Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining High-Purity Carbon Materials and Recovering Valuable Metals from Shungite Rocks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- General information about shungite rocks
- Analysis of current technologies for shungite rock beneficiation
2. Materials and Methods
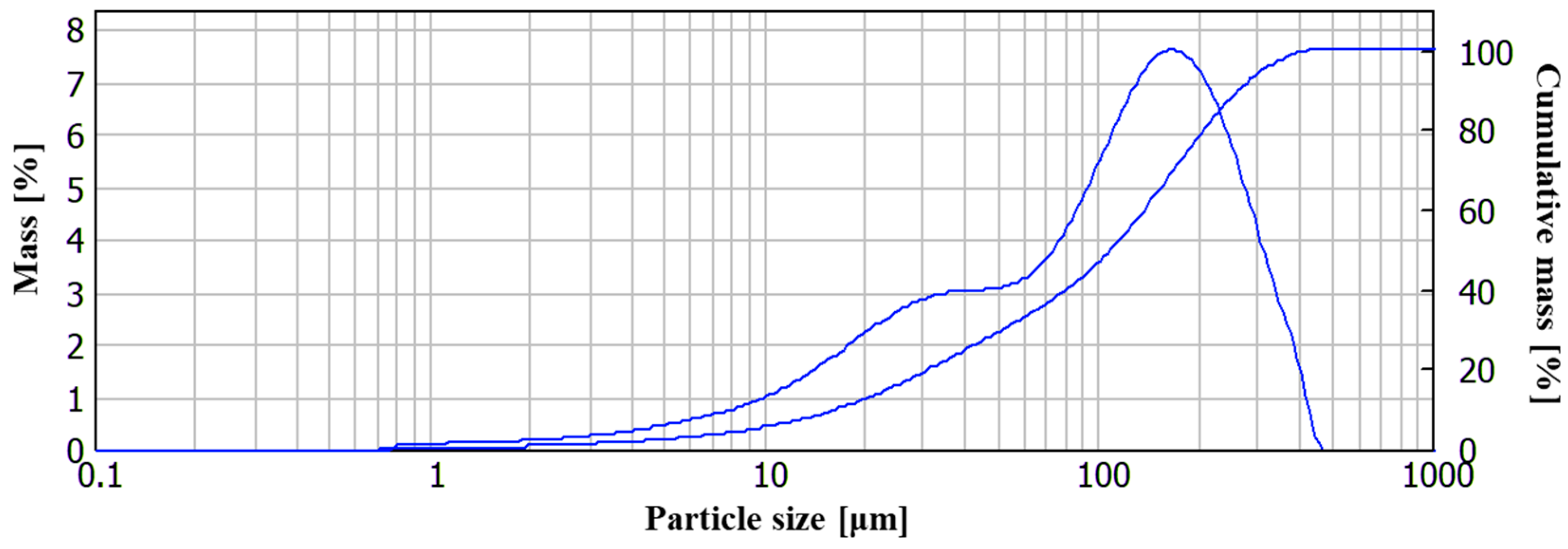
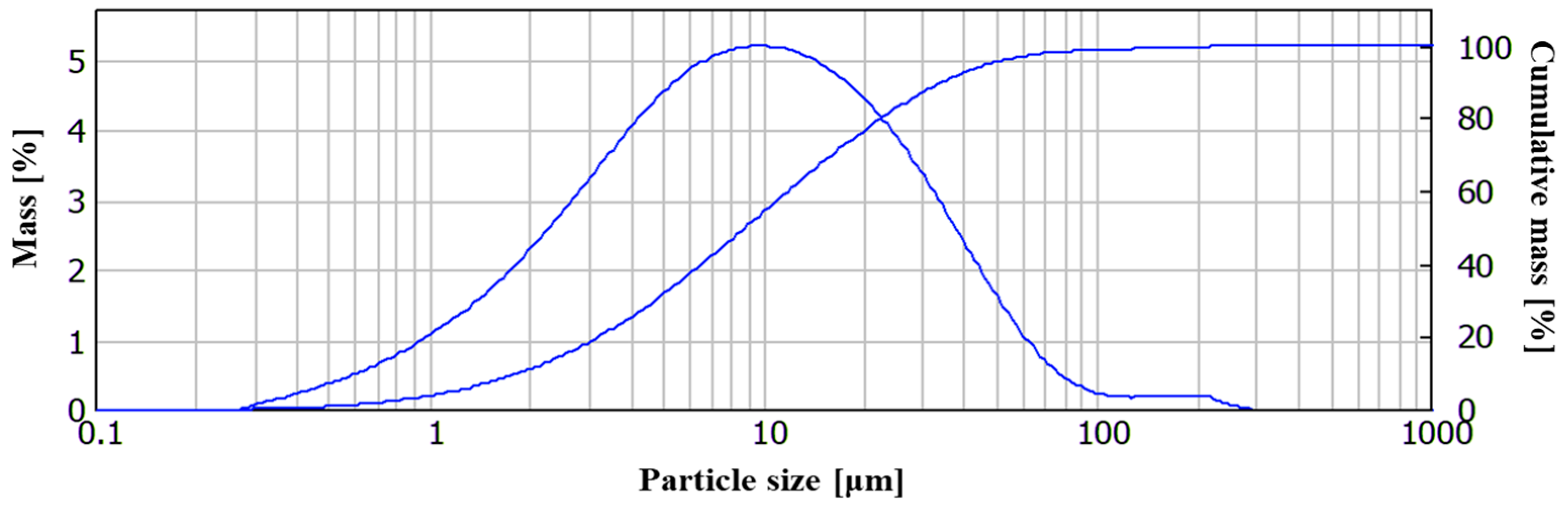
2.1. Materials
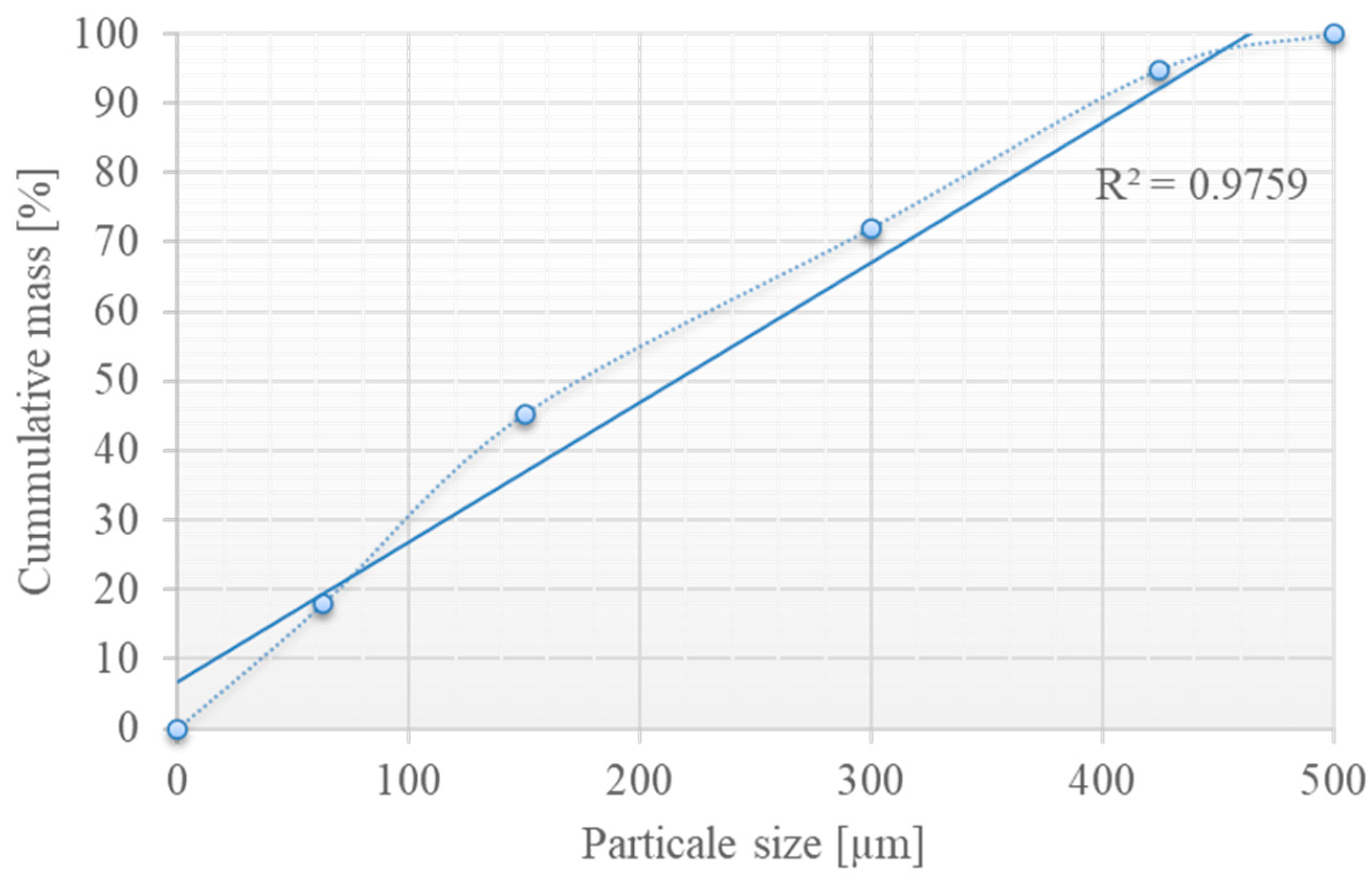
2.2. Methods
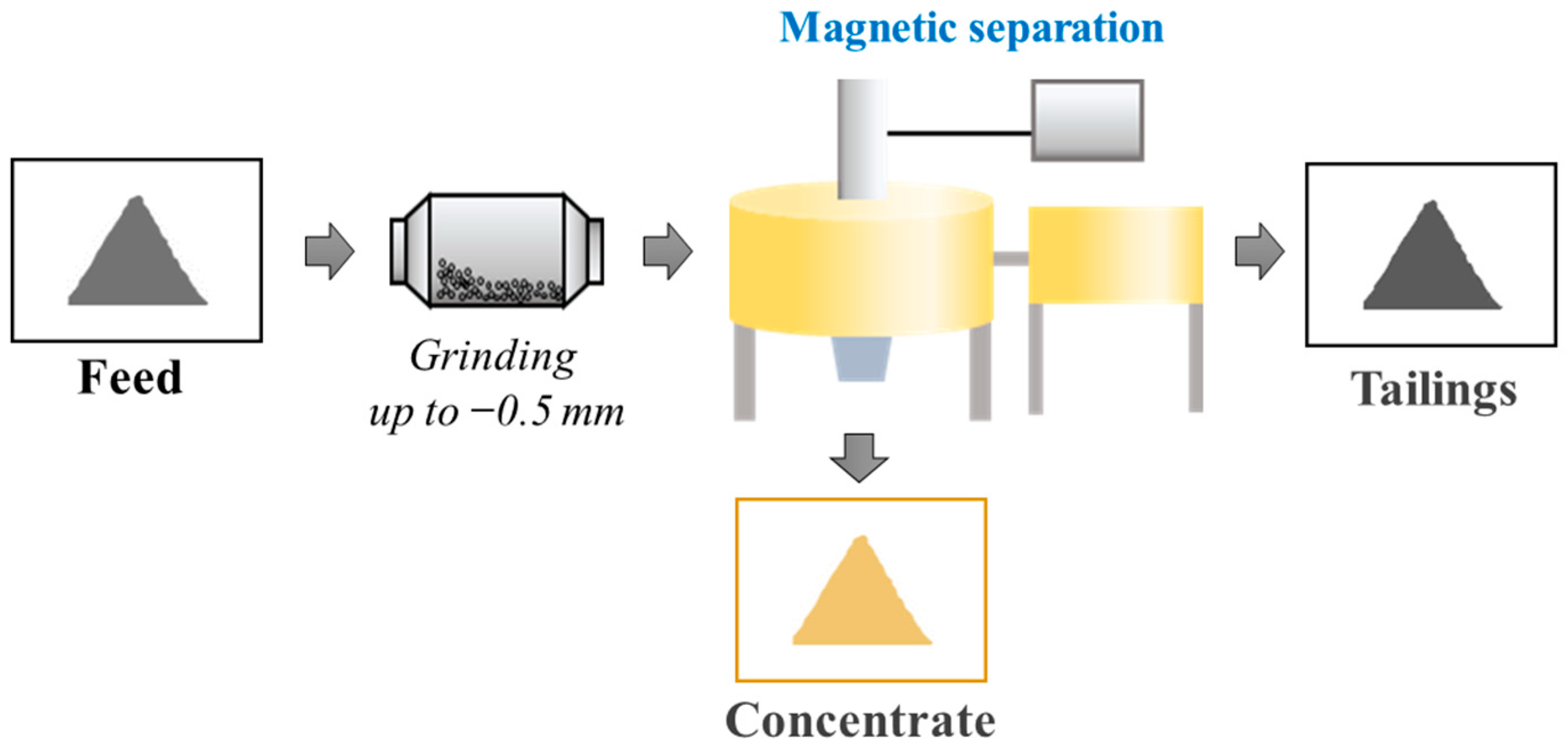
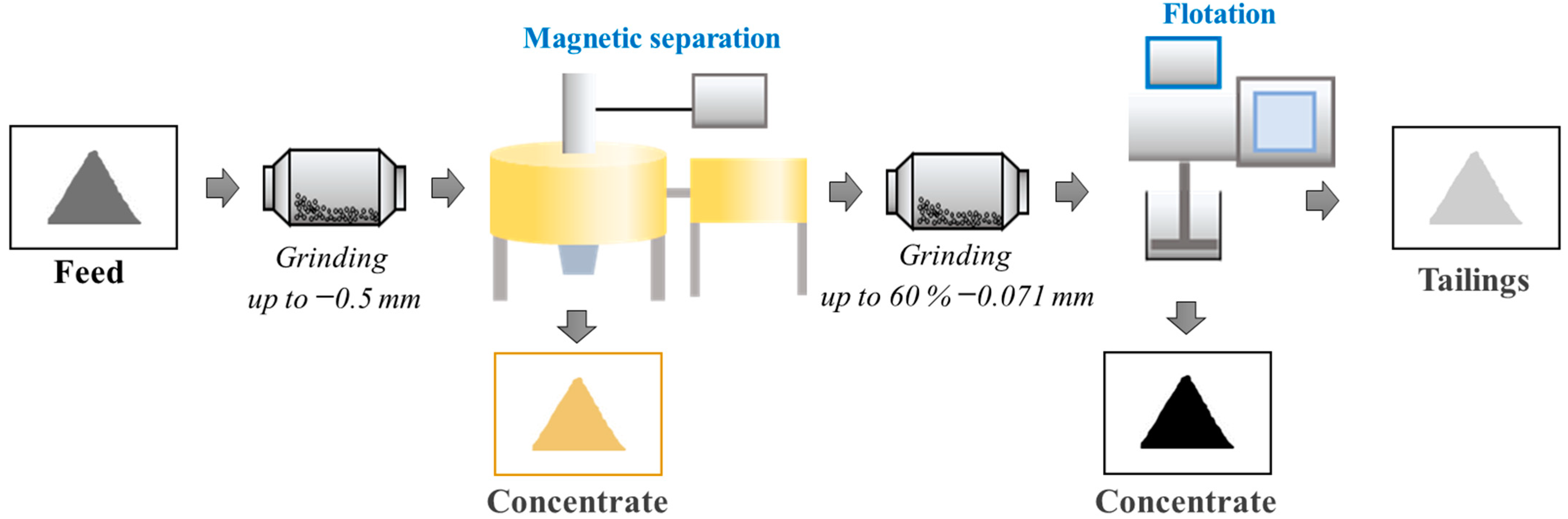
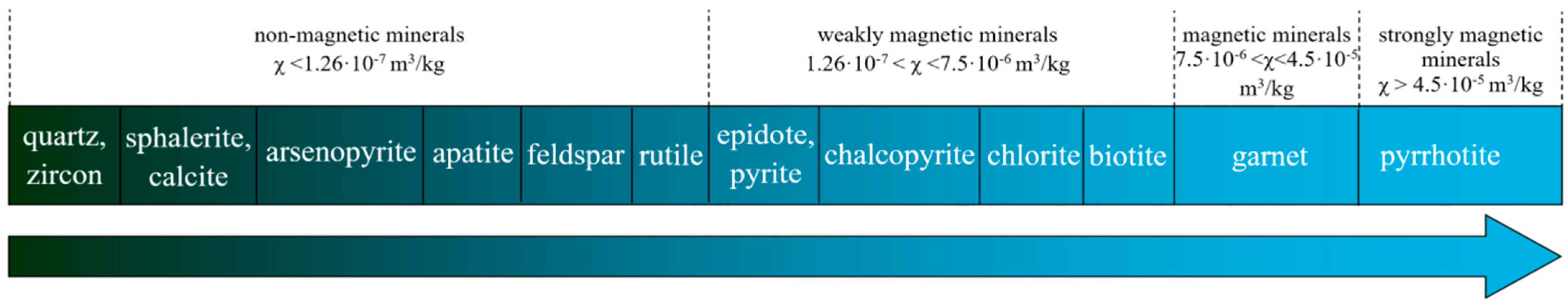
2.2.1. Experimental Investigations of Magnetic Separation
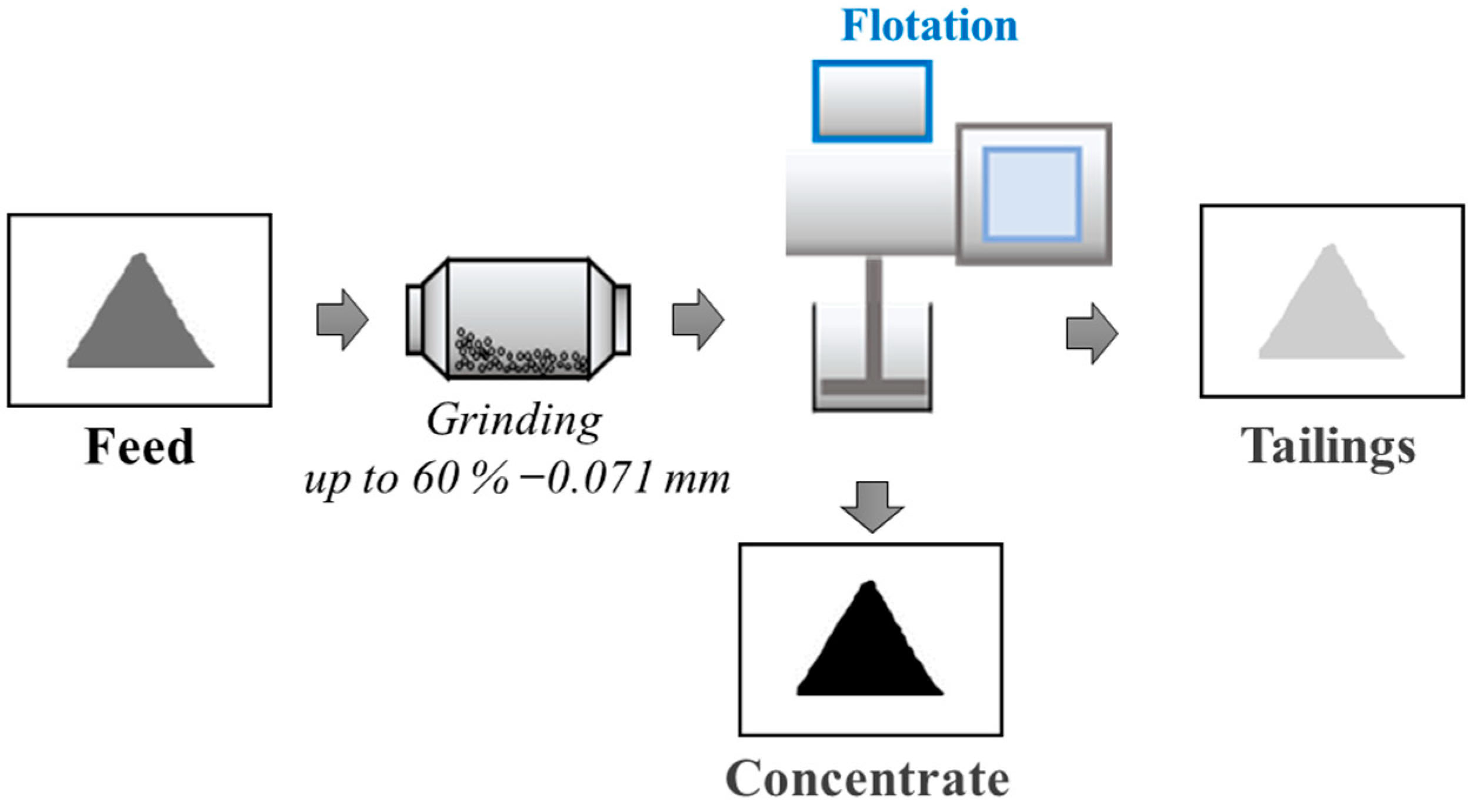
2.2.2. Experimental Investigations of Flotation
3. Results and Discussion
- Investigation of the possibility of obtaining a metal-bearing concentrate containing strategic metals from shungite rock using high-gradient magnetic separation;
- Investigation of the possibility of recovering high-purity shungite carbon material in a flotation concentrate using an apolar collector emulsion.
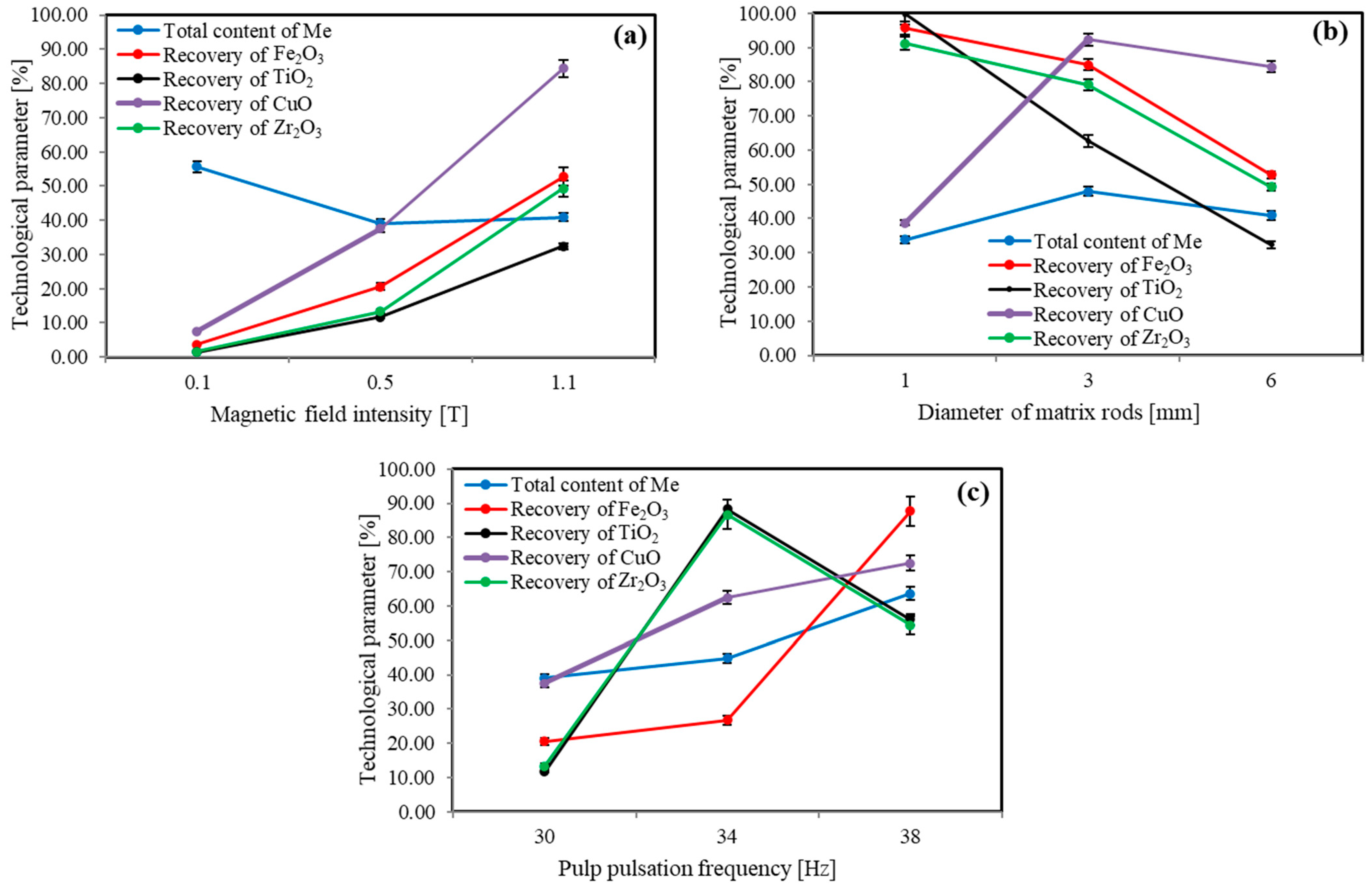
3.1. Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining a Metal-Bearing Concentrate Containing Strategic Metals from Shungite Rock Using High-Gradient Magnetic Separation
3.2. Investigation of the Possibility of Recovering High-Purity Shungite Carbon Material into Flotation Concentrate Using an Apolar Collector Emulsion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skublov, S.G. Geological structure and mineral resources of Russia. J. Min. Inst. 2022, 255, 273–274. [Google Scholar]
- Litvinenko, V.S.; Sergeev, I.B. Innovations as a Factor in the Development of the Natural Resources Sector. Stud. Russ. Econ. Dev. 2019, 30, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinenko, V.S.; Petrov, E.I.; Vasilevskaya, D.V.; Yakovenko, A.V.; Naumov, I.A.; Ratnikov, M.A. Assessment of the Role of the State in the Management of Mineral Resources. J. Min. Inst. 2022, 259, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburri, E.; Carcione, R.; Politi, S.; Angjellari, M.; Lazzarini, L.; Vanzetti, L.E.; Macis, S.; Pepponi, G.; Terranova, M.L. Shungite Carbon as Unexpected Natural Source of Few-Layer Graphene Platelets in a Low Oxidation State. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 8487–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanturiya, V.A. Scientific substantiation and development of innovative processes for the extraction of zirconium and rare earth elements in the deep and comprehensive treatment of eudialyte concentrate. J. Min. Inst. 2022, 256, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchiptsov, V.V.; Kevlich, V.I.; Pervunina, A.V. Shungite-bearing rocks of the Zazhoginskoe ore field (Republic of Karelia): From geology to processing technology. Obogashchenie Rud. 2021, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashova, N.I.; Medvedev, P.V. Carbon bearing rocks (shungites). Are they so safe for drinking water purification? Bull. Tomsk. Polytech. Univ. Geo Assets Eng. 2021, 332, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevsky, V.V. Structure of shungite carbon. Chem. Nat. Graph. 1994, 39, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rafienko, V.A.; Anufrieva, S.I. Carbonaceous Compounds: Shungite Rocks and Peculiarities of Their Industrial Use; Moscow: Nauka, Russia, 2008; 71p. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrova, T.; Nikolaeva, N.; Afanasova, A.; Romashev, A.; Aburova, V.; Prokhorova, E. Extraction of Low-Dimensional Structures of Noble and Rare Metals from Carbonaceous Ores Using Low-Temperature and Energy Impacts at Succeeding Stages of Raw Material Transformation. Minerals 2023, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, T.N.; Afanasova, A.V.; Aburova, V.A. “Invisible” noble metals in carbonaceous rocks and beneficiation products: Feasibility of detection and coarsening. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafienko, V.A. Technology of Processing of Shungite Rocks; GEOS: Moscow, Russia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalevskii, S.V.; Moshnikov, I.A.; Kovalevski, V.V. Heat-treated nano-structured shungite rocks and electrophysical properties associated. Nanosyst. Phys. Chem. Math. 2018, 9, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Adamczyk, A.; Gierszewska, M.; Grabska-Zielińska, S. Comparison of How Graphite and Shungite Affect Thermal, Mechanical, and Dielectric Properties of Dielectric Elastomer-Based Composites. Energies 2022, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Aoki, T.; Ponou, J.; Dodbiba, G.; He, C.; Wang, K.; Ning, S.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y. Removal of Impurities from Shungite Via a Combination of Physical and Chemical Treatments. Minerals 2021, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremov, S.A. Shungite rock processing technology. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2010, 83, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushina, T.I.; Rafienko, V.A. Technology of processing shungite rocks to obtain dispersed shungite concentrates of high quality. Gorn. Zhurnal 2013, 10, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, S.; Cheng, W.; Sun, Z.; Lu, D.; Wang, Y. Effect of plate teeth spacing on particle capture in high intensity magnetic separation adopting grooved plates with elliptic teeth. Miner. Eng. 2024, 213, 108755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratev, S.A.; Khamzina, T.A. Improvement of concentrate quality in flotation of low-rank coal. J. Min. Inst. 2024, 265, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yunash, A.A.; Ivanov, G.V.; Petukhov, V.N. Increasing the efficiency of apolar reagents by their modification. Bull. Kuzbass State Tech. Univ. 2004, 4, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Mao, Z.; Qian, Y. Enhanced fine flake graphite flotation and reduced carbon emission by a novel water-in-oil kerosene emulsion. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 650, 129603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.-Z.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.-H.; Lu, Y.-T.; Hu, J. Study of flotation performance of kerosene after ultrasonic emulsified. J. China Coal Soc. 2008, 33, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Bu, X.; Shao, H.; Hu, Y.; Alheshibri, M.; Xie, G. Effects of emulsified kerosene nanodroplets on the entrainment of gangue materials and selectivity index in aphanitic graphite flotation. Miner. Eng. 2020, 158, 106592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilyalova, S.M.; Euengaziev, A.M.; Mukhanova, A.S.; Nurpeisova, K.K.; Mukataeva, N.N. Study of the effect of concentration and size of dispersed phase of the emulsion on the surface activity. In Proceedings of the XXVI International Scientific and Technical conference Within the Framework of the XIX Ural Mining Decade, Yekaterinburg, Russia, 26–27 May 2021; pp. 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Bazhin, V.Y.; Kuskov, V.B.; Kuskova, Y.V. Processing of low-demand coal and other carbon-containing materials for energy production purposes. Inżynieria Miner. 2019, 21, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabaev, S.O.; Kharchenko, A.V.; Gainullina, I.P.; Kudryavtseva, V.A.; Shigaeva, T.D. Natural carbon matrices based on brown coal, humic acids and humine extracted from it for purification of aqueous solutions from low molecular weight organic impurities. J. Min. Inst. 2024, 267, 402–412. [Google Scholar]
- Vakhonina, T.E.; Klein, M.S.; Patrakov, Y.F.; Semenova, S.A. Influence of Dispersiveness of Emulsion Composed of Oily Regents on Coal Flotation Results. J. Min. Sci. 2020, 5, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, V.V.; Pestryak, I.V.; Erdenezuul, J. Analysis of the concentration of non-ionogenic collector in the flotation of copper-molybdenum ores. In Proceedings of the XXV International Scientific and Technical conference Within the Framework of the XVIII Ural Mining Decade, Yekaterinburg, Russia, 2–11 April 2020; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, W.; Liu, J.; Ren, H.; Zhu, Y.; Han, W.; Han, Y. Enhanced mixed flotation of copper–molybdenum ore using dodecyl dimethyl betaine-emulsified kerosene as environmentally friendly collector. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, A.A. Collected Works. Volume 7. Flotation. Reagent-Gathering Agents: Textbook; Moscow: Gornaya Kniga, Russia, 2012; 656p. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, S.; Brownfield, I.K. Magnetic Susceptibilities of Minerals; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; pp. 99–529. [CrossRef]
- Denisova, O.V.; Karapetyan, K.G. Carbon materials surface modified with transition metal ions. Tsvetnye Met. 2023, 8, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Mi, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. Carbon nanofibers supported sorbents with enhanced performance via microwave-assisted in-situ structural modifications for H2S removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 350, 127883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, Z.V.; Vasekha, M.V.; Tyulyaev, V.S. Evaluation of the efficiency of sorbents for accidental oil spill response in the Arctic waters. J. Min. Inst. 2023, 264, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonenko, V.V.; Glukhareva, N.A.; Pletnev, M.Y. Effect of surfactant dispersants on the size of calcium soap particles formed in hard water. Colloid J. 2002, 64, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murhula, E.; Hashan, M.; Otsuki, A. Effect of Solid Concentration and Particle Size on the Flotation Kinetics and Entrainment of Quartz and Hematite. Metals 2023, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, T.N.; Prokhorova, E.O. Modification of properties of rock-forming minerals during flotation. Min. Inf. Anal. Bull. 2023, 12, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, T.N.; Kuskov, V.B.; Afanasova, A.V.; Kuznetsov, V.V. Improvement of the fine coking coal flotation technology. Obogashchenie Rud 2021, 3, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Liu, D. The Role of Water Glass in the Flotation Separation of Fine Fluorite from Fine Quartz. Minerals 2017, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Component | C | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | K2O | S | TiO2 | As2O3 |
| Content [%] | 31.43 | 39.97 | 0.760 | 11.90 | 8.53 | 2.24 | 1.432 | 0.657 | 0.551 |
| Component | MnO | ZnO | CuO | ZrO2 | V2O5 | SrO | Cr2O3 | Y2O3 | NiO |
| Content [%] | 0.220 | 0.038 | 0.025 | 0.036 | 0.069 | 0.065 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 0.033 |
| Mineral | Content [%] | Mineral | Content [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (shungite) | 31.4 | Pyrite, pyrrhotite | 2.8 |
| Quartz | 35.9 | Calcite | 2.1 |
| Serizite, hydromica | 14.2 | Arsenopyrite | 1.9 |
| Garnet, iron oxide | 6.2 | Rutile | 0.9 |
| Chlorite, biotite, zircon, apatite, etc. | 4.2 | Sulphide (chalcopyrite, sphalerite, etc.) | 0.4 |
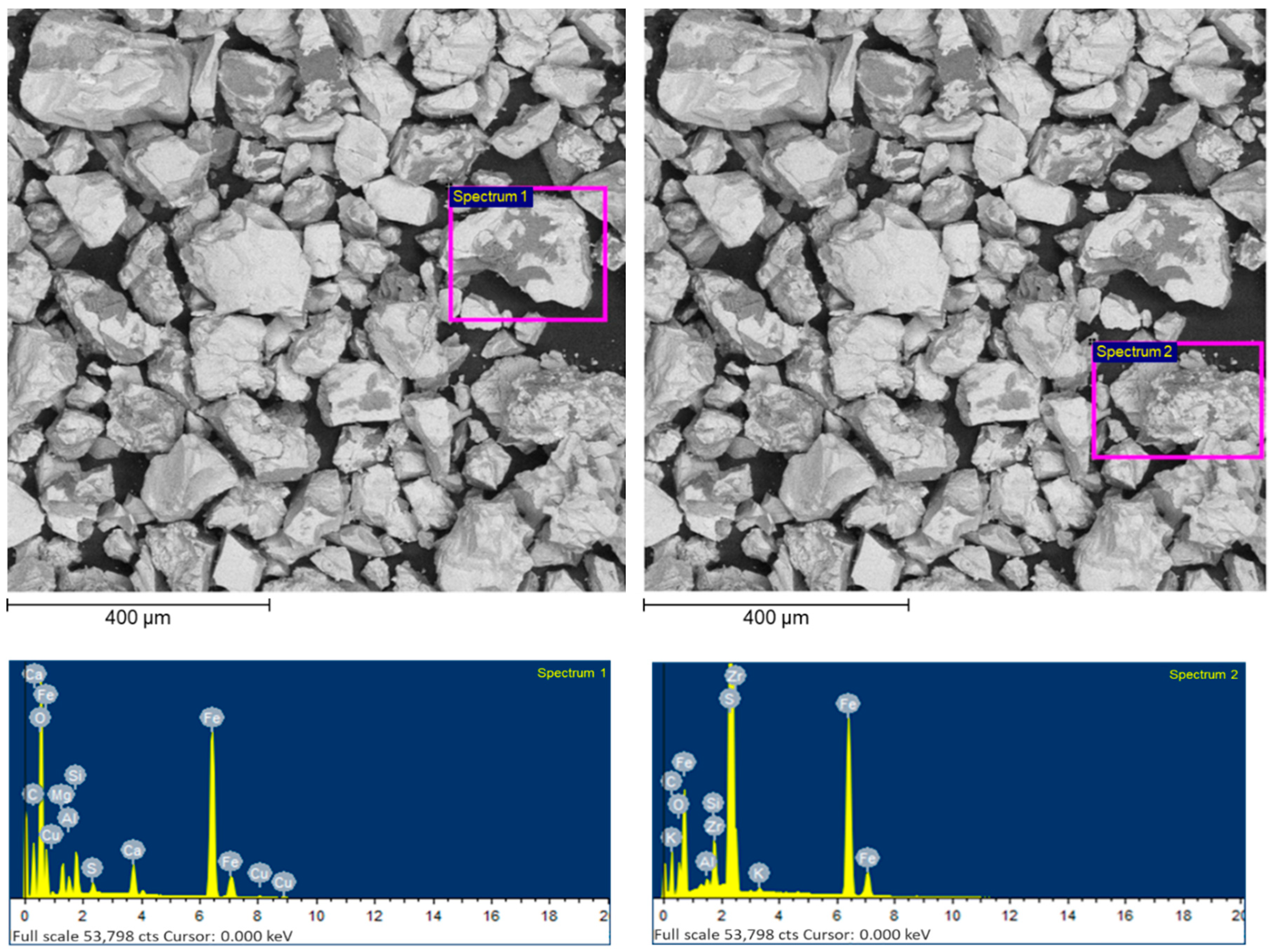
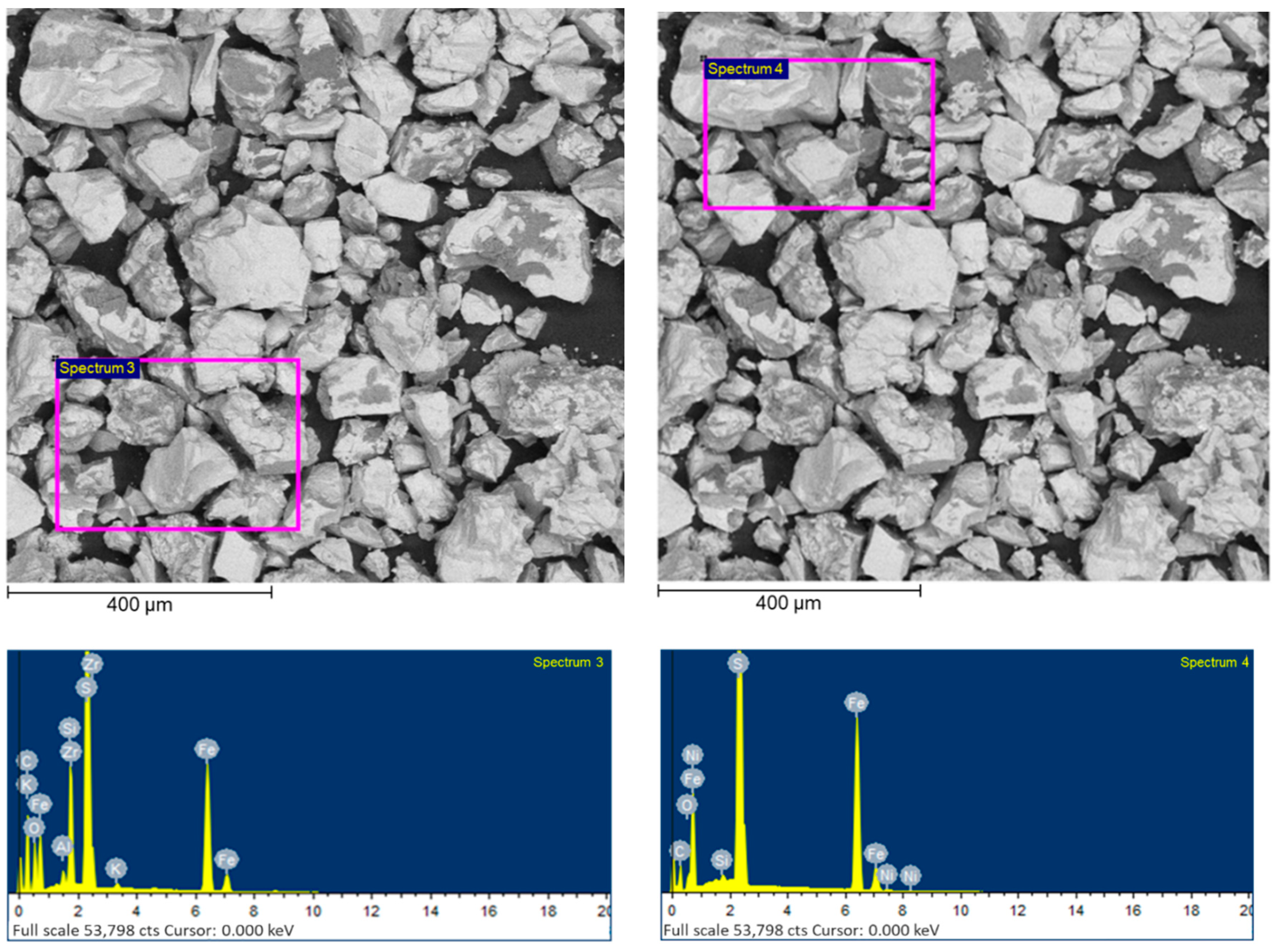
| Number of Spectra | Content, wt. [%] | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Fe | S | Si | Mg | Al | K | Cu | Zr | Ni | Ca | |
| Spectrum 1 | 29.11 | 7.93 | 28.74 | 19.95 | 3.72 | 4.07 | 1.97 | - | 0.98 | - | - | 3.53 |
| Spectrum 2 | 37.86 | 5.73 | 25.86 | 28.10 | 1.21 | - | 0.24 | 0.17 | - | 0.84 | - | - |
| Spectrum 3 | 49.78 | 8.70 | 18.71 | 18.54 | 3.09 | - | 0.40 | 0.19 | - | 0.58 | - | - |
| Spectrum 4 | 27.53 | 1.92 | 33.09 | 36.81 | 0.21 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.42 | - |
| Liquid Phase | σL-G, mN/m | η, mPa·s |
|---|---|---|
| Straw oil | 30.24 | 21.0 |
| Distilled water | 72.04 | 1.01 |
| Neonol (1% solution) | 29.44 | 1.93 |
| Neonol (2% solution) | 29.99 | 2.34 |
| Neonol (5% solution) | 30.13 | 7.26 |
| Neonol (10% solution) | 30.22 | 21.4 |
| The Mass Ratio of Straw Oil to Neonol | 20:80 | 30:70 | 40:60 | 50:50 | 60:40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σL-G, mN/m | 30.14 | 30.15 | 30.16 | 30.18 | 30.18 |
| η, mPa·s | 36.3 | 39.6 | 39.8 | 39.9 | 39.9 |
| Product | Yield [%] | Content [%] | ||||||||
| C | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | S | TiO2 | ZnO | CuO | ZrO2 | ||
| Metal-bearing concentrate | 17.35 | 2.91 | 12.76 | 0.12 | 60.14 | 7.432 | 2.12 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Carbon concentrate | 31.41 | 88.15 | 5.99 | 0.09 | 2.12 | 0.084 | 0.47 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| Tailings | 51.24 | 6.32 | 69.64 | 1.39 | 1.57 | 0.228 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.009 | 0.03 |
| Shungite rocks | 100.00 | 31.43 | 39.78 | 0.76 | 11.90 | 1.432 | 0.66 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Product | Recovery [%] | |||||||||
| C | SiO2 | CaO | Fe2O3 | S | TiO2 | ZnO | CuO | ZrO2 | ||
| Metal-bearing concentrate | 1.61 | 5.57 | 2.74 | 87.66 | 90.05 | 56.03 | 67.77 | 72.52 | 54.42 | |
| Carbon concentrate | 88.09 | 4.73 | 3.72 | 5.59 | 1.84 | 22.47 | 16.36 | 18.57 | 9.86 | |
| Tailings | 10.31 | 89.71 | 93.54 | 6.75 | 8.11 | 21.50 | 15.87 | 8.91 | 35.72 | |
| Shungite rocks | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aleksandrova, T.; Afanasova, A.; Nikolaeva, N.; Romashev, A.; Aburova, V.; Prokhorova, E. Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining High-Purity Carbon Materials and Recovering Valuable Metals from Shungite Rocks. Minerals 2025, 15, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010090
Aleksandrova T, Afanasova A, Nikolaeva N, Romashev A, Aburova V, Prokhorova E. Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining High-Purity Carbon Materials and Recovering Valuable Metals from Shungite Rocks. Minerals. 2025; 15(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleAleksandrova, Tatiana, Anastasia Afanasova, Nadezhda Nikolaeva, Artyem Romashev, Valeriya Aburova, and Evgeniya Prokhorova. 2025. "Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining High-Purity Carbon Materials and Recovering Valuable Metals from Shungite Rocks" Minerals 15, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010090
APA StyleAleksandrova, T., Afanasova, A., Nikolaeva, N., Romashev, A., Aburova, V., & Prokhorova, E. (2025). Investigation of the Possibility of Obtaining High-Purity Carbon Materials and Recovering Valuable Metals from Shungite Rocks. Minerals, 15(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15010090











