Subduction-Induced Fractionated Highly Siderophile Element Patterns in Forearc Mantle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Setting and Sample Description
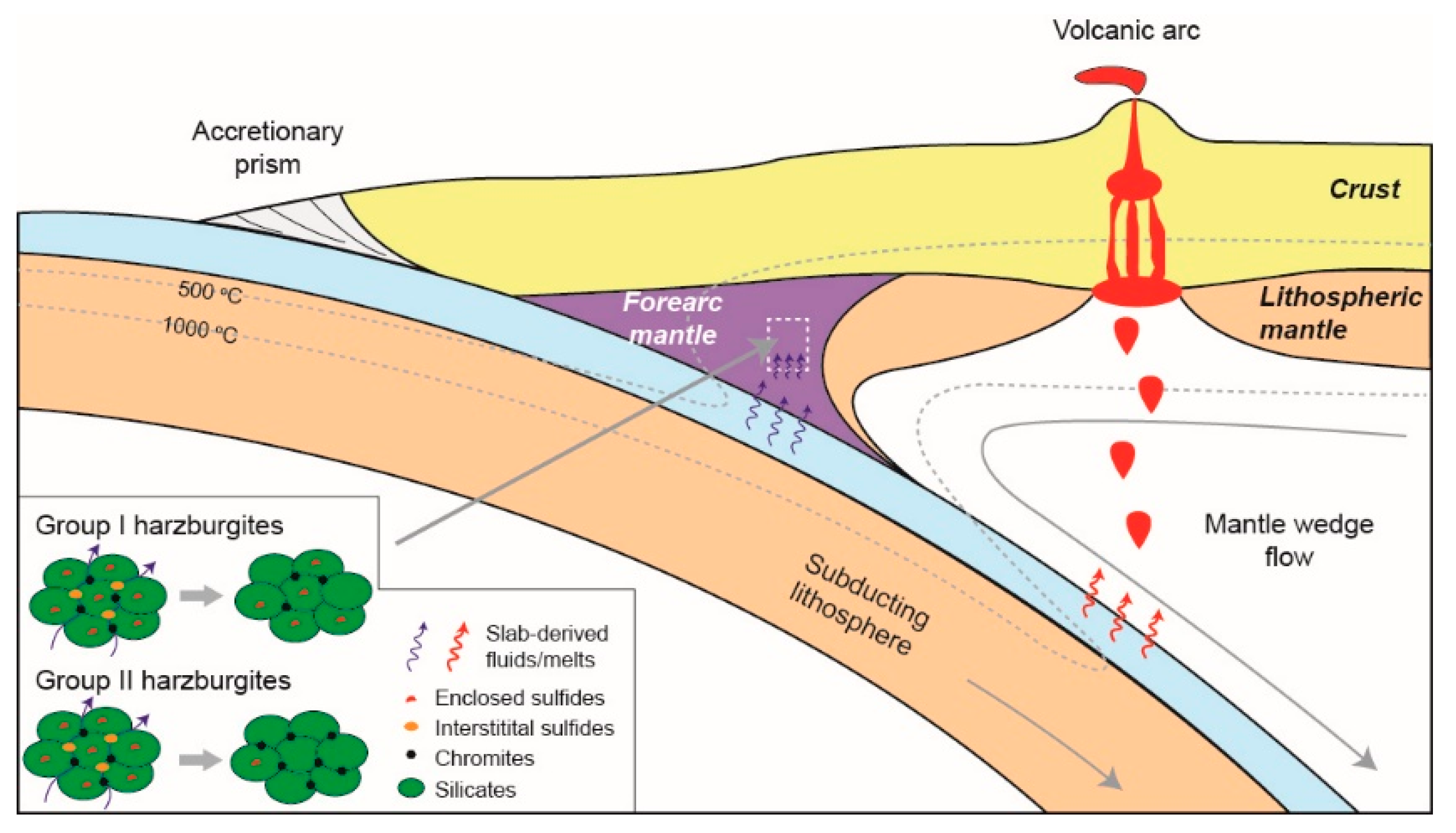
2.1. Geological Setting
2.2. Sample Description
3. Analytical Methods
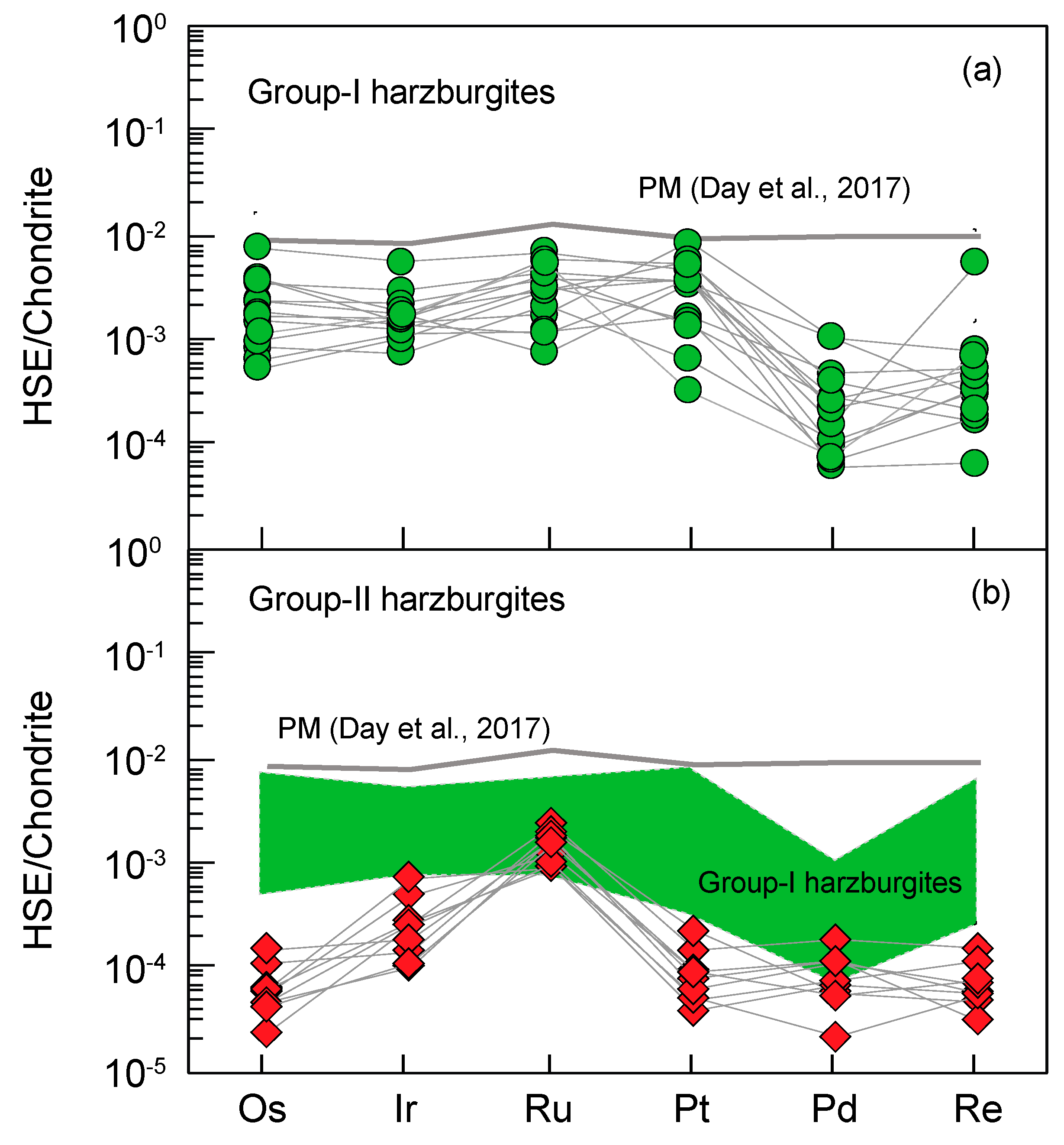
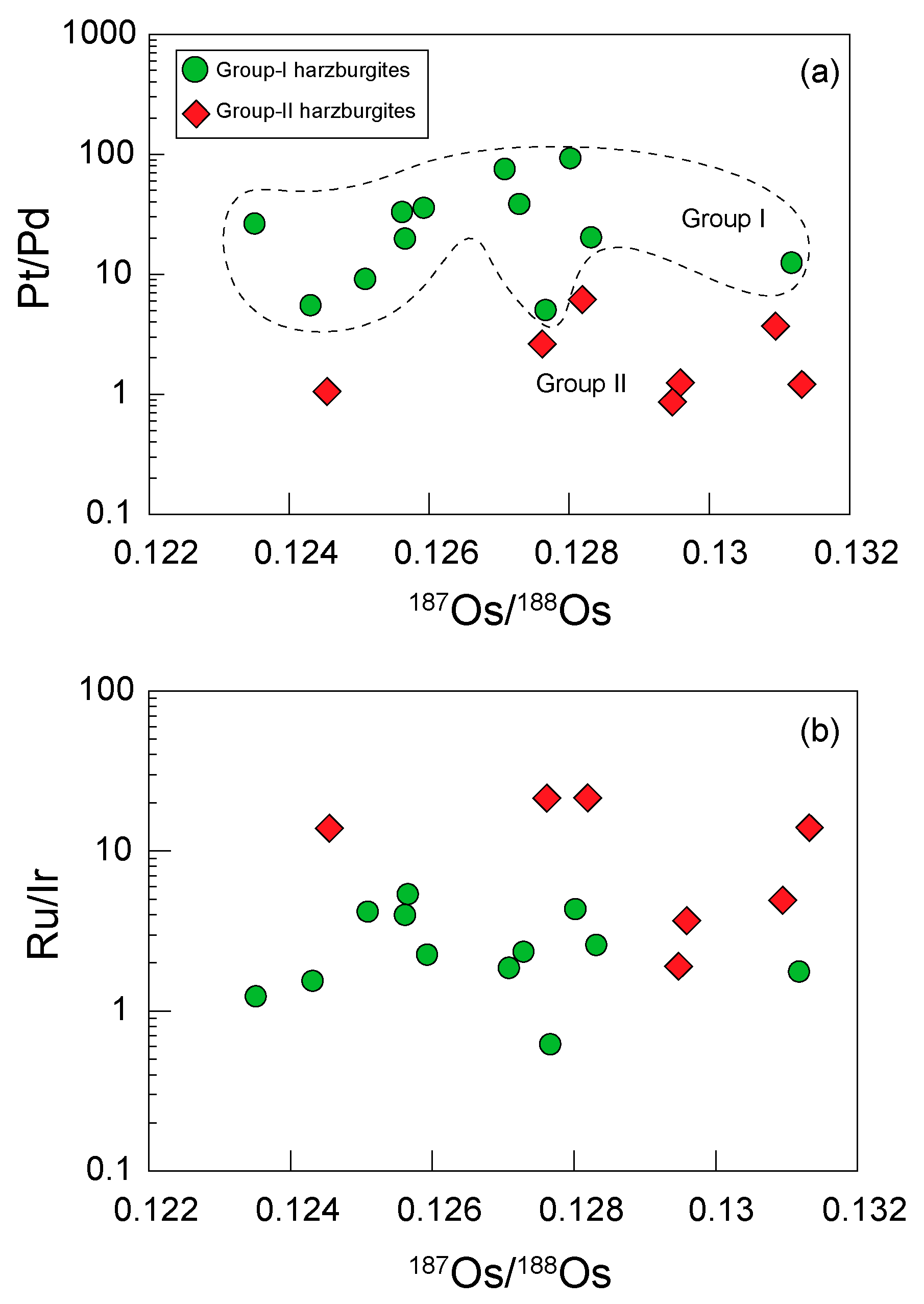
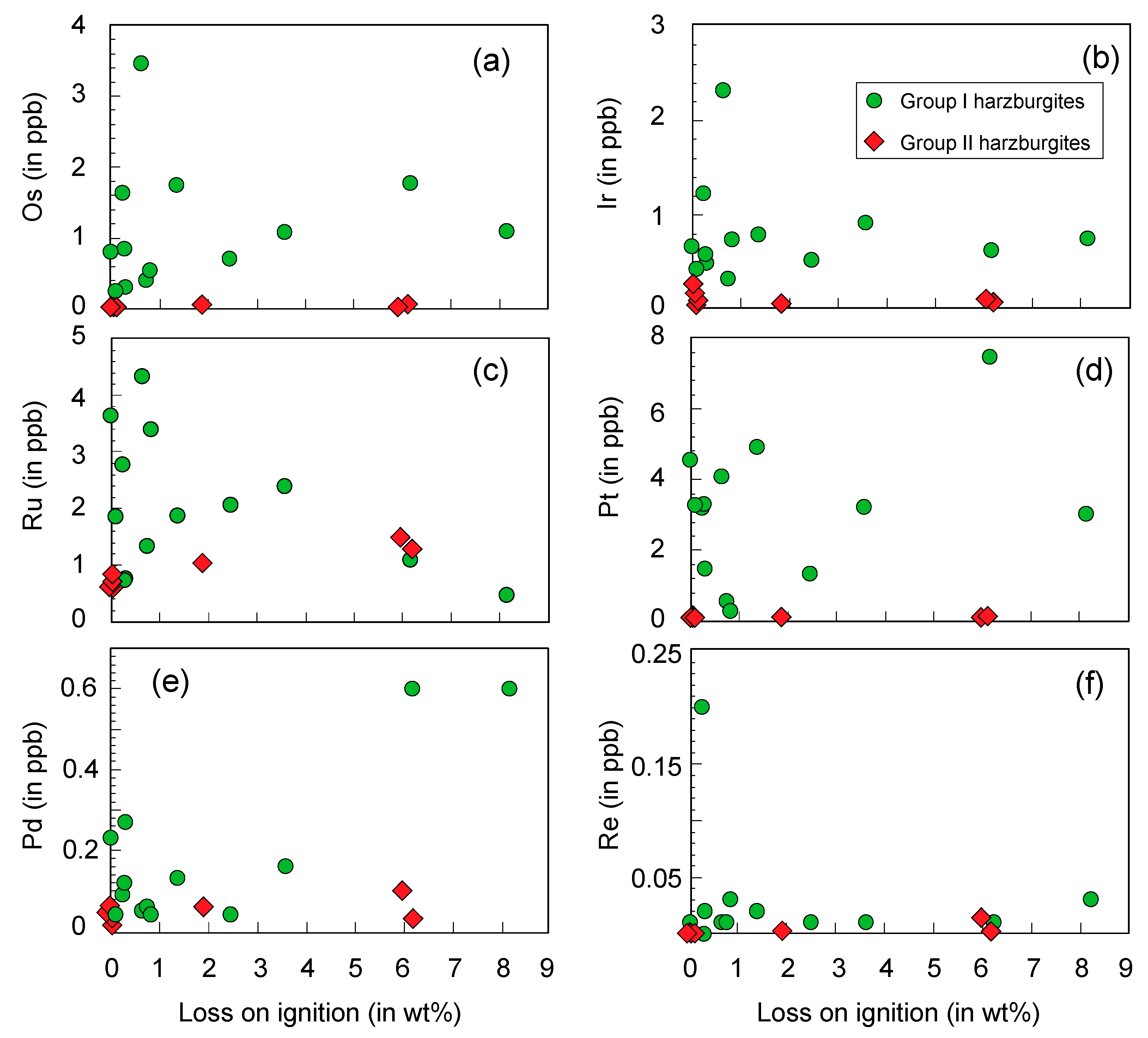
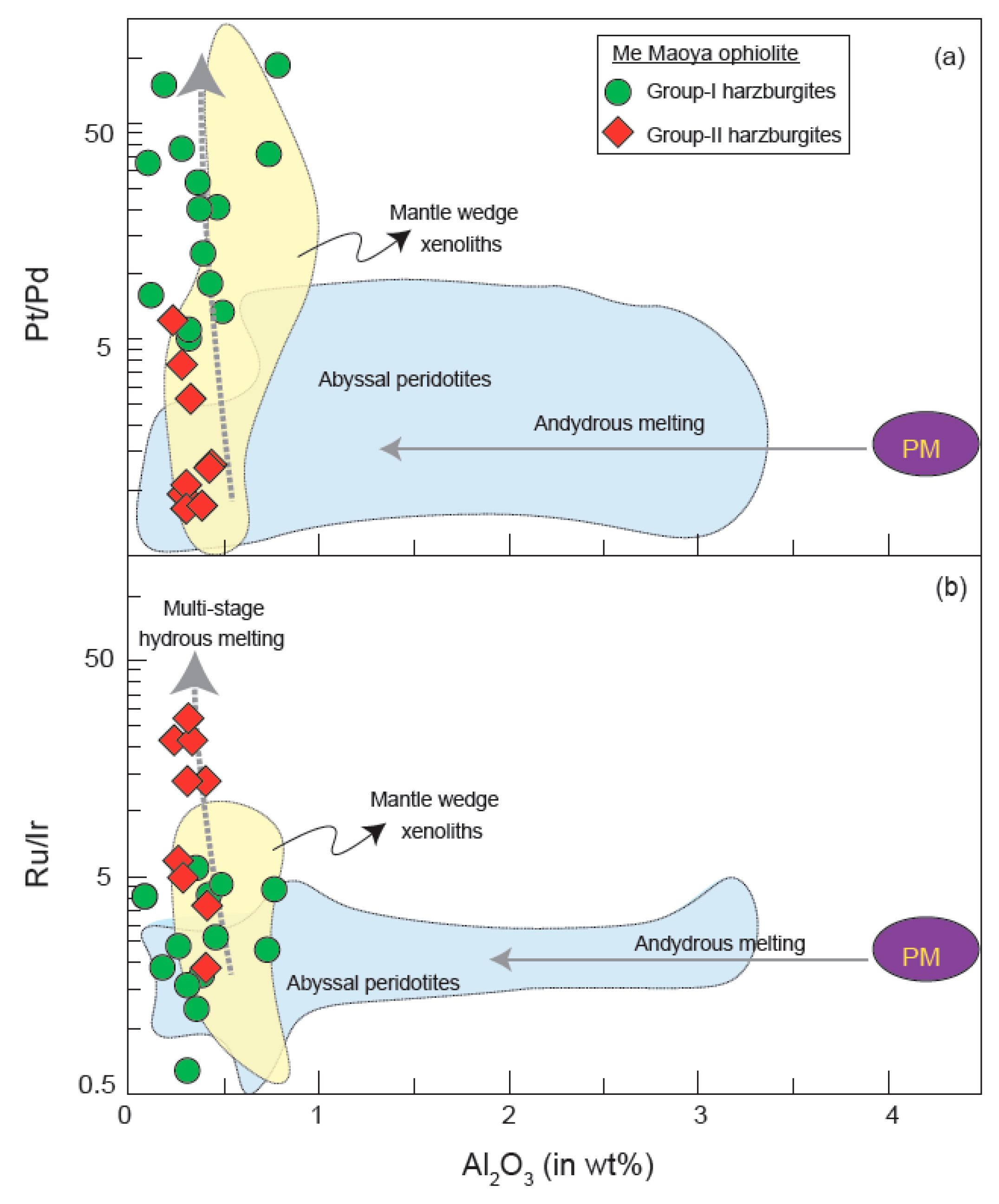
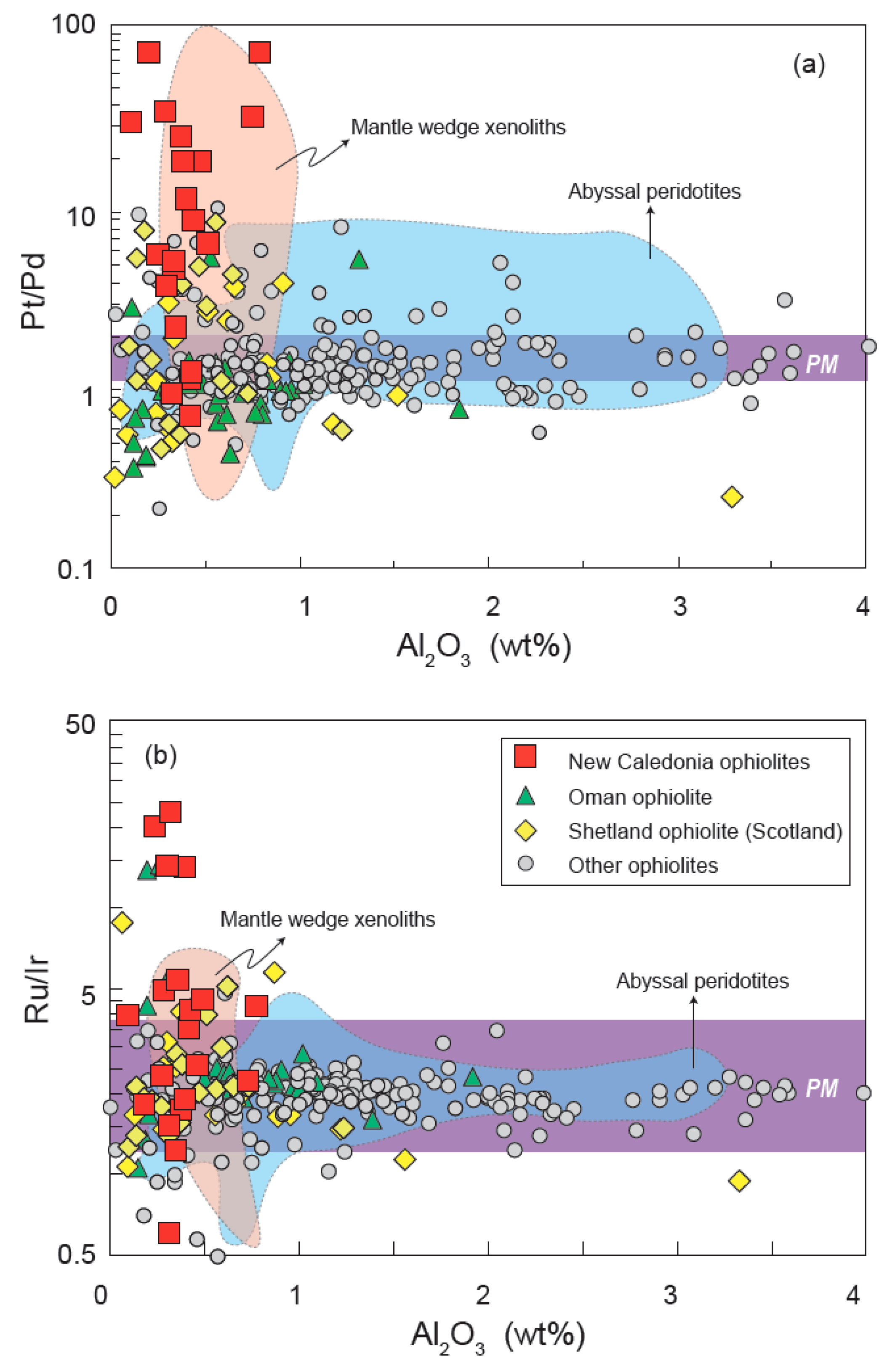
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Day, J.M.D.; Brandon, A.D.; Walker, R.J. Highly siderophile elements in Earth, Mars, the Moon, and asteroids. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2016, 81, 161–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.L. Fractionation of siderophile elements in the Earth’s upper mantle. Proc. Lunar Planet. Sci. 1978, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Holzheid, A.; Sylvester, P.; O’Neill, H.S.C.; Rubie, D.C.; Palme, H. Evidence for a late chondritic veneer in the Earth’s mantle from high-pressure partitioning of palladium and platinum. Nature 2000, 406, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottke, W.F.; Walker, R.J.; Day, J.M.D.; Nesvorny, D.; Elkins-Tanton, L. Stochastic late accretion to Earth, the Moon, and Mars. Science 2010, 330, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattou, L.; Lorand, J.P.; Gros, M. Non-chondritic platinum-group element ratios in the Earth’s mantle. Nature 1996, 379, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehkämper, M.; Halliday, A.N.; Alt, J.; Fitton, J.G.; Zipfel, J.; Takazawa, E. Non-chondritic platinum-group element ratios in oceanic mantle lithosphere: Petrogenetic signature of melt percolation? Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1999, 172, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, J.E.; Schmidt, G. Constraints on Earth accretion deduced from noble metals in the oceanic mantle. Nature 1998, 391, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Horan, M.F.; Walker, R.J.; Gao, S.; Lorand, J.P.; Rudnick, R.L. Highly siderophile element composition of the Earth’s primitive upper mantle: Constraints from new data on peridotite massifs and xenoliths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 4528–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alard, O.; Griffin, W.L.; Lorand, J.P.; Jackson, S.E. Non-chondritic distribution of the highly siderophile elements in mantle sulphides. Nature 2000, 407, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorand, J.P.; Luguet, A.; Alard, O. Platinum group elements: A new set of key tracers for the Earth’s interior. Elements 2009, 4, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.; König, S.; Luguet, A. The effects of melt depletion and metasomatism on highly siderophile and strongly chalcophile elements: S–Se–Te–Re–PGE systematics of peridotite xenoliths from Kilbourne Hole, New Mexico. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 166, 210–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepezhinskas, P.; Defant, M.J. Nonchondritic Pt/Pd ratios in arc mantle xenoliths: Evidence for platinum enrichment in depleted island-arc mantle sources. Geology 2001, 29, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, B.I.; McBride, J.S.; Evans, N.J.; Lambert, D.D.; Andrew, A.S. Osmium isotope constraints on ore metal recycling in subduction zones. Science 1999, 286, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, A.D.; Creaser, R.A.; Shirey, S.B.; Carlson, R.W. Osmium recycling in subduction zones. Science 1996, 272, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirard, C.; Hermann, J.; O’Neill, H.S.C. Petrology and geochemistry of the crust-mantle boundary in a nascent arc, Massif du Sud Ophiolite, New Caledonia, SW Pacific. J. Petrol. 2013, 54, 1759–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, C.; Garrido, C.J.; Godard, M.; Belley, F.; Ferré, E. Migration and accumulation of ultra-depleted subduction-related melts in the Massif du Sud ophiolite (New Caledonia). J. Petrol. 2009, 266, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whattam, S.A. Arc-continent collisional orogenesis in the SW Pacific and the nature, source and correlation of emplaced ophiolitic nappe components. Lithos 2009, 113, 88–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdrolias, M.; Müller, R.D.; Gaina, C. Tectonic evolution of the southwest Pacific using constraints from backarc basins. In Evolution and Dynamics of the Australian Plate; Hillis, R.R., Müller, R.D., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2003; pp. 343–359. [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel, D.; Aitchison, J.C.; Picard, C. Tectonic accretion and underplating of mafic terranes in the Late Eocene intraoceanic fore-arc of New Caledonia (Southwest Pacific): Geodynamic implications. Tectonophysics 2001, 340, 23–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collot, J.Y.; Malahoff, A.; Recy, J.; Latham, G.; Missegue, F. Overthrust Emplacement of New Caledonia Ophiolite: Geophysical Evidence. Tectonics 1987, 6, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriat, M.; Collot, J.; Etienne, S.; Poli, S.; Clerc, C.; Mortimer, N.; Pattier, F.; Juan, C.; Roest, W.R. New Caledonia obducted Peridotite Nappe: offshore extent and implications for obduction and postobduction processes. Tectonics 2018, 37, 1077–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, J. Forearc ophiolites: A view from the western Pacific. In Ophiolites in Earth History; Dilek, Y., Robinson, P.T., Eds.; Geological Society of London Special Publication: London, UK, 2003; Volume 218, pp. 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel, D.; Jourdan, F.; Meffre, S.; Maurizot, P.; Lesimple, S. The metamorphic sole of New Caledonia ophiolite:40Ar/39Ar, U-Pb, and geochemical evidence for subduction inception at a spreading ridge. Tectonics 2012, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzel, D.; Meffre, S.; Maurizot, P.; Crawford, A.J. Earliest Eocene (53Ma) convergence in the Southwest Pacific: evidence from pre-obduction dikes in the ophiolite of New Caledonia. Terra Nova 2006, 18, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, F.Y. Limited recycling of crustal osmium in forearc mantle during slab dehydration. Geology 2018, 43, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cluzel, D.; Maurizot, P.; Collot, J.; Sevin, B.J.E. An outline of the Geology of New Caledonia; from Permian-Mesozoic Southeast-Gondwanaland active margin to Tertiary obduction and supergene evolution. Epis. -Newsmag. Int. Geol. Sci. 2012, 35, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Z.Y.; Wu, F.Y.; Walker, R.J.; Rudnick, R.L.; Pitcher, L.; Puchtel, I.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Wilde, S.A. Temporal Evolution of the Lithospheric Mantle beneath the Eastern North China Craton. J. Petrol. 2009, 50, 1857–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birck, J.L.; Roy-Barman, M.; Capmas, F. Re-Os isotopic measurements at the femtomole level in natural samples. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 1997, 21, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.M.D.; Waters, C.L.; Schaefer, B.F.; Walker, R.J.; Turner, S. Use of Hydrofluoric Acid Desilicification in the Determination of Highly Siderophile Element Abundances and Re-Pt-Os Isotope Systematics in Mafic-Ultramafic Rocks. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2016, 40, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.; Senda, R.; Suzuki, K.; Dale, C.W.; Meisel, T. Re-evaluating digestion methods for highly siderophile element and 187Os isotope analysis: Evidence from geological reference materials. Chem. Geol. 2014, 384, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, P.P.; Liu, J.G.; Wang, X.C.; Yang, A.Y.; Wang, G.Q.; Xu, J.F. Reassessment of Hydrofluoric acid desilicification in the Carius tube digestion technique for Re–Os isotopic determination in geological samples. Geostand. Geoanal. Res. 2015, 39, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.M.D.; Walker, R.J.; Warren, J.M. 186Os–187Os and highly siderophile element abundance systematics of the mantle revealed by abyssal peridotites and Os-rich alloys. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2017, 200, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Gödde, M.; Becker, H.; Wombacher, F. Rhodium, gold and other highly siderophile element abundances in chondritic meteorites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 356–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, C.W.; Cluzel, D. Nickel Laterite Ore Deposits: Weathered Serpentinites. Elements 2013, 9, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Gödde, M.; Becker, H.; Wombacher, F. Rhodium, gold and other highly siderophile elements in orogenic peridotites and peridotite xenoliths. Chem. Geol. 2011, 280, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foustoukos, D.I.; Bizimis, M.; Frisby, C.; Shirey, S.B. Redox controls on Ni–Fe–PGE mineralization and Re/Os fractionation during serpentinization of abyssal peridotite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 150, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luguet, A.; Lorand, J.P.; Seyler, M. Sulfide petrology and highly siderophile element geochemistry of abyssal peridotites: a coupled study of samples from the Kane Fracture Zone (45°W 23°20N, MARK area, Atlantic Ocean). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 1553–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.G.; Irvine, G.J.; Ionov, D.A.; Boyd, F.R.; Dreibus, G.E. Re–Os isotope systematics and platinum group element fractionation during mantle melt extraction: a study of massif and xenolith peridotite suites. Chem. Geol. 2004, 208, 29–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockrath, C.; Ballhaus, C.; Holzheid, A. Fractionation of the platinum-group elements during mantle melting. Science 2004, 305, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballhaus, C.; Bockrath, C.; Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser, C.; Laurenz, V.; Berndt, J. Fractionation of the noble metals by physical processes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2006, 152, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Barnes, S.-J.; Makovicky, E.; Rose-Hansen, J.; Makovicky, M. Partitioning of nickel, copper, iridium, rhenium, platinum, and palladium between monosulfide solid solution and sulfide liquid: Effects of composition and temperature. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augé, T.Y.; Cabri, L.J.; Legendre, O.; McMahon, G.; Cocherie, A. PGE distribution in base-metal alloys and sulfides of the New Caledonia Ophiolite. Can. Mineral. 1999, 37, 1147–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Brandon, A.D.; Snow, J.E.; Walker, R.J.; Morgan, J.W.; Mock, T.D. 190Pt–186Os and 187Re–187Os systematics of abyssal peridotites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 177, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Snow, J.E.; Brügmann, G.; Hellebrand, E.; Hofmann, A.W. Non-chondritic HSE budget in Earth’s upper mantle evidenced by abyssal peridotites from Gakkel ridge (Arctic Ocean). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 283, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, C.; Garrido, C.J.; Harvey, J.; González-Jiménez, J.M.; Hidas, K.; Lorand, J.-P.; Gervilla, F. Platinum-group elements, S, Se and Cu in highly depleted abyssal peridotites from the Mid-Atlantic Ocean Ridge (ODP Hole 1274A): Influence of hydrothermal and magmatic processes. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2013, 166, 1521–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handler, M.R.; Bennett, V.C.; Dreibus, G. Evidence from correlated Ir/Os and Cu/S for late-stage Os mobility in peridotite xenoliths: Implications for Re-Os systematics. Geology 1999, 27, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubie, D.C.; Laurenz, V.; Jacobson, S.A.; Morbidelli, A.; Palme, H.; Vogel, A.K.; Frost, D.J. Highly siderophile elements were stripped from Earth’s mantle by iron sulfide segregation. Science 2016, 353, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luguet, A.; Shirey, S.B.; Lorand, J.-P.; Horan, M.F.; Carlson, R.W. Residual platinum-group minerals from highly depleted harzburgites of the Lherz massif (France) and their role in HSE fractionation of the mantle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3082–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, B.; Garwood, R.; Day, J.M.D.; Wogelius, R. Platinum-group element remobilization and concentration in the Cliff chromitites of the Shetland Ophiolite Complex, Scotland. Mineral. Mag. 2018, 82, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorand, J.P.; Luguet, A. Chalcophile and Siderophile Elements in Mantle Rocks: Trace Elements Controlled By Trace Minerals. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2016, 81, 441–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, M.L.; Beresford, S.W.; Barley, M.E. Ruthenium-chromium variation: A new ltihogeochemical tool in the exploration for komatiite-hosted Ni-Cu-(PGE) deposit. Econ. Geol. 2008, 103, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locmelis, M.; Pearson, N.L.; Barnes, S.J.; Fiorentini, M.L. Ruthenium in komatiitic chromite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 3645–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, B.; Walker, R.J.; Day, J.M.D.; Ash, R.D.; Daly, J.S. Generations of melt extraction, melt–rock interaction and high-temperature metasomatism preserved in peridotites of the∼ 497 Ma Leka Ophiolite Complex, Norway. J. Petrol. 2015, 56, 1797–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagé, P.; Barnes, S.J.; Bédard, J.H.; Zientek, M.L. In situ determination of Os, Ir, and Ru in chromites formed from komatiite, tholeiite and boninite magmas: Implications for chromite control of Os, Ir and Ru during partial melting and crystal fractionation. Chem. Geol. 2012, 302–303, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, C.J.; Drake, M.J. Partitoning of ruthenium, rhodium, and palladium between spinel and silicate melt and implications for platinum group element fractionation trends. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brounce, M.; Kelley, K.A.; Cottrell, E.; Reagan, M.K. Temporal evolution of mantle wedge oxygen fugacity during subduction initiation. Geology 2015, 43, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, M.A.; Riddle, J.; Desjardins-Langlais, Y.; Baker, D.R. The effect of water on the sulfur concentration at sulfide saturation (SCSS) in natural melts. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 160, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanghøj, K.; Kelemen, P.B.; Hassler, D.; Godard, M. Composition and Genesis of Depleted Mantle Peridotites from the Wadi Tayin Massif, Oman Ophiolite; Major and Trace Element Geochemistry, and Os Isotope and PGE Systematics. J. Petrol. 2010, 51, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, C.J.; Lissenberg, C.J.; Bibby, L.E. “Moist MORB” axial magmatism in the Oman ophiolite: The evidence against a mid-ocean ridge origin. Geology 2013, 41, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, B.; Day, J.M.D.; Walker, R.J.; Daly, J.S.; Mcdonough, W.F.; Piccoli, P.M. Chemical heterogeneity in the upper mantle recorded by peridotites and chromitites from the Shetland Ophiolite Complex, Scotland. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 333–334, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, B.; Walker, R.J.; Clay, P.L.; Day, J.M.D.; Ash, R.D.; Daly, J.S. Length-scales of chemical and isotopic heterogeneity in the mantle section of the Shetland Ophiolite Complex, Scotland. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 488, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldanmaz, E.; Koprubasi, N. Platinum-Group-Element Systematics of Peridotites from Ophiolite Complexes of Northwest Anatolia, Turkey: Implications for Mantle Metasomatism by Melt Percolation in a Supra-subduction Zone Environment. Int. Geol. Rev. 2006, 48, 420–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batanova, V.G.; Brügmann, G.E.; Bazylev, B.A.; Sobolev, A.V.; Kamenetsky, V.S.; Hofmann, A.W. Platinum-group element abundances and Os isotope composition of mantle peridotites from the Mamonia complex, Cyprus. Chem. Geol. 2008, 248, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchl, A.; Brügmann, G.; Batanova, V.G.; Münker, C.; Hofmann, A.W. Melt percolation monitored by Os isotopes and HSE abundances: A case study from the mantle section of the Troodos Ophiolite. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 204, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Wu, F.Y.; Wilde, S.A.; Yu, L.J.; Li, J.L. Anorthitic plagioclase and pargasitic amphibole in mantle peridotites from the Yungbwa ophiolite (southwestern Tibetan Plateau) formed by hydrous melt metasomatism. Lithos 2010, 114, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, C.Z.; Zhang, C.; Ji, W.B.; Xu, Y. Reconsideration of Neo-Tethys evolution constrained from the nature of the Dazhuqu ophiolitic mantle, southern Tibet. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 2019, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, J.E.; Schmidt, G.; Rampone, E. Os isotopes and highly siderophile elements (HSE) in the Ligurian ophiolites, Italy. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2000, 175, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, I.; Ersoy, E.Y.; Karslı, O.; Dilek, Y.; Sadıklar, M.B.; Ottley, C.J.; Tiepolo, M.; Meisel, T. Coexistence of abyssal and ultra-depleted SSZ type mantle peridotites in a Neo-Tethyan Ophiolite in SW Turkey: Constraints from mineral composition, whole-rock geochemistry (major–trace–REE–PGE), and Re–Os isotope systematics. Lithos 2012, 132–133, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Robinson, P.T.; Malpas, J.; Edwards, S.J.; Qi, L. REE and PGE Geochemical Constraints on the Formation of Dunites in the Luobusa Ophiolite, Southern Tibet. J. Petrol. 2005, 46, 615–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, R.F.; Schilling, M.; Anma, R.; Farquhar, J.; Horan, M.F.; Komiya, T.; Piccoli, P.M.; Pitcher, L.; Walker, R.J. Chemical and chronologic complexity in the convecting upper mantle: Evidence from the Taitao ophiolite, southern Chile. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 5793–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Al2O3 | MgO | CaO | LOI | Ol Fo | Sp Cr# | Os | Ir | Ru | Pt | Pd | Re | (Os/Ir)N | (Ru/Ir)N | (Ru/Os)N | (Pt/Pd)N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standards | ||||||||||||||||
| WPR-1 | 16.9 | 16.7 | 23.7 | 308 | 240 | 11.2 | ||||||||||
| UB-N | 3.54 | 3.20 | 6.33 | 6.95 | 5.83 | 0.22 | ||||||||||
| BHVO-2 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 5.52 | 2.73 | 0.57 | ||||||||||
| Group-I harzburgites | ||||||||||||||||
| 15NC11 | 0.39 | 43.41 | 0.36 | 6.17 | 0.92 | 0.55 | 1.76 | 0.62 | 1.09 | 7.46 | 0.60 | 0.011 | 2.59 | 1.18 | 0.46 | 8.10 |
| 15NC12 | 0.32 | 42.37 | 0.40 | 8.15 | 0.91 | 0.55 | 1.09 | 0.75 | 0.46 | 3.01 | 0.60 | 0.029 | 1.32 | 0.41 | 0.31 | 3.27 |
| 15NC17 | 0.19 | 45.53 | 0.45 | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.68 | 3.45 | 2.32 | 4.33 | 4.07 | 0.05 | 0.013 | 1.36 | 1.25 | 0.92 | 53.03 |
| 15NC21 | 0.43 | 45.68 | 0.48 | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.32 | 1.33 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 0.012 | 1.11 | 2.79 | 2.51 | 6.08 |
| 15NC23 | 0.32 | 46.53 | 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 1.47 | 0.27 | 0.019 | 0.56 | 1.04 | 1.86 | 3.55 |
| 15NC25 | 0.74 | 45.09 | 0.51 | 0.24 | 0.93 | 0.57 | 1.62 | 1.23 | 2.78 | 3.19 | 0.09 | 0.197 | 1.20 | 1.52 | 1.26 | 23.09 |
| 15NC27 | 0.47 | 43.40 | 0.56 | 3.58 | 0.91 | 0.55 | 1.07 | 0.92 | 2.40 | 3.23 | 0.16 | 0.006 | 1.06 | 1.75 | 1.65 | 13.15 |
| 15NC28 | 0.28 | 45.09 | 0.42 | 1.36 | 0.91 | 0.66 | 1.73 | 0.79 | 1.87 | 4.90 | 0.13 | 0.016 | 2.00 | 1.59 | 0.80 | 24.56 |
| 15NC29 | 0.36 | 45.29 | 0.56 | 0.28 | 0.91 | 0.59 | 0.84 | 0.58 | 0.72 | 3.29 | 0.12 | 0.001 | 1.32 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 17.86 |
| 15NC30 | 0.78 | 44.45 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.92 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.43 | 1.86 | 3.26 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.51 | 2.90 | 5.70 | 53.10 |
| 15NC31 | 0.10 | 45.24 | 0.22 | 2.46 | 0.91 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.52 | 2.06 | 1.33 | 0.04 | 0.010 | 1.23 | 2.66 | 2.17 | 21.66 |
| 15NC31-R | 0.46 | 0.66 | 2.68 | 1.20 | 0.15 | 0.020 | 0.64 | 2.72 | 4.29 | 5.21 | ||||||
| 15NC33 | 0.50 | 44.84 | 0.42 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 3.40 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.026 | 0.65 | 3.08 | 4.72 | 4.56 |
| 15NC34 | 0.37 | 45.42 | 0.49 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.79 | 0.67 | 3.64 | 4.55 | 0.23 | 0.008 | 1.07 | 3.64 | 3.39 | 12.89 |
| Group-II harzburgites | ||||||||||||||||
| 15NC13 | 0.41 | 43.33 | 0.42 | 5.96 | 0.92 | 0.59 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 1.43 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.005 | 0.18 | 9.59 | 52.63 | 0.78 |
| 15NC15 | 0.24 | 43.72 | 0.36 | 6.18 | 0.92 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 1.21 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.002 | 0.76 | 13.53 | 17.81 | 3.91 |
| 15NC20 | 0.42 | 45.99 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.92 | 0.60 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.72 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.001 | 0.09 | 2.42 | 26.50 | 0.87 |
| 15NC22 | 0.41 | 45.50 | 0.37 | −0.06 | 0.92 | 0.63 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.10 | 1.29 | 13.25 | 0.49 |
| 15NC24 | 0.29 | 45.75 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.92 | 0.64 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.54 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.25 | 3.29 | 13.25 | 2.61 |
| 15NC24-R | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.60 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.09 | 4.03 | 44.17 | 0.65 | ||||||
| 15NC26 | 0.31 | 45.46 | 0.32 | 1.88 | 0.92 | 0.59 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 1.01 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.001 | 0.78 | 9.68 | 12.39 | 0.65 |
| 15NC26-R | 0.02 | 0.04 | 1.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.46 | 17.95 | 39.38 | 0.54 | ||||||
| 15NC32 | 0.33 | 45.87 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.92 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.92 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.46 | 15.43 | 33.86 | 1.52 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Liu, C.-Z. Subduction-Induced Fractionated Highly Siderophile Element Patterns in Forearc Mantle. Minerals 2019, 9, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060339
Xu Y, Liu C-Z. Subduction-Induced Fractionated Highly Siderophile Element Patterns in Forearc Mantle. Minerals. 2019; 9(6):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060339
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yang, and Chuan-Zhou Liu. 2019. "Subduction-Induced Fractionated Highly Siderophile Element Patterns in Forearc Mantle" Minerals 9, no. 6: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060339
APA StyleXu, Y., & Liu, C.-Z. (2019). Subduction-Induced Fractionated Highly Siderophile Element Patterns in Forearc Mantle. Minerals, 9(6), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9060339





