Fluid Inclusions and S–Pb Isotopes of the Reshui Porphyry Mo Deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
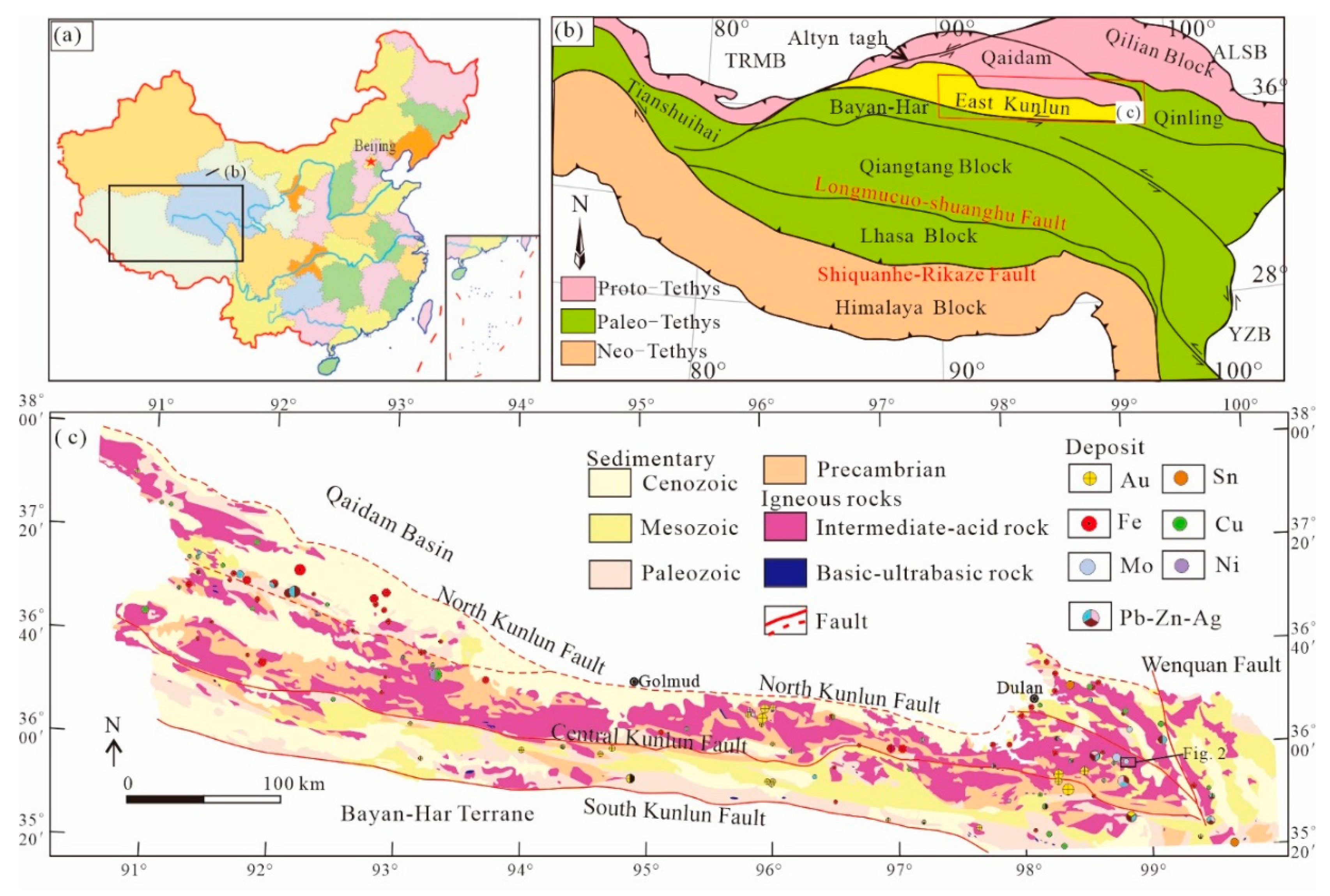
2. Regional Geology
3. Ore Deposit Geology
4. Analytical Methods
4.1. Fluid Inclusion Measurements
4.2. Isotopic Analysis
5. Results
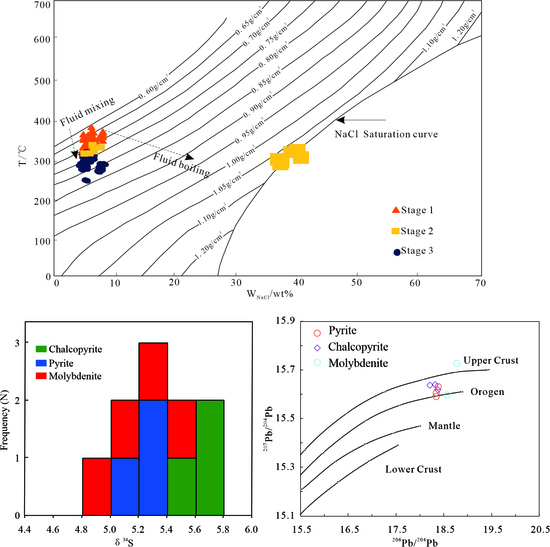
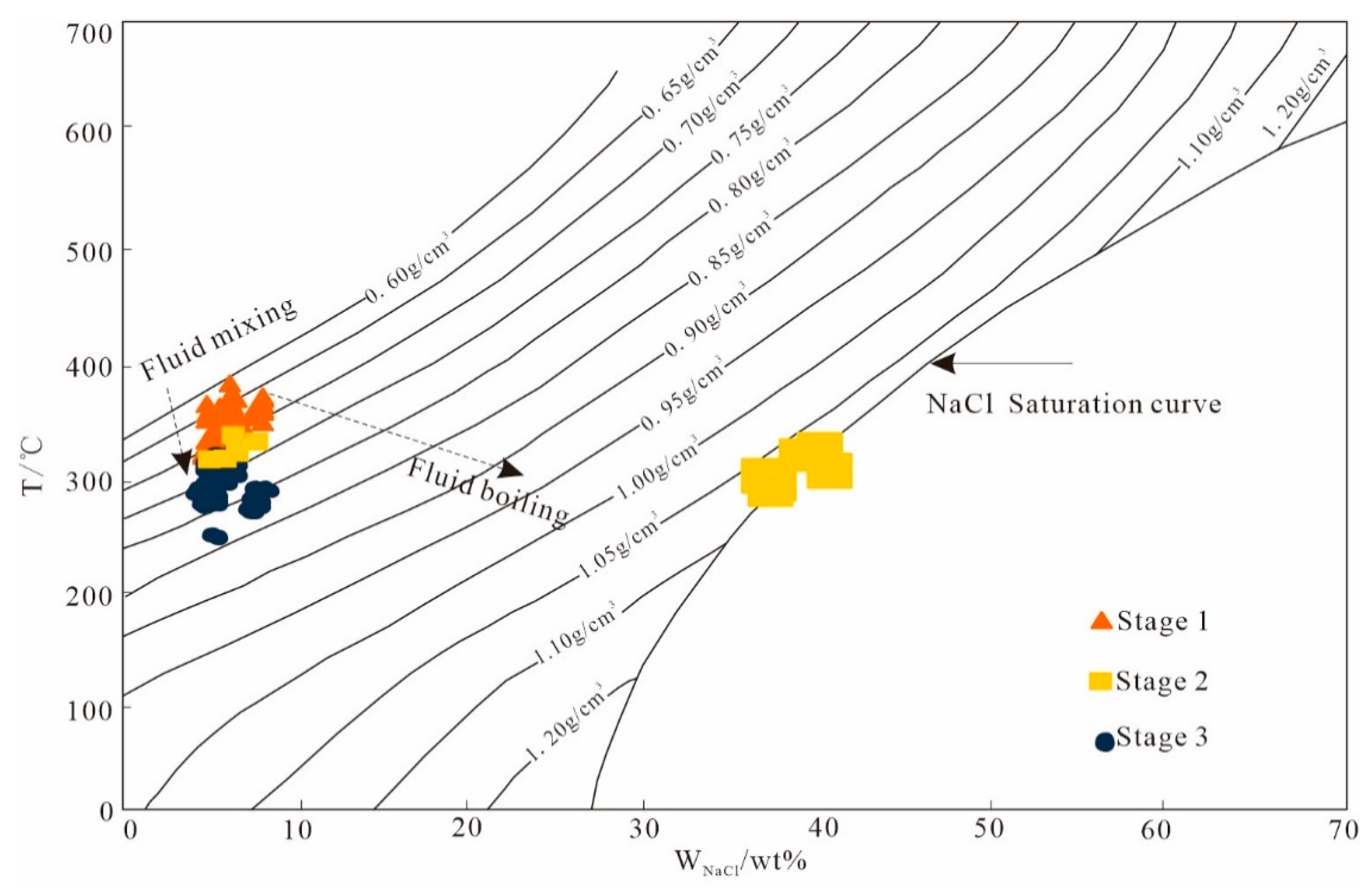
5.1. Fluid Inclusion Analysis
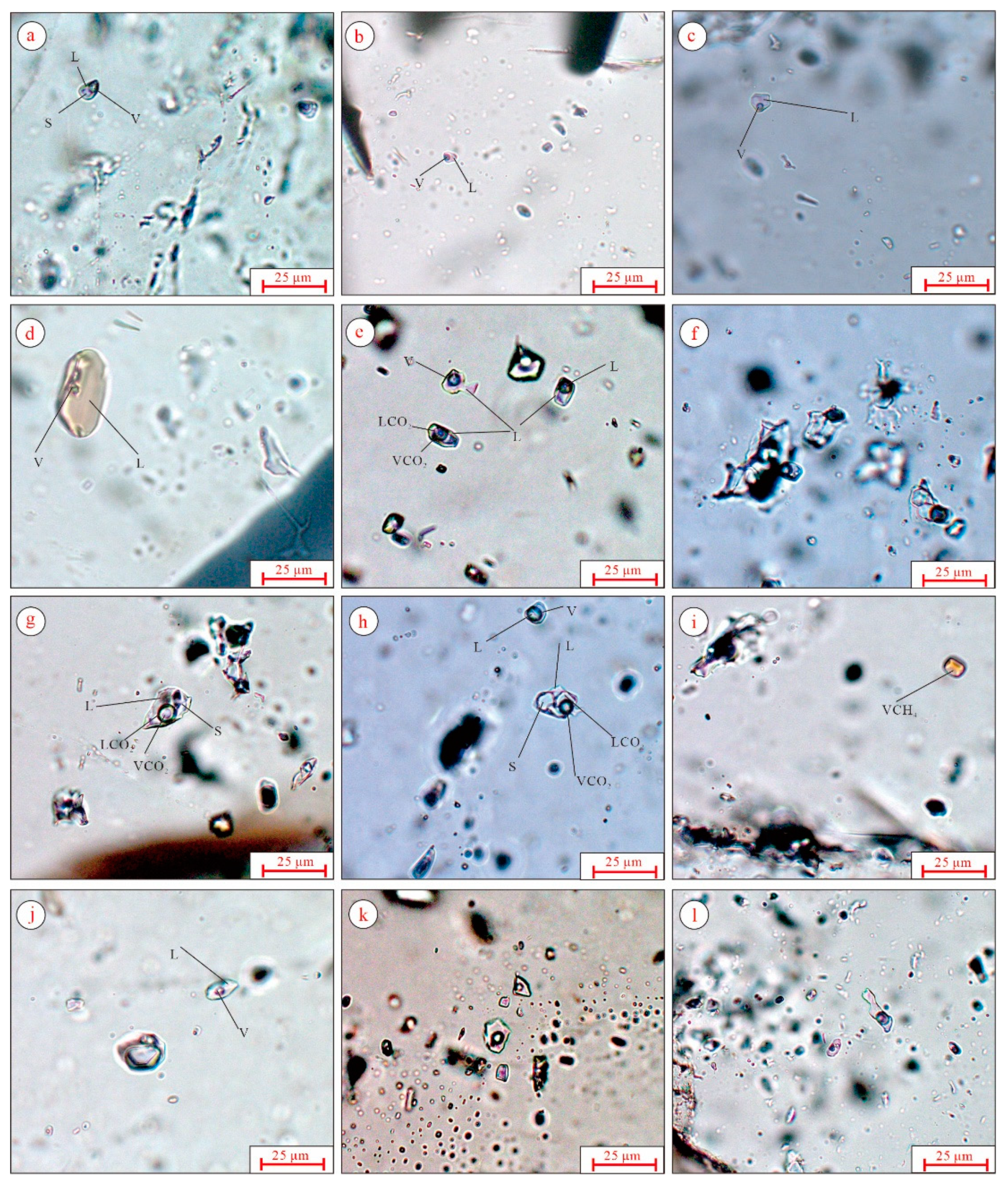
5.1.1. Petrography
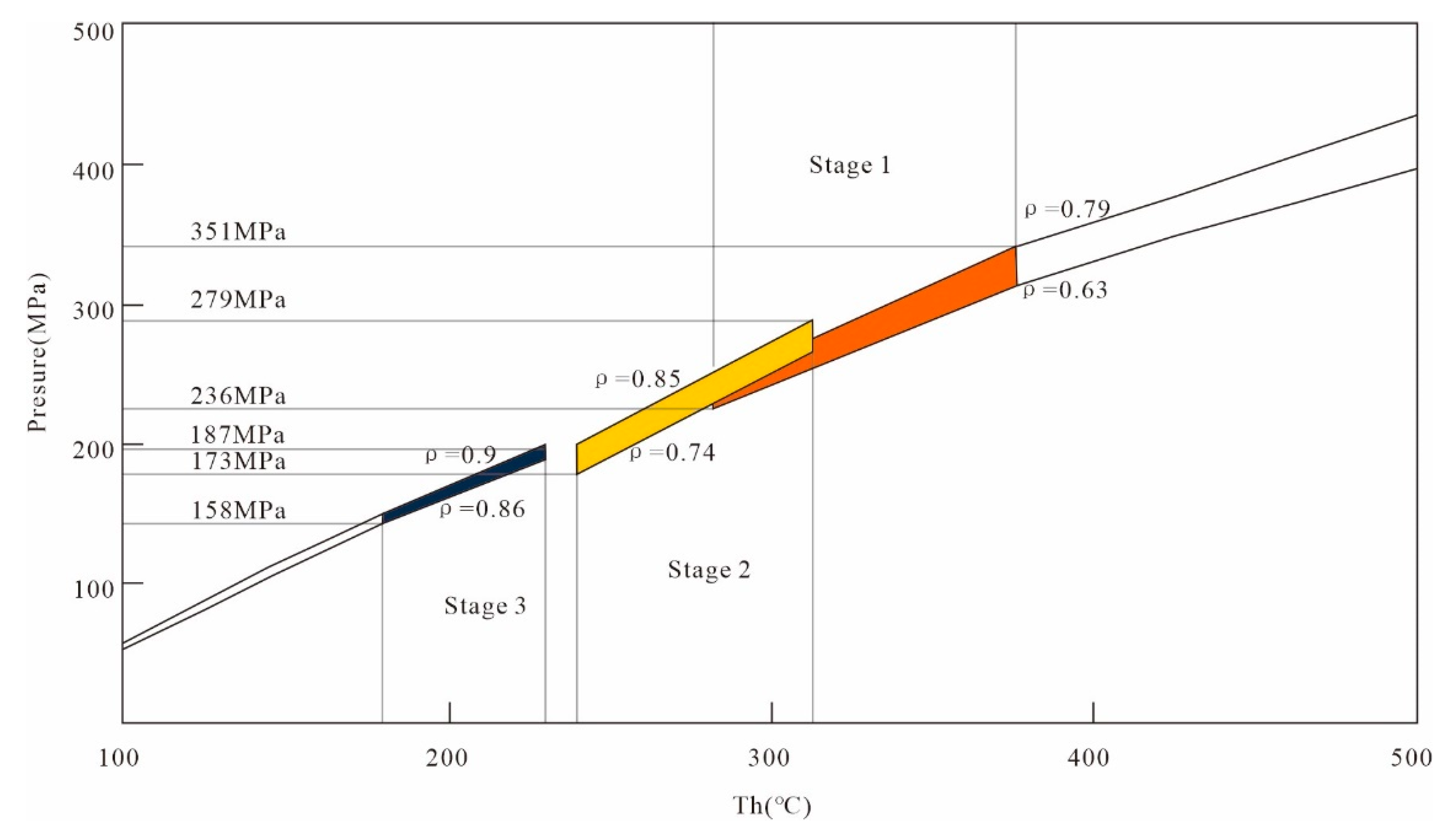
5.1.2. Microthermometry
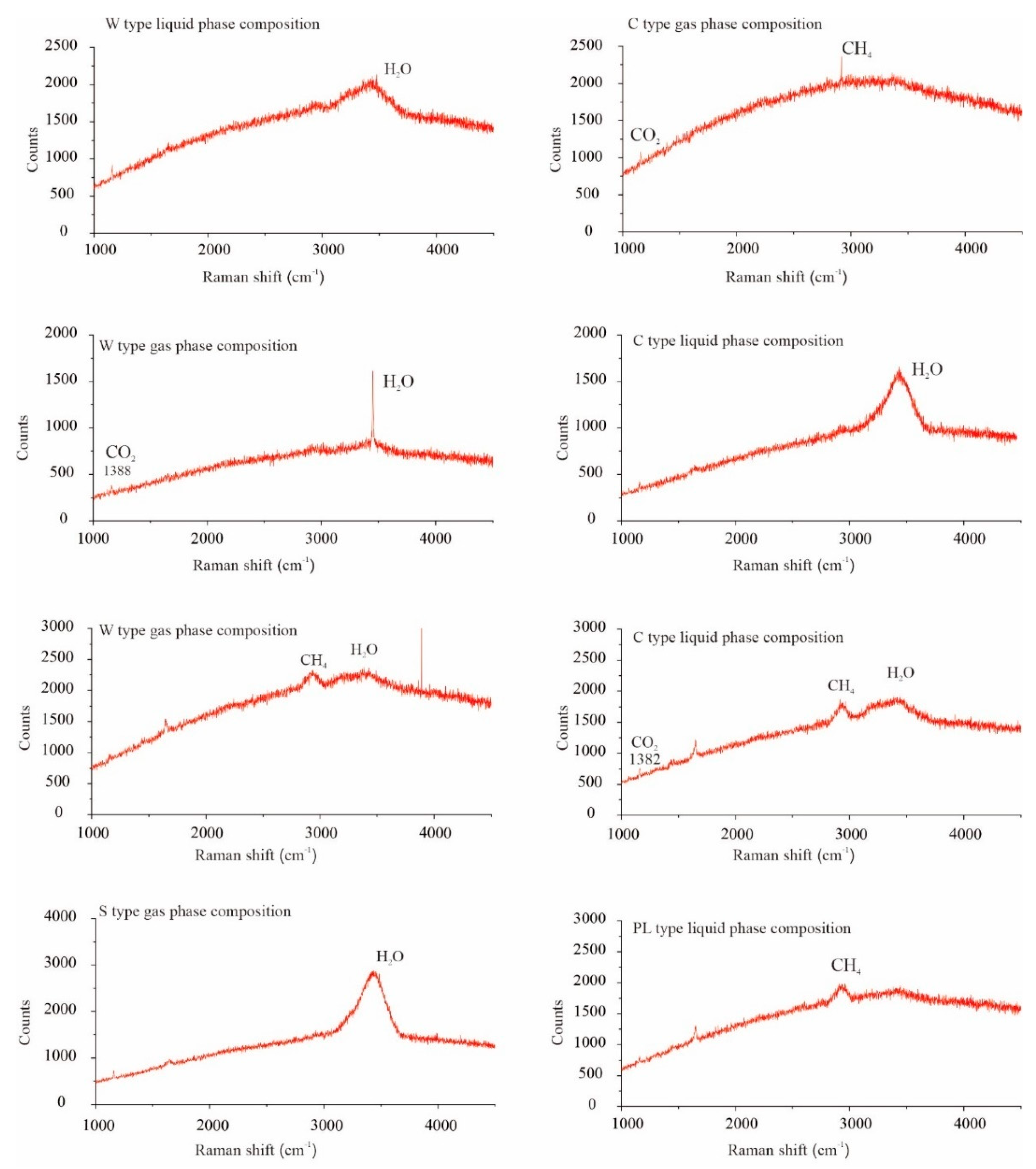
5.1.3. Laser Raman Spectroscopy
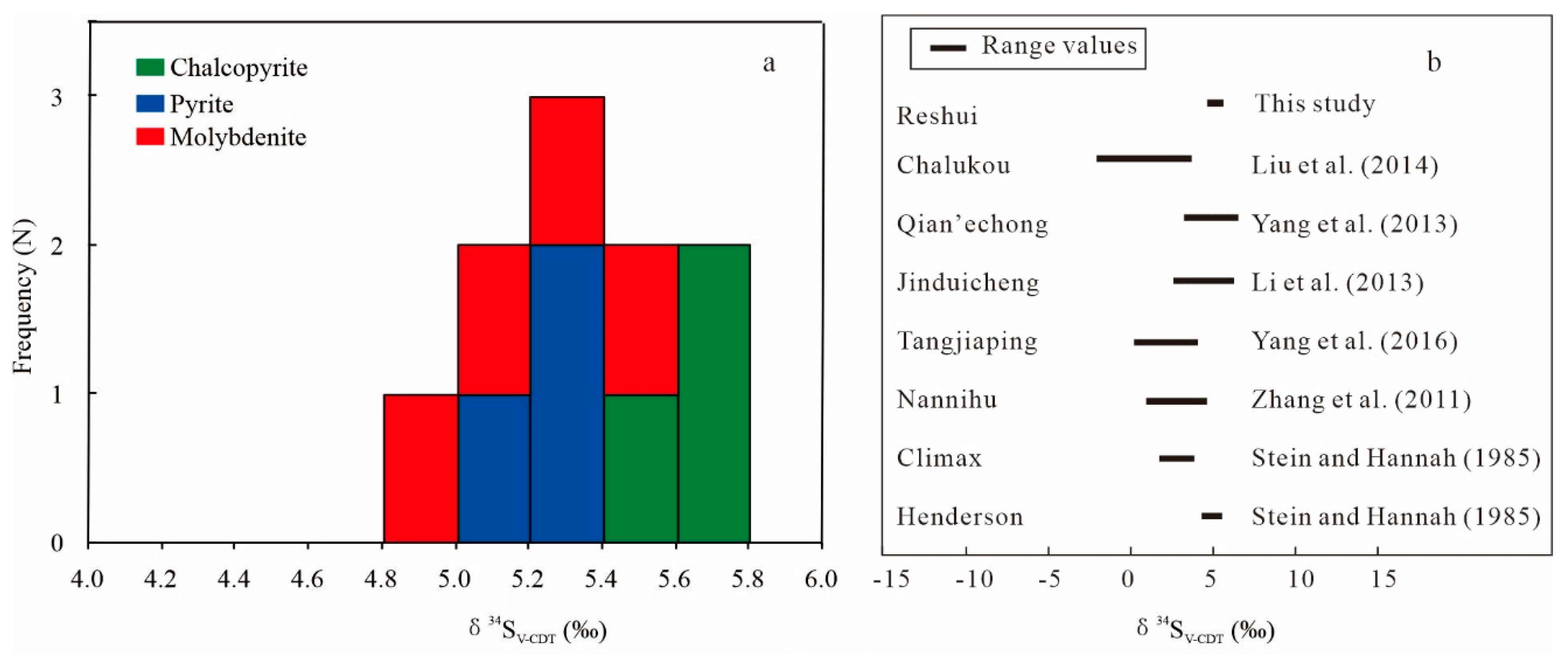
5.2. S and Pb Isotopes
6. Discussion
6.1. Timing of Magmatism and Mineralization
6.2. Evolution of the Ore-Forming Fluid
6.3. Source of Ore-Forming Materials
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liou, J.G.; Ernst, W.G.; Song, S.G.; Jahn, B.M. Tectonics and HP–UHP metamorphism of northern Tibet-preface. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Wang, P. Geology, geochemistry and tectonic settings of molybdenum deposits in Southwest China: A review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 965–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, D.L.; Li, S.Z.; Wang, Q.; Somerville, I.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhao, S.J.; Li, X.Y.; Yu, S.Y.; Suo, Y.H. Early Paleozoic Orocline in the Central China Orogen. Gondwana Res. 2018, 63, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Wei, J.H.; Fu, L.B.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhan, X.F.; Tan, J. Multiple sources of the Early Mesozoic Gouli batholith, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau: Linking continental crustal growth with oceanic subduction. Lithos 2017, 292–293, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.L.; Niu, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Kong, J.J.; Duan, M. Petrogenesis of Triassic granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Tibetan Plateau and their tectonic implications. Lithos 2017, 282–283, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.P.; He, D.F.; Sun, S.S.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhang, F.F.; Yang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, G.C.; Li, J.H. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 186, 231–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.G.; Li, W.Y.; Jia, Q.Z.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, Z.A.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, J.W.; Qian, B. The dynamic sulfide saturation process and a possible slab break-off model for the giant Xiarihamu magmatic nickel ore deposit in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Econ. Geol. 2018, 113, 1383–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Qian, B.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhang, D.Y.; Lü, P.R.; Dong, J. Metallogeny and tectonomagmatic setting of Ni-Cu magmatic sulfide mineralization, number I Shitoukengde mafic-ultramafic complex, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 96, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, C.M.; Qing, M.; Deng, J.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Li, W.L.; Guo, X.D.; Ge, L.S.; Yu, W.Q. Molybdenite Re–Os, zircon U–Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of the Shuangqing Fe–Pb–Zn–Cu skarn deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 66, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, C.Y.; Li, R.X.; Li, D.X. Geological characteristics, metallogenesis, and tectonic setting of porphyry-skarn Cu deposits in East Kunlun Orogen. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Lü, Z.C.; Zhao, C.S.; Pang, Z.S.; Yu, X.F.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, M.C. Zircon U–Pb geochronological, trace element, and Hf isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Fe and Cu skarn deposits in the Qiman Tagh area, Qinghai Province, Eastern Kunlun Orogen, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; An, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.K.; Gao, Y.N.; Yang, L.W. Fractal characteristics of fault systems and their geological significance in the Hutouya poly-metallic orefield of Qimantage, East Kunlun, China. Geol. J. 2017, 52, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Dai, T.G.; Mao, X.C.; Lei, Y.B.; Lai, J.Q.; Tian, H.L. Finite difference modeling of metallogenic processes in the Hutouya Pb–Zn deposit, Qinghai, China: Implications for hydrothermal mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 91, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Wu, L.; Jiang, H.A.; Liu, B. Geochemistry, zircon U–Pb ages and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopes of an Ordovician appinitic pluton in the East Kunlun orogen: New evidence for Proto-Tethyan subduction. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 111, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Huang, X.F.; Luo, M.F.; Dong, G.C.; Mo, X.X. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the Mid-Triassic lavas from East Kunlun, northern Tibetan Plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2015, 105, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Feng, C.Y.; Santosh, M.; Mao, J.W.; Zhu, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.M.; Li, D.X.; Li, B. The Qiman Tagh Orogen as a window to the crustal evolution in northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 167, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, C.Q.; Xiong, F.H.; Liu, B. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Late Permian-Middle Triassic calc-alkaline granites in the Balong region, eastern Kunlun Orogen, China. Geol. Mag. 2012, 149, 892–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, C.M.; Qing, M.; Li, W.L.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Guo, X.D.; Ge, L.S.; Zeng, G.Z. Zircon U–Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotopes for the Nan’getan granodiorites and mafic microgranular enclaves in the East Kunlun Orogen: Record of closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos 2015, 234–235, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.Y.; Wang, S.; Li, G.C.; Ma, S.C.; Li, D.S. Middle to Late Triassic granitoids in the Qimantage area, Qinghai Province, China: Chronology, geochemistry and metallogenic significances. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 665–678. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.G.; Chen, Z.G.; Li, W.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Kou, X.; Jia, Q.Z.; Zhang, Z.W.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.L.; You, M.X. The Cu–Ni mineralization potential of the Kaimuqi mafic-ultramafic complex and the indicators for the magmatic Cu–Ni sulfide deposit exploration in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 198, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Guo, Y.P.; Zeng, Q.D.; Guo, L.X. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Shiduolong skarn Pb–Zn deposit in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Constraints from whole-rock geochemical, zircon U–Pb and Hf isotope analyses. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 1022–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Xia, R.; Qin, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, D.; Sun, H.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, P.; Zhou, A.B. Re–Os molybdenite ages of the Shenduolong skarn Mo–Pb–Zn deposit and geodynamic framework, Qinghai Province. Rock Miner. Anal. 2014, 33, 900–907. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.Z.; Jia, Q.Z.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Li, J.C.; Li, Y.Z.; Kong, H.L. Re–Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from Reshui molybdenum polymetallic deposit in the East Kunlun and its geological significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 2818–2829. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.Z.; Jia, Q.Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Li, J.C.; Kong, H.L.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y. Zircon U–Pb geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Reshui monzogranite in the Eastern Kunlun and their tectonic significances. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2016, 35, 1318–1328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.Z.; Jia, Q.Z.; Li, J.C.; Kong, H.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Xu, R.K.; Nan, K.E.W. Geochemical characteristics and geochronology of porphyroid biotite monzogranite from the Reshui Mo polymetallic deposit, East Kunlun Mountains. Geol. China 2016, 43, 1165–1177. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.T.; Wang, L.S.; Li, R.S.; Yuan, S.; Ji, W.H.; Yin, F.G.; Zhang, W.P.; Wang, B.D. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, Z.C.; Liu, Z.Q.; Chen, G.C.; Chen, Y.X.; Wei, F.H.; Gao, J.M.; Liu, C.J.; Pei, L. Geological characteristics of Late Palaeozoic–Mesozoic unconformities and their response to some significant tectonic events in eastern part of Eastern Kunlun. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Pei, X.Z.; Li, R.B.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Chen, G.C.; Liu, Z.G.; Ding, S.P.; Guo, J.F. Zircon U–Pb age of Xiaomiao Formation of Proterozoic in the eastern section of the East Kunlun orogenic belt. Geoscience 2011, 25, 510–521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Niu, Y.L.; Li, J.Y.; Ye, L.; Kong, J.J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.R. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the late Triassic mafic dikes and felsic volcanic rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibet Plateau. Lithos 2016, 245, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, F.H.; Ma, C.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, B. The origin of mafic microgranular enclaves and their host granodiorites from East Kunlun, Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for magma mixing during subduction of Paleo-Tethyan lithosphere. Mineral. Petrol. 2012, 104, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Feng, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Li, D.X. Genesis of post-collisional calc-alkaline and alkaline granitoids in Qiman Tagh, East Kunlun, China. Lithos 2015, 239, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.S.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, W.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Sun, T.; Ripley, E.M. Geochronology, petrology and Hf–S isotope geochemistry of the newly-discovered Xiarihamu magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposit in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau, western China. Lithos 2015, 216, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, B.L.; Wang, G.; Li, S.J.; Zhao, T.F.; Li, L.; Zhi, Y.B. The geochemistry and geochronology of the Xiarihamu II mafic–ultramafic complex, Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China: Implications for the genesis of magmatic Ni–Cu sulfide deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 73, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Wu, Z.M.; Zhu, L.S.; Qiu, Y.S.; Qian, S.Y.; Zhu, H.; Ma, Y.G.; Zhu, X.Y. Geological Survey and Exploration Report of Reshui Molybdenum Polymetallic Deposit in Dulan County, Qinghai Province; 5635-Z01; Zhejiang Geology And Mineral Resources Institute: Hangzhou, China, 2012; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar, R.J. A method of calculating fluid inclusion volumes based on vapor bubble diameters and P-V-T-X properties of inclusion fluids. Econ. Geol. 1983, 78, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Duan, G.X. The density and isochoric formulae for NaCl–H2O fluid inclusions (salinity ≤25 wt %) and their applications. Acta Mineral. Sin. 1987, 7, 345–352. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Density and isochoric formulae for NaCl–H2O inclusions with medium and high salinity and their applications. Geol. Rev. 2001, 47, 617–622. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Naldrett, A.J. Secular variation of magmatic sulfide deposits and their source magmas. Econ. Geol. 2010, 105, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffett, J.M. High Cu grades in porphyry Cu deposits and their relationship to emplacement depth of magmatic sources. Geology 2009, 37, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hoog, J.; Hattori, K.H.; Hoblitt, R.P. Oxidized sulfur-rich mafic magma at Mount Pinatubo, Philippines. In Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology; Hoefs, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; Volume 146, pp. 750–761. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wang, P.; Li, N.; Yang, Y.F.; Pirajno, F. The collision-type porphyry Mo deposits in Dabie Shan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 81, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.W.; Holm, R.J. Tectonic preconditioning and the formation of giant porphyry deposits. In Tectonics Metallogeny, and Discovery the North American Cordillera and Similar Accretionary Settings; Colpron, M., Bissig, T., Rusk, B.G., Thompson, J.F.H., Eds.; Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2013; pp. 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.W.; Xie, G.Q.; Duan, C.; Pirajno, F.; Ishiyama, D.; Chen, Y.C. A tectono-genetic model for porphyry-skarn-stratabound Cu–Au–Mo–Fe and magnetite-apatite deposits along the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2011, 43, 294–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, B.Q.; Chen, D.F. Molybdenum deposits in the eastern Qinling, central China: Constraints on the geodynamics. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 261–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Q.; Xiong, F.H.; Yin, S.; Wang, L.X.; Gao, K. Intensity and cyclicity of orogenic magmatism: An example from a Paleo-Tethyan granitoid batholith, Eastern Kunlun, northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2015, 31, 3555–3568. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.Y.; Li, D.S.; Wu, Z.S.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, A.K.; Shu, X.F.; Su, S.S. Major types, time-space distribution and metallogeneses of polymetallic deposits in the Qimantage metallogenic belt, Eastern Kunlun Area. Northwestern Geol. 2010, 43, 10–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.L.; Sun, F.Y.; Li, B.L.; Qian, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.Q. Geochronological dating, geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of the granite-porphyry in the Mohexiala silver polymetallic deposit, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geotecton. Metallog. 2014, 38, 421–433. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J.; Sun, F.Y.; Feng, C.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhao, J.W.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, S. Geochronological study on Yazigou polymetallic deposit in Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai Province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2008, 82, 949–955. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, S.Y.; Li, D.S.; Li, L.L.; Qi, L.Y.; He, S.F. Re–Os age of molybdenite from the Yazigou Copper (Molybdenum) mineralized area in Eastern Kunlun of Qinghai Province, and its geological significance. Geotecton. Metallog. 2009, 33, 236–242. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Li, B.; Li, S.P.; Tan, S.X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Q.M. Geological and gechemical characteristics of the ore-bearing intrusions from the Lalingzaohuo Mo polymetallic deposit and its metallogenic significance. Geol. Explor. 2013, 49, 813–824. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.C.; Chen, J.; Xie, Z.Y.; Li, S.P.; Tan, S.X.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, T. Geological features and Re–Os isotopic dating of the Lalingzaohuo molybdenum polymetallic deposit in East Kunlun. Geol. China 2013, 40, 1209–1217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.L. Study on Metallogenesis of porphyry deposits in Eastern Kunlun orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.; Qin, M.; Wang, C.M.; Li, W.L. The genesis of the ore-bearing porphyry of the Tuoketuo porphyry Cu–Au (Mo) deposit in the East Kunlun, Qinghai Province: Constraints from zircon U–Pb geochronological and geochemistry. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2014, 44, 1502–1524. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.N.; Feng, C.Y.; Qi, F.; Li, G.C.; Ma, S.S.; Xiao, Y. SIMS zircon U–Pb dating and fluid inclusion studies of Xiadeboli Cu–Mo ore district in Dulan County, Qinghai Province, China. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2012, 28, 679–690. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Li, B.L.; Xu, Q.L.; Zhang, B.S. Zircon U–Pb ages and its geological significance of the monzonitic granite in the Aikengdelesite, Eastern Kunlun. Northwestern Geol. 2013, 46, 56–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Audétat, A.; Li, W. The genesis of Climax-type porphyry Mo deposits: Insights from fluid inclusions and melt inclusions. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 436–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Pirajno, F.; Li, N. The Mo deposits of Northeast China: A powerful indicator of tectonic settings and associated evolutionary trends. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 602–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.P. Tectono-magmatic precursors for porphyry Cu–(Mo–Au) deposit formation. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1515–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirajno, F. The Geology and Tectonic Settings of China’s Mineral Deposits; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.R.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.Q.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, T.; Quan, Z.X.; Wu, H.; Li, T.G.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.C. Molybdenite Re–Os age, H–O–C–S–Pb isotopes, and fluid inclusion study of the Caosiyao porphyry Mo deposit in Inner Mongolia, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 81, 728–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, J.W.; Wu, G.; Wang, F.; Luo, D.F.; Hu, Y.Q.; Li, T.G. Fluid inclusions and H–O–S–Pb isotope systematics of the Chalukou giant porphyry Mo deposit, Heilongjiang Province, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 59, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirajno, F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, L.W. Review of the systematics of CO2–H2O fluid inclusions. Lithos 2001, 55, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, T.; Günther, D.; Heinrich, C.A. Gold concentrations of magmatic brines and the metal budget of porphyry copper deposits. Nature 1999, 399, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Audétat, A. What caused the formation of the giant Bingham Canyon porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit? Insights from melt inclusions and magmatic sulfides. Econ. Geol. 2017, 112, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Wang, Y.H.; Liu, J.J. Fluid inclusions and H–O–S–Pb isotope systematics of the Baishan porphyry Mo deposit in Eastern Tianshan, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2016, 78, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.A.C.; Moura, M.A. The Tocantinzinho Paleoproterozoic porphyry-style gold deposit, Tapajós Mineral Province (Brazil): Geology, petrology and fluid inclusion evidence for ore-forming processes. Minerals 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Baker, M.J.; Han, J.S.; Xiao, B.; Yang, J.T.; Jourdan, F. Multiple mineralization events of the Paleozoic Tuwu porphyry copper deposit, Eastern Tianshan: Evidence from geology, fluid inclusions, sulfur isotopes, and geochronology. In Mineralium Deposita; Hu, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.J.; Qin, K.Z.; Li, G.M.; Evans, N.J.; Jin, L.Y. Abiogenic Fischer–Tropsch synthesis of methane at the Baogutu reduced porphyry copper deposit, western Junggar, NW-China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2014, 141, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Pirajno, F.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Qi, J.P.; Li, N. Geology, geochronology, fluid inclusion and H–O isotope geochemistry of the Luoboling porphyry Cu–Mo deposit, Zijinshan Orefield, Fujian Province, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2014, 57, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yang, K.; Lentz, D.; Jeong, H.; Kil, Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, S. Low-salinity liquid-rich or vapor-like fluids in a porphyry-type Mo deposit, South Korea. Can. Mineral. 2016, 54, 715–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, S.E.; Ohmoto, H. Chemical evolution and mineral deposition in boiling hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 1985, 80, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.J. Fluid inclusion study of the Nannihu giant porphyry Mo–W deposit, Henan Province, China: Implications for the nature of porphyry ore-fluid systems formed in a continental collision setting. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 46, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, N.; Mi, M.; Xu, Y.L.; Li, F.L.; Wan, S.Q. Fluid inclusion and isotope geochemistry of the Qian’echong giant porphyry Mo deposit, Dabie Shan, China: A case of NaCl-poor, CO2-rich fluid systems. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ulrich, T.; Chen, Y.; Thomsen, T.B.; Pease, V.; Pirajno, F. Fluid evolution of the Yuchiling porphyry Mo deposit, East Qinling, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Y. Fluid inclusion study of the Tangjiaping Mo deposit, Dabie Shan, Henan Province: Implications for the nature of the porphyry systems of post-collisional tectonic settings. Int. Geol. Rev. 2011, 53, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, P.; Wang, G.G.; Yu, W.; Chen, H.; Jiang, L.L.; Wang, B.H.; Zhang, H.D.; Xu, Y.F. Evidence of fluid inclusions for two stages of fluid boiling in the formation of the giant Shapinggou porphyry Mo deposit, Dabie Orogen, Central China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.J.; Pirajno, F.; Li, N. Evolution of ore fluids in the Donggou giant porphyry Mo system, East Qinling, China, a new type of porphyry Mo deposit: Evidence from fluid inclusion and H–O isotope systematics. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 65, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Duan, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D. A model for single-phase PVTx properties of CO2–CH4–C2H6–N2–H2O–NaCl fluid mixtures from 273 to 1273 K and from 1 to 5000 bar. Chem. Geol. 2010, 275, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwe, Y.Y.; Morteani, G. Fluid evolution in the H2O–CH4–CO2–NaCl system during emerald mineralization at Gravelotte, Murchison greenstone belt, Northeast Transvaal, South Africa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.E.; Lamb, W.M. PVT properties of fluids in the system H2O ± CO2 ± NaCl: New graphical presentations and implications for fluid inclusion studies. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seedorff, E.; Einaudi, M.T. Henderson porphyry molybdenum system, Colorado: II. Decoupling of introduction and deposition of metals during geochemical evolution of hydrothermal fluids. Econ. Geol. 2004, 99, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.D.; Ye, H.S.; Mao, J.W.; Wang, H.; Chu, S.T.; Cheng, G.X.; Liu, Y.W. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Leimengou porphyry Mo deposit and its geological significance, West Henan province. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 85, 1629–1643. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Xu, H.; Quan, S.L.; Zang, Y.Q.; Wang, T. Geology, hydrothermal fluids, H–O–S–Pb isotopes, and Rb–Sr geochronology of the Daxintun orogenic gold deposit in Heilongjiang province, NE China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 92, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, M.; Haase, K.M.; Klemd, R.; Krumm, S.; Strauss, H. Systematic variations of trace element and sulfur isotope compositions in pyrite with stratigraphic depth in the Skouriotissa volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposit, Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus. Chem. Geol. 2016, 423, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Brugger, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Contrasting regimes of Cu, Zn and Pb transport in ore-forming hydrothermal fluids. Chem. Geol. 2015, 395, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Stable isotope geochemistry of ore deposits. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1986, 16, 491–559. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Pirajno, F.; McCuaig, T.C.; Yu, M.; Xia, S.L.; Song, Q.J.; Chang, H.F. Geology, S–Pb isotopes, and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Zhaxikang Sb–Pb–Zn–Ag deposit in Southern Tibet: Implications for multiple mineralization events at Zhaxikang. Miner. Depos. 2018, 53, 435–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.F.; Yan, W.; Zhang, B.L. Sulfur-and lead-isotope geochemistry of the Balugou Cu–Pb–Zn skarn deposit in the Wulonggou area in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, NW China. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 27, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.Q.; Wang, L.X.; Deng, T.; Xu, D.R.; Chen, G.W.; Yu, D.H.; Ye, T.W.; Gao, Y.W. Origin of the ore-forming fluids and metals of the Hetai goldfield in Guangdong Province of South China: Constraints from C–H–O–S–Pb–He–Ar isotopes. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.X.; Hu, R.Z.; Bi, X.W.; Peng, J.T.; Tang, Q.L. Ore lead isotopes as a tracer for ore-forming material sources: A review. Geol. -Geochem. 2002, 30, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Schiano, P.; Birck, J.; Allègre, C.J. Osmium-strontium-neodymium-lead isotopic covariations in mid-ocean ridge basalt glasses and the heterogeneity of the upper mantle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1997, 150, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, R.J.; Groves, D.I. Orogenic gold: Common or evolving fluid and metal sources through time. Lithos 2015, 233, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zartman, R.E.; Doe, B.R. Plumbotectonics—the model. Tectonophysics 1981, 75, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.L. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 22–70. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Mao, J.W.; Ye, H.S.; Li, Y.F. Origins of ore-forming fluid and material of the quartz–vein type Mo deposits in the East Qinling–Dabie molybdenum belt: A case study of the Qianfanling Mo deposit. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 185, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, I.; Jung, S.; Romer, R.L.; Garbe-Schönberg, D.; Berndt, J. Geochemical and Nd–Sr–Pb isotope characteristics of synorogenic lower crust-derived granodiorites (Central Damara orogen, Namibia). Lithos 2017, 274, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Ye, H.S.; Wang, X.X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.Y. Geology and ore fluid geochemistry of the Jinduicheng porphyry molybdenum deposit, East Qinling, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.J.; Hannah, J.L. Movement and origin of ore fluids in Climax-type systems. Geology 1985, 13, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Stage | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | W | C | W | S | C | W |
| Number | 78 | 4 | 51 | 7 | 12 | 31 |
| Tm-ice(°C) | −5.2–−2.8 | −4.2–−2.6 | −2.1–−2.8 | |||
| Tm-CO2/°C | −58.3–57.6 | −59.4–−56.9 | ||||
| Tm-cla/°C | 6.5–6.8 | 5.3–6.1 | ||||
| Th-CO2/°C | 29.3–30.8 | 28.6–31.2 | ||||
| Th(°C) | 282.3–376.8 | 327.4–352.3 | 238.7–312.6 | 335–352.6 | 261.2–283.1 | 198.3–228.9 |
| Ts(°C) | 335–352.6 | |||||
| Salinity (%NaCl eq.) | 4.65–8.14 | 6.12–6.63 | 4.34–6.74 | 39.04–42.64 | 7.31–8.61 | 3.55–4.65 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 0.63–0.79 | 0.68–0.73 | 0.74–0.86 | 1.11–1.13 | 0.82–0.85 | 0.86–0.9 |
| Sample Number | Mineral | Mineralization Stage | δ34SV-CDT (‰) | 206Pb/204Pb | 208Pb/204Pb | 207Pb/204Pb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15RSP1-SPb1 | molybdenite | 2 | 4.9 | 18.578 | 0.001 | 38.292 | 0.002 | 15.595 | 0.001 |
| 15RSP2-SPb1 | molybdenite | 2 | 5.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14RSTWS01 | chalcopyrite | 3 | 5.3 | 18.356 | 0.003 | 38.406 | 0.007 | 15.602 | 0.003 |
| 14RSTWS02 | chalcopyrite | 3 | 5.1 | 18.355 | 0.003 | 38.354 | 0.006 | 15.589 | 0.002 |
| 14RSTWS05 | chalcopyrite | 3 | 5.4 | 18.401 | 0.004 | 38.509 | 0.011 | 15.629 | 0.004 |
| 14RSTWS07 | pyrite | 3 | 5.6 | 18.374 | 0.005 | 38.431 | 0.011 | 15.617 | 0.005 |
| 14RSTWS08 | pyrite | 3 | 5.7 | 18.316 | 0.002 | 38.460 | 0.003 | 15.640 | 0.001 |
| 14RSTWS09 | pyrite | 3 | 5.8 | 18.210 | 0.002 | 38.298 | 0.004 | 15.636 | 0.002 |
| 15RSP1-SPb2 | molybdenite | 3 | 5.5 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 15RSP2-SPb2 | molybdenite | 3 | 5.1 | 18.786 | 0.002 | 39.126 | 0.003 | 15.723 | 0.001 |
| Deposit | Mineralization System | Samples | Age (Ma) | Analytical Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changshan | Porphyry Mo | Zircon | 220 ± 1 | SHRIMP U–Pb | [41] |
| Molybdenite | 218,228 | Re–Os | [41] | ||
| Mohexiala | Porphyry Ag–Pb–Zn | Zircon | 222 ± 1 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [42] |
| Yazigou | Porphyry Cu–Mo | Zircon | 224.0 ± 1.6 | SHRIMP U–Pb | [43] |
| Molybdenite | 224.7 ± 3.4 | Re–Os | [44] | ||
| Lalingzaohuo | Porphyry Mo | Zircon | 242.6 ± 3.4 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [45] |
| Zircon | 226 ± 1 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [45] | ||
| Molybdenite | 240.8 ± 4.0 | Re–Os | [46] | ||
| Molybdenite | 214.5 ± 4.9 | Re–Os | [46] | ||
| Halongxiuma | Porphyry W–Mo | Zircon | 230 ± 1 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [47] |
| Tuoketuo | Porphyry Cu–Au(Mo) | Zircon | 232.5 ± 0.9 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [48] |
| Zircon | 232.6 ± 1.2 | LA-ICP-MS U–Pb | [48] | ||
| Reshui | Porphyry Mo | Molybdenite | 230.2 ± 2.5 | Re–Os | [23] |
| Zircon | 231 ± 1 | LA-ICP-MS | [24] | ||
| Zircon | 230.9 ± 1.4 | LA-ICP-MS | [25] | ||
| Xiadeboli | Porphyry Cu–Mo | Zircon | 244.2 ± 2.1 | SIMS U–Pb | [49] |
| Aikengdelisite | Porphyry Mo–Cu | Zircon | 248.4 ± 0.83 | LA-ICPMS U–Pb | [50] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Lü, X.; Jia, Q.; Li, J.; Kong, H. Fluid Inclusions and S–Pb Isotopes of the Reshui Porphyry Mo Deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090547
Guo X, Lü X, Jia Q, Li J, Kong H. Fluid Inclusions and S–Pb Isotopes of the Reshui Porphyry Mo Deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China. Minerals. 2019; 9(9):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090547
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xianzheng, Xinbiao Lü, Qunzi Jia, Jinchao Li, and Huilei Kong. 2019. "Fluid Inclusions and S–Pb Isotopes of the Reshui Porphyry Mo Deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China" Minerals 9, no. 9: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090547
APA StyleGuo, X., Lü, X., Jia, Q., Li, J., & Kong, H. (2019). Fluid Inclusions and S–Pb Isotopes of the Reshui Porphyry Mo Deposit in East Kunlun, Qinghai Province, China. Minerals, 9(9), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9090547