In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
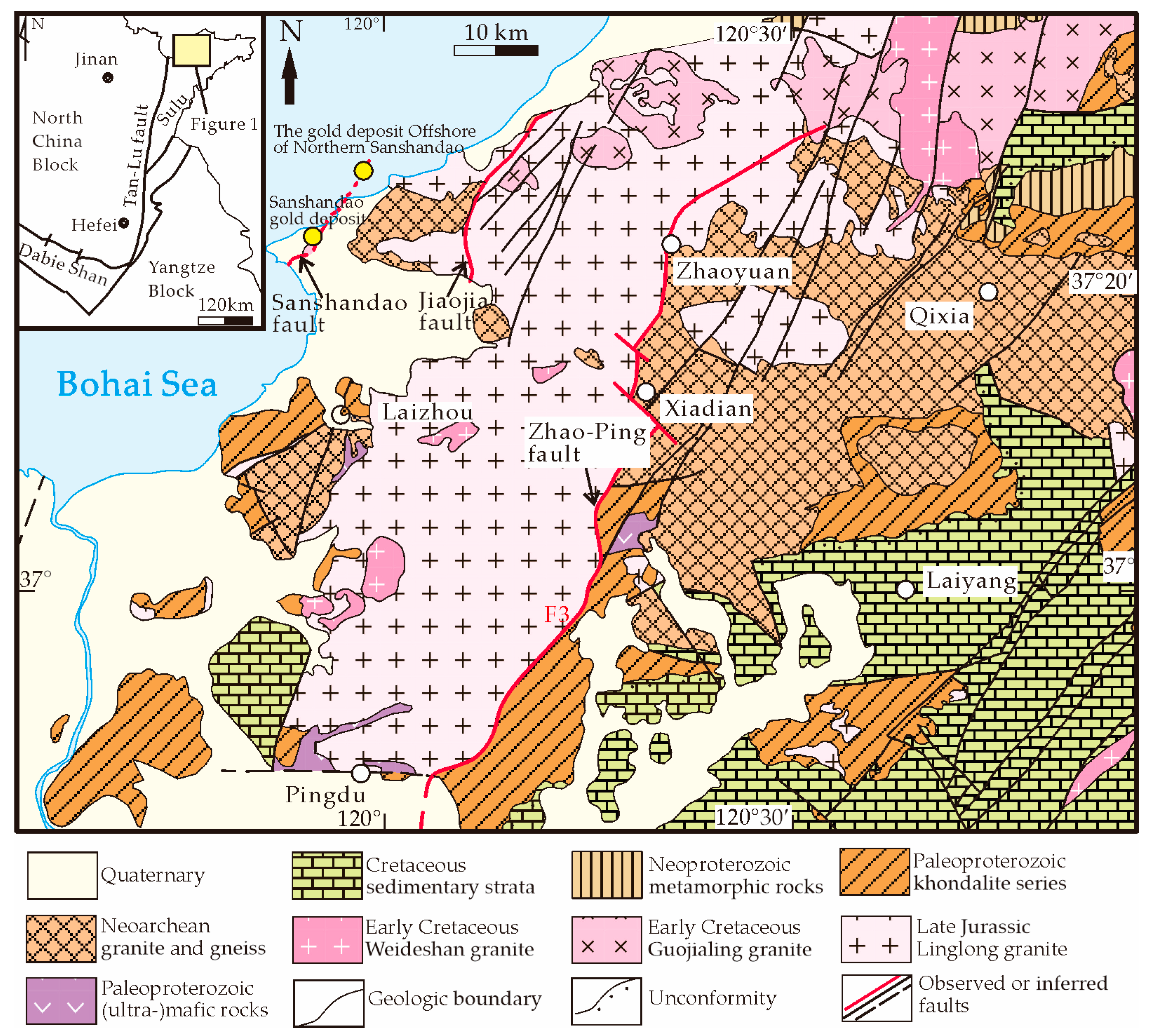
2. Regional Geological Background
3. Ore Deposit Geology
4. Sampling and Analytical Methods
4.1. Backscattered Electron (BSE) Imaging and Wavelength Dispersive Elemental Maps
4.2. In-Situ Trace Element Analysis of Pyrite Using LA-ICP-MS
4.3. In-Situ S Isotope Analysis of Pyrite Using LA-MC-ICP-MS
4.4. Rb–Sr Dating
5. Results
5.1. Wavelength Dispersive Elemental Maps
5.2. In-Situ Trace Element Compositions
5.3. In-Situ Sulfur Isotopic Compositions
5.4. Rb–Sr Age
6. Discussion
6.1. Trace Element Distribution Characteristics of Pyrite
6.2. Occurrence of Gold
6.3. Metallogenic Age
6.4. Sources of Ore-Forming Material
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.K.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, W.D.; Luo, H. Geodynamic setting for formation of large-superlarge gold deposits and Mesozoic granites in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 2005, 24, 361–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Ge, L.S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, B.F.; Zhou, Y.F.; Jiang, S.Q. Research advances in the Mesozoic tectonic regimes during the formation of Jiaodong ore cluster area. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2006, 16, 777–784. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Wang, Q.F. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res. 2016, 36, 219–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.R.; Santosh, M. Metallogeny and craton destruction: Records from the North China Craton. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 56, 376–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Santosh, M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique? Geosci. Front. 2014, 5, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.C.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Song, Y.X.; Bo, J.W.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Li, S.Y.; Li, J.J.; Li, R.X. Geology and mineralization of the Sanshandao supergiant gold deposit (1200 t) in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A review. China Geol. 2021, 4, 686–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.F.; Goldfarb, R.J. Gold Deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2020; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.C.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, P.J.; Yang, L.Q.; Liu, D.H.; Ding, Z.J.; Song, Y.X. Discover and tectonic-magmatic background of superlarge gold deposit in offshore of northern Sanshandao, Shandong peninsula. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 365–383. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.H.; Lv, G.X.; Zhang, P.J.; Ding, Z.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Lin, D.W.; Lv, C.X.; Wang, Z.Y. A study of 3D ore-controlling of the tectonic altered rocks of the Sanshandao fault in Jiaodong Peninsular and the discovery of an offshore super-large gold deposit in China. Earth Sci. Front. 2015, 22, 162–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.W.; Shen, J.F.; Li, G.W.; Wang, L.M.; Sun, N.Y.; Liu, H.D.; Chi, L.; Zhang, H.F.; Du, B.S. Characteristics of Cell Parameters and Thermoelectricity of the Pyrite in the Sanshandao North Offshore Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2020, 39, 1205–1214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.W.; Liu, W.Q.; Deng, H.J.; Shen, J.F.; Zhao, G.C. Hydrothermal Alteration Characteristics and Migration Rules of Trace Elements in the North Sanshandao Sea Gold Deposit, Shandong, China. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 56, 245–253. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Mao, M.Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, X.W.; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, G.L. The Genesis of the Haiyu Gold deposit in the northern part of Sanshandao gold metallogenic belt in the eastern Shandong: Constraints from geological characteristics and fluid inclusion study. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2023, 43, 521–532. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.X.; Li, S.R.; Shen, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.T.; Zeng, Y.J. Characteristics and prospecting significance of thermoluminescence patterns and cell parameters of quartz from the undersea gold deposit off northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 305–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, L.X.; Ma, S.M.; Tang, S.X.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhou, W.W. Application of the multi-attribute anomaly model for prospecting potential at depth: A case study of the Haiyu Au deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. J. Assoc. Explor. Geochem. 2019, 207, 106359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.P. Geochemical Mechanism of Gold Accumulation in Offshore of Northern Sanshandao Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Gold Province, Eastern China. Ph.D Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, T.; Liu, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.D. Hydrothermal alteration of the xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong, China. Acta Pet. Sin. 2016, 32, 2433–2450. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.C. Origins of Ore-Forming Materials and the Metallogenic Model of Gold Deposits in the Jiaoxibei Area. Ph.D Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.J. Study on Metallogenic Regularity of Mesozoic Precious and Non-Ferrous Deposits in Jiaodong Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.S.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Chen, H.H.; Hu, S.H. “Wave” Signal-Smoothing and Mercury-Removing Device for Laser Ablation Quadrupole and Multiple Collector ICPMS Analysis: Application to Lead Isotope Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Hu, Z.C.; Gao, S.; Gunther, D.; Xu, J.; Gao, C.G.; Chen, H.H. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chem. Geol. 2008, 257, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.L.; Hu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zong, K.Q.; Gao, S.; Hu, S.H. In situ sulfur isotopes (δ34S and δ33S) analyses in sulfides and elemental sulfur using high sensitivity cones combined with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation MC-ICP-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 911, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.C.; Liu, Y.S. Iso-Compass: New freeware software for isotopic data reduction of LA-MC-ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.P. The Mesozoic Gold Polymetallic Regional Metallogeny in Qipengfu Ore Concentration Area, Jiaodong Peninsula. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.G.; Liu, H.B.; Li, G.Z.; Xiao, Z.B.; Tu, J.R.; Li, H.M. The Application of Ion Exchange Resins in Sr-Nd Isotopic Assay of Geological Samples. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 91, 2584–2592. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barker, S.L.; Hickey, K.A.; Cline, J.S.; Dipple, G.M.; Kilburn, M.R.; Vaughan, J.R.; Longo, A.A. Uncloaking invisible gold: Use of nanoSIMS to evaluate gold, trace elements, and sulfur isotopes in pyrite from Carlin-type gold deposits. Econ. Geol. 2009, 104, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Utsunomiya, S.; Kogagwa, M.; Green, L.; Gilbert, S.; Wade, B. Gold-telluride nanoparticles revealed in arsenic-free pyrite. Am. Mineral. 2012, 97, 1515–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, C.L.; Cook, N.J.; Pring, A.; Brugger, J.; Danyushevsky, L.V.; Shimizu, M. ‘Invisible gold’ in bismuth chalcogenides. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 1970–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Meria, D.; Silcock, D.; Wade, B. Arsenopyrite-Pyrite Association in an Orogenic Gold Ore: Tracing Mineralization History from Textures and Trace Elements. Econ. Geol. Bull. Soc. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N.J.; Ciobanu, C.L.; Mao, J.W. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang, and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China). Chem. Geol. 2009, 264, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.; Long, D.G.F.; Kamber, B.S.; Whitehouse, M.J. In Situ Trace Element and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite in a Paleoproterozoic Gold Placer Deposit, Pardo and Clement Townships, Ontario, Canada. Econ. Geol. 2011, 106, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.R.; Li, X.H.; Zuo, Y.B.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, F.F.; Feng, K. In-situ LA-(MC)-ICPMS and (Nano) SIMS trace elements and sulfur isotope analyses on sulfides and application to confine metallogenic process of ore deposit. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2018, 34, 3479–3496. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Zhao, G.; Hong, J.X.; Liu, J.J.; Zhai, D.G. In situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite and its application in study of Au deposit. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 1182–1199. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.L.; Zeng, Q.D.; Sun, G.T.; Duan, X.X.; Bonnetti, C.; Biegler, T.; Long, D.G.F.; Kamber, B. Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) elemental mapping and its applications in ore geology. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 1964–1978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koglin, N.; Frimmel, H.E.; Lawrie Minter, W.E.; Brätz, H. Trace-element characteristics of different pyrite types in Mesoarchaean to Palaeoproterozoic placer deposits. Miner. Depos. 2010, 45, 259–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bralia, A.; Sabatini, G.; Troja, F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems. Miner. Depos. 1979, 14, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Palenik, C.S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Ewing, R.C. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, X.F.; Xiong, L.; Zhu, Z.X. In-situ trace element analysis characteristics of pyrite in Sanshandao Gold Deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula: Implications for ore genesis. Adv. Earth Sci. 2019, 34, 399–413. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A.P.; Reich, M.; Kesler, S.E.; Utsunomiya, S.; Chryssoulis, S.L.; Walshe, J.; Ewing, R.C. The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 140, 644–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, S.F.; White, N.C.; John, D.A. Geological Characteristics of Epithermal Precious and Base Metal Deposits. In One Hundredth Anniversary Volume; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 485–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.X.; Zhao, X.F.; Lin, Z.W.; Zhao, S.R. In Situ Trace Elements and Sulfur Isotope Analysis of Pyrite from Jinchiling Gold Deposit in the Jiaodong Region: Implications for Ore Genesis. Earth Sci. 2020, 45, 945–959. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, M.G.; Fan, H.R.; Yang, J.H.; Miao, L.C. Large-scale cluster of gold deposits in east Shandong: Anorogenic metallogenes. Earth Sci. Front. 2004, 11, 85–98. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F.; Goldfarb, R.; Yang, L.Q.; Zi, J.W.; Geng, J.Z.; Ma, Y. In Situ Dating of Hydrothermal Monazite and Implications for the Geodynamic Controls on Ore Formation in the Jiaodong Gold Province, Eastern China. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Jiang, P.; Fan, H.R.; Zuo, Y.B.; Yang, Y.H. Tectonic transition from a compressional to extensional metallogenic environment at similar to 120 Ma revealed in the Hushan gold deposit, Jiaodong, North China Craton. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 160, 408–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weinberg, R.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Sai, S.X.; Matchan, E.; Phillips, D.; Kohn, B.P.; Miggins, D.P.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mesozoic Orogenic Gold Mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A Focused Event at 120 +/− 2 Ma During Cooling of Pregold Granite Intrusions. Econ Geol. 2020, 115, 415–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.F.; Fan, H.R.; Santosh, M.; Hu, F.F.; Wilde, S.A.; Lan, T.G.; Lu, L.N.; Liu, Y.S. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos 2012, 146, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.G.; Qiu, Y.M.; McNaughton, N.J.; Groves, D.I.; Luo, Z.K.; Huang, J.Z.; Liu, Y.K. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geol. Rev. 1998, 13, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.F.; Fan, H.R.; Jiang, X.H.; Yang, K.F. Fluid inclusions in different depths at Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Implication for ore genesis. Geofluids 2013, 13, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Yu, X.W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, Q.Y.; Guo, R.P. 40Ar/39Ar Age and Its Significance of Sericite in Pyrite Sericite in Sanshandao Gold Deposit in Northwest of Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2020, 36, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cawood, P.A.; Wilde, S.A.; Liu, R.; Song, H.; Li, W.; Snee, L.W. Geology and timing of mineralization at the Cangshang gold deposit, north-western Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Miner. Depos. 2003, 38, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Systematics of Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes in Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. Econ. Geol. 1972, 67, 551–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussidon, M.; Albarède, F.; Sheppard, S.M.F. Sulphur isotope variations in the mantle from ion microprobe analyses of micro-sulphide inclusions. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 1989, 92, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollinson, H.R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation; Routledge: London, UK, 1993; Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781315845548/using-geochemical-data-hugh-rollinson (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Wen, B.J.; Fan, H.R.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.F.; Sun, Z.F.; Sun, Z.F. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions. J. Geochem. Explor. J. Assoc. Explor. Geochem. 2016, 171, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z. Characteristics of the Ore-Forming Fluid and Thermodynamic Simulation of Water-Rock Interaction at the Sanshandao Gold Deposit, Shandong Province, China. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.X.; Fan, H.R.; Li, J.W.; Meng, Q.R.; Li, S.R.; Zeng, Q.D. Decratonic gold deposits. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, C.M.; Bagas, L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Lu, Y.J. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Miner. Depos. 2015, 50, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Zhu, F.S.; Gong, R.T. Tectonic isotope geochemistry—Further study on sulphur isotope of Jiaodong Gold Concentration Area. Gold 2002, 23, 1–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Y. Sulfur isotope studies of the metallogenic series of gold deposits in Jiaodong area. Miner. Depos. 1994, 13, 75–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Q.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Guo, L.N.; Song, M.C.; Zheng, X.L. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2014, 30, 2447–2467. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Song, M.C.; Liang, J.L.; Jiang, M.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Su, F. Source of ore-forming fluids of the Jiaojia deeplyseated gold deposit: Evidences from trace elements and sulfur-helium-argon isotopes of pyrite. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 36, 297–313. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; An, M.Y.; Song, M.C.; Wang, M.Y.; Ding, Z.J.; Bao, Z.Y.; Wang, S.S. Sulfur isotopic composition and its source of Jiaodong gold deposit. Geol. Bull. China 2022, 41, 993–1009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Fan, H.R.; Groves, D.I.; Yang, K.F.; Hu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Cai, Y.C. Geochronological and sulfur isotopic evidence for the genesis of the post-magmatic, deeply sourced, and anomalously gold-rich Daliuhang orogenic deposit, Jiaodong, China. Miner. Depos. 2020, 55, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, L.Q.; Groves, D.I.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, K.F.; Wang, Q.F. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 208, 103274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.L.; Jiang, S.Y.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ling, H.F. S-Pb isotope geochemistry and Rb-Sr geochronology of the Penglai gold field in the eastern Shangdong province. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2006, 22, 2525–2533. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Pirajno, F.; Lai, Y.; Li, C. Metallogenic time and tectonic setting of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2004, 20, 907–922. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, M.; Caridroit, M.; Charvet, J. The Late Jurassic oblique collisional orogen of SW Japan: New structural data and synthesis. Tectonics 1986, 5, 1089–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L. Sr and O isotopic characteristics of porphyries in the Qinling molybdenum deposit belt and their implication To genetic mechanism and type. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2001, 43, 82–94. [Google Scholar]








| Sample Serial Number | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Ag | Sb | Au | Pb | Bi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK8401-1 | 3.37 | - | 0.10 | 1.32 | 125 | 0.19 | - | 0.01 | 1.87 | 9.35 |
| ZK8401-2 | 5.22 | 0.06 | 2.24 | 1.04 | 68 | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 8.40 | 10 |
| ZK8401-3 | 3.08 | 1.29 | 1.21 | 1.09 | 30 | 0.67 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 15 | 6.94 |
| ZK8401-4 | 134 | 42 | 2.14 | 0.66 | 25 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 4.89 | 2.72 |
| ZK8401-5 | 130 | 38 | 5.16 | 1.26 | 22 | 2.58 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 77 | 43 |
| ZK8401-6 | 457 | 19 | 1.05 | 1.33 | 9 | 1.70 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 107 | 10 |
| ZK8401-7 | 7 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 1.36 | 35 | 0.07 | - | - | 1.45 | 4.93 |
| ZK8401-8 | 180 | 30 | 0.49 | 0.79 | 25 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 5.40 | 19 |
| ZK8401-9 | 89 | 58 | 0.24 | 0.70 | 12 | - | - | - | 0.65 | 2.02 |
| ZK8401-10 | 274 | 27 | 1.26 | 1.30 | 24 | 0.79 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 35 | 13.20 |
| ZK3612-1 | 20 | 1.50 | 31 | 4216 | 109 | 40 | 12 | 0.23 | 18,400 | 0.20 |
| ZK3612-2 | 47 | 24 | 23 | 2.90 | 8019 | 51 | 13 | 0.99 | 21,290 | 0.15 |
| ZK3612-3 | 24 | 25 | 11 | 1.50 | 7915 | 18 | 8.04 | 0.64 | 3750 | 0.03 |
| ZK3612-4 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 6.95 | 1.02 | 52 | 14 | 3.58 | 0.14 | 4386 | 0.02 |
| ZK3612-5 | 10 | 0.62 | 5.29 | 0.94 | 49 | 7.66 | 1.56 | 0.12 | 247 | - |
| ZK3612-6 | 0.23 | 0.55 | 0.19 | 1.49 | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 7.86 | - |
| ZK3612-7 | 1.06 | 10 | 277 | 37 | 920 | 551 | 127 | 3.84 | 57,880 | 0.62 |
| ZK3612-8 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 13 | 0.94 | 166 | 33 | 7.13 | 0.15 | 9332 | 0.17 |
| ZK3612-9 | 0.06 | 3.02 | 59 | 1.83 | 4103 | 197 | 22 | 1.42 | 45,896 | 0.58 |
| ZK3612-10 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 88 | 15 | 468 | 6.12 | 1.97 | 0.25 | 492 | 0.05 |
| ZK3410-1 | 1.45 | 6.50 | 1.01 | 1.66 | 230 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 10 | 7.02 |
| ZK3410-2 | 3.76 | 4.51 | 0.55 | 1.24 | 136 | 0.40 | 0.12 | - | 3.87 | 6.52 |
| ZK3410-3 | 34 | 17 | 1.08 | 1.39 | 190 | 2.09 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 15 | 43 |
| ZK3410-4 | 4.65 | 5.60 | 0.56 | 1.14 | 87 | 0.08 | - | - | 2.04 | 1.81 |
| ZK3410-5 | 6.45 | 7.46 | 0.41 | 1.03 | 160 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 3.29 | 4.88 |
| ZK3410-6 | 23 | 13 | 3.53 | 0.55 | 438 | 3.94 | 2.31 | 0.37 | 18 | 10 |
| ZK3410-7 | 1.41 | 2.78 | 0.51 | 1.29 | 143 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 5.43 | 1.43 |
| ZK3410-8 | 27 | 9.20 | 20 | 1.32 | 270 | 5.55 | 4.07 | 0.17 | 100 | 30 |
| ZK3410-9 | 61 | 13 | 41 | 2.73 | 206 | 4.88 | 3.27 | 0.06 | 80 | 17 |
| ZK3410-10 | 2.43 | 2.03 | 3.37 | 1.17 | 574 | 2.79 | 2.36 | 0.07 | 23 | 4.17 |
| Sample Serial Number | Mineral | δ34SCDT (‰) | Sample Serial Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZK8401-1 | Pyrite | 11.9 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-2 | Pyrite | 12.6 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-3 | Pyrite | 12.6 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-4 | Pyrite | 12.1 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-5 | Pyrite | 12.0 | 920.0 m |
| ZK8401-6 | Pyrite | 11.6 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-7 | Pyrite | 12.4 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-8 | Pyrite | 11.4 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-9 | Pyrite | 12.1 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-10 | Pyrite | 11.6 | 963.5 m |
| ZK8401-11 | Pyrite | 10.5 | 963.5 m |
| ZK3612-1 | Pyrite | 11.1 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-2 | Pyrite | 12.0 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-3 | Pyrite | 11.3 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3612-4 | Pyrite | 12.9 | 1537.0 m |
| ZK3410-1 | Pyrite | 10.0 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-2 | Pyrite | 10.3 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-3 | Pyrite | 10.6 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-4 | Pyrite | 11.9 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-5 | Pyrite | 11.4 | 1552.0 m |
| ZK3410-6 | Pyrite | 10.8 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-7 | Pyrite | 10.6 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-8 | Pyrite | 13.0 | 1613.0 m |
| ZK3410-9 | Pyrite | 12.8 | 1613.0 m |
| Sample Serial Number | Ore Type | 87Rb/86Sr | 87Sr/86Sr | StdErr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK3410-2 | Pyrite | 2.466515 | 0.715794 | 0.000012 |
| ZK3410-5 | Pyrite | 3.847805 | 0.718191 | 0.000022 |
| ZK3410-7 | Pyrite | 21.364224 | 0.747714 | 0.000019 |
| ZK3410-9 | Pyrite | 19.944731 | 0.745217 | 0.000017 |
| ZK3410-11 | Pyrite | 8.088107 | 0.725319 | 0.000015 |
| ZK3410-12 | Pyrite | 0.797712 | 0.713049 | 0.000024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Ren, T.; Sun, B. In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals 2024, 14, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
Tian J, Wang J, Tian T, Wang L, Wang Y, Yu X, Zhang W, Ren T, Sun B. In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals. 2024; 14(5):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Jiepeng, Jinhui Wang, Tongliang Tian, Ligong Wang, Yingpeng Wang, Xiaowei Yu, Wen Zhang, Tianlong Ren, and Bin Sun. 2024. "In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization" Minerals 14, no. 5: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456
APA StyleTian, J., Wang, J., Tian, T., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Yu, X., Zhang, W., Ren, T., & Sun, B. (2024). In-Situ Geochemical and Rb–Sr Dating Analysis of Sulfides from a Gold Deposit Offshore of Northern Sanshandao, Jiaodong Peninsula, North China: Implications for Gold Mineralization. Minerals, 14(5), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14050456






