Classification and Controlling Factors of Different Types of Pore Throat in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Fractal Features—A Case Study of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Settings and Experimental Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Geological Structure
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Physical Properties, Thin Section and Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.2. XRD Whole Rock Test
2.2.3. High Pressure Mercury Intrusion
2.3. Fractal Method of Mercury Intrusion Curves
3. Results
3.1. Petrological Characterization
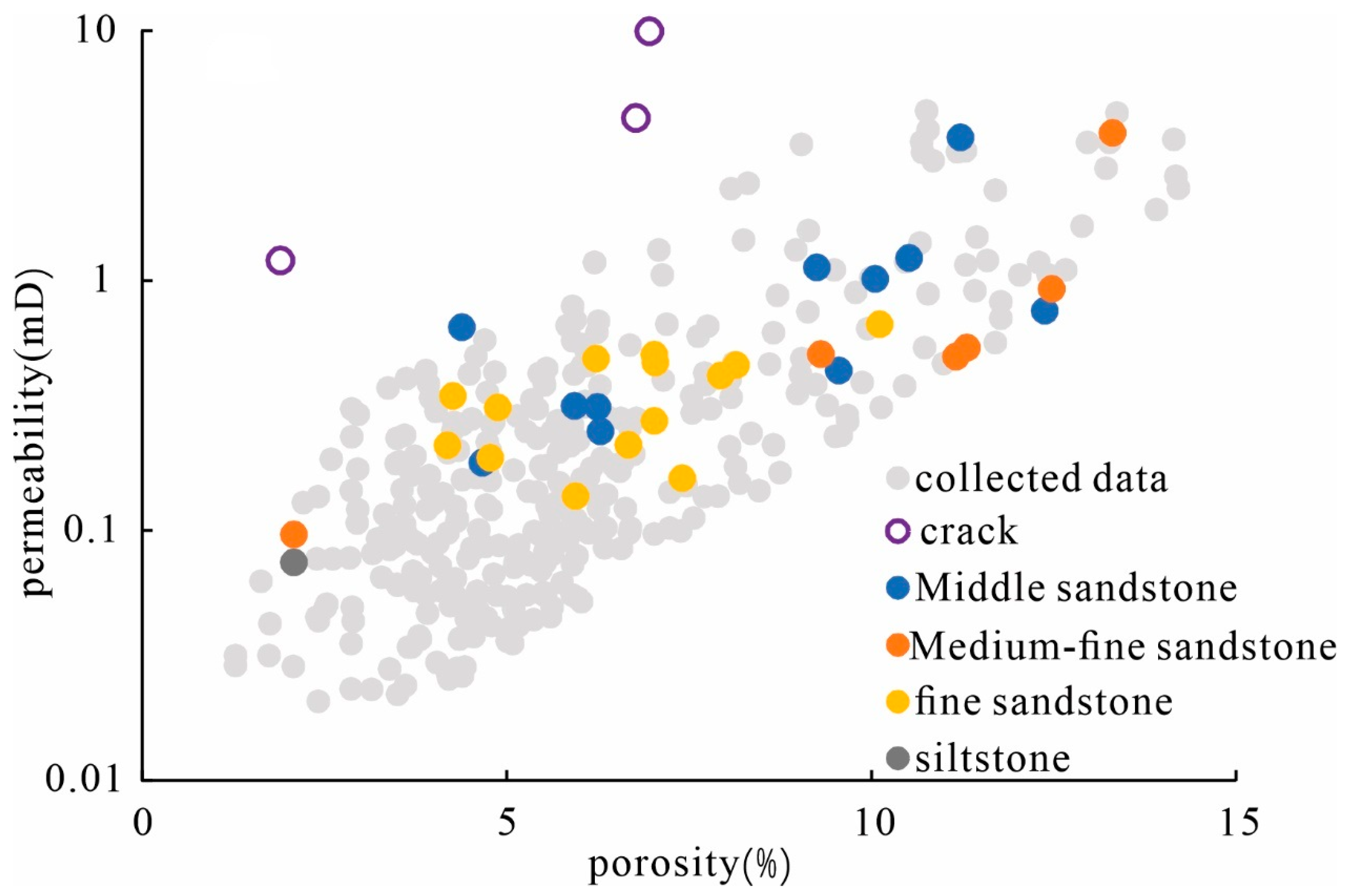
3.2. Physical Property Features
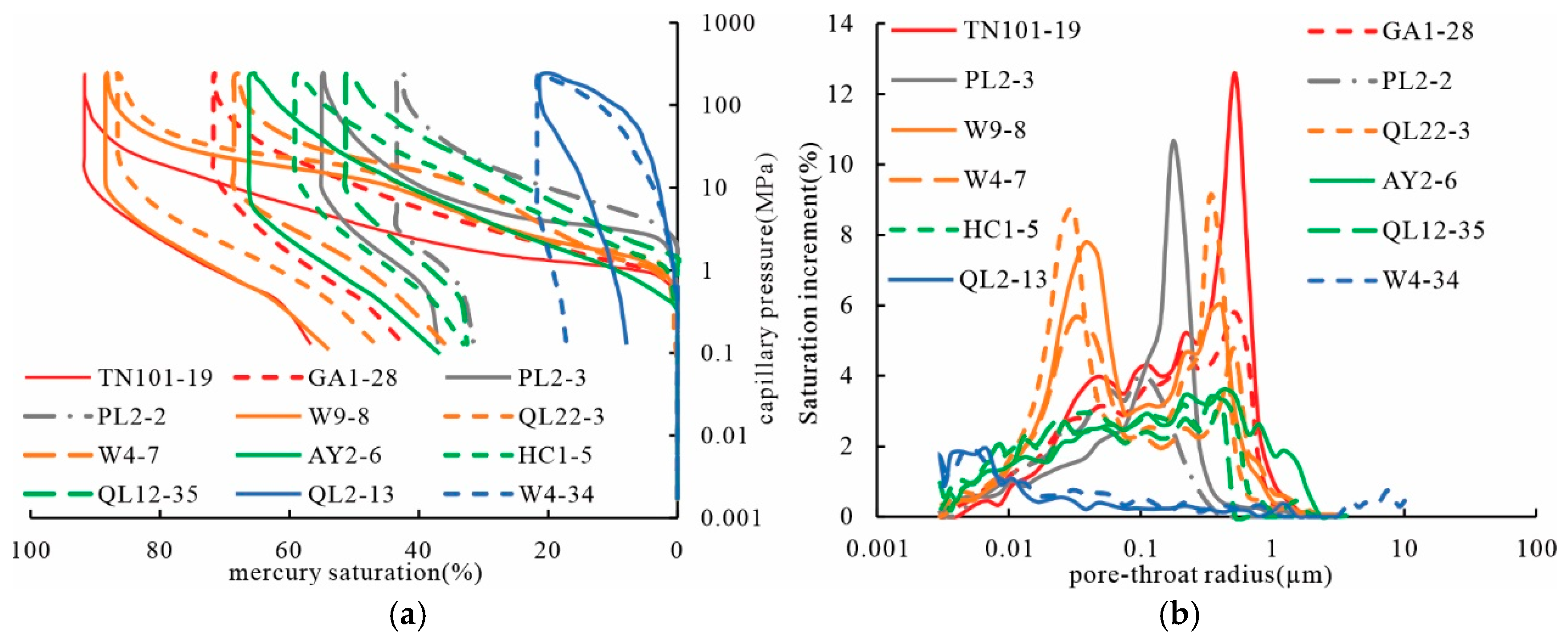
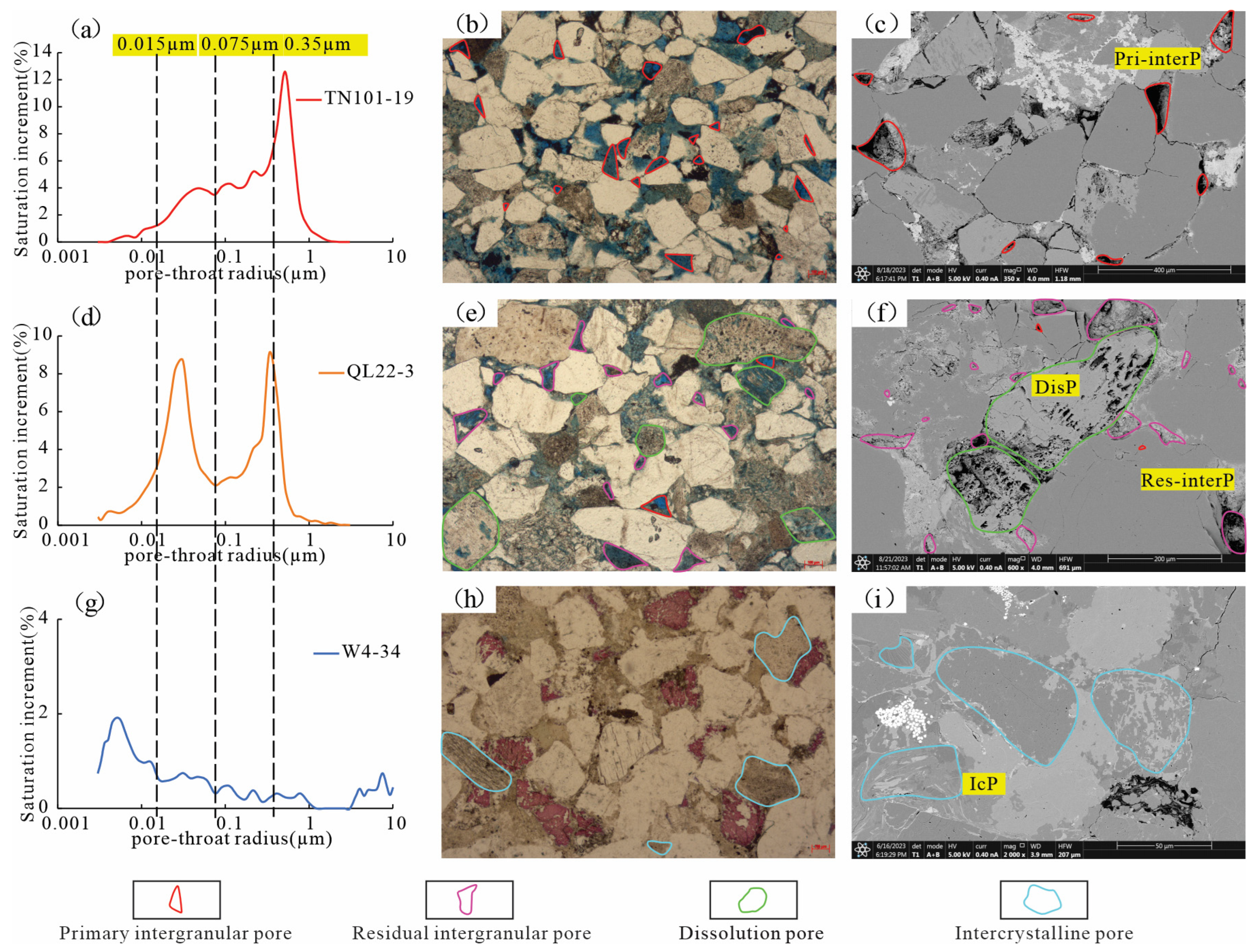
3.3. Pore Structure Characteristics
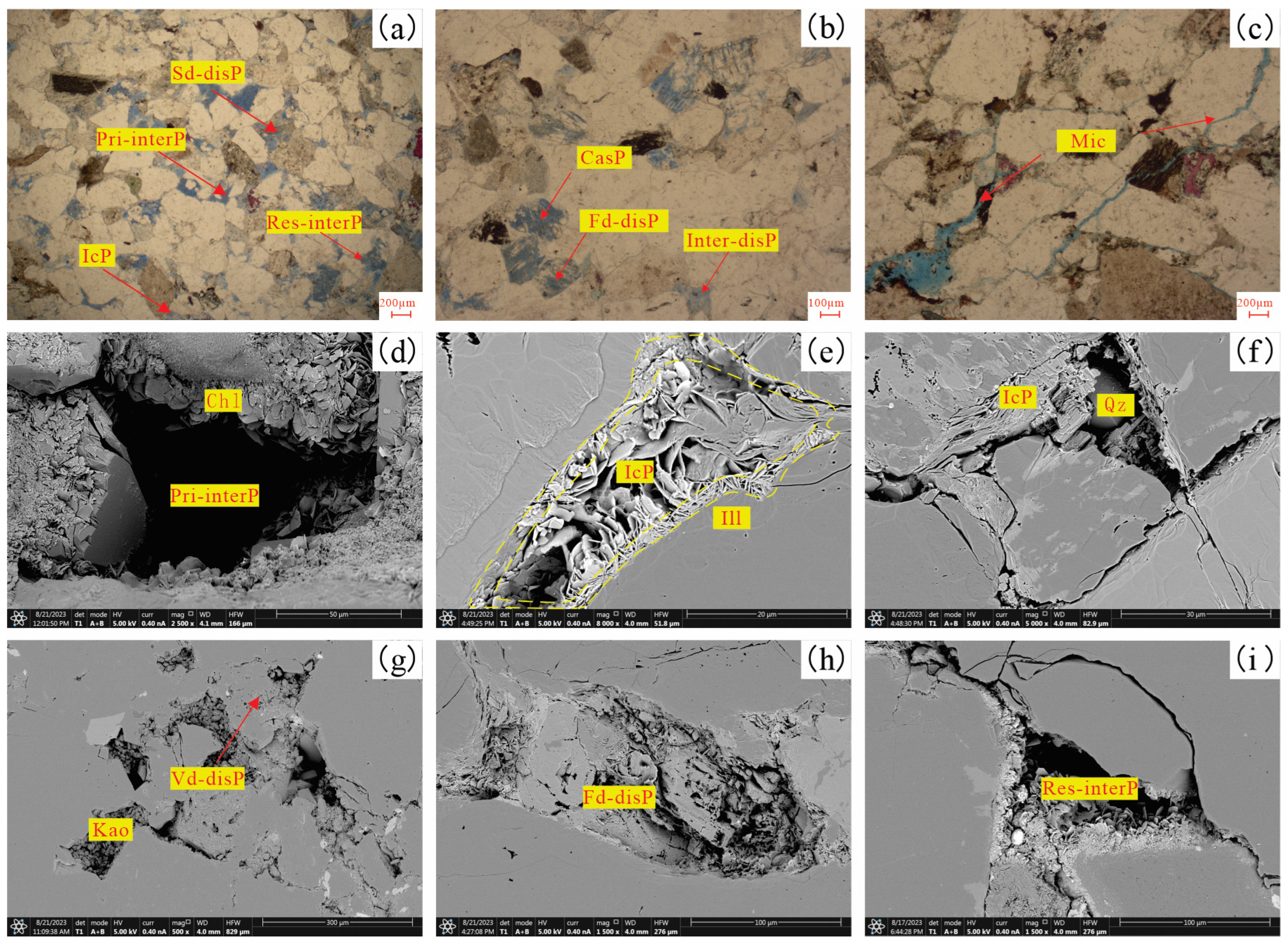
3.3.1. Types of Reservoir Spaces
3.3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Pore Throats
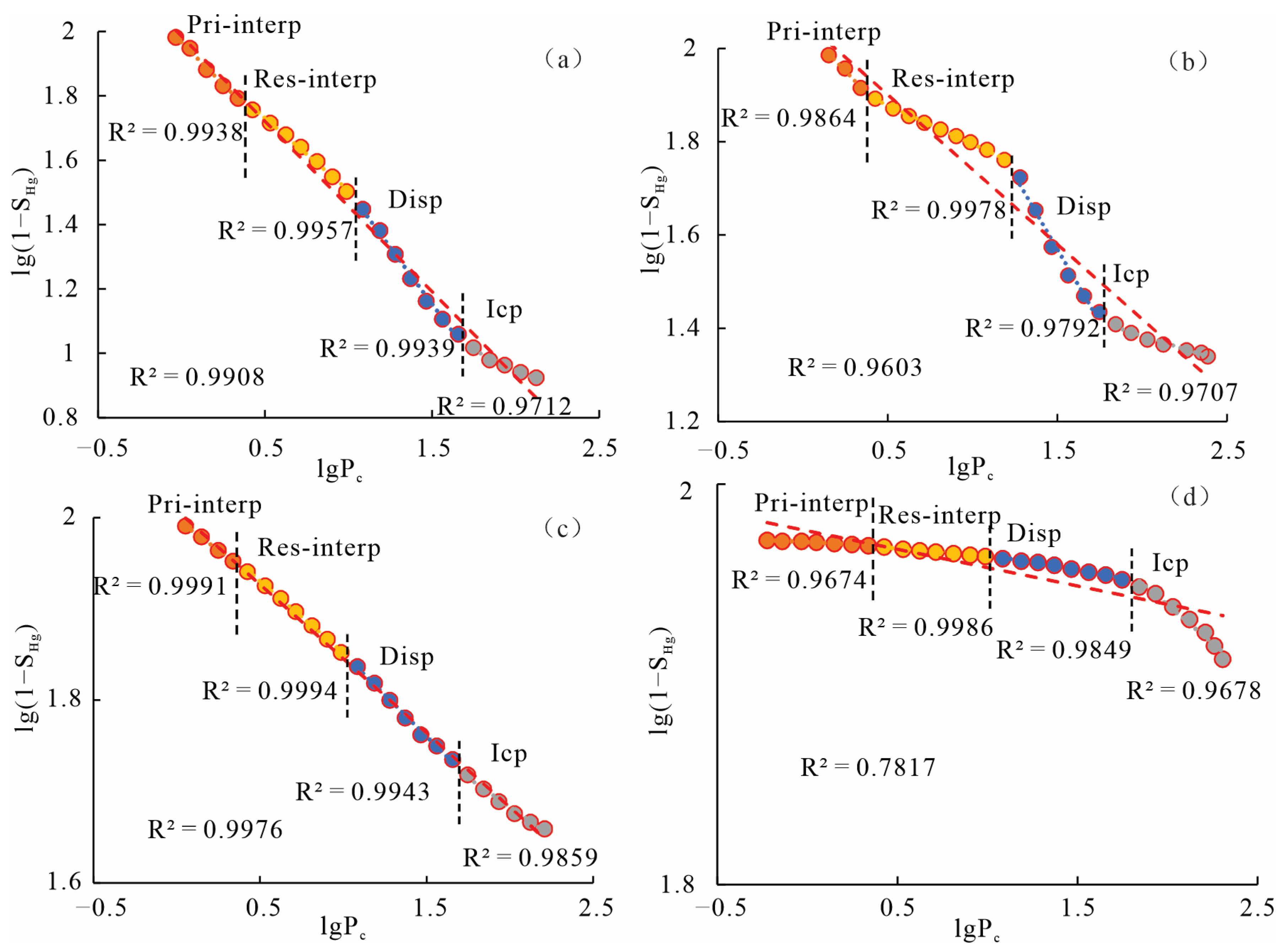
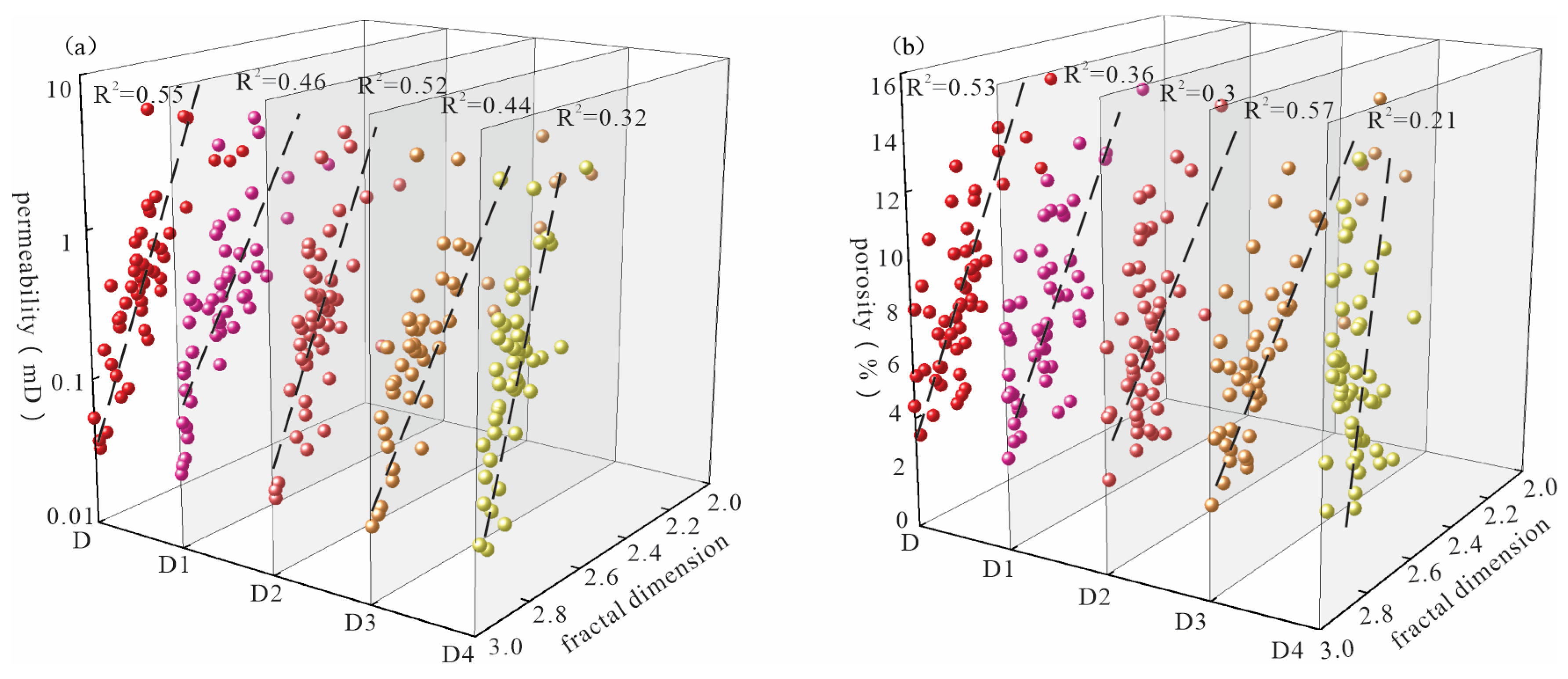
3.4. Fractal Characteristics of Pore Structure
4. Discussions
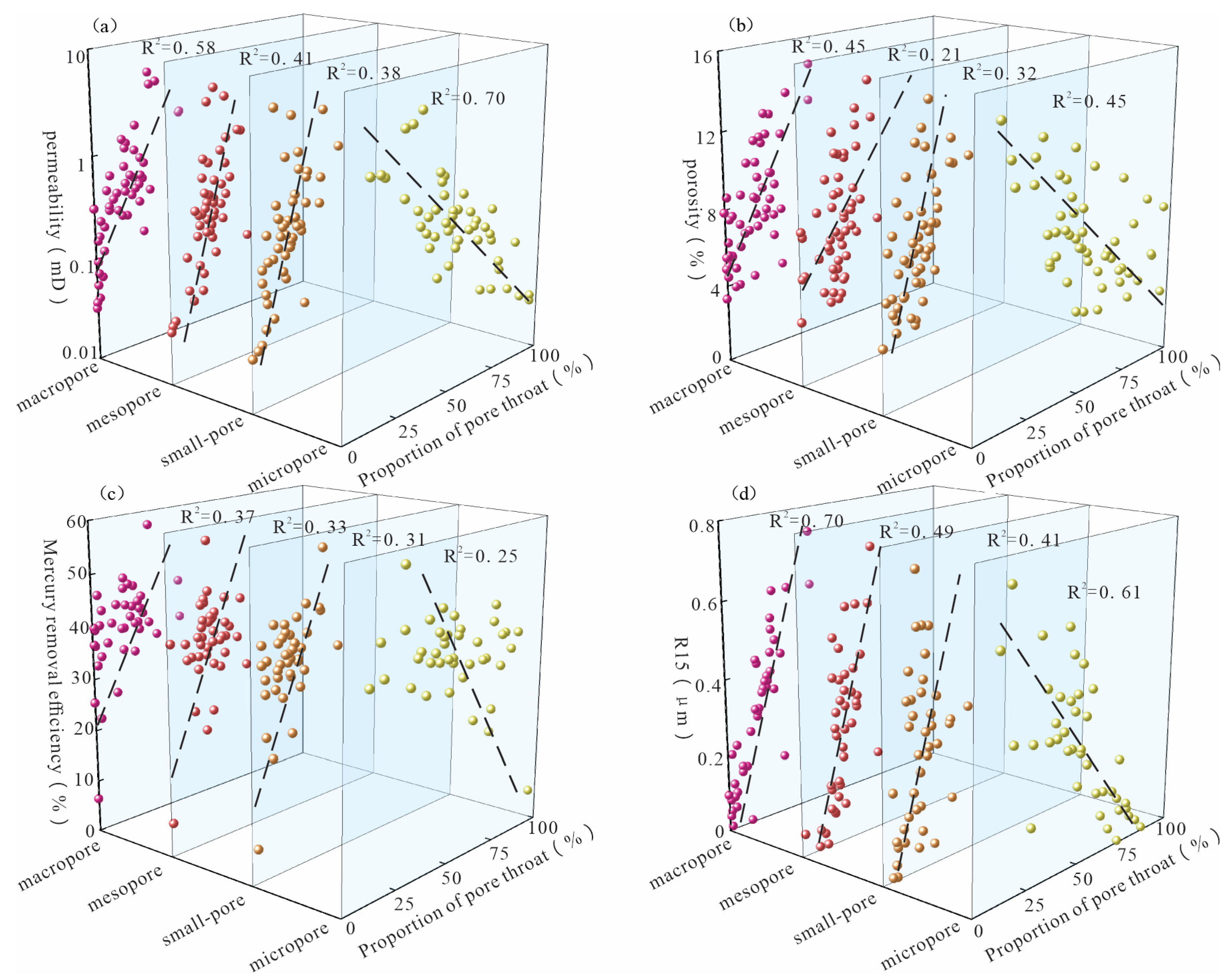
4.1. Classification of Pore-Throat Types
4.2. Control Factors of Different Types of Pore-Throat Development
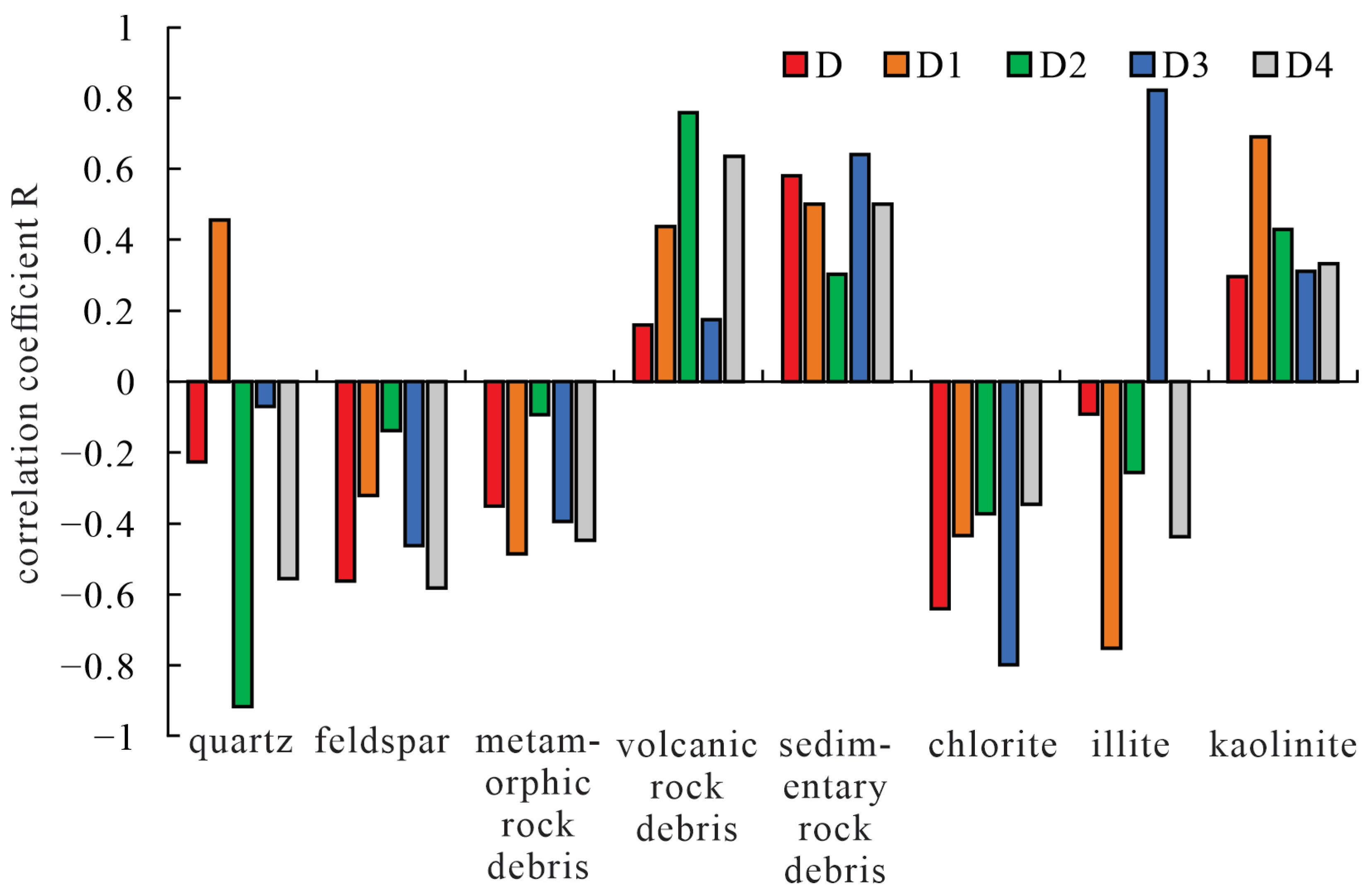
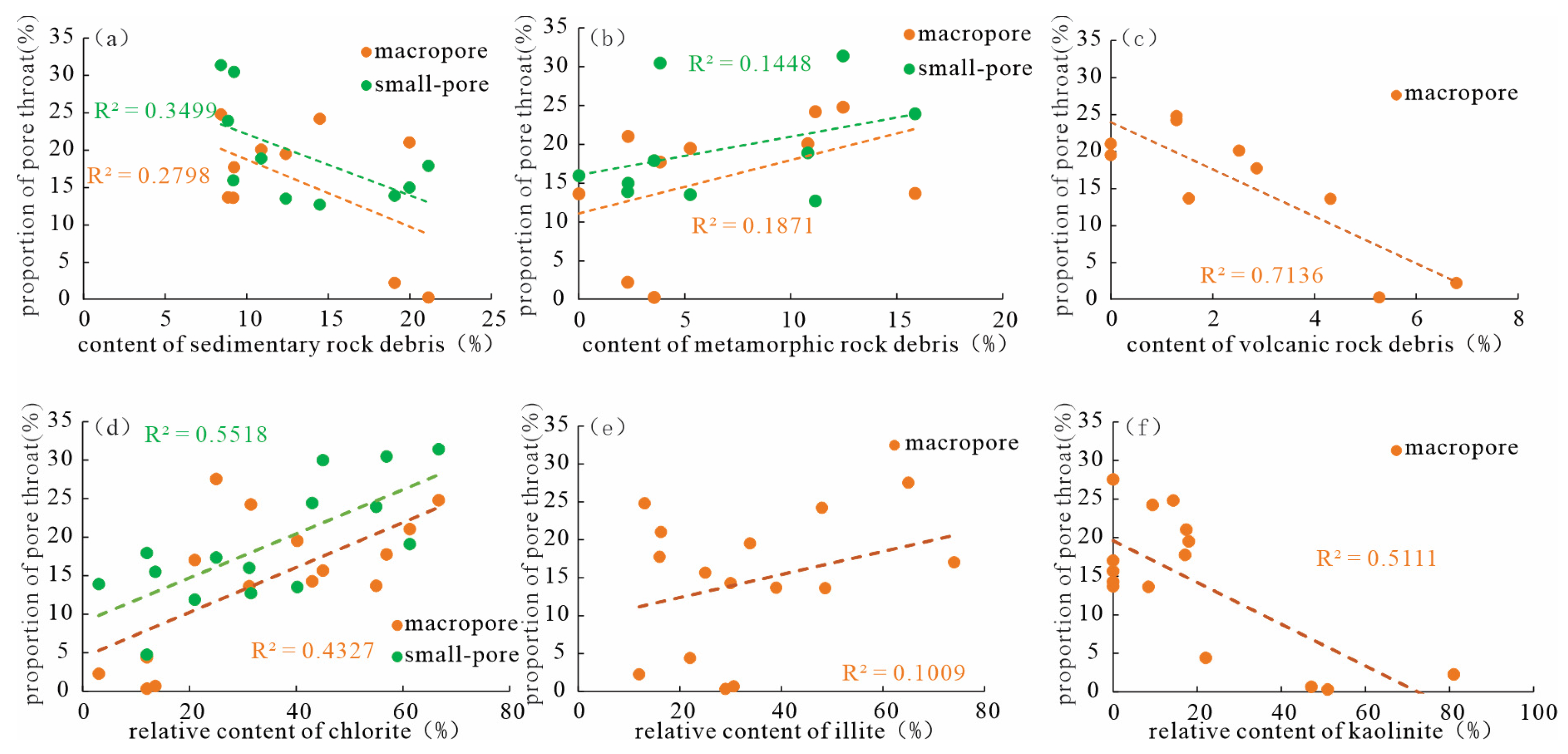
4.3. Influence of Rock Composition
4.4. Control Factors for the Development of Tight Sandstone Reservoirs
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on fractal inflection points, the pore-throats of T3x4 are divided into macropores (>350 nm), mesopores (75–350 nm), small-pores (16–75 nm), and micropores (<16 nm), mainly corresponding to the primary intergranular pore-throats, residual intergranular pore-throats, dissolution pore-throats, and intercrystalline pore-throats, respectively.
- (2)
- The pore-throats of the Xujiahe Formation exhibits four segment fractal features, and the overall fractal dimension D increases with the decrease of particle size. The proportion of intercrystalline pore throats in clay is the largest, followed by residual intergranular pore throats and dissolution pore throats, and the proportion of primary intergranular pore throats is the smallest. The contribution of different types of pore throats to physical properties of tight sandstone is influenced by their respective homogeneity. The permeability has a better relationship with the proportion and fractal dimension of primary intergranular pore-throats and residual intergranular pore-throats of tight reservoir of the Xujiahe Formation. The relationship between porosity and the proportion and fractal dimension of primary intergranular pore-throats and dissolution pore-throats is better.
- (3)
- The impact of mineral compositions on the homogeneity of different types of pore-throats is variable. Illite film, chlorite film, and metamorphic rock debris are conducive to the homogeneity of primary intergranular pore-throats, but kaolinite and sedimentary rock debris are harmful to the homogeneity of primary intergranular pore-throats. Quartz cementation promotes the development of residual intergranular pore-throats, while volcanic rock debris damages the development of residual intergranular pore-throats. Chlorite film and feldspar are beneficial for the homogeneity of dissolution pore-throats, while sedimentary rock debris is harmful to the homogeneity of dissolution pore-throats.
- (4)
- The high-quality reservoirs in T3x4 are controlled by the development of primary intergranular pores and dissolution pores, mainly developed in underwater distributary channels with strong hydrodynamic conditions, large particle size, high content of brittle minerals (quartz and metamorphic rock debris), development of illite film, chlorite film, and feldspar, and low content of sedimentary rock debris, matrix, and cements.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, A.L.; Wei, Y.S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, G.T.; Meng, D.W.; Huang, S.Q. Development status and prospect of tight sandstone gas in China. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Li, J.Q.; Lu, S.F.; Chen, G.H.; Pang, X.T.; Zhang, P.F.; He, T.H. Evaluation of gas-in-place content and gas-adsorbed ratio using carbon isotope fractionation model: A case study from Longmaxi shales in Sichuan Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2022, 249, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.W.; Lu, J.M.; Lu, S.F.; Zhang, P.F.; Wang, M.; Lin, Z.Z.; Jiang, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, G.S. Depositional and diagenetic controls over reservoir quality of tight sandstone and conglomerate in the lower Cretaceous Shahezi formation, Xujiaweizi fault depression, Songliao basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2023, 155, 106374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.N.; Zhu, R.K.; Liu, K.Y.; Su, L.; Bai, B.; Zhang, X.X.; Yuan, X.J.; Wang, J.H. Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: Characteristics and recognition criteria. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 88, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, S.H.; Xia, D.L.; He, S.C.; Zhang, X.F. An investigation into pore structure and petrophysical property in tight sandstones: A case of the Yanchang Formation in the southern Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 97, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Ran, Y.; Zhou, Z.L. Predictive distribution of high-quality reservoirs of tight gas sandstones by linking diagenesis to depositional facies: Evidence from Xu-2 sandstones in the Penglai area of the central Sichuan basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 23, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Zeng, J.H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y. Impacts of sedimentology and diagenesis on pore structure and reservoir quality in tight oil sandstone reservoirs: Implications for macroscopic and microscopic heterogeneities. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 111, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.B.; Xiao, W.L.; Zheng, L.L.; Lei, Q.H.; Qin, C.Z.; He, Y.A.; Liu, S.S.; Li, M.; Li, Y.M.; Zhao, J.Z.; et al. Pore throat structure heterogeneity and its effect on gas-phase seepage capacity in tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 2892–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.P.; Liu, C.L.; Ouyang, S.Q.; Luo, B.; Zhao, D.D.; Sun, W.; Awan, R.S.; Lu, Z.D.; Li, G.X.; Zang, Q.B. Investigation of pore-throat structure and fractal characteristics of tight sandstones using HPMI, CRMI, and NMR methods: A case study of the lower Shihezi Formation in the Sulige area, Ordos Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, R.; Alvarado, V.; Gonzalez, H. Fractal Dimensions from Mercury Intrusion Capillary Tests. In Proceedings of the SPE Latin America Petroleum Engineering Conference, Caracas, Venezuela, 8–11 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, X.Q.; Ding, C.; Chen, D.; Li, M. Pore Structure and Fractal Characteristics of Yan 10 Tight Sandstone Reservoir in Wuqi Area. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 12474–12483. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Liu, J.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xiao, K.H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Fan, L.X.; Li, J.T. Genetic mechanisms of high-quality tight siliciclastic reservoirs: A case study from the upper triassic xujiahe formation in the yuanba area, sichuan basin, China. Energy Geosci. 2024, 5, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, L.B.; Zhai, C.B.; Chen, H.D.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, Y.H.; Deng, X.L. Impacts of lithologic characteristics and diagenesis on reservoir quality of the 4th member of the upper triassic xujiahe formation tight gas sandstones in the western sichuan basin, southwest china. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 107, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Liu, J.D.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.J. Occurrence and origin of chlorite and associated impact on tight sandstone reservoir quality: A case study of the Xujiahe Formation (NE Sichuan Basin, China). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 209, 109859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Zhang, C.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Hou, S. Investigation on pore structure characteristics of ultra-tight sandstone reservoirs in the upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation of the northern Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 138, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.W.; Mu, X.J.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Ge, J.; Xu, S.; Zhou, S.B. Development characteristics of rock debris in the Lower Shihezi Formation of the Permian in the Hangjinqi area of the Ordos Basin and their impact on reservoir properties. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 2019, 40, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, L.K.; Liu, K.Y.; Cao, B.F.; Gao, J.L.; Qiu, G.Q. Diagenetic history and reservoir evolution of tight sandstones in the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 201, 108451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xiao, K.H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Jin, W.J. Characterization of favorable lithofacies in tight sandstone reservoirs and its significance for gas exploration and exploitation: A case study of the 2~(nd) member of triassic xujiahe formation in the xinchang area, sichuan basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.S.; Guo, X.S.; Guo, T.L.; Huang, R.; Cai, X.Y.; Li, G.X. The puguang gas field: New giant discovery in the mature sichuan basin, southwest china. Aapg Bull. 2007, 91, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Song, Y.; Pang, X.Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Yang, K.N.; Li, B.Y. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of the upper Triassic T3x5 source rocks in the western Sichuan Depression: Assessment for unconventional natural gas. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2015, 89, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.F.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Zhu, F.; Tang, Q.S.; Gao, W.L. Fluid–rock interaction and its effects on the Upper Triassic tight sandstones in the Sichuan Basin, China: Insights from petrographic and geochemical study of carbonate cements. Sediment. Geol. 2019, 383, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Wang, G.W.; Fan, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.C.; Zhou, Z.L.; Fan, X.Q. Insight into the pore structure of tight sandstones using nmr and hpmi measurements. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 10200–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, E. Note on a method of determining the distribution of pore sizes in a porous material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1921, 7, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.Y.; Cheng, Q.M.; Ling, Q.C.; Li, B.; Bao, Z.Y.; Fan, P. Fractal and multifractal analysis of carbonate pore-scale digital images of petroleum reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2010, 27, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Z.; Hua, M.Q. Fractal geometry description of reservoir pore structure. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 1998, 19, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K. Analytical derivation of brooks–corey type capillary pressure models using fractal geometry and evaluation of rock heterogeneity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 73, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merinero, R.; Cárdenes, V.; Lunar, R.; Boone, M.; Cnudde, V. Representative size distributions of framboidal, euhedral, and sunflower pyrite from high-resolution x-ray tomography and scanning electron microscopy analyses. Am. Mineral. 2017, 102, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhang, S.C.; Lang, Z.X. Calculate the fractal dimension of pore structure using segmented regression method. J. Pet. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2004, 28, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, M.; Fernandes, C.P.; da Cunha Neto, J.A.; Wolf, F.G.; dos Santos, V.S. Characterization of pore systems in seal rocks using nitrogen gas adsorption combined with mercury injection capillary pressure techniques. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2013, 39, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.S.; Gao, Y.; Peng, S.C.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Lu, S.F. Classification and control factors of pore-throat systems in hybrid sedimentary rocks of Jimusar Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.P.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Xie, Y.Y.; Shang, Y.H.; Chen, T.T.; Zhang, Z.W. Research on the microscopic pore-throat structure and reservoir quality of tight sandstone using fractal dimensions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhu, S.F.; Wang, J.P.; Gao, Y.; Wan, C.F.; Tong, H. Physical Properties, Pore-throat Structure, Fractal Characteristics and Their Effects on the Gas-Bearing Capacity of Tight Sandstone: A Case Study from the Northern Tianhuan Depression, Ordos Basin, China. Nat. Resour. Res. 2022, 31, 1559–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.X.; Xiao, D.S.; Jiang, S.; Lu, S.F.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.M. Application of the combination of high-pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance to the classification and evaluation of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Linxing Block in the Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2020, 7, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Deng, Z.; Hu, H.Y.; Tian, F.H.; Ding, R.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Z.R.; Hou, S.Y.; Li, X.G.; Dai, R.R.; et al. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of transitional shales with different lithofacies from the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin. Energy Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 3979–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.J.; Lai, F.Q.; Gao, X.B.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, N.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, S.C.; Luo, X.; et al. Characteristics and Genetic Mechanism of Pore Throat Structure of Shale Oil Reservoir in Saline Lake—A Case Study of Shale Oil of the Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin. Energies 2021, 14, 8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Sun, F.N.; Liu, Y.F.; Sun, Z.M. Micro/nanoscale pore structure and fractal characteristics of tight gas sandstone: A case study from the Yuanba area, northeast Sichuan Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 98, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Han, H.D.; Xia, Q.S.; Li, B. Fractal characteristic of microscopic pore structure of tight sandstone reservoirs in Kalpintag Formation in Shuntuoguole area, Tarim Basin. Pet. Res. 2020, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhong, Q.; Li, G.F.; Fu, X.H.; Duan, C.C.; Liu, H.H.; Xu, H.J. Fluid distribution and pore structure multifractal characteristics analysis of coal measure mudstone. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2021, 88, 103810. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Mao, C.; Li, Q.; Jin, W.; Zhu, S.M.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, Z.G.; He, J.Y.; Shen, J.G.; Zhu, Y.P.; et al. Pore throat characteristics of tight reservoirs by a combined mercury method: A case study of the member 2 of Xujiahe Formation in Yingshan gasfield, North Sichuan Basin. Open Geosci. 2021, 13, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.G.; Zhou, X.F.; Shamil, S.; Yuriy, K.; Yang, E.L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, A.L. High-pressure mercury intrusion analysis of pore structure in typical lithofacies shale. Energy 2024, 295, 130879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Z.; Hou, J.G.; Liu, Y.M.; Dou, L.X.; Wang, X.X. The pore structures of different lithofacies in low-permeability sandy conglomerate reservoirs and their diagenetic impacts: A case study from the Es4 member of the northern steep slope in Dongying depression, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 136, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, F.C.; Lin, L.B.; Lai, Y.T.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z.B. Research on Fractal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Pore-throats in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs: A Case Study of Chang 6 of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Huaqing Area, Ordos Basin, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Lu, S.F.; Lin, L.M.; Zhou, N.W.; Liu, Y. Differential development characteristics of secondary pores and effects on pore structure and movable fluid distribution in tight gas sandstones in the lower Permian, northeastern Ordos Basin, China. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 224, 211580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yue, D.L.; Jones, S.J.; Li, S.X.; Wang, W.R.; Bai, B.; Hou, X.L.; Li, Z.; Wu, S.H.; Li, Q. Lithofacies assemblage and effects on diagenesis in lacustrine tight sandstone reservoirs: Samples from Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 167, 107001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, W.; Xiong, F.Y.; Ji, W.; Jia, J.K.; Tang, X.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Gao, J.W.; Luo, B. Pore-throat structure and fractal characteristics of Shihezi Formation tight gas sandstone in the Ordos Basin, China. Fractals-Complex Geom. Patterns Scaling Nat. Soc. 2018, 26, 1840005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Li, Q.; Zhu, R.K.; Mao, Z.G.; Chen, H.H. Crystal chemistry and formation of authigenic chlorite: Influence on tight sandstone reservoir in the Yanchang formation, Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 165, 106874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Qu, X.Y.; Miao, C.S.; Zhu, J.F.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.M. Effect of Authigenic Chlorite on the Pore Structure of Tight Clastic Reservoir in Songliao Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, B.; Bocker, J.; Hilgers, C. Improved reservoir quality assessment by evaluating illite grain coatings, quartz cementation, and compaction—Case study from the Buntsandstein, Upper Rhine Graben, Germany. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 241, 213141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.J.; Huang, K.K.; Ye, L.M.; Lan, Y.F.; Liu, L. Diagenesis of tight sandstone reservoirs of Xujiahe Formation (Upper Triassic), the Xinchang Gas Field, western Sichuan Basin, China. Geol. J. 2020, 55, 4604–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Hu, W.X.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.L.; Tang, Q.S.; Wu, H.G.; Xu, K. Diagenetic constraints on the heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study on the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin, southwest China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2018, 92, 650–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Yao, S.P.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ning, S.K.; Jia, B.F.; Zhou, Y.S.; Zhang, W.J. Influence of coupled dissolution-precipitation processes on the pore structure, characteristics, and evolution of tight sandstone: A case study in the upper Paleozoic reservoir of Bohai Bay Basin, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 262, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lin, L.B.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.D. Source of quartz cement in tight gas sandstone: Evidence from the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the western Sichuan Basin, SW China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Dong, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.Y. Experimental investigation of the petrophysical properties, minerals, elements and pore structures in tight sandstones. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 76, 103189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.F.; Tang, H.Z.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Xiao, W.H.; Li, J. The occurrence status, genetic mechanism, and impact on physical properties of sandstone kaolinite: A case study of Xiagou Formation in Yinger Depression, Jiuquan Basin. J. Northeast. Pet. Univ. 2019, 43, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.L.; Sun, H.S.; Jia, B.; Yu, J.J.; Luo, W.J. Genesis of chlorite in tight sandstone reservoirs of the Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan and its relationship with high-quality reservoirs. Pet. Nat. Gas Geol. 2012, 33, 751–757. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.R.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.X.; Yan, B.Q.; Liu, R.H. Analysis of Controlling Factors of Pore Structure in Different Lithofacies Types of Continental Shale—Taking the Daqingzi Area in the Southern Songliao Basin as an Example. Minerals 2024, 14, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngia, N.R.; Hu, M.Y.; Gao, D. The interplay between dolomitizing fluids, tectonically-controlled saddle dolomite and calcite cements in Lower Cambrian to Furongian strata in the Tazhong Uplift. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 167, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Pang, X.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X. Fractal Analysis of Pore Network in Tight Gas Sandstones Using NMR Method: A Case Study from the Ordos Basin, China. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 10358–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.G.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhang, X.G. Evaluation of sweet spots for a tight sandstone reservoir: A quantitative study of diagenesis in the fourth member of the Oligocene Huagang Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 163, 106799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wang, R.; Shi, W.Z.; Geng, F.; Luo, F.S.; Li, G.P.; Li, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Ostadhassan, M. Integrated controls of tectonics, diagenesis and sedimentation on sandstone densification in the Cretaceous paleo-uplift settings, north Tarim Basin. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples ID | Depth (m) | Lithology | Porosity (%) | Permeability (mD) | Mineral Content by XRD (%) | Relative Content of Clay (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | K-Feldspar | Plagioclase | Calcite | Dolomite | Clay | Kaolinite | Chlorite | Illite | |||||
| JM103-1 | 4194.58 | SC | 2.52 | 0.3081 | 51.3 | 0 | 0 | 20.3 | 22.4 | 4.8 | 54.8 | 11.3 | 25.0 |
| JM103-2 | 4196.21 | MS | 4.67 | 0.1860 | 78.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 18.3 | 63.0 | 7.9 | 19.6 |
| JM103-5 | 4203.95 | S | 2.09 | 0.0743 | 54.3 | 0 | 0.4 | 7.4 | 5.2 | 30.3 | 47.1 | 13.6 | 30.6 |
| GA1-4 | 1903.91 | MS | ND | ND | 80.7 | 8.8 | 6.5 | 0.4 | 0 | 3.4 | 9.9 | 35.3 | 50.5 |
| GA1-7 | 1911.52 | FS | ND | ND | 88.5 | 2.4 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 8.6 | 37.6 | 47.4 |
| GA1-10 | 1918.64 | FS | 6.23 | 0.4868 | 77.6 | 4.9 | 10.4 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 5.8 | 17.3 | 34.6 | 39.0 |
| GA1-19 | 1926.65 | FS | 7.05 | 0.4676 | 63.2 | 5.0 | 18.1 | 1.3 | 2.9 | 9.5 | 17.4 | 61.3 | 16.3 |
| GA1-21 | 1934.21 | MS | 11.23 | 3.7255 | 68.6 | 15.0 | 9.1 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 6.2 | 14.3 | 66.7 | 13.1 |
| AJ1-9 | 2168.28 | FS | 8.15 | 0.4586 | 65.1 | 4.5 | 18.9 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 8.9 | 8.4 | 31.2 | 48.6 |
| HC101-2 | 2073.69 | FS | 4.27 | 0.3438 | 65.1 | 7.4 | 15.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 11.3 | 9.4 | 31.5 | 48.0 |
| HC101-4 | 2076.25 | MS | 6.77 | 4.4631 | 81.0 | 4.6 | 9.1 | 0.2 | 0 | 4.4 | 9.5 | 40.6 | 32.9 |
| YQ101-1 | 2753.14 | FS | 4.19 | 0.2190 | 50.2 | 5.1 | 13.8 | 23.9 | 0 | 5.6 | 7.3 | 33.7 | 48.1 |
| YQ101-3 | 2758.12 | FS | 7.94 | 0.4151 | 62.5 | 7.3 | 18.8 | 0.4 | 0 | 11.0 | 18.0 | 40.2 | 33.8 |
| YQ101-14 | 2774.05 | MS | 4.39 | 0.6499 | 61.7 | 3.9 | 6.5 | 9.3 | 0.9 | 16.5 | 8.3 | 27.2 | 49.2 |
| YQ101-16 | 2778.97 | MS | 5.93 | 0.3146 | 81.7 | 4.2 | 7.0 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 6.2 | 13.1 | 38.2 | 42.2 |
| QL22-3 | 3542.55 | MFS | 12.48 | 0.9218 | 60.9 | 6.1 | 19.6 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 11.9 | 17.1 | 56.9 | 16.0 |
| QL22-6 | 3557.39 | MS | 6.25 | 0.3114 | 76.1 | 7.3 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0 | 13.9 | 8.9 | 37.0 | 44.6 |
| QL22-17 | 3574.20 | MFS | 2.09 | 0.0962 | 63.0 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 15.0 | 1.0 | 9.3 | 6.3 | 13.4 | 66.9 |
| PL2-1 | 3229.30 | FS | 7.56 | 13.4186 | 78.1 | 0 | 13.0 | 0 | 1.4 | 7.5 | 46.0 | 13.0 | 35.0 |
| PL2-2 | 3237.30 | FS | 4.89 | 0.3098 | 75.7 | 0 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 9.3 | 51.0 | 12.0 | 29.0 |
| PL2-3 | 3244.00 | FS | 7.41 | 0.1613 | 82.4 | 0 | 9.4 | 0 | 1.1 | 6.3 | 81.0 | 3.0 | 12.0 |
| H4-5 | 3060.42 | MFS | 4.78 | 0.1944 | 79.2 | 0 | 5.4 | 0 | 0 | 13.5 | 22.0 | 12.0 | 22.0 |
| Z1-2 | 3717.55 | SC | ND | ND | 8.7 | 0 | 0.8 | 36.2 | 51.3 | 3.0 | 0 | 58.0 | 27.0 |
| W4-1 | 3516.60 | FS | ND | ND | 79.2 | 3.3 | 4.9 | 1.6 | 0 | 11.0 | 0 | 53.0 | 40.0 |
| W4-2 | 3518.40 | S | ND | ND | 68.4 | 3.8 | 2.2 | 4.2 | 0 | 15.5 | 0 | 58.0 | 33.0 |
| W4-3 | 3522.15 | MS | 6.96 | 9.9057 | 77.2 | 5.4 | 0 | 5.0 | 0 | 8.5 | 0 | 43.0 | 45.0 |
| W4-5 | 3525.16 | MFS | 1.90 | 1.2002 | 50.5 | 3.3 | 0 | 28.7 | 0 | 13.1 | 0 | 40.0 | 46.0 |
| W4-6 | 3533.70 | MS | 9.25 | 1.1261 | 81.8 | 3.5 | 0 | 0.7 | 1.7 | 12.2 | 0 | 43.0 | 30.0 |
| W4-7 | 3535.25 | MFS | 11.31 | 0.5372 | 76.8 | 7.2 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 0 | 10.2 | 0 | 45.0 | 25.0 |
| W4-8 | 3541.84 | MS | ND | ND | 90.0 | 2.0 | 0 | 2.3 | 0 | 5.1 | 0 | 35.0 | 58.0 |
| W4-9 | 3547.58 | FS | 7.03 | 0.5029 | 79.0 | 5.0 | 0 | 3.9 | 0 | 10.1 | 0 | 21.0 | 74.0 |
| W4-10 | 3549.32 | MS | 6.21 | ND | 88.2 | 1.4 | 0 | 6.2 | 0 | 3.4 | 0 | 43.0 | 51.0 |
| W4-11 | 3554.25 | MS | 10.06 | 1.0137 | 81.7 | 3.7 | 0 | 5.2 | 0 | 9.4 | 0 | 55.0 | 39.0 |
| W4-12 | 3560.50 | MS | 6.29 | 0.2490 | 70.3 | 6.2 | 0 | 12.3 | 0 | 10.0 | 0 | 41.0 | 51.0 |
| W4-14 | 3571.38 | C | ND | ND | 38.1 | 1.1 | 0 | 36.5 | 0 | 3.6 | 9.0 | 26.0 | 53.0 |
| W4-15 | 3574.68 | S | ND | ND | 52.8 | 7.6 | 0 | 1.2 | 9.2 | 29.1 | 0 | 43.0 | 40.0 |
| W6-1 | 3664.20 | MS | 10.52 | 1.2276 | 83.5 | 0 | 3.2 | 3.9 | 0 | 8.7 | 0 | 16.0 | 80.0 |
| W6-2 | 3667.30 | MFS | 13.31 | 3.8826 | 83.3 | 0 | 4.0 | 1.5 | 0 | 11.2 | 0 | 25.0 | 65.0 |
| W6-3 | 3678.40 | FS | 6.67 | 0.2192 | 64.0 | 13.8 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 0 | 14.0 | 0 | 29.0 | 66.0 |
| W6-5 | 3709.70 | MS | ND | ND | 92.2 | 0 | 0 | 1.3 | 0 | 6.5 | 0 | 42.0 | 51.0 |
| AY2-5 | 2016.80 | FS | 10.12 | 0.6670 | 74.9 | 4.8 | 14.1 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 4.6 | ND | ND | ND |
| AY2-6 | 2019.35 | FS | 5.95 | 0.1370 | 52.5 | 6.8 | 19.0 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 17.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| AY2-8 | 2066.70 | MFS | 9.31 | 0.5070 | 69.0 | 6.9 | 15.4 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 7.1 | ND | ND | ND |
| HC1-6 | 2041.85 | MFS | 11.16 | 0.4950 | 76.8 | 6.2 | 9.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 6.9 | ND | ND | ND |
| HC1-8 | 2044.13 | MS | 12.38 | 0.7540 | 77.0 | 0 | 9.6 | 0.3 | 3.1 | 10.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| HC1-9 | 2044.62 | MS | 9.56 | 0.4350 | 72.5 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 7.1 | ND | ND | ND |
| HC1-11 | 2048.06 | FS | 7.03 | 0.2740 | 64.6 | 10.1 | 10.0 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 11.8 | ND | ND | ND |
| Y2-3 | 2054.90 | FS | 7.10 | 0.0437 | 59.6 | 7.4 | 18.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 13.3 | ND | ND | ND |
| Y2-4 | 2057.82 | FS | 2.84 | 0.0070 | 53.7 | 6.9 | 17.9 | 18.2 | 0.3 | 3.0 | ND | ND | ND |
| Samples ID | Depth (m) | Mudstone Debris (%) | Sandstone Debris (%) | Carbonate Rock Debris (%) | Metamorphic Rock Debris (%) | Volcanic Rock Debris (%) | Chert (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA1-10 | 1918.64 | 0.00 | 8.21 | 0.00 | 9.94 | 4.76 | 0.00 |
| GA1-21 | 1934.21 | 0.17 | 8.27 | 0.00 | 12.47 | 1.29 | 5.91 |
| AJ1-9 | 2168.28 | 7.64 | 0.00 | 1.55 | 0.00 | 4.31 | 0.00 |
| HC101-2 | 2073.69 | 0.80 | 12.98 | 0.70 | 11.16 | 1.29 | 0.00 |
| YQ101-1 | 2753.14 | 4.04 | 0.85 | 5.98 | 0.00 | 4.16 | 0.00 |
| YQ101-3 | 2758.12 | 10.32 | 2.08 | 0.00 | 5.26 | 0.00 | 0.97 |
| YQ101-16 | 2778.97 | 7.77 | 6.36 | 0.00 | 3.45 | 1.35 | 0.00 |
| QL22-3 | 3542.55 | 8.88 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 3.83 | 2.87 | 0.00 |
| PL2-2 | 3237.30 | 1.91 | 18.65 | 0.58 | 3.56 | 5.28 | 0.00 |
| PL2-3 | 3244.00 | 1.25 | 17.82 | 0.00 | 2.31 | 6.79 | 2.10 |
| W4-11 | 3554.25 | 0.83 | 6.07 | 1.96 | 15.86 | 1.53 | 1.16 |
| AY2-5 | 2016.80 | 10.58 | 5.18 | 0.10 | 1.81 | 0.47 | 0.16 |
| AY2-6 | 2019.35 | 14.96 | 2.55 | 2.48 | 2.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| HC1-8 | 2044.13 | 0.00 | 10.60 | 0.30 | 10.81 | 2.52 | 1.14 |
| Y2-4 | 2057.82 | 5.57 | 2.31 | 3.56 | 1.20 | 1.03 | 0.00 |
| Lithology | D | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max (Average) | Min–Max (Average) | Min–Max (Average) | Min–Max (Average) | Min–Max (Average) | |
| medium sandstone | 2.65–2.83 (2.74) | 2.8–2.86 (2.83) | 2.81–2.87 (2.83) | 2.35–2.69 (2.53) | 2.75–2.91 (2.85) |
| medium-fine sandstone | 2.58–2.91 (2.75) | 2.77–2.93 (2.86) | 2.7–2.89 (2.82) | 2.15–2.95 (2.64) | 2.56–2.98 (2.82) |
| fine sandstone | 2.75–2.88 (2.82) | 2.78–2.99 (2.9) | 2.79–2.89 (2.83) | 2.58–2.89 (2.82) | 2.7–2.96 (2.84) |
| Parameter | Total | Macropore | Mesopore | Small-Pore | Micropore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D/Proportion | D1/Proportion | D2/Proportion | D3/Proportion | D4/Proportion | |
| permeability | 0.55/ND | 0.46/0.58 | 0.52/0.41 | 0.44/0.38 | 0.32/0.7 |
| porosity | 0.53/ND | 0.36/0.45 | 0.3/0.21 | 0.57/0.32 | 0.21/0.45 |
| Mercury removal efficiency | 0.15/ND | 0.06/0.37 | 0.11/0.33 | 0.21/0.31 | 0.04/0.25 |
| R15 | 0.34/ND | 0.4/0.7 | 0.47/0.49 | 0.22/0.41 | 0.22/0.61 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, X.; Xiao, D.; Jin, H.; Cui, J.; Wang, M.; Shao, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, R. Classification and Controlling Factors of Different Types of Pore Throat in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Fractal Features—A Case Study of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression. Minerals 2025, 15, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010018
Guan X, Xiao D, Jin H, Cui J, Wang M, Shao H, Zheng L, Wang R. Classification and Controlling Factors of Different Types of Pore Throat in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Fractal Features—A Case Study of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression. Minerals. 2025; 15(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Xiaodie, Dianshi Xiao, Hui Jin, Junfeng Cui, Min Wang, Haoming Shao, Lehua Zheng, and Rui Wang. 2025. "Classification and Controlling Factors of Different Types of Pore Throat in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Fractal Features—A Case Study of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression" Minerals 15, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010018
APA StyleGuan, X., Xiao, D., Jin, H., Cui, J., Wang, M., Shao, H., Zheng, L., & Wang, R. (2025). Classification and Controlling Factors of Different Types of Pore Throat in Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Fractal Features—A Case Study of Xujiahe Formation in Western Sichuan Depression. Minerals, 15(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010018







