Silica Colloid Ordering in a Dynamic Sedimentary Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Material
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Opal Mineralogy
3.2. Colloid Flow Structures in Fractures
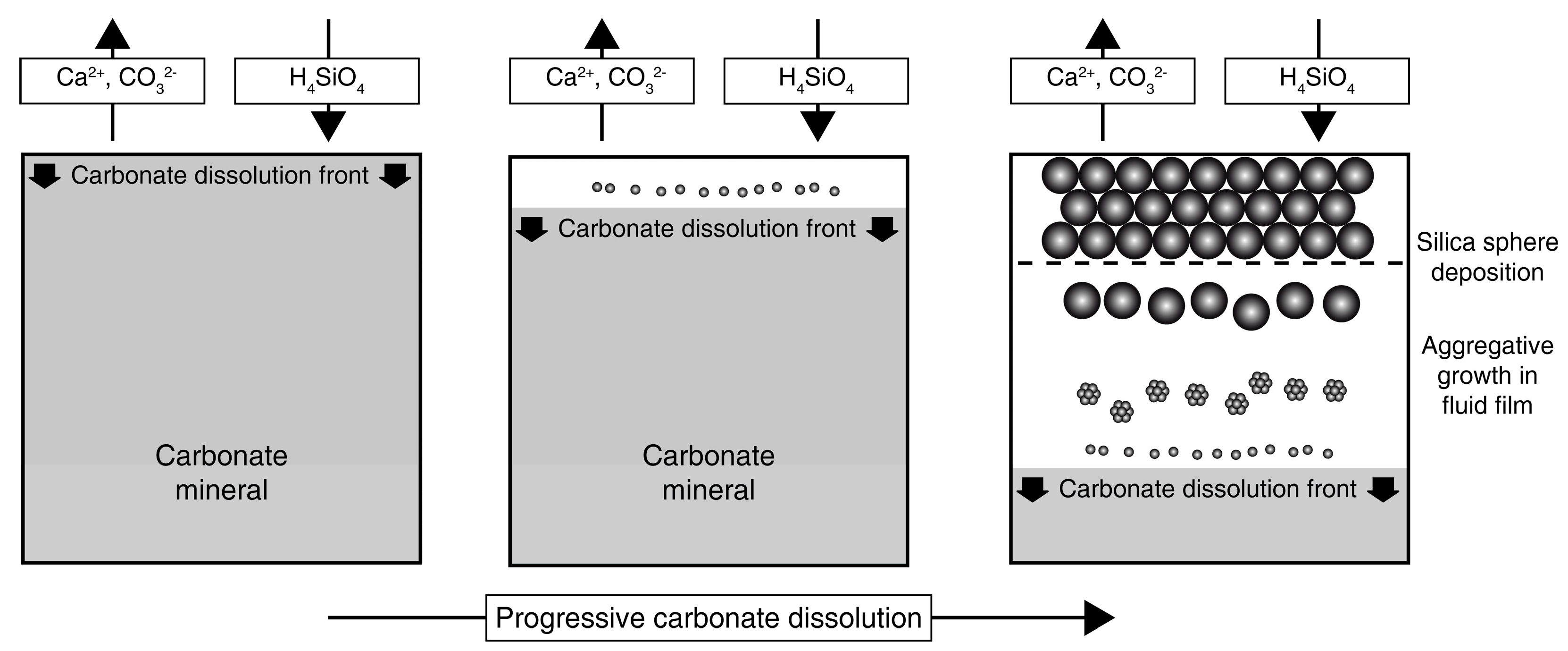
3.3. Carbonate Replacement Structures
3.4. Polyhedral Particle Shapes and Crystal Bending
4. Discussion
4.1. Flow-Induced Ordering
4.2. Mineral Replacement
4.3. Post-Depositional Lattice Deformation
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rey, P.F. Opalisation of the Great Artesian Basin (central Australia): An Australian story with a Martian twist. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 60, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, M.; Milnes, A.R.; Rayot, V.; Simon-Coinçon, S. Interpretation of palaeoweathering features and successive silicifications in the Tertiary regolith of Inland Australia. J. Geol. Soc. 2006, 163, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.A.; Crerar, D.A. Silica diagenesis, II, General mechanisms. J. Sediment. Res. 1985, 55, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darragh, P.; Gaskin, A.; Terrell, B.; Sanders, J. Origin of precious opal. Nature 1966, 209, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillou, E.; Fritsch, E.; Aguilar-Reyes, B.; Rondeau, B.; Post, J.; Barreau, A.; Ostroumov, M. Common gem opal: An investigation of micro- to nano-structure. Am. Mineral. 2008, 93, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesegang, M.; Milke, R. Australian sedimentary opal-A and its associated minerals: Implications for natural silica sphere formation. Am. Mineral. 2014, 99, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesegang, M.; Milke, R.; Kranz, C.; Neusser, G. Silica nanoparticle aggregation in calcite replacement reactions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flörke, O.W.; Graetsch, H.; Röller, K.; Martin, B.; Wirth, R. Nomenclature of micro-and non-crystalline silica minerals, based on structure and microstructure. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie Abhandlungen 1991, 163, 19–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, J.V. Colour of precious opal. Nature 1964, 204, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewkliang, B.; Pring, A.; Brugger, J. The formation of precious opal: Clues from the opalisation of bone. Can. Mineral. 2008, 46, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecover, S.R. Australian Opal Resources: Outback Spectral Fire. Rocks Miner. 2007, 82, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, L.C.; Townsend, I.J.; Robertson, R.S.; Scott, D.C. Opal: South Australia’s Gemstone (Handbook No. 5); Department of Mines and Energy, Geological Survey of South Australia: Parkside, Australia, 1992; pp. 19–26, 37–51. ISBN 978-0730817093. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B.; Segnit, E.R. The nature of opal I. Nomenclature and constituent phases. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1971, 18, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, P. Structural studies of silicate glasses and melts-applications and limitations of Raman spectroscopy. Am. Mineral. 1984, 69, 622–644. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig, C.M.; Rahn, L.A. Bound hydroxyl in vitreous silica. J. Chem. Phys. 1977, 67, 4260–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, A.G.; Thomas, P.S.; Ray, A.S. Characterisation of sedimentary opals by Fourier transform Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A 1997, 53, 2341–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.G.; Simpson, E.L.; Eriksson, K.A.; Bumby, A.J.; Steyn, G.L.; Sarkar, S. Muddy roll-up structures in siliciclastic interdune beds of the c. 1.8 Ga Waterberg Group, South Africa. Palaios 2000, 15, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.G.; Olliver, J.G.; Conor, C.H.H.; Scott, D.C. Andamooka Opal Fields: The Geology of the Precious Stones Field and the Results of the Subsidised Mining Program; Report of Investigations 51; Department of Mines and Energy, Geological Survey of South Australia: Adelaide, Australia, 1979; pp. 17–18. ISBN 0724354980.
- Dickinson, E. Structure and rheology of colloidal particle gels: Insight from computer simulation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 199, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iler, R.K. The Chemistry of Silica: Solubility, Polymerization, Colloid and Surface Properties, and Biochemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 222–239. ISBN 978-0471024040. [Google Scholar]
- Carcouët, C.C.M.C.; van de Put, M.W.P.; Mezari, B.; Magusin, P.C.M.M.; Laven, J.; Bomans, P.H.H.; Friedrich, H.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; van Benthem, R.A.T.M.; et al. Nucleation and growth of monodisperse silica nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixinho, J.; Nouar, C.; Desaubry, C.; Théron, B. Laminar transitional and turbulent flow of yield stress fluid in a pipe. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 2005, 128, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Long, Y.; Zhong, K.; Song, K.; Yang, G.; Tung, C.H. Modifying the symmetry of colloidal photonic crystals: A way towards complete photonic bandgap. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4100–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Shen, T.Z.; Song, J.K. Flow-induced alignment of disk-like graphene oxide particles in isotropic and biphasic colloids. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2015, 610, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Derks, D.; van Blaaderen, A.; Imhof, A. Melting and crystallization of colloidal hard-sphere suspensions under shear. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10564–10569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermant, J.; Solomon, M.J. Flow-induced structure in colloidal suspensions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R187–R216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurfield, G.; Segnit, E. Petrifaction of wood by silica minerals. Sediment. Geol. 1984, 39, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins, S.; Trebotich, D.; Yang, L.; Ajo-Franklin, J.B.; Ligocki, T.J.; Shen, C.; Steefel, C.I. Pore-scale controls on calcite dissolution rates from flow-through laboratory and numerical experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7453–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putnis, A.; Putnis, C.V. The mechanism of reequilibration of solids in the presence of a fluid phase. J. Solid State Chem. 2007, 180, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.H.; Chen, Z.M.; Zhang, K.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, W.Z.; Yang, B. Nonspherical colloidal crystals fabricated by the thermal pressing of colloidal crystal chips. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8987–8991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhof, A.; van Blaaderen, A.; Dhont, J.K.G. Shear melting of colloidal crystals of charged spheres studied with rheology and polarizing microscopy. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monovoukas, Y.; Gast, A.P. A study of colloidal crystal morphology and orientation via polarizing microscopy. Langmuir 1991, 7, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Oxide | Andamooka | Mintabie | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vein Opal | Twinned Crystal 1 | Rhombs 1 | Inverse Opal | Cement | Transparent | White Roll-Ups | |
| SiO2 | 90.60 | 92.63 | 87.90 | 84.45 | 90.25 | 90.72 | 89.98 |
| TiO2 | 0.05 | 0.06 | <LLD | <LLD | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Al2O3 | 0.93 | 1.23 | 1.40 | 1.42 | 1.17 | 1.13 | 1.18 |
| Fe2O3-total | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| MgO | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| CaO | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| SrO | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| BaO | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| Na2O | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.18 |
| K2O | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.32 |
| SUM Total | 92.08 | 94.79 | 90.01 | 86.50 | 92.21 | 92.65 | 92.07 |
| SUM impurities | 2.19 | 2.16 | 2.11 | 2.06 | 1.96 | 1.93 | 2.08 |
| (H2O + OH) 2 | 10.73 | 5.21 | 9.99 | 13.50 | 7.79 | 7.35 | 7.93 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liesegang, M.; Milke, R. Silica Colloid Ordering in a Dynamic Sedimentary Environment. Minerals 2018, 8, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8010012
Liesegang M, Milke R. Silica Colloid Ordering in a Dynamic Sedimentary Environment. Minerals. 2018; 8(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiesegang, Moritz, and Ralf Milke. 2018. "Silica Colloid Ordering in a Dynamic Sedimentary Environment" Minerals 8, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8010012
APA StyleLiesegang, M., & Milke, R. (2018). Silica Colloid Ordering in a Dynamic Sedimentary Environment. Minerals, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8010012





