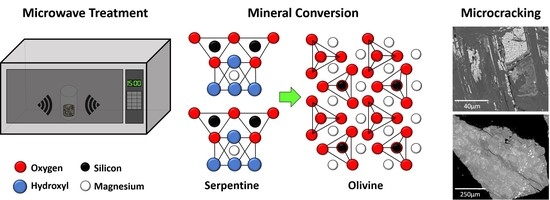
Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feedstock
2.2. Microwave Heating
2.3. Grinding
2.4. Materials Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microwave Heating
3.2. Mineralogy
3.2.1. XRD
3.2.2. FTIR
3.2.3. SEM
3.3. Grindability
3.3.1. Product Size and Relative Work Index
3.3.2. Size-By-Size Analysis
3.3.3. Hardness Measurements
3.3.4. Crack Analysis
3.3.5. Pentlandite Liberation and Specific Surface Area
3.3.6. Energy Considerations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.; Xi, L.; Bobicki, E.R.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Probing anisotropic surface properties and interaction forces of chrysotile rods by atomic force microscopy and rheology. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10809–10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, A.M.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Understanding interaction mechanisms between pentlandite and gangue minerals by zeta potential and surface force measurements. Miner. Eng. 2014, 69, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Dai, Z.; Dong, J.; Ford, F.; Lee, A. Fibrous minerals in ultramafic nickel sulphide ores. In Proceedings of the 49th Conference of Metallurgists, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 October 2010; CIM: Westmount, QC, Canada, 2010; pp. 223–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ndlovu, B.N.; Forbes, E.; Becker, M.; Deglon, D.A.; Franzidis, J.P.; Laskowski, J.S. The effects of chrysotile mineralogical properties on the rheology of chrysotile suspensions. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Effect of microwave pre-treatment on ultramafic nickel ore slurry rheology. Miner. Eng. 2014, 61, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, G.D.; Thomas, S.A. Development and implementation of a new flowsheet for the flotation of a low-grade nickel ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2005, 78, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Mineral carbon storage in pre-treated ultramafic nickel ores. Miner. Eng. 2014, 70, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, C. AMicrowaves in extractive metallurgy: Part 1—Review of Fundamentals. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, K.E. Microwave energy for mineral treatment processes—A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1999, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, C.A. Microwaves in extractive metallurgy: Part 2—A review of applications. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziszewski, P. Energy recovery potential in comminution processes. Miner. Eng. 2013, 46–47, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amankwah, R.K.; Ofori-Sarpong, G. Microwave heating of gold ores for enhanced grindability and cyanide amenability. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingman, S.W.; Jackson, K.; Cumbane, A.; Bradshaw, S.M.; Rowson, N.A.; Greenwood, R. Recent developments in microwave-assisted comminution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkiewicz, J.W.; Clark, A.E.; McGill, S.L. Microwave-assisted grinding. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henda, R.; Hermas, A.; Gedye, R.; Islam, M.R. Microwave enhanced recovery of nickel-copper ore: Comminution and flotability aspects. Int. Microw. Power Inst. 2005, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttress, A.J.; Katrib, J.; Jones, D.A.; Batchelor, A.R.; Craig, D.A.; Royal, T.A.; Dodds, C.; Kingman, S.W. Towards large scale microwave treatment of ores: Part 1—Basis of design, construction and commissioning. Miner. Eng. 2017, 109, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Xu, C.; Lyu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Chi, R. Enhancing mineral liberation of a Canadian rare earth ore with microwave pretreatment. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingman, S.W.; Vorster, W.; Rowson, N.A. The influence of mineralogy on microwave assisted grinding. Miner. Eng. 2000, 13, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, J.; Maham, Y.; Bobicki, E.R. Microwave heating of magnesium silicate minerals. Powder Technol. 2018, 339, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Hua, Y. Application of microwave radiation to extractive metallurgy. Chin. J. Metall. Sci. Technol. 1990, 6, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Balucan, R.D. Dehydroxylation of serpentine minerals: Implications for mineral carbonation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 31, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, T.F.; Bruce, R.W. A simple method of determining the grindability or ores. Can. Min. J. 1966, 7, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheon, R.M.; De Jong, M.S.; Adams, F.P. A system for rapid measurement of RF and microwave properties up to 1400 °C. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 1992, 27, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robie, R.A.; Hemingway, B.S. Thermodynamic Properties of Minerals and Related Substances at 298.15K and 1 Bar Pressure and at Higher Temperatures; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Volume 2131, p. 470.
- Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Microwave heating of ultramafic nickel ores and mineralogical effects. Miner. Eng. 2014, 58, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, Y.; Linares, J.; Mellini, M. Mӧssbauer and infrared spectrometry of lizardite-1T from Monte Fico, Elba. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1998, 26, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresti, E.; Fornero, E.; Lesci, I.G.; Rinaudo, C.; Zuccheri, T.; Roveri, N. Asbestos health hazrd: A spectroscopic study of synthetic geoinspried F-doped chrysotile. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1070–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellini, M.; Fuchs, Y.; Viti, C.; Lemaire, C.; Linarés, J. Insights into the antigorite structure from Mӧssbauer and FTIR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Miner. 2002, 14, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, G.; Sivakumar, G.; Prabakaran, A.R.; Gunasekaran, S. Spectroscopic characterization of natural chrysotile. Vib. Spectrosc. 2010, 52, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Q.; Hu, H.; Yin, Z. Characterization of lizardite in Yuanjiang laterite ore. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 47, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialips, C.; Petit, S.; Decarreau, A.; Beaufort, D. Influence of synthesis pH on kaolinite “crystallinity” and surface properties. Clays Clay Miner. 2000, 48, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtzová, E.; Tunega, D.; Nagy, L.T. Theoretical study of cation substitution in trioctahedral sheet of phyllosilicates. An effect on inner OH group. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem) 2003, 620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Ramírez-Valle, V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, J.L. Spectroscopic study of the dehydroxylation process of a sonicated antigorite. Eur. J. Mineral. 2006, 18, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.D.J.; Longstaffe, F.J.; King, P.L.; Larson, T.E. The oxygen-isotope composition of chondrules and isolated forsterite and olivine grains from the Tagish Lake carbonaceous chondrite. Geochem. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 2484–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makreski, P.; Jovanovski, G.; Stojančeska, S. Minerals from Macedonia XIII: Vibration spectra of some commonly appearing nesosilicate minerals. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–547, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L.; Palmer, S.J.; Reddy, B.J. Near-infrared and mid-IR spectroscopy of selected humite minerals. Vib. Spectrosc. 2007, 44, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alstadt, K.N.; Katti, D.R.; Katti, K.S. An in situ FTIR step-scan photoacoustic investigation of kerogen and minerals in oil shale. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 89, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, V.C. The Infrared Spectra of Minerals; Mineralogical Society: London, UK, 1974; p. 539. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, A.J.; Hermann, J.; O’Neill, H.S.C.; Foran, G.J. Fingerprinting the water site in mantle olivine. Geology 2005, 33, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trittschack, R.; Grobety, B. Dehydroxylation kinetics of lizardite. Eur. J. Mineral. 2012, 24, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etschmann, B.; Pring, A.; Putnis, A.; Grguric, B.A.; Studer, A. A kinetic study of the exsolution of pentlandite (Ni,Fe)9S8 from the monosulfide solid solution (Fe,Ni)S. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Isothermal kinetics of the pentlandite exsolution from mss/pyrrhotite using model-free method. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2006, 11, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kullerud, G. Thermal stability of pentlandite. Can. Mineral. 1963, 7, 353–366. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, V. Fe-Ni-S (Iron-Nickel-Sulfur). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2004, 25, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaki, A.; Kitakaze, A. High form pentlandite and its thermal stability. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitakaze, A.; Sugaki, A.; Itoh, H.; Komatsu, R. A revision of phase relations in the system Fe-Ni-S from 650 °C to 450 °C. Can. Mineral. 2011, 49, 1687–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E. Comminution behaviour of microwave heated two sulphide copper ores. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2010, 17, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Manchak, N.; Xu, M. Effect of microwave pre-treatment on grindability of ultramafic nickel ores. In Proceedings of the 2013 Materials Science and Technology (MS&T), Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- RRUFF. Handbook of Mineralogy (PDF). 2012. Available online: http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/hom/ (accessed on 9 January 2018).
- Jones, D.A.; Kingman, S.W.; Whittles, D.N.; Lowndes, I.S. Understanding microwave assisted breakage. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| MgO | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe | Ni | S | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | XRF | XRF | XRF | XRF | ICP | ICP | CHNS |
| OK Ore (wt %) | 45.8 | 0.8 | 40.7 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 0.26 | 0.66 |
| Pipe Ore (wt %) | 39.5 | 1.1 | 34.8 | 1.8 | 6.0 | 0.23 | 2.18 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobicki, E.R.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z. Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects. Minerals 2018, 8, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110524
Bobicki ER, Liu Q, Xu Z. Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects. Minerals. 2018; 8(11):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110524
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobicki, Erin R., Qingxia Liu, and Zhenghe Xu. 2018. "Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects" Minerals 8, no. 11: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110524
APA StyleBobicki, E. R., Liu, Q., & Xu, Z. (2018). Microwave Treatment of Ultramafic Nickel Ores: Heating Behavior, Mineralogy, and Comminution Effects. Minerals, 8(11), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110524