Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Analysis and Characterization Methods
2.3. Adsorption Tests
3. Results
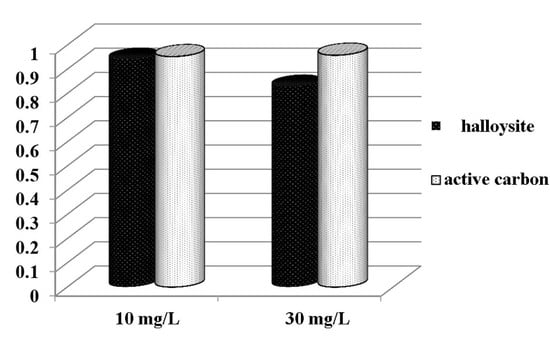
3.1. Adsorption Characteristics of HNTs Toward CIP
3.2. Adsorbent Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Stelten, J.; Silva, F.; Belin, D.; Silhavy, T.J. Effects of antibiotics and a proto-oncogene homolog on destruction of protein translocator secy. Science 2009, 325, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Shi, Y.; Dong, W.; Wen, X.; Jiang, M.; Lu, J. Thermo-activated persulfate oxidation system for tetracycline antibiotics in degradation aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the aquatic environment in China: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Wong, M.H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, I.; Bachmann, J.; Kuhnen, U.; Kuster, A.; Kussatz, C.; Maletzki, D.; Schluter, C. Toxicity of the fluoroquinolone antibiotics enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin to photoautotrophic aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, X.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Demeestere, K. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics: An emerging class of environmental micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 500–501, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ying, G.G.; Pan, C.G.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L. Comprehensive evaluation of antibiotics emission and fate in the river basins of China: Source analysis, multimedia modeling, and linkage to bacterial resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Meng, Y.; Yin, B.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, W. Efficient and stable Nb2O5 modified g-C3N4 photocatalyst for removal of antibiotic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Gao, G.; Yang, T.T.; Chen, X.; Chao, Y.; Na, G.; Ge, L.; Huang, L.N. Effects of fluoroquinolone antibiotics on reactor performance and microbial community structure of a membrane bioreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, S.; Kurniawan, T.A. Low-cost adsorbents for heavy metals uptake from contaminated water: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puanngam, M.; Unob, F. Preparation and use of chemically modified MCM-41 and silica gel as selective adsorbents for Hg (II) ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, D.M.; Noeline, B.F.; Anirudhan, T.S. Adsorption performance of Al-pillared bentonite clay for the removal of cobalt (II) from aqueous phase. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Leng, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Tian, W. Recent advances on surface modification of halloysite nanotubes for multifunctional applications. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Chiappisi, L.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Gradzielski, M.; Lazzara, G. A structural comparison of halloysite nanotubes of different origin by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and electric birefringence. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 160, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Möhwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for controlled release of protective agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Evtugyn, G.V.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Rozhina, V.E.; Fakhrullin, F.R. Halloysite nanotubes: Controlled access and release by smart gates. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Rong, R.; Gui, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, X. Halloysite nanotubes-induced al accumulation and fibrotic response in lung of mice after 30-day repeated oral administration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavitskaya, A.V.; Novikov, A.A.; Kotelev, M.S.; Kopitsyn, D.S.; Rozhina, E.V.; Ishmukhametov, I.R.; Fakhrullin, R.F.; Ivanov, E.V.; Lvov, Y.M.; Vinokurov, V.A. Fluorescence and cytotoxicity of cadmium sulfide quantum dots stabilized on clay nanotubes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F.; Evtugyn, V.; Rozhina, E.; Fakhrullin, R. Nanohydrogel formation within the halloysite lumen for triggered and sustained release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 8265–8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzara, G.; Cavallaro, G.; Panchal, A.; Fakhrullin, R.; Stavitskaya, A.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y. An assembly of organic-inorganic composites using halloysite clay nanotubes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yang, D.; Deng, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, R.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation, characterization and application of N-2-pyridylsuccinamic acid-functionalized halloysite nanotubes for solid-phase extraction of Pb(II). Water Res. 2013, 47, 3976–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslehyani, A.; Mobaraki, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T.; Hashemifard, S.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Mayahi, A.; Rezaei DashtArzhandi, M.; Soheilmoghaddam, M.; Shamsaei, E. Effect of HNTs modification in nanocomposite membrane enhancement for bacterial removal by cross-flow ultrafiltration system. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 95, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Abdullayev, E.; Lvov, Y.M.; Zeitoun, A.; Cingolani, R.; Rinaldi, R.; Leporatti, S. Cytocompatibility and uptake of halloysite clay nanotubes. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouquerol, J.; Llewellyn, P.; Rouquerol, F. Is the bet equation applicable to microporous adsorbents? Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Angar, Y.; Djelali, N.E.; Kebbouche-Gana, S. Investigation of ammonium adsorption on Algerian natural bentonite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11078–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltalı, K.; Sarı, A.; Aydın, M. Removal of ammonium ion from aqueous solution by natural Turkish (yıldızeli) zeolite for environmental quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 derived nanoporous carbon as an effective and recyclable adsorbent for removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calagui, M.J.C.; Senoro, D.B.; Kan, C.C.; Salvacion, J.W.L.; Futalan, C.M.; Wan, M.W. Adsorption of indium (III) ions from aqueous solution using chitosan-coated bentonite beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshameri, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Assabri, A.M.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Yan, C. The investigation into the ammonium removal performance of yemeni natural zeolite: Modification, ion exchange mechanism, and thermodynamics. Powder Technol. 2014, 258, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, N.; Khani, H.; Gupta, V.K.; Amereh, E.; Agarwal, S. Adsorption process of methyl orange dye onto mesoporous carbon material–kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Colloid Interfce Sci. 2011, 362, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Struvite crystallization combined adsorption of phosphate and ammonium from aqueous solutions by mesoporous MgO-loaded diatomite. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 506, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Yuan, S.; Xie, W.; Zhang, W.; Tong, M.; Wang, K. Adsorption of nitrogen-heterocyclic compounds on bamboo charcoal: Kinetics, thermodynamics, and microwave regeneration. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 390, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uğurlu, M.; Karaoğlu, M.H. Adsorption of ammonium from an aqueous solution by fly ash and sepiolite: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 139, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, T.; Nayaka, Y.A.; Viswanatha, R.; Basavanna, S.; Venkatesha, T.G. Kinetics and thermodynamics studies on the adsorption of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution using zinc oxide nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2012, 217, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Adebowale, K.O.; Olu-Owolabi, B.I.; Yang, L.Z.; Kong, L.X. Adsorption of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from aqueous solutions onto sodium tetraborate-modified kaolinite clay: Equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Hydrometallurgy 2008, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, U.; Anand, N.; Kumar, D. Synergistic effect of modified activated carbon and ionic liquid in the conversion of microcrystalline cellulose to 5-hydroxymethyl furfural. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olusegun, S.J.; de Sousa Lima, L.F.; Mohallem, N.D.S. Enhancement of adsorption capacity of clay through spray drying and surface modification process for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, J.; Ye, L.; Wu, J. Toughening epoxies with halloysite nanotubes. Polymer 2008, 49, 5119–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J. Study on the adsorption of neutral red from aqueous solution onto halloysite nanotubes. Water Res. 2009, 44, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.S.; Ferreira, F.J.L.; Silva, M.S.; Citó, A.M.G.L.; Meneguin, A.B.; Sábio, R.M.; Barud, H.S.; Bezerra, R.D.S.; Osajima, J.A.; Silva Filho, E.C. Potential of amino-functionalized cellulose as an alternative sorbent intended to remove anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, A.; Dai, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, P.; He, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, Y. Ultrahigh adsorption of typical antibiotics onto novel hierarchical porous carbons derived from renewable lignin via halloysite nanotubes-template and in-situ activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Jana, S. A tubular nanoreactor directing the formation of in situ iron oxide nanorods with superior photocatalytic activity. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Z.; Ouyang, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, D. Highly dispersed sepiolite-based organic modified nanofibers for enhanced adsorption of congo red. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 157, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z. Effects of microstructure of clay minerals, montmorillonite, kaolinite and halloysite, on their benzene adsorption behaviors. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, M.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Aw, Y.K.; Lee, S.M.; Milioto, S. Effect of morphology and size of halloysite nanotubes on functional pectin bionanocomposites for food packaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater Inter. 2017, 9, 17476–17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Parisi, F.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Colloidal Stability of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes. Ceram. Int. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Biopolymer-targeted adsorption onto halloysite nanotubes in aqueous media. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3317–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, G.; Lazzara, G.; Milioto, S.; Parisi, F. Hydrophobically modified halloysite nanotubes as reverse micelles for water-in-oil emulsion. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7472–7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, G.; Wiles, D.M. Programmed-life plastics from polyolefins: A new look at sustainability. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Kinetic Model | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1)/k2 (g/(mg·min)) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | Fitting Error | |
| Pseudo-first-order | 0.0462 | 0.1443 | 0.80626 | 0.00788 |
| Pseudo-second-order | 0.4342 | 1.0172 | 0.99955 | 0.00735 |
| Isotherm Model | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir model | qmax (mg/g) | k (L/mg) | R2 | fitting error |
| HNTs | 25.09 | 0.7425 | 0.96564 | 0.00431 |
| Freundlich model | kF (L/mg) | 1/n | R2 | fitting error |
| HNTs | 2.69 | 0.4927 | 0.74749 | 0.15675 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, R.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Du, C. Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin. Minerals 2018, 8, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8090387
Cheng R, Li H, Liu Z, Du C. Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin. Minerals. 2018; 8(9):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8090387
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Rongqing, Haipeng Li, Zhiliang Liu, and Chunfang Du. 2018. "Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin" Minerals 8, no. 9: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8090387
APA StyleCheng, R., Li, H., Liu, Z., & Du, C. (2018). Halloysite Nanotubes as an Effective and Recyclable Adsorbent for Removal of Low-Concentration Antibiotics Ciprofloxacin. Minerals, 8(9), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8090387