Sediment-Hosted Rare-Earth Elements Mineralization from the Dian-Qian District, Southwest China: Mineralogy and Mode of Occurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction
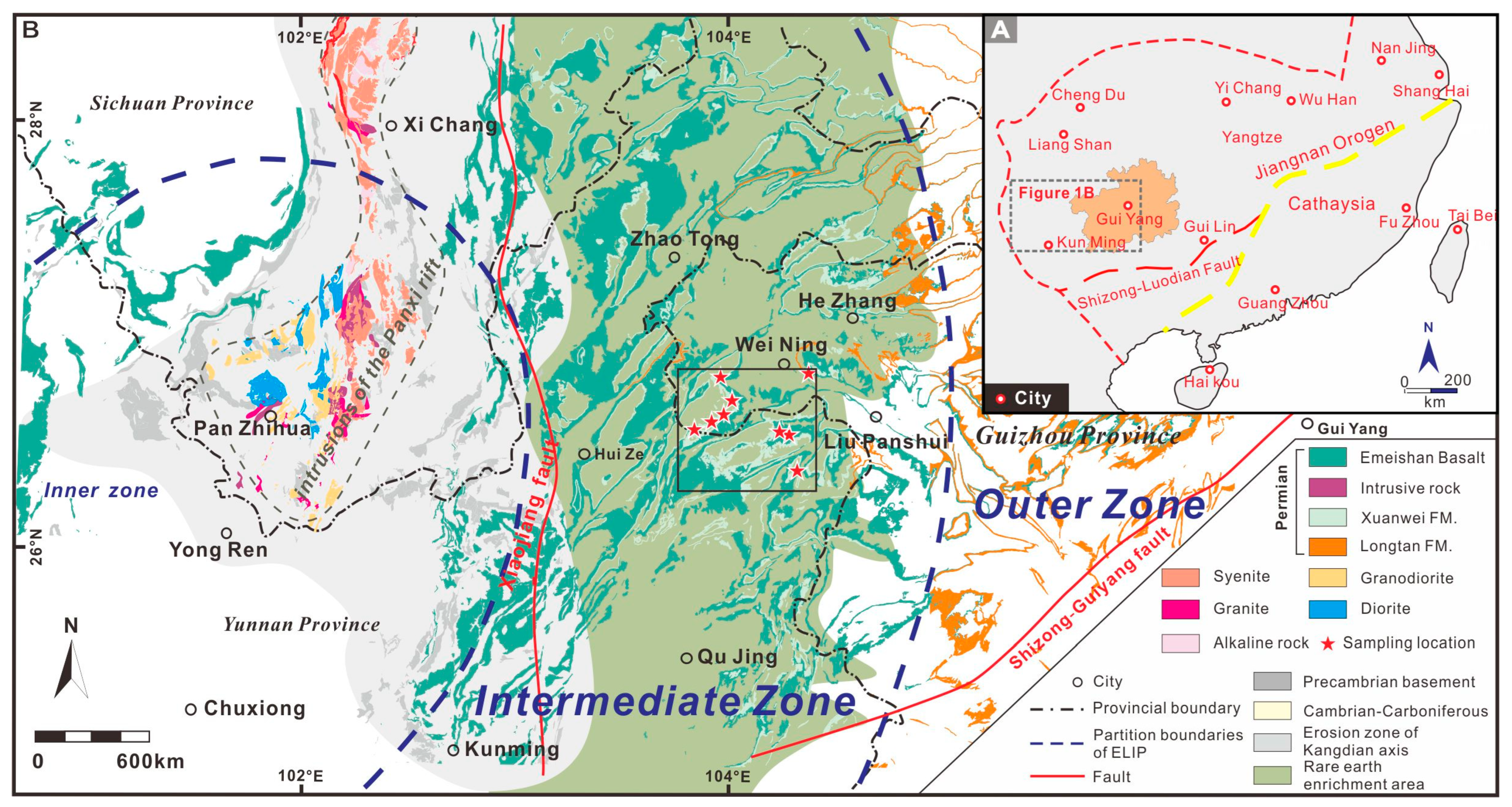
2. Geological Background
3. Sampling and Analytical Techniques
4. Results
4.1. Mineralogical Composition of the Samples
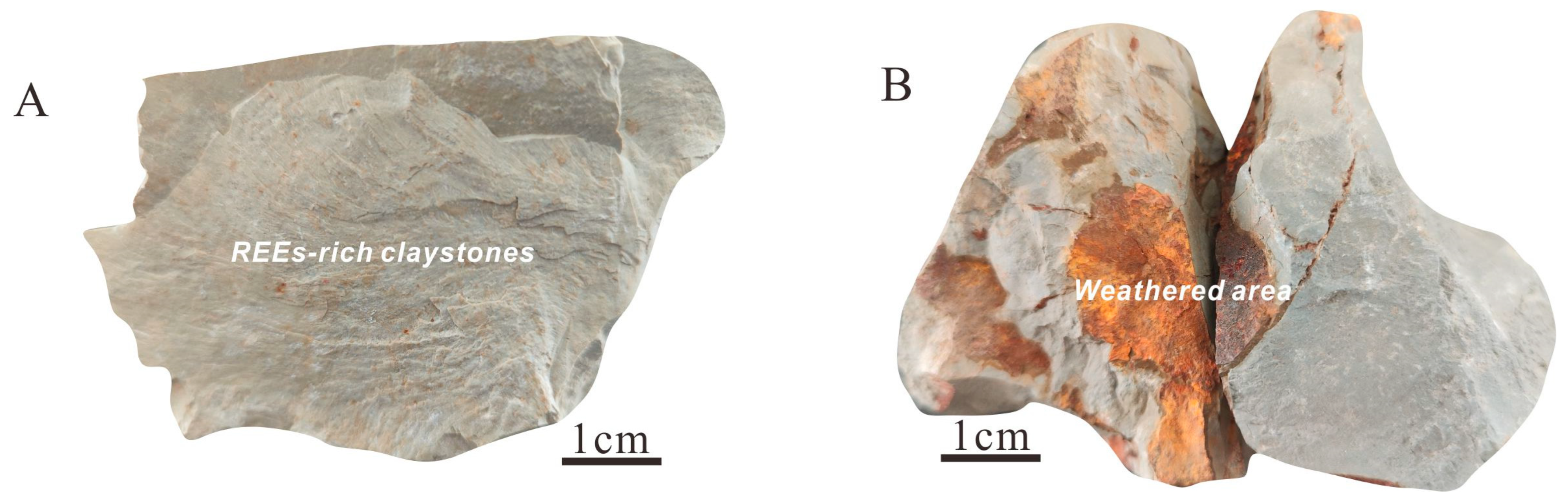
4.2. Texture of the Samples
4.3. EPMA Analysis of Clay Minerals
4.4. Continuous Extraction Results
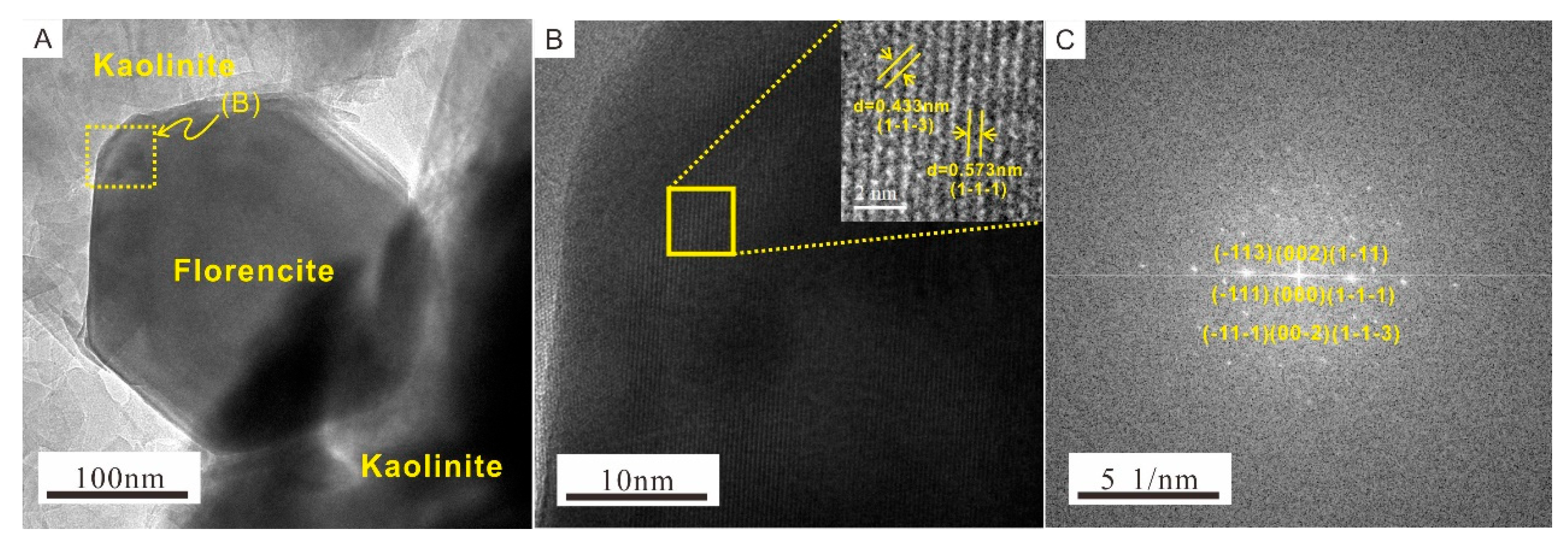
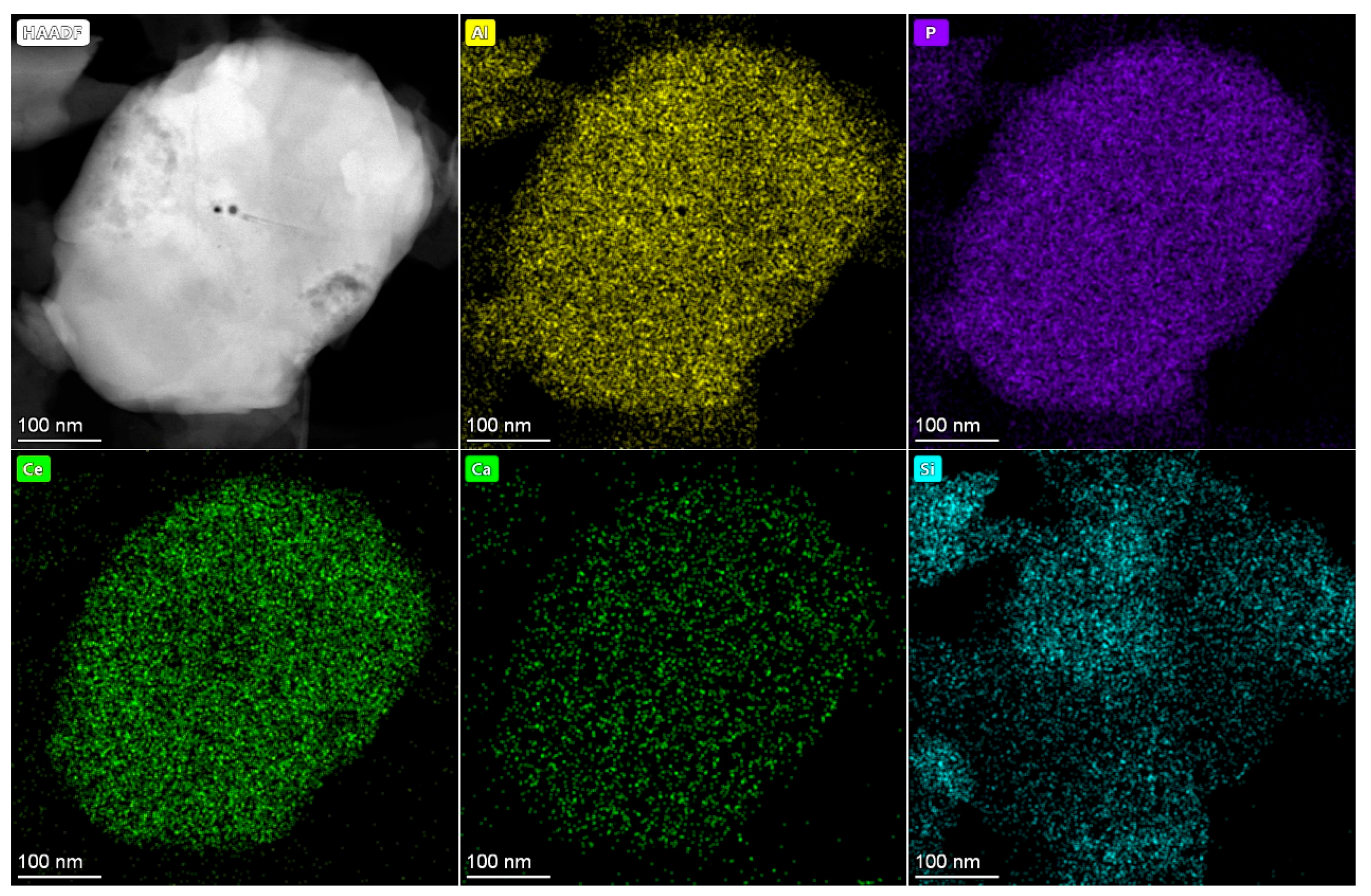
4.5. TEM Analysis of Samples
5. Discussion
5.1. Occurrence of REEs
5.2. Implications for Utilization of Rare-Earth Resources
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Gosen, B.S.; Verplanck, P.L.; Seal, R.R., II; Long, K.R.; Gambogi, J. Rare-Earth Elements; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Blissett, R.S.; Smalley, N.; Rowson, N.A. An Investigation into Six Coal Fly Ashes from the United Kingdom and Poland to Evaluate Rare Earth Element Content. Fuel 2014, 119, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.R.; Van Gosen, B.S.; Foley, N.K.; Cordier, D. The Principal Rare Earth Elements Deposits of the United States: A Summary of Domestic Deposits and a Global Perspective; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; ISBN 90-481-8678-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Nakamura, K.; Takaya, Y.; Kitamura, K.; Ohta, J.; Toda, R.; Nakashima, T.; Iwamori, H. Deep-Sea Mud in the Pacific Ocean as a Potential Resource for Rare-Earth Elements. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, M.; Rollinson, G.; Mondillo, N.; Balassone, G.; Santoro, L. Quantitative Mineralogical Characterization of Karst Bauxite Deposits in the Southern Apennines, Italy. Econ. Geol. 2013, 108, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Chekryzhov, I.Y.; Seredin, V.V.; Nechaev, V.P.; Graham, I.T.; Hower, J.C.; Ward, C.R.; Ren, D.; Wang, X. Metalliferous Coal Deposits in East Asia (Primorye of Russia and South China): A Review of Geodynamic Controls and Styles of Mineralization. Gondwana Res. 2016, 29, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, E.Y.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, J.J.; Qin, J.H.; Lai, Y.; Ke, K.; Tian, K.Z.; Zhang, J.W.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.L. Origin and Metal-Enrichment Mechanism of Sedimentary Rare Earth Element Deposits in Yunnan and Guizhou Provinces, Western Yangtze Block, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2023, 156, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Gong, D.; Qin, J.; Tian, E.; Hui, B.; Xu, L.; Gao, Z. Sedimentary Rare Earths from Eastern Yunnan to Western Guizhou: A New Type of Rare Earth Resource and Its Development and Utilization Potential. Geol. China 2022, 49, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar]
- He, P.; He, M.; Zhang, H. State of Rare Earth Elements in the Rare Earth Deposits of Northwest Guizhou, China. Acta Geochim. 2018, 37, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.X. Ion-adsorbed rare earth minerals discovered in western Guizhou. Guizhou Geol. 1989, 3, 272. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Gong, D.; Hui, B. Study on the Occurrence State of Rare Earth Elements in the Rare Earth-Rich Rock Series of the Permian Xuanwei Formation in a Place in Guizhou. Multipurp. Util. Miner. Resour. 2018, 6, 90–94, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L. A Method for Selectively Leaching Sedimentary Rare Earth Ores. China Patent ZL201811407361.2, 24 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Huang, Q.; He, L.L.; Lv, S.Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, X.Y.; Zhao, T. The occurrence state of rare earth elements in sedimentary rare earth deposits in Mazha area, northwest Guizhou. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2023, 46, 786–798. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.F.; Xiang, Z.Z.; Wu, L.; Xiao, X.G.; Ye, L.; Zeng, D.G.; Huang, W.H. Occurrence forms of rare earths in Nb-REE enriched layers in Yulong area, northwest Guizhou. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2022, 42, 555–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Wu, C.; Zheng, C.; Yao, J.; Xiao, C. Extreme Enrichment of Rare Earth Elements in Hard Clay Rocks and Its Potential as a Resource. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 72, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Graham, I. Origin of the Alkali Tonsteins from Southwest China: Implications for Alkaline Magmatism Associated with the Waning Stages of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 63, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dai, S.; Graham, I.T.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Song, X.; Hower, J.C.; Zhou, Y. Cryptic Sediment-Hosted Critical Element Miner-alization from Eastern Yunnan Province, Southwestern China: Mineralogy, Geochemistry, Relationship to Emeishan Alkaline Magmatism and Possible Origin. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 80, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; You, F.; Wu, C.; Zheng, C. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics in the Paleo-Weathering Crust Sedimentary Type REE Deposits, Western Guizhou, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 73, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordens, A.; Cheng, Y.P.; Waters, K.E. A Review of the Beneficiation of Rare Earth Element Bearing Minerals. Miner. Eng. 2013, 41, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Xu, Y.G.; Chung, S.L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Y. Sedimentary Evidence for a Rapid, Kilometer-Scale Crustal Doming Prior to the Eruption of the Emeishan Flood Basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2003, 213, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.Y.; Gao, C.X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Guo, L.J.; Gao, C.H. Sequence-Palaeogeography and Coal Accumulation of Late Permian in Southwestern China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2013, 31, 856–866. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Luo, P.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Feng, M.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y. Enrichment of Ion-Exchangeable Rare Earth Elements by Felsic Volcanic Rock Weathering in South China: Genetic Mechanism and Formation Preference. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 114, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.M.; Zhou, M.F.; Williams-Jones, A.E. Controls on the Dynamics of Rare Earth Elements during Subtropical Hillslope Processes and Formation of Regolith-Hosted Deposits. Econ. Geol. 2020, 115, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.M.; Zhao, W.W.; Zhou, M.F. Nature of Parent Rocks, Mineralization Styles and Ore Genesis of Regolith-Hosted REE Deposits in South China: An Integrated Genetic Model. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2017, 148, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanematsu, K.; Kon, Y.; Imai, A.; Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, Y. Geochemical and Mineralogical Characteristics of Ion-Adsorption Type REE Mineralization in Phuket, Thailand. Miner. Depos. 2013, 48, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P. The Occurrence of Rare Earth Elements in the Weathered Basalt of Northwest Guizhou Province and Their Metallurgy Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, D.; Xue, K.; Liu, J. A review of flotation reagents for bastnäsite-(Ce) rare earth ore. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 321, 103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, A.; Xiong, W.L.; Chen, D.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, P. Research on the occurrence and acid leaching of rare earth elements in deep sea sediments at a certain station in the Pacific Ocean. China Rare Earth Soc. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, R.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, J.; He, H. Influence of Interlayer Species on the Thermal Characteristics of Montmo-rillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author (s) and contributor (s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor (s). MDPI and/or the editor (s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |

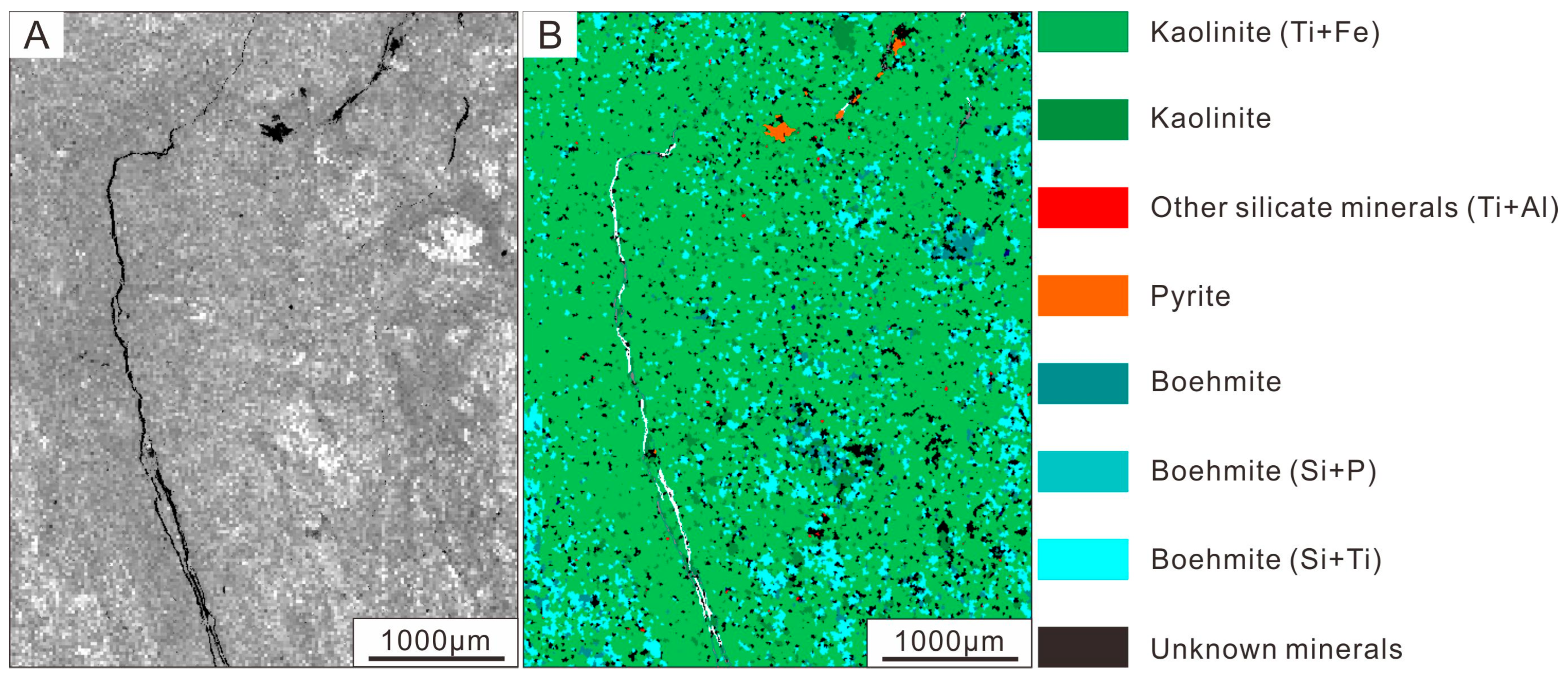

| Mineral | Content (wt.%) |
|---|---|
| Kaolinite (Ti + Fe) | 86.51 |
| Kaolinite (Fe) | 2.94 |
| Boehmite | 6.40 |
| Boehmite (Si + P) | 0.92 |
| Boehmite (Si + Ti) | 0.67 |
| Quartz | 1.10 |
| Other silicate minerals (Ti + Al) | 0.24 |
| Pyrite | 0.17 |
| Rutile/anatase | 0.06 |
| Unknow minerals + holes | 0.99 |
| Sample | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MnO | FeO | MgO | CaO | TiO2 | La2O3 | Ce2O3 | Nd2O3 | Dy2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.92 | 43.85 | bdl | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | bdl |
| 2 | 39.01 | 43.54 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | bdl |
| 3 | 38.55 | 44.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 4 | 39.01 | 45.17 | 0.03 | 0.19 | bdl | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl |
| 5 | 39.14 | 44.32 | 0.02 | 0.05 | bdl | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | bdl | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 6 | 39.25 | 44.09 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| 7 | 39.15 | 44.22 | bdl | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | bdl |
| 8 | 39.10 | 42.38 | bdl | 0.07 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | 0.03 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl |
| 9 | 39.11 | 44.01 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl | 0.03 | bdl | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | bdl |
| 10 | 39.17 | 45.05 | bdl | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | bdl | bdl |
| Average | 39.04 | 44.06 | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Sample | Ho2O3 | Er2O3 | Tm2O3 | Yb2O3 | Lu2O3 | Eu2O3 | Tb2O3 | Gd2O3 | Sm2O3 | Total | REO |
| 1 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.03 | bdl | 0.01 | 83.16 | 0.28 |
| 2 | bdl | 0.08 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl | 0.04 | bdl | bdl | bdl | 83.05 | 0.21 |
| 3 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl | bdl | 82.84 | 0.18 |
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | 84.58 | 0.12 |
| 5 | bdl | bdl | 0.02 | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | bdl | 83.62 | 0.06 |
| 6 | 0.01 | 0.02 | bdl | 0.01 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl | bdl | bdl | 83.57 | 0.10 |
| 7 | bdl | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | bdl | 83.58 | 0.12 |
| 8 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.02 | bdl | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | bdl | 0.01 | 81.71 | 0.15 |
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | bdl | bdl | 0.01 | 0.02 | bdl | bdl | 83.29 | 0.12 |
| 10 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.06 | bdl | bdl | 84.75 | 0.25 |
| Average | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | bdl | bdl | 83.42 | 0.27 |
| REE Deportment | Ratio (wt.%) |
|---|---|
| Water-solution/ion-adsorbed | 16.94 |
| Carbonate-bound | 0.76 |
| Amorphous iron–manganese-bound | 34.10 |
| Crystalline iron–manganese-bound | 3.48 |
| Residue | 44.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hui, B.; Gong, D.; Xu, L.; Lai, Y.; Qin, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, W.; Lin, H. Sediment-Hosted Rare-Earth Elements Mineralization from the Dian-Qian District, Southwest China: Mineralogy and Mode of Occurrence. Minerals 2024, 14, 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14090903
Hui B, Gong D, Xu L, Lai Y, Qin J, Xu Y, Yang W, Lin H. Sediment-Hosted Rare-Earth Elements Mineralization from the Dian-Qian District, Southwest China: Mineralogy and Mode of Occurrence. Minerals. 2024; 14(9):903. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14090903
Chicago/Turabian StyleHui, Bo, Daxing Gong, Lu Xu, Yang Lai, Jianhua Qin, Ying Xu, Wei Yang, and Haitao Lin. 2024. "Sediment-Hosted Rare-Earth Elements Mineralization from the Dian-Qian District, Southwest China: Mineralogy and Mode of Occurrence" Minerals 14, no. 9: 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14090903
APA StyleHui, B., Gong, D., Xu, L., Lai, Y., Qin, J., Xu, Y., Yang, W., & Lin, H. (2024). Sediment-Hosted Rare-Earth Elements Mineralization from the Dian-Qian District, Southwest China: Mineralogy and Mode of Occurrence. Minerals, 14(9), 903. https://doi.org/10.3390/min14090903





