Review on Beneficiation Techniques and Reagents Used for Phosphate Ores
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Beneficiation Techniques for Phosphate Ores
2.1. Flotation
2.2. Attrition Scrubbing and Desliming
2.3. Electrostatic Separation
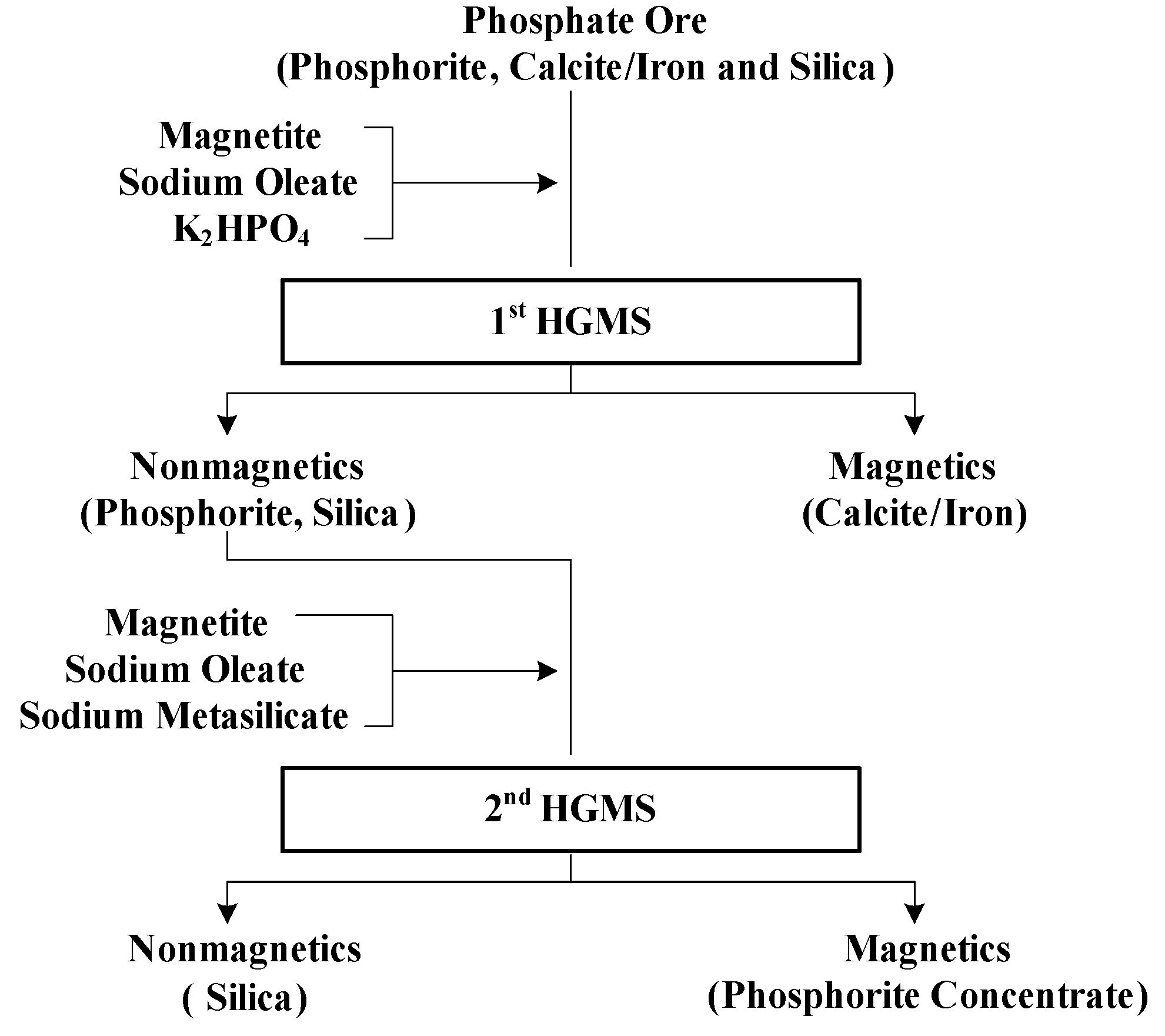
2.4. Magnetic Separation
2.5. Gravity Separation
2.6. Calcination
2.7. Acid Leaching
3. Factors Affecting the Flotation of Phosphate Ore
3.1. Mineralogical Properties
3.1.1. Mineral Type
3.1.2. Mineral Granularity
3.2. Properties of Flotation Reagents
3.2.1. Depressants
3.2.2. Collectors
3.3. Properties of Flotation Medium
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Geological Survey. Mineral Commodity Summaries; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; pp. 122–123.
- Abouzeid, A.-Z.M. Physical and thermal treatment of phosphate ores—An overview. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2008, 85, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sis, H.; Chander, S. Reagents used in the flotation of phosphate ores: A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.I.; Anwar, M.M.; Pritchard, D.W. Innovations in beneficiation technology for low grade phosphate rocks. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosys. 1996, 46, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, F.; Chi, R. Effects of metal ions on the flotation of apatite, dolomite and quartz. Minerals 2018, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yu, Y.; Bogan, M. Challenging the “Crago” double float process Ⅱ. Amine-fatty acid flotation of siliceous phosphates. Miner. Eng. 1997, 10, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzeid, A.-Z.M.; Negm, A.T.; Elgillani, D.A. Upgrading of calcareous phosphate ores by flotation: Effect of ore characteristics. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 90, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.D.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Selective Flotation of Phosphate Minerals with Hydroxamate Collectors. U.S. Patent 6341697, 29 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, F.; Chi, R. Ambient temperature flotation of sedimentary phosphate ore using cottonseed oil as a collector. Minerals 2017, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fariss, T.F.; Ozbelge, H.O.; Abdel Aleem, F.A.; Abdulrazik, S.M. Evaluation of Sandi phosphate rocks for wet process phosphoric acid production. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 1992, 4, 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.M. Discussion of scrubbing and desliming of phosphate ore in Dianchi area. Ind. Miner. Process. 1986, 6, 52–53. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Yang, W.; Li, R.; Yu, L. Study on flotation of scrubbed tailings from phosphate ore. Ind. Miner. Process. 2015, 11, 4–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gallala, W.; Herchi, F.; BenAli, I.; Abbassi, L.; Gaied, M.E.; Montacer, M. Beneficiation of phosphate solid coarse waste from Redayef (Gafsa Mining Basin) by grinding and flotation techniques. Procedia Eng. 2016, 138, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, A.; Tao, D. Innovative RTS technology for dry beneficiation of phosphate. Procedia Eng. 2014, 83, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Peng, H.; Fu, L.; Lu, Y. Application practice and evaluation of photoelectric separation in a phosphate mining industry. Non Met. Mines 2018, 41, 73–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.C.; Peres, A.E.C. Interfering ions in the flotation of a phosphate ore in a batch column. Miner. Eng. 1999, 12, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazy, P.; Jdid, E.A. Removal of ferriferous dolomite by magnetic separation from the Egyptian Abu Tartur phosphate ore. Int. J. Min. Process. 1997, 49, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzi, N.; Aïfa, T.; Merabet, D.; Pivan, J.-Y. Magnetic properties of the Bled El Hadba phosphate-bearing formation (Djebel Onk, Algeria): Consequences on the enrichment of the phosphate ore deposit. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2006, 50, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.M.H.; Dixit, S.G. Beneficiation of phosphate ores using high gradient magnetic separation. Int. J. Min. Process. 1993, 37, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y. Heavy-media separation industrial production practice of Yichang Huaguoshu Phosphorite. J. Wuhan Inst. Tech. 2011, 33, 48–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Teague, A.J.; Lollback, M.C. The beneficiation of ultrafine phosphate. Min. Eng. 2012, 27–28, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.I.; Anwar, M.M.; Pritchard, D.W. Optimization of thermal beneficiation of a low grade dolomitic phosphate rock. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1995, 43, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watti, A.; Alnjjar, M.; Hammal, A. Improving the specifications of Syrian raw phosphate by thermal treatment. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, A.K. The characteristics of phosphate rock for upgrading in a fluidized bed. Adv. Powder Technol. 2003, 14, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.I.; Ashraf, M. Selective leaching kinetics of calcareous phosphate rock in lactic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 131, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Z.I.; Anwar, M.M.; Pritchard, D.W. Selective leaching of calcareous phosphate rock in formic acid: Optimisation of operating conditions. Min. Eng. 2006, 19, 1459–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Zafar, I.Z.; Ansari, T.M. Selective leaching kinetics and upgrading of lowgrade calcareous phosphate rock in succinic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 80, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Eishah, S.I.; Muthaker, M.; Touqan, N. A new technique for the beneficiation of low grade carbonate-rich phosphate rocks by digestion with dilute acetic acid solutions: Pilot plant testing results. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharabaghi, M.; Noaparast, M.; Irannajad, M. Selective leaching kinetics of low-grade calcareous phosphate ore in acetic acid. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 95, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharabaghi, M.; Irannajad, M.; Noaparast, M. A review of the beneficiation of calcareous phosphate ores using organic acid leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 103, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.J.; Brandao, P.R.G. The influence of crystal chemistry properties on the floatability of apatites with sodium oleate. Miner. Eng. 1993, 6, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, R.C.; Duarte, C.R.; Ataide, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Flotation selectivity of phosphate ore: Effect of particle size and reagent concentration. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, R.C.; Farnese, A.C.C.; Fortes, M.C.B.; Ataide, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Influence of particle size and reagent dosage on the performance of apatite flotation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 64, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, J. Separation strategies for Jordanian phosphate rock with siliceous and calcareous gangues. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 97, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wakeela, M.I.; Lin, C.L.; Miller, J.D. Significance of liberation characteristics in the fatty acid flotation of Florida phosphate rock. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, W.; Heiskanen, K. Batch flotation tests by fatty acid on a phosphate-iron oxide-silicate regolith ore sample from Sokli, Finland. Miner. Eng. 1990, 3, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.P.; Baltar, C.A.M.; Gonzaga, R.S.G.; Peres, A.E.C.; Leite, J.Y.P. Identification of sodium silicate species used as flotation depressants. Min. Met. Process. 2012, 29, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.S.; Vijayakumar, T.V.; Angadi, S.; Prabhakar, S.; Raju, G.B. Effects of modulus and dosage of sodium silicate on limestone flotation. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2010, 4, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Sayilgan, A.; Arol, A.I. Effect of carbonate alkalinity on flotation behavior of quartz. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, S.; Brandao, P.R.G. Adsorption of starch, amylose, amylopectin and glucose monomer and their effect on the flotation of hematite and quartz. Min. Eng. 2003, 16, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.C.; Araujo, A.C.; Peres, A.E.C. Reagents in igneous phosphate ores flotation. Min. Eng. 2005, 18, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Smith, R.W. Dolomite depressants in the flotation of apatite and collophane from dolomite. Min. Eng. 1997, 10, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ge, Y.; Guo, X.; Guo, W. The depression effect and mechanism of NSFC on dolomite in the flotation of phosphate ore. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Arps, P.J.; Smith, R.W. Adhesion of two bacteria onto dolomite and apatite: Their effect on dolomite depression in anionic flotation. Int. J. Min. Process. 2001, 62, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaran, P.; Wang, D.Z. Solution Chemistry: Minerals and Reagents, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Elgillani, D.A.; Abouzeid, A.-Z.M. Flotation of carbonates from phosphate ores in acidic media. Int. J. Min. Process. 1993, 38, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Liu, R. Effect of sodium pyrophosphate on the reverse flotation of dolomite from apatite. Minerals 2018, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fariss, T.F.; Arafat, Y.; Abd El-Aleem, F.A.; El-Midany, A.A. Investigating sodium sulphate as a phosphate depressant in acidic media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 124, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mofty, S.E.; El-Midany, A.A. Role of calcium ions and their interaction with depressants in phosphate flotation. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 2641–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Snow, R. Evaluation of phosphate depressants in the phosphate/silica system. Miner. Metall. Process. 2009, 26, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, D.R.; Rothenberg, A.S.; Lipp, D.W.; Panzer, H.P. Low molecular weight polyacrylamide-based polymers as modifiers in phosphate beneficiation. Int. J. Min. Process. 1987, 20, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dho, H.; Iwasaki, I. Role of sodium silicate in phosphate flotation. Min. Metallurgy Explor. 1990, 7, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, P.R.; Lloyd, G.M.; Zhang, J.P.; Richardson, S.G.; Birky, B.K.; Stewart, K.J. An Investigation of Flotation Reagents; Florida Institute of Phosphate Research: Bartow, FL, USA; p. 2008.
- Nagaraj, D.R.; Rothenberg, A.S.; Lambert, A.S. Flotation Beneficiation Process for Non-Sulfide Minerals. U.S. Patent 4720339, 19 January 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.C.C.; Correia, J.C.G.; Monte, M.B.M.; Seidl, P.R.; Mothe, C.G.; Lima, C.A. Cashew gum: A new depressor for limestone in the phosphate minerals flotation. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.; Anazia, I. Fatty acid separation of siliceous carbonate phosphates. Miner. Metall. Process. 1990, 10, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, J.R.; Hsieh, S. Beneficiation of High Carbonate Phosphate Ores. U.S. Patent 4287053, 1 September 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, S.; Lehr, J.R. Method of Beneficiating High Carbonate Phosphate Ore. U.S. Patent 4486301, 4 December 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, D.V.; Narayanan, M.K.; Nayak, U.B.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.; Somasundaran, P. Flotation of calcareous Mussorie phosphate ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1985, 14, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, A.; Khalek, M.A.; Ammar, M. Cellulase as a new phosphate depressant in dolomite-phosphate flotation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Smani, S.M. Process for Enrichment by Flotation of Phosphate Ores with Gangues Containing Carbonates. U.S. Patent 4008151, 15 February 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadkhani, M.; Noaparast, M.; Shafaei, S.Z.; Amini, A.; Amini, E.; Abdollahi, H. Double reverse flotation of a very low grade sedimentary phosphate rock, rich in carbonate and silicate. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, P.R.P.; Monte, M.B.M.; Simao, R.A.; Gaspar, J.C. In situ AFM study of potassium oleate adsorption and calcium precipitate formation on an apatite surface. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.P.; Dutra, A.J.B.; Oliveira, J.F. The effect of jojoba oil on the surface properties of calcite and apatite aiming at their selective flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 143, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Pan, Z.; Ping, X. Synthesis and application of a flotation collector for collophanite. In Beneficiation of Phosphates: New Thought, New Technology, New Development; Zhang, P., Miller, J., El-Shall, H., Eds.; SME: Denver, CO, USA, 2012; pp. 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, M.S.; Santana, R.C.; Ataíde, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Recovery of apatite from flotation tailings. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, J. Selective separation of silica from a siliceous-calcareous phosphate rock. Min. Sci. Technol. (China) 2011, 21, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, H.; Rath, S.S.; Das, B.; Mishra, B.K. Flotation of quartz using ionic liquid collectors with different functional groups and varying chain lengths. Miner. Eng. 2016, 95, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.M.; Peres, A.E.C. The effect of amine type, pH, and size range in the flotation of quartz. Min. Eng. 2007, 20, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.P.L.; Pinto, C.L.L.; Valadao, G.E.S.; Viana, P.R.M. Floatability studies of wavellite and preliminary results on phosphorus removal from a Brazilian iron ore by froth flotation. Miner. Eng. 2012, 39, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Jiang, C.L.; Parekh, B.K. Enhanced flotation separation of phosphate and dolomite using a new amphoteric collector. Miner. Metall. Process. 1998, 15, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, M. Separation of dolomite from phosphate minerals by flotation with a new amphoteric surfactant as collector. Trans. Inst. Min. Met. C 2001, 110, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Elmahdy, A.M.; El-Midany, A.A.; Abdel-Khalek, N.A. Application of amphoteric collector for dolomite separation by statistically designed experiments. Trans. Inst. Min. Met. C 2007, 116, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, D. Flotation of apatite and calcite using α-amino aryl phosphoric acid as collector. Nonferrous Met. 1992, 44, 41–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, Z. Interactions of amphoteric amino phosphoric acids with calcium-containing minerals and selective flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2003, 72, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, I.V.; Filippov, L.O.; Duverger, A.; Severov, V.V. Synergetic effect of a mixture of anionic and nonionic reagents: Ca mineral contrast separation by flotation at neutral pH. Min. Eng. 2014, 66–68, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.H.; Forssberg, K.S.E. Mixed collector systems in flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 51, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Javadian, S.; Gharibi, H.; Bromand, Z.; Sohrabi, B. Electrolyte effect on mixed micelle and interfacial properties of binary mixtures of cationic and nonionic surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 318, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, K.; Janczuk, B. The adsorption at solution-air interface and volumetric properties of mixtures of cationic and nonionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2007, 293, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sis, H.; Chander, S. Adsorption and contact angle of single and binary mixtures of surfactants on apatite. Min. Eng. 2003, 16, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sis, H.; Chander, S. Improving froth characteristics and flotation recovery of phosphate ores with nonionic surfactants. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nguyen, A.V.; Miller, J.D. Selective attachment and spreading of hydroxamic acid–alcohol collector mixtures in phosphate flotation. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 78, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, L.O.; Duverger, A.; Filippova, I.V.; Kasaini, H.; Thiry, J. Selective flotation of silicates and Ca-bearing minerals: The role of non-ionic reagent on cationic flotation. Min. Eng. 2012, 36–38, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.H.; Dwari, R.K.; Lu, S.; Vilinska, A.; Somasundaran, P. Mixed anionic/non-ionic collector in phosphate gangue flotation from magnetite fines. Open Miner. Process. J. 2011, 4, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.V. Enhanced Flotation Reagents for Beneficiation of Phosphate Ores. U.S. Patent 5962828, 5 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Preller, G.S.; Schoeman, B.J.K. Flotation of Apatite. U.S. Patent 3405802, 15 October 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Huang, G.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Deng, Q.; Gu, X. Process study on some low grade collophanite with high content of magnesium. Non Met. Mines 2016, 39, 63–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hefner, R.E., Jr. N-Aminoethylpiperazine Condensates for Beneficiation of Phosphate Ore. U.S. Patent 4301004, 17 November 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, C. Method for Conditioning Phosphate Ores. U.S. Patent 4556545, 12 March 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Dorrepaal, W.; Haak, G.M. Process for the Flotation of Ores. U.S. Patent 4200522, 29 April 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Giesekke, E.W.; Harris, P.J. The role of polyoxyethylene alkyl ethers in apatite flotation at foskor, phalaborwa (South Africa). Min. Eng. 1994, 7, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, L.; Xie, B.; Ou, S. Effect of Ca2+, Mg2+, PO43− and SO42− on the flotation of phosphate. In Beneficiation of Phosphates: New Thought, New Technology, New Development; Zhang, P., Miller, J., El-Shall, H., Eds.; SME: Denver, CO, USA, 2012; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.A.; Santana, R.C.; Capponi, F.; Ataíde, C.H.; Barrozo, M.A.S. Effect of ionic species on the performance of apatite flotation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, B.; Grimm, D.; Pawlik, M. Anionic flotation of high-iron phosphate ores—Control of process water chemistry and depression of iron minerals by starch and guar gum. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2009, 92, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Beneficiation Techniques | Phosphate Rock Types | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Flotation | Siliceous phosphate rock Calcareous phosphate rock Calcareous-siliceous phosphate rock | Widely applied in the beneficiation of various phosphate rocks on a large scale, especially for refractory sedimentary phosphate ore |
| Attrition scrubbing-desliming | Weathered phosphate ores | Used for discarding clay minerals and eliminating the detrimental effect of slimes on the subsequent flotation process |
| Gravity separation | Sedimentary phosphate rock characterized by a strip texture | Discarding gangues to achieve the preconcentration of phosphate minerals |
| Magnetic separation | Phosphate ores containing magnetic gangues | |
| Calcination | Calcareous phosphate rock | Acceptable for areas that have low cost energy and limited water resources |
| Electrostatic separation | Coarse gained siliceous phosphate rock | Mostly are experimental studies in laboratory scale |
| Acid leaching | Calcareous phosphate rock |
| Mineral to Be Depressed | Name of Depressant | References |
|---|---|---|
| Silicate minerals | Sodium silicate | [36,52] |
| Sodium and calcium lignin sulfonates | [53] | |
| Copolymers or terpolymers derived from acrylamide units and N-acrylamidoglycolic acid units | [54] | |
| Carbonate minerals | Carboxymethyl cellulose, citric acid, naphtyl anthyl sulfonates | [42] |
| β-naphthyl sulfonate formaldehyde condensate | [43] | |
| Phosphate minerals | Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium pyrophosphate | [46,47] |
| Sodium tripolyphosphate, fluosilicic acid, diphosphonic acid, starch | [50] | |
| Cashew gum | [55] | |
| Sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid | [46,56] | |
| Alkyl phosphate acids, hydrofluoric acid | [57,58] | |
| Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate | [59] | |
| Cellulase enzyme | [60] | |
| Iron/aluminum sulfate, tartaric acid | [61,62] |
| Type of Mixed Collector | Primary Collector | Auxiliary Reagent | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anionic-anionic | Fatty acids | petroleum sulfonates and ethoxylated alcohol ether sulfates | [85] |
| Fatty acids | alkyl aryl sulphonate and sulphated fatty acid | [86] | |
| Oleic acid | Sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and oxidized paraffin soap | [87] | |
| Cationic-anionic | N-aminoethylpiperazine | Fatty acids | [88] |
| Cationic-nonionic | Primary amine (Cataflot) | Iso-tridecanol (PX4826) | [83] |
| Anionic-nonionic | Fatty acids | hydrocarbon oil such as kerosene or fuel oils | [89] |
| Fatty acids | Esters of orthophthalic acid or maleic acid | [90] | |
| Fatty acids | Alkylphenol ethoxylates | [81,91] | |
| hydroxamate (AERO 6493), di-2-(ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (D2EHPA) | Iso-tridecanol (PX4826) | [76] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruan, Y.; He, D.; Chi, R. Review on Beneficiation Techniques and Reagents Used for Phosphate Ores. Minerals 2019, 9, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9040253
Ruan Y, He D, Chi R. Review on Beneficiation Techniques and Reagents Used for Phosphate Ores. Minerals. 2019; 9(4):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9040253
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuan, Yaoyang, Dongsheng He, and Ruan Chi. 2019. "Review on Beneficiation Techniques and Reagents Used for Phosphate Ores" Minerals 9, no. 4: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9040253
APA StyleRuan, Y., He, D., & Chi, R. (2019). Review on Beneficiation Techniques and Reagents Used for Phosphate Ores. Minerals, 9(4), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9040253





