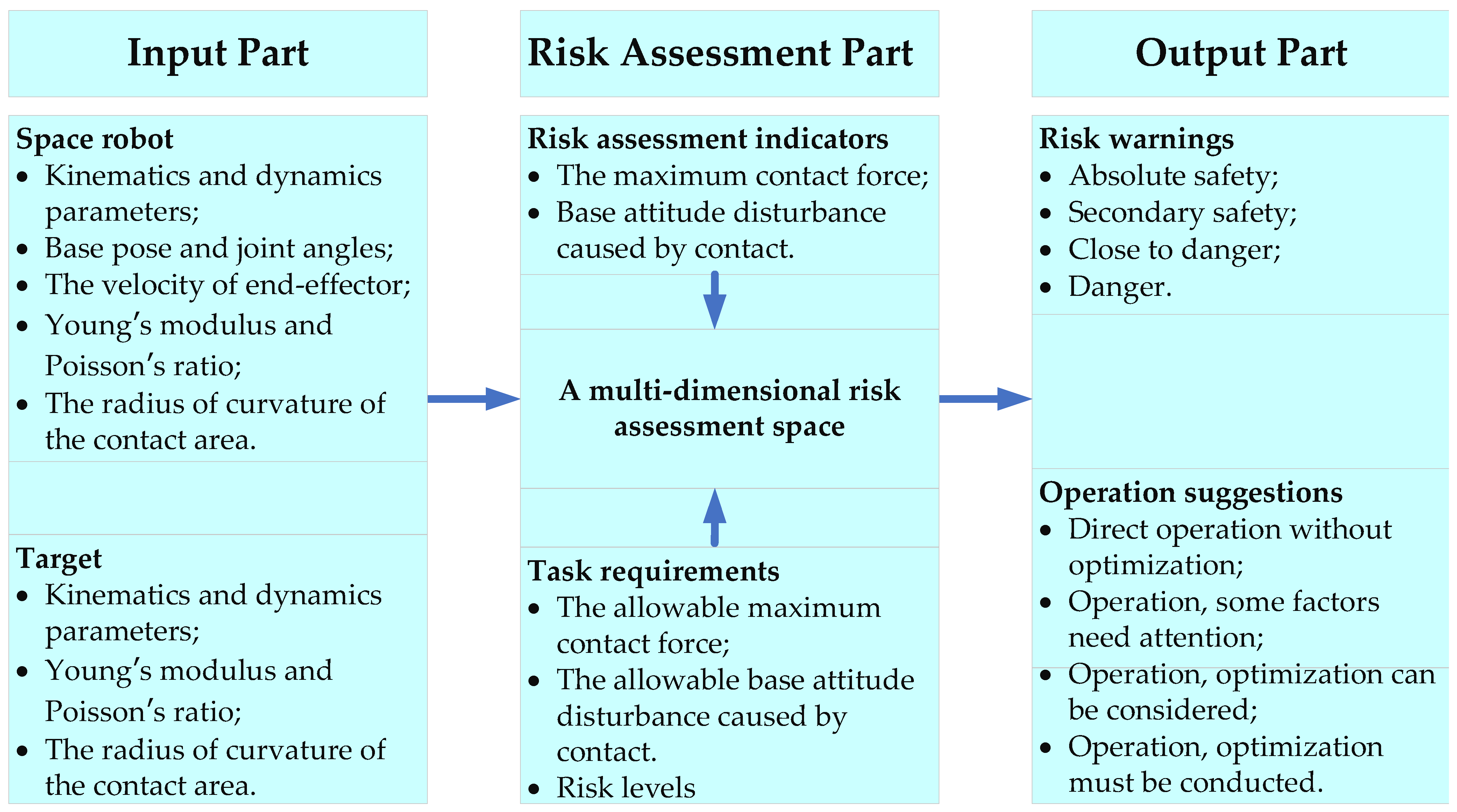
Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Performing Contact Task
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamics Model of Free-Floating Space Robot
3. Contact Risk Assessment Indicators
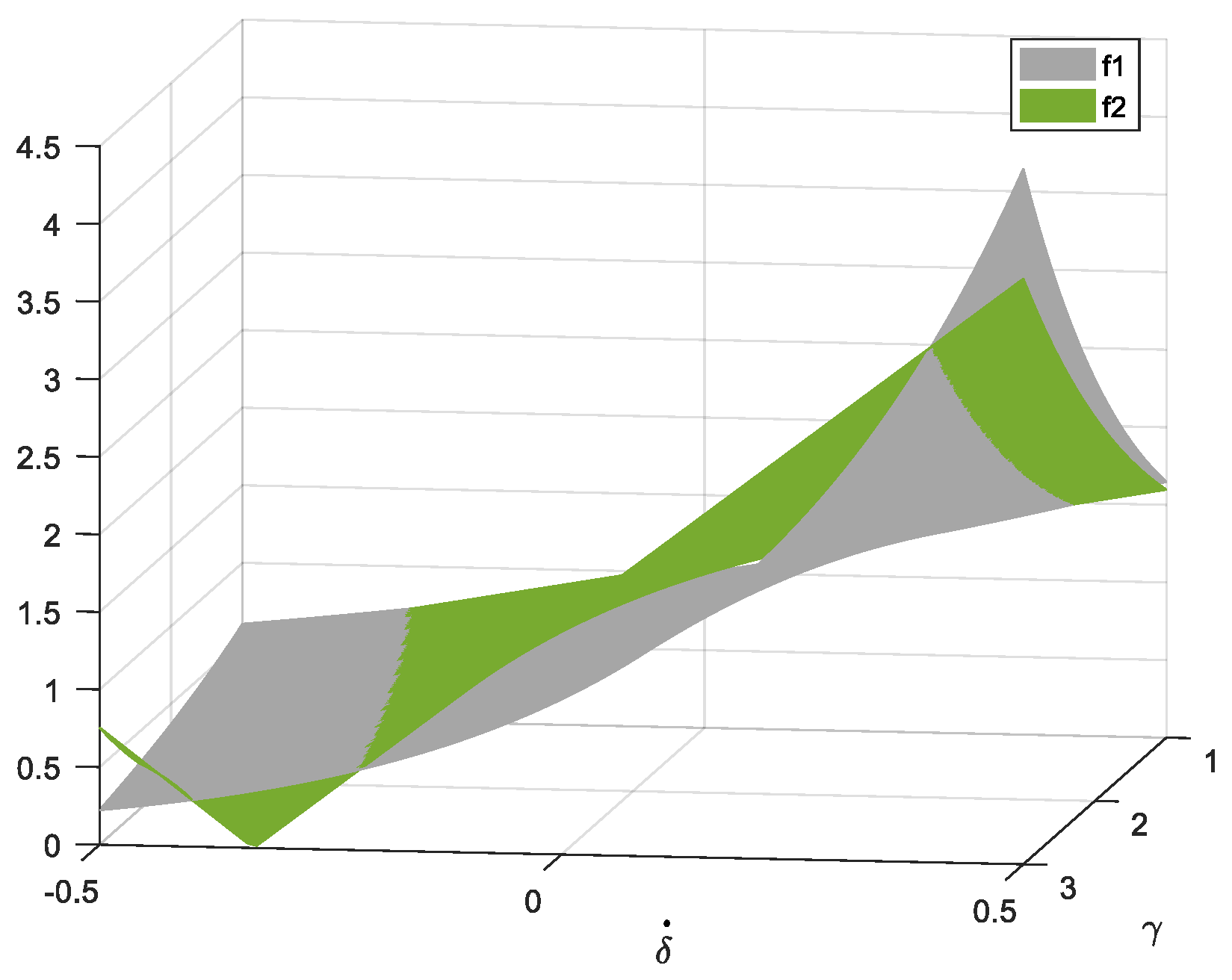
3.1. The Maximum Contact Force
3.2. The Base Attitude Disturbance Caused by Contact
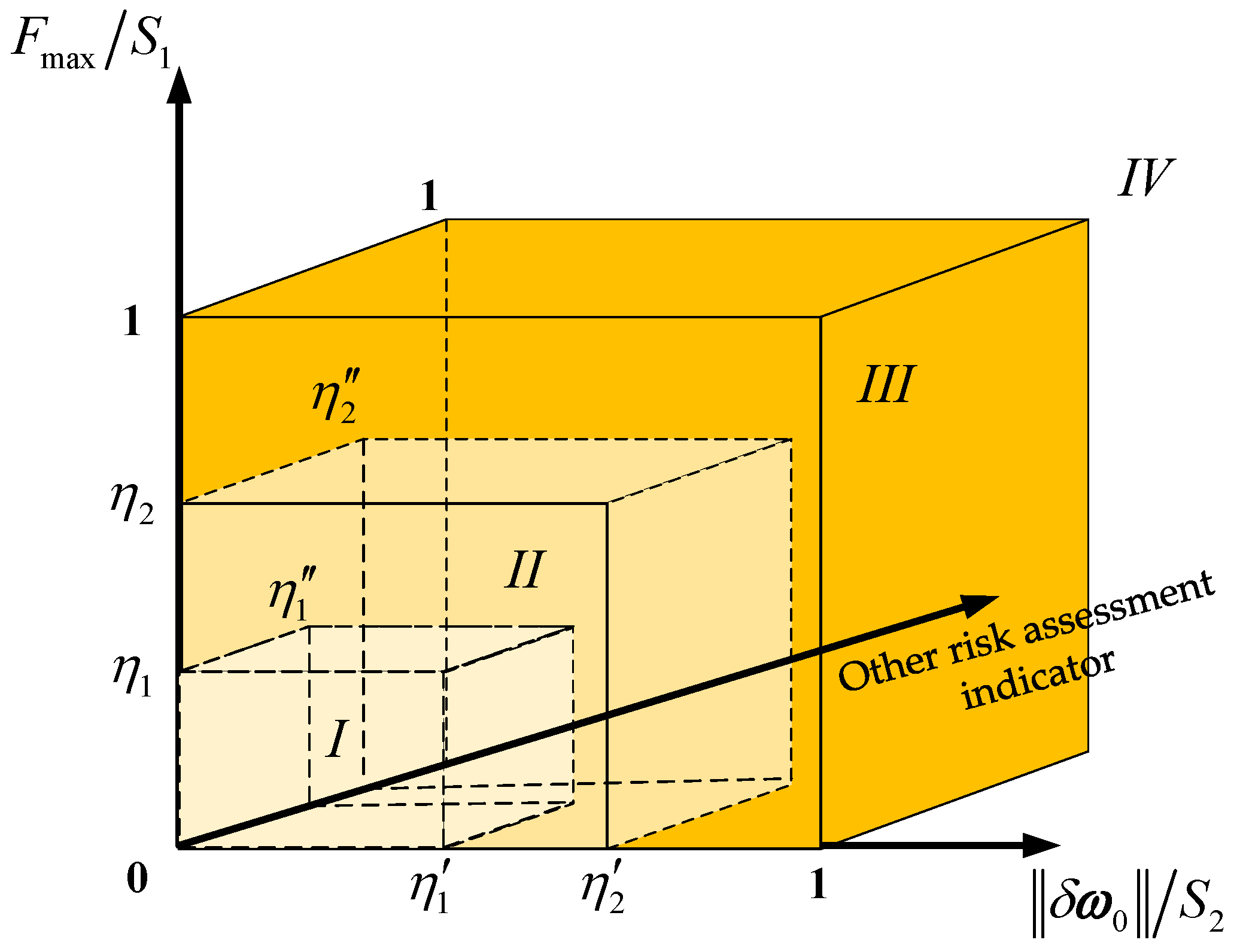
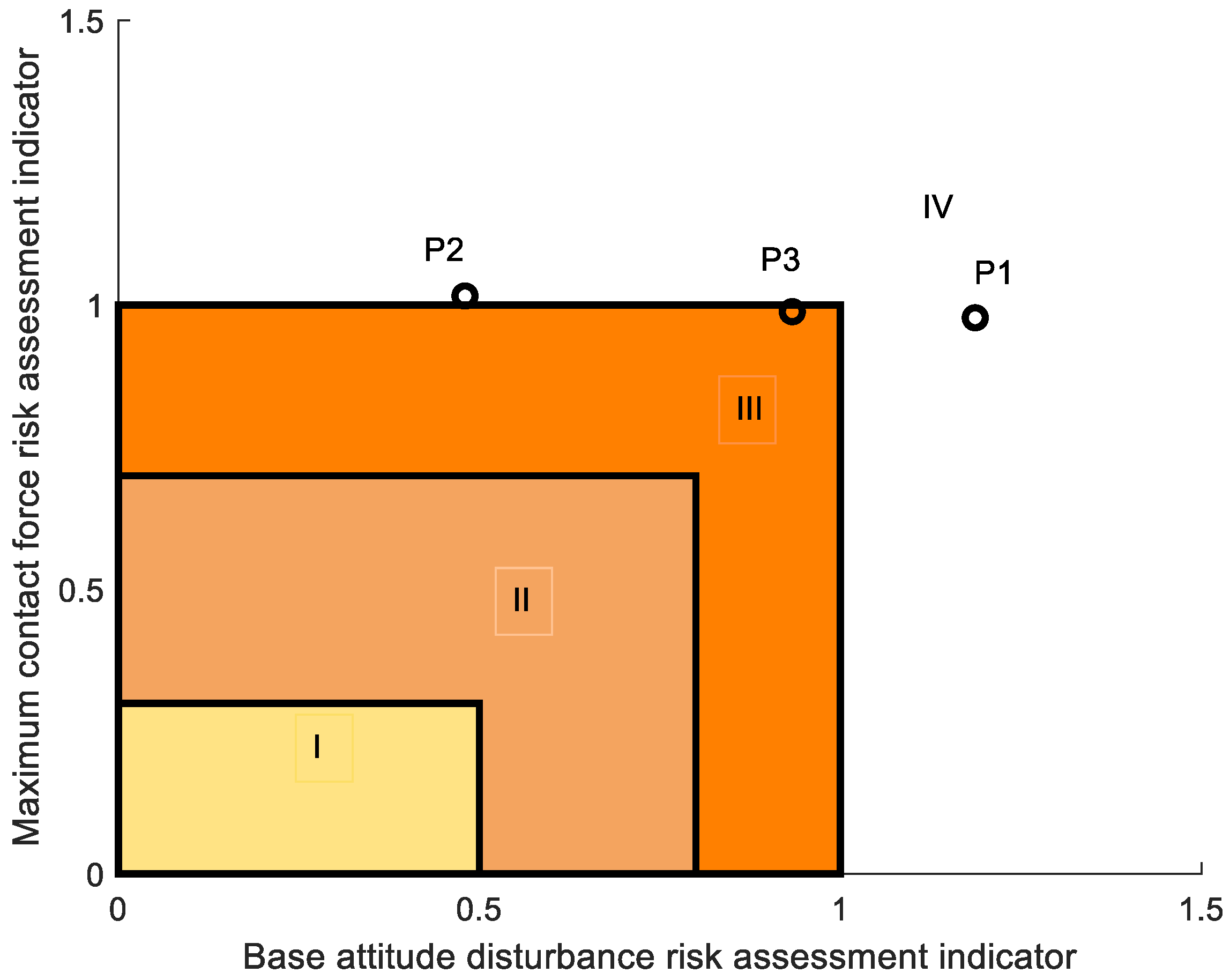
4. Contact Risk Assessment Model
5. Contact Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization
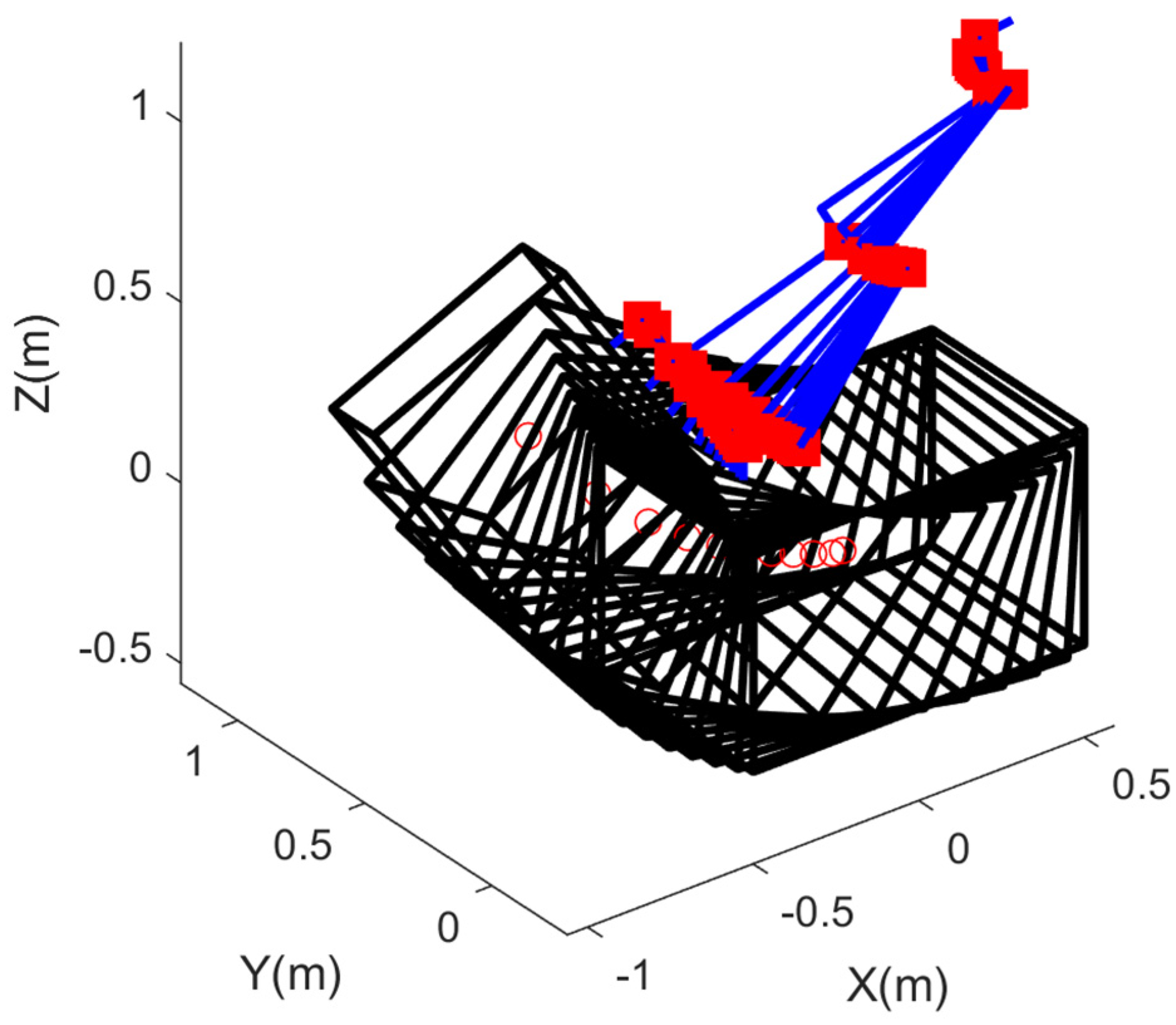
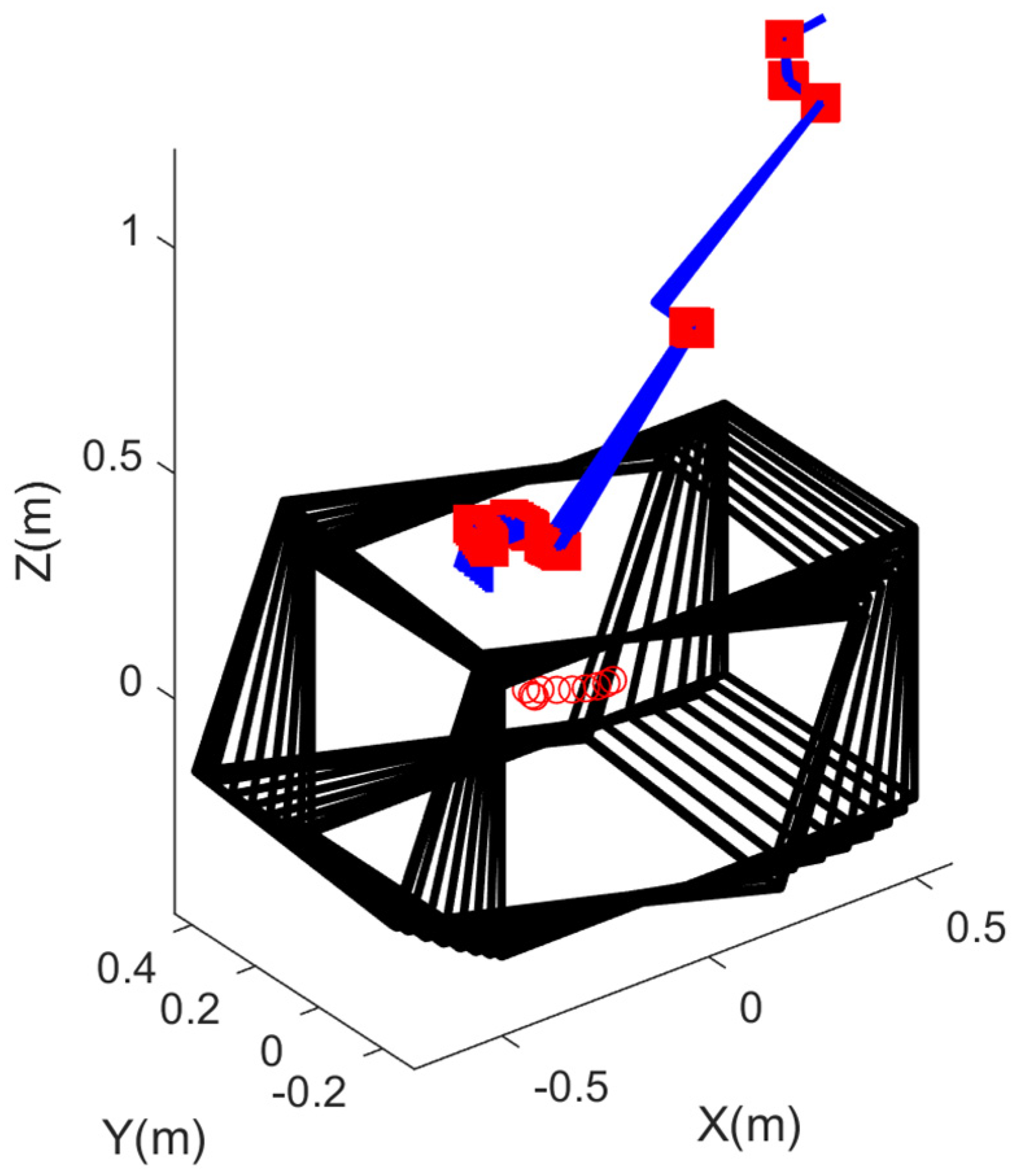
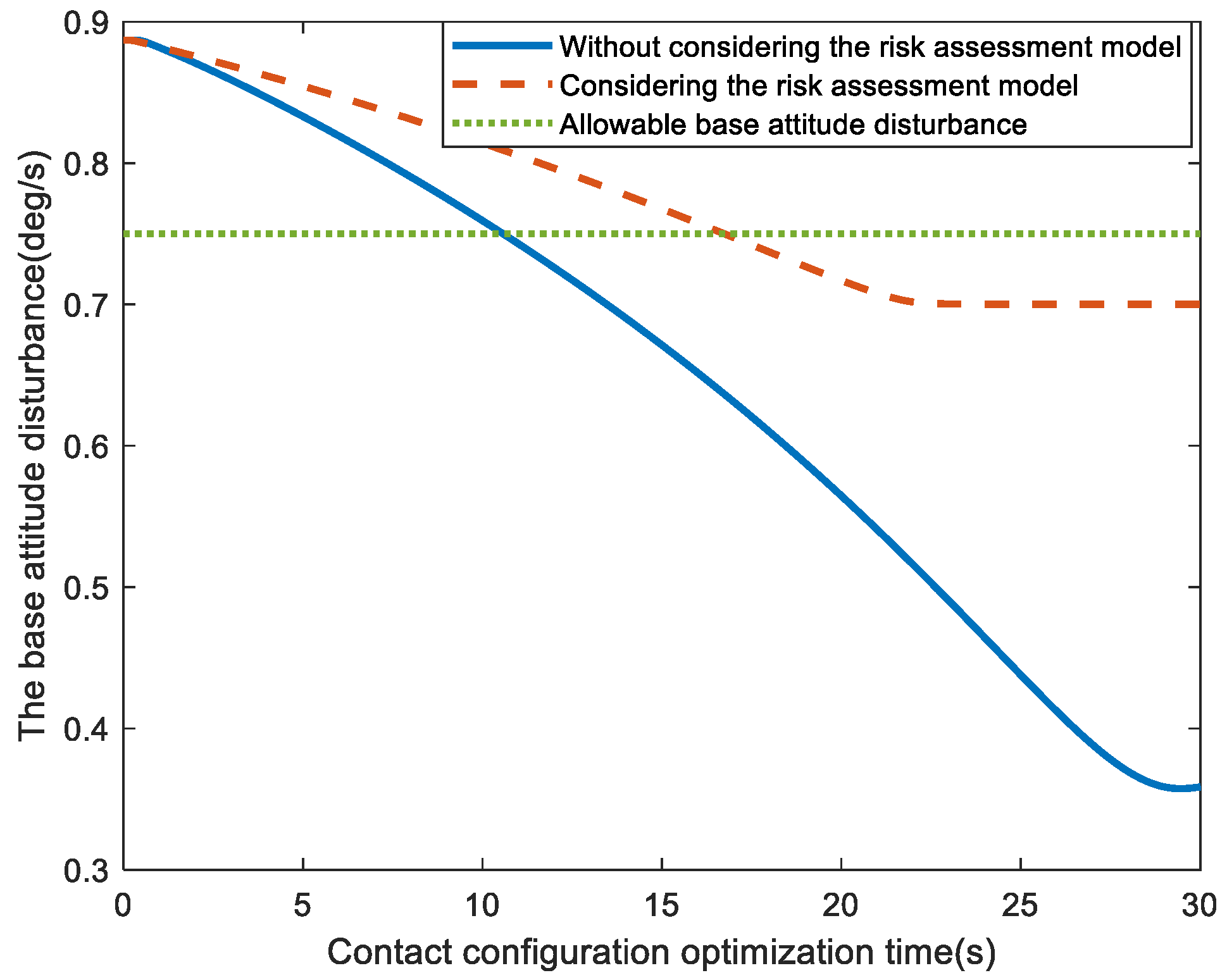
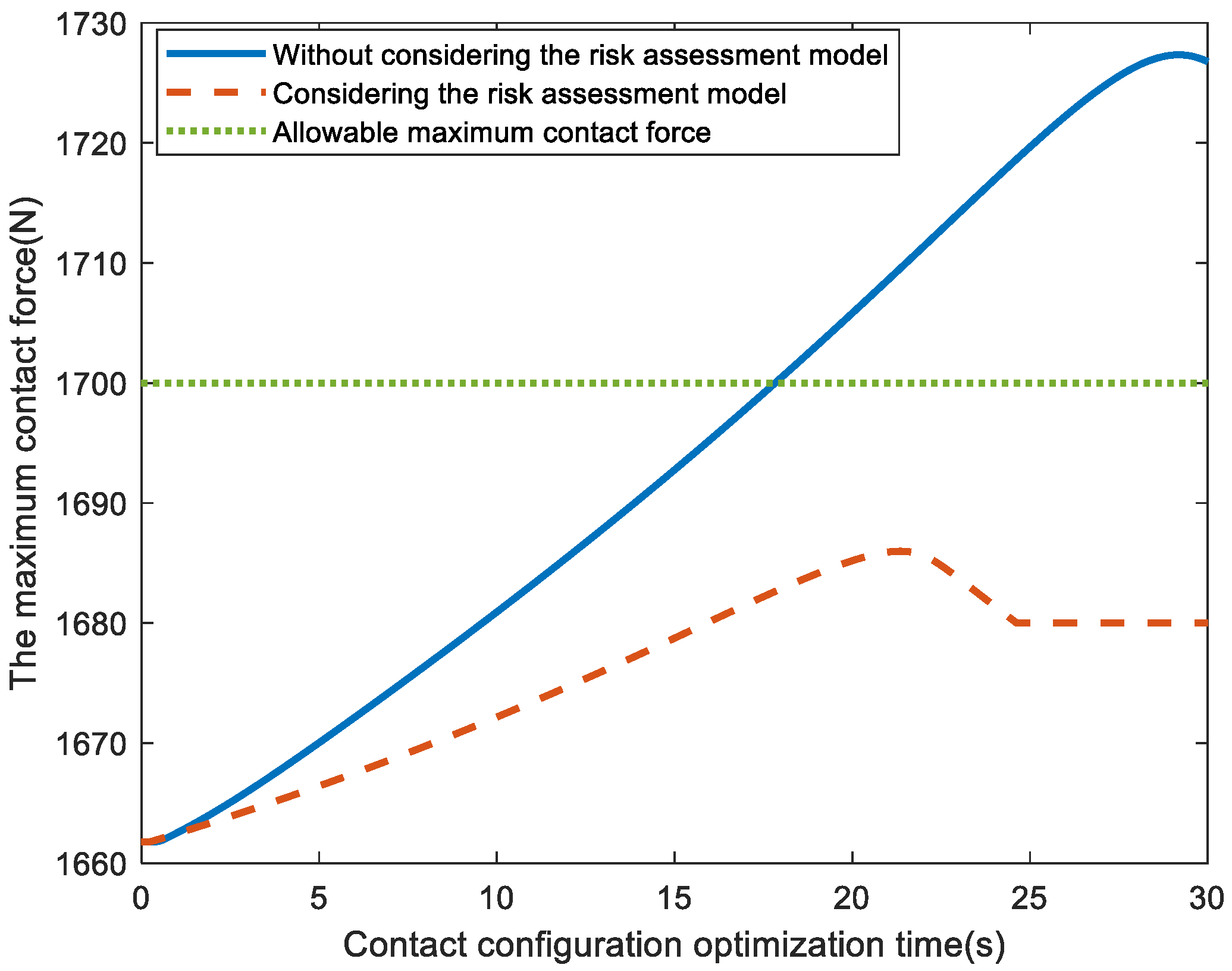
6. Numerical Simulations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xue, Z.H.; Liu, J.G.; Wu, C.C.; Tong, Y.C. Review of In-Space Assembly Technologies. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 24, 21–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, A.; Ai, H.; Chen, L. A Fuzzy Logic Reinforcement Learning Control with Spring-Damper Device for Space Robot Capturing Satellite. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Abad, A.; Ou, M.; Pham, K.; Ulrich, S. A Review of Space Robotics Technologies for On-Orbit Servicing. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2014, 68, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Dragomir, N. Space Robot Impact Analysis and Satellite-Base Impulse Minimization Using Reaction Null-Space. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nagoya, Japan, 21–27 May 1995; pp. 1271–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Jia, Q.X.; Sun, H.X.; Hong, L. Analysis on Impact Motion of Space Robot in the Object Capturing Process. Jiqiren 2010, 32, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, D.; Gora, S.; Maheshwari, D.; Shah, S.V. Impact Modeling and Reactionless Control for Post-Capturing and Manoeuvring of Orbiting Objects Using a Multi-Arm Space Robot. Acta. Astronaut. 2021, 182, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tang, L. Impact Analysis and Trajectory Planning Stabilization Control for Space Robot after Capturing Target. Yuhang Xuebao 2021, 42, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, L.B.; Walker, M.W. On the Dynamics of Contact Between Space Robots and Configuration Control for Impact Minimization. IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom. 1993, 9, 581–591. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Sun, H.X. Pre-Impact Trajectory Optimization of Redundant Space Manipulator with Multi-Target Fusion. Yuhang Xuebao 2014, 35, 639–647. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.C.; Wang, T.S. Pre-Impact Configuration Designing of a Robot Manipulator for Impact Minimization. J. Mech. Robot. 2017, 9, 031010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, Q.X.; Chen, G.; Sun, H.X. The Precollision Trajectory Planning of Redundant Space Manipulator for Capture Task. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 371673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Moreira, P.; Flores, P.; Lankarani, H.M. Compliant Contact Force Models in Multibody Dynamics: Evolution of the Hertz Contact Theory. Mech. Mach. Theory. 2012, 53, 99–121. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, P.; Machado, M.; Miguel, T.S.; Martins, J.M. On the Continuous Contact Force Models for Soft Materials in Multibody Dynamics. Multibody. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 25, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.H.; Zhao, L.; He, G.P. A Continuous Contact Force Model for Impact Analysis in Multibody Dynamics. Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 153, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Cui, M.M. Space Robot Capture Collision Force Control Method Based on Explicit Force Control. Chin. Space Sci. Technol. 2019, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.W.; Li, M.; Wang, X.C.; Li, Y.; Dou, L.H. Contact-Impact Dynamics Simulation for Space Manipulator Using Equivalent Spring-Damping Model. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Shenyang, China, 29 June–4 July 2014; pp. 3186–3191. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Mou, F.L.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J. Contact Dynamics and Control of a Space Robot Capturing a Tumbling Object. Acta Astronaut. 2018, 151, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, Q.X.; Chen, G.; Sun, H.X.; Cao, L.F. Impact Analysis of Space Manipulator Collision with Soft Environment. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Hangzhou, China, 9–11 June 2014; pp. 1965–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G.; Sun, H.X. Collision Analysis of Space Manipulator Multibody System Based on Equivalent Mass. Yuhang Xuebao 2015, 36, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Capturing Tumbling Target. Aerospace 2022, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.L.; Katupitiya, J.; Kinkaid, N. A Robust Attitude Controller for a Spacecraft Equipped with a Robotic Manipulator. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 4966–4971. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, D.N.; Yoshida, K. Utilization of the Bias Momentum Approach for Capturing a Tumbling Satellite. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; pp. 3333–3338. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Huang, P.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, Y. Combined Spacecraft Stabilization Control After Multiple Impacts During the Capture of a Tumbling Target by a Space Robot. Acta. Astronaut. 2020, 176, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.R.; Wu, X.D.; Inamori, T.; Shi, Z.; Sun, X.Z.; Cui, H.T. Compensation of Base Disturbance Using Optimal Trajectory Planning of Dual-Manipulators in a Space Robot. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, W.F.; Hu, Z.H.; Liang, B. Multi-Objective Configuration Optimization for Coordinated Capture of Dual-Arm Space Robot. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 167, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, D.S. Trajectory Planning of 7-DOF Space Manipulator for Minimizing Base Disturbance. Int. J. Adv. Rob. Syst. 2016, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, F.; Shah, S.V.; Singh, A.K.; Madhava, K.K.; Misra, A.K. Reactionless Maneuvering of a Space Robot in Precapture Phase. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2016, 39, 2417–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenchev, D.N.; Yoshida, K. Impact Analysis and Post-Impact Motion Control Issues of a Free-Floating Space Robot Subject to a Force Impulse. IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom. 1999, 15, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.C.; Sun, Z.W. Pre-Impact Configuration Planning for Capture Object of Space Manipulator. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aerospace and Astronautics, Shenzhen, China, 10–12 December 2008; p. 4776179. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, P.C.; Zhang, X. Preimpact Configuration Analysis of a Dual-Arm Space Manipulator with a Prismatic Joint for Capturing an Object. Robotica 2013, 31, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, Q.X.; Chen, G.; Sun, H.X. Pre-impact Trajectory Planning for Minimizing Base Attitude Disturbance in Space Manipulator Systems for a Capture Task. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2015, 28, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Xu, W.F. Space Robotics: Modelling, Planning and Control; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.F.; Liang, B.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.S. Autonomous Target Capturing of Free-Floating Space Robot: Theory and Experiments. Robotica 2009, 27, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O. Inertial Properties in Robotic Manipulation. An Object-level Framework. Int. J. Rob. Res. 1995, 14, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, H. Über Die Berührung Fester Elastischer Körper. J. Reine Angew. Math. 1881, 92, 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, P.; Ambrósio, J.; Claro, J.C.P.; Lankarani, H.M. Contact-Impact Force Models for Mechanical Systems. In Kinematics and Dynamics of Multibody Systems with Imperfect Joints: Models and Case Studies; Friedrich, P., Peter, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 34, pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Jia, Q.X.; Sun, H.X. Singularity Analysis of Redundant Space Robot with the Structure of Canadarm2. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 735030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

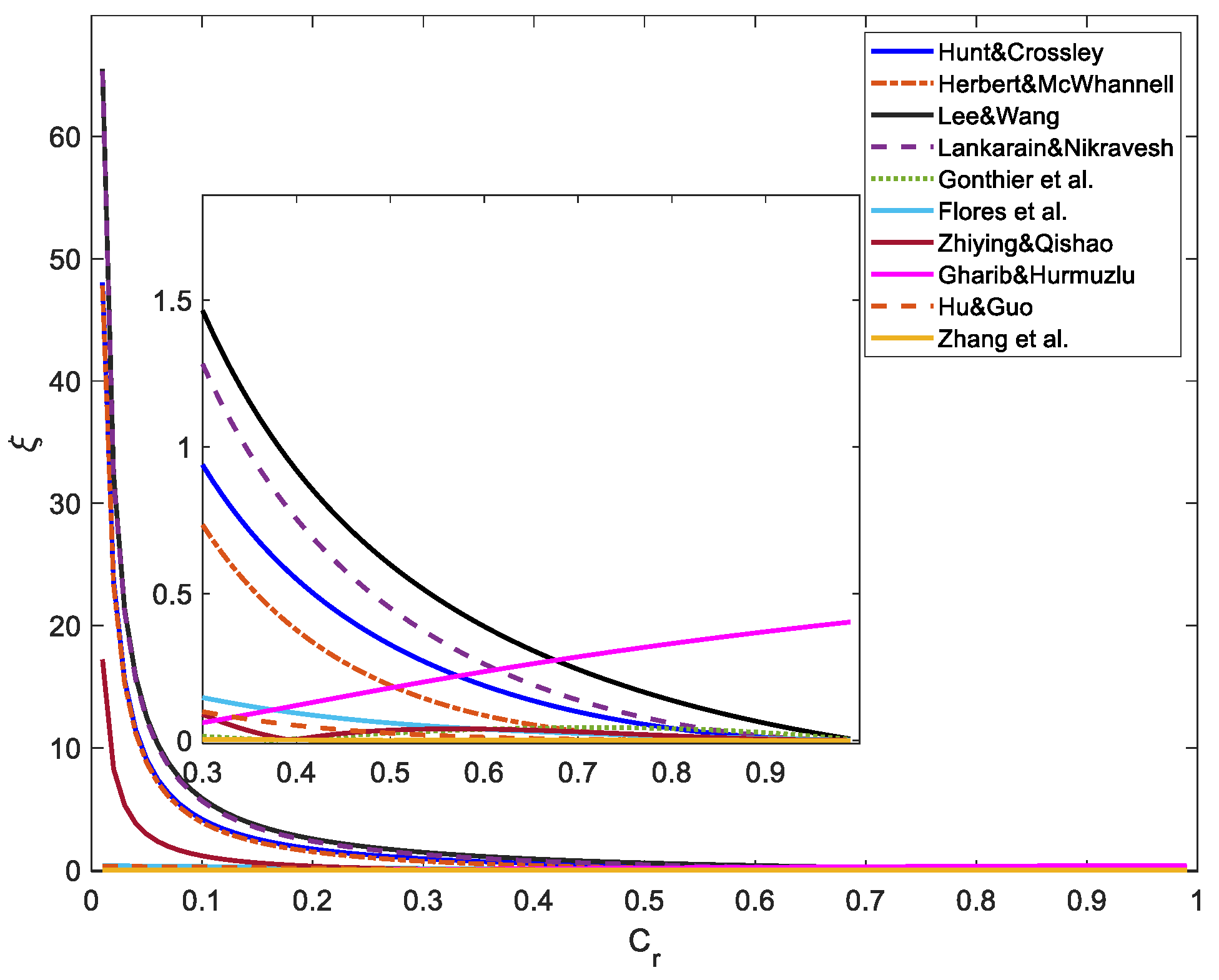





| Model | Hysteresis Damping Factor | Model | Hysteresis Damping Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Herbert–McWhannell | Hunt-Crossley | ||
| Lankarain–Nikravesh | Lee-Wang | ||
| Flores et al. | Gonthier et al. | ||
| Zhiying–Qishao | Hu-Guo | ||
| Zhang et al. | Gharib–Hurmuzlu |
| Part | Mass (kg) | Inertia Matrix (kg·m2) |
|---|---|---|
| Link 1 | 4 | diag ([0.50, 0.12, 0.50]) |
| Link 2 | 4 | diag ([0.50, 0.12, 0.50]) |
| Link 3 | 8 | diag ([0.46, 5.02, 5.02]) |
| Link 4 | 8 | diag ([0.46, 5.02, 5.02]) |
| Link 5 | 4 | diag ([0.50, 0.50, 0.12]) |
| Link 6 | 4 | diag ([0.50, 0.50, 0.12]) |
| Link 7 | 5 | diag ([0.50, 0.50, 0.12]) |
| Base | 100 | diag ([50, 50, 50]) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Performing Contact Task. Machines 2022, 10, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090720
Zhang L, Wang S. Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Performing Contact Task. Machines. 2022; 10(9):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090720
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Long, and Shuquan Wang. 2022. "Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Performing Contact Task" Machines 10, no. 9: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090720
APA StyleZhang, L., & Wang, S. (2022). Risk Assessment Model-Guided Configuration Optimization for Free-Floating Space Robot Performing Contact Task. Machines, 10(9), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10090720






