Research on Parameter Design and Control Method for Current Source Inverter–Fed IM Drive Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Topology and Mathematical Model
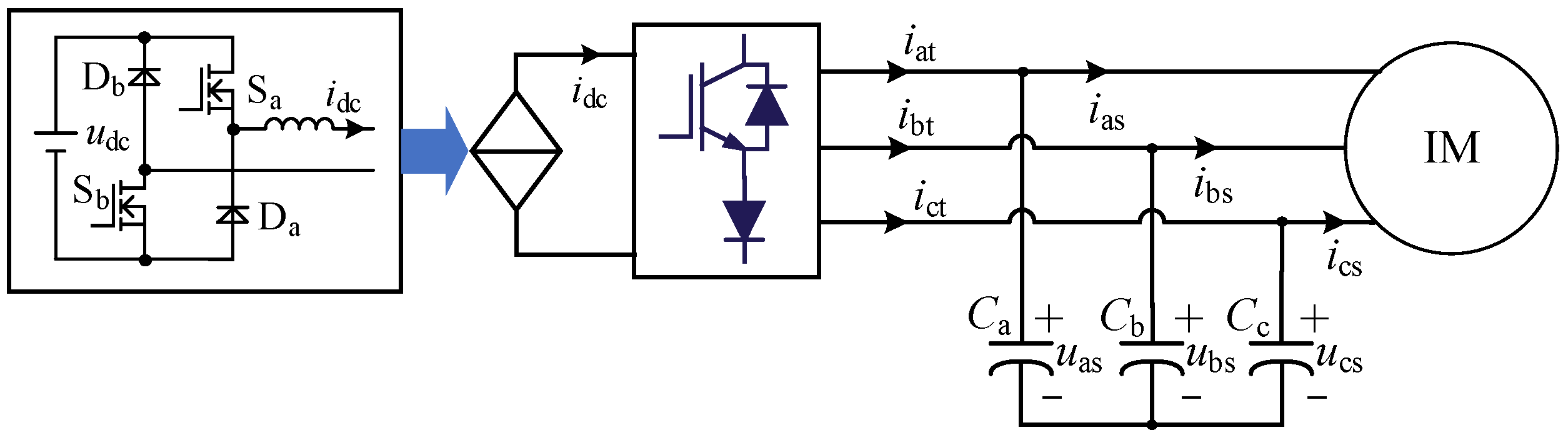
2.1. Topology of CSI-Fed IM Drive System with Bidirectional DC Chopper
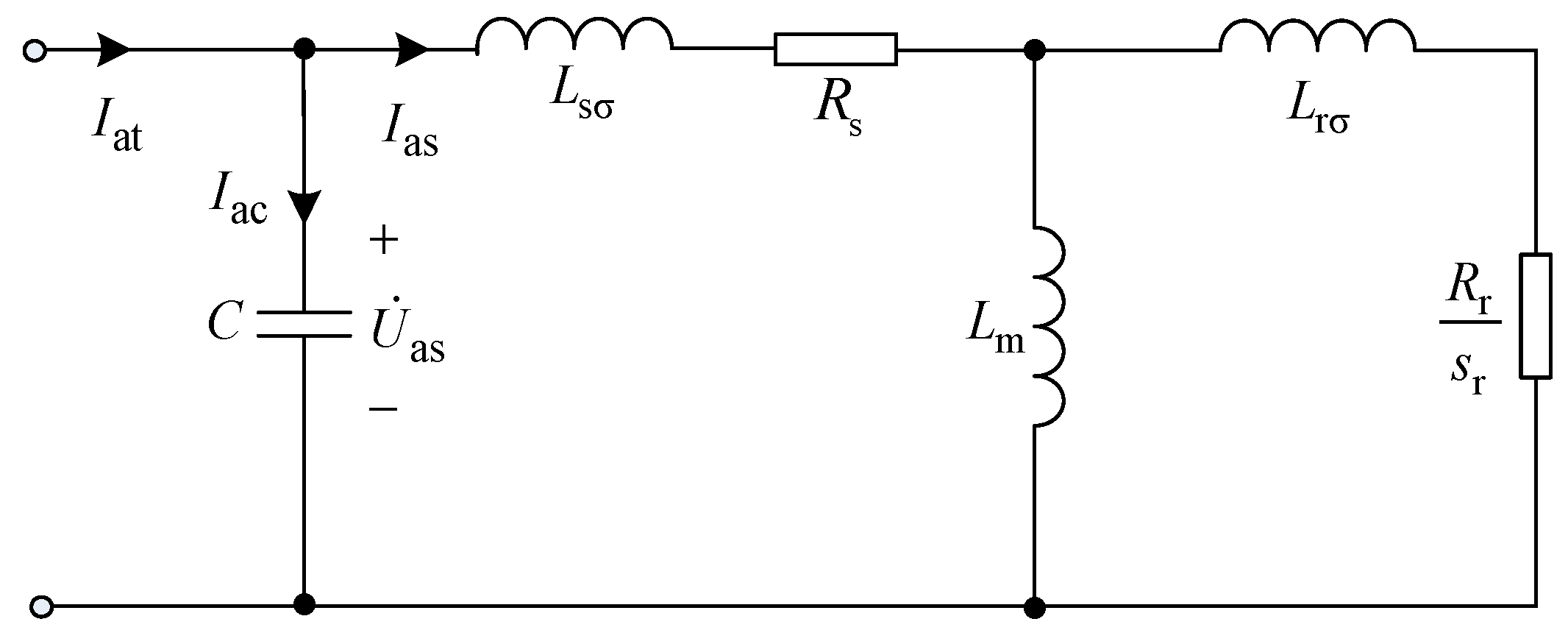
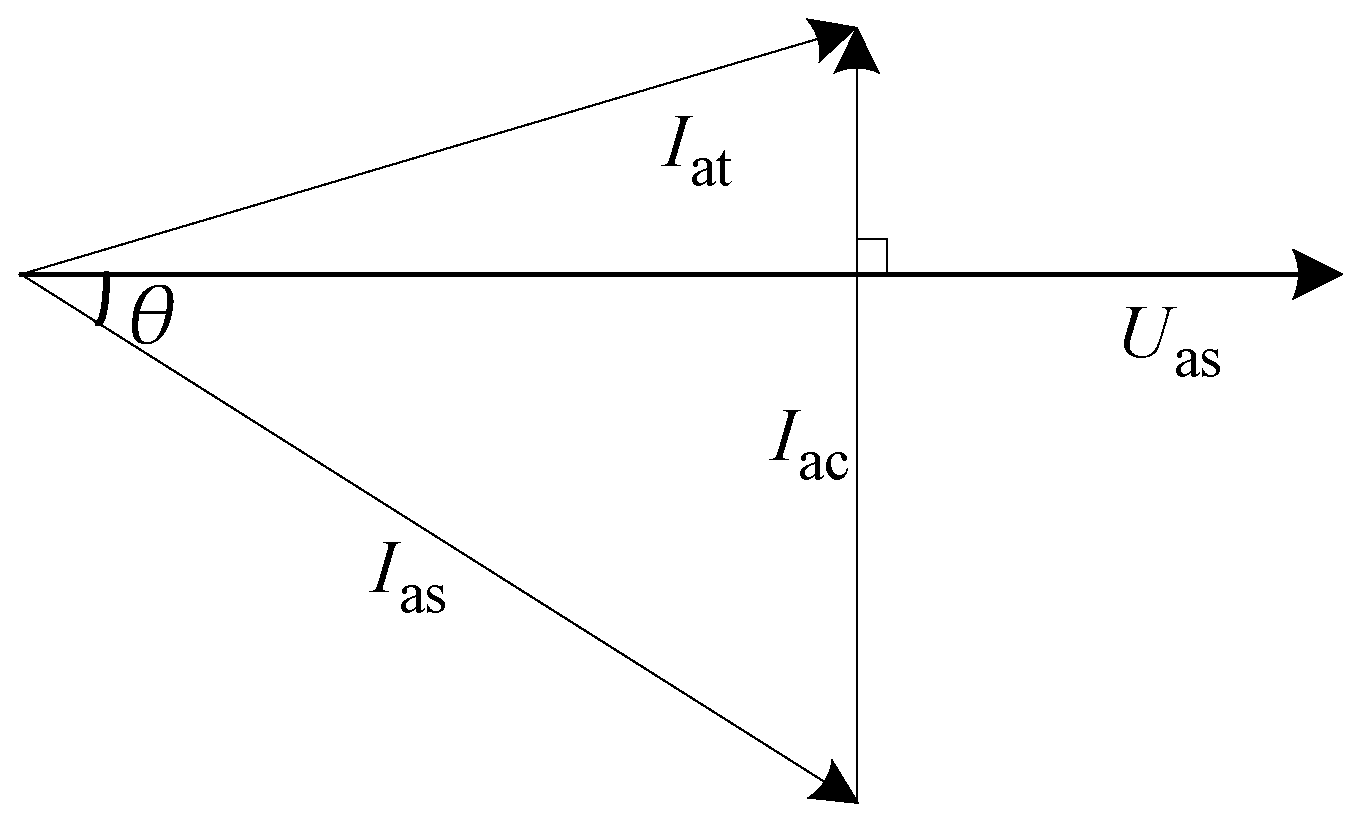
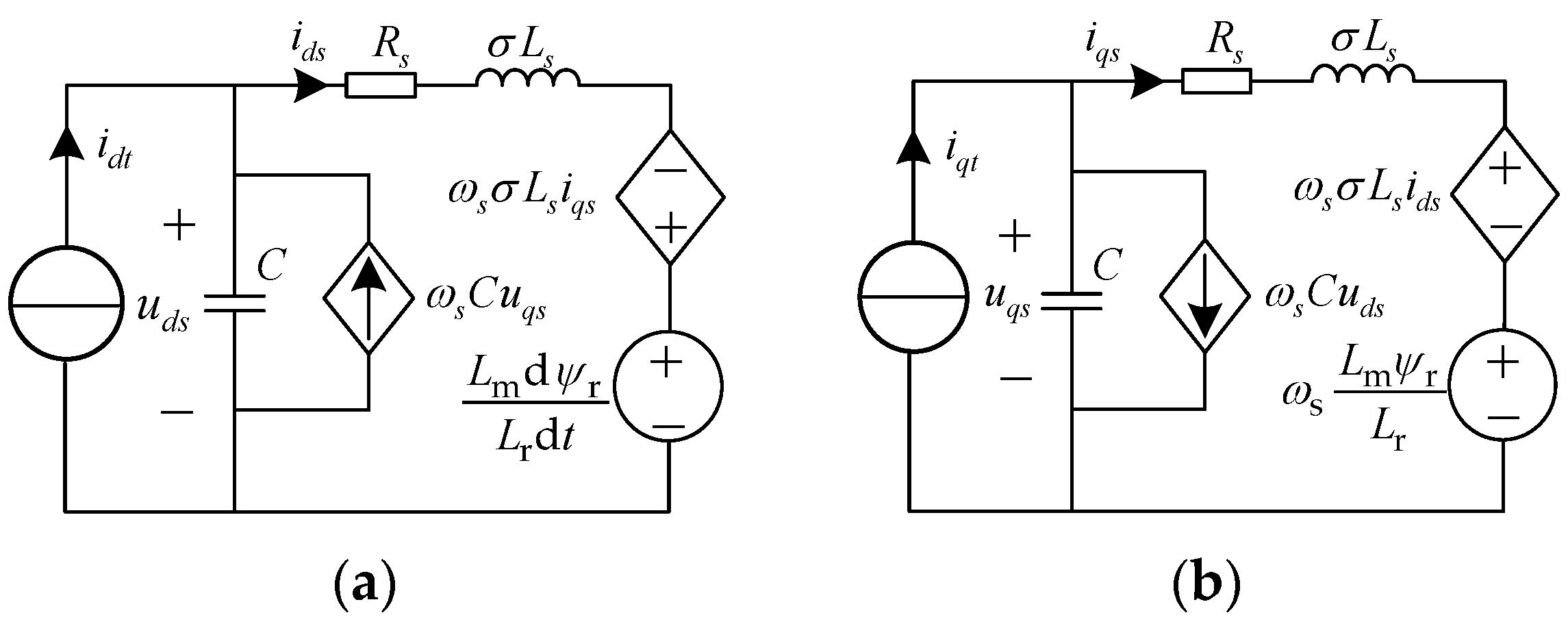
2.2. Mathematical Model of Filter Capacitors and IM
3. Parameter Design of DC-Link Inductance and AC-Filter Capacitance
3.1. Selection Range of DC-Link Inductance
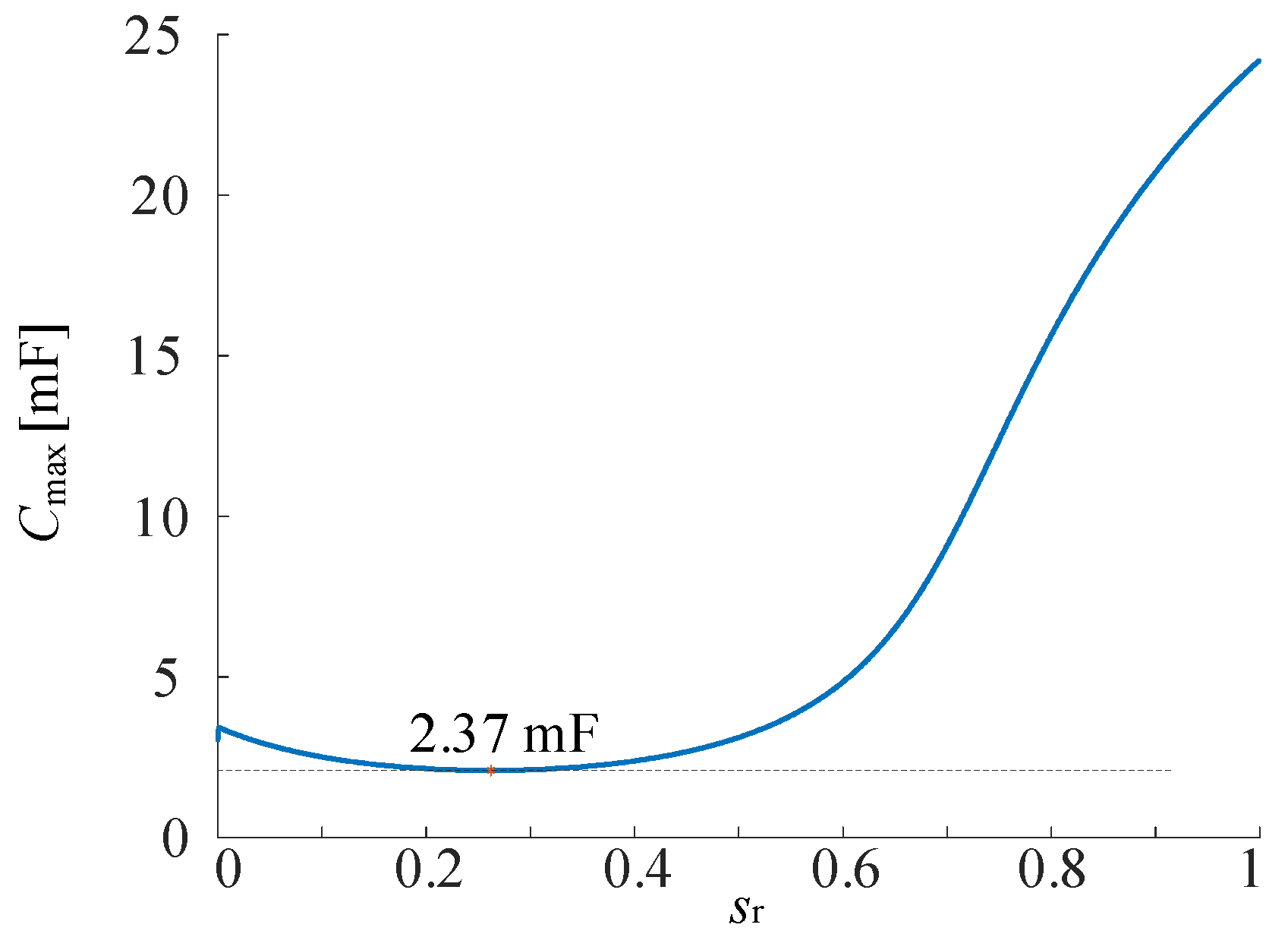
3.2. Selection Range of AC-Filter Capacitance
4. Design Principle for Vector Control Strategy of CSI-Fed IM Drive System
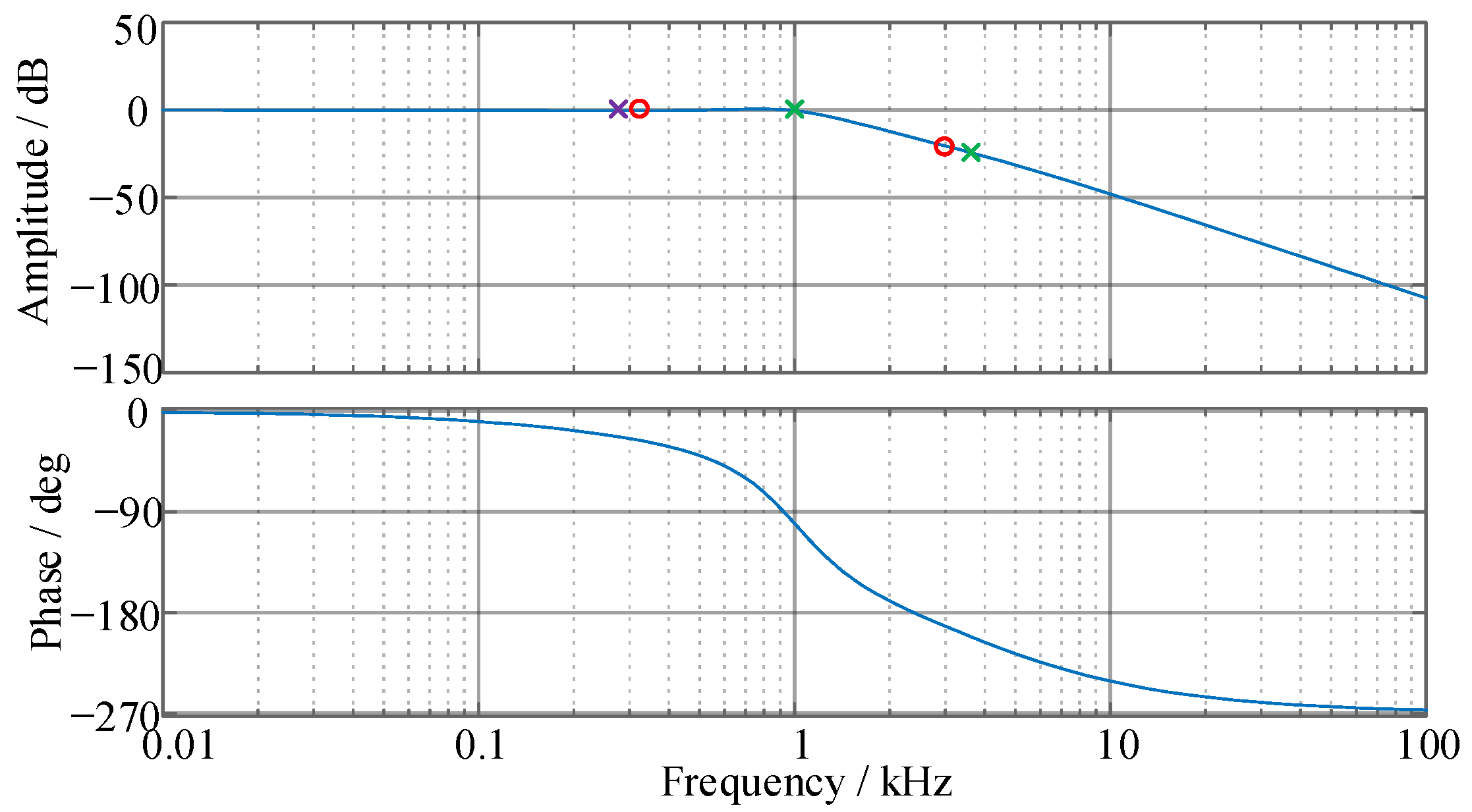
4.1. Analysis and Parameter Design for Current Loop
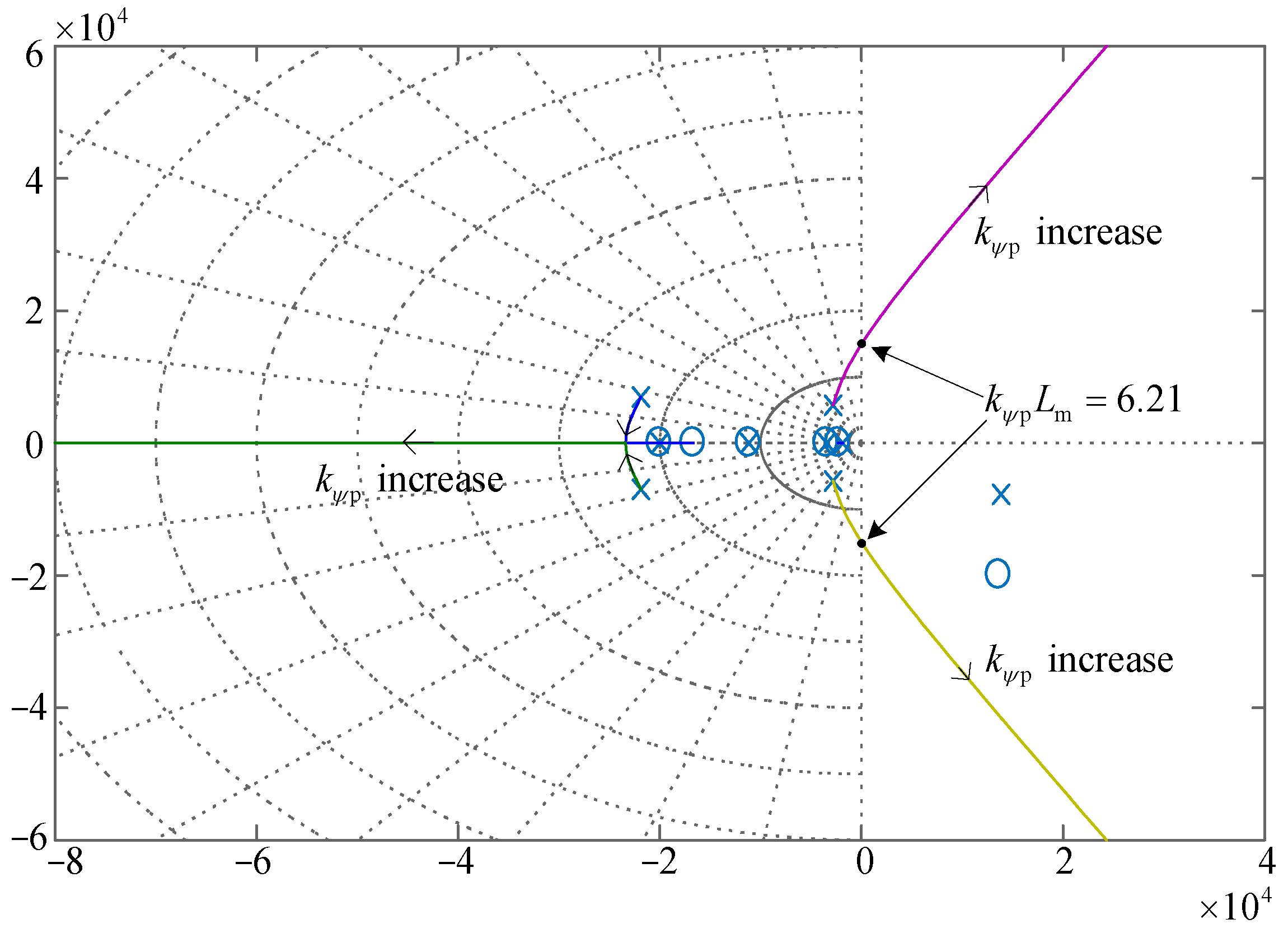
4.2. Analysis and Parameter Design for Flux Loop
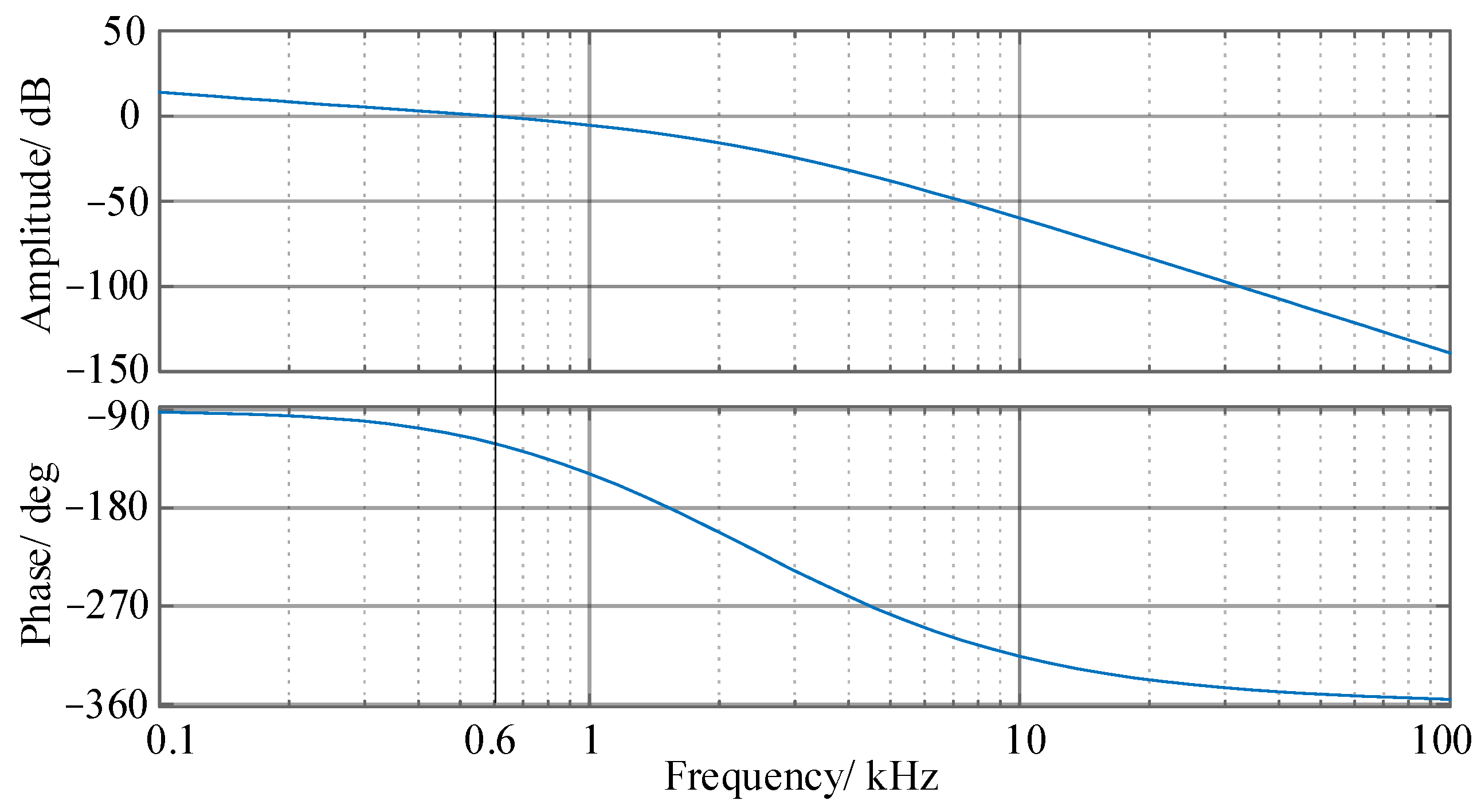
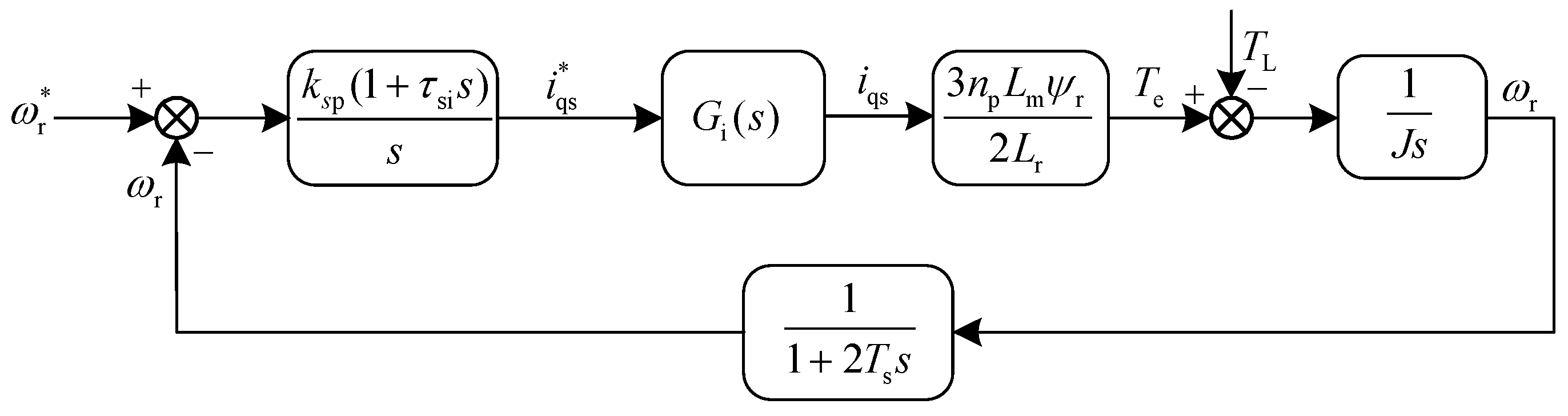
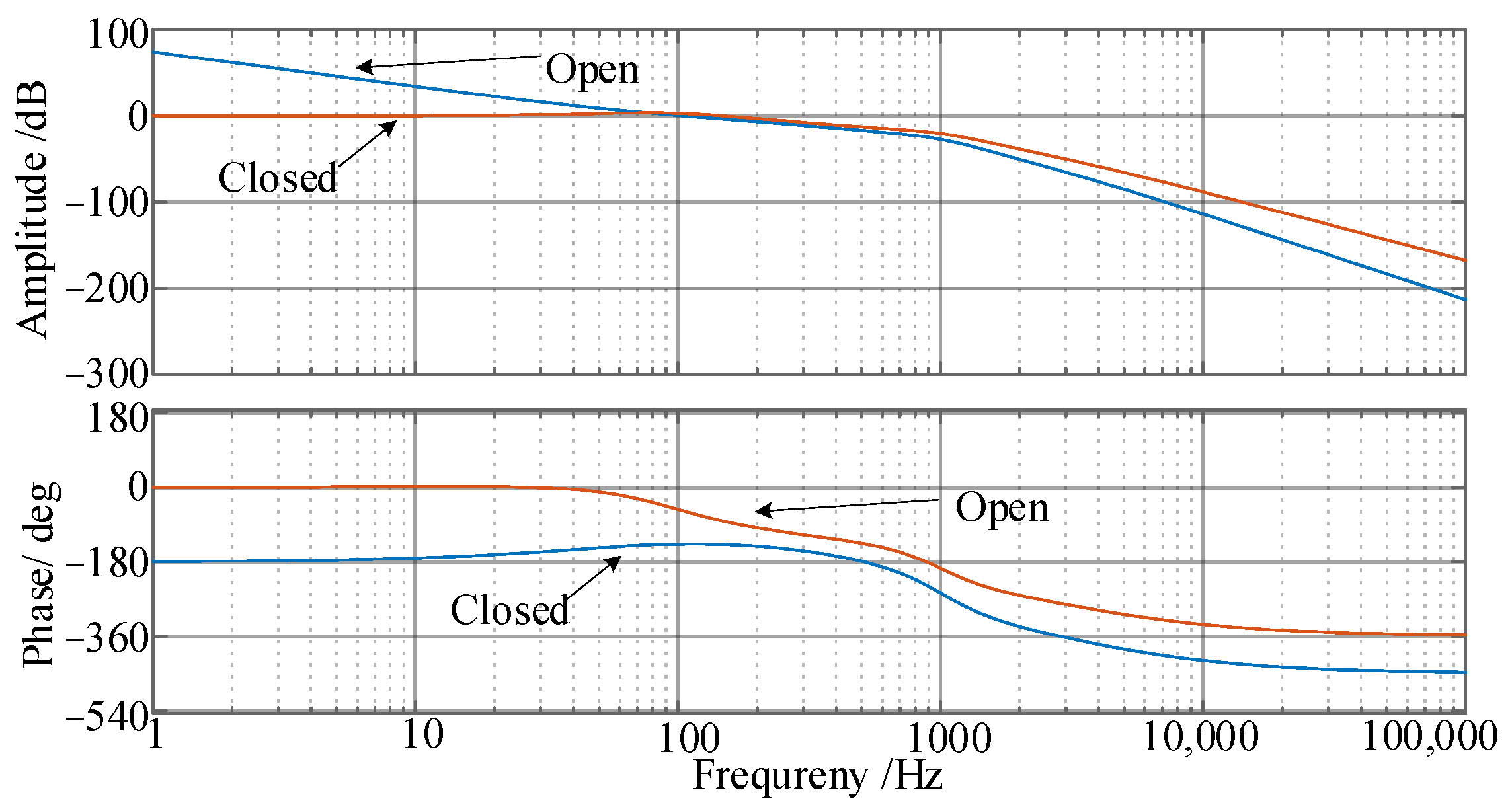
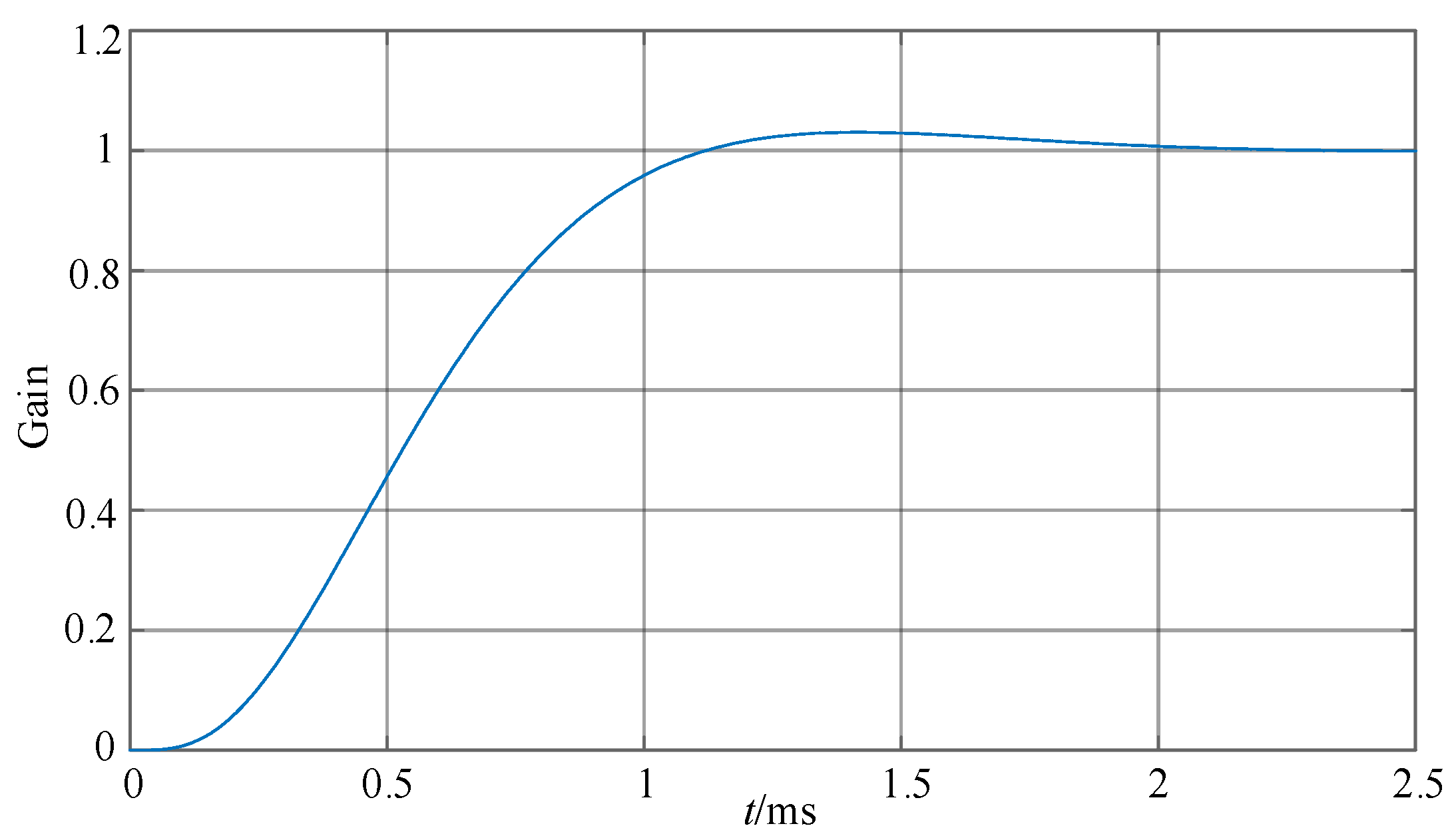
4.3. Analysis and Parameter Design for Speed Loop
5. Simulation Results
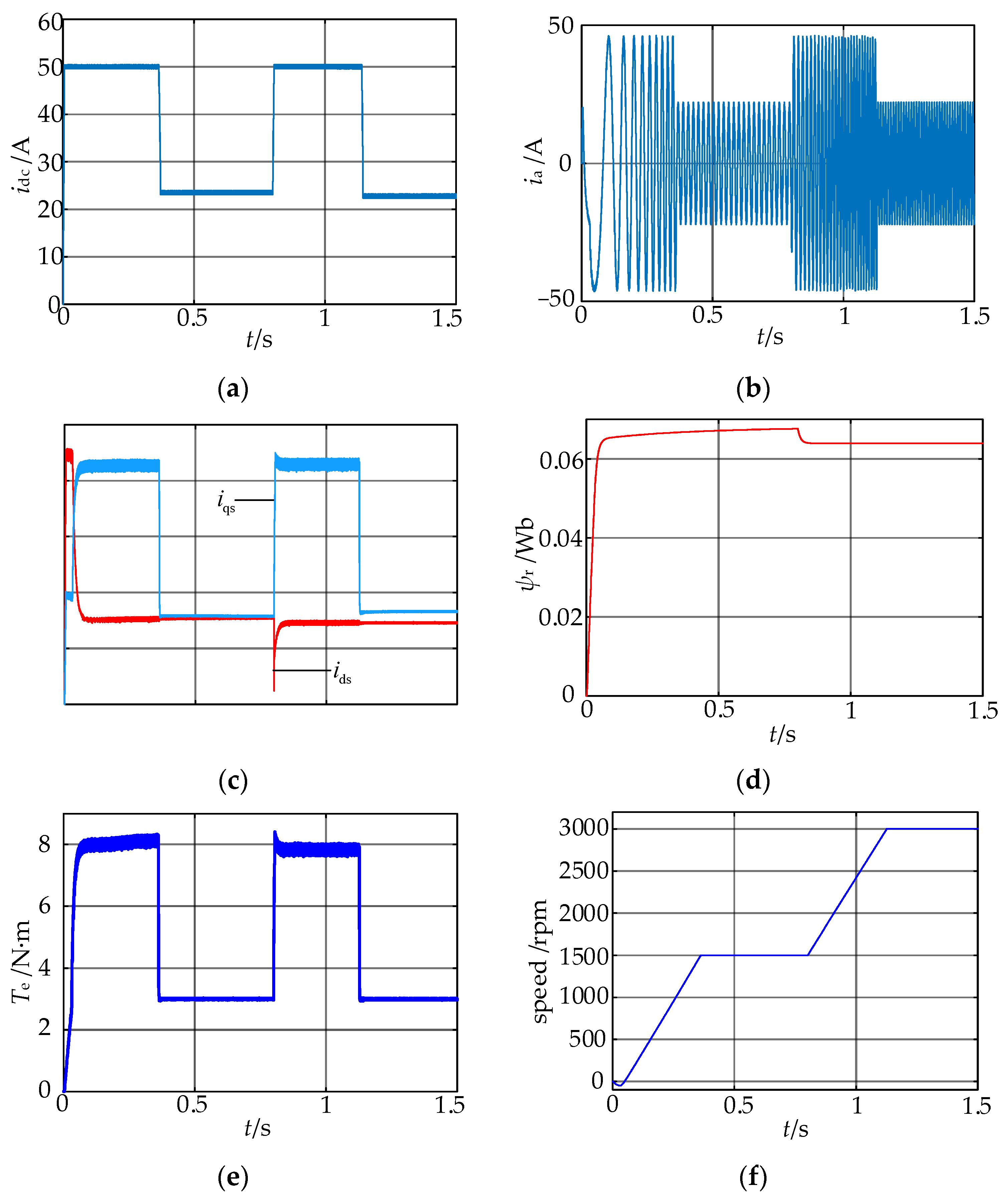
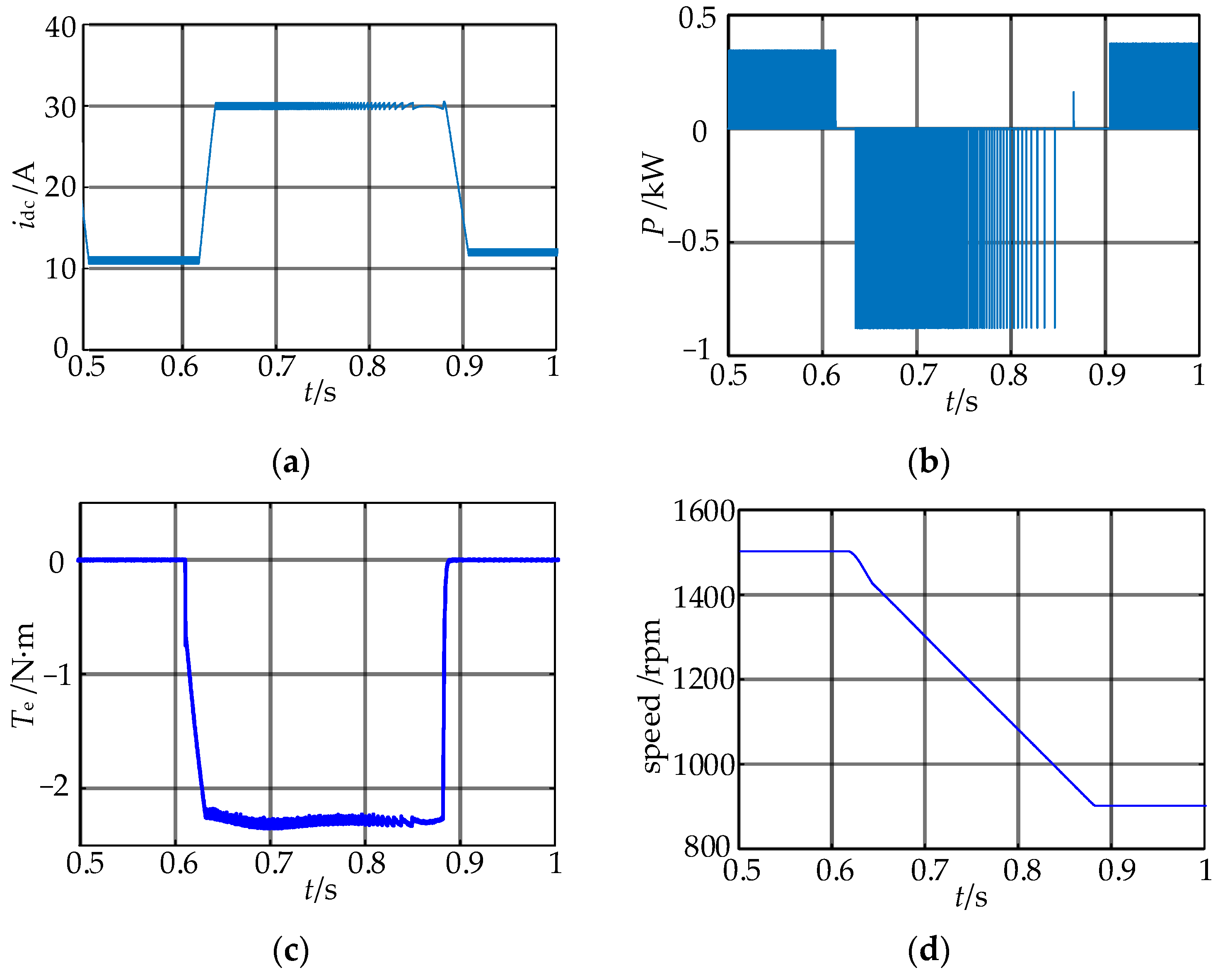
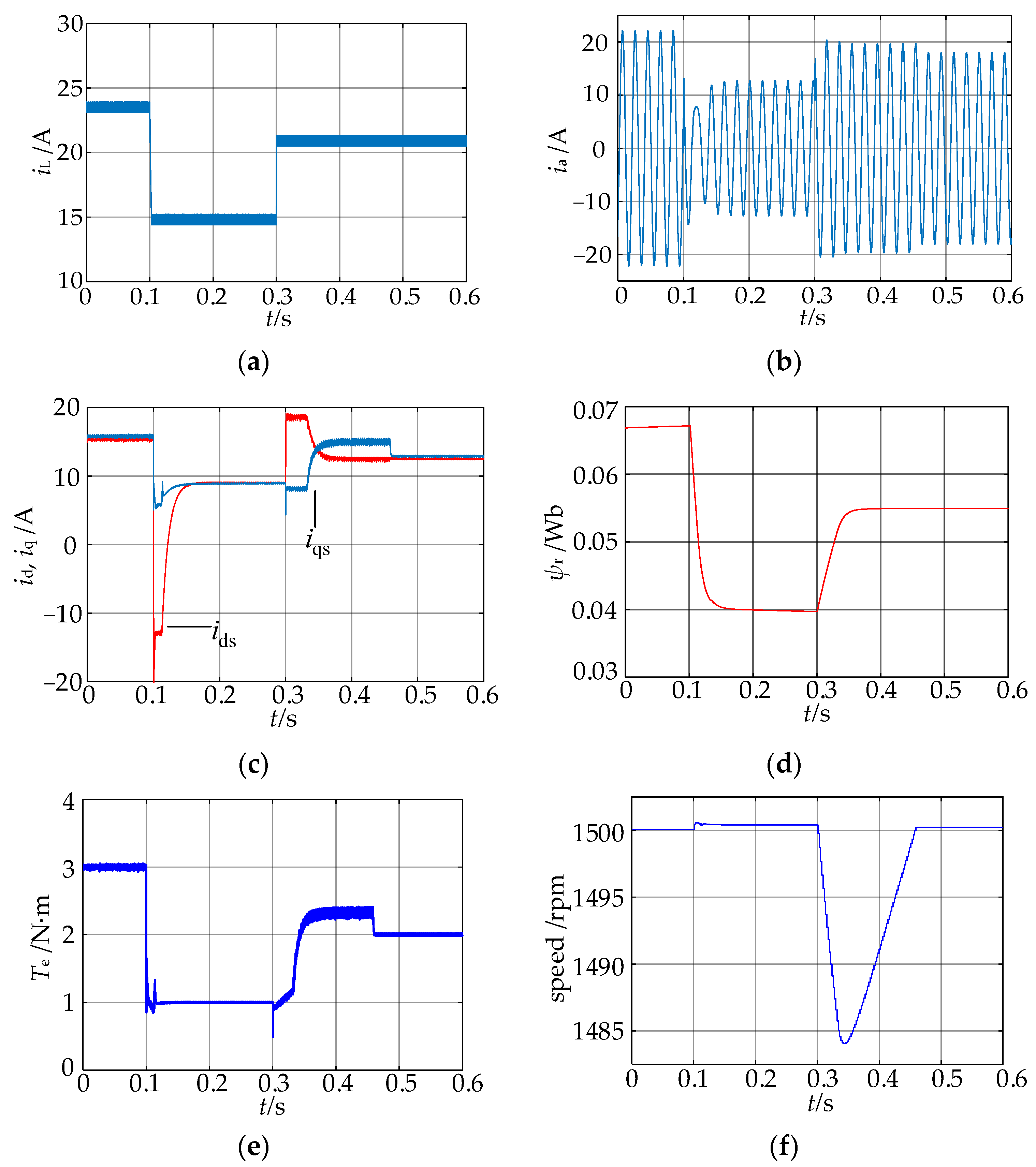
5.1. Load Acceleration Condition
- A.
- In the dynamic process, in order to provide greater torque, the reference DC-link current is set to 50 A, which is the maximum current of the DC-link inductor.
- B.
- In the steady state, the references of rotor flux and DC-link current are adjusted according to the load torque and speed, which are shown in Table 4.
5.2. Deceleration Condition with No Load
5.3. Load Disturbance Condition
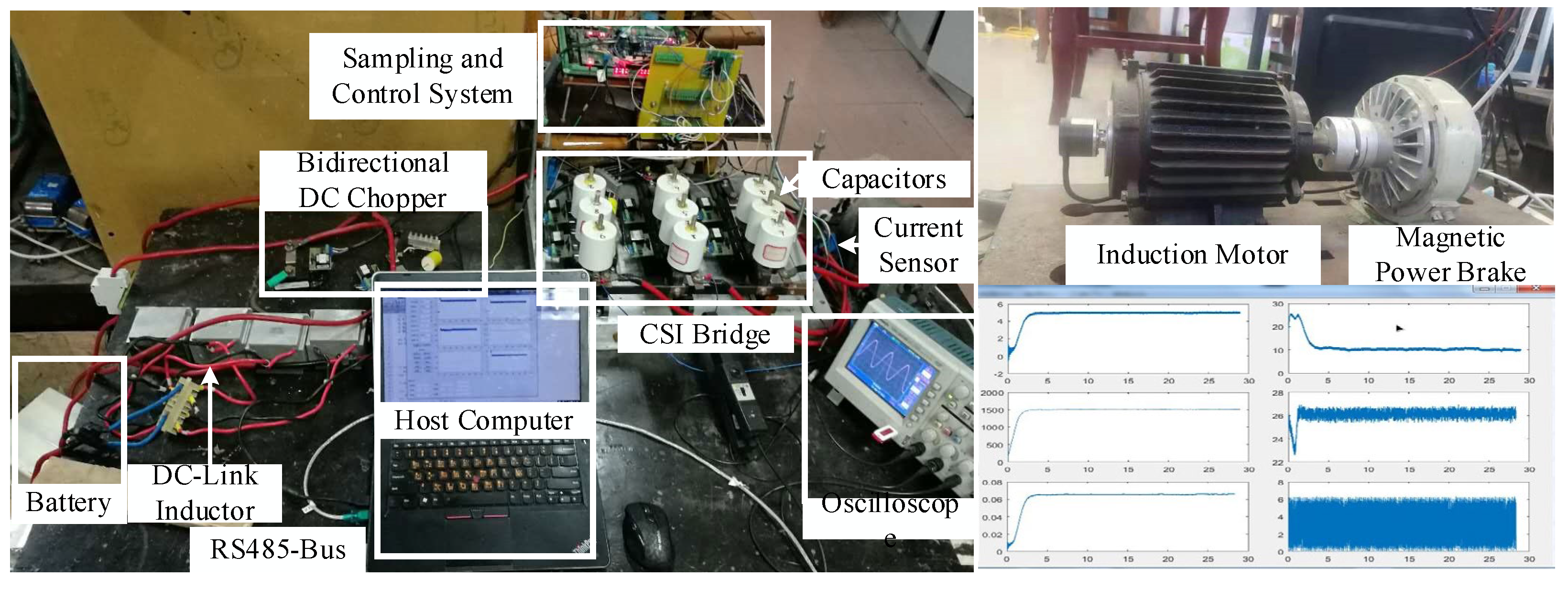
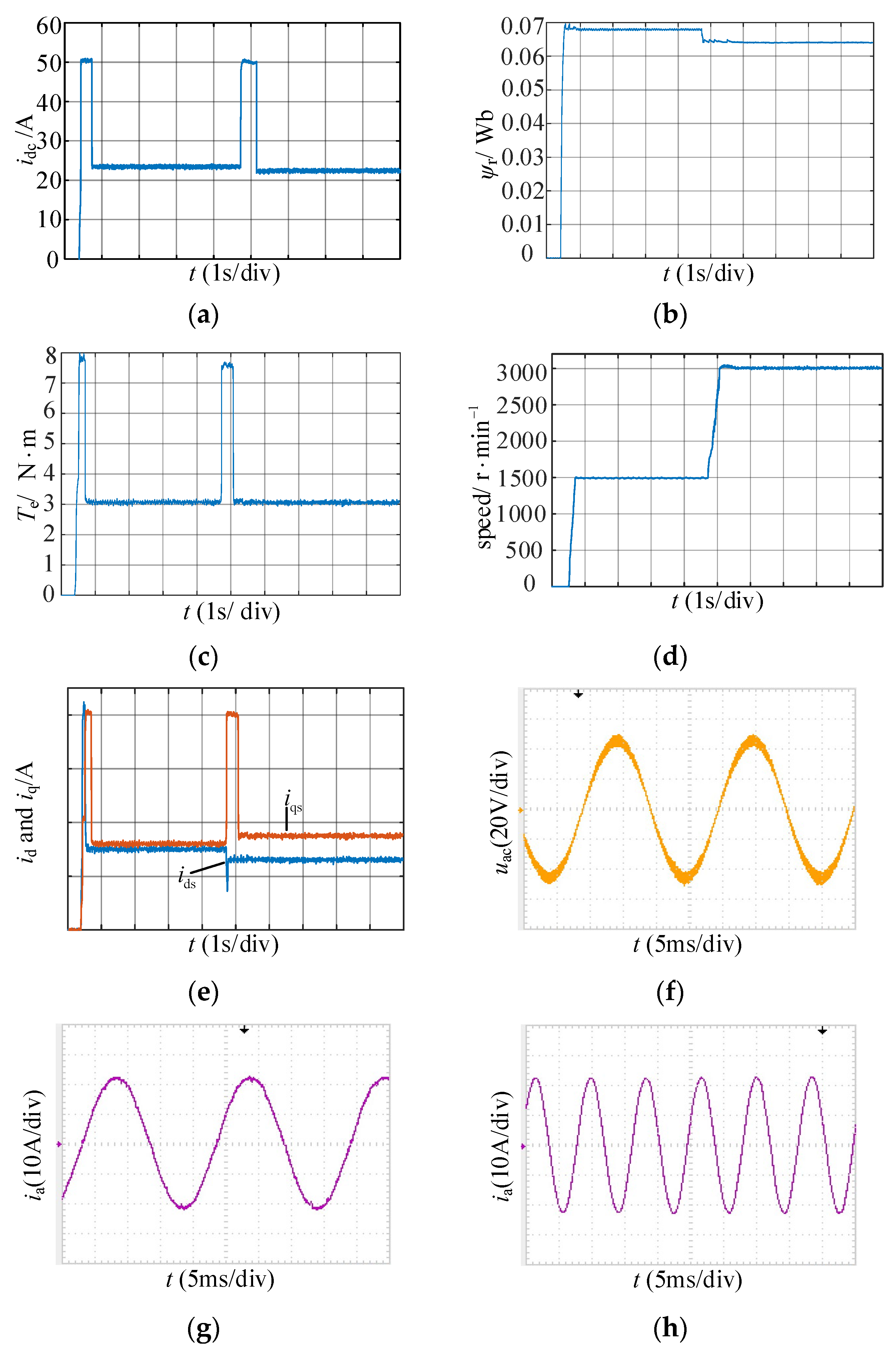
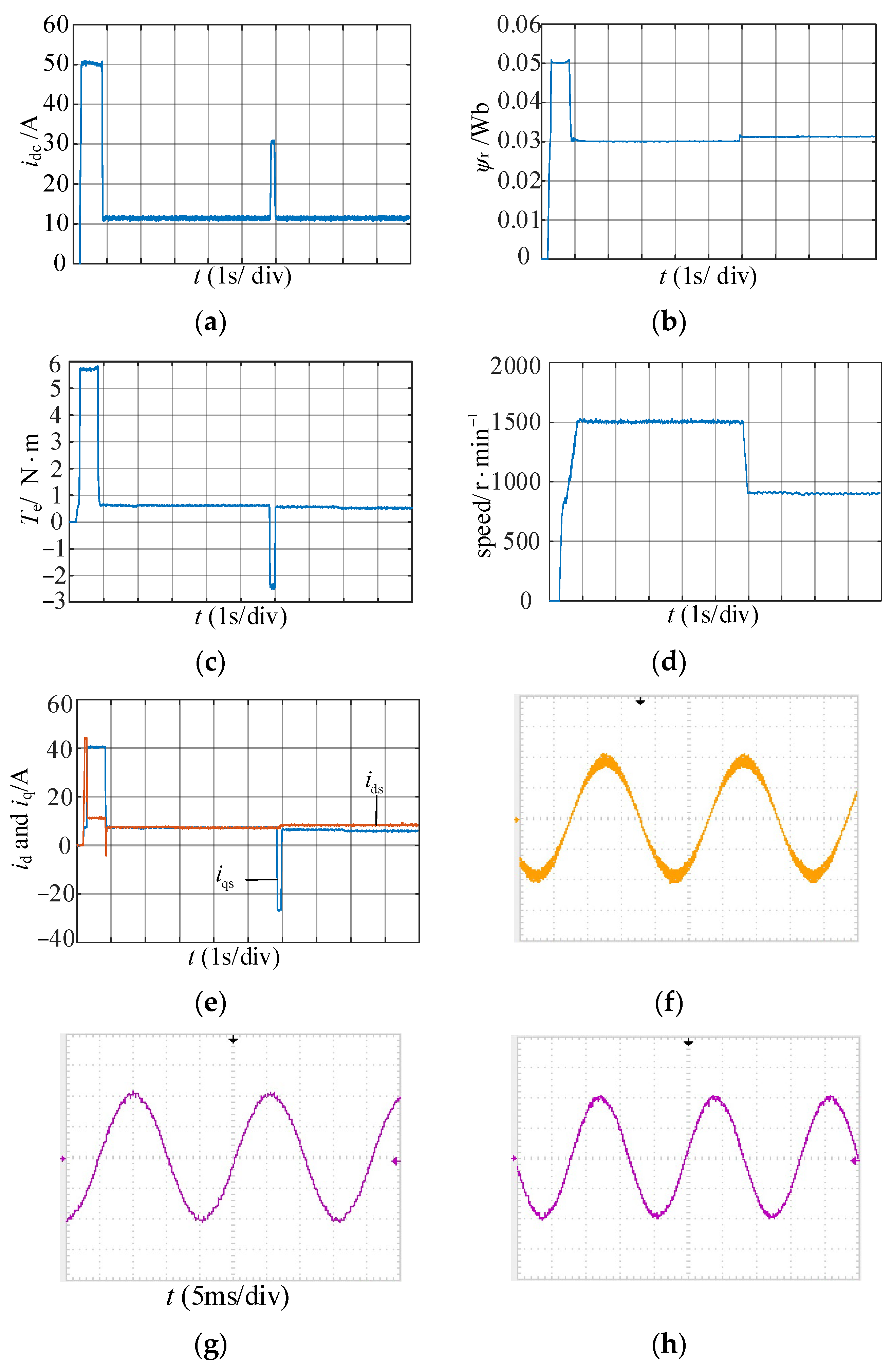
6. Experimental Results
6.1. Performance under Acceleration with Load of 3 N·m
6.2. Performance under Deceleration with No Load
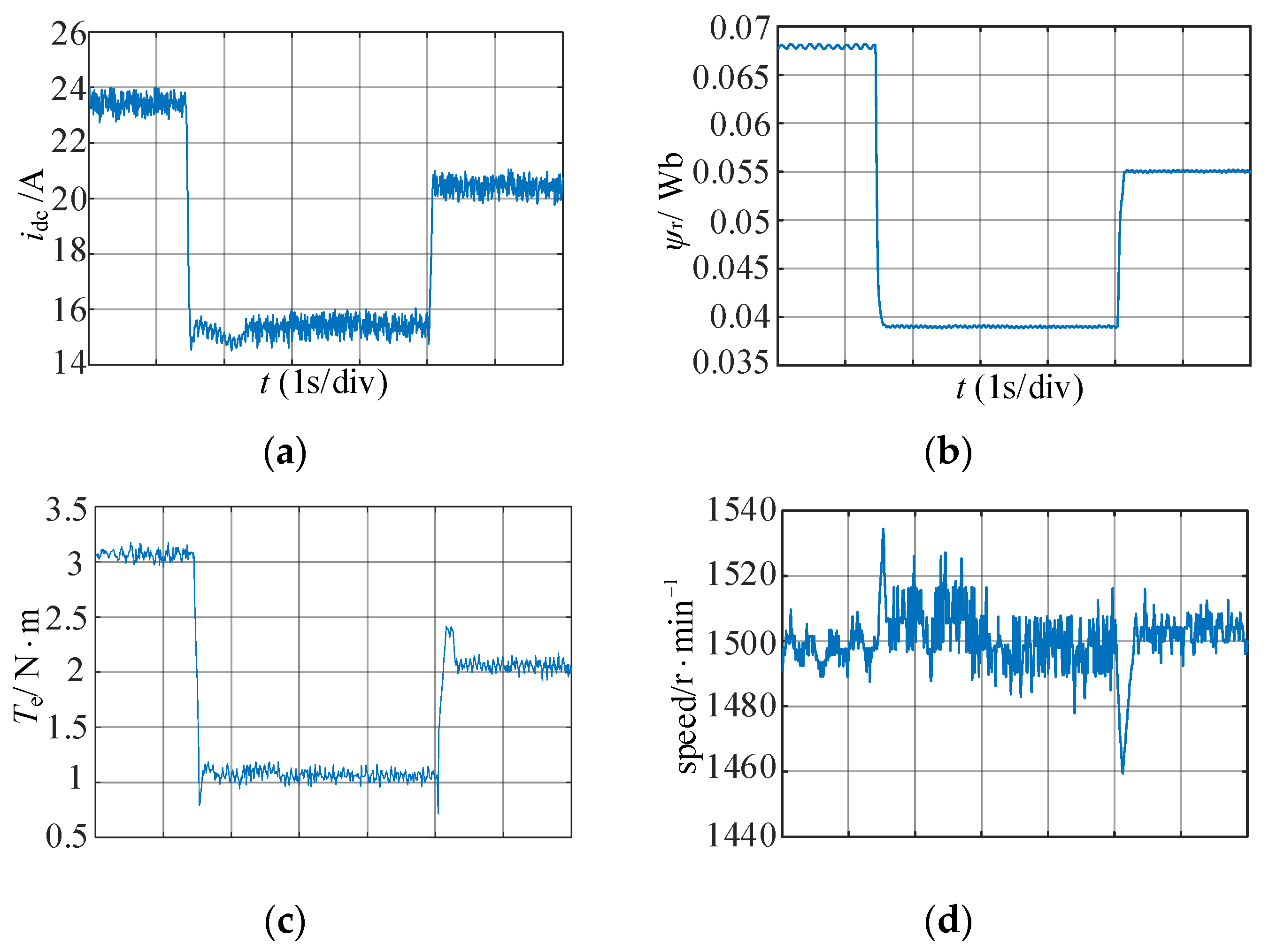
6.3. Performance under Different Loads
7. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under consideration of the dynamic response speed and current ripple, the range expression of the DC-link inductance is derived.
- (2)
- Under consideration of the DC-link current utilization and harmonic suppression, the range expression of the AC-filter inductance is derived.
- (3)
- The simulation and experimental results show that the fast dynamic performance of speed and flux with no overshoot and a stator current with low harmonic distortion can be obtained by the vector control strategy without voltage loop for current source inverter–fed inductor motor drive systems. The analytical expressions of the control parameters derived in this paper are also suitable for other IM parameters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lorenzani, E.; Migliazza, G.; Immovilli, F.; Buticchi, G. CSI and CSI7 current source inverters for modular transformerless PV inverters. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2019, 5, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y. An eight-switch five-level current source inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 8389–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, K.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Q. Harmonic-Separation-Based Direct Extraction and Compensation of Inverter Nonlinearity for State Observation Control of PMSM. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142028–142045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Liu, S. Suppression of Dual-Harmonic Components for Five-Phase Series-Winding PMSM. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Mao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, D. An Improved Deadbeat Current Controller of PMSM Based on Bilinear Discretization. Machines 2022, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, H. Study on a new control strategy based on three phase current inverter. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), Hangzhou, China, 3–5 November 2017; pp. 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeev, M.; Agarwal, V. Single phase current source inverter with multiloop control for transformerless grid—PV interface. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Jiang, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F. Single-stage three-phase current-source photovoltaic grid-connected inverter high voltage transmission ratio. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 7591–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wei, Q. Series-connected current source inverters with less switches. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 5553–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Wu, J.; Cheng, M. A new control method for current-source inverter fed motor drive system without additional DC-link current regulator. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 382–387. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, M. The modulation and control strategy of storage inductance current for single-phase current source inverter. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2018, 33, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Operation and modulation of H7 current-source inverter with hybrid SiC and Si semiconductor switches. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 6, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Pande, M.; Zargari, N.R.; Wu, B. DC-link current minimization for high-power current-source motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 24, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Li, Y.W.; Zargari, N.R. Discrete-time SMO sensorless control of current source converter-fed PMSM drives with low switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, F.Z.; Lei, Q.; Inoshita, R.; Qian, Z. Current-fed quasi-Z-source inverter with voltage Buck–Boost and regeneration capability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 47, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; He, J. A Soft-Switching Current-Source-Inverter-Fed Motor Drive With Reduced Common-Mode Voltage. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P. Optimal control strategy of storage inductor current and rotor flux for current source inverter motor drive system. Proc. CSEE 2021, 39, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Migliazza, G.; Buticchi, G.; Carfagna, E.; Lorenzani, E.; Madonna, V.; Giangrande, P.; Galea, M. DC current control for a single-stage current source inverter in motor drive application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 3367–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Jung, S.; Sul, S.-K. A current controller design for current source inverter-fed AC machine drive system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, F.W.; Kloenne, A. DC link and dynamic performance features of PWM IGBT current source converter induction machine drives with respect to industrial requirements. In Proceedings of the 4th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC), Xi’an, China, 14–16 August 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1393–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Hua, Z.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Z. Control strategy for three-phase current source inverter based on optimal given value of DC storage inductance current. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2019, 34, 349–362. [Google Scholar]





| Sector | On-State Switch | Voltage of Ldc |
|---|---|---|
| II (active vector 1) | S1 and S2 | uac |
| II (active vector 2) | S2 and S3 | ubc |
| III (active vector 1) | S2 and S3 | ubc |
| III (active vector 2) | S3 and S4 | uba |
| IV (active vector 1) | S3 and S4 | uba |
| IV (active vector 2) | S4 and S5 | uca |
| V (active vector 1) | S4 and S5 | uca |
| V (active vector 2) | S5 and S6 | ucb |
| VI (active vector 1) | S5 and S6 | ucb |
| VI (active vector 2) | S6 and S1 | uab |
| Parameters | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω) | Stator resistance | 0.07 |
| Rr (Ω) | Rotor resistance | 0.05 |
| Ls (mH) | Stator inductance | 4.51 |
| Lr (mH) | Rotor inductance | 4.63 |
| Lm (mH) | Mutual inductance | 4.38 |
| σ | Flux leakage coefficient | 0.088 |
| Pn (kW) | Rated power | 1.2 |
| Un (V) | Rated voltage | 48 |
| fn (Hz) | Rated frequency | 50 |
| J (kg·m2) | Rotational inertia | 0.001 |
| np | Number of pole pairs | 2 |
| Rs (Ω) | Stator resistance | 0.07 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| DC-link inductor Ldc | 4 mH |
| Filter capacitor Ca, Cb, Cc | 66 µF |
| DC-bus voltage udc | 20 V |
| Switching frequency | 10 kHz |
| Sampling frequency | 10 kHz |
| Te (N·m) | Speed (rpm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1500 | 0.03 | 11.5 |
| 0 | 900 | 0.031 | 12 |
| 1 | 1500 | 0.039 | 14.8 |
| 2 | 1500 | 0.055 | 20.9 |
| 3 | 1500 | 0.068 | 23.5 |
| 3 | 3000 | 0.064 | 22.8 |
| Category | Part Number | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| DC-link inductor Ldc | custom-made | 4 mH |
| Filter capacitor Ca, Cb, Cc | MKP1847610354P4 | 66 µF |
| DC-bus voltage udc | Battery | 24 V |
| Current sensors | LEM LA28-P | / |
| Diode modules | RM300HA-24F | 240 V/300 A |
| IGBT modules | PM400HSA120 | 400 V/120 A |
| DSP | TMS320F28335 | / |
| Encoder | OIH, 2500C/T | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, P.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Research on Parameter Design and Control Method for Current Source Inverter–Fed IM Drive Systems. Machines 2022, 10, 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100922
Song P, Liu Y, Liu C. Research on Parameter Design and Control Method for Current Source Inverter–Fed IM Drive Systems. Machines. 2022; 10(10):922. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100922
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Pengyun, Yanghui Liu, and Chao Liu. 2022. "Research on Parameter Design and Control Method for Current Source Inverter–Fed IM Drive Systems" Machines 10, no. 10: 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100922
APA StyleSong, P., Liu, Y., & Liu, C. (2022). Research on Parameter Design and Control Method for Current Source Inverter–Fed IM Drive Systems. Machines, 10(10), 922. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10100922






