Kinetics of Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experiment Setup
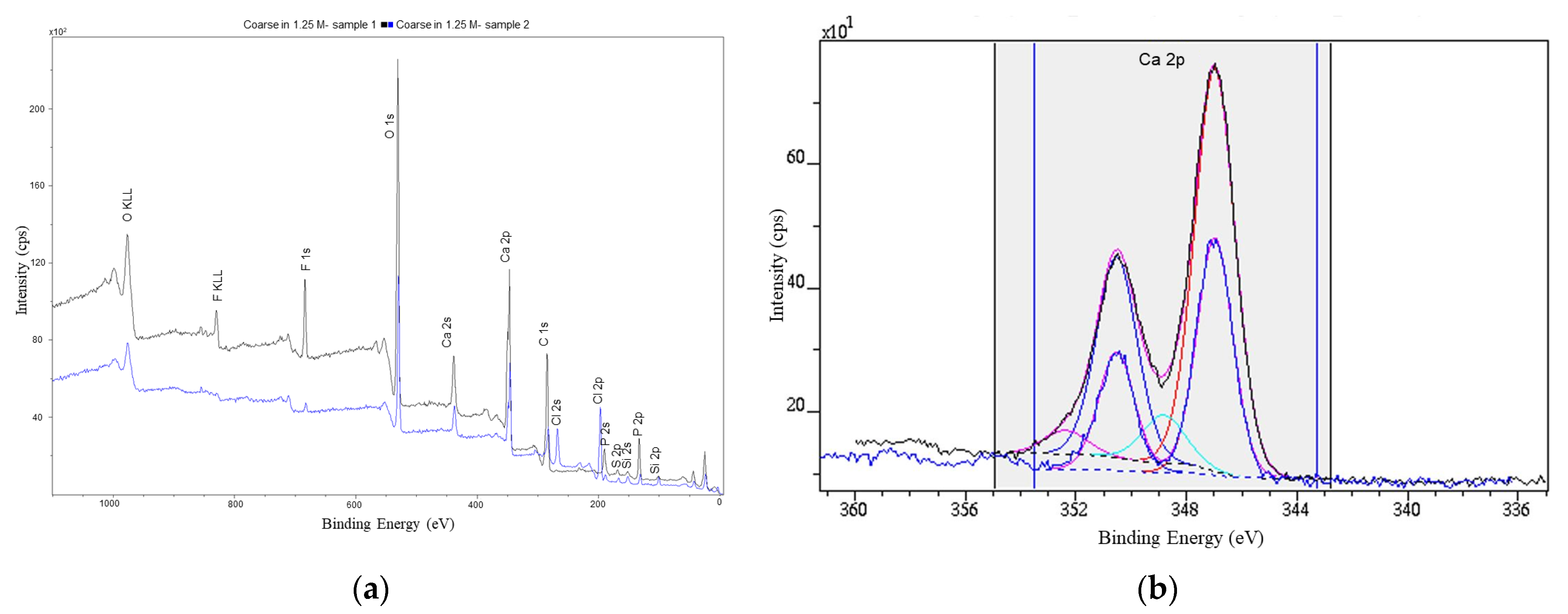
2.2.2. Analysis and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
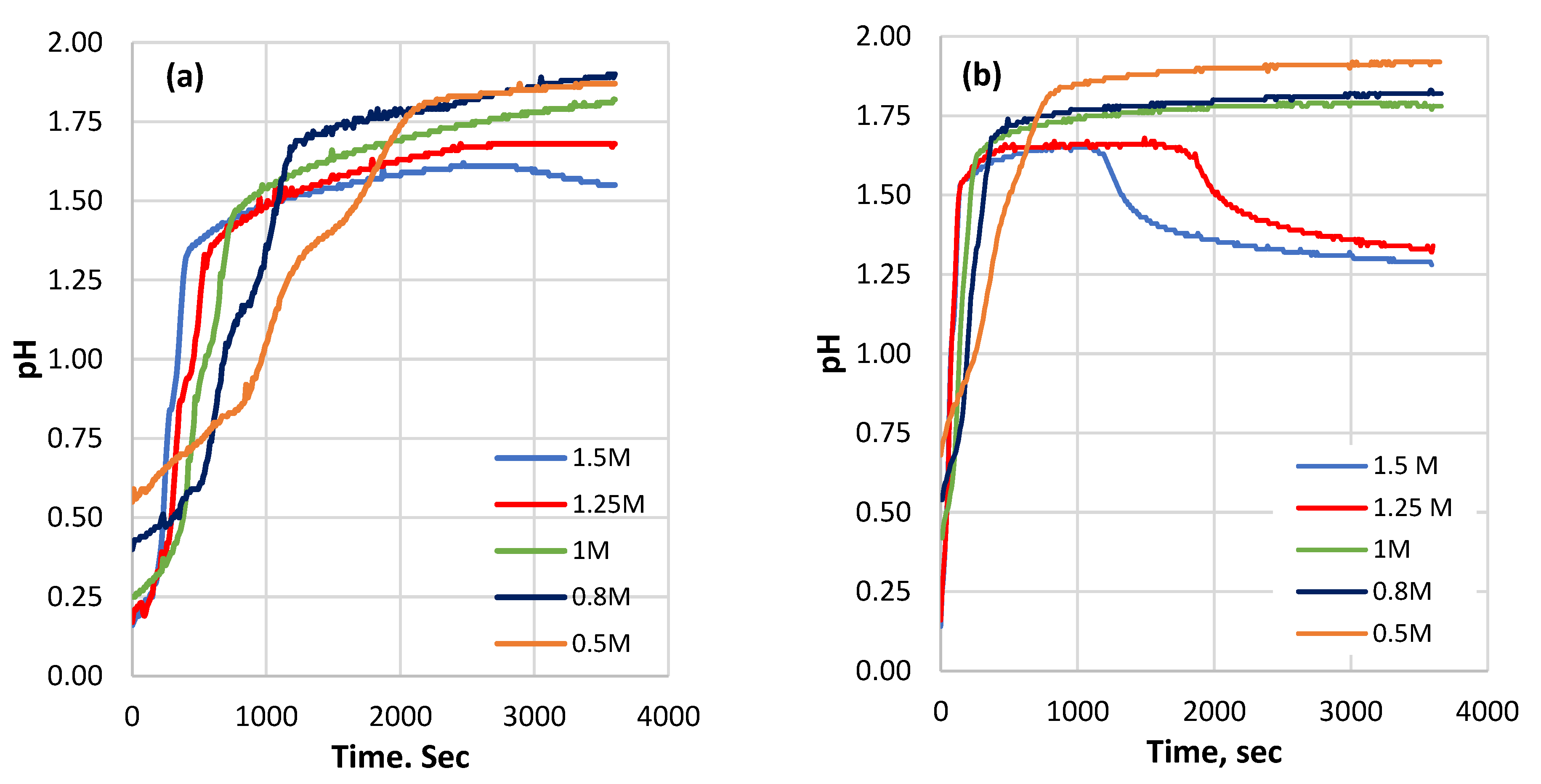
3.1. The pH Changes during the Dissolution Process
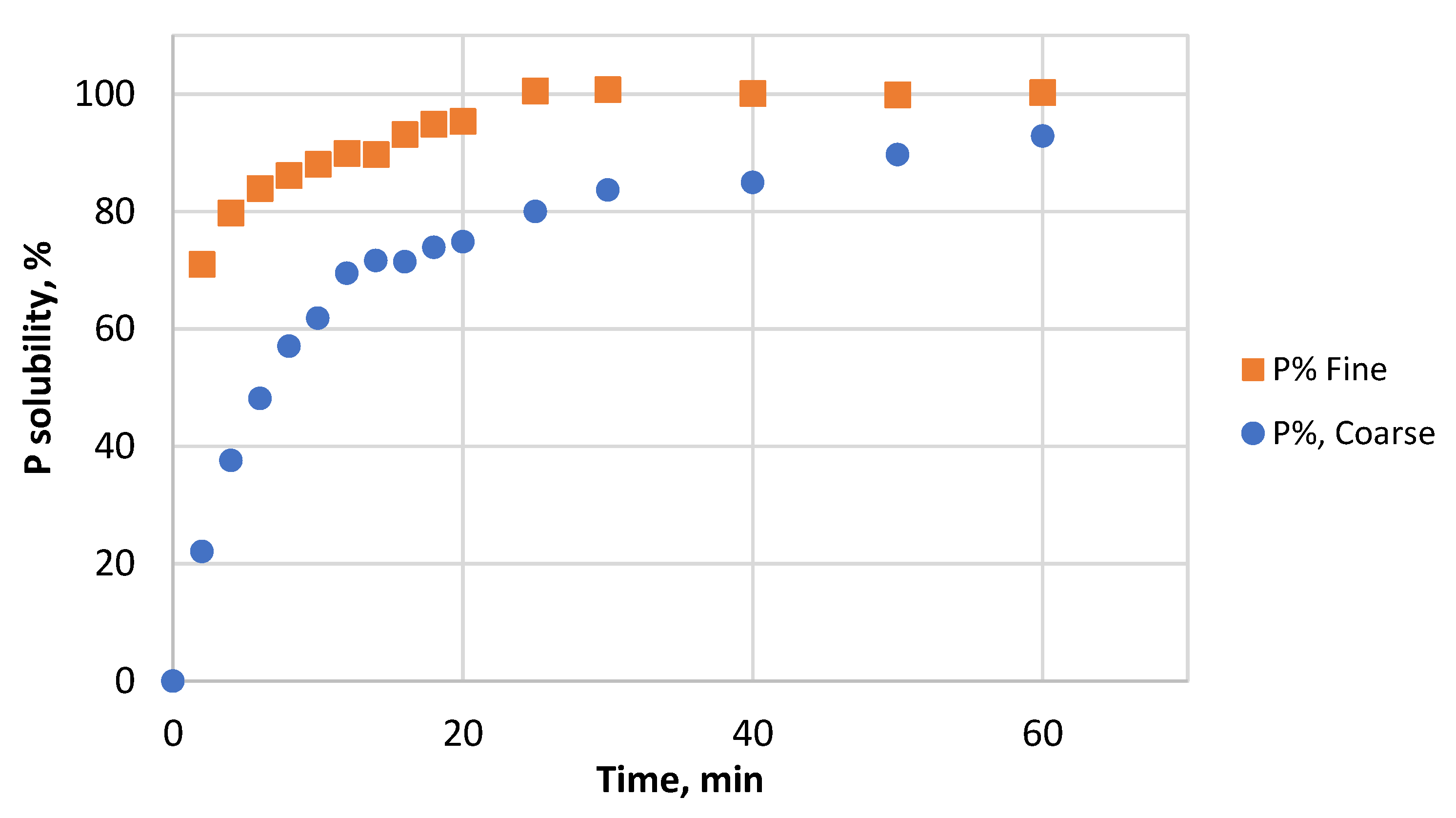
3.2. Effect of Particle Size and HCl Concentration on Solubility of P
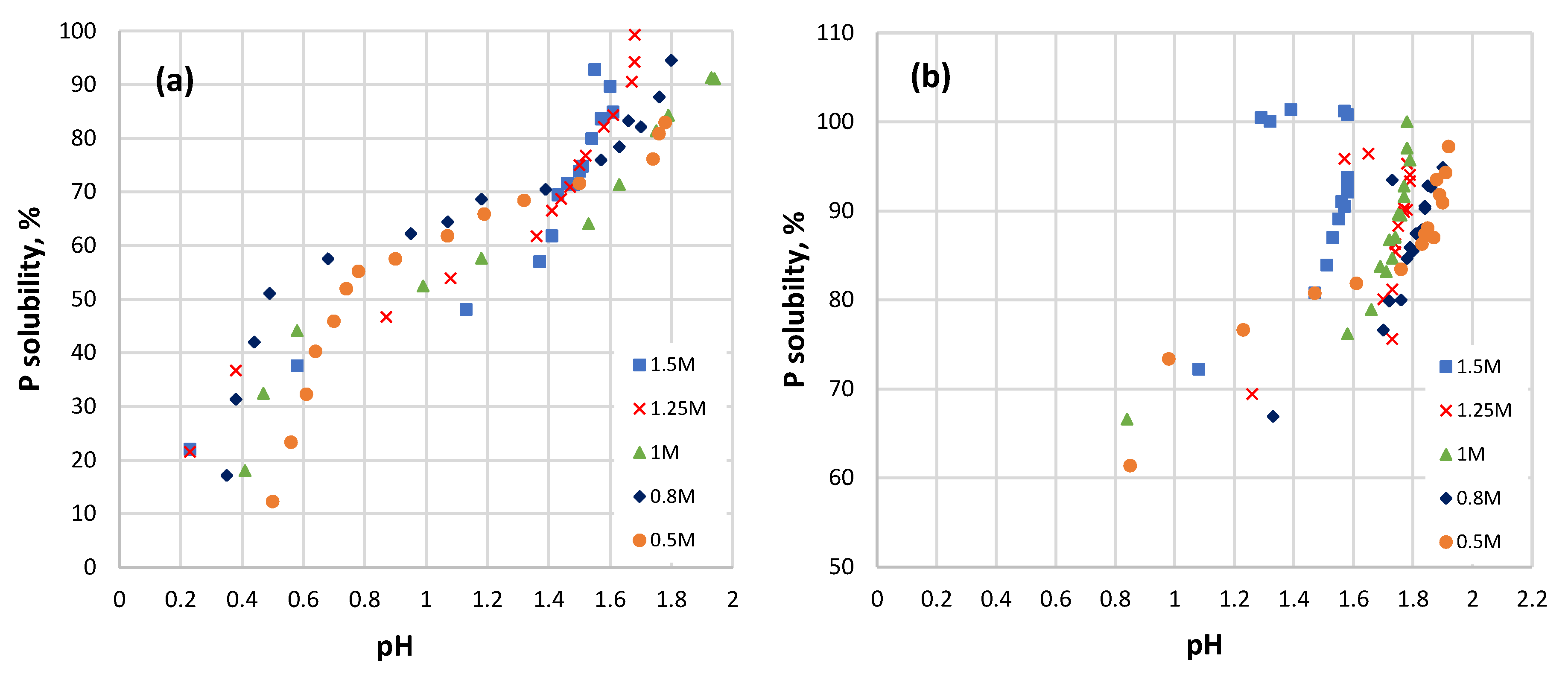
3.3. P Solubility and pH Variation
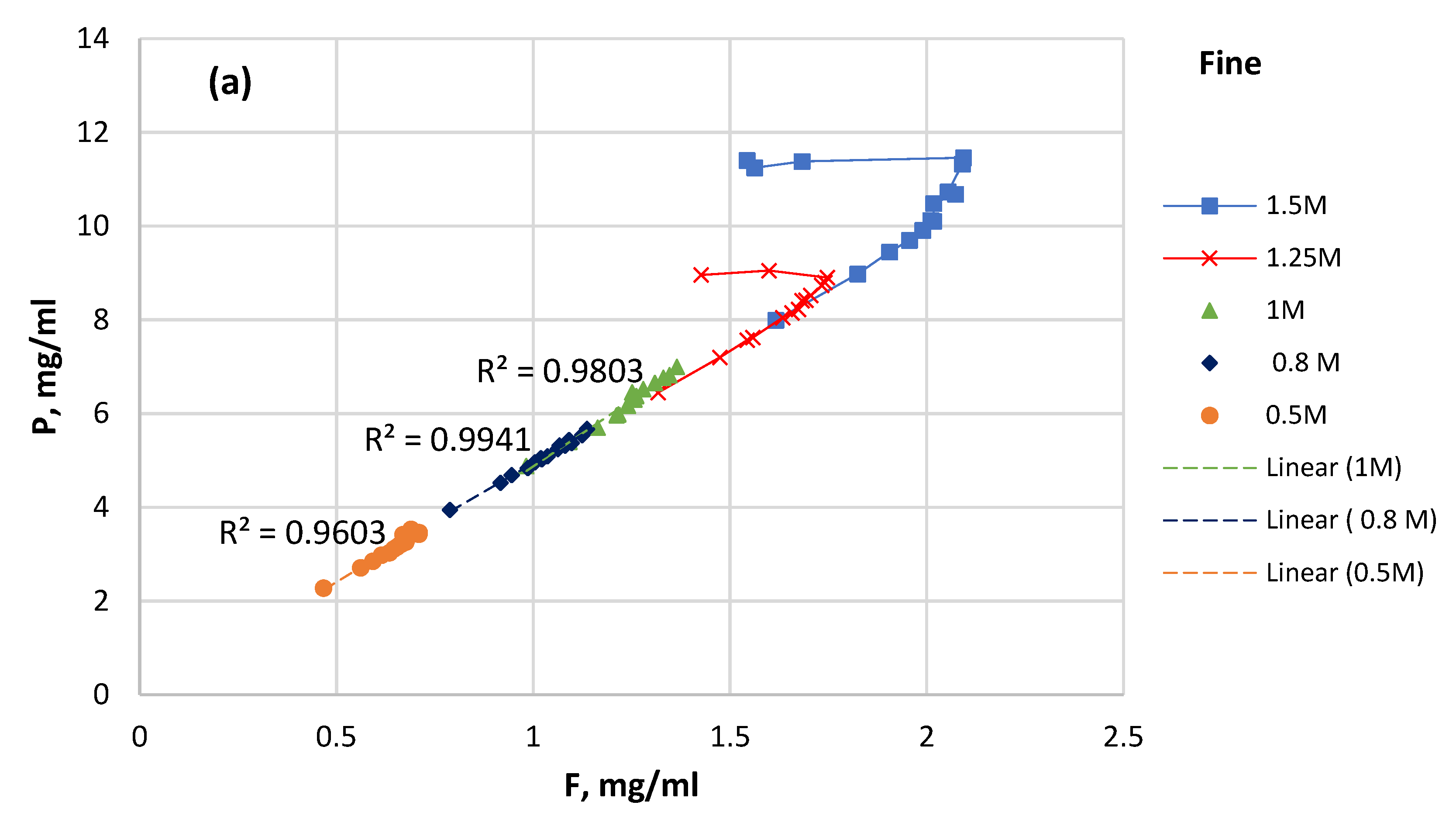
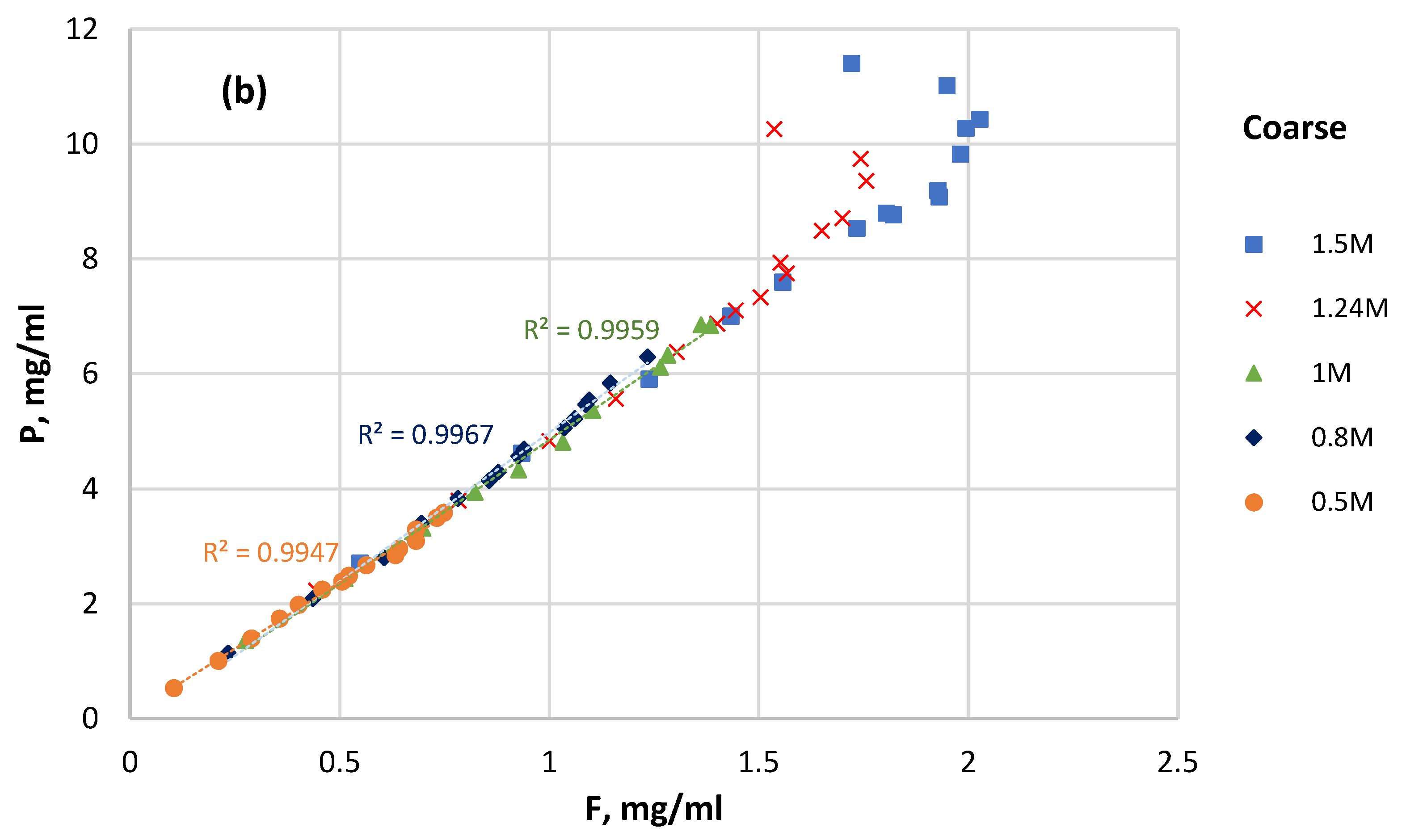
3.4. P Solubility versus F Solubility
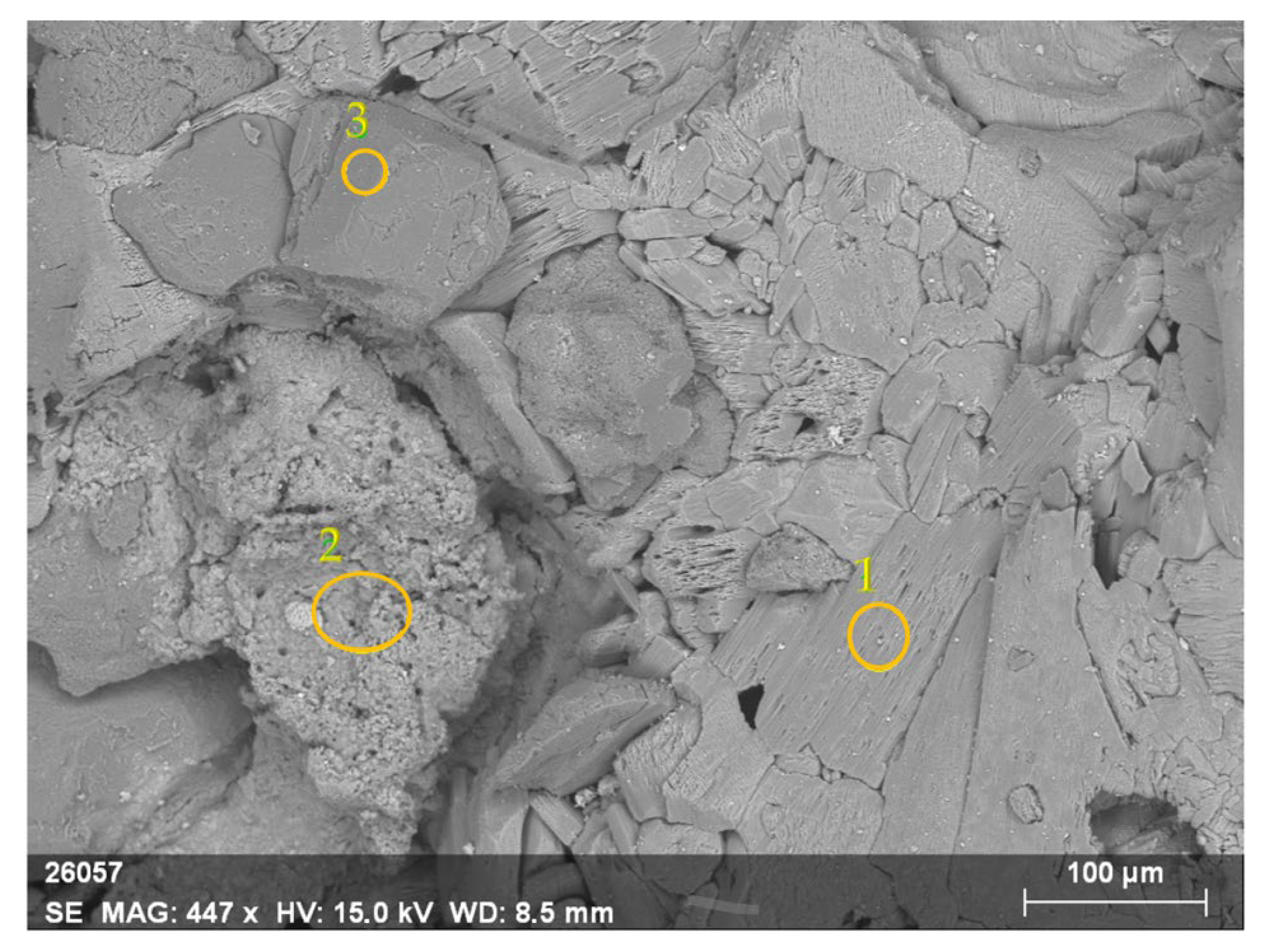
3.5. PR Particle Surface Analysis—Before and after Dissolution
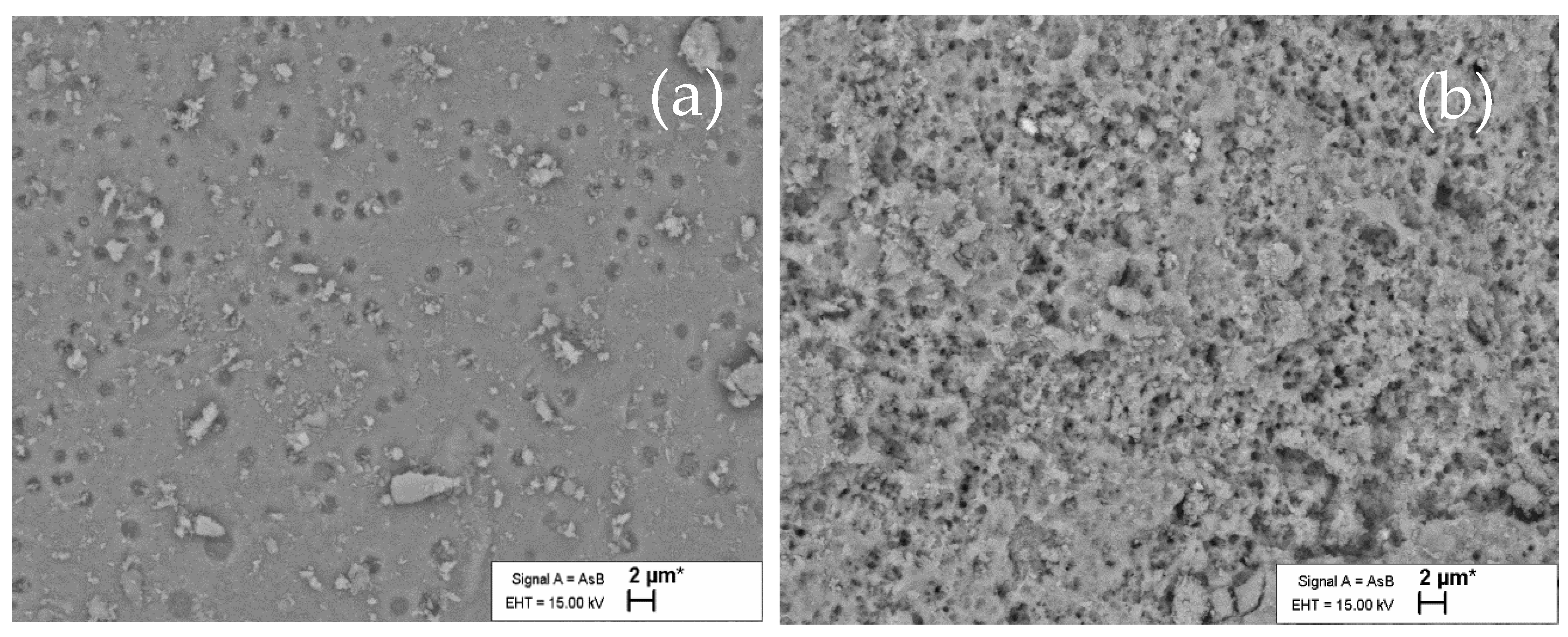
3.5.1. SEM Observations
3.5.2. XPS Data
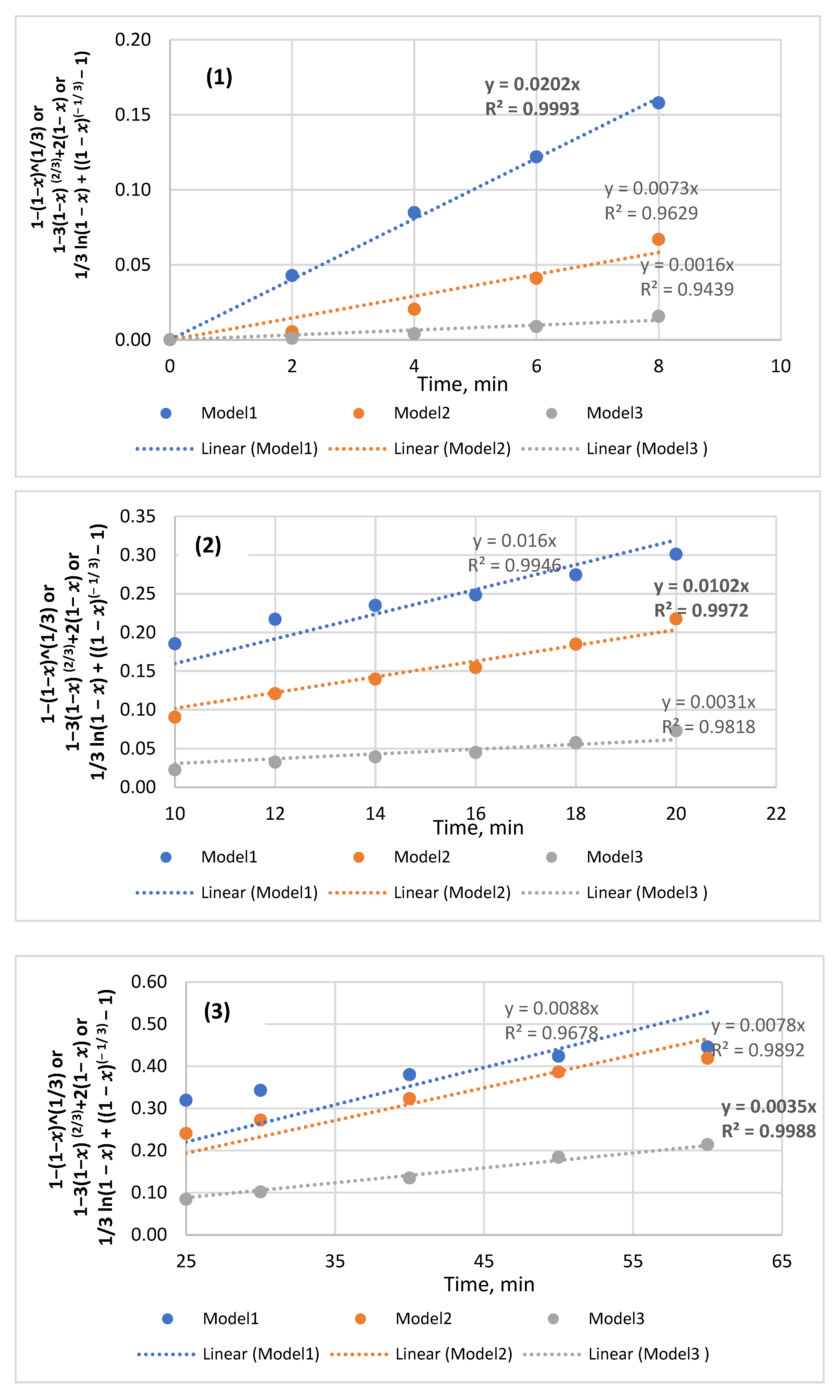
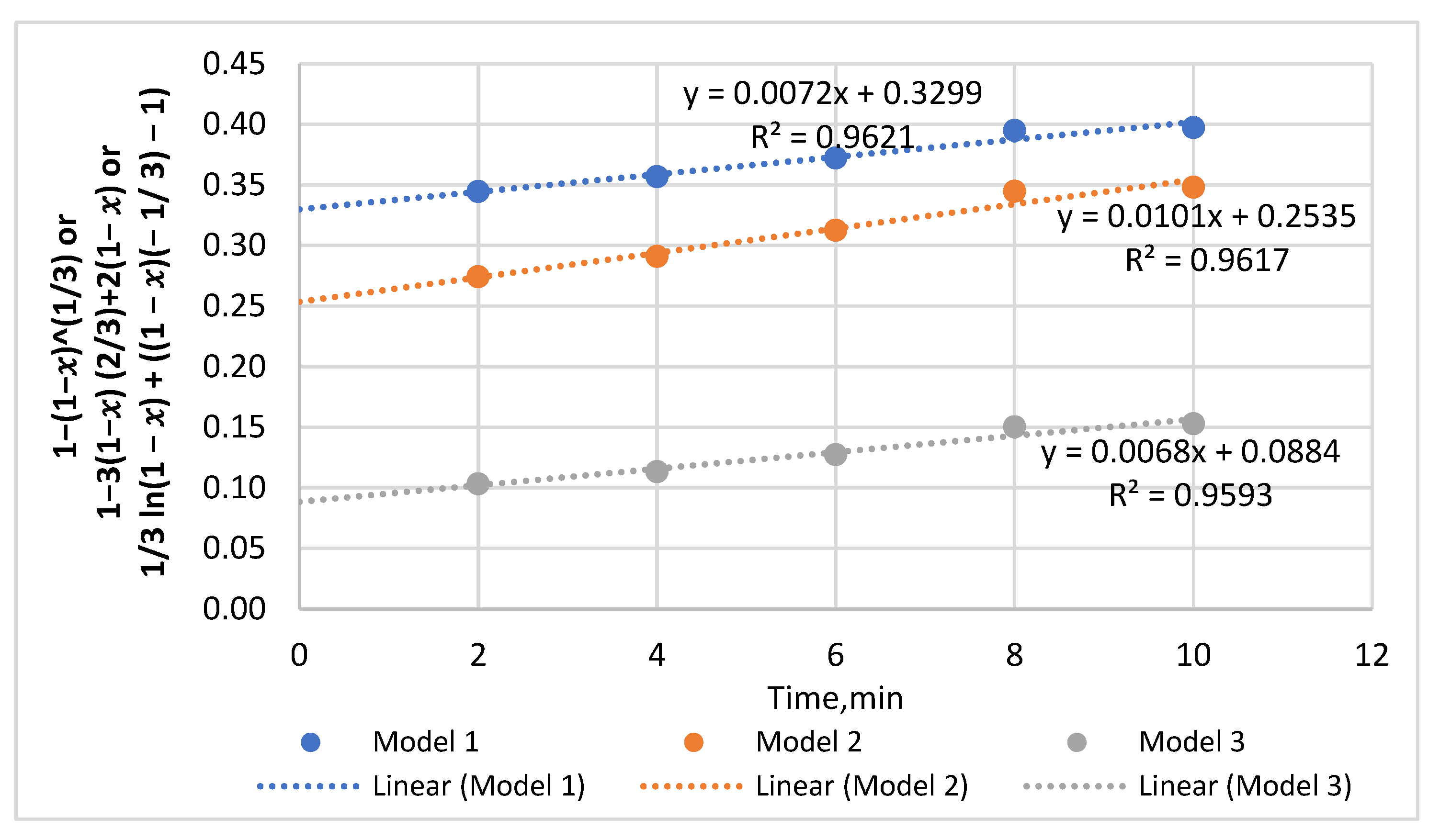
3.6. Dissolution Kinetics—Models and Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Bobba, S.; Carrara, S.; Huisman, J.; Mathieux, F.; Pavel, C.; European Commission. Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU: A Foresight Study; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosu, L.; Vind, J.; Lumiste, K.; Polikarpus, M.; Tarros, S.; Pärn, J.; Kansi, K.; Tamm, K.; Bauert, H.; Kaasik, T.; et al. Exploration of Phosphorite and Black Shale in North-Eastern Estonia; Geological Survey of Estonia (EGT): Rakvere, Estonia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Raukas, A.; Teedumäe, A. (Eds.) Geology and Mineral Resources of Estonia; Estonian Academy Publishers: Tallinn, Estonia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; El-Shall, H.; Moudgil, B.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Z. Simultaneous recovery of rare earths and uranium from wet process phosphoric acid using solvent extraction with D2EHPA. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 175, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Cui, D. Simultaneous recovery of rare earth elements and phosphorus from phosphate rock by phosphoric acid leaching and selective precipitation: Towards green process. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; El-Shall, H.; Moudgil, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Recovery of rare earth elements from phosphate rock by hydrometallurgical processes—A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 774–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, L.; Kraus, F.; Hermann, R. Phosphorus processing-potentials for higher efficiency. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banihashemi, S.R.; Taheri, B.; Razavian, S.M.; Soltani, F. Selective Nitric Acid Leaching of Rare-Earth Elements from Calcium and Phosphate in Fluorapatite Concentrate. JOM 2019, 71, 4578–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, A.M.T.S.; Senanayake, G. Leachability of rare-earth, calcium and minor metal ions from natural Fluorapatite in perchloric, hydrochloric, nitric and phosphoric acid solutions: Effect of proton activity and anion participation. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 153, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, K.; Bandara, A.M.T.S.; Senanayake, G.; Jayasekera, S. Processing of rare earth phosphate concentrates: A comparative study of pre-leaching with perchloric, hydrochloric, nitric and phosphoric acids and deportment of minor/major elements. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, A.M.T.S.; Senanayake, G. Dissolution of calcium, phosphate, fluoride and rare earth elements (REEs) from a disc of natural fluorapatite mineral (FAP) in perchloric, hydrochloric, nitric, sulphuric and phosphoric acid solutions: A kinetic model and comparative batch leaching of major and minor elements from FAP and RE-FAP concentrate. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 184, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Y.; Elghali, A.; Hakkou, R.; Benzaazoua, M. Towards zero solid waste in the sedimentary phosphate industry: Challenges and opportunities. Minerals 2021, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniel, A.; Blumberg, R. Process for the Preparation of Phosphoric Acid. U.S. Patent WO 2,880,063, 31 March 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Long, R.S.; Ellis, D.A. Preparation of Phosphoric Acid. U.S. Patent WO 3,072,461, 29 July 1960. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/48/fc/e3/81d33d394b3b6d/US3072461.pdf> (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Baniel, A.M.; St, H.; Blumberg, R.; St, V.; Carmel, M.; Alon, A. Process for Preparation of Substantially Pure Phosphoric Acid; 1967. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US3338674A/en (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Sandström, Å.; Fredriksson, A. Apatite for extraction: Leaching of Kiirunavaara apatite for simultaneous production of fertilizers and REE. In XXVI International Mineral Processing Congress: IMPC 2012; The Indian Institute of Metals: New Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 4707–4714. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, R.; Cho, H.; Han, K.N.; Kim, K.; Mun, M. Optimization of acid leaching of rare-earth elements from mongolian apatite-based ore. Minerals 2016, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amine, M.; Asafar, F.; Bilali, L.; Nadifiyine, M. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching Study of Rare Earth Elements from Moroccan Phosphate. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 4675276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Eishah, S.I.; Abu-Jabal, N.M. Parametric study on the production of phosphoric acid by the dihydrate process. Chem. Eng. J. 2001, 81, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Dissolution Kinetics of Single Fluoroapatite Crystals in Phosphoric Acid Solution under the Conditions of the Wet-Process Phosphoric Acid Production. J. Prakt. Chem. 1996, 338, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashi, F.; Awadalla, F.T.; Yao, X.-B. The Hydrochloric Acid Route for Phosphate Rock. J. Chern. Technol. Biorechnol. 1987, 38, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N. Effect of Anions on the Solubility of Rare Earth Element-Bearing Minerals in Acids. Min. Metall. Explor. 2019, 36, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tõnsuaadu, K.; Kallas, J.; Kuusik, R.; Hacialioglu-Erlenheim, G.; Trikkel, A. A new perspective on fluorapatite dissolution in hydrochloric acid: Thermodynamic calculations and experimental study. Inorganics 2021, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlewit, H. Treatment of phosphate rocks with hydrochloric acid. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2011, 287, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colton, E. Fluosilicic acid. J. Chem. Educ. 1958, 35, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendah, H.; Khattech, I.; Jemal, M. Synthesis, characterization, and thermochemistry of acid attack of B type carbonate fluorapatites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, F.; Abdollahy, M.; Petersen, J.; Ram, R.; Javad Koleini, S.M.; Moradkhani, D. Leaching and recovery of phosphate and rare earth elements from an iron-rich fluorapatite concentrate: Part II: Selective leaching of calcium and phosphate and acid baking of the residue. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 184, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, Å.; Sjöberg, S. Surface complexation and proton-promoted dissolution in aqueous apatite systems. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath Misra, D. Interaction of Citric or Hydrochloric Acid with Calcium Fluorapatite: Precipitation of Calcium Fluoride. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 220, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Dissolution mechanism of calcium apatites in acids: A review of literature. World J. Methodol. 2012, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure and Chemistry of the Apatites and Other Calcium Orthophosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; p. 387. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, P. Phosphates and phosphoric acid: Raw materials technology and economics of the wet process. In Fertilizer Science and Technology Series; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 6, p. 760. [Google Scholar]
- Hocking, M.B. Modern Chemical Technology and Emission Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachkar-Zamouri, O.; Brahim, K.; Bennour, F.; Khattech, I. Dissolution of Tunisian phosphate ore by a mixture of sulfuric and phosphoric acid: Kinetics study by means of differential reaction calorimetry. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2019, 55, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Z.; Deng, J.; He, D.; Zhao, H.; Liang, H. Leaching kinetics of rare earth elements in phosphoric acid from phosphate rock. Metals 2021, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshdy, O.E.; Haggag, E.A.; Masoud, A.M.; Bertau, M.; Haneklaus, N.; Pavón, S.; Hussein, A.E.; Khawassek, Y.M.; Taha, M.H. Leaching of rare earths from Abu Tartur (Egypt) phosphate rock with phosphoric acid. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadi-Selmi, H.; Antar, K.; Khattech, I. Thermochemical and kinetic study of the attack of fluorapatite by sulfuric acid solution at different temperatures. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 141, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, F.; Saraç, H.; Kocakerim, M.M.; Yartaş, A. Dissolution kinetics of phosphate ore in H2SO4 solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.N.; Posner, A.M.; Quirk, J.P. A Model Describing the Kinetics of Dissolution of Hydroxyapatite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 62, 475–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Xue, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. Separation and recovery of associated rare earths from the Zhijin phosphorite using hydrochloric acid. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Zheng, D.; Tang, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W. Phosphate ore particles dissolution kinetics in hydrochloric acid based on a structure-related segmented model. Powder Technol. 2021, 392, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Mottaleb, M.; Cheira, M.F.; Gouda, G.A.H.; Ahmed, A.S.A. Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Egyptian Western Desert Phosphate Rocks using HCl. Chem. Adv. Mater. 2016, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Aly, H.F.; Ali, M.M.; Taha, M.H. Dissolution kinetics of Western Desert phosphate rocks, Abu Tartur with hydrochloric acid. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2013, 46, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Brahim, K.; Soussi-Baatout, A.; Khattech, I.; Jemal, M. Dissolution kinetics of fluorapatite in the hydrochloric acid solution. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 129, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmanovici, C.E.; Gilot, B.; Laguérie, C. Mechanism and Kinetics for the Dissolution of Apatitic Materials in Acid Solutions. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 14, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tõnsuaadu, K.; Kallas, J.; Kallaste, T.; Urtson, K.; Einard, M.; Martin, R.; Kuusik, R.; Trikkel, A. Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid: Optimization of Acid Dosage and Concentration. Minerals 2023, 13, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, P.; Haikel, Y.; Voegel, J.C.; Gramain, P. Surface reactions of hydroxyapatite in the presence of fluoride ions 2. Effects of calcium and phosphate in saturated solutions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 88, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaïrat, C.; Oelkers, E.H.; Schott, J.; Lartigue, J.E. Fluorapatite surface composition in aqueous solution deduced from potentiometric, electrokinetic, and solubility measurements, and spectroscopic observations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5888–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wang, L.; Orme, C.A.; Bonstein, T.; Bush, P.J.; Nancollas, G.H. Dissolution at the Nanoscale: Self-Preservation of Biominerals. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 2751–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Wang, L.; Naacollas, G.H. Size-effects in the dissolution of hydroxyapatite: An understanding of biological demineralization. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2341–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirioux, L.; Baillif, P.; Touray, J.C.; Ildefonse, J.P. Surface reactions during fluorapatite dissolution-recrystallization in acid media (hydrochloric and citric acids). Geochim. Et Cosmochmica Acta 1990, 54, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, E.I.F. On the Dissolution of Hydroxyapatite in Acid Solutions. J. Dent. Res. 1988, 67, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Orme, C.A.; Nancollas, G.H. Dissolution of crystallites: Surface energetic control and size effects. ChemPhysChem 2004, 5, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Acidic dissolution mechanism of natural fluorapatite II. Nanolevel of investigations. J. Cryst. Growth 1997, 182, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Acidic dissolution mechanism of natural fluorapatite I. Milli-and microlevels of investigations. J. Cryst. Growth 1997, 182, 125–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Inorganic chemistry of the dissolution phenomenon: The dissolution mechanism of calcium apatites at the atomic (ionic) level. Comments Inorg. Chem. 1999, 20, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, C.F.; Heal, G.R. Solid-liquid diffusion controlled rate equations. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 340–341, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Minerals | % |
|---|---|
| Apatite | 67.0 |
| Quartz | 32.0 |
| Pyrite | 0.7 |
| Orthoclase | n.d |
| Gypsum | n.d |
| Chemical composition | % |
| P2O5 | 25.4 |
| CaO | 38.1 |
| F | 2.2 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.8 |
| MgO | 0.3 |
| CO2 | 1.7 |
| Sample | Ca/P |
|---|---|
| Surface of untreated particle | 1.94 |
| Bulk solution | 1.69 |
| Surface of acid-treated+ water-washed | 1.56 |
| Sample | Orbital | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca 2p 3/2 | P 2p3/2 | O 1 s | F 1 s | C 1 s | |
| PR −1.24 M HCl+ water-washed | 346.988 | 132.835 | 530.755 | 684.090 | 284.621 |
| Parameter | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 − (1 − x) 1/3 | 1 − 3(1 − x) 2/3 + 2(1 – x) | 1/3 ln (1 − x) + ((1 − x) (−1/3) − 1) | |||||||
| HCl Concentration, M | Time, min | K1 | R2 | Time, min | K2 | R2 | Time, min | K3 | R2 |
| 0.5 | 0–8 | 0.0202 | 0.9993 | 10–20 | 0.0102 | 0.9972 | 25–60 | 0.0035 | 0.9988 |
| 0.8 | 0–8 | 0.0282 | 0.9972 | 10–20 | 0.0171 | 0.9986 | 20–50 | 0.0083 | 0.9981 |
| 1 | 0–8 | 0.0286 | 0.9977 | 10–25 | 0.0164 | 0.9969 | 25–60 | 0.0077 | 0.9975 |
| 1.24 | 0–6 | 0.0332 | 0.9951 | 8–60 | 0.0153 | 0.9955 | - | ||
| 1.48 | - | 0–10 | 0.0179 | 0.9907 | 12–50 | 0.0072 | 0.9959 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azeez, R.S.; Tõnsuaadu, K.; Kaljuvee, T.; Trikkel, A. Kinetics of Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals 2024, 14, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030322
Azeez RS, Tõnsuaadu K, Kaljuvee T, Trikkel A. Kinetics of Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals. 2024; 14(3):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030322
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzeez, Ruhany Sheherazad, Kaia Tõnsuaadu, Tiit Kaljuvee, and Andres Trikkel. 2024. "Kinetics of Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid" Minerals 14, no. 3: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030322
APA StyleAzeez, R. S., Tõnsuaadu, K., Kaljuvee, T., & Trikkel, A. (2024). Kinetics of Estonian Phosphate Rock Dissolution in Hydrochloric Acid. Minerals, 14(3), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14030322







