Abstract
Variations in clay mineral assemblages have been widely used to understand changes in sediment provenance during glacial and interglacial periods. Smectite clay minerals, however, have a range of various elemental compositions that possibly originated from multiple different sources. Therefore, it might be crucial to distinguish the various types of smectites by analyzing their elemental composition in order to verify the sediment provenances with certainty. This hypothesis was tested for the clay mineral characteristics in a marine sediment core from the southern Drake Passage (GC05-DP02). Rare earth elements and data had previously indicated that fine grained detritus was supplied from the Weddell Sea to the core site during interglacial periods, when the sediments contained more Al-rich smectite (montmorillonite). Indeed, marine sediments collected close to the Larsen Ice Shelf on the eastern Antarctic Peninsula continental shelf, western Weddell Sea embayment, show more Al-rich smectite components as compared with other possible West Antarctic sources, such as the Ross Sea embayment or King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Furthermore, two types of smectite (Al-rich and Al-poor) were identified in core GC360 from the Bellingshausen Sea shelf, suggesting that during glacial periods some sediment is derived from subglacial erosion of underlying pre-Oligocene sedimentary strata containing predominantly Al-rich montmorillonite. This finding reveals different sources for smectites in sediments deposited at site GC360 during the last glacial period and during the present interglacial that show only minor differences in smectite contents. For the interglacial period, two groups of smectite with a wide range of Al-rich and Mg–Fe-rich were identified, which indicate delivery from two different sources: (1) the detritus with high contents of Mg–Fe-rich smectite supplied from Beethoven Peninsula, southwestern Alexander island and (2) the detritus with higher contents of Al-rich smectite (montmorillonite) possibly derived from the subglacial reworking of pre-Oligocene sedimentary strata. These results demonstrate that the elemental compositions of smectites can be used to differentiate the sources of smectites in marine sediments, which is an important tool to define sediment provenance in detail, when down-core changes observed in clay mineral assemblages are interpreted.
1. Introduction
Smectite clay minerals, a common product of chemical weathering of volcanic material or igneous rock under warm, humid conditions [1] and hydrothermal alteration of pyroclastic products [2,3], are ubiquitous in marine sediments [2]. Smectite has a range of various elemental compositions, such as nontronite (Fe-rich), saponite (Mg-rich), and montmorillonite-beidellite (Al-rich) [1,2]. Clay mineral assemblages in the clay-size fraction (<2 µm) of marine sediments are frequently being used to reconstruct sediment provenance [4,5,6], depositional processes [7], and transport pathways of fine-grained terrigenous detritus [8]. In particular, down-core changes in the relative amount of clay minerals are utilized to reconstruct sediment transport pathways by comparing a specific clay mineral composition to those of potential source rocks and sediments in nearby coastal regions [5,9,10,11]. The clay mineral assemblages of seafloor surface sediments in the South China Sea has revealed that fine-grained particles were supplied from South China, Taiwan, and Luzon, and that the delivery of these particles was associated with East Asian monsoon evolution [8]. In the Antarctic region, the clay mineral composition of seabed surface sediments collected close to the ice margin has been used to identify and distinguish the provenance of rocks and sedimentary strata in catchment areas of ice streams draining to the coast today, for example of those draining into the Amundsen Sea [12]. In addition, the geographical changes in clay mineral assemblages of surface sediments across and along the West Antarctic continental margin in combination with the distinct clay mineralogical “fingerprint” of specific source areas in West Antarctica, such as enrichments of smectite around the South Shetland Islands (northwestern Antarctic Peninsula), chlorite on the western Antarctic Peninsula continental shelf, illite on the southern Bellingshausen Sea shelf, and kaolinite on the Amundsen Sea shelf, were also utilized to trace transport pathways of fine-grained detritus supplied from multiple sources [12,13,14]. Nonetheless, there is little understanding of clay mineral provenance of marine sediments recovered far offshore due to the mixing of detritus with various clay mineral compositions in the marine realm, which is caused by delivery of fine-grained detritus from multiple proximal and distal sources [10,12]. This is especially true for Antarctica, where the geology of the ice-sheet covered hinterland is poorly known. In particular, the origins of smectite clay minerals cannot be identified with certainty by just analyzing smectite content of the sediments unless the various types of smectites are differentiated based on their elemental composition at a nanoscale. Recently, variations in geochemical compositions (40Ar/39Ar ages of coarse-grained biotite and hornblende grains, Nd and Sr isotopes of the fine-grained detrital fraction <63 µm) of marine sediments were also analyzed in order to trace their provenance [15,16,17]. However, also the use of geochemical characteristics of sediments for determining their provenance must be carried out with caution due to the increasing mixing of particles originating from various sources with increasing distance from the coast [17,18].
In this study, nanoscale measurements of the elemental compositions of smectite minerals are conducted in order to determine sediment provenance by differentiating various types of smectite. This approach is successfully applied to a Late Quaternary sedimentary record from Drake Passage, which is characterized by well-pronounced glacial-interglacial changes in sediment provenance observed in Nd-isotope data ( values) [15], and also used to determine the sources of sediments in core from the continental shelf in the Bellingshausen Sea, which span the last glacial period until today [10]. This new approach will improve our interpretation of glacial–interglacial provenance changes in sediments supplied from multiple sources.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Location
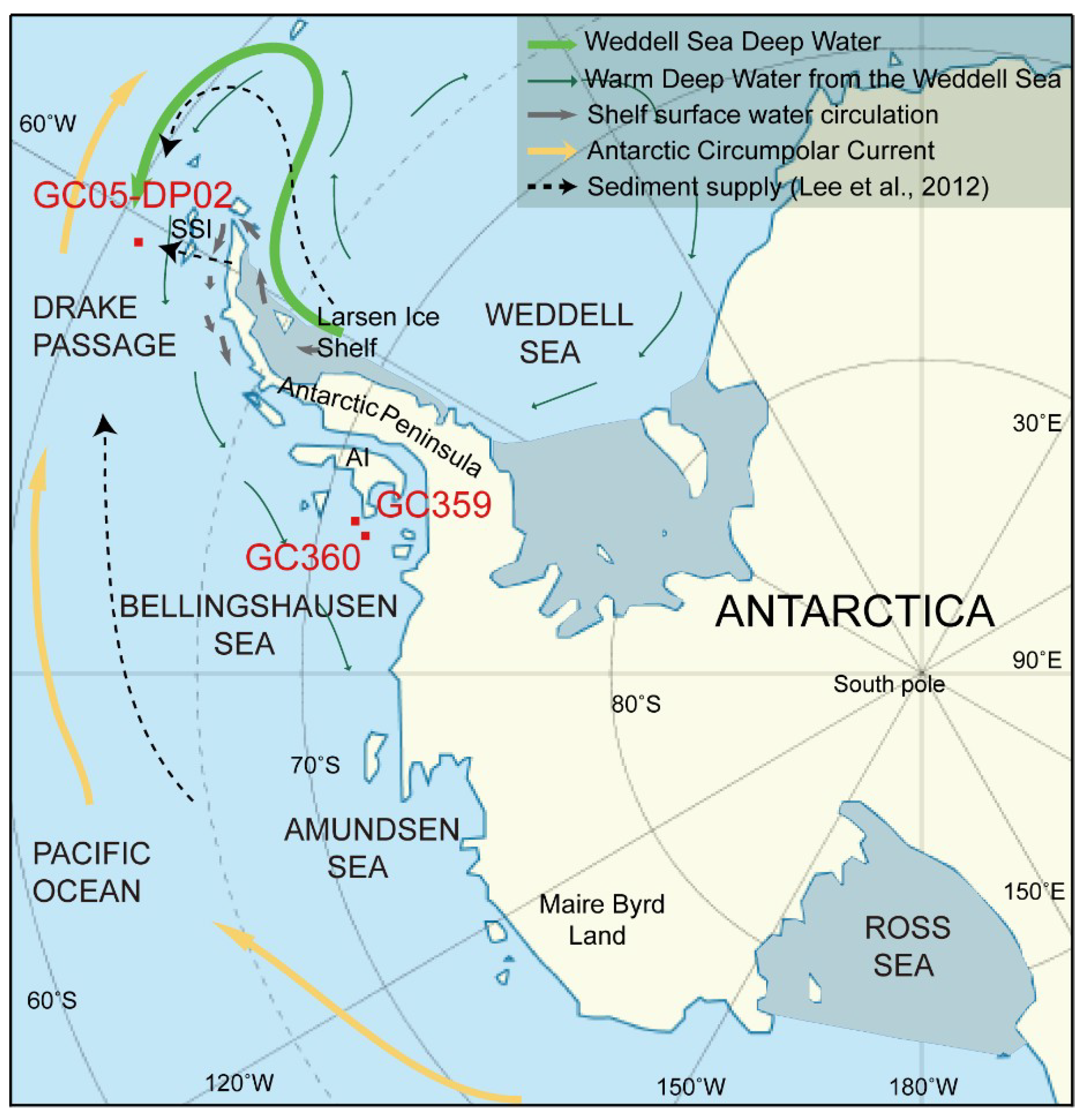
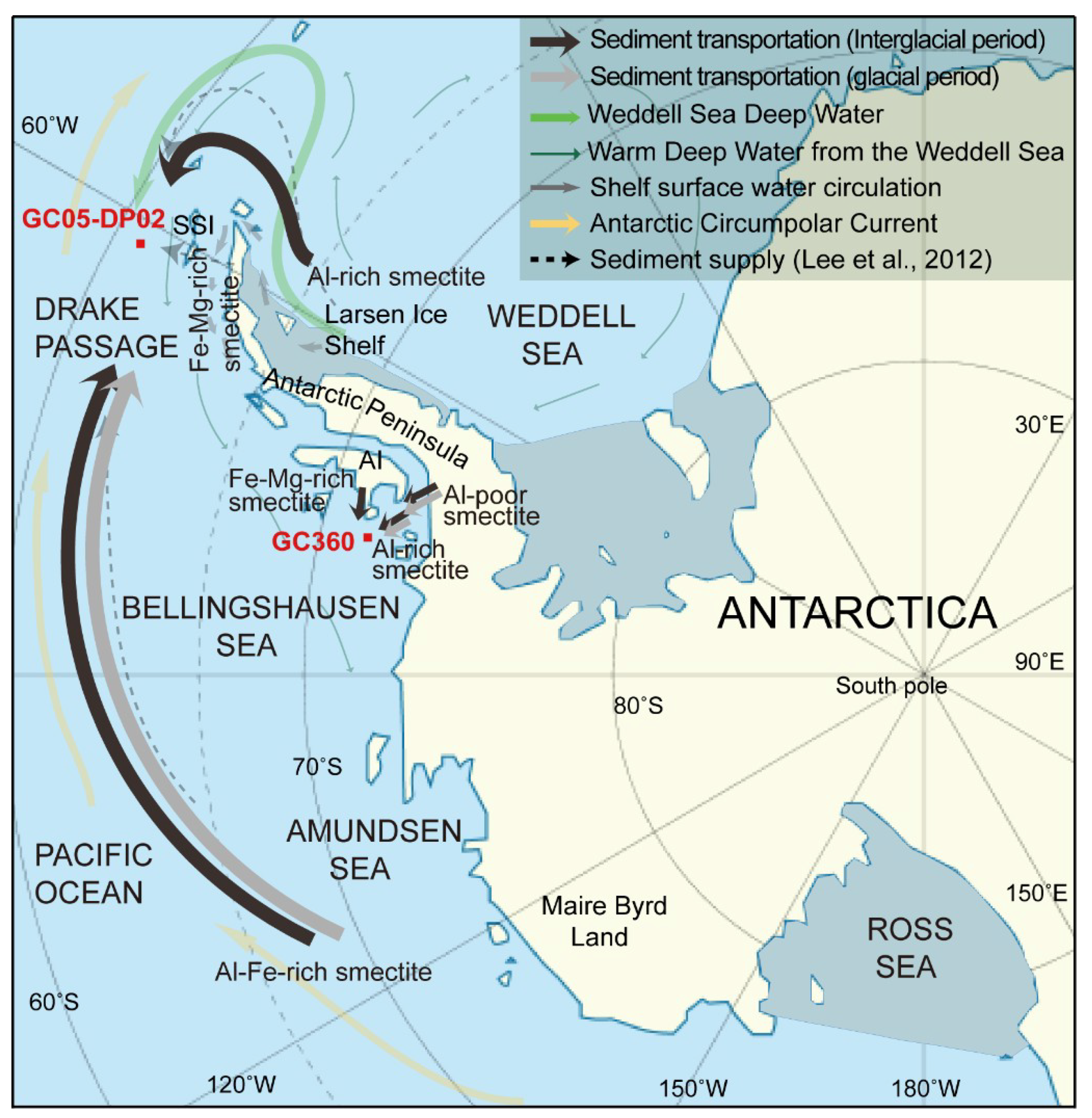
Gravity core GC05-DP02 (core length 595 cm, water depth 3503 m) was collected from the southern Drake Passage during a cruise of the Korea Arctic and Antarctic Research Program in 2005 and 2006 [15] (Figure 1). The Drake Passage, located at 56–60° S, provides a pathway for the eastward flowing Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) (affecting surface, deep, and bottom waters in the Southern Ocean) [15], the anticlockwise flowing Antarctic Coastal Current (affecting surface waters on the shelf) and the anticlockwise circulation of Weddell Sea Deep Water and Warm Deep Water out of the Weddell Sea along the slope and rise to the west of the Antarctic Peninsula [19]. The down-core variations in values of sediments (<63 µm) from core GC05-DP02 indicate that the Weddell Sea embayment was a more likely source for sediments deposited during interglacial periods than the Antarctic Peninsula or more distal sources along the West Antarctic continental margin [15] (Figure 1).
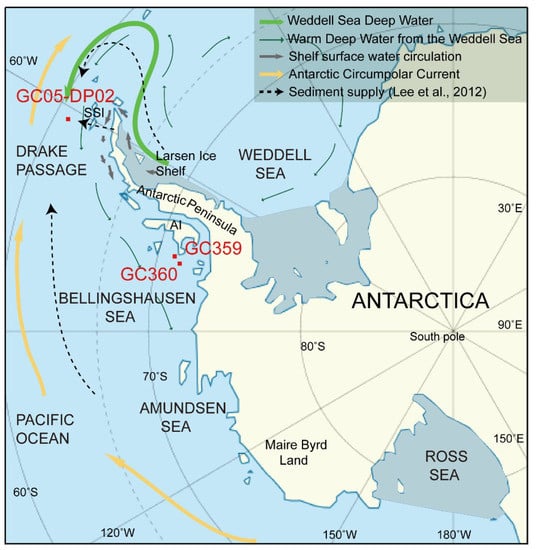
Figure 1.
Location of core GC05-DP02 in southern Drake Passage and cores GC359 and GC360 on the shelf of the Bellingshausen Sea, Antarctica. Deep and shallow water circulation paths are from the modified of Hernández-Molina et al. (2006) [19]. SSI = South Shetland Island, AI = Alexander Island.
Gravity core GC360 (core length 171 cm) was collected offshore from Ronne Entrance on the continental shelf in the Bellingshausen Sea during cruise JR104 with RRS James Clark Ross in 2004 [10] (Figure 1). The ice sheet in the Bellingshausen Sea is assumed to have advanced across the continental shelf after ~36 ka B.P. [20], retreated from the outer shelf at ~25.5 ka B.P., and from the inner shelf in Ronne Entrance at ~6.3 ka B.P. [20]. Following the last deglaciation, the West Antarctic Ice Sheet [21] and the Antarctic Peninsula Ice Sheet [22] underwent only minor retreat along the Pacific margin, but dramatically renewed retreat has occurred over the last few decades and is still in progress [23]. Previous investigations showed that the amounts of smectite in neighboring sediment cores GC360 and GC359 were substantially different in subglacial and grounding line proximal diamictons deposited during at the end of the last glacial period [10]. Clay mineral assemblages in the glacial diamicton at site GC359 are characterized by significantly lower contents of smectite, which was likely supplied subglacially from the southwestern Antarctic Peninsula, as compared with the smectite-enriched sub- and proglacial diamictons deposited at site GC360. During the present interglacial period, both sites are characterized by deposition of glacimarine sediments with nearly identical smectite contents, which was attributed to detrital supply from sources both on the southwestern Antarctic Peninsula and on Beethoven Peninsula (southwestern Alexander Island). During the last deglaciation, however, smectite contents at site GC359 consistently increased from lower glacial to the higher interglacial values, whereas they initially decreased and then increased to interglacial values slightly lower than the glacial values at site GC360. These differences in down-core smectite changes between sites GC359 and GC360 were attributed to glacial time smectite supply to site GC360 from two different sources, one located on the southwestern Antarctic Peninsula and the other one cropping out at the seabed in Ronne Entrance. This implied that the latter source, which was concluded to consist of pre-Oligocene sedimentary strata, would only be “active” when being eroded by grounded ice [10]. Core GC360, therefore, provides excellent sample material for identifying different sources for smectite by distinguishing smectite types on the basis of their elemental compositions.
2.2. X-ray Diffractometry
We collected 40 subsamples (~50 mg of each sample) from core GC05-DP02 at 10–15 cm intervals, depending on changes in sedimentary facies, colors, and depth of geochemical analysis. The sediment samples from core GC05-DP02 were treated with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to disperse the particles by removing the organic matter [24], and then the clay fractions (<2 ) were separated from the coarser grain-size fractions in a settling tube (settling in accordance with Stokes’ Laws [25]). The clay samples (15 mg) were sonicated in an Eppendorf tip (1.5 mL) filled with distilled water, and the X-ray slides were prepared for the diffractometer measurements [6,25]. The X-ray profiles were recorded at a range from 2–65° 2 with a scanning speed of 1.5°/min and a step size of 0.02° using a MiniFlex II (Rigaku) operating at 30 kV and 15 mA with Cu-Kα radiation at Yonsei University, Seoul. The Crystallographica Search-Match program (version 2.0.3.1) was used to identify the major clay minerals by comparing the basal reflections for the glycolated and air-dried samples [7]. Kaolinite and chlorite were differentiated by resolving, respectively, their second and fourth order basal X-ray diffraction peaks at 3.57 Å and 3.54 Å peaks [10,26,27]. The relative percentages of smectite, chlorite, illite, and kaolinite were determined using empirically estimated weighting factors [7,26], and the clay mineral ratio of smectite/ (chlorite + illite) was calculated using the semiquantitative clay mineral contents [11].
2.3. Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis was performed to acquire the structural and chemical variations in smectite clay minerals using a JEOL JEM-ARM200F STEM fitted with an INCA energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS) for JEM-ARM200F operated at a voltage of 200 kV at Yonsei University, Song-do, Korea. The TEM samples were selected from glacial and interglacial sediment intervals in the cores. In core GC05-DP02 these samples were taken from 20 cm below seafloor (cmbsf) and 350 cmbsf for the glacial periods (Marine Oxygen Isotope Stages (MIS) 2, 4, and 10) and 300 cmbsf and 385 cmbsf for the interglacial periods (MIS 9 and MIS 11). In core GC360, the samples were taken from 140 cmbsf (last glacial period) and 15 cmbsf (present interglacial). The samples were then impregnated with LR White resin followed by application of a water/methanol exchanging process [28] to prevent layer collapse in the smectite (from 13 Å to 10 Å, with the latter spacing being identical to the illite spacings) under the high-energy electron beam during TEM operation. The impregnated samples were then sectioned at a 100 nm thickness using a diamond knife ultramicrotome (ULTRACUT UCT, Leica, installed at Eulji University, Seongnam, Korea), and then placed on a holey carbon TEM grid [25]. Hundreds of bright-field lattice fringe images with corresponding selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns and EDS were recorded for smectite clay minerals and then analyzed using Digital MicrographTM software (Version 3.22. 1461. 0, Gatan Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA). The EDS was quantified to measure the elemental composition of smectite packets based on 20 oxygen atoms and 4 hydroxyl groups [29]. The mechanical error range for the TEM-EDS quantification (wt. %) was approximately <0.5%. In order to reduce the operational error, ~130 and ~80 packets of smectite packets were measured on the samples from cores GC05-DP02 and GC360, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Semiquantification of Clay Minerals
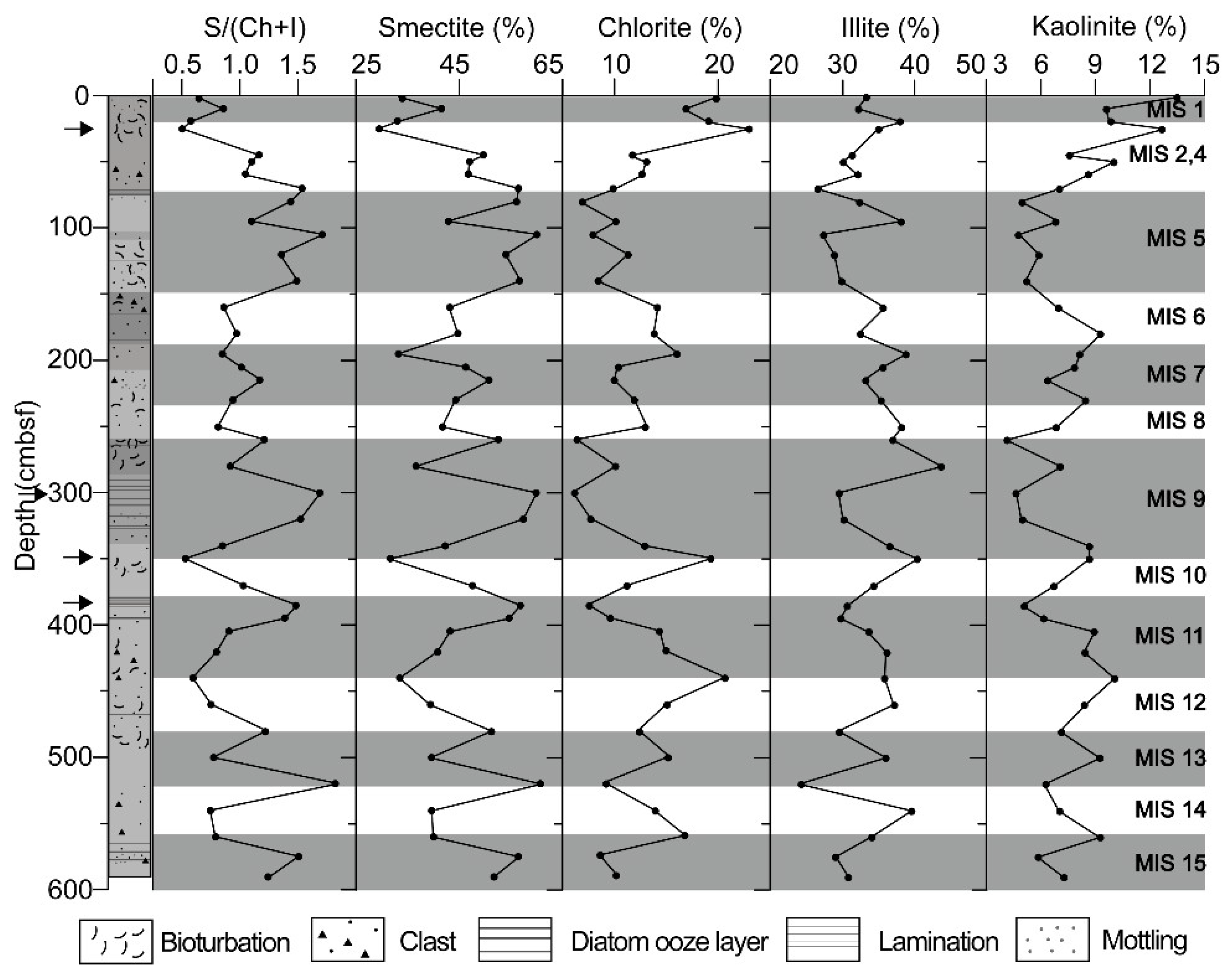
The clay mineral assemblages in core GC05-DP02 comprise smectite, illite, chlorite, and kaolinite (Figure 2). Illite and smectite mixed layer (XRD peak at 9.84 degree 2-theta) has not been observed for glycolated sample (Supplementary Materials Figure S1). The other minerals in core GC05-DP02 comprise albite and quartz throughout the whole depth (Figure S1). The variations in smectite and chlorite contents are negatively correlated and, in general, correspond to glacial and interglacial period in MIS, with smectite contents being increased in interglacial sediments and chlorite contents being increased in glacial sediments [15]. The average content of smectite in interglacial sediments is 37.4–55.1% as compared with contents of only 36.4–43.8% in glacial sediments in clay fraction. Chlorite contents vary from 8.6 to 18.2% in interglacial sediments and from 13.1 to 17.8% in glacial sediments. In contrast, the illite contents show no systematic glacial-interglacial changes in downcore (average values 32.2–34.7%). Kaolinite only forms a minor component of the clay mineral assemblages (contents are less than 9.2% in most samples) and also does not show systematic glacial-interglacial changes (Figure 2). Smectite maxima occur in bioturbated or laminated sedimentary facies, whereas, smectite minima are observed in structureless sandy mud with clasts (Figure 2). These sediment facies were assigned to interglacial and glacial MIS, which is supported for the Latest Quaternary by radiocarbon ages [15]. The average smectite/ (chlorite + illite) ratios vary from 0.74 to 1.42 in interglacial sediments and from 0.67 to 1 in glacial sediments. The ratio reaches maxima in interglacial MIS 5, 9, 11, and 13, and minima in glacial MIS 2, 4, 8, 10, and 12 (Figure 2).
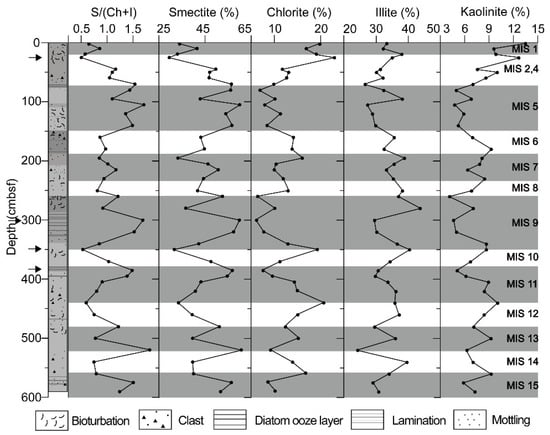
Figure 2.
Sedimentary facies and contents of smectite, chlorite, illite, and kaolinite in sediment from core GC05-DP02 in southern Drake Passage. Marine Oxygen Isotope Stage (MIS) assignment following Lee et al. (2012) [15]. Arrows indicate the depth of TEM samples.
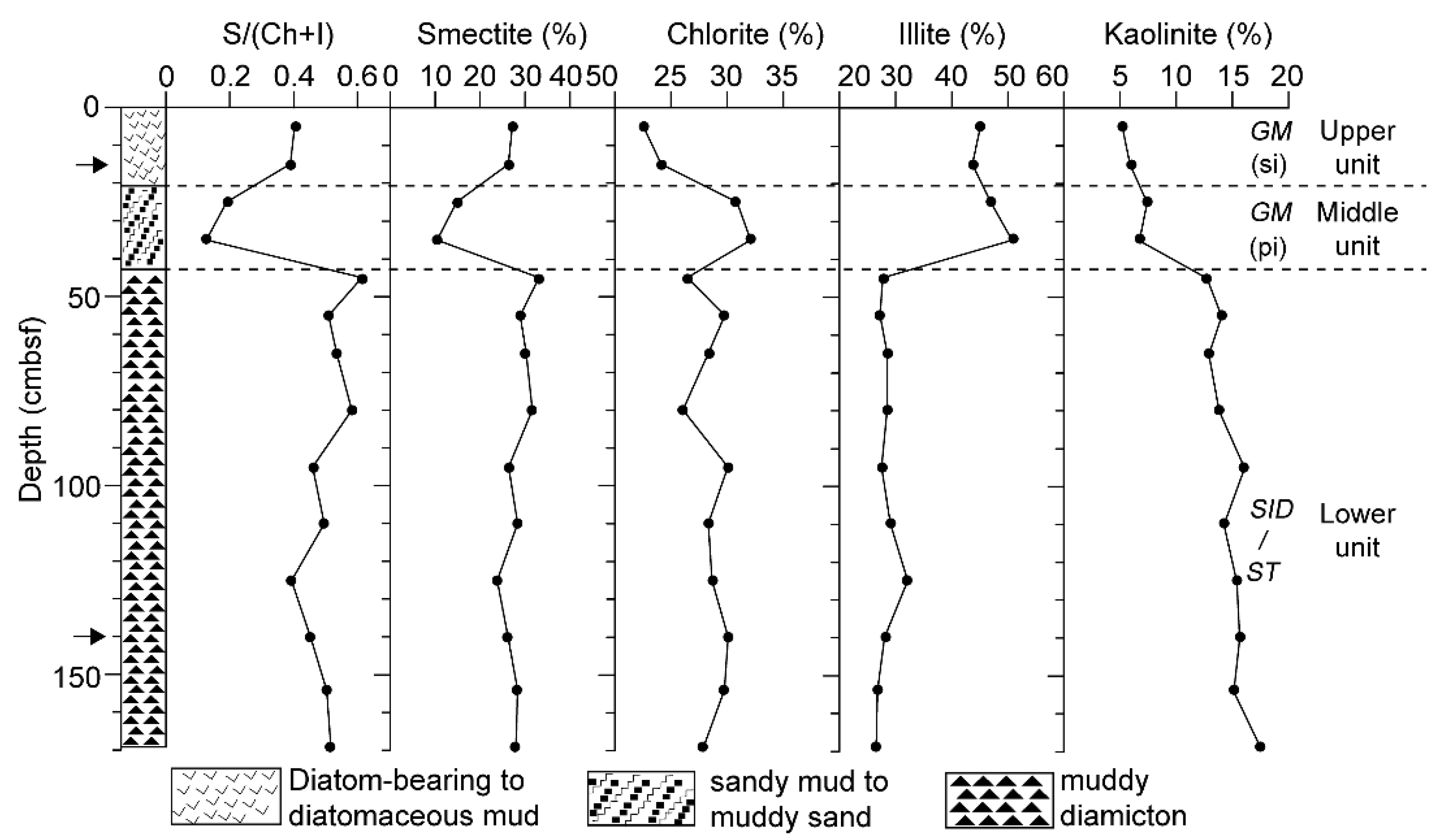
The sediments in core GC360 were subdivided into three distinct lithological units by Hillenbrand et al. [10,20]. The clay mineral assemblages in the sediments comprise smectite, chlorite, illite, and kaolinite (Figure 3). The clay mineral content in the lower unit of core GC360, which consists of structureless subglacial till and grounding-line proximal sub-ice shelf diamicton deposited during and at the end of the last glacial period [20], is remarkably uniform, with average contents of 28.5% for smectite, 28.2% for illite, 28.5% for chlorite, and 14.8% for kaolinite in clay fraction [10]. In the middle unit, which consists of homogenous gravelly sandy mud deposited under an ice canopy distal from the grounding line during the last deglaciation, smectite content is on average 12.6%, illite content is 48.8%, chlorite content is 31.5% and kaolinite content is 7.1%. In the upper unit, which consists of bioturbated diatom-bearing mud deposited in a seasonal open marine setting during the present interglacial, smectite content is on average 26.7%, illite content is 44.4%, chlorite content is 23.3%, and kaolinite content is 5.6% [10] (Figure 3). The smectite/ (chlorite + illite) ratio varies from 0.5 in the glacial sediments of the lower unit to 0.2 in deglacial sediments of the middle unit to 0.4 in the interglacial sediments of the upper unit (Figure 3).
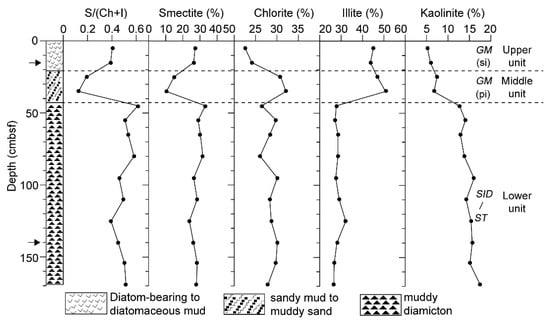
Figure 3.
Sedimentary facies (three distinct units from glacimarine sediment to proximal sub-ice shelf diamicton/soft till), contents of smectite, chlorite, illite, and kaolinite in core GC360. (GM: glacimarine sediment, ST: soft till, SID: proximal sub-ice shelf diamicton, si: seasonal sea-ice cover, pi: permanent sea-ice cover/distal ice-shelf cover) (Modified from Hillenbrand et al., 2009 [10]). Arrow indicates the depth of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) samples.
3.2. TEM Analysis
3.2.1. TEM Analysis of Samples from Core GC05-DP02
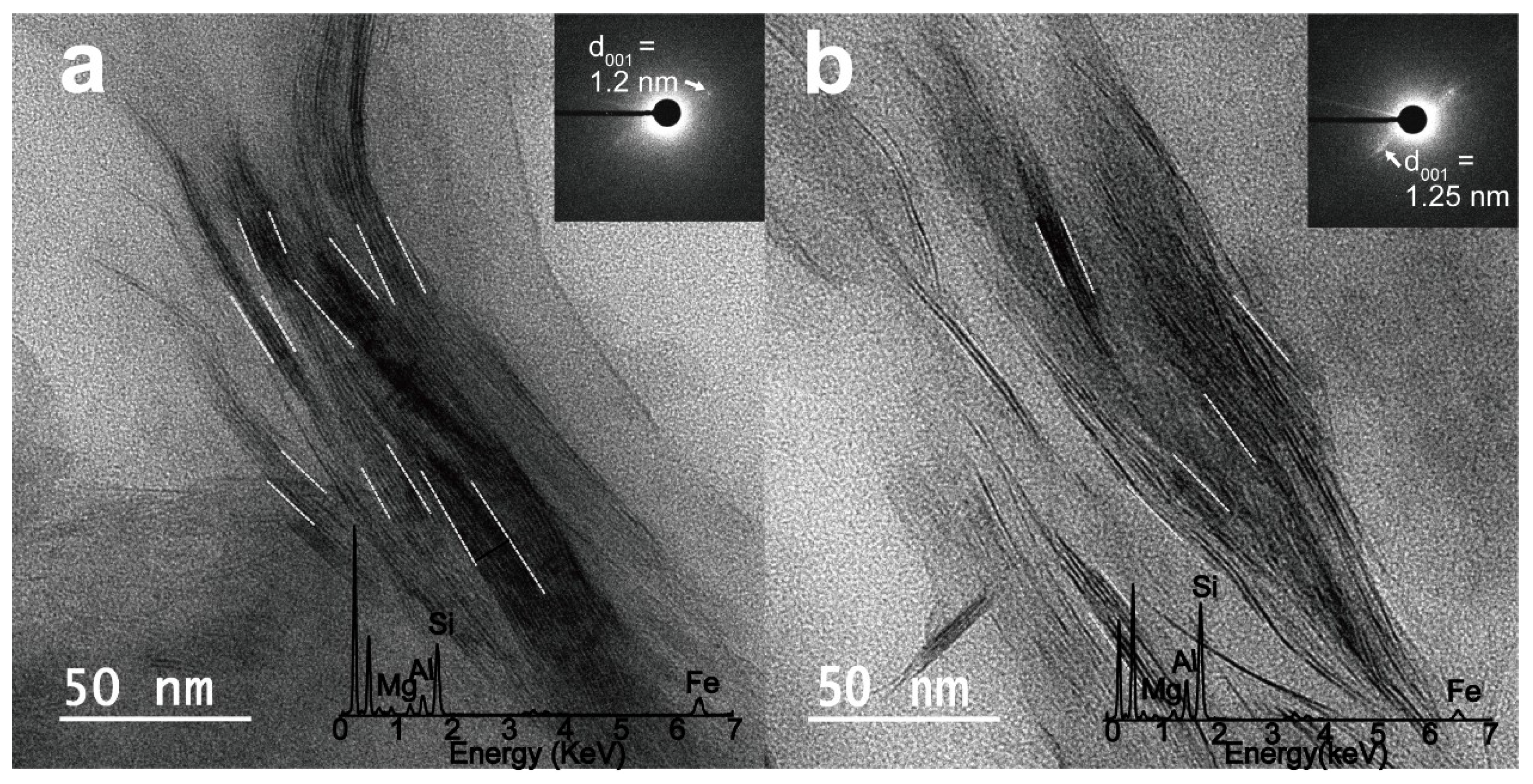
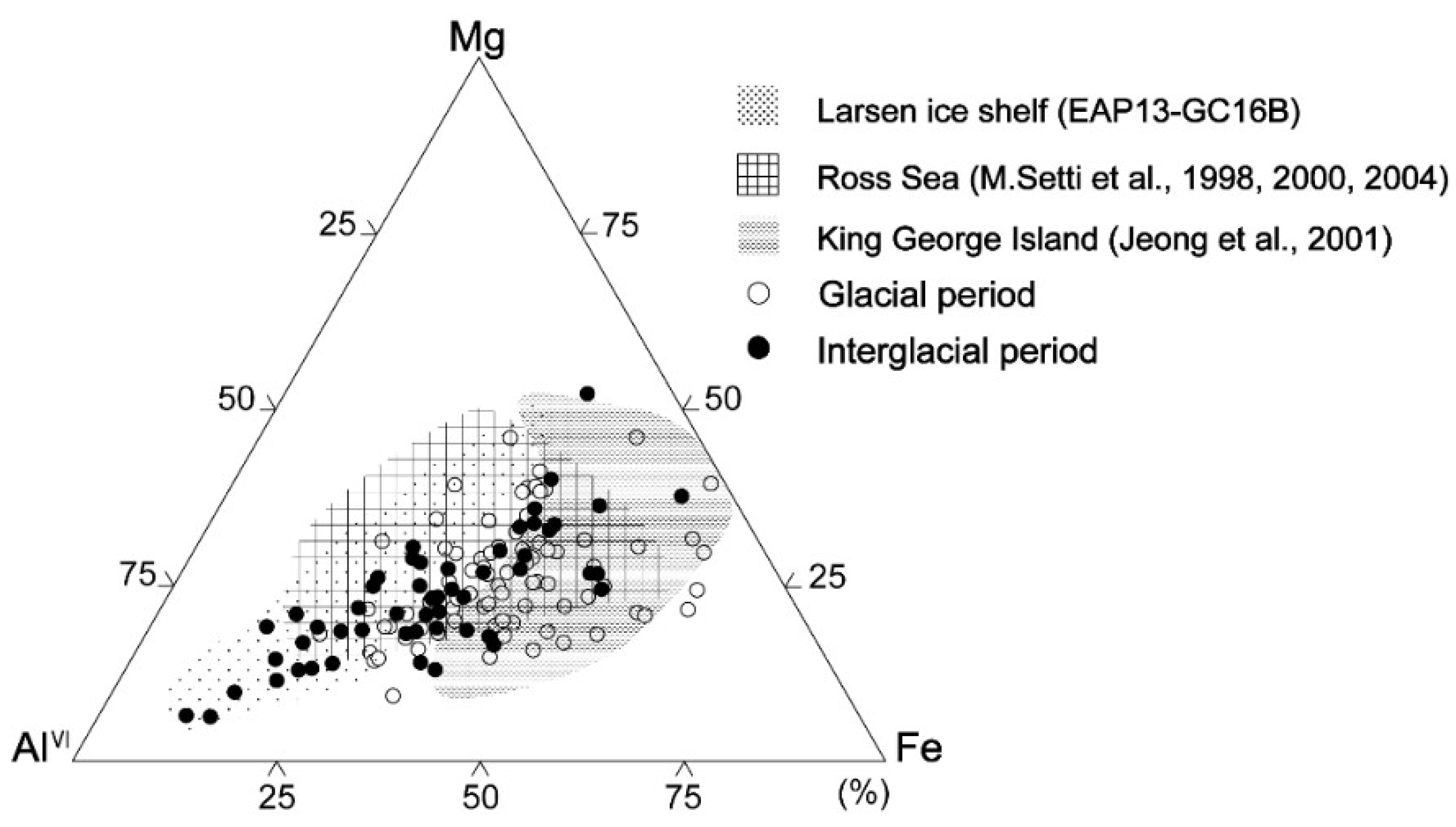
A representative smectite packet for glacial and interglacial sediments was analyzed in lattice fringe images along with the insets of the corresponding SAED pattern and EDS (Figure 4). Smectite packets (outlined by white dotted lines) with a hairy morphology and discontinuous lattice fringe were distinguished from other clay minerals. The inset images in Figure 4a,b show the SAED patterns of the glacial and interglacial smectite, with diffused Bragg’s reflection for a range of d001 = 1.2–1.25 nm. The EDS profiles (Figure 4b) show a wide range of Al contents (7.5–27.7 wt. %) in smectites from interglacial sediments, as compared with Al contents in smectites from glacial sediments (15–19.3 wt. %). The elemental compositions of the analyzed smectites, specifically their Al–Mg–Fe ratios, are plotted as white (glacial smectite) and black (interglacial smectite) points in a ternary diagram and compared with previously reported smectite compositions in potential West Antarctic source areas, such as King George Island (South Shetland Islands), the Ross Sea shelf, and the eastern Antarctic Peninsula shelf (offshore from the Larsen Ice Shelf) [30,31,32,33] (Figure 5). The compositions of smectites ((Ca0–0.63Na0–0.6K0–0.86)(Al0.09–2.49Mg0.38–2.44Fe0.88–3.04)(Si5.66–7.94Al0.06–2.34)O20(OH)4) in the glacial sediments of core GC05-DP02 are similar to those of smectites from King George Island and the Ross Sea shelf (Figure 5, Table S1). The range of elemental compositions of smectites in the interglacial sediments (Ca0.04–0.52Na0–0.26K0–0.75)(Al0.29–3.3Mg0.25–2.62Fe0.43–2.6)(Si6.66–7.98Al0.02–1.34)O20(OH)4 are compatible with those of smectites in sediments from King George Island, the Ross Sea shelf, and the shelf offshore from the Larsen Ice Shelf (Figure 5, Table S2).
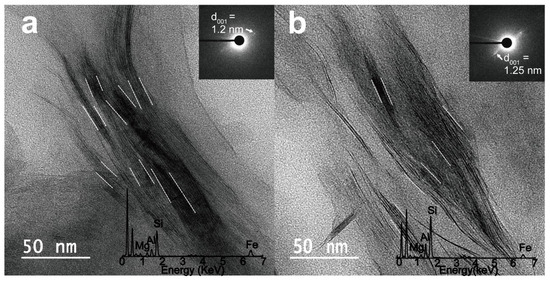
Figure 4.
Representative TEM micrographs of lattice fringes in smectites from core GC05-DP02 from (a) a glacial MIS 10 (with an inset figure of the selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of smectite (d001 = 1.2 nm)) and (b) an interglacial MIS 9 (with an inset figure of the SAED pattern of smectite (d001 = 1.25 nm)). The elemental composition of smectite was obtained using TEM-energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer (TEM-EDS).
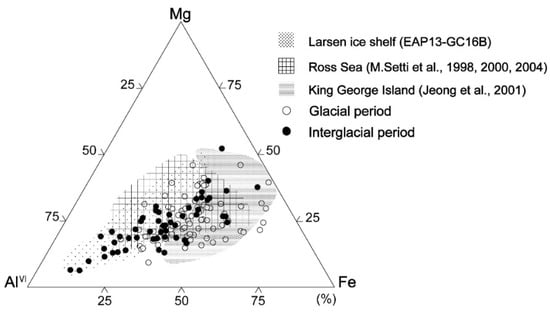
Figure 5.
Ternary Al–Fe–Mg plot of the octahedral site composition of smectites for the glacial (white circle, MIS 2, 4, and 10) and the interglacial (black circle, MIS 9 and 11) sediments from core GC05-DP02. The compositional fields for smectites in sediments from near the Larsen Ice Shelf (core EAP13-GC16B), Ross Sea shelf (Setti et al., 1998, 2000, 2004 [30,31,32]), and King George Island (Jeong & Yoon, 2001 [33]) are also shown.
3.2.2. TEM Analysis of Samples from Core GC360
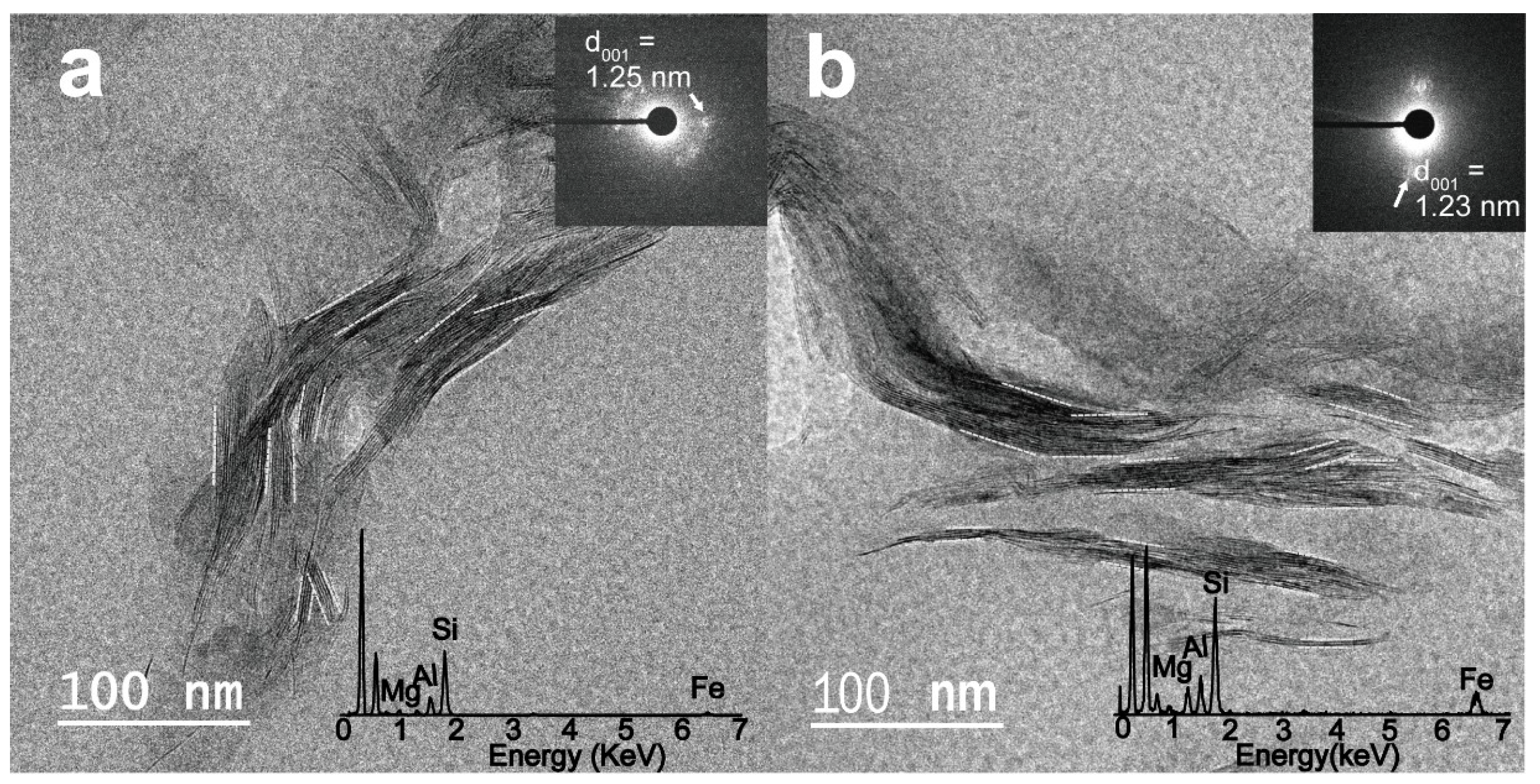
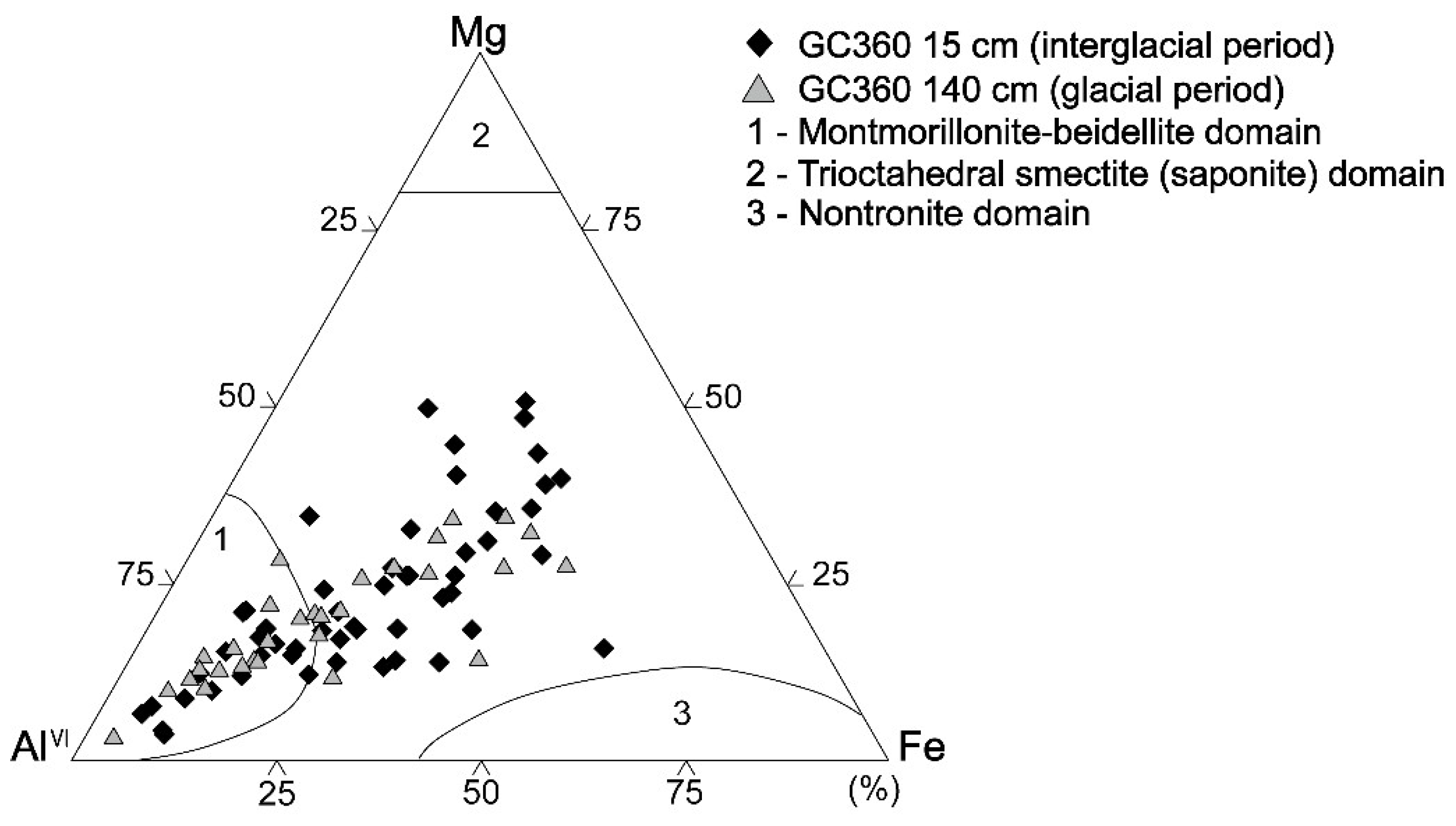
In core GC360, the TEM micrographs of a randomly oriented smectite packet displayed hairy and discontinuous lattice fringes, with corresponding diffused SAED patterns and EDS profiles (Figure 6). The inset SAED patterns of glacial and interglacial smectites (Figure 6a,b) show representative structure of randomly ordered/diffused Bragg’s reflections (d001 = 1.23–1.25 nm). All smectite layers of the TEM sample treated with LR White resin display d-spacing varying from 1.2 to 1.3 nm, similar to those of the hydrated smectite layer [25,34,35]. The EDS profiles of the smectites (Figure 6a,b) indicate Fe contents of 2.5–26.2 wt. % with Mg contents of 0.81–13.1 wt. % in interglacial smectites and Fe contents of 1.72–23.5 wt. % with Mg contents of 0.74–8.8 wt. % in glacial smectites. The Al contents of glacial smectites show slightly higher values (15.7–31.2 wt. %) as compared with Al contents of interglacial smectites (11.5–29.4 wt. %) (Figure 6). The Al–Mg–Fe ratios of the smectites are plotted in a ternary diagram (Figure 7). The elemental compositions of the smectites in core GC360 vary between glacial ((Ca0–0.32Na0–0.23K0.03–0.81)(Al0.96–3.86Mg0.13–1.66Fe0.15–2.3Ti0.003–0.09)(Si6.14–7.73Al0.27–1.86)O20(OH)4) and interglacial periods ((Ca0–0.19Na0–0.75K0–0.91)(Al0.93–3.64Mg0.14–2.48Fe0.22–2.6Ti0–0.21)(Si6.05–7.97Al0.03–1.95)O20(OH)4) (Tables S3 and S4). For a refined identification of the mineralogical compositions of the smectites in core GC360, the elemental compositional ranges of montmorillonite-beidellite (Al-rich, area 1), trioctahedral smectite (saponite, Mg-rich) (area 2) and nontronite (Fe-rich, area 3) [2] are also displayed in the ternary diagram (Figure 7). Subsequently, we gave a name to each chemical component-rich smectite when the measured Al–Fe–Mg ratio of the smectite was close value of the compositional ranges of each smectite domain [2,36].
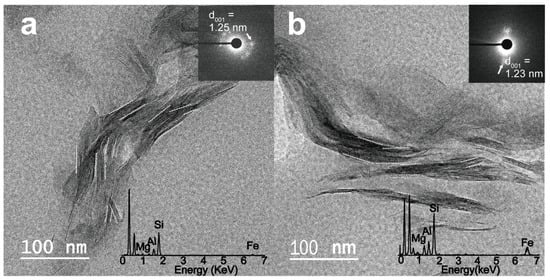
Figure 6.
Representative TEM micrographs of lattice fringes of smectites in sediments from (a) the last glacial period (with an inset figure of the SAED pattern of smectite (d001 = 1.25 nm)), and (b) the present interglacial period (with an inset figure of the SAED pattern of smectite (d001 = 1.23 nm)) in cores from GC360. The elemental composition of smectite was measured using TEM-EDS.
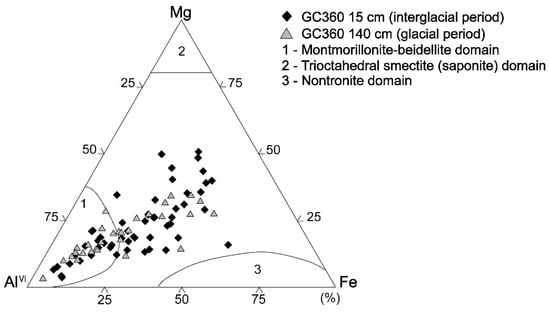
Figure 7.
Ternary Al–Fe–Mg plot of the octahedral site compositions of smectites for the glacial (triangle, 140 cmbsf) and the interglacial (diamond, 15 cmbsf) sediments from core GC360. Note that area 1 = montmorillonite-beidellite, area 2 = trioctahedral smectite (saponite), and area 3 = nontronite (Weaver and Pollard, 1973 [2]).
4. Discussion
4.1. Glacial-Interglacial Changes in Clay Mineral Provenance of Core GC05-DP02 from Drake Passage
4.1.1. Clay Mineral Assemblages
The relative percentage of clay minerals in the Drake Passage reveal that smectite, chlorite, and illite are the dominant components, with only minor amounts of kaolinite (Figure 2). Throughout the Late Quaternary, the clay mineral assemblages in core GC05-DP02 are smectite-rich (37.4–55.1%) and relatively chlorite-poor (8.6–18.2%) in interglacial sediments, and relatively smectite-poor (36.4–43.8%) and chlorite enriched (13.1–17.8%) in glacial-time sediments (Figure 2). These variations are comparable to the fluctuations of clay minerals reported from other Late Quaternary sedimentary sequences recovered from the western Antarctic Peninsula continental rise further to the Southwest [37]. Clay mineral assemblages in core GC05-DP02 exhibit significantly higher smectite contents than these other cores because site GC05-DP02 is located closer to the South Shetland Islands, which are a known source of smectite [37,38]. The decrease in smectite and increase in chlorite contents during glacial periods is likely caused by a higher supply of glacially eroded chlorite enriched terrigenous detritus from igneous and low-grade metamorphic rocks on the Antarctic Peninsula (sources for chlorite and illite) [4,14,37,39]. Because site GC05-DP02 is located offshore from the South Shetland Islands, which were not overridden by the Antarctic Peninsula Ice Sheet during glacial periods (e.g., [22]), the chlorite-enriched detritus must have been delivered either from further west within the ACC or from the northernmost tip of the Antarctic Peninsula (Figure 1). Rare earth element contents (REE) and values (more negative Eu anomaly, higher La/Sm and Th/Sc ratio, and low value < −6 during interglacial period [15]) in the sediments of core GC05-DP02 indicate that fine-grained detritus was transported from the Weddell Sea margin of the Antarctic Peninsula to this site during interglacial periods [15] (Figure 8). However, the relative contents of clay minerals do not allow for distinguishing and identifying possible multiple sources of the clay minerals as indicated by the geochemical data of the smectites (see Section 4.1.2). Therefore, it is essential to analyze the elemental composition of the smectites to distinguish the different types of smectite.
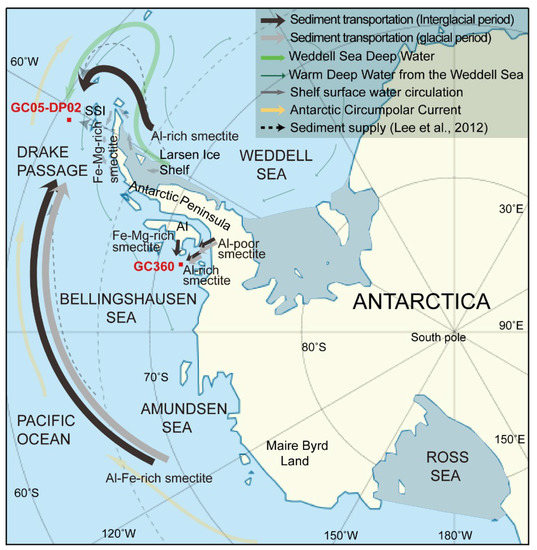
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram showing possible transport routes of fine-grained detritus. Gray and black arrows indicate smectite transport during glacial and interglacial periods, respectively. Ocean circulation given as in Figure 1. SSI = South Shetland Island, AI = Alexander Island.
4.1.2. Elemental Composition of Smectites
The elemental compositions of smectites in the interglacial sediments of core GC05-DP02 show a wider range of Al contents as compared with those of the glacial-time sediments. These observations indicate that the interglacial sediments may have multiple sources. The elemental composition of smectite with high Fe–Mg and Al–Fe content indicates a detrital supply from King George Island [33] and the Ross Sea embayment [30,32,40] during both interglacial and glacial periods (Figure 5). The Fe–Mg-rich smectites prevail in the glacial-time sediments indicating that they are mainly derived from altered volcanic glass on King George Island and were supplied to the deep sea by the advance of grounded ice to the shelf break during glacial periods [15,33]. The Al–Fe-rich smectites are more common in the interglacial sediments. Because such smectites are typical for detrital smectites in the Ross Sea embayment [31], we assume that they were supplied with the eastward flowing ACC [41]. Interestingly, Al-rich smectites (montmorillonite) appear only in the interglacial sediments of core GC05-DP02, indicating that Al-rich smectites (montmorillonite), which were observed in sediments [6] and on islands [42] on the eastern Antarctic Peninsula shelf, were transported within the anticlockwise flow of the deep and bottom water currents from the Weddell Sea to Drake Passage, as it is also suggested by the REE data and values (Figure 5). Glacigenic debris flow deposits reported from the eastern Antarctic Peninsula continental slope document that detritus eroded along the eastern Antarctic Peninsula shelf can be entrained into Weddell Sea Deep Water (WSDW) and warm deep water flowing out of the Weddell Sea to Drake Passage (Figure 8).
4.2. Glacial-Interglacial Changes in the Smectite Composition in Core GC360 from the Bellingshausen Sea Shelf
The elemental compositions of smectites deposited at site GC360 during the last glacial period reveals two different types of smectites, Al-rich and Al-poor smectites (Figure 7). Subglacial erosion of pre-Oligocene sedimentary strata proposed to be cropping out at the seabed in Ronne Entrance [10] probably supplied the Al-rich smectites (montmorillonite) (Figure 8), which were reworked into the till layer at the base of grounded ice advancing across the southern Bellingshausen Sea shelf during the last glacial period [20] (Figure 3 and Figure 7). In addition, other parts of the Antarctic margin in pre-Oligocene sedimentary strata, sometimes only cropping out at the seafloor, have been suggested to be an important source for Al-rich smectites (montmorillonite) found in Neogene and Quaternary marine sediments [43,44]. Al-poor smectites, typically derived from volcanic rocks in the Antarctic Peninsula [2], were also mixed into the till layer and advected across the shelf (Figure 8), as is evident from the smectite compositions observed in the glacial-time sediments deposited at site GC360 (Figure 7). In addition, including Al-poor smectites that are probably delivered by tidal- and wind-driven currents from the southwestern Antarctic Peninsula coast, the smectites in the interglacial sediments of core GC360 are enriched in Fe and Mg (Figure 7). The increase of these Fe-Mg-rich smectites originated from the supply of fine-grained terrigenous detritus derived from the Beethoven Peninsula on southwestern Alexander Island [45,46] (Figure 8). The outcrops of Neogene post-subduction alkali basalts are widespread on Beethoven Peninsula [46,47]. These volcanic rocks contain abundant ferro-magnesian minerals, including nontronite (Fe-rich smectite) and saponite (Mg-rich smectite) [1].
5. Conclusions
Investigations into the variations of the elemental compositions of smectites are useful for tracing source rocks and strata and for understanding the transport pathways of fine-grained terrigenous detritus, particularly, contributions from multiple sources. Interglacial sediments of core GC05-DP02 are composed of smectites transported from King George Island, the Ross Sea embayment, and the Weddell Sea. Interestingly, fine-grained detritus transported from the Weddell Sea to the southern Drake Passage was inferred via Al-rich smectites in the ternary diagram. Glacial sediments in cores from GC360 and Al-rich smectite observed in the subglacial till layer are likely to result from the reworking of old sedimentary layers via erosion by grounded ice. On the contrary, seasonally open marine sediments during interglacial periods suggest that high smectite content and Fe–Mg-rich smectites indicate a supply of fine-grained terrigenous detritus derived from volcanic rock outcrops on the Beethoven Peninsula. Late Quaternary sediments in cores GC05-DP02 and GC360 clearly show that the changes in sediment provenance over glacial–interglacial cycles can be reconstructed in detail by combining analyses of clay mineral assemblages and the elemental composition of smectites. Comparing the elemental compositions of smectites in marine sediments with those of smectites from possible source areas is a new effective approach for disentangling the contributions of clay mineral assemblages supplied from multiple sources.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials can be accessed at: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-163X/9/5/322/s1. Figure S1: X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of air-dried and glycolated clay (<2 μm) in sediment core from GC05-DP02 at representative glacial-interglacial period depth (S: smectite, Ch: chlorite, K: kaolinite, I: illite, A: albite, Q: quartz); Table S1: Elemental composition of smectites in glacial period from core GC05-DP02; Table S2: Elemental composition of smectites in interglacial period from core GC05-DP02 (calculated with O = 20 and OH = 4) obtained by TEM-EDS; Table S3: Elemental composition of smectites in glacial period from core GC360 (calculated with O = 20 and OH = 4) obtained by TEM-EDS (calculated with O = 20 and OH = 4) obtained by TEM-EDS; Table S4: Elemental composition of smectites in interglacial period from core GC360 (calculated with O = 20 and OH = 4) obtained by TEM-EDS
Author Contributions
J.K. designed the study concept, data interpretation, and revised the manuscript; Y.K.P. and J.J. contributed to the experimental settings, data production, and manuscript preparation; J.I.L., K.-C.Y., and C.-D.H. collected the sediment core and interpreted the sedimentary facies and depositional environments.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No. NRF-2018R1A2B6002036) and the Antarctic Project of KOPRI (PE19030) to J.K.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the scientists and crew members of the KOPRI for their effort in collecting core samples and interpretations. We also thank W. Ehrmann (Leipzig University, Germany) for providing clay-fraction samples from core GC360.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Velde, B. Origin and Mineralogy of Clays: Clays and the Environment; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, C.E.; Pollard, L.D. The Chemistry of Clay Minerals (Developments in Sedimentology); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1973; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- García-Romero, E.; Vegas, J.; Baldonedo, J.L.; Marfil, R. Clay minerals as alteration products in basaltic volcaniclastic deposits of La Palma (Canary Islands, Spain). Sediment. Geol. 2005, 174, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petschick, R.; Kuhn, G.; Gingele, F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the South Atlantic: sources, transport, and relation to oceanography. Mar. Geol. 1996, 130, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandarinath, K. Clay minerals in SW Indian continental shelf sediment cores as indicators of provenance and palaeomonsoonal conditions: a statistical approach. Int. Geol. Rev. 2009, 51, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Yoo, K.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, J. Clay Mineralogical Characteristics of Sediments Deposited during the Late Quaternary in the Larsen Ice Shelf B Embayment, Antarctica. Minerals 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaye, P.E. Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1965, 76, 803–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Colin, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tuo, S.; Chen, Z.; Siringan, F.P.; Liu, J.T.; Huang, C.-Y.; You, C.-F. Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea and surrounding fluvial drainage basins: source and transport. Mar. Geol. 2010, 277, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, W.U.; Melles, M.; Kuhn, G.; Grobe, H. Significance of clay mineral assemblages in the Antarctic Ocean. Mar. Geol. 1992, 107, 249–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, C.D.; Ehrmann, W.; Larter, R.D.; Benetti, S.; Dowdeswell, J.A.; Ó Cofaigh, C.; Graham, A.G.C.; Grobe, H. Clay mineral provenance of sediments in the southern Bellingshausen Sea reveals drainage changes of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet during the Late Quaternary. Mar. Geol. 2009, 265, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Trentesaux, A.; Clemens, S.C.; Colin, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, B.; Boulay, S. Clay mineral assemblages in the northern South China Sea: implications for East Asian monsoon evolution over the past 2 million years. Mar. Geol. 2003, 201, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrmann, W.; Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Smith, J.A.; Graham, A.G.; Kuhn, G.; Larter, R.D. Provenance changes between recent and glacial-time sediments in the Amundsen Sea embayment, West Antarctica: clay mineral assemblage evidence. Antarct. Sci. 2011, 23, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Grobe, H.; Diekmann, B.; Kuhn, G.; Fütterer, D.K. Distribution of clay minerals and proxies for productivity in surface sediments of the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas (West Antarctica) —Relation to modern environmental conditions. Mar. Geol. 2003, 193, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Ehrmann, W. Distribution of Clay Minerals in Drift Sediments on the Continental Rise West of the Antarctic Peninsula, ODP Leg 178, Sites 1095 and 1096. Available online: http://www-odp. tamu. edu/publications/178_SR/VOLUME/CHAPTERS/SR178_08. PDF. (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Lee, J.I.; Yoon, H.I.; Yoo, K.-C.; Lim, H.S.; Lee, Y.I.; Kim, D.; Bak, Y.-S.; Itaki, T. Late Quaternary glacial–interglacial variations in sediment supply in the southern Drake Passage. Quat. Res. 2012, 78, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões Pereira, P.; van de Flierdt, T.; Hemming, S.R.; Hammond, S.J.; Kuhn, G.; Brachfeld, S.; Doherty, C.; Hillenbrand, C.-D. Geochemical fingerprints of glacially eroded bedrock from West Antarctica: Detrital thermochronology, radiogenic isotope systematics and trace element geochemistry in Late Holocene glacial-marine sediments. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 182, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; van de Flierdt, T.; Hemming, S.R.; Goldstein, S.L. 40Ar/39Ar ages of hornblende grains and bulk Sm/Nd isotopes of circum-Antarctic glacio-marine sediments: Implications for sediment provenance in the southern ocean. Chem. Geol. 2007, 244, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemming, S.; Van de Flierdt, T.; Goldstein, S.; Franzese, A.; Roy, M.; Gastineau, G.; Landrot, G. Strontium isotope tracing of terrigenous sediment dispersal in the Antarctic Circumpolar Current: Implications for constraining frontal positions. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2007, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Molina, F.; Larter, R.; Rebesco, M.; Maldonado, A. Miocene reversal of bottom water flow along the Pacific Margin of the Antarctic Peninsula: Stratigraphic evidence from a contourite sedimentary tail. Mar. Geol. 2006, 228, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Larter, R.D.; Dowdeswell, J.; Ehrmann, W.; Cofaigh, C.Ó.; Benetti, S.; Graham, A.G.; Grobe, H. The sedimentary legacy of a palaeo-ice stream on the shelf of the southern Bellingshausen Sea: Clues to West Antarctic glacial history during the Late Quaternary. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2010, 29, 2741–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larter, R.D.; Anderson, J.B.; Graham, A.G.; Gohl, K.; Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Jakobsson, M.; Johnson, J.S.; Kuhn, G.; Nitsche, F.O.; Smith, J.A. Reconstruction of changes in the Amundsen Sea and Bellingshausen sea sector of the West Antarctic ice sheet since the last glacial maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 100, 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofaigh, C.Ó.; Davies, B.J.; Livingstone, S.J.; Smith, J.A.; Johnson, J.S.; Hocking, E.P.; Hodgson, D.A.; Anderson, J.B.; Bentley, M.J.; Canals, M. Reconstruction of ice-sheet changes in the Antarctic Peninsula since the Last Glacial Maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 100, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rignot, E.; Mouginot, J.; Scheuchl, B.; van den Broeke, M.; van Wessem, M.J.; Morlighem, M. Four decades of Antarctic Ice Sheet mass balance from 1979–2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis: Advanced Course; UW-Madison Libraries Parallel Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Kim, J.-W.; Kogure, T.; Dong, H.; Baik, H.; Hoppie, B.; Harris, R. Smectite, illite, and early diagenesis in South Pacific Gyre subseafloor sediment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaye, P.E. Distinction between kaolinite and chlorite in recent sediments by X-ray diffraction. Am. Miner. J. Earth Planet. Mater. 1964, 49, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, G.; Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Kasten, S.; Smith, J.A.; Nitsche, F.O.; Frederichs, T.; Wiers, S.; Ehrmann, W.; Klages, J.P.; Mogollón, J.M. Evidence for a palaeo-subglacial lake on the Antarctic continental shelf. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Peacor, D.R.; Tessier, D.; Elsass, F. A technique for maintaining texture and permanent expansion of smectite interlayers for TEM observations. Clays Clay Miner. 1995, 43, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.S.; Hendricks, S.B. Minerals of the montmorillonite group, their origin and relation to soils and clays. USGS Numbered Ser. 1945, 205, 23–79. [Google Scholar]
- Setti, M.; Marinoni, L.; López-Galindo, A.; Aboud, A.B. TEM observations and trace element analysis on the clay minerals of the CRP-1 Core (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Terra Antartica 1998, 5, 621–626. [Google Scholar]
- Setti, M.; Marinoni, L.; López-Galindo, A.; Delgado-Hubertas, A. Compositional and morphological features of the smectites of the sediments of CRP-2/2A, Victoria Land Basin, Antarctica. Terra Antart. 2000, 7, 581–587. [Google Scholar]
- Setti, M.; Marinoni, L.; Lopez-Galindo, A. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics (major, minor, trace elements and REE) of detrital and authigenic clay minerals in a Cenozoic sequence from Ross Sea, Antarctica. Clay Miner. 2004, 39, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Yoon, H. The origin of clay minerals in soils of King George Island, South Shetland Islands, West Antarctica, and its implications for the clay-mineral compositions of marine sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 2001, 71, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Dong, H.; Seabaugh, J.; Newell, S.W.; Eberl, D.D. Role of microbes in the smectite-to-illite reaction. Science 2004, 303, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.-h.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.-w. Biogeochemical dissolution of nontronite by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1: Evidence of biotic illite formation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, L.; Setti, M.; Salvi, C.; Lopez-Galindo, A. Clay minerals in late Quaternary sediments from the south Chilean margin as indicators of provenance and palaeoclimate. Clay Miner. 2008, 43, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Ehrmann, W. Late Neogene to Quaternary environmental changes in the Antarctic Peninsula region: evidence from drift sediments. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2005, 45, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, B.; Kuhn, G.; Rachold, V.; Abelmann, A.; Brathauer, U.; Fütterer, D.K.; Gersonde, R.; Grobe, H. Terrigenous sediment supply in the Scotia Sea (Southern Ocean): Response to Late Quaternary ice dynamics in Patagonia and on the Antarctic Peninsula. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2000, 162, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchi, R.; Rebesco, M.; Camerlenghi, A.; Busetti, M.; Tomadin, L.; Villa, G.; Persico, D.; Morigi, C.; Bonci, M.; Giorgetti, G. Mid-late Pleistocene glacimarine sedimentary processes of a high-latitude, deep-sea sediment drift (Antarctic Peninsula Pacific margin). Mar. Geol. 2002, 189, 343–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setti, M.; Marinoni, L.; López-Galindo, A. Crystal-chemistry of smectites in sediments of CRP-3 drillcore (Victoria Land Basin, Antarctica): preliminary results. Terra Antart. 2001, 8, 543–550. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, H.I.; Yoo, K.-C.; Bak, Y.-S.; Lee, Y.I.; Lee, J.I. Core-based reconstruction of paleoenvironmental conditions in the southern Drake Passage (West Antarctica) over the last 150 ka. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2009, 29, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, K.K.D.; Schaefer, C.E.G.; Simas, F.N.B.; Spinola, D.N.; de Paula, M.D. Soil formation in Seymour Island, Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Geomorphology 2014, 225, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.B. Clay mineral changes in Antarctic deep-sea sediments and Cenozoic climatic events. J. Sediment. Res. 1974, 44, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Hillenbrand, C.-D.; Ehrmann, W. Palaeoenvironmental implications of Tertiary sediments from Kainan Maru Seamount and northern Gunnerus Ridge. Antarct. Sci. 2003, 15, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, M.; Smellie, J.L.; Marriner, G. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of Cenozoic alkaline alkaline basalts from Alexander Island, Antarctic Peninsula. In Geological evolution of Antarctica. Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Antarctic Earth Sciences, Cambridge, UK, 23–28 August 1987; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987; pp. 521–526. [Google Scholar]
- Smellie, J. Lithostratigraphy of Miocene–Recent, alkaline volcanic fields in the Antarctic Peninsula and eastern Ellsworth Land. Antarct. Sci. 1999, 11, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarron, J.J. A unifying lithostratigraphy of late Cretaceous–early Tertiary fore-arc volcanic sequences on Alexander Island, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).