Origins and Geochemistry of Dolomites and Their Dissolution in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Western Sichuan Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Petrography
4.1.1. Dolomicrite
4.1.2. Fabric-Retentive Dolomite
4.1.3. Fabric-Destructive Dolomite
4.2. Pore Types
4.3. Cathodoluminescence (CL) Analysis
4.4. Geochemistry
4.4.1. δ13C and δ18O Isotopes
4.4.2. Strontium Isotopes
4.4.3. Major Elements
Calcium and Magnesium
4.4.4. Trace Elements
Strontium
Sodium
Iron and Manganese
5. Discussion
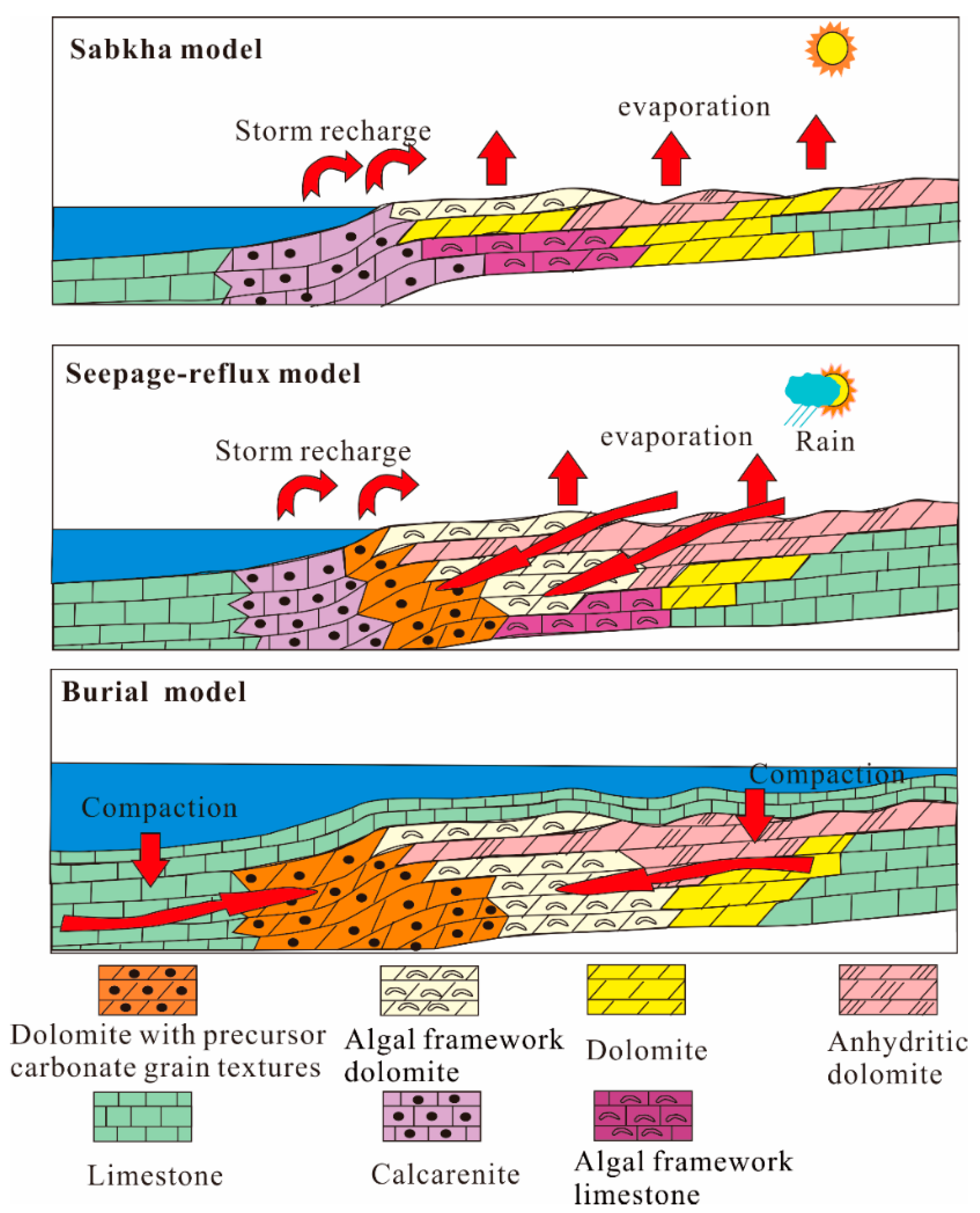
5.1. Dolomitization Models
5.1.1. Sabkha Model
5.1.2. Seepage-Reflux Model
5.1.3. Burial Model
5.2. Dissolution Models
5.2.1. Contemporaneous Dissolution
5.2.2. Burial Dissolution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, B.F.; Bai, G.P.; Wang, Y.F. More attention recommended for global deep reservoirs. Oil Gas J. 2013, 111, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.S.; Cai, X.Y.; Zhao, P.R. The research status and advances in porosity evolution and diagenesis of deep carbonate reservoir. Earth Sci. Front. 2011, 18, 181–192, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhang, S.C.; Wang, H.J. Analysis on forming conditions of deep marine reservoirs and their concentration belts in superimposed basins in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.H. Carbonate Reservoirs: Porosity, Evolution and Diagenesis in a Sequence Stratigraphic Framework; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, F.J. Carbonate Reservoir Characterization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Springer, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, M.E.; Wright, V.P. Carbonate Sedimentology; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Scholle, P.A.; Ulmer-Scholle, D.S. A color guide to the petrography of carbonate rocks: Grains, textures, porosity, diagenesis. AAPG Mem. 2003, 77, 1–486. [Google Scholar]
- Aqrawi, A.M.; Keramati, M.; Ehrenberg, S.N.; Pickard, N.; Moallemi, A.; Svånå, T.; Darke, G.; Dickson, J.A.D.; Oxtoby, N.H. The origin of dolomite in the Asmari Formation (Oligocene-lower Miocene), Dezful Embayment, SW Iran. J. Pet. Geol. 2006, 29, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purser, B.; Tucker, M.; Zenger, D. Dolomites: A Volume in Honour of Dolomieu; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Heydari, E.; Moore, C.H. Burial diagensis and thermochemical sulfate reduction, Smackover Formation, southeastern Mississippi salt basin. Geology 1989, 17, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Gong, Y.C.; Huang, K.K.; Tong, H.P. The influence of burial history on Carbonate Dissolution and Precipitation—A case study from Feixianguan Formation of Triassic, NE Sichuan and Ordovician Carbonate of Northern Tarim Basin. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 25, 381–390, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Machel, H.G. Bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction in diagenetic settings-old and new insights. Sediment. Geol. 2001, 140, 143–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, H.; Jafarian, A.; Husinec, A.; Koeshidayatullah, A.; Swennen, R. Microfacies, depositional environment and diagenetic evolution controls on the reservoir quality of the Permian Upper Dalan Formation, Kish Gas Field, Zagros Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, S.N.; Eberli, G.P.; Keramati, M.; Moallemi, S.A. Porosity-permeability relationships in interlayered limestone-dolostone reservoirs. AAPG Bull. 2006, 90, 91–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Hu, X.Y.; Shi, Y.Q.; Xiao, K.H.; Jia, Y.W.; Wei, X.P.; Feng, Q. Sequence division and controlling factors of reservoir development of the 4th Member of Leikoupo Formation in foreland of Longmen Mountains in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2017, 38, 753–763, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.B.; Xu, G.M.; Song, X.B. Forming conditions of Pengzhou large gas field of Leikoupo Formation in Longmenshan piedmont tectonic belt, western Sichuan Basin. China Pet. Explor. 2016, 3, 74–82, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.X.; Li, H.T.; Long, S.X.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, C.L.; Zhang, J.T. A study on characteristics and diagenesis of carbonate reservoirs in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in western Sichuan Depression. Oil Gas Geol. 2011, 32, 542–550, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W. Geochemical characteristics and origin of natural gas reservoir the natural gas reservoir in the 4th Member of the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2017, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Zeng, D.; Feng, M. The three different types of paleokarstification and reservoir distribution of Leikoupo Formation, Middle Triassic in the Northern Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tan, X.; Cao, J.; Zou, C.; Ding, X.; Yang, G.; Ying, D. Origins of evaporites in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation of the Sichuan Basin, southwest China and their geological implications. Carbonates Evaporites 2014, 29, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savard, M.M.; Veizer, J.; Hinton, R. Cathodoluminescene at low Fe and Mn concentrations: A SIMS study of zones in natural calcites. J. Sediment. Res. 1995, 65, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machel, H.G. Concepts and models of dolomitization: A critical reappraisal. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2004, 235, 7–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanez, I.P.; Read, J.F. Fluid-rock interaction history during stabilization of early dolomites, Upper Knox Group (Lower Ordovician), US Appalachians. J. Sediment. Res. 1992, 62, 753–778. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shazly, S.H. Stable isotope of some selected Egyptian pectinids and their paleoenvironmental implications. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2011, 59, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.L.; Weber, J.N. Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1964, 28, 1787–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Yang, L. Carbon and oxygen isotope relations and its significance. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 2009, 73, A1407. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, P.; Smith, D.G.W. The isotopic composition of secondary dolomite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1970, 34, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, J.A.D.; Coleman, M.L. Changes in carbon and oxygen isotope composition during limestone diagenesis. Sedimentology 1980, 27, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Xinfeng, N.I.; Huang, L. Characteristics, origin and distribution of dolomite reservoirs in lower-middle cambrian, tarim basin, NW China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhong, D.; Gao, C.; Sun, H.; Peng, H.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, C. Origin of dolomite of the lower Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation, eastern Sichuan Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Mazzullo, S.J. Dolomitization of lower permian platform facies, Wichita Formation, north platform, Midland basin, Texas. Carbonates Evaporites 1993, 8, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J. Dolomite: Occurrence, evolution and economically important associations. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2000, 52, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.A.; Burns, S.J. Occurrence and formation of dolomite in organic rich continental margin sediments. AAPG Bull. 1985, 9, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, H.; Mountjoy, E.W. Multistage dolomitization in rainbow buildups, middle devonian keg river formation, Alberta, Canada. J. Sediment. Res. 1989, 59, 114–126. [Google Scholar]
- Modarres, M.H.; Adabi, M.H.; Fayazi, F.; Ghobishavi, A.; Moradpour, M. Petrography and geochemical composition of the middle Eocene, the Shahabazan Formation at Kialu Section, Zagros Basin, Southwestern Iran. Carbonates Evaporites 2018, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veizer, J.; Lemieux, J.; Jones, B.; Gibling, M.R.; Savelle, J. Paleosalinity and dolomitization of a lower paleozoic carbonate sequen. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1978, 15, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.R.; Wiggins, W.D. Dolomite reservoirs: Geochemical techniques for evaluating origin and distribution. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1993, 14, 262–263. [Google Scholar]
- Budd, D.A. Cenozoic dolomites of carbonate islands: Their attributes and origin. Earth-Sci. Rev. 1997, 42, 1–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, S.; Zou, N.; Sun, G.; Zhang, S. The origin and formation model of Permian dolostones on the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmy, K.; Veizer, J.; Misi, A.; Oliveira, T.F.D.; Sanches, A.L.; Dardenne, M.A. Dolomitization and isotope stratigraphy of the Vazante Formation, Sao Francisco Basin, Brazil. Precambr. Res. 2001, 112, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.Y.; Yong, I.L. Origin and modification of early dolomites in cyclic shallow platform carbonates, Yeongheung Formation (middle Ordovician), Korea. Sediment. Geol. 1998, 118, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Alsharhan, A.S.; Whittle, G.L. Sedimentary-diagenetic interpretation and reservoir characteristics of the Middle Jurassic (Araej Formation) in the southern Arabian Gulf. Mar. Pet. Geol. 1995, 12, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour-Bonab, H.; Esrafili-Dizaji, B.; Tavakoli, V. Dolomitization and anhydrite precipitation in Permo-Triassic carbonates at the south pars gas field, offshore Iran: Controls on reservoir quality. J. Pet. Geol. 2010, 33, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Huang, K.K.; Lu, J.; Lan, Y.F. The relationship between dolomite textures and their formation temperature: A case study from the Permian Triassic of the Sichuan Basin and the lower Paleozoic of the Tarim Basin. Pet. Sci. 2014, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.H.; Chowdhury, A. Upper Jurassic Smackover Platform Dolomitization, Northwestern Gulf of Mexico: A Tale of Two Waters. In Sedimentology and Geochemistry of Dolostones; Shukla, V., Baker, P.A., Eds.; Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists (SEMP): Tulsa, OK, USA, 1988; pp. 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Jiao, Y.; Rong, H.; Li, R.; Wang, R. Origins and Geochemistry of Oolitic Dolomite of the Feixianguan Formation from the Yudongzi Outcrop, Northwest Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2017, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.S.; Abd-Ellatif, M.T. Dolomitization of the Miocene carbonates in Gebel Abu Shaar El Qiblie and Salum area, Egypt: A petrographical and geochemical comparative study. Carbonates Evaporites 2013, 28, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong-Altrin, J.S.; Verma, S.P.; Lee, Y.I.; Worden, R.H. Carbon, oxygen, and strontium isotope geochemistry of carbonate rocks of the upper Miocene Kudankulam Formation, southern India: Implications for paleoenvironment and diagenesis. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2009, 69, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Adabi, M.H.; Aghanabati, A.; Majidifard, M.R.; Jamali, A.M. Dolomitization Mechanism Based on Petrography and Geochemistry in the Shotori Formation (Middle Triassic), Central Iran. Open J. Geol. 2016, 6, 1149–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Luo, P.; Chen, G.; Cao, H.; Zhang, B. Origin and reservoir rock characteristics of dolostones in the early triassic Feixianguan formation, NE Sichuan basin, China: Significance for future gas exploration. J. Pet. Geol. 2010, 28, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, F.I.; Abdullah, F.A.; Gharib, I.M. Petrography, diagenesis and isotope geochemistry of dolostones and dolocretes in the Eocene Dammam Formation, Kuwait, Arabian Gulf. Carbonates Evaporites 2017, 1–3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Well | Depth (m) | Lithology | MgO% | CaO% | Sr (μg/g) | Na (μg/g) | Fe (μg/g) | Mn (μg/g) | δ13C PDB | δ18O PDB | Sr isotope Ratio | Salinity Index Z | Paleo Temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 87Sr/86Sr | 2σ(±) | |||||||||||||
| Ys1 | 6238.9 | Dolomicrite | 19.7 | 29.1 | 3968.9 | 1060.0 | 190.0 | 11.9 | 2.64 | −1.70 | 0.707680 | 0.000010 | 131.9 | 41.8 |
| Ys1 | 6243.4 | Dolomicrite | 19.0 | 29.2 | 1122.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 | 10.5 | 2.48 | −1.67 | 0.707778 | 0.000014 | 131.5 | 41.6 |
| Yas1 | 5779.4 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.8 | 30.8 | 108.7 | 900.0 | 560.0 | 28.6 | - | - | 0.708605 | 0.000011 | - | - |
| Yas1 | 6220.0 | Algal framework dolomite | 20.4 | 29.9 | 107.7 | 870.0 | 170.0 | 24.3 | 2.52 | −2.96 | 0.708104 | 0.000013 | 131.0 | 49.8 |
| Yas1 | 5793.9 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.4 | 30.4 | 106.6 | 900.0 | 300.0 | 25.7 | 5.62 | −3.77 | 0.708067 | 0.000010 | 136.9 | 55.2 |
| Ys1 | 6213.8 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.4 | 30.1 | 87.3 | 1050.0 | 170.0 | 21.5 | 2.77 | −2.85 | 0.707998 | 0.000012 | 131.6 | 49.1 |
| Yas1 | 5775.8 | Algal framework dolomite | 20.7 | 30.1 | 83.3 | 840.0 | 130.0 | 25.0 | 2.58 | −4.13 | 0.708094 | 0.000012 | 130.5 | 57.7 |
| Yas1 | 5787.8 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.2 | 29.4 | 95.5 | 870.0 | 310.0 | 25.9 | 1.95 | −5.64 | 0.708053 | 0.000013 | 128.5 | 68.6 |
| Ys1 | 6196.3 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.0 | 31.1 | 107.3 | 790.0 | 120.0 | 23.0 | 6.10 | −3.55 | 0.708033 | 0.000014 | 138.0 | 53.7 |
| Yas1 | 5759.0 | Algal framework dolomite | 19.6 | 29.5 | 92.5 | 850.0 | 480.0 | 25.9 | - | - | 0.707694 | 0.000010 | - | - |
| Yas1 | 5770.5 | Algal framework dolomite | 23.0 | 32.4 | 126.2 | 810.0 | 540.0 | 23.6 | - | - | 0.708154 | 0.000011 | - | - |
| Ys1 | 6197.9 | Algal framework dolomite | 21.9 | 30.9 | 91.7 | 910.0 | 100.0 | 20.9 | - | - | 0.707912 | 0.000011 | - | - |
| Ys1 | 6205.7 | Dolomite with precursor carbonate grain textures | 21.1 | 29.9 | 103.1 | 930.0 | 80.0 | 27.2 | 2.14 | −6.10 | 0.707969 | 0.000012 | 128.6 | 72.1 |
| Yas1 | 5762.4 | Dolomite with precursor carbonate grain textures | 21.3 | 30.9 | 91.1 | 830.0 | 160.0 | 25.6 | 2.97 | −4.97 | 0.707994 | 0.000010 | 130.9 | 63.7 |
| Yas1 | 5791.7 | Dolomite with precursor carbonate grain textures | 21.9 | 31.8 | 97.8 | 880.0 | 230.0 | 25.0 | 5.73 | −4.95 | 0.708246 | 0.000011 | 136.6 | 63.5 |
| Ys1 | 6216.2 | Dolomite with precursor carbonate grain textures | 20.6 | 28.3 | 119.1 | 810.0 | 220.0 | 26.9 | 2.83 | −2.50 | 0.708050 | 0.000012 | 131.9 | 46.8 |
| Yas1 | 5788.8 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 22.7 | 30.4 | 65.2 | 800.0 | 280.0 | 25.2 | - | - | 0.708049 | 0.000013 | - | - |
| Yas1 | 5722.1 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 22.1 | 30.9 | 74.2 | 800.0 | 170.0 | 31.7 | - | - | 0.708103 | 0.000012 | - | - |
| Yas1 | 5774.4 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 21.1 | 30.3 | 65.4 | 770.0 | 300.0 | 29.8 | 2.36 | −7.01 | 0.707909 | 0.000009 | 128.6 | 79.2 |
| Yas1 | 5781.0 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 21.6 | 30.9 | 91.5 | 780.0 | 410.0 | 27.3 | 2.60 | −6.62 | 0.707965 | 0.000013 | 129.3 | 76.1 |
| Ys1 | 6183.9 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 21.1 | 32.3 | 78.8 | 810.0 | 230.0 | 25.4 | - | - | 0.708039 | 0.000011 | - | - |
| Yas1 | 5782.3 | Fabric-destructive dolomite | 21.2 | 29.5 | 59.6 | 840.0 | 280.0 | 25.3 | 2.63 | −6.75 | 0.707669 | 0.000012 | 129.3 | 77.1 |
| Ys1 | 5735.0 | Pore-filling calcite | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.50 | −8.54 | - | - | 91.7 | |
| Ys1 | 5735.0 | Pore-filling calcite | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.31 | −7.92 | - | - | 86.5 | |
| Ys1 | 5769.7 | Pore-filling calcite | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.11 | −8.11 | - | - | 88.1 | |
| Ys1 | 6199.8 | Pore-filling calcite | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.13 | −7.25 | - | - | 81.1 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Lv, Z.; Wen, Y.; Liu, S. Origins and Geochemistry of Dolomites and Their Dissolution in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Western Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals 2018, 8, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070289
Zhang S, Lv Z, Wen Y, Liu S. Origins and Geochemistry of Dolomites and Their Dissolution in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Western Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals. 2018; 8(7):289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070289
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shunli, Zhengxiang Lv, Yi Wen, and Sibing Liu. 2018. "Origins and Geochemistry of Dolomites and Their Dissolution in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Western Sichuan Basin, China" Minerals 8, no. 7: 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070289
APA StyleZhang, S., Lv, Z., Wen, Y., & Liu, S. (2018). Origins and Geochemistry of Dolomites and Their Dissolution in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation, Western Sichuan Basin, China. Minerals, 8(7), 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8070289




