Abstract
The Kumishi ophiolitic mélange contains well-preserved large-scale serpentinites and their accompanying granulites in the eastern South Tianshan Accretionary Complex (STAC), southwestern Altaids. Previous studies have mainly focused on the thermodynamic conditions and tectonic setting of granulites. However, the petrogenesis of the widespread serpentinites in the Kumishi ophiolitic mélange remains largely unexplored. In this paper, petrological, geochemical, and geochronological studies were carried out on the Kumishi serpentinites, as well as the host sediment and intermediate–felsic volcanic rocks. The serpentinites show variable LOI values of 8.3–16.5 wt% and relatively consistent SiO2/(sum oxides) ratios of 0.81, which demonstrate that the major elements of their protoliths have been preserved well during serpentinization. Multi-trace element and REE diagrams suggest that the protoliths of the Kumishi serpentinites have experienced varying degrees of refertilization, with distinct natures seen between the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan serpentinites. Zircon U-Pb chronology of the Tonghuahsan serpentinites yields a mean age of 355.8 ± 7.3 Ma (MSWD = 1.0, N = 26). Detrital zircons from the host sediment record a maximum depositional age of 375 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 0.4, N = 3), with a peak at ca.419 Ma. Subduction-related volcanic rocks yield ages of ca.437 Ma. Hence, clues are provided to the petrogenesis of the Kumishi serpentinites, with calls for future in-depth works from an isotopic perspective.
1. Introduction
Serpentinites have gained tremendous attention due to their key role in the (re)cycling of water [1,2,3], carbon [4,5,6,7,8], halogens [9,10,11], and fluid-mobile elements [12,13,14,15] in subduction zones and on oceanic floors. They appear in variable geodynamic settings through plate driving, when the hydration of mantle peridotites occurs at mid-ocean ridges and/or abyssal basins. Detachment faults and the supra-subduction forearc mantle are the key domains in which infiltration and serpentinization occur [16,17,18]. Serpentinites have a large pressure–temperature stability field in subduction zones and thus can transfer volatiles to subarcs [18], shape the architecture of plate interfaces [19,20], contribute to the formation of arc lavas [21], and also affect intermediate-depth seismicity [22]. Meanwhile, serpentinites and/or metaperidotites may be linked to the processes of subduction infancy [23,24,25,26], progressive subduction [19], and (ultra-)high-pressure rock exhumation [15].
The Kumishi ophiolitic mélange in the eastern STAC, southwest Altaids, comprises a thick body of serpentinized and strongly deformed mantle peridotites accompanied by granulites (Figure 1). Previous studies have mainly focused on the metamorphic conditions of the Yushugou granulites [27,28,29] and regional magmatism [30,31]. A recent study proposed that the Yushugou granulites and metaperidotites may represent the remnants of metamorphic soles and their associated ophiolites, which are related to the intra-oceanic subduction initiation of the South Tianshan Ocean (STO) [32]. However, the large scale of the Kumishi serpentinites has received little attention. It is still unclear whether, as a whole, they represent the infant mantle wedge during subduction initiation or whether they have diverse origins.
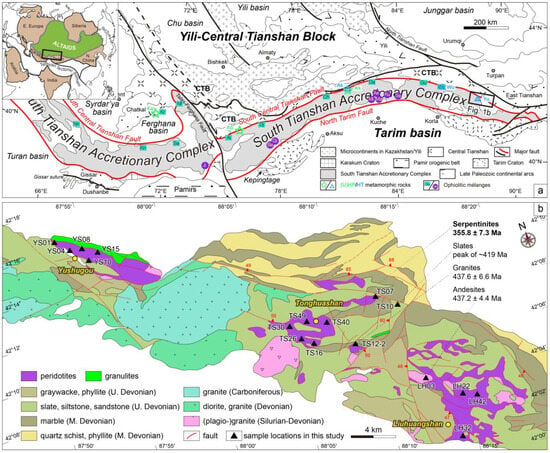
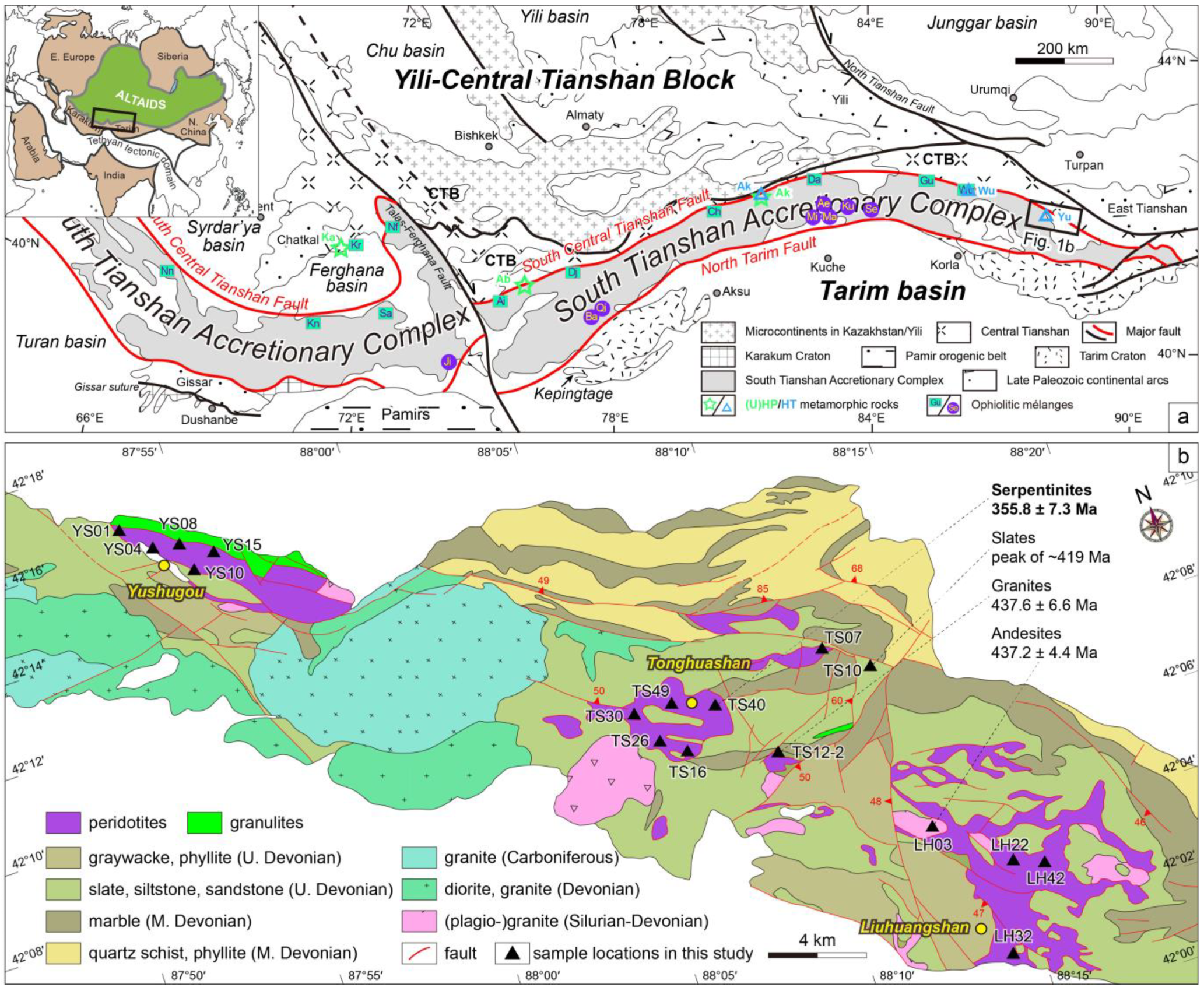
Figure 1.
(a) Tectonic framework of the southwestern Altaids, modified from [32,33]. (b) Geological map of Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan ophiolitic mélanges in the Kumishi region (compiled from the 1:50,000-scale geological map). Sample locations and zircon ages found in this study are marked.
The aim of this paper is to delineate the nature and petrogenesis of the Kumishi serpentinites based on their field structure, geochemistry, and geochronological data.
2. Geological Setting
The STAC, in the southwest Altaids, is located between the South Central Tianshan Fault (SCTF) to the north and the North Tarim Fault (NTF) to the south (Figure 1a). It is generally considered a wide forearc accretionary complex that developed during the northward subduction of the STO, with intensive Paleozoic magmatism found within the STAC and in the Yili–Central Tianshan Block [33,34]. Ophiolitic mélanges, yielding zircon U-Pb ages of ca.450–330 Ma, are distributed sparsely along the SCTF and NTF [33,35,36]. Representative oceanic-type (ultra-)high-pressure and low-temperature metamorphic rocks have been reported in the Akeyazi, Atbashi, and Kassan areas, showing relatively identical eclogite facies metamorphisms at ca. 320–310 Ma [37,38]. High-temperature metamorphic terranes discovered in the Yushugou, Wuwamen, and Akeyazi areas reveal the amphibolite-to-granulite facies metamorphism at ca. 390–350 Ma [29,32,39,40]. In addition, it is suggested that the Paleo-Asian Ocean may have experienced an initiation of diachronous subduction between 536 and 528 Ma [41] and then final closure in the early Triassic [42].
The Kumishi ophiolitic mélange is situated in the eastern section of the STAC, mainly outcropping in the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan areas, with an overall area of up to 90 km2 (Figure 1b). The long axis of the mélange strikes NW-SE (~120 °), which generally corresponds to the orientation of the SCTF. The mélange predominantly consists of ultramafic rocks, intermediate–felsic volcanic rocks, and minor gabbros, which are embedded in the siliceous rocks, (meta-)sediments, and marbles. Tectonically, it is strongly deformed and bounded by faults. In the Yushugou ophiolitic mélange, the elongated lens mainly consists of serpentinized peridotites and granulites [27,28,29]. Plagiogranites and anorthosites with ages of ca. 439–435 Ma are explained as being due to the formation of the oceanic crust [30]. It should be noted that the Yushugou granulites, with P-T conditions of ~840–940 °C and ~0.92–1.02 GPa, may disclose a Devonian intra-oceanic subduction initiation process in the STO [32]. In contrast, the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan ophiolitic mélanges have irregular shapes and mainly consist of serpentinites and plagiogranites. It has been suggested that ages of ca. 420 Ma from the dacites and granodiorites in the Yushugou and Tonghuashan mélanges represent regional Silurian subduction-related magmatism [30]. Carboniferous–Permian granitoids may be related to the evolutionary process of the STO from subduction to post-collision [43].
3. Analytical Methods
3.1. Major and Trace Elements
Major and trace element analyses of bulk rock were performed at the Wuhan Sample Solution Analytical Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China. Relevant data are listed in Table S1.
Major elements were measured by a Zsx Primus II wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, produced by Rigaku in Tokyo, Japan. The test conditions include a 50 kV voltage and 60 mA current. GBW07101-14 was used to create the standard curve. The data were corrected by the theoretical α coefficient method and the relative standard deviation is less than 2%. Sample pretreatment was carried out using the melting method. The melting temperature was 1050 °C and the melting time was 15 min. LOI was measured after heating to 1000 °C. The whole-rock Fe2O3 content is constrained by potassium permanganate titration.
Trace elements analyses were conducted on an Agilent 7700e ICP-MS. The detailed sample-digesting procedure was as follows: (1) the 200-mesh sample powder was dried for 12 h at 105 °C; (2) 1 mL HNO3 and 1 mL HF were slowly added into the Teflon bomb; (3) the Teflon bomb was placed in a stainless steel pressure jacket and heated to 190 °C for over 24 h; (4) 1 mL HNO3 was added and evaporated to dry; (5) 1 mL of HNO3, 1 mL of MQ water, and 1 mL of internal standard solution of 1 ppm In were added; and (6) the final solution was diluted to 100 g by the addition of 2% HNO3 for ICP-MS analyses.
3.2. Zircon U-Pb Dating
Zircon U-Pb dating and trace element analysis were simultaneously conducted by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry at the Beijing Geochronology Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China. Laser sampling was performed using a GeolasPro laser ablation system that consists of a COMPexPro 102 ArF excimer laser (wavelength of 193 nm and maximum energy of 200 mJ) and a MicroLas optical system. An Agilent 7900 ICP-MS instrument was used to acquire ion signal intensities. The detailed procedures used were described by [44]. The spot size and frequency of the laser were set to 20 µm and 8 Hz, respectively. Standard zircons, SRM 612, 91500, GJ-600, and Ple-337, were analyzed twice every ten spots. Relevant data are listed in Table S2.
4. Results
In this study, a total of fourteen serpentinized samples were collected from the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan ophiolitic mélanges. One representative serpentinite sample (TS40) and one sedimentary sample (TS10) from the Tonghuashan mélange were selected for geochronological analyses. Two intermediate–felsic subduction-related volcanic samples were found in the Tonghuashan (TS12-2) and Liuhuangshan (LH03) areas. Sample locations are shown in Figure 1b.
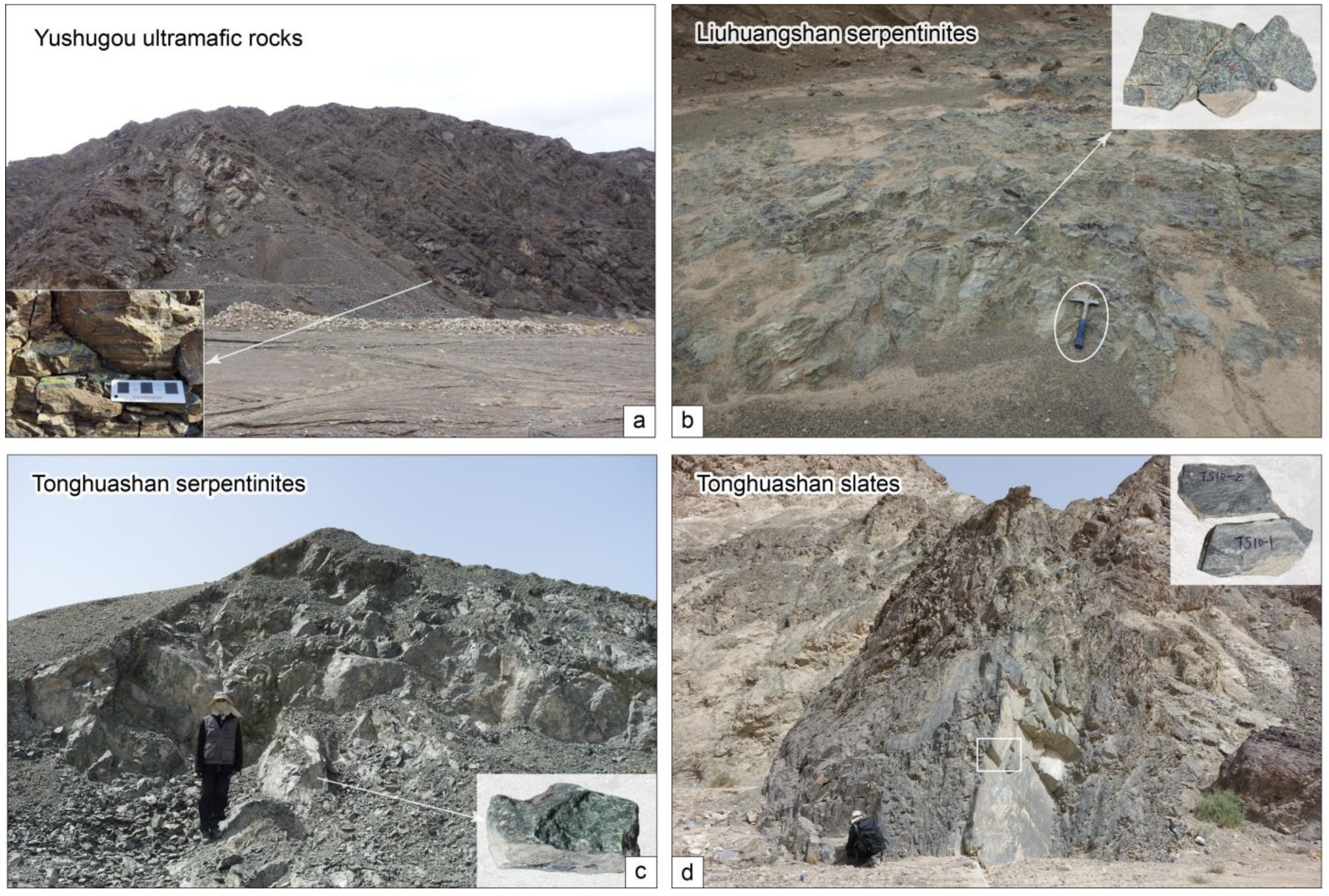
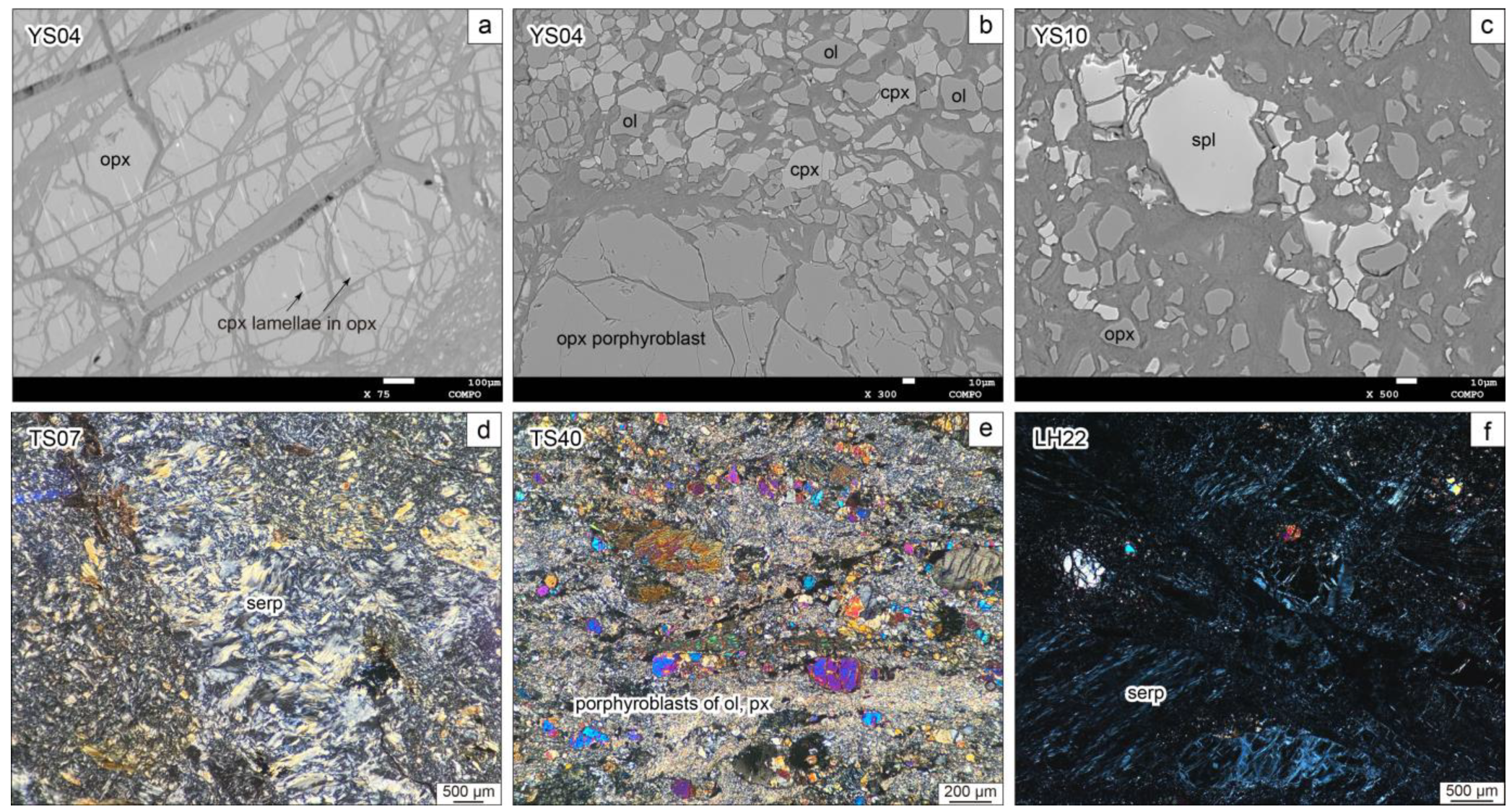
The Yushugou ultramafic rocks, accompanied by intermediate/high-pressure garnet orthopyroxene granulites [28,32], exhibit extensive mylonitization and are mostly made up of banded pyroxene serpentinites and olivine pyroxene mylonites (Figure 2a). Clinopyroxene lamellae can be found in the orthopyroxene porphyroblasts, which are often surrounded by small grain-sized olivine, clinopyroxene, and spinel (Figure 3a,b). The spinel is broken and anhedral (Figure 3c).

Figure 2.
Field photographs of (a) the Yushugou ultramafic rocks, (b) Liuhuangshan serpentinites, and (c,d) the Tonghuashan serpentinites and slates.
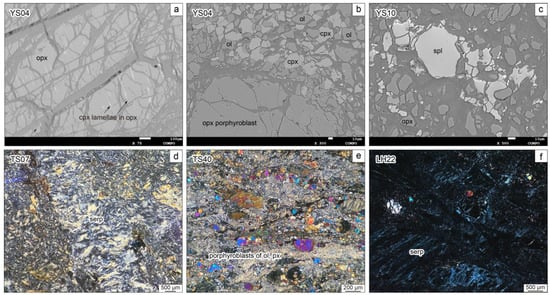
Figure 3.
Microphotographs of serpentinites in the (a–c) Yushugou, (d,e) Tonghuashan, and (f) Liuhuangshan areas. Mineral abbreviations: cpx—clinopyroxene; ol—olivine; opx–orthopyroxene; px—pyroxene; serp—serpentine; spl—spinel.
The Tonghuashan ophiolitic mélange has experienced comparatively severe alteration, epidotization, and muscovitization. Its peridotites have nearly changed into grayish-green serpentinites and are locally preserved as peridotite blocks (Figure 2c). Its ferromagnesian minerals have been replaced by serpentines, with a small portion of pyroxene relicts (Figure 3d,e). Sedimentary sample TS10 was selected from the host rock of the Tonghuashan serpentinites for geochronological dating.
The Liuhuangshan ophiolitic blocks are irregular and broken in structure. Most of them are mylonitic and/or cataclastic. Well-preserved Liuhuangshan serpentinites mainly outcrop in the riverbed (Figure 2b). Their olivine and pyroxene grains almost disappear and are replaced by serpentines (Figure 3f).
4.1. Bulk-Rock Geochemistry
The major and trace element compositions of the Kumishi serpentinites, slates, and subduction-related granitic and andesitic samples in this study are listed in Table S1.
The Kumishi serpentinites show LOI values of 8.3–16.5 wt% and relatively consistent concentrations (anhydrous) of 40.7–48.1 wt% SiO2 and 36.5–44.1 wt% MgO. Their CaO and Al2O3 contents range between 0.04 and 10.14 wt% and 0.40 and 4.27 wt%, respectively (Figure 4a–c). They are comparable in their major element compositions to those of the South Tianshan serpentinites reported by [45].
In the trace element diagrams, Ti could be a fingerprint reflecting the degree of magmatic depletion and refertilization and further identify the protolith of the serpentinites [16]. It suggests that mantle wedge serpentinite plot in the realm of 2–50 ppm, with subducted serpentinites of Ti > 50 ppm and abyssal serpentinites of 10–130 ppm. Depletion of high-field-strength elements (HFSEs; e.g., Nb and Ta) could reflect a subduction-related influence [46]. Light rare earth elements (LREEs; such as La) are more easily mobilized than heavy rare earth elements (HREEs; such as Yb) and HFSEs [16,47]. Large ion lithophile elements (LILEs; e.g., Th and U) prefer to be incorporated into fluids rather than mineral grains and thus are enriched in serpentinites [18,48].
The Kumishi serpentinites have Ti contents of 53–695 ppm, Yb of 0.05–0.38 ppm, La/Yb of 0.29–8.87 ppm, Th of 0.005–0.136 ppm, and U of 0.002–0.320 ppm. Further from the mantle wedge serpentinites, they tend to fall near the range of abyssal and/or subducted serpentinites (Figure 4d–f). Their normalized multi-element spider and rare earth element (REE) patterns are characterized by a peak of U, relative depletion of Nb and Ta, and low and flat contents of REEs and a range from weakly negative to moderately positive Eu anomalies (Figure 5). Their normalized REEs are below 1, with (Eu/Eu*)N values of 0.57–2.60, La/YbN of 0.19–5.63, and Gd/YbN of 0.26–1.68. The Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan serpentinites can be separated into two groups based on their REE patterns: LILE- and LREE-enriched (La/LuN of 3.07–5.59, Gd/YbN of 0.58–1.68) vs. LILE-depleted and HREE-enriched (La/LuN of 0.19–0.56, Gd/YbN of 0.58–0.95). The LILE-depleted and HREE-enriched serpentinites show higher concentrations of Al2O3 and Ti. In contrast, the Yushugou serpentinites are characterized by LREE depletion and progressive HREE increases (La/LuN of 0.44–1.88, Gd/YbN of 0.26–1.30).
In addition, granites and andesites cutting the host (meta-)sediments display negative Nb and Ta anomalies (Figure 6).
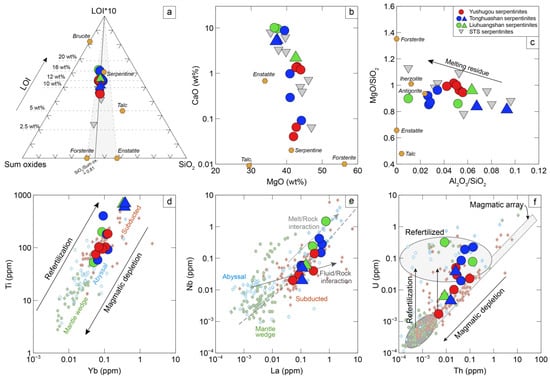
Figure 4.
Major and trace element diagrams for the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan serpentinites (modified from [16]). (a) Ternary plot of LOI*10 (wt%)−SiO2 (wt%)−Sum oxides (wt%). Sum oxides = TiO2 + Al2O3 + TFe2O3 + MnO + MgO + CaO + Na2O + K2O + P2O5. (b) CaO (wt%) versus MgO (wt%) diagram. (c) MgO/SiO2 versus Al2O3/SiO2 diagram. All oxides are recalculated on a volatile-free basis. The South Tianshan (STS) serpentinites are from [45]. (d) Ti (ppm) versus Yb (ppm) diagram. (e) Nb (ppm) versus La (ppm) diagram. Dashed line represents linear regression of abyssal peridotites from [47]. (f) Th (ppm) versus U (ppm) diagram. The gray ellipse represents serpentinites deriving from refertilized protoliths. Data on mantle wedge, abyssal, and subducted serpentinites are cited from [16]. Two groups of the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan serpentinites can be distinguished based on the REE patterns in Figure 5. Detailed descriptions can be found herein and in [16].
Figure 4.
Major and trace element diagrams for the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan serpentinites (modified from [16]). (a) Ternary plot of LOI*10 (wt%)−SiO2 (wt%)−Sum oxides (wt%). Sum oxides = TiO2 + Al2O3 + TFe2O3 + MnO + MgO + CaO + Na2O + K2O + P2O5. (b) CaO (wt%) versus MgO (wt%) diagram. (c) MgO/SiO2 versus Al2O3/SiO2 diagram. All oxides are recalculated on a volatile-free basis. The South Tianshan (STS) serpentinites are from [45]. (d) Ti (ppm) versus Yb (ppm) diagram. (e) Nb (ppm) versus La (ppm) diagram. Dashed line represents linear regression of abyssal peridotites from [47]. (f) Th (ppm) versus U (ppm) diagram. The gray ellipse represents serpentinites deriving from refertilized protoliths. Data on mantle wedge, abyssal, and subducted serpentinites are cited from [16]. Two groups of the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan serpentinites can be distinguished based on the REE patterns in Figure 5. Detailed descriptions can be found herein and in [16].
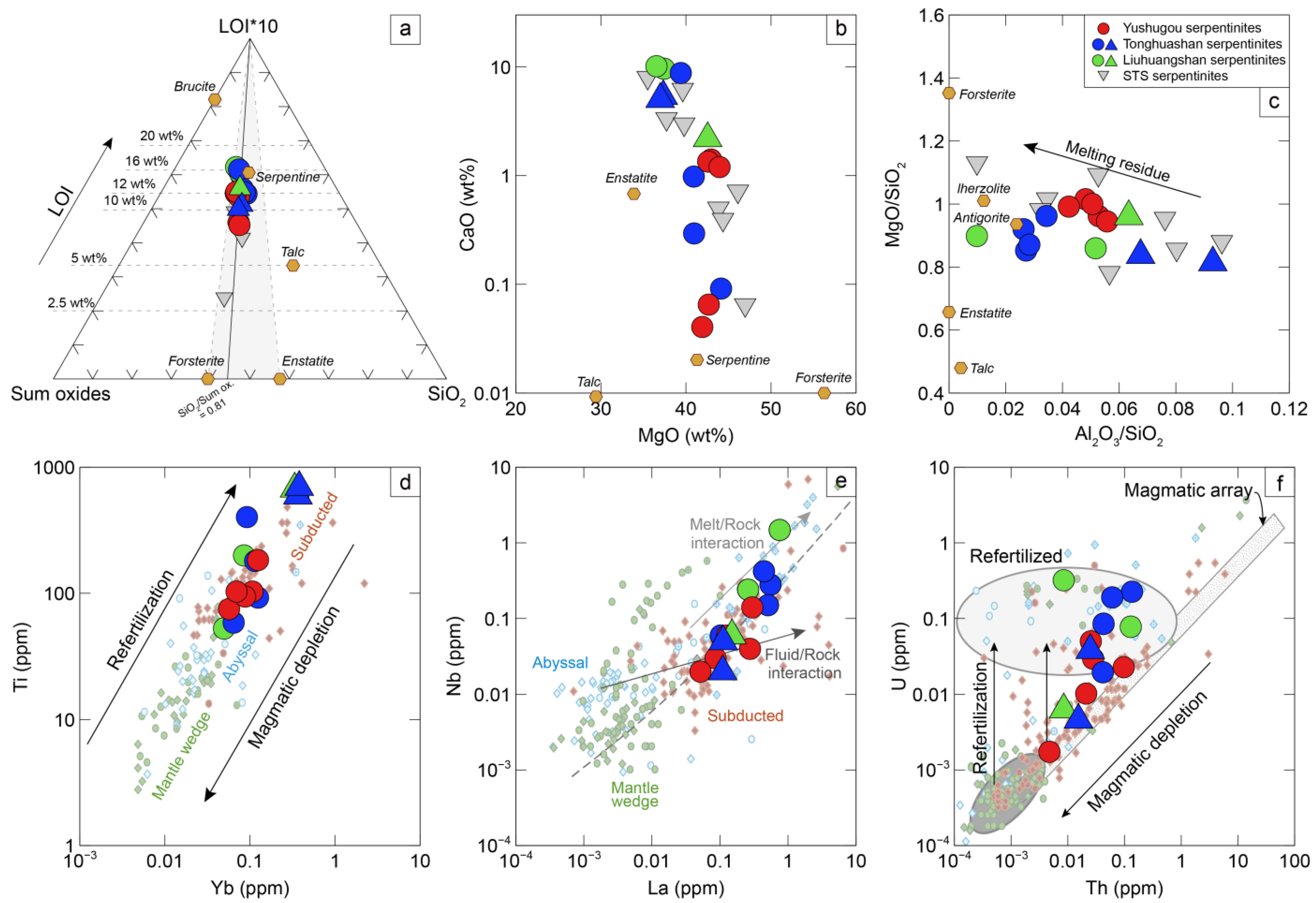
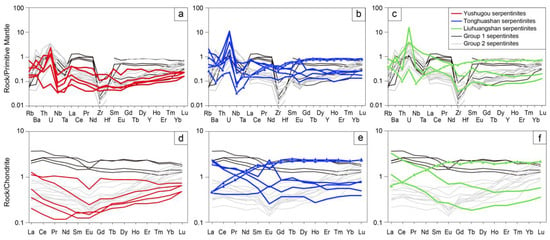
Figure 5.
(a–c) Primitive mantle-normalized diagrams and (d–f) CI-normalized REE patterns of the Kumishi serpentinites in this study. Serpentinites from groups 1 and 2 are cited from [13]. Primitive mantle- and CI-normalized values are from [49]. The data represented by triangle labels match those in Figure 4.
Figure 5.
(a–c) Primitive mantle-normalized diagrams and (d–f) CI-normalized REE patterns of the Kumishi serpentinites in this study. Serpentinites from groups 1 and 2 are cited from [13]. Primitive mantle- and CI-normalized values are from [49]. The data represented by triangle labels match those in Figure 4.
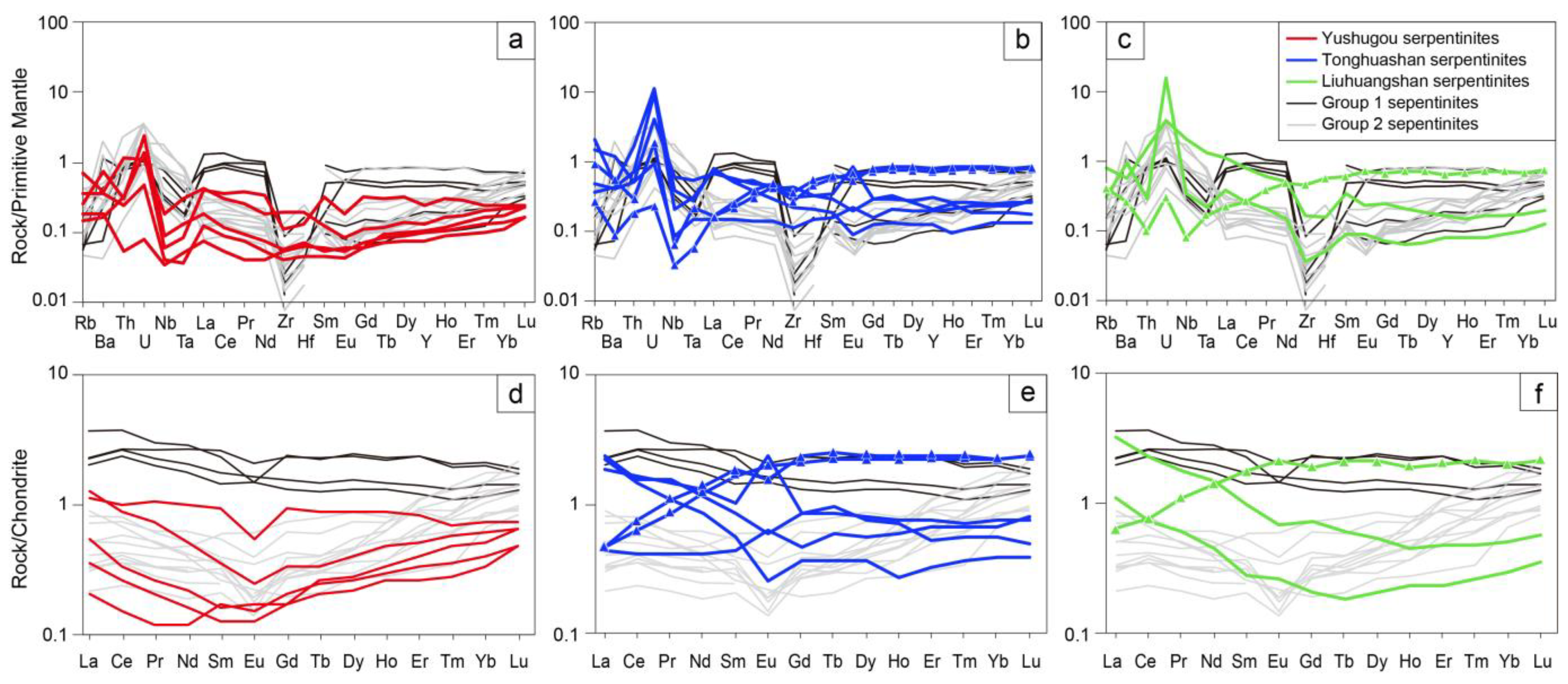
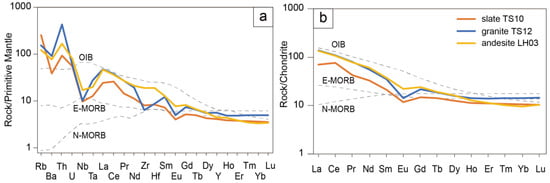
Figure 6.
(a) Primitive mantle-normalized diagrams and (b) CI-normalized REE patterns of slate, granite, and andesite samples in this study. Normalized values, normal mid-oceanic-ridge basalt (N-MORB), enriched mid-oceanic-ridge basalt (E-MORB), and oceanic island basalt (OIB) are from [49].
Figure 6.
(a) Primitive mantle-normalized diagrams and (b) CI-normalized REE patterns of slate, granite, and andesite samples in this study. Normalized values, normal mid-oceanic-ridge basalt (N-MORB), enriched mid-oceanic-ridge basalt (E-MORB), and oceanic island basalt (OIB) are from [49].
4.2. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology
A Zircon U-Pb dating analysis was conducted on the samples of serpentinite (TS40), slate (TS10), granite (TS12-2), and andesite (LH03). Detailed data are listed in Table S2.
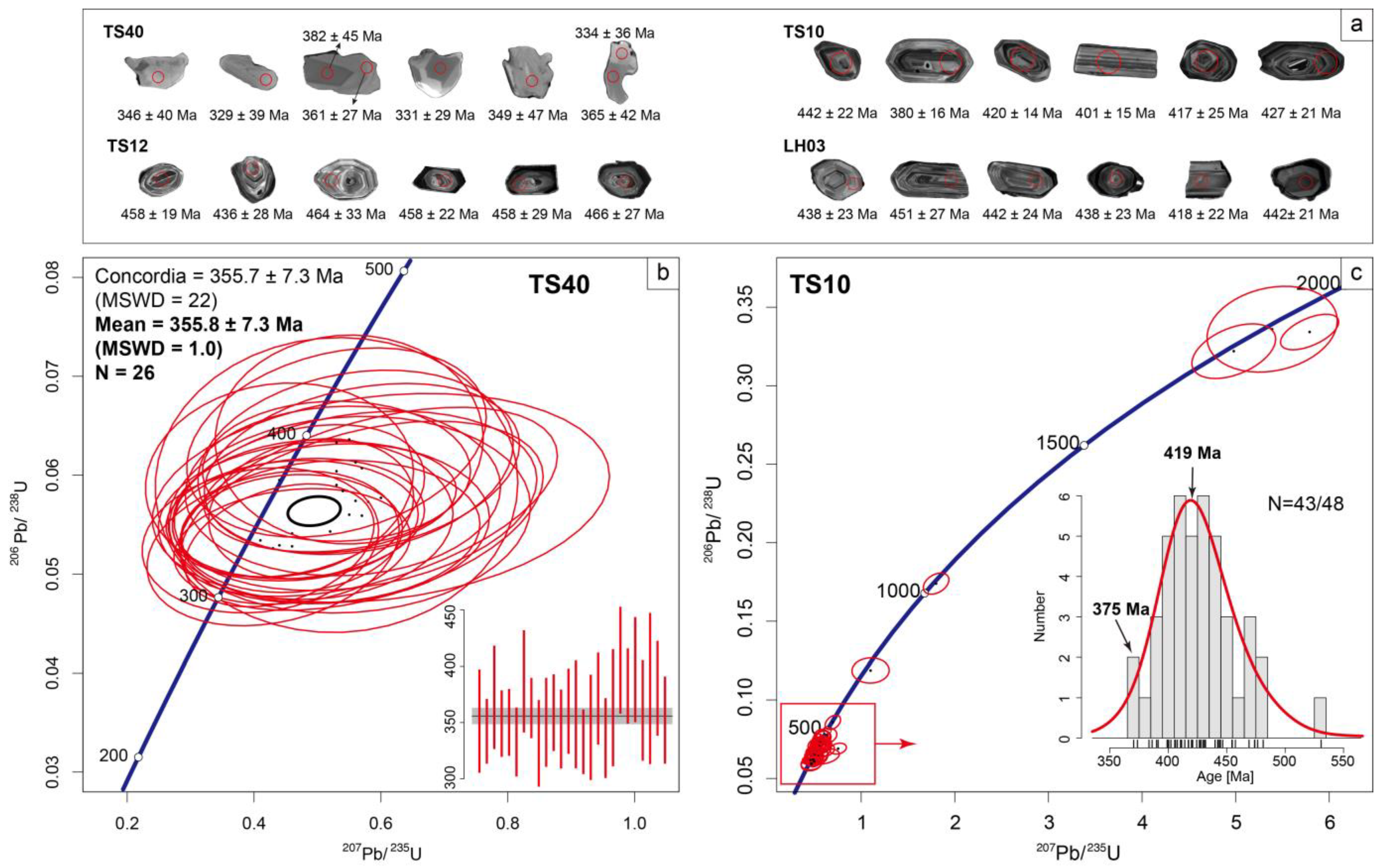
In the fourteen serpentinites in this study, zircon grains were only found in sample TS40. The zircon grains of sample TS40 are irregular in shape, with rounded and obtuse edges. They are bright-to-gray in the Cathodoluminescence images, with no obvious oscillatory zonings (Figure 7a), providing a weighted mean age of 355.8 ± 7.3 Ma (MSWD = 1.0, N = 26) from the results of 329–396 Ma (Figure 7b).
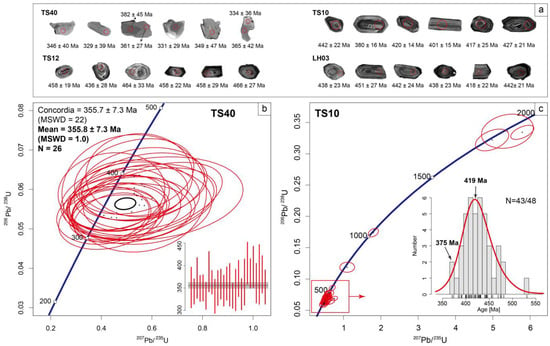
Figure 7.
(a) Representative zircon Cathodoluminescence images in this study. Red circles denote analysis spots sized 20 µm. (b,c) Zircon U-Pb dating results of serpentinite and host sediment samples from the Tonghuashan area.
Host sedimentary sample TS40 has magmatic zircon grains with a euhedral shape and oscillatory zonings (Figure 7a). Among the 48 analysis results from 1940 Ma to 369 Ma, 43 Paleozoic zircon ages show a median of ca.419 Ma (Figure 7c). Half of them are between 450 and 400 Ma (mean = 419.0 ± 2.9 Ma, MSWD = 3.3, N = 28). The three youngest zircon grains have a maximum depositional age of 375.0 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 0.4, N = 3).
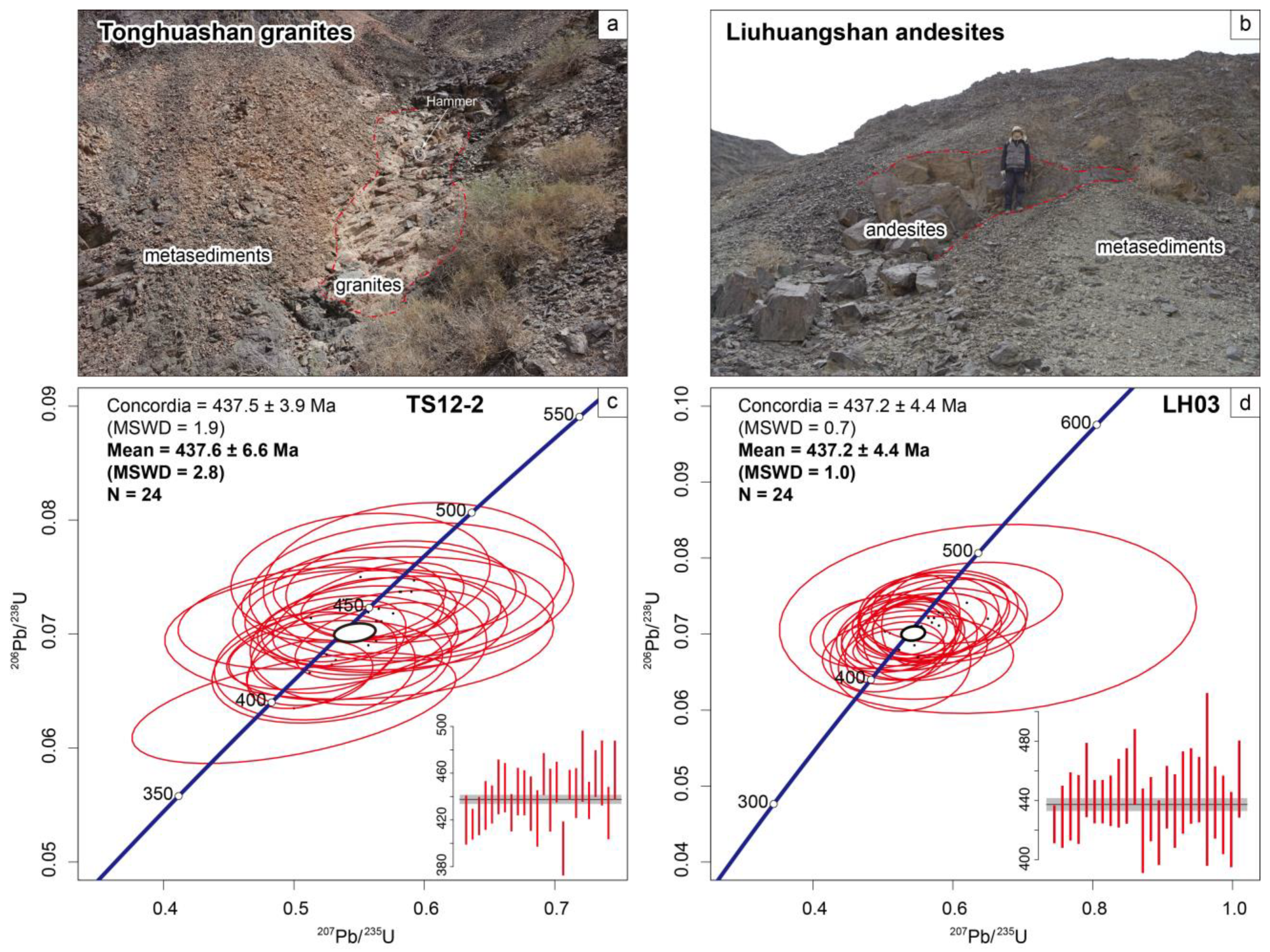
Granite sample TS12-2 and andesite sample LH03, cutting the host (meta-)sediments, have weighted mean ages of 437.6 ± 6.6 Ma (MSWD = 2.8, N = 24) and 437.2 ± 4.4 Ma (MSWD = 1.0, N = 24), respectively (Figure 8).
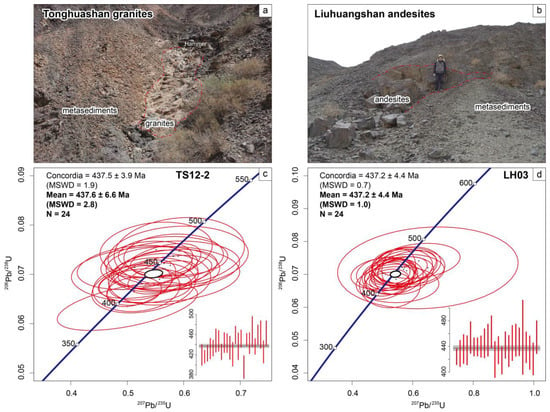
Figure 8.
Field pictures and zircon U-Pb dating results of granites and andesites in this study. (a,c) Tonghuashan granites; (b,d) Liuhuangshan andesites.
5. Discussion
Serpentinization has been proven to play a significant role in subduction plate interfaces, volatile transport, and global tectonics [2,7,13]. By compiling serpentinites from different tectonic settings, researchers have linked their geochemical characteristics to specific tectonic settings [13,16,18]. The serpentinites exhibit variations of orders of magnitude in their element concentrations, which may result from their complex magmatic evolution and serpentinization processes.
The serpentinites in this study have SiO2/(sum oxides) values of 0.81 over a wide range of LOI values, which suggests that major elements of the protolith have been preserved well during serpentinization [16] (Figure 4a). The variable concentrations of CaO, Al2O3, and immobile trace elements (such as Ti and Yb) reflect the complex pre-serpentinization magmatic history of melt extraction and refertilization due to melt–rock reactions (Figure 4b–d). Incompatible elements (such as La, Th, and U) prefer to enter fluid rather than mineral phases. The Kumishi serpentinites are characterized by an enrichment of U (Figure 4f), which, however, is not only constrained by fluid–rock reactions during serpentinization but also melt–rock reactions during refertilization [13,14]. In the multi-trace element diagrams and REE patterns, the Yushugou serpentinites are distinct from those in the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan areas (Figure 5). The Yushugou serpentinites have U-shaped REE patterns and are characterized by LREE depletion and progressive HREE increases, which are comparable to those of group 2 serpentinites from [13]. These features may support variably prominent refertilization upon melt–rock reactions, with additional melt extraction [13,18,20]. Such REE patterns can be found in the serpentinites from supra-subduction zone (SSZ) settings [16]. As suggested by [32], the Yushugou granulites could be relicts of metamorphic soles, revealing a Devonian intra-oceanic subduction initiation process in the STO. Hence, the Yushugou serpentinized ultramafic rocks are tentatively proposed to be mantle wedge serpentinites formed during the subduction infancy, which have been impacted by a degree of subduction-related disturbance and were exhumated along with the high-temperature sole. As for the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan serpentinites, they exhibit a large range of bulk-rock geochemical compositions and at least two types of REE patterns (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The LILE- and LREE-enriched serpentinites may be related to subduction melt or fluid metasomatism, while the LILE-depleted and HREE-enriched serpentinites are similar to residual abyssal peridotites. Their relatively high TiO2 (~0.11 wt%) contents could be explained by melt infiltration, seafloor alteration, and/or prograde metamorphism [50]. Future studies should be conducted on these serpentinites’ mineral compositions (olivine, pyroxene, spinel, etc.), fluid-mobile elements, and isotopic compositions (such as Boron), as well as their platinum elements, to further constrain their geochemical behavior to a specific tectonic evolution history.
In general, zircon crystals are scarce in ultramafic rocks due to their low Zr and Si contents. In this study of serpentinites, zircon grains were found in the Tonghuashan samples. These bright-to-gray zircon grains have irregular shapes, with rounded and obtuse edges (Figure 7a), which can rule out a magmatic origin. They have a weighted mean age of 355.8 ± 7.3 Ma (MSWD = 1.0, N = 26), which is younger than the maximum depositional age of 375.0 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 0.4, N = 3) of their host sediments (Figure 7). Thus, zircons may not be introduced into ultramafic rocks through secondary processes, such as tectonic mixing or sedimentary deposition in ophiolitic sequences. Taking these facts into consideration, we suggest that hydrothermal alteration (e.g., serpentinization) may be a reasonable process to consider when zirconium precipitates in fractures or veins within ultramafic rocks [51,52]. Similarly, the late Devonian to early Carboniferous ages are sporadically reported in the Yushugou area [28,29,32] but are related to the process of dynamic recrystallization which occurs during late alterations and fluid–rock reactions. We also do respect the possibility of metasomatic processes occurring, although regional magmatic episodes mainly occurred at ca. 440–400 Ma [30,31,32,33].
6. Conclusions
Our field observations and geochemical and geochronological data, integrated with compiled serpentinites from different tectonic settings, enable us to conclude the following:
- (1)
- The Kumishi serpentinites outcrop in the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan areas. Composed of granulites and serpentinized peridotite, the lens-shape Yushugou ophiolitic mélange is proposed to be related to the process of intra-oceanic subduction initiation in the STO [32], while the Tonghuashan and Liuhuangshan serpentinites experienced relatively strong alteration, mylonitization, and/or cataclasis.
- (2)
- The Kumishi serpentinites have LOI values of 8.3–16.5 wt%, with relatively consistent SiO2/(sum oxides) ratios of 0.81. Based on our multi-trace element diagrams, protoliths of the Kumishi serpentinites have experienced variable degrees of refertilization. Their REE patterns may imply distinct natures between the Yushugou, Tonghuashan, and Liuhuangshan serpentinites.
- (3)
- Zircon U-Pb dating results show that the Tonghuashan serpentinites have a mean age of 355.8 ± 7.3 Ma (MSWD = 1.0, N = 26). Detrital zircons from the host sediment have a maximum depositional age of 375 ± 10 Ma (MSWD = 0.4, N = 3), with a peak at ca.419 Ma. Regional subduction-related volcanic rocks yield ages of ca.437 Ma.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/min15030229/s1, Table S1: Bulk-rock geochemistry of the Kumishi serpentinites, slates, granites, and andesites in this study; Table S2: Zircon U-Pb ages in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.G. and Z.T.; Methodology, L.G.; Resources, W.X. and Z.T.; Writing—original draft, L.G.; Writing—review & editing, L.G., W.X. and Z.T.; Supervision, W.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2024M762401.
Data Availability Statement
Data are presented as a Supplementary File.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LOI | Loss on ignition |
| NTF | North Tarim Fault |
| REE | Rare earth element |
| SCTF | South Central Tianshan Fault |
| STAC | South Tianshan Accretionary Complex |
| STO | South Tianshan Ocean |
References
- Albers, E.; Kahl, W.-A.; Beyer, L.; Bach, W. Variant Across-Forearc Compositions of Slab-Fluids Recorded by Serpentinites: Implications on the Mobilization of FMEs from an Active Subduction Zone (Mariana Forearc). Lithos 2020, 364–365, 105525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamadrid, H.M.; Rimstidt, J.D.; Schwarzenbach, E.M.; Klein, F.; Ulrich, S.; Dolocan, A.; Bodnar, R.J. Effect of Water Activity on Rates of Serpentinization of Olivine. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, J.C.; Garrido, C.J.; Shanks, W.C.; Turchyn, A.; Padrón-Navarta, J.A.; López Sánchez-Vizcaíno, V.; Gómez Pugnaire, M.T.; Marchesi, C. Recycling of Water, Carbon, and Sulfur during Subduction of Serpentinites: A Stable Isotope Study of Cerro Del Almirez, Spain. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 327–328, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, M.D.; Garrido, C.J.; López Sánchez-Vizcaíno, V. Fluid-Mediated Carbon Release from Serpentinite-Hosted Carbonates during Dehydration of Antigorite-Serpentinite in Subduction Zones. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 531, 115964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scambelluri, M.; Bebout, G.E.; Belmonte, D.; Gilio, M.; Campomenosi, N.; Collins, N.; Crispini, L. Carbonation of Subduction-Zone Serpentinite (High-Pressure Ophicarbonate; Ligurian Western Alps) and Implications for the Deep Carbon Cycling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2016, 441, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, E.M.; Früh-Green, G.L.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Alt, J.C.; Plas, A. Serpentinization and Carbon Sequestration: A Study of Two Ancient Peridotite-Hosted Hydrothermal Systems. Chem. Geol. 2013, 351, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, H.; Sun, W.; Deng, J.; Zartman, R.E.; Guo, J.; Bao, Z.; Zong, C. Boron, Arsenic and Antimony Recycling in Subduction Zones: New Insights from Interactions between Forearc Serpentinites and CO2-Rich Fluids at the Slab-Mantle Interface. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 298, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, E.M.; Vogel, M.; Früh-Green, G.L.; Boschi, C. Serpentinization, Carbonation, and Metasomatism of Ultramafic Sequences in the Northern Apennine Ophiolite (NW Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, G.M.; Barnes, J.D.; John, T.; Hoffmann, J.E.; Chatterjee, R.; Stockli, D.F. Global Halogen Flux of Subducting Oceanic Crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 594, 117750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, M.A.; Barnes, J.D. Sediments, Serpentinites, and Subduction: Halogen Recycling from the Surface to the Deep Earth. Elements 2022, 18, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, M.A.; Marks, M.A.W.; Godard, M. Halogens in Serpentinised-Troctolites from the Atlantis Massif: Implications for Alteration and Global Volatile Cycling. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2022, 177, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Waldman, R.; Yogodzinski, G.; Bizimis, M.; Ryan, J.; Leeman, W.; Scher, H.; Hoernle, K. Boron Isotopes Identify Deep-Slab Serpentinite in the Source of Aleutian Arc Magma. Geology 2025, 53, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettke, T.; Bretscher, A. Fluid-Mediated Element Cycling in Subducted Oceanic Lithosphere: The Orogenic Serpentinite Perspective. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 225, 103896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressico, F.; Cannaò, E.; Olivieri, O.S.; Pastore, Z.; Peverelli, V.; Malaspina, N.; Vitale Brovarone, A. Behaviour of Fluid-Mobile Elements across a High-Pressure Serpentinization Front (Monte Maggiore Unit, Alpine Corsica). Chem. Geol. 2024, 662, 122228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannaò, E.; Agostini, S.; Scambelluri, M.; Tonarini, S.; Godard, M. B, Sr and Pb Isotope Geochemistry of High-Pressure Alpine Metaperidotites Monitors Fluid-Mediated Element Recycling during Serpentinite Dehydration in Subduction Mélange (Cima Di Gagnone, Swiss Central Alps). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 163, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, F.; Godard, M.; Guillot, S.; Hattori, K. Geochemistry of Subduction Zone Serpentinites: A Review. Lithos 2013, 178, 96–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, S.; Schwartz, S.; Reynard, B.; Agard, P.; Prigent, C. Tectonic Significance of Serpentinites. Tectonophysics 2015, 646, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scambelluri, M.; Cannaò, E.; Gilio, M. The Water and Fluid-Mobile Element Cycles during Serpentinite Subduction. A Review. Eur. J. Mineral. 2019, 31, 405–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, P.; Plunder, A.; Angiboust, S.; Bonnet, G.; Ruh, J. The Subduction Plate Interface: Rock Record and Mechanical Coupling (from Long to Short Timescales). Lithos 2018, 320–321, 537–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannaò, E.; Scambelluri, M.; Agostini, S.; Tonarini, S.; Godard, M. Linking Serpentinite Geochemistry with Tectonic Evolution at the Subduction Plate-Interface: The Voltri Massif Case Study (Ligurian Western Alps, Italy). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 190, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.-Q.; Chen, Y.-X.; Chen, R.-X.; Zhao, Z.-F.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Subducted Serpentinite Contributes to the Formation of Arc Lavas with Heavy Mo Isotopic Compositions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 369, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrand, T.P.; Hilairet, N.; Incel, S.; Deldicque, D.; Labrousse, L.; Gasc, J.; Renner, J.; Wang, Y.; Green II, H.W.; Schubnel, A. Dehydration-Driven Stress Transfer Triggers Intermediate-Depth Earthquakes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilairet, N.; Reynard, B.; Wang, Y.; Daniel, I.; Merkel, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Petitgirard, S. High-Pressure Creep of Serpentine, Interseismic Deformation, and Initiation of Subduction. Science 2007, 318, 1910–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, C.; Agard, P.; Guillot, S.; Godard, M.; Dubacq, B. Mantle Wedge (De)Formation During Subduction Infancy: Evidence from the Base of the Semail Ophiolitic Mantle. J. Petrol. 2018, 59, 2061–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, R.; Alard, O.; Schaefer, B.; Ali, L.; Sajid, M.; Khedr, M.Z.; Shah, M.T.; Anjum, M.N. Geochemistry of Waziristan Ophiolite Complex, Pakistan: Implications for Petrogenesis and Tectonic Setting. Minerals 2023, 13, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, M.Z.; Takazawa, E.; Hauzenberger, C.; Tamura, A.; Arai, S.; Stern, R.J.; Morishita, T.; El-Awady, A. Petrogenesis of Arc-Related Serpentinized Peridotites (Egypt): Insights into Neoproterozoic Mantle Evolution beneath the Arabian-Nubian Shield. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 226, 105078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Su, L.; Jian, P.; Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Lu, G.; Wang, J. Zircon U-Pb SHRIMP ages of high-pressure granulite in Yushugou ophiolitic terrane in southern Tianshan and their tectonic implications. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1411–1415, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, Z. High-Temperature Metamorphism of the Yushugou Ophiolitic Slice: Late Devonian Subduction of Seamount and Mid-Oceanic Ridge in the South Tianshan Orogen. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 132, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xia, B.; Lü, Z. Metamorphic P-T Path and Zircon U-Pb Dating of HP Mafic Granulites in the Yushugou Granulite-Peridotite Complex, Chinese South Tianshan, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 153, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. U-Pb ages of zircons from ophiolite and related rocks in the Kumishi region at the southern margin of Middle Tianshan, Xinjiang: Evidence of Early Paleozoic oceanic basin. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2011, 27, 77–95, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jian, P.; Kröner, A.; Jahn, B.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Ma, H. Zircon Ages of Metamorphic and Magmatic Rocks within Peridotite-Bearing Mélanges: Crucial Time Constraints on Early Carboniferous Extensional Tectonics in the Chinese Tianshan. Lithos 2013, 172–173, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Xiao, W.; Tan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Mao, Q.; Wang, H.; Jia, X.; Sang, M.; Guo, Y.; Tan, Y. Probing Intra-oceanic Subduction Infancy in Ancient Orogenic Belts: Example from Chinese South Tianshan. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2024, 42, 1099–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-S.; Klemd, R.; Gao, J.; Jiang, T.; Li, J.-L.; Xue, S.-C. Final Assembly of the Southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt as Constrained by the Evolution of the South Tianshan Orogen: Links with Gondwana and Pangea. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 7361–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Windley, B.F.; Allen, M.B.; Han, C. Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan Orogenic Collage. Gondwana Res. 2013, 23, 1316–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegner, E.; Alexeiev, D.V.; Willbold, M.; Kröner, A.; Topuz, G.; Mikolaichuk, A.V. Early Silurian Tholeiitic-Boninitic Mailisu Ophiolite, South Tianshan, Kyrgyzstan: A Geochemical Record of Subduction Initiation. Int. Geol. Rev. 2020, 62, 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, M.; Xiao, W.; Orozbaev, R.; Bakirov, A.; Sakiev, K.; Pak, N.; Ivleva, E.; Zhou, K.; Ao, S.; Qiao, Q.; et al. Structural Styles and Zircon Ages of the South Tianshan Accretionary Complex, Atbashi Ridge, Kyrgyzstan: Insights for the Anatomy of Ocean Plate Stratigraphy and Accretionary Processes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 153, 9–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Agard, P.; Monié, P.; Gao, J.; John, T.; Bayet, L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, X.-S.; Hong, T.; Wan, B.; et al. Architecture and P-T-Deformation-Time Evolution of the Chinese SW-Tianshan HP/UHP Complex: Implications for Subduction Dynamics. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loury, C.; Rolland, Y.; Guillot, S.; Lanari, P.; Ganino, C.; Melis, R.; Jourdon, A.; Petit, C.; Beyssac, O.; Gallet, S.; et al. Tectonometamorphic Evolution of the Atbashi High-P Units (Kyrgyz CAOB, Tien Shan): Implications for the Closure of the Turkestan Ocean and Continental Subduction–Exhumation of the South Kazakh Continental Margin. J. Metamorph. Geol. 2018, 36, 959–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Klemd, R.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Jiang, T.; Zong, K.; Xue, S. Paleozoic Subduction-Accretion in the Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights From the Wuwamen Accretionary Complex of the Chinese South Tianshan. Tectonics 2022, 41, e2021TC006965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X. Discovery of Mafic Granulites in the Muzhaerte Area, SW Tianshan, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Pastor–Galán, D.; Smit, M.A.; Miao, L.; Dong, M.; Zhang, F.; Sanchir, D.; Ganbat, A.; Liu, C.; Luo, Y.; et al. Ophiolites in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt Record Cambrian Subduction Initiation Processes. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Xiao, W.; Mao, Q.; Wang, H.; Sang, M.; Li, R.; Gao, L.; Guo, Y.; Gan, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Final Closure of the Paleo Asian Ocean Basin in the Early Triassic. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Weng, K.; Cao, K.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y. Petrogenesis of Carboniferous-Permian Granitoids in the Kumishi Area of Tianshan, China: Insights into the Geodynamic Evolution Triggered by Subduction and Closure of the South Tianshan Ocean. Minerals 2024, 14, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, K.; Klemd, R.; Yuan, Y.; He, Z.; Guo, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z. The Assembly of Rodinia: The Correlation of Early Neoproterozoic (ca. 900 Ma) High-Grade Metamorphism and Continental Arc Formation in the Southern Beishan Orogen, Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt (CAOB). Precambrian Res. 2017, 290, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Hermann, J.; Zhang, L.; Lü, Z.; Padrón-Navarta, J.A.; Xia, B.; Bader, T. UHP Metamorphism Documented in Ti-Chondrodite- and Ti-Clinohumite-Bearing Serpentinized Ultramafic Rocks from Chinese Southwestern Tianshan. J. Petrol. 2015, 56, 1425–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.A.; Lippard, S.J.; Roberts, S. Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Supra-Subduction Zone Ophiolites. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1984, 16, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulick, H.; Bach, W.; Godard, M.; De Hoog, J.C.M.; Suhr, G.; Harvey, J. Geochemistry of Abyssal Peridotites (Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 15°20′N, ODP Leg 209): Implications for Fluid/Rock Interaction in Slow Spreading Environments. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, D.; Bretscher, A.; John, T.; Scambelluri, M.; Pettke, T. Fluid-Mobile Elements in Serpentinites: Constraints on Serpentinisation Environments and Element Cycling in Subduction Zones. Chem. Geol. 2017, 466, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.S.; McDonough, W.F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 1989, 42, 313–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossley, R.J.; Evans, K.A.; Reddy, S.M.; Lester, G.W. Redistribution of Iron and Titanium in High-Pressure Ultramafic Rocks. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2017, 18, 3869–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Gao, J.; Raschke, M.B. Zircon Alteration as a Proxy for Rare Earth Element Mineralization Processes in Carbonatite-Nordmarkite Complexes of the Mianning-Dechang Rare Earth Element Belt, China. Econ. Geol. 2019, 114, 719–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lankvelt, A.; Schneider, D.A.; Biczok, J.; McFarlane, C.R.M.; Hattori, K. Decoding Zircon Geochronology of Igneous and Alteration Events Based on Chemical and Microstructural Features: A Study from the Western Superior Province, Canada. J. Petrol. 2016, 57, 1309–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).