An Iterative Modified Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition Method and Its Application on Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Bearings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Description and Characteristics Study on ACMD
2.1. Basic Theory of ACMD
2.2. Ensemble L-Kurtosis Indicator
2.3. Research on the Influence of ACMD Parameters
2.3.1. Bearing Fault Simulating Signal
2.3.2. Study on Decomposition Characteristics of ACMD with Different Parameters
3. Proposed IMACMD Method
3.1. Overview of the Novel Iteration Fault Diagnostic Strategy
3.2. Determination of Maximum Iteration Number (K) and Instantaneous Frequencies (fc) of ACMD
3.2.1. Initialization
3.2.2. Adjustment
3.3. Weight Factor (α) Selection for ACMD
3.4. Feature Extraction Results of Each Iteration
4. Application Procedures of the Proposed Method
5. Experimental Signal Verification
5.1. Experimental Setup Introduction
5.2. Single Fault Signal Analysis and Comparison
5.3. Compound Fault Signal Analysis and Comparison
6. Engineering Signal Verification
6.1. Wind Turbine Introduction
6.2. Engineering Signal Analysis and Comparison
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMD | adaptive chirp mode decomposition |
| CYCBD | cyclostationary blind deconvolution |
| EMD | empirical mode decomposition |
| IMACMD | iterative modified adaptive chirp mode decomposition |
| LMD | local mean decomposition |
| MCKD | maximum correlated kurtosis deconvolution |
| MED | minimum entropy deconvolution |
| MOEDA | multipoint optimal minimum entropy deconvolution adjusted |
| SK | spectral kurtosis |
| SSD | singular spectrum decomposition |
| SSC | singular spectrum component |
| VMD | variational mode decomposition |
| Notations | |
| A | amplitude value of each local maximum |
| An | amplitude of cycle impacts |
| Bj | amplitude of jth random impulse |
| Ck | amplitude of kth harmonic component |
| d | difference between the sequences |
| ɛ | remanent energy ratio |
| f | potential instantaneous frequency |
| fc | instantaneous frequency |
| fcage | cage fault characteristic frequency |
| fin | inner race fault characteristic frequency |
| fk | resonance frequency of kth harmonic component |
| fm | coefficient of resonance frequency |
| fn | resonance frequency of cycle impacts |
| fout | outer race fault characteristic frequency |
| fr | rotating frequency |
| froller | roller fault characteristic frequency |
| fs | sampling frequency |
| fv | resonance frequency of random impulses |
| I | number of cycle impacts |
| J | number of random impulses |
| K | maximum iteration number |
| kb | boundary value of the local maximum |
| Kc | number of harmonic components |
| kn | number of local maximum values |
| N | sampling points |
| q | number of sequences |
| sm | impulse response function of the rotating machinery system |
| t | time |
| Ta | period of cycle impacts |
| Tj | occurrence time of jth random impulse |
| w | mode of IMACMD |
| α | weight factor |
| βm | coefficient of resonance damping |
| γ | specifies the slippage characteristic |
| μr | rth L-moment |
| ρ | Spearman rank correlation coefficient values |
| φk | phase of kth harmonic component |
| φm | coefficient of phase |
References
- Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Spectrum-based, full-band preprocessing, and two-dimensional separation of bearing and gear compound faults diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3513216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, R. Enhanced symplectic characteristics mode decomposition method and its application in fault diagnosis of rolling bearing. Measurement 2020, 166, 108108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhuo, S.; Li, C.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, G. An enhanced intrinsic time-scale decomposition method based on adaptive lévy noise and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. Symmetry 2021, 13, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chu, F.; Han, Q.; Kong, Y. Compound faults detection in gearbox via meshing resonance and spectral kurtosis methods. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 392, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Si, Z.; Xiang, J. A compound fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on wavelet scattering transform and improved soft threshold denoising algorithm. Measurement 2022, 196, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. Compound fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on improved tunable Q-factor wavelet transform. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Su, S.; Jing, X.; Li, D. Vibration mechanism analysis for cylindrical roller bearings with single/multi defects and compound faults. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 144, 106903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bao, W.; Tu, X.; Li, F.; Li, K. An adaptive spectral kurtosis method and its application to fault detection of rolling element bearings. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lei, Y.; Jia, F.; Xing, S. An intelligent fault diagnosis approach based on transfer learning from laboratory bearings to locomotive bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 692–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yan, R. Compound fault diagnosis of rolling bearing using PWK-sparse denoising and periodicity filtering. Measurement 2021, 181, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Hua, L.; Tao, L.; Xing, W.; Qing, C. An enhanced frequency band entropy method for fault feature extraction of rolling element bearings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 5780–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mo, L.; Yan, R. Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on WHVG and GCN. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3519811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, P.; Jia, M. Fault diagnosis of rolling-element bearing using multiscale pattern gradient spectrum entropy coupled with Laplacian score. Complexity 2020, 2020, 4032628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, J. Research on remaining useful life prediction of rolling element bearings based on time-varying Kalman filter. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Mo, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Dai, W.; Miao, Q. Multiple discolored cyclic harmonic ratio diagram based on meyer wavelet filters for rotating machine fault diagnosis. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3132–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Han, Q.; Chu, F.; Feng, Z. A new SKRgram based demodulation technique for planet bearing fault detection. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 385, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, J. The infogram: Entropic evidence of the signature of repetitive transients. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 74, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshrefzadeh, A.; Fasana, A. The Autogram: An effective approach for selecting the optimal demodulation band in rolling element bearings diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 105, 294–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zuo, M.J.; Peng, D. Accugram: A novel approach based on classification to frequency band selection for rotating machinery fault diagnosis. ISA Trans. 2019, 95, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naima, G.; Elias, H.A.; Salah, S. An improved fast kurtogram based on an optimal wavelet coefficient for wind turbine gear fault detection. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Miao, Y.; Lin, J.; Yi, Y. Adaptive maximum second-order cyclostationarity blind deconvolution and its application for locomotive bearing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 158, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, D.; Long, J.; Sun, H.; Campman, X.; Buyukozturk, O. Multi-component deconvolution interferometry for data-driven prediction of seismic structural response. Eng. Struct. 2021, 241, 112405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cui, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J. Vibration mechanism and improved phenomenological model of the planetary gearbox with broken ring gear fault. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, W. Adaptive multipoint optimal minimum entropy deconvolution adjusted and application to fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 12153–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, X.; He, Y. Weak fault detection for wind turbine bearing based on ACYCBD and IESB. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, W.; Song, D.; Cheng, Y. Blind deconvolution assisted with periodicity detection techniques and its application to bearing fault feature enhancement. Measurement 2020, 159, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Nazari, M.; Tang, G. Recursive variational mode extraction and its application in rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 165, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J. Identification of mechanical compound-fault based on the improved parameter-adaptive variational mode decomposition. ISA Trans. 2019, 84, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Qin, Y. Improved EMD with a soft sifting stopping criterion and its application to fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 55, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, X. Complete ensemble local mean decomposition with adaptive noise and its application to fault diagnosis for rolling bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 106, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, G.; He, Y. Application of RSSD-OCYCBD strategy in enhanced fault detection of rolling bearing. Complexity 2020, 2020, 5424236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, L.; Liu, F. Bearing fault diagnosis based on improved VMD and DCNN. J. Vibroeng. 2020, 22, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Li, N.; Selesnick, I.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z. Nonconvex group sparsity signal decomposition via convex optimization for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 4863–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, A.; Zhang, X. A novel hybrid approach for damage identification of wind turbine bearing under variable speed condition. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 169, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dong, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Meng, G. Nonlinear chirp mode decomposition: A variational method. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 65, 6024–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X. Detection of rub-impact fault for rotor-stator systems: A novel method based on adaptive chirp mode decomposition. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 440, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lu, F.; Liu, S.; Li, X. A parameter-adaptive ACMD method based on particle swarm optimization algorithm for rolling bearing fault diagnosis under variable speed. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 1851–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Two-step Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition for time-varying bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 3055291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, G.; Yan, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine bearing based on optimized Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13649–13666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Dong, X.; Zhang, W.; Meng, G. Adaptive chirp mode pursuit: Algorithm and applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 116, 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ruan, J.; Zhuang, Z. Fault diagnosis for circuit-breakers using adaptive chirp mode decomposition and attractor’s morphological characteristics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 145, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J.; Ding, C.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Z. A novel indicator to improve fast kurtogram for the health monitoring of rolling bearing. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 12252–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Tu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, F. Envelope spectrum L-Kurtosis and its application for fault detection of rolling element bearings. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xiang, J.; Hou, S.; Tang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Ye, S. Method using L-Kurtosis and enhanced clustering-based segmentation to detect faults in axial piston pumps. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Park, S. An analysis of correlation between personality and visiting place using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2020, 14, 1951–1966. [Google Scholar]
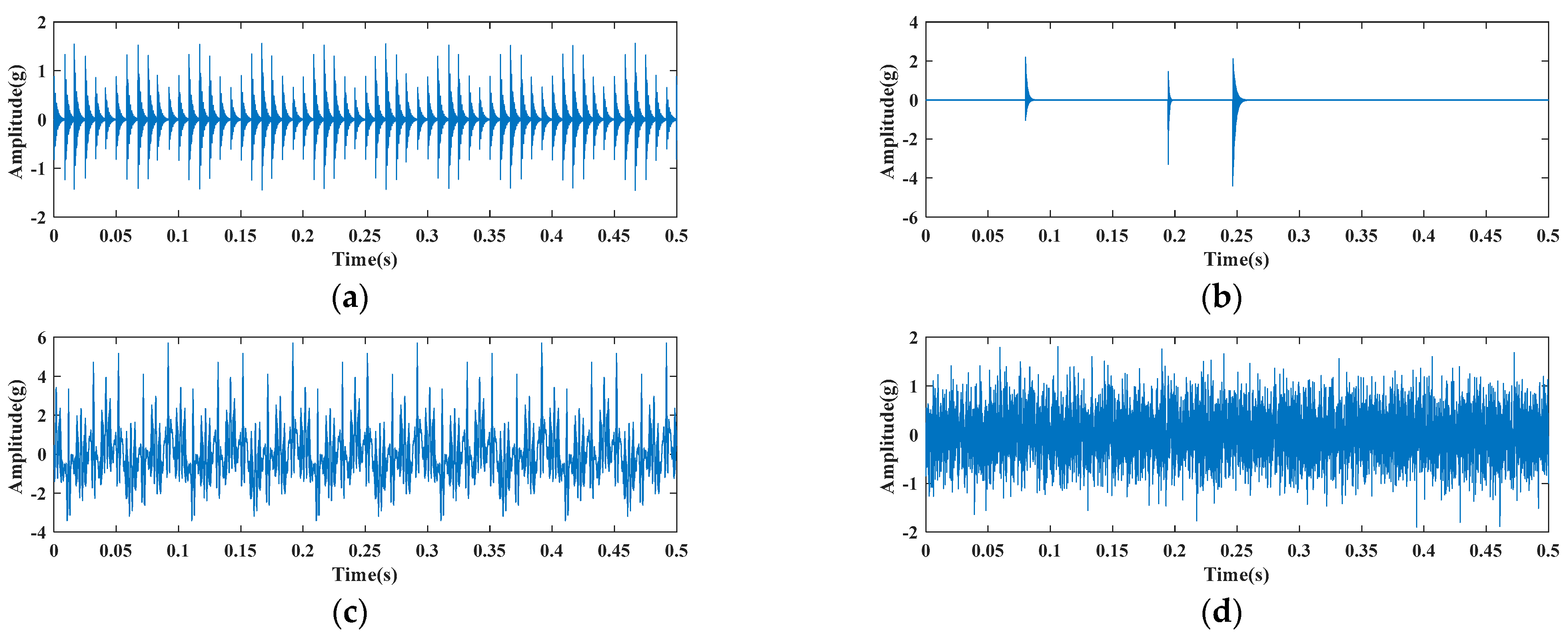





























| Parameter | Meaning | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Fault feature signal | ||
| I | Number of cycle impacts | 165 |
| A | Amplitude of cycle impacts | 1.1 |
| fn | Resonance frequency of cycle impacts | 5500 Hz |
| Ta | Period of cycle impacts | 0.0083 s |
| γ | Specifies the slippage characteristic | random value in 1–2% Ta |
| Random impulses | ||
| J | Number of random impulses | 3 |
| B1, B2, B3 | Amplitude of jth random impulse | 2, 3, 4 |
| fv | Resonance frequency of random impulses | 4000 Hz |
| T1, T2, T3 | Occurrence time of jth random impulse | 0.08 s, 0.20 s, 0.25 s |
| Harmonic components | ||
| K | Number of harmonic components | 8 |
| C1–C8 | Amplitude of kth harmonic component | 0.7, 0.8, 0.6, 0.5 0.3, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3 |
| f1–f8 | Resonance frequency of kth harmonic component | 300, 400, 500, 600, 2850, 3000, 3150, 3300 |
| φk | Phase of kth harmonic component | π/2 |
| Ball Number | Ball Diameter | Pitch Diameter | Contact Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 7.94 mm | 39.04 mm | 0° |
| Ball Number | Ball Diameter | Pitch Diameter | Contact Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 41.275 mm | 190 mm | 0° |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, A.; Tang, G.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Fan, S. An Iterative Modified Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition Method and Its Application on Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Bearings. Machines 2022, 10, 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10080704
Ding A, Tang G, Wang X, He Y, Fan S. An Iterative Modified Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition Method and Its Application on Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Bearings. Machines. 2022; 10(8):704. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10080704
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Ao, Guiji Tang, Xiaolong Wang, Yuling He, and Shiyan Fan. 2022. "An Iterative Modified Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition Method and Its Application on Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Bearings" Machines 10, no. 8: 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10080704
APA StyleDing, A., Tang, G., Wang, X., He, Y., & Fan, S. (2022). An Iterative Modified Adaptive Chirp Mode Decomposition Method and Its Application on Fault Diagnosis of Wind Turbine Bearings. Machines, 10(8), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10080704







