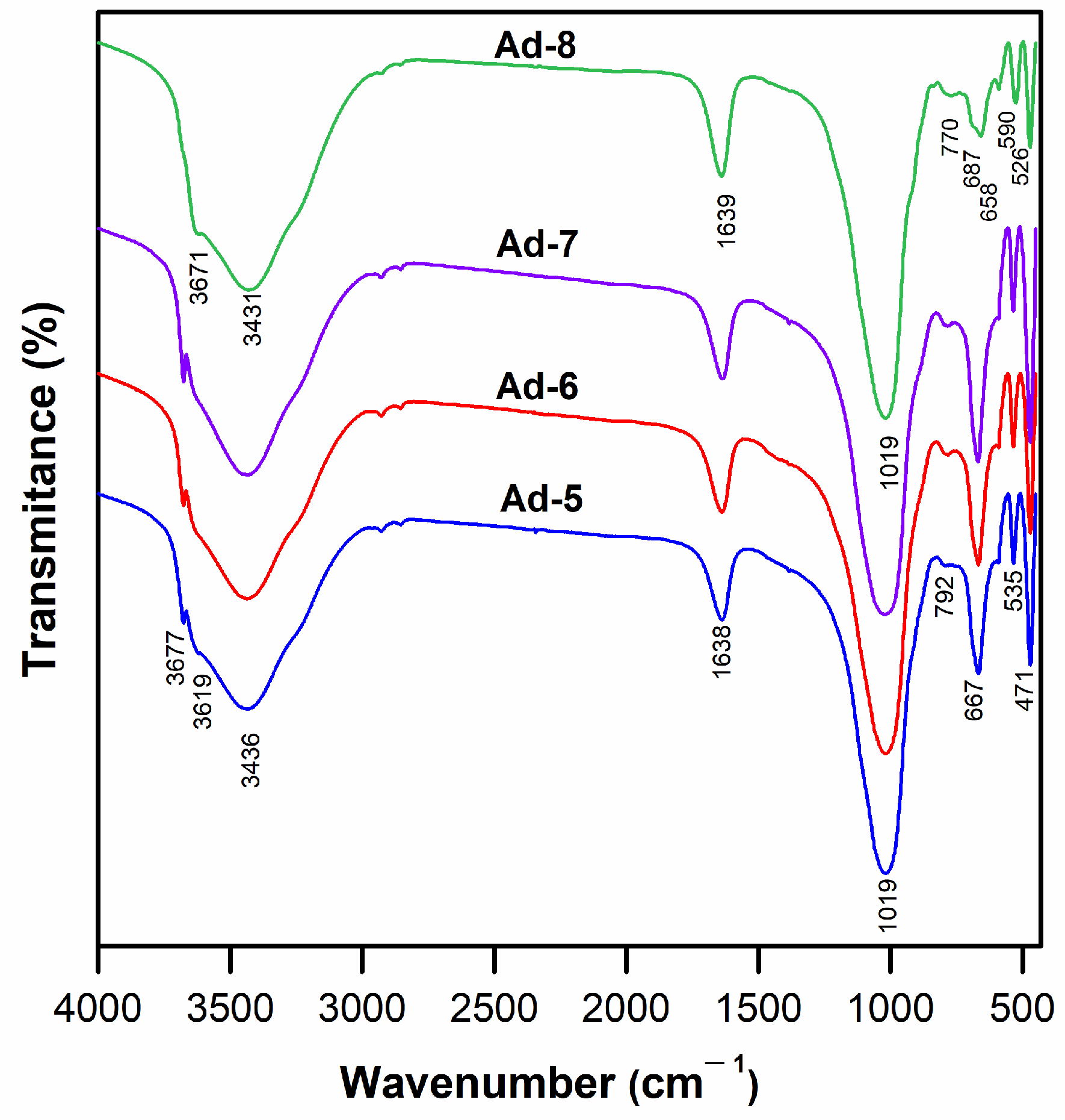
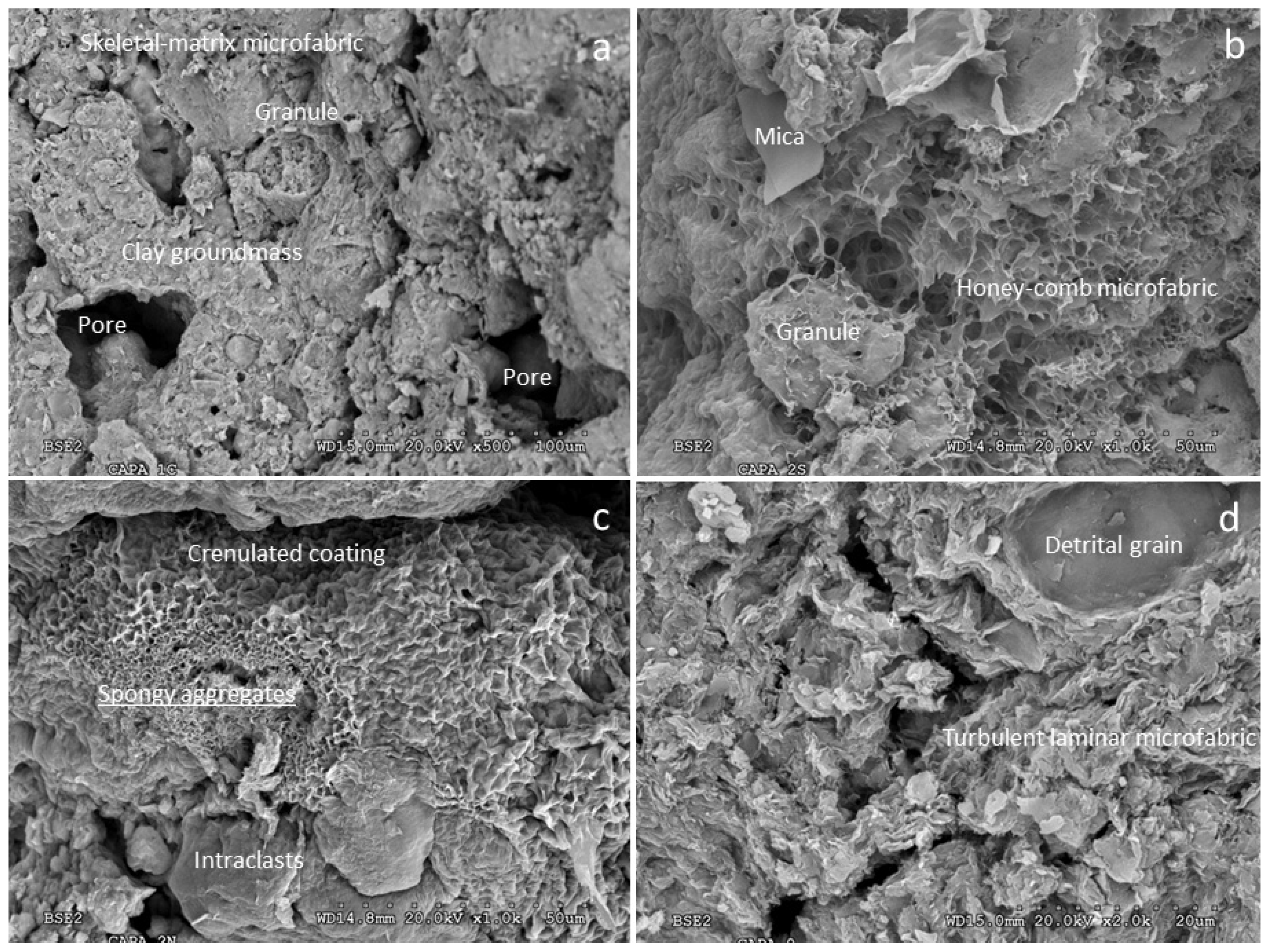
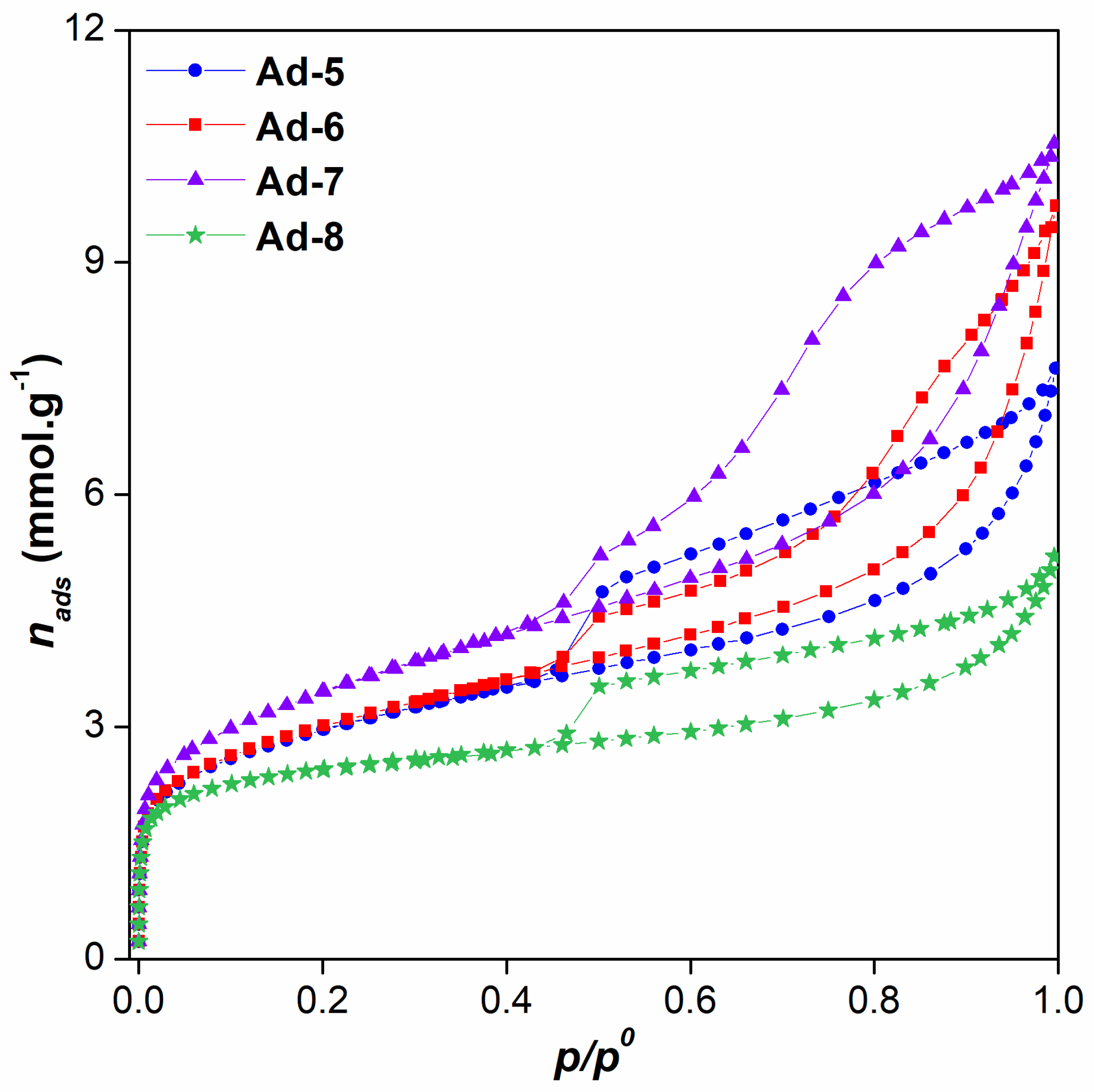
3.1. Characterization of Mg-Clays
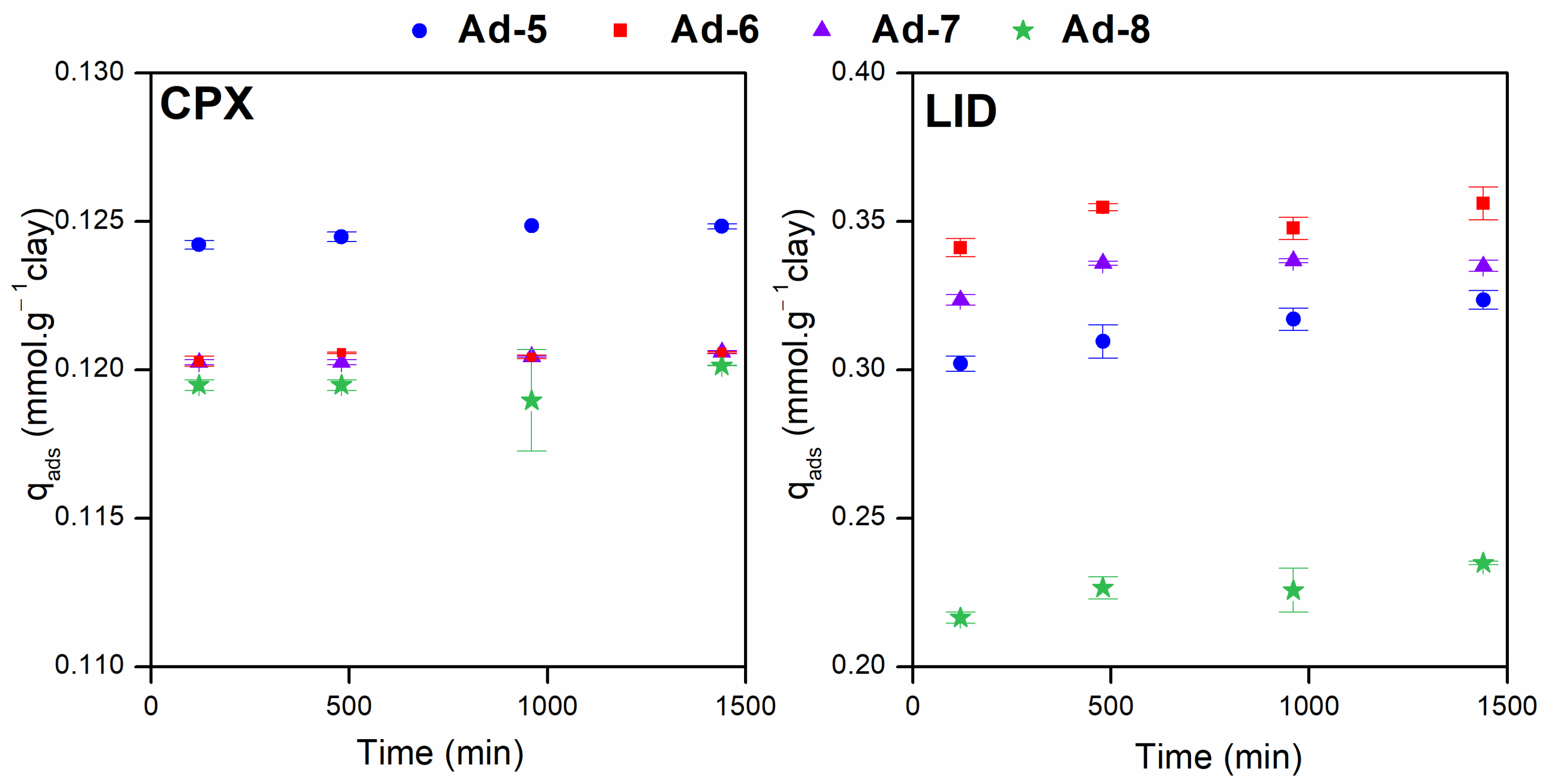
3.2. Adsorption Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikolenko, O.; Pujades, E.; Teixidó, M.; Sáez, C.; Jurado, A. Contaminants of emerging concern in the urban aquifers of Barcelona: Do they hamper the use of groundwater? Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, A.; Santamaría, L.; Korili, S.A.; Vicente, M.A.; Barbosa, L.V.; de Souza, S.D.; Marçal, L.; de Faria, E.H.; Ciuffi, K.J. A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay based adsorbents for contaminants removal: Synthesis, perspectives and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.L.; Winter, M.J.; Norton, W.H.J.; Tyler, C.R. The potential for adverse effects in fish exposed to antidepressants in the aquatic environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16299–16312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, G.; Hilgert, S.; Fuchs, S.; Azevedo, J.C.R. Emerging contaminants and antibiotic resistance in the different environmental matrices of Latin America. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Nishita, N.; Navish, K.; Seyed Ali, J.; Syed Zaheer Ud, D.; Jiang, Z.; Khoo, K.S.; Shi, X. Deciphering the dysbiosis caused in the fish microbiota by emerging contaminants and its mitigation strategies—A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Shukla, P.; Giri, B.S.; Chowdhary, P.; Chandra, R.; Gupta, P.; Pandey, A. Prevalence and hazardous impact of pharmaceutical and personal care products and antibiotics in environment: A review on emerging contaminants. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofrano, G.; Sacco, O.; Venditto, V.; Carotenuto, M.; Libralato, G.; Guida, M.; Meric, S.; Vaiano, V. Occurrence and potential risks of emerging contaminants in water. In Visible Light Active Structured Photocatalysts for the Removal of Emerging Contaminants: Science and Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pulingam, T.; Parumasivam, T.; Gazzali, A.M.; Sulaiman, A.M.; Chee, J.Y.; Lakshmanan, M.; Chin, C.F.; Sudesh, K. Antimicrobial resistance: Prevalence, economic burden, mechanisms of resistance and strategies to overcome. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 170, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polianciuc, S.I.; Gurzău, A.E.; Kiss, B.; Georgia Ștefan, M.; Loghin, F. Antibiotics in the environment: Causes and consequences. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2020, 93, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Hoang, L.; Nghiem, L.D.; Nguyen NM, H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Trinh, Q.T.; Mai, N.H.; Chen, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Occurrence and risk assessment of multiple classes of antibiotics in urban canals and lakes in Hanoi. Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rúa-Gómez, P.C.; Püttmann, W. Impact of wastewater treatment plant discharge of lidocaine, tramadol, venlafaxine and their metabolites on the quality of surface waters and groundwater. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Cobos, L.; Peñafiel, M.E.; Montero, C.; Menendez, M.; Pinos-Vélez, V. Ciprofloxacin Removal Using Pillared Clays. Water 2023, 15, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Cobos, L.; Abad-Delgado, D.; Ponce-Montalvo, J.; Menendez, M.; Peñafiel, M.E. Removal of ciprofloxacin from an aqueous medium by adsorption on natural and hydrolyzed bentonites. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1239754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwegbe, C.A.; Oba, S.N.; Aniagor, C.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Ighalo, J.O. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rúa-Gómez, P.C.; Püttmann, W. Occurrence and removal of lidocaine, tramadol, venlafaxine, and their metabolites in German wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, K.D.; Han, B.; Pichtel, J.; Zubkov, T. Removal efficiency of commonly prescribed antibiotics via tertiary wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6301–6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.M.; Reyhani, R.D.; Asghari JafarAbadi, M.; Fathifar, Z. Diversity of antibiotics in hospital and municipal wastewaters and receiving water bodies and removal efficiency by treatment processes: A sys-tematic review protocol. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangia, S.; Bangia, R.; Daverey, A. Pharmaceutically active compounds in aqueous environment: Recent developments in their fate, occurrence and elimination for efficient water purification. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangla, D.; Annu; Sharma, A.; Ikram, S. Critical review on adsorptive removal of antibiotics: Present situation, challenges and future perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhry, A.; Sharma, A.; Khan, T.A.; Chaudhry, S.A. Flax seeds based magnetic hybrid nanocomposite: An advance and sustainable material for water cleansing. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsha, M.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Senthil Rathi, B. A review on recent trends in the removal of emerging contaminants from aquatic environment using low-cost adsorbents. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakan, S.; Aghazadeh, V. The advantages of clay mineral modification methods for enhancing adsorption efficiency in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 2572–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, D.B.; Trigueiro, P.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Fonseca, M.G.; Jaber, M. Monitoring diclofenac adsorption by organophilic alkylpyridinium bentonites. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharmavaram, M.; Pandey, G.; Rawtani, D. Surface modified halloysite nanotubes: A flexible interface for biological, environmental and catalytic applications. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2018, 261, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, L.; Cheng, H. Rational design of kaolinite-based photocatalytic materials for environment decontamination. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 208, 106098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Hursthouse, A.; McLellan, I.; Wang, Z. Treatment of environmental contamination using sepiolite: Current approaches and future potential. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2679–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmin, R.; Sarkar, B.; Biswas, B.; Churchman, J.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Structural, electrokinetic and surface properties of activated palygorskite for environmental application. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maged, A.; Kharbish, S.; Ismael, I.S.; Bhatnagar, A. Characterization of activated bentonite clay mineral and the mechanisms underlying its sorption for ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32980–32997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.A.; Roca-Jalil, M.E.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Sapag, K.; Baschini, M.T. Fe- and SiFe-pillared clays from a mineralogical waste as adsorbents of ciprofloxacin from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 220, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziti, C.; Zaibet, W.; Benaidj, Y. Removal of ibuprofen from water using recycled clay waste. Tob. Regul. Sci. (TRS) 2023, 9, 4793–4804. [Google Scholar]
- Akyuz, S.; Akyuz, T.; Akalin, E. Adsorption of isoniazid onto sepiolite-palygorskite group of clays: An IR study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 75, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, J.; Dirocie, N.; Yunta, F.; Delgado, C.G.; Santamaría DE, G.; Ruiz, A.I.; Férnández, R.; Eymar, E. Evaluation of the sorption potential of mineral materials using tetracycline as a model pollutant. Minerals 2019, 9, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, H.B.; da Silva, E.; Saltarelli, M.; Crispim, D.; Nassar, E.J.; Trujillano, R.; Rives, V.; Vicente, M.A.; Gil, A.; Korili, S.A.; et al. Inorganic–organic hybrids based on sepiolite as efficient adsorbents of caffeine and glyphosate pollutants. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2020, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, G.; Gong, L.; Chen, B.; Kong, L.; Liang, J. Evaluation of natural sepiolite clay as adsorbents for aflatoxin B1: A comparative study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Avilés, A.; Sellaoui, L.; Badawi, M.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Bedia, J.; Belver, C. Simultaneous adsorption of acetaminophen, diclofenac and tetracycline by organo-sepiolite: Experiments and statistical physics modelling. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoud, B.; Mohadeseh, Z.; Shaziya, S. Investigation of Adsorptive Properties of Surfactant Modified Sepiolite for Removal of Ciprofloxacin. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2020, 10, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Damacena DH, L.; Trigueiro, P.; Monteiro, V.H.; Honorio LM, C.; Duarte, T.M.; Cunha, R.; Furtini, M.B.; Fonseca, M.G.; da Silva-Filho, E.C.; Osajima, J.A. Saponite-inspired Materials as Remediation Technologies for Water Treatment: An Overview. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón-Herrero, R.; García-Delgado, C.; Alonso-Izquierdo, M.; García-Rodríguez, G.; Cuevas, J.; Eymar, E. Comparative adsorption of tetracyclines on biochars and stevensite: Looking for the most effective adsorbent. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vidales JL, M.; Pozo, M.; Alia, J.M.; Garcia-Navarro, F.; Rull, F. Kerolite-Stevensite mixed-layers from the Madrid basin, Central Spain. Clay Miner. 1991, 26, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, M.; Casas, J. Origin of kerolite and associated Mg clays in palustrine-lacustrine environments. The Esquivias deposit (Neogene Madrid Basin, Spain). Clay Miner. 1999, 34, 395418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, H.; Sohling, U.; Suck, K.; Ruf, F.; Niemeyer, B. Selective adsorption of aromatic ketones on kerolite clay for separation in biocatalytic applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 377, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich Sohling, F.; Haimeirl Agnes, H. Use of Stevensite for Mycotoxin Adsorption. U.S. Patent No. 8,221,807, 17 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ureña-Amate, M.D.; Socías-Viciana, M.; González-Pradas, E.; Saifi, M. Effects of ionic strength and temperature on adsorption of atrazine by a heat treated kerolite. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarén, J. Properties and applications of magnesian clays. In Magnesian Clays: Characterization, Origin and Applications; Pozo, M., Galán, E., Eds.; AIPEA Educational Series; Pub. Nº 2; Digilabs: Bari, Italy, 2015; pp. 123–174. ISBN 978-88-7522-093-8. [Google Scholar]
- Elass, K.; Laachach, A.; Alaoui, A.; Azzi, M. Removal of methyl violet from aqueous solution using a stevensite-rich clay from Morocco. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 54, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Ruiz, A.I.; García-Delgado, C.; González-Santamaría, D.E.; Antón-Herrero, R.; Yunta, F.; Poyo, C.; Hernández, A.; Eymar, E.; Cuevas, J. Stevensite-based geofilter for the retention of tetracycline from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pradas, E.; Socías-Viciana, M.; Saifi, M.; Ureña-Amate, M.D.; Flores-Céspedes, F.; Fernández-Pérez, M.; Villafranca-Sánchez, M. Adsorption of atrazine from aqueous solution on heat treated kerolites. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socías-Viciana, M.M.; Tévar de Fez, J.; Ureña-Amate, M.D.; González-Pradas, E.; Fernández-Pérez, M.; Flores-Céspedes, F. Removal of chloridazon by natural and ammonium kerolite samples. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 6053–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using pillared clays. Materials 2017, 10, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Toschi, F.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Silica pillared montmorillonites as possible adsorbents of antibiotics from water media. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pan, C.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.; Xu, L.; Xu, G.; Peng, X. Removal of ciprofloxacin with aluminum-pillared kaolin sodium alginate beads (CA-Al-KABs): Kinetics, isotherms, and BBD model. Water 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo, M.; Calvo, J.P. An overview of authigenic magnesian clays. Minerals 2018, 8, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, L.G. Quantitative Interpretation of Mineralogical Composition from X-ray and Chemical Data for the Pierre Shale. 1964. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0391c/report.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2024).
- Meier, L.P.; Kahr, G. Determination of the Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) of Clay Minerals Using the Complexes of Copper (II) Ion with Triethylenetetramine and Tetraethylenepentamine. Clays Clay Miner. 1999, 47, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Barrera, D.; García Blanco, A.A.; Roca Jalil, M.E.; Sapag, K. Importance of the αs-plot Method in the Characterization of Nanoporous Materials: Enhanced Reader. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, C.D.; Wiese, J.S.; Crane, C.C.; Harris, K.J.; Kloss, H.G.; Baltrusaitis, J. Water adsorption on clay minerals as a function of relative humidity: Application of BET and Freundlich adsorption models. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1790–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, I.D.; Likos, W.J.; Asce, M. Evaluation of Isotherm Models for Water Vapor Sorption Behavior of Expansive Clays. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2017, 31, D4016001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Influence of pH and antibiotic solubility on the removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous media using montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.-O. Ciprofloxacin: Analytical Profile. Profiles Drug Subst. Excip. Relat. Methodol. 2004, 31, 179–207. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, M.F. Lidocaine and lidocaine hydrochloride. Anal. Profiles Drug Subst. 1986, 15, 761–779. [Google Scholar]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Sanchez, M.; Pozo, M.; Soria, C.O.; Vela, L.; Gurnik, N.; Baschini, M. Assessment of natural and enhanced peloids from the Copahue thermal system (Argentina): Effects of the drying procedure on lidocaine adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 196, 105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberl, D.D.; Jones, B.F.; Khoury, H.N. Mixed-layer kerolite/stevensite from the Amargosa Desert, Nevada. Clays Clay Miner. 1982, 30, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.E.; Koutsopoulou, E. A simple approach to the identification of trioctahedral smectites by X-ray diffraction. Clay Miner. 2013, 48, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J.; Gates, W.P.; Petit, S. IR Spectra of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2017, 8, 107–149. [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim, S.; Koster van Groos, A.F. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clays: Thermal analysis. Clays Clay Miner. 2001, 49, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakizci, M.; Erdoǧan Alver, B.; Alver, Ö.; Yörükoǧullari, E. Spectroscopic and thermal studies of bentonites from Ünye, Turkey. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 969, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, R.; Rowland, R. Differential thermail analysis of clay minerals and other hydrous materials. Part 1. Am. Mineral. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1942, 27, 746–761. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowska-Olszewska, B.; Osipov, V.; Sokolov, V. Atlas of the Microstructure of Clay Soils; Panstwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Varsovia, Poland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- El Mouzdahir, Y.; Elmchaouri, A.; Mahboub, R.; ElAnssari, A.; Gil, A.; Korili, S.A.; Vicente, M.A. Interaction of stevensite with Cd2+ and Pb2+ in aqueous dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 35, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Santamaría, D.E.; López, E.; Ruiz, A.; Fernández, R.; Ortega, A.; Cuevas, J. Adsorption of phenanthrene by stevensite and sepiolite. Clay Miner. 2017, 52, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.H.; Smith, D. A General Treatment and Classification of the Solute Adsorption Isotherm. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1974, 47, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.F. Organic pollutant adsorption on clay minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2018, 9, 195–253. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Hong, H.; Liao, L.; Ackley, C.J.; Schulz, L.A.; MacDonald, R.A.; Mihelich, A.L.; Emard, S.M. A mechanistic study of ciprofloxacin removal by kaolinite. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genç, N.; Dogan, E.C.; Yurtsever, M. Bentonite for ciprofloxacin removal from aqueous solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 848–855. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Sánchez, P.; Hrichi, A.; Garrido-Zoido, J.M.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Larriba, M.; Victoria Gil, M.; Ben Amor, H.; García, J. Natural clays as adsorbents for the efficient removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from wastewaters: Experimental and theoretical studies using DFT method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 134, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ciprofloxacin | Lidocaine | |
|---|---|---|
| Structure |  | 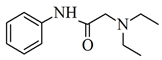 |
| Chemical formula | C17H18FN3O3 | C₁₄H₂₂N₂O |
| Molecular weight (g.mol−1) | 331.45 | 288.80 |
| Molecular dimensions (nm) | 1.30 × 0.30 × 0.70 [60] | 1.04 × 0.60 × 0.59 * |
| pKa | pKa1 = 5.90; pKa2 = 8.90 | pKa = 7.92 |
| Samples | Bulk Mineralogy | Clay Fraction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phy | Qz | Kf | Pl | Sme | Ill | K/St | |
| Ad-5 | 99 | <1 | <1 | - | 87 | 13 | - |
| Ad-6 | 99 | 1 | Tr | - | - | - | K20St80 |
| Ad-7 | 98 | 2 | - | - | - | - | K80St20 |
| Ad-8 | 96 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 97 | 3 | - |
| Chemical Analysis (%) | Ad-5 | Ad-6 | Ad-7 | Ad-8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 50.15 | 51.43 | 53.17 | 48.23 |
| Al2O3 | 4.96 | 2.54 | 1.27 | 9.37 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.92 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 3.03 |
| MnO | 0.025 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.045 |
| MgO | 23.09 | 24.79 | 27.09 | 14.37 |
| CaO | 0.54 | 0.96 | 0.38 | 0.87 |
| Na2O | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.22 |
| K2O | 0.91 | 0.6 | 0.34 | 1.11 |
| TiO2 | 0.233 | 0.115 | 0.058 | 0.363 |
| P2O5 | 0.08 | 0.03 | <0.01 | 0.07 |
| LOI | 18.15 | 17.34 | 16.09 | 20.57 |
| Ad-5 | Ad-6 | Ad-7 | Ad-8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEC (cmol(+).Kg−1) SBET (m2.g−1) | 53 240 | 48.6 244 | 38.4 280 | 90.86 203 |
| Sext (m2.g−1) | 195 | 201 | 245 | 116 |
| VT (cm3.g−1) | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.17 |
| Vμp (cm3.g−1) | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Vmp (cm3.g−1) | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.31 | 0.10 |
| Ad-5 | Ad-6 | Ad-7 | Ad-8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
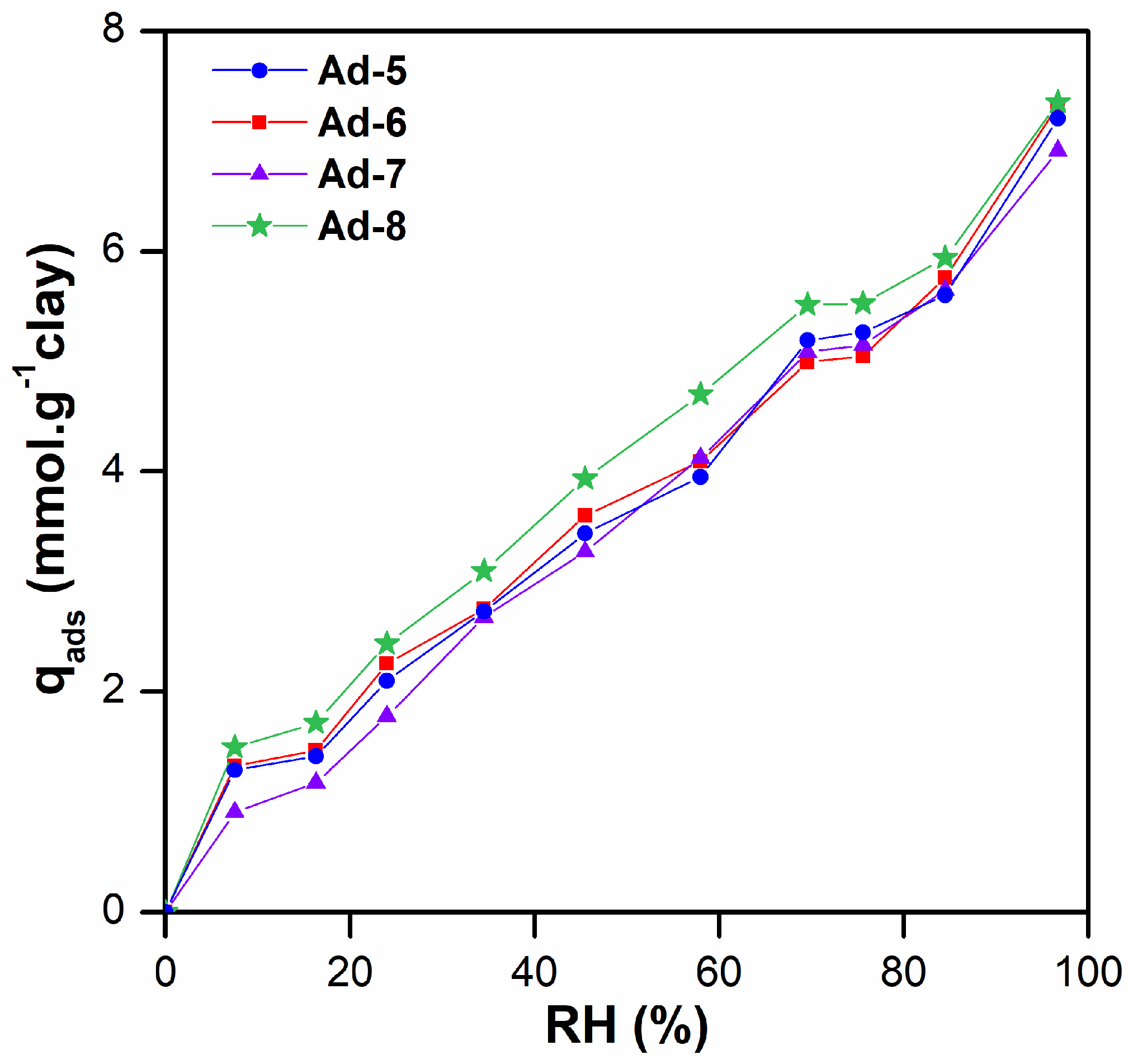
| NH (%) | 5.10 | 3.56 | 3.05 | 3.58 |
| qads (mmol.g−1) | 1.41 | 1.47 | 1.17 | 1.72 |
| S (m2.g−1) | 90.2 | 93.6 | 74.8 | 109.5 |
| Ad-5 | Ad-6 | Ad-7 | Ad-8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPX | LID | CPX | LID | CPX | LID | CPX | LID | ||
| Langmuir | qm (mmol g−1) | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.48 | 0.65 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.45 |
| k (L mmol−1) | 13.5 | 16.4 | 47.9 | 8.22 | 11.9 | 19.3 | 75.4 | 3.00 | |
| R2 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.99 | |
| Freundlich | kf (L g−1) | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 0.74 | 0.35 |
| n | 6.34 | 6.92 | 6.18 | 5.93 | 6.11 | 7.63 | 6.01 | 2.34 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.95 | |
| Sips | qm (mmol g−1) | 1.81 | 0.41 | 0.80 | 0.48 | 1.26 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.51 |
| b (L mmol−1)1/n | 0.01 | 16.4 | 10.2 | 8.22 | 0.34 | 3.96 | 32.1 | 2.57 | |
| n | 4.39 | 1.00 | 3.01 | 1.00 | 4.07 | 3.40 | 1.95 | 1.09 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.84 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| Adsorbent | qm CPX (pH) (mmol.g−1) | Adsorbent dosage (g.L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| kaolinite | 0.02 (5–6) | 0.2 | [75] |
| Na-Bentonite from Turkey | 0.44 (4.5) | 2.5 | [76] |
| Na-Montmorillonite from Argentine | 0.42 (6) | 2.5 | [60] |
| Ca-bentonite | 0.49 (6.5) | 0.2 | [12] |
| Clay 4 (Na-montmorillonite type) | 0.58 (6–7.6) | 1.0 | [77] |
| Clay 2 (Kaolin type) | 0.09 (6–7.6) | ||
| Ad-5 | 0.44 | 2.5 | This work |
| Ad-6 | 0.80 | ||
| Ad-7 | 0.55 | ||
| Ad-8 | 0.91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roca-Jalil, M.E.; Musso, T.; Rodriguez-Ameijide, V.; Sanchez, M.; Maggio, A.; Baschini, M.T.; Pettinari, G.; Villa, L.; Pozo, M.; Pérez-Abad, A. Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Lidocaine by Non-Fibrous Raw Mg-Clays: The Role of Composition and Texture. Minerals 2024, 14, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100966
Roca-Jalil ME, Musso T, Rodriguez-Ameijide V, Sanchez M, Maggio A, Baschini MT, Pettinari G, Villa L, Pozo M, Pérez-Abad A. Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Lidocaine by Non-Fibrous Raw Mg-Clays: The Role of Composition and Texture. Minerals. 2024; 14(10):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100966
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoca-Jalil, Maria Eugenia, Telma Musso, Vanina Rodriguez-Ameijide, Micaela Sanchez, Andrea Maggio, Miria Teresita Baschini, Gisela Pettinari, Luis Villa, Manuel Pozo, and Alejandro Pérez-Abad. 2024. "Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Lidocaine by Non-Fibrous Raw Mg-Clays: The Role of Composition and Texture" Minerals 14, no. 10: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100966
APA StyleRoca-Jalil, M. E., Musso, T., Rodriguez-Ameijide, V., Sanchez, M., Maggio, A., Baschini, M. T., Pettinari, G., Villa, L., Pozo, M., & Pérez-Abad, A. (2024). Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin and Lidocaine by Non-Fibrous Raw Mg-Clays: The Role of Composition and Texture. Minerals, 14(10), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14100966










