1. Introduction
Due to the vast energy costs involved in manufacturing, improving the energy efficiency is a good approach to improving energy savings. Multi-axis end milling is widely used in machining free-form surfaces, for which high levels of machining accuracy and efficiency are required. In aviation, aerospace, shipbuilding, and nuclear industries, complex parts such as blisks and blades are machined using high speed multi-axis end milling, especially in semi-finish and finish machining operations. The high hardness and large size of the machined parts usually lead to long machining times. Considering the high power of multi-axis machine tools, a significant amount of electric energy is consumed as a result. For example, according to Edem [
1], more than 20,000 euros worth of electricity is consumed in five-axis machining, and the energy costs account for one-third of the total machining costs (including operation, maintenance, and depreciation). Molds and dies are changed according to the customers’ requirements, but blisks and blades will generally remain the same for a long period. Thus, even a small energy reduction in such a machining process would mean a huge energy-efficiency promotion in the long term.
Multi-axis end milling is a complicated process involving three independent phases. At the computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) phase, tool paths are generated according to the properties of the machining materials, tool cutter, and the machine tool configuration. Specific machining strategies are used in work piece coordinate systems (WCSs). Afterward, at the data conversion and numerical control (CNC) phase, the geometric data for the tool path is converted into a G-code, which can be executed directly by the machine tool according to inverse kinematics properties of the machine tool. Finally, at the execution stage, the G-code program is executed and the energy consumption can be estimated. This complete machining process contains a series of inter-related machining parameters. Finding the optimal parameter combination and optimizing energy consumption in the machining process draw lots of attention. A comprehensive review of energy consumption models in five-axis machining was made by Zhou et al. [
2]. It was noticed that the material removal rate (MRR) is the dominant factor that determines the energy efficiency of the machining process, and the MRR can be impacted by a series of machining parameters, including the cutting force, feed rate, and scallop height requirement. Energy consumption data were studied by Aramcharoen et al. [
3], and it was noticed that there was a linear correlation between the feed rate and driving power. Thus, the spiral tool path, especially the changing of the orientation of the tool, will improve the energy efficiency due to the elimination of unnecessary air cuts. Additionally, the feed rate and other machining parameters are highly coupled and determine the energy cost of the machine tool. The characteristics of energy consumption were studied using the systematic analysis method considering the material properties of the workpiece. S/N analysis was applied to investigate the relations between process parameters and energy consumption [
4]. Detailed explanations have been given to illustrate the different optimization trends for two kinds of specific energy consumption. Some equipment for CNC systems has been developed to help to improve the energy efficiency of the machining process. For example, the conventional numerical control strategy of an energy-efficient stepper drive was demonstrated by Arzhanov et al. [
5]. Considering the configuration properties of a feed drive system, including the masses, sizes, and moments of inertia, an analytical model optimizing the driving energy consumption machining process was constructed by Ryuta et al. [
6]. From the perspective of data mining, ANN has been utilized to construct a predictive model of energy consumption, where the spindle speed, feed rate, cutting depth, and cutting stripe width are optimized simultaneously [
7]. Additionally, the energy consumption of the whole manufacturing process, which involves milling, turning, and grinding, can be optimized using the modified heuristic algorithms [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
The aforementioned studies on machining energy consumption tend to optimize the tool path at the second or third phase of the CNC machining process. For multi-axis end milling, for which the machining quality is the dominant requirement, the adjustable parameters of the last two stages are the spindle speed and feed rate. However, there is no room to adjust these parameters due to a series of constraints involved, such as machine tool kinematics and cutting condition requirements. Therefore, this paper focuses on the most dominant factor of a multi-axis end milling process, i.e., the tool path. Plenty of optimization methods have been proposed in the last two decades. As the machined stripe width can change along with the equivalent curvature of the cutter at each CC point, Marciniak et al. [
12] proposed a tool path generation method that could obtain the maximum cutting stripe width by matching the principal curvatures of the work piece and the cutter. However, unforeseen overcuts and undercuts may occur when the tool orientation changes abruptly, meaning the machining quality will be reduced due to the scratching on the machined surface. In addition to obtaining the maximum cutting stripe width, the elimination of sudden changes in neighboring cutter postures also deserves researchers’ attention. Therefore, smoothing methods for the tool path, which involves a series of CC points, have been studied by many researchers. The C-space model [
13], which was first used for robot joint movement planning, could significantly help minimize the movements of the feed drive systems of machine tools. The same movements of the cutter, including translational movements and rotational movements, can be executed in different ways due to the specific kinematic configuration of each machine tool [
14]. Cong et al. [
15] employed a modified interpolation algorithm to simultaneously optimize the tool path of the tool cutter and for interpolation of tool orientation vectors. As the energy is consumed by the machine tool, it can be concluded that optimizing the movements in the MCS is more efficient than optimizing the tool orientation in the WCS. Algorithm studies were conducted by Wang et al. [
16], Yu et al. [
17], and Tian et al. [
18] to improve the efficiency of tool path generation methods.
The above methods optimize the tool path, aiming to improve the machining efficiency while guaranteeing the machining quality. They set the time efficiency as the optimization object but ignore the consideration of the energy consumption of the machining process. However, energy savings represent a dominant factor that could enhance the economic benefits. Thus, this paper focuses on the tool path’s energy consumption, i.e., optimizing the tool path to improve the energy efficiency during machining. It has to be noted that this paper focuses on point milling due to its high adaptivity, despite the fact that flank milling has higher machining efficiency and material removal rates. In this field, relevant research has also been carried out. Aramcharoen et al. [
3] and Kara et al. [
19] explored the relationships between energy consumption and different tool paths. Xu et al. [
20] proposed a tool path generation method to reduce the total amount of energy consumption by constructing an algebraic model called a machine-dependent energy potential field on the surfaces of the part. Li et al. [
21] presented a methodology to optimize the tool path for high efficiency, low energy consumption, and a small carbon footprint in the milling process. Hu et al. [
22] introduced a model for the single objective optimization problem that minimizes the energy consumption of machining tools during the feature transitions, which include the tool path and tool change operations. However, all of these studies focused on tool path selection optimization. The tool orientation of the cutter at each cutter contact (CC) point is derived based on the largest cutting width. Hence, the tool orientation of the cutter is uniquely defined as long as the CC curve is known. However, the total energy consumption is closely related to the tool orientation of the cutter and the adjustment of the tool cutter’s posture. When the largest cutting width, there will be an admissible domain of the tool orientation of the cutter at each CC point, meaning the over-cut and global collision can be avoided in a tool path. Through more refined optimization of the tool path, for example by using the optimal tool orientation sequence, the total amount of energy consumption in a single cutting path can be further reduced. Degradation of the cutting width can be compensated for and optimized in the configuration of adjacent cutting paths. This is a feasible scheme for further reducing the total energy consumption during curved surface machining. This paper makes a contribution to this field.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, a geometry analysis at the CC point is conducted and the equivalent cutting stripe width is estimated. In
Section 3, the global energy consumption, including the cutting energy consumption, driving energy consumption, and idle energy consumption, is analyzed in detail. Additionally, an energy efficiency index (SEC) is defined as the optimization object. In
Section 4, the discrete energy consumption path (DECP) model is constructed and the most energy-efficient tool orientation sequence is found based on this. The simulation cutting experiments are carried out in
Section 5, and the energy consumption data for the proposed method and iso-scallop height method are compared, showing that the energy consumption after implementing the optimization method results in significant savings. Finally, conclusions are summarized in
Section 6.
2. Geometry Analysis at the CC Point
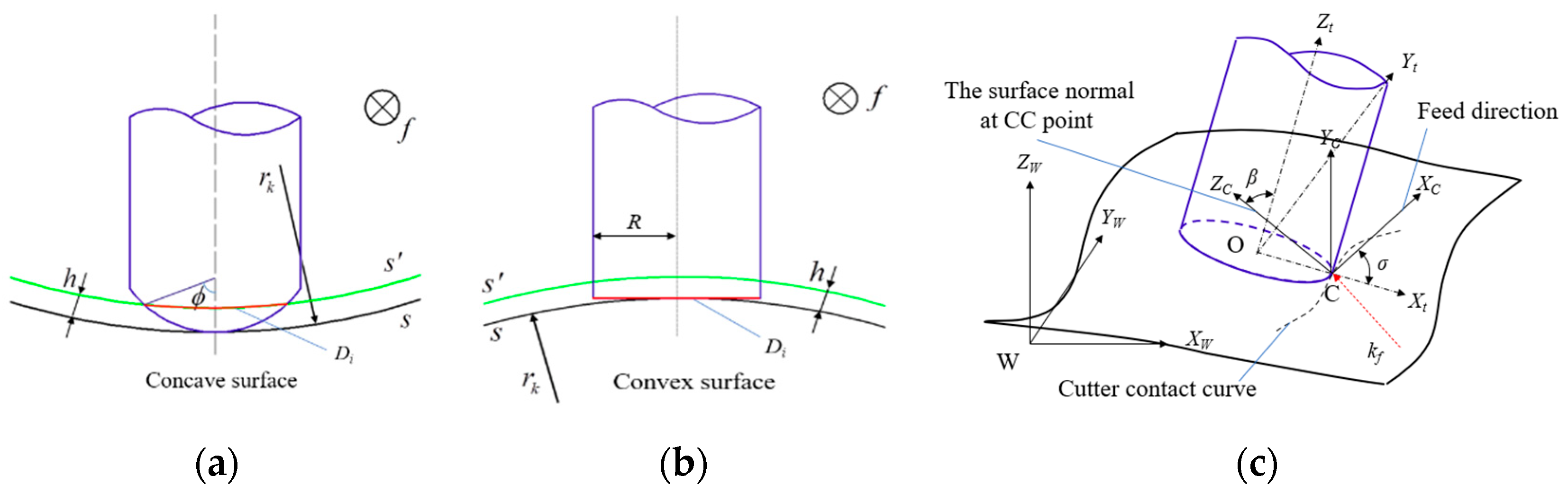
There are actually two kinds of end cutters used in the milling process, i.e., ball-end cutters and cylinder cutters (including flat-end and toroidal cutters). A flat-end cutter is used in this paper, as shown in
Figure 1. In the figure,
f is the feed direction, s is the nominal surface, and s
’ is the tolerance surface.
The local coordinate system CXCYCZC is defined at the cutter contact point (CC point) C. The cutter feeds along the direction of axis XC, ZC is the normal vector of the work piece surface at CC point, and YC is the cross-product of XC and ZC. The cutter coordinate system is defined with the center point of the cutter bottom circle O as the origin. Zt is the instantaneous cutter orientation, Xt is the tangent direction of the cutter generatrix, and Yt is the cross-product of Xt and Zt. The cutter posture can be defined with β (the angle between ZC axis and Zt axis) and σ (the angle between XC axis and Xt axis).
The following research is based on the assumption that global and local collisions are avoided. The rotary angle
σ is initially assumed to be 0 to make the tilt angle the only factor that impacts the cutter orientation. The cutter’s projection along the feed direction is an ellipse. With the given cutter radius
R, the equivalent radius at the CC point can be theoretically estimated as [
23]:
Based on the estimation of the cutter’s equivalent cutting radius, the cutting width can be calculated according to whether the machined surface is convex or concave, as shown in
Figure 1. Referring to [
24], the cutting stripe width can be estimated as:
where
h is the constant cutting remnant depth and
rk is the surface radius of curvature perpendicular to the feed direction.
To better estimate the energy efficiency of the tool path, the “specific energy consumption” index is proposed [
25], which is utilized to describe the energy consumption for removing a unit volume of material. As the thickness of remnant material before the finishing machining is constant, the swept area of the tool path is needed to calculate the specific energy consumption. The swept area from CC point
Pi to
Pi+1, which is denoted as
Areai, can be estimated as
Additionally, the chord error
e of neighboring CC points has to be within the given requirements. Correspondingly, an excessively large step size of the tool path
Lf can lead to dissatisfaction of the chord error requirements. According to the geometric analysis of the machined surface, it can be realized that
Lf is highly dependent on the local curvature of the machined surface. Thus, the step size can be estimated by adopting a simplistic circular arc approximation [
26]:
where
κf is the local curvature of the machined surface along the feed direction and
Lf-floor is the set to be the floor limit if
Lf is infinite. The chord error
e is shown in
Figure 2 below.
4. The Energy Efficiency Optimization of the Tool Path Using the Discrete Energy Consumption Path Model
To find the optimal solution to the global energy consumption model proposed in
Section 3, the following three steps are carried out: (1) discretizing the domain of admissible orientations at a CC point to transform an NP hard problem into an exhaustion problem; (2) constructing the discrete energy consumption path model to describe the exhaustion problem; (3) finding the shortest path in the discrete energy consumption path model to obtain the energy-efficient orientation sequence of a single tool path.
4.1. Discretization of the Domain of Admissible Orientations at a CC Point
As the tilt angle is the only variable expressing the tool orientation, the admissible domain of a CC point can be visualized as an arc that lies between the corresponding minimal and maximal admissible tilt angles. A minimal inclination angle is the inclination angle limit to avoid over-cutting. A maximal inclination angle is the inclination angle limit to avoid a global collision.
According to the inverse kinematic transformation analysis of the AC-type machine tool, a specific tool orientation is determined by the angle position of two rotary axes in AC-type machine tools. The mapping relation of rotary axes’ angle position and the tool orientation vector can be expressed by:
where (
α,
γ) defines the rotary axes’ angle position and (
x, y, z) defines the tool orientation vector in WCS.
Inspired by Plakhotnik [
33], we realized that the discretization of admissible domains of tool orientations is efficient to find an optimal solution for a tool path. The aim is minimizing the SEC of a tool path, and the tool orientation can be expressed by its admissible domain [
τmin,
τmax], such that the energy-efficient solution can be obtained by finding a sequence of
τs at each CC point.
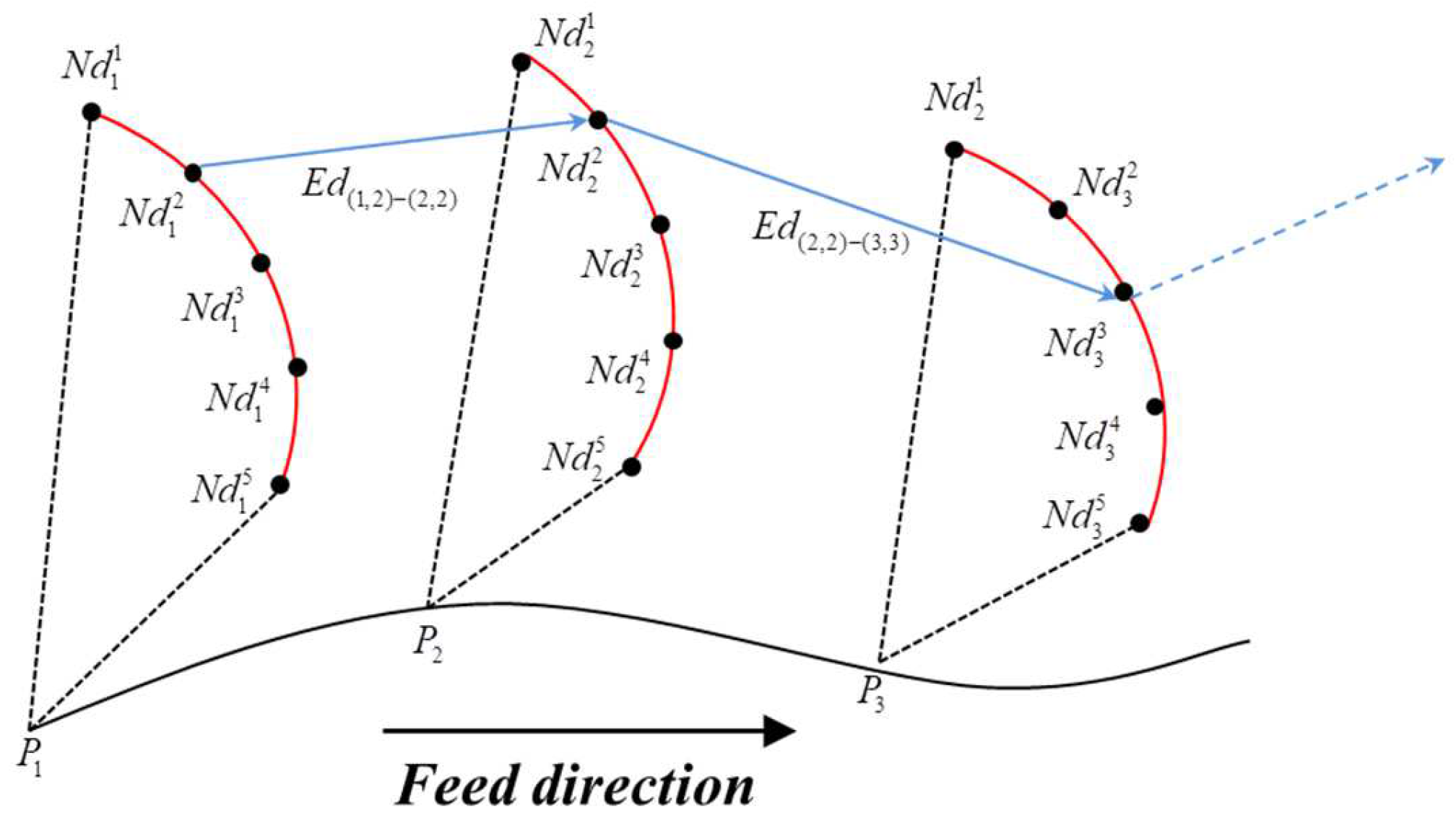
Each discrete domain of admissible orientations is composed of a group of nodes that represent a specific posture of the tool cutter. In order to describe the tool orientation sequence of the tool path, one node from each volume is selected and connected as shown in
Figure 3. It has to be noted that the dots in
Figure 3 are physically virtual, and each of them represents a potential choice of tool orientation. Regarding the edges, they represent the rotary movements transforming from one posture to another. The optimal tool orientation sequence can be solved by finding the shortest path from the start point to the end point.
4.2. Construction of Discrete Energy Consumption Path Model
Based on the discretization of admissible domains of tool orientations, the DECP model can be constructed in a similar way to that shown in
Figure 4. As the cutting energy consumption
ET is only relevant to the posture of the tool cutter, the cutting energy of each posture at a CC point is a form of static data that can be stored in the volumes of nodes.
Regarding the driving energy consumption ED, this is determined by how the tool orientation changes, meaning it is a form of dynamic data that can be stored in edges connecting two neighboring volumes of nodes. The swept area per feed can be stored in the same way as the driving energy consumption ED.
Based on the aforementioned profile of the DECP model, it can be detailed as follows:
Definition of nodes: According to Equations (7)–(9), the cutting energy consumption is only relevant to the posture of the tool cutter, meaning the
jth node at the
ith CC point corresponds to a cutting energy consumption value
ET(
i,j). The cutting energy consumption sequence of a tool path can be expressed as:
where
n is the CC point number of a tool path. Additionally, the positions of two rotary axes in the machine coordinate system are stored in volumes of nodes as:
Thus, a specific node that contains information regarding the cutting energy and positions on rotary axes can be expressed as:
Definition of edges: According to Equation (13), the driving energy consumption is relevant to the angle changes of two rotary axes, meaning the movements from one posture to the next should be defined first as:
where it should be noted that ∆
Axis is a vector that can indicate whether the rotary axes are in acceleration or deceleration.
The velocity of two rotary axes can be estimated according to Equation (21):
The corresponding acceleration can be estimated similarly:
To avoid confusion regarding the variable naming in Equations (20)–(22), there should be a special illustration; if the
jth node in the
ith column is selected, when it comes to the (
i + 1)th column, the number of selected nodes will be
j’. In the same way, the naming will be conducted in the (
i + 1)th column, i.e., the number of the selected node will be
j’’. Thus, the driving energy consumed between two adjacent postures can be estimated as:
where
μ,
F, and
J are respectively the friction coefficient, velocity friction coefficient, and inertia of each rotary axis. Thus, a specific edge that connects two neighboring nodes can be expressed as:
In order to optimize the energy efficiency of a tool path, the specific energy consumption is set as the cost function of the optimization process as:
4.3. Finding the Most Energy-Efficient Path in the DECP Model
To find the most energy-efficient path in the DECP model, an energy efficiency solution graph (EESG) is first constructed. Columns of nodes and edges connecting adjacent columns are contained in the EESG. The frame of the EESG inherits that of the DECP, i.e., each column of nodes represents the specific orientations at each CC point, as shown in
Figure 5. As the energy consumption
Eij-i’j’ and swept area
Areaij-i’j’ from one specific tool orientation to another can be calculated, the edges connecting two arbitrary nodes of neighboring columns record the energy consumption and the swept area from one tool posture to another, i.e.,
The value of each node is assigned as the optimal solution from the start point. The assignment can be concluded as:
where
N is the total number of nodes in the (
i − 1)th column.
The nodes are assigned column by column and the node with the lowest assignment represents the selected node of the optimal orientation sequence. Then, the most energy-efficient path can be obtained by following the selected edges from the end node to the start node. The validity of the assignment can be illustrated as follows:
- (1)
Illustration of the initial assignments.
When
I is initially set as 1, the graph shown in
Figure 6 represents the first two columns of nodes. The node with the lowest assignment in (
i + 1)th (that is, the 2nd) column indicates the selected node that is involved in the optimal orientation sequence.
- (2)
Illustration of the transitivity.
From the aforementioned illustration, it can be concluded that each node of the (i − 1)th column represents the most energy-efficient path, meaning the nodes of ith column can inherit the superiority from the (i − 1)th column, and the minimization process of Equation (27) can select the most energy-efficient path. AS the value of i increases, each column of nodes is assigned with the lowest SEC.
5. Experiment and Discussion
Firstly, a simulation experiment is carried out. The whole optimization process is implemented in MATLAB R2017b and is run on a computer (Intel/Core i5 CPU, 3.10 GHz, and 6 GB RAM with a Windows 7 operating system). A five-axis machine tool with a double pendulum working table is chosen to experiment on. Without loss of generality, the configuration of the machine tool is chosen as the orthogonal AC type, i.e., the motion axes are composed of three orthogonal translational axes and two orthogonal rotary axes.
The machining parameters used in the simulation, including configuration parameters and graphical parameters, are shown in
Table 1. Moreover, the accuracy of the optimized orientation sequence will be higher if the tool orientations are sampled at a higher density. However, the marginal unity when increasing the sampling efficiency is degressive. Therefore, the sampling density is set to 0.1° based on our previous work [
29,
34] in this paper. In addition, it should be pointed out that the determination of other related authentic intrinsic parameters of a particular five-axis machine, e.g., coefficients involved in the calculation of the cutting force, are in another important paper. The values of these coefficients are determined by referring to the relevant references [
20,
21,
29] in this paper.
A free-form surface is chosen to prove the validity of the proposed method. The offset distance is given as 3 mm, i.e., the thickness of the remnant material on the surface is 3 mm. To obtain the largest cutting stripe width, the initial tool paths are generated by the iso-scallop height algorithm on the free-form surface and a single path is chosen to verify the optimization method.
The chosen path is firstly discretized into a series of points on the path according to Equation (4) to satisfy the requirement of the chord error. Thus, 94 points are extracted from the chosen path to constitute the optimization domain of the proposed energy-saving optimization method. With the length of the tool path L = 203.4 mm and the feed rate FR = 600 mm/min substituted, the idle energy consumption during the machining process along the chosen path can be easily estimated: Eidle = Pidle·L/FR = 4068 J.
Next, for comparative analysis, the cutting energy and driving energy respectively consumed by the iso-scallop height algorithm and the method proposed in this paper are calculated. For the iso-scallop height algorithm, the cutting energy and driving energy consumed are ET = 10916.34 J and ED = 2015.76 J, respectively, and the accumulated machining area is Areainit = 175.48 mm2; thus, the specific energy of the tool path is SECinit = 96.88 J/mm2 considering the idle energy consumption Eidle = 4068 J. Correspondingly, for the method proposed in this paper, the machining energy and driving energy consumed are respectively ET-Opti = 8718.37 J and ED-Opti = 2045.23 J, and the accumulated machining area is Areainit = 170.11 mm2; thus, the specific energy of the tool path is SECOpti = 87.19 J/mm2 considering the idle energy consumption Eidle = 4068 J.
As shown in
Table 2, it can be found that the machining energy decreases with the deterioration of the cutting stripe width, while the driving energy stays relevantly stable. However, the specific energy consumption of the tool path is optimized, i.e., the specific energy consumption decreases from 96.88 J/mm
2 to 87.19 J/mm
2, which implies a 10.01% energy saving when removing a specific volume of material. Among the three energy consumption components, the idle running energy is unchanged because only a single tool path is studied, the driving energy stays relevantly stable, and the change of cutting energy is relatively large. This is due to the shearing energy no longer being the same under different tool orientation sequences, even with the same volume of material removed, because the cutter–workpiece engagement during the cutting process has changed. Based on the further comparative analysis of some segments of the tool path, it can be found that larger cutting stripe widths are obtained by changing the tool orientation acutely, although the cutting energy increases. Sometimes it is not economically feasible to drive rotary axes of the machine tool to obtain the largest cutting stripe because a nonlinear relationship exists with the driving energy, meaning the marginal benefits will be reduced in certain segments of the tool path. Therefore, it is not smart to acquire a large MMR blindly. The proposed optimization method makes the rotary motions of the machine tool smarter, meaning the machine tool can adjust its rotary axes to obtain the largest marginal energy benefit. Then, the SEC value when cutting a single tool path is reduced and also lays the foundation for further reductions in global energy consumption during the machining of complete curved surfaces.