Comparative Study of Colloidal and Rheological Behaviors of Mixed Palygorskite–Montmorillonite Clays in Freshwater and Seawater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Clay Dispersions
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
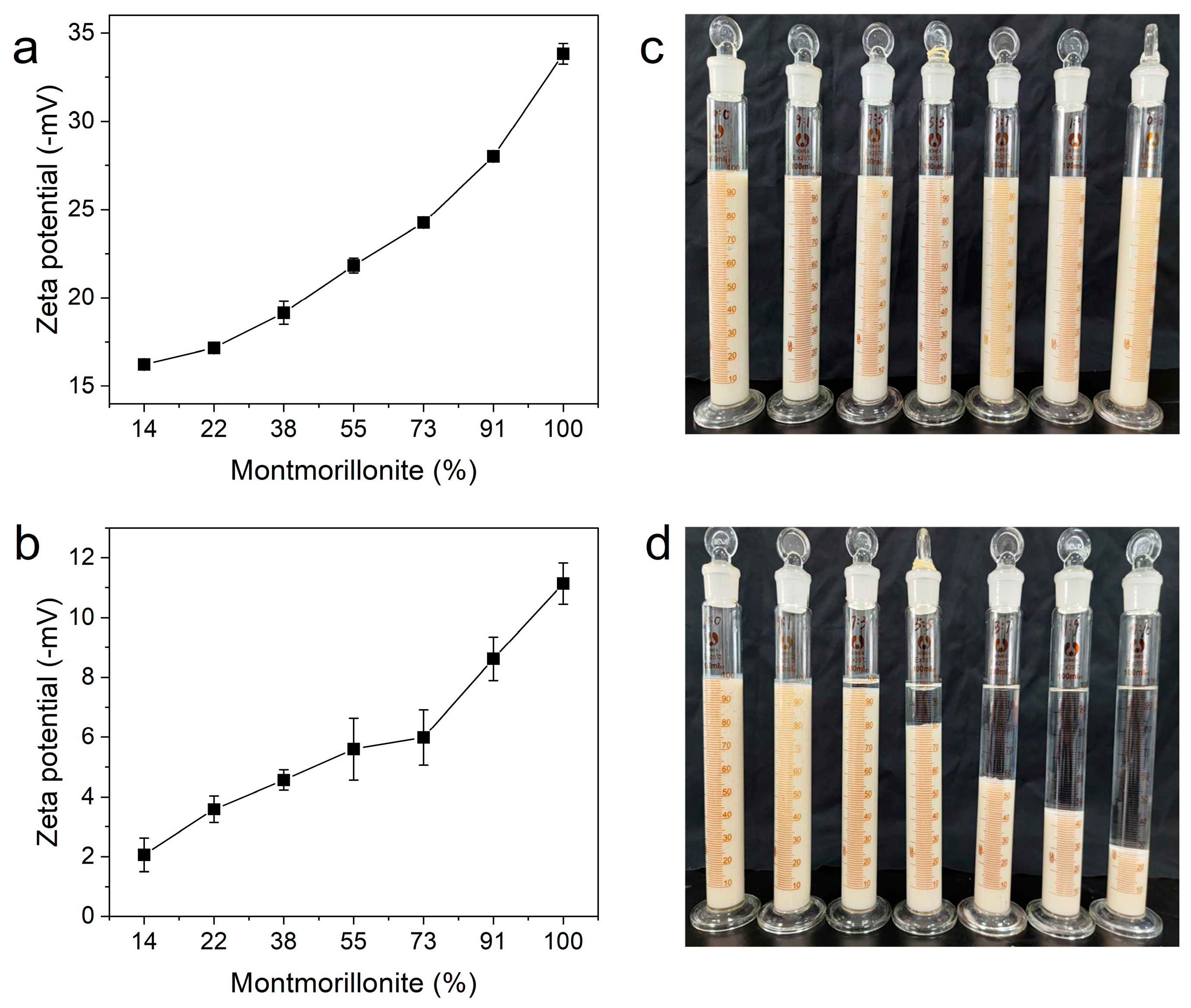
3.1. Colloidal Properties
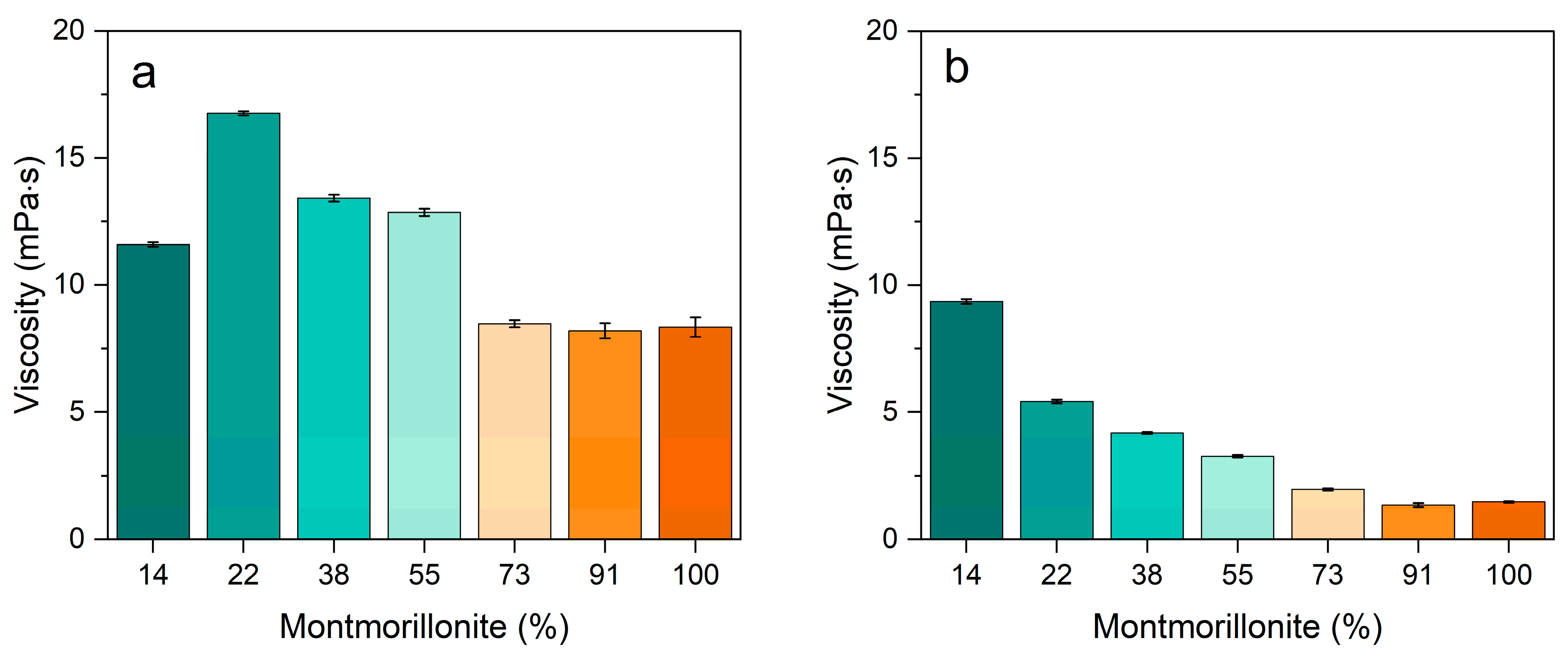
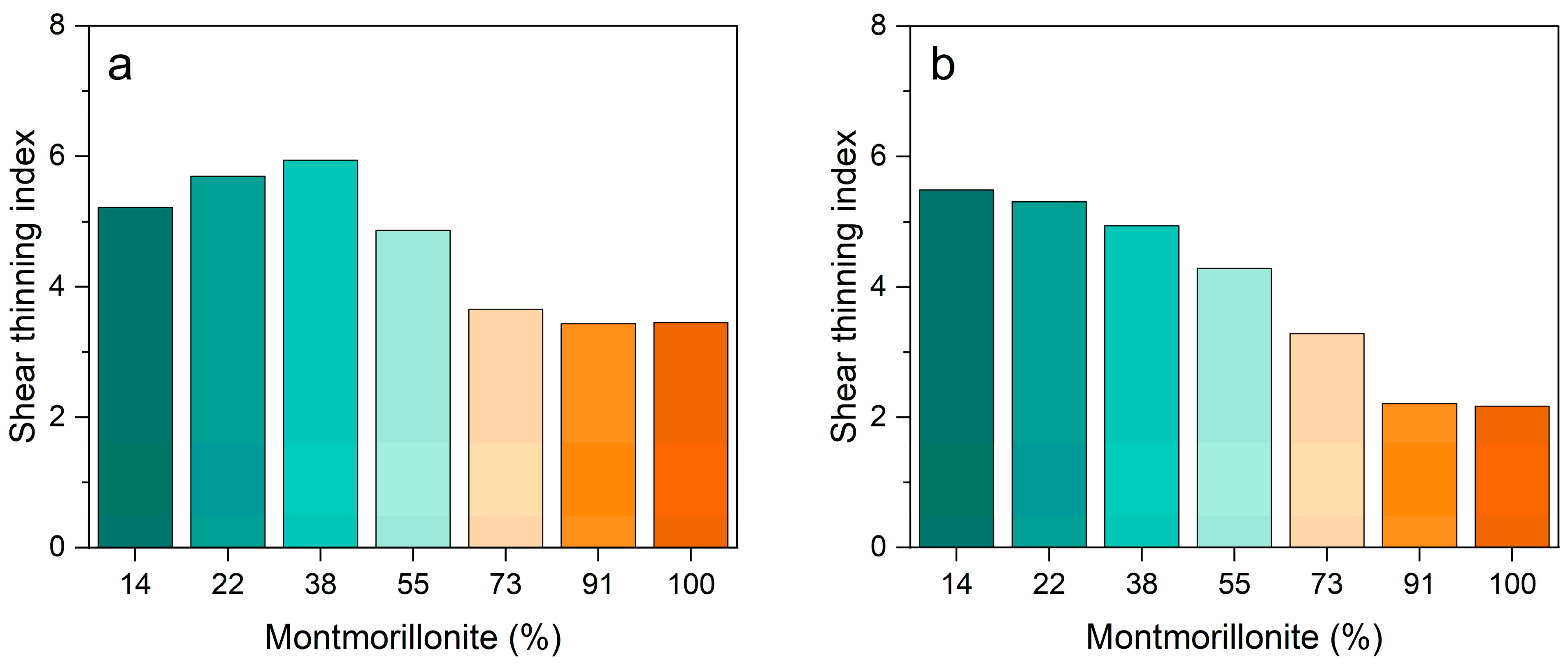
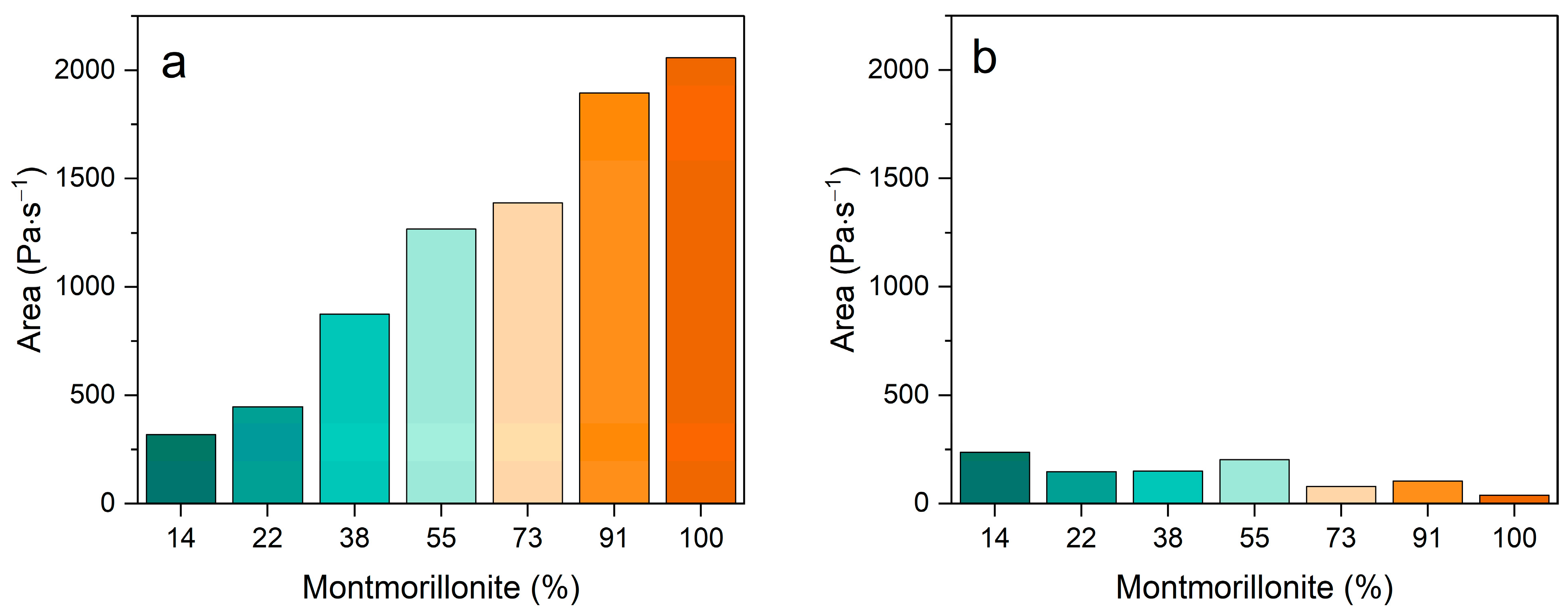
3.2. Rheological Behavior
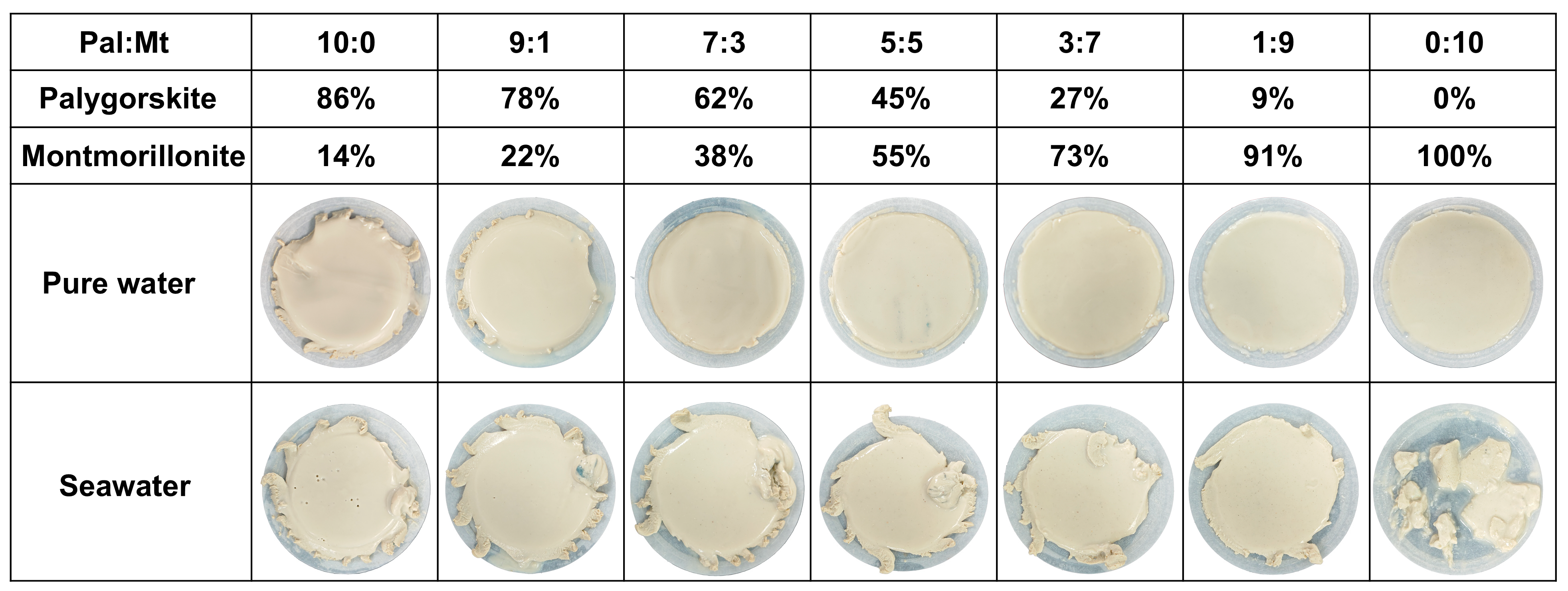
3.3. Filtration Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, H.H. Traditional and new applications for kaolin, smectite, and palygorskite: A general overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 17, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G. Chapter 1—General Introduction: Clays, Clay Minerals, and Clay Science. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri, M.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Casula, L.; Barbosa, R.d.M.; Sandri, G.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Viseras, C. Clay-Based Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Vehicles of Curcumin Nanocrystals for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Casula, L.; Sandri, G.; Perioli, L.; Cardia, M.C.; Lai, F.; Viseras, C. Bentonite- and Palygorskite-Based Gels for Topical Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caenn, R.; Darley, H.C.H.; Gray, G.R. (Eds.) Chapter 1—Introduction to Drilling Fluids. In Composition and Properties of Drilling and Completion Fluids, 7th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.R.; Xu, M.D.; Christidis, G.E.; Zhou, C.H. Clay minerals in drilling fluids: Functions and challenges. Clay Miner. 2020, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Bergaya, F.; Yuan, P. Chapter 2—Application of bentonite in water-based drilling fluids. In Clay Science in Drilling and Drilling Fluids; Zhuang, G., Yuan, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 21–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Bergaya, F.; Yuan, P. Chapter 3—Application of fibrous clay minerals in water-based drilling fluids. In Clay Science in Drilling and Drilling Fluids; Zhuang, G., Yuan, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 55–82. [Google Scholar]
- Caenn, R.; Darley, H.C.H.; Gray, G.R. (Eds.) Chapter 4—Clay Mineralogy and the Colloid Chemistry of Drilling Fluids. In Composition and Properties of Drilling and Completion Fluids, 7th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 93–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, G.; Li, Q.; Bergaya, F.; Yuan, P. Chapter 1—The significance of clay minerals in drilling and drilling fluids. In Clay Science in Drilling and Drilling Fluids; Zhuang, G., Yuan, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhuang, G.; Yuan, P.; Bergaya, F. Chapter 12—Future challenges related to clay minerals in drilling and drilling fluids. In Clay Science in Drilling and Drilling Fluids; Zhuang, G., Yuan, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Galán, E.; Theng, B.K.G. Chapter 2—Structure and Mineralogy of Clay Minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Bergaya, F., Lagaly, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 21–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bergaya, F.; Vayer, M. CEC of clays: Measurement by adsorption of a copper ethylenediamine complex. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, A.K. The Limited Swelling of Montmorillonite. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1998, 207, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-H, G.; Duplay, J.; Martinez, L.; Geraud, Y.; Rousset-Tournier, B. Influence of interlayer cations on the water sorption and swelling–shrinkage of MX80 bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2003, 23, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devineau, K.; Bihannic, I.; Michot, L.; Villiéras, F.; Masrouri, F.; Cuisinier, O.; Fragneto, G.; Michau, N. In situ neutron diffraction analysis of the influence of geometric confinement on crystalline swelling of montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhou, A.; Shen, S.-L.; Lin, X.; Bu, Y.; Kodikara, J. Revealing crucial effects of temperature and salinization on swelling behavior of montmorillonite. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132263. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Deshun, Y.; Zhai, R. Rheological behavior of bentonite-water suspension at various temperatures: Effect of solution salinity. Eng. Geol. 2021, 295, 106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paineau, E.; Bihannic, I.; Baravian, C.; Philippe, A.-M.; Davidson, P.; Levitz, P.; Funari, S.S.; Rochas, C.; Michot, L.J. Aqueous Suspensions of Natural Swelling Clay Minerals. 1. Structure and Electrostatic Interactions. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5562–5573. [Google Scholar]
- Paineau, E.; Michot, L.J.; Bihannic, I.; Baravian, C. Aqueous Suspensions of Natural Swelling Clay Minerals. 2. Rheological Characterization. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7806–7819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, J. Rheology of bentonite dispersions: Role of ionic strength and solid content. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 214, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Adachi, Y. Effects of electrolyte concentration and pH on the sedimentation rate of coagulated suspension of sodium montmorillonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Leong, Y.-K.; Chen, T.; Au, P.-I.; Liu, X.; Qiu, Z. Surface chemistry and rheological properties of API bentonite drilling fluid: pH effect, yield stress, zeta potential and ageing behaviour. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 561–569. [Google Scholar]
- Montoro, M.A.; Francisca, F.M. Effect of ion type and concentration on rheological properties of natural sodium bentonite dispersions at low shear rates. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 178, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenheim, S.; Krekeler, M.P.S. Chapter 1—The Structures and Microtextures of the Palygorskite–Sepiolite Group Minerals. In Developments in Clay Science; Galàn, E., Singer, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Galan, E. Properties and applications of palygorskite-sepiolite clays. Clay Miner. 1996, 31, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garciá-Romero, E.; Suárez, M. On the Chemical Composition of Sepiolite and Palygorskite. Clays Clay Miner. 2010, 58, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, A.; Santarén, J.; Esteban-Cubillo, A.; Aparicio, P. Chapter 12—Current Industrial Applications of Palygorskite and Sepiolite. In Developments in Clay Science; Galàn, E., Singer, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Neaman, A.; Singer, A. Rheological properties of aqueous suspensions of palygorskite. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaman, A.; Singer, A. The effects of palygorskite on chemical and physico-chemical properties of soils: A review. Geoderma 2004, 123, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanna, V.C.; Silva, S.L.; Silva, R.P.; Castro Dantas, T.N. Use of palygorskite as a viscosity enhancer in salted water-based muds: Effect of concentration of palygorskite and salt. Clay Miner. 2020, 55, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santanna, V.C.; Araújo, G.C.N.; Andrade da Silva, M.T.; Castro Dantas, T.N.d.; Pimentel, P.M. Water-based drilling fluid with palygorskite: Cutting carrying and contaminants. Clay Miner. 2023, 58, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choupani, M.A.; Tabatabaee Moradi, S.S.; Tabatabaei Nejad, S.A. Study on Attapulgite as Drilling Fluid Clay Additive in Persian Gulf Seawater. Int. J. Eng. 2022, 35, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q.; Fan, W.; Li, Q. Application of Nanofibrous Clay Minerals in Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Principles, Methods, and Challenges. Minerals 2024, 14, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, C.A.M.; da Luz, A.B.; Baltar, L.M.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Bezerra, F.J. Influence of morphology and surface charge on the suitability of palygorskite as drilling fluid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 42, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckham, P.F.; Rossi, S. The colloidal and rheological properties of bentonite suspensions. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1999, 82, 43–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abend, S.; Lagaly, G. Sol–gel transitions of sodium montmorillonite dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 16, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaly, G.; Ziesmer, S. Colloid chemistry of clay minerals: The coagulation of montmorillonite dispersions. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Colloidal behavior of aqueous montmorillonite suspensions: The specific role of pH in the presence of indifferent electrolytes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neaman, A.; Singer, A. Rheology of mixed palygorskite-montmorillonite suspensions. Clays Clay Miner. 2000, 48, 713–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemeda, Y.C.; Christidis, G.E.; Khan, N.M.T.; Koutsopoulou, E.; Hatzistamou, V.; Kelessidis, V.C. Rheological properties of palygorskite–bentonite and sepiolite–bentonite mixed clay suspensions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 90, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, F. Effects of pH on the gel properties of montmorillonite, palygorskite and montmorillonite-palygorskite composite clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1141-98; Standard Practice for Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Liu, T.L.; Jiang, G.S.; Zhang, P.; Sun, J.X.; Sun, H.C.; Wang, R.; Zheng, M.M. A new low-cost drilling fluid for drilling in natural gas hydrate-bearing sediments. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, M. Mechanism and method for controlling low-temperature rheology of water-based drilling fluids in deepwater drilling. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 154, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhou, F.; Wei, Z. Gel Stability of Calcium Bentonite Suspension in Brine and Its Application in Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels 2022, 8, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulani, M.; Michael, D.; Nugrahanti, A.; Rosyidan, C.; Samura, L.; Satiyawira, B.; Prima, A. Optimizing the impact of rheological properties on bentonite pre-hydrated based drilling mud through the utilization of pre-hydration. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1339, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API. SPEC 13A: Drilling Fluids Materials, 19th ed.; American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, G.; Gao, J.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Z. Synergistically using layered and fibrous organoclays to enhance the rheological properties of oil-based drilling fluids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 172, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, S.; Gao, J.; Jaber, M. Enhancing the rheological properties and thermal stability of oil-based drilling fluids by synergetic use of organo-montmorillonite and organo-sepiolite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, H.; Tang, J. Structures and rheological properties of organo-sepiolite in oil-based drilling fluids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 154, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.S.; Sansom, K.G. The rheological properties of dispersions of Laponite, a synthetic hectorite-like clay, in electrolyte solutions. Clay Miner. 1971, 9, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, E.; Alves, L.; Sanguino, P.; Santarén, J.; Rasteiro, M.G.; Gamelas, J.A.F. Stabilization of Palygorskite Aqueous Suspensions Using Bio-Based and Synthetic Polyelectrolytes. Polymers 2021, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middea, A.; Fernandes, T.L.A.P.; Neumann, R.; Gomes, O.d.F.M.; Spinelli, L.S. Evaluation of Fe(III) adsorption onto palygorskite surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, A. Electrokinetic and Colloidal Properties of Homogenized and Unhomogenized Palygorskite in the Presence of Electrolytes. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, F.; Xue, B.; Sun, M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X. Wet grinding of montmorillonite and its effect on the properties of mesoporous montmorillonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 356, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, O.; Tunç, S. Electrokinetic and rheological properties of Na-bentonite in some electrolyte solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şans, B.E.; Güven, O.; Esenli, F.; Çelik, M.S. Contribution of cations and layer charges in the smectite structure on zeta potential of Ca-bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Du, M.; Au, P.I.; Clode, P.; Liu, J. Microstructure of Sodium Montmorillonite Gels with Long Aging Time Scale. Langmuir 2018, 34, 9673–9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, P.; Wong, J.-E.; Clode, P.L.; Liu, J.; Leong, Y.-K. Colloidal forces, microstructure and thixotropy of sodium montmorillonite (SWy-2) gels: Roles of electrostatic and van der Waals forces. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 195, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.-K.; Liu, P.; Au, P.-I.; Clode, P.; Liu, J. Microstructure and Time-Dependent Behavior of STx-1b Calcium Montmorillonite Suspensions. Clays Clay Miner. 2021, 69, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.-K.; Liu, P.; Clode, P.; Liu, J. Ageing behaviour spanning months of NaMt, hectorite and Laponite gels: Surface forces and microstructure—A comprehensive analysis. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil’Ko, S.L.; Titov, E.V. Flow Peculiarities of the Aqueous Suspensions of Palygorskite and Bentonite Clays. Colloid. J. 2002, 64, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Liao, L. The structure and rheology of organo-montmorillonite in oil-based system aged under different temperatures. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 124, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liao, L. Rheological properties of organo-palygorskite in oil-based drilling fluids aged at different temperatures. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 137, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haden, W. Attapulgite: Properties and Uses. Clays Clay Miner. 1961, 10, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caenn, R.; Darley, H.C.H.; Gray, G.R. (Eds.) Chapter 7—The Filtration Properties of Drilling Fluids. In Composition and Properties of Drilling and Completion Fluids, 7th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 245–283. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Preparation and Rheological Properties of Attapulgite Gel for Aqueous Suspensions. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016), Shenyang, China, 29–31 December 2016; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 547–559. [Google Scholar]
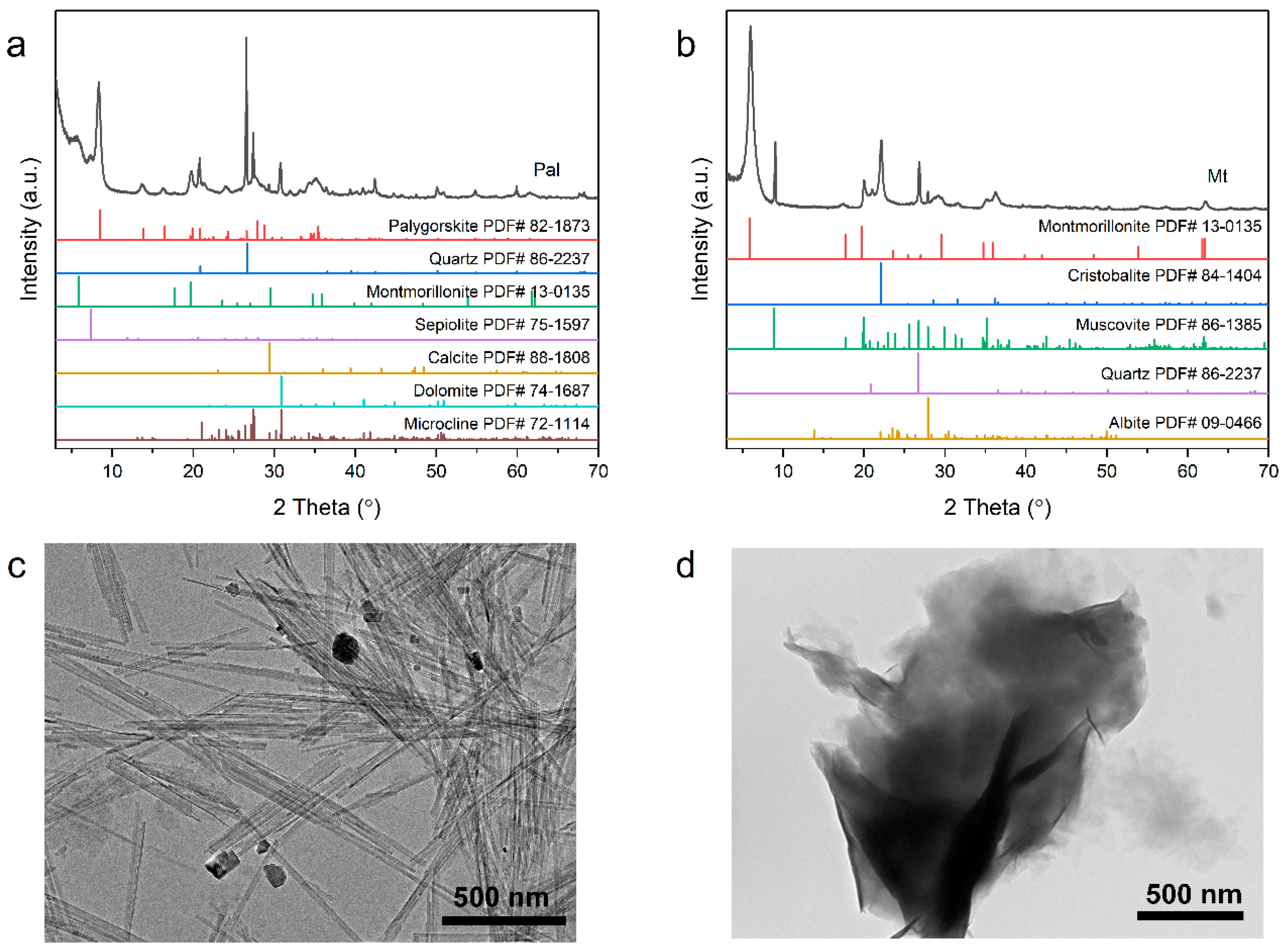


| Composition | Palygorskite | Montmorillonite | Microcline | Quartz | Dolomite | Sepiolite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass % | 75.3 | 12.5 | 5.5 | 3.3 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Composition | Montmorillonite | Muscovite | Cristobalite | Quartz | Albite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass % | 80.8 | 11.9 | 4.7 | 2.3 | 0.3 |
| Pal:Mt (mass) | 10:0 | 9:1 | 7:3 | 5:5 | 3:7 | 1:9 | 0:10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palygorskite | 86% | 78% | 62% | 45% | 27% | 9% | 0% |
| Montmorillonite | 14% | 22% | 38% | 55% | 73% | 91% | 100% |
| Pal:Mt | Palygorskite | Montmorillonite | Fluid Loss (mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Water | Seawater | |||
| 10:0 | 86% | 14% | 134 | 138 |
| 9:1 | 78% | 22% | 91 | 143 |
| 7:3 | 62% | 38% | 47 | 149 |
| 5:5 | 45% | 55% | 34 | 153 |
| 3:7 | 27% | 73% | 21 | 153 |
| 1:9 | 9% | 91% | 21 | 150 |
| 0:10 | 0% | 100% | 19 | 148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhuang, G.; Chen, J.; Fan, W.; Fan, J.; Kuang, Z.; Liu, D. Comparative Study of Colloidal and Rheological Behaviors of Mixed Palygorskite–Montmorillonite Clays in Freshwater and Seawater. Minerals 2025, 15, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030251
Zhang J, Zhuang G, Chen J, Fan W, Fan J, Kuang Z, Liu D. Comparative Study of Colloidal and Rheological Behaviors of Mixed Palygorskite–Montmorillonite Clays in Freshwater and Seawater. Minerals. 2025; 15(3):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030251
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiajun, Guanzheng Zhuang, Jinrong Chen, Wenxiao Fan, Jixing Fan, Zhuhua Kuang, and Dong Liu. 2025. "Comparative Study of Colloidal and Rheological Behaviors of Mixed Palygorskite–Montmorillonite Clays in Freshwater and Seawater" Minerals 15, no. 3: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030251
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhuang, G., Chen, J., Fan, W., Fan, J., Kuang, Z., & Liu, D. (2025). Comparative Study of Colloidal and Rheological Behaviors of Mixed Palygorskite–Montmorillonite Clays in Freshwater and Seawater. Minerals, 15(3), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/min15030251









