Kinematic Calibration Method for Large-Sized 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Kinematic Modeling
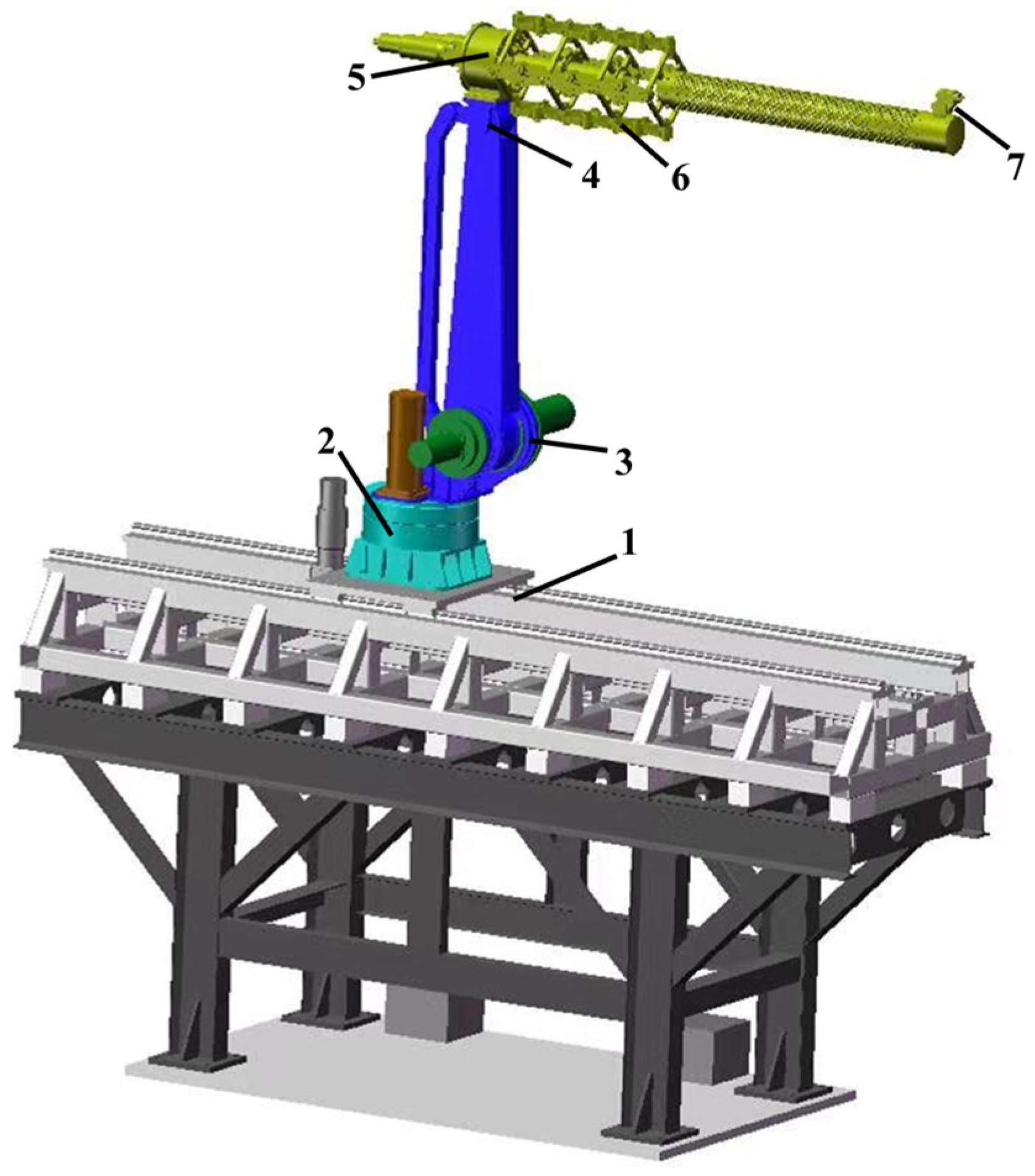
3.1. Introduction to Robot Configuration
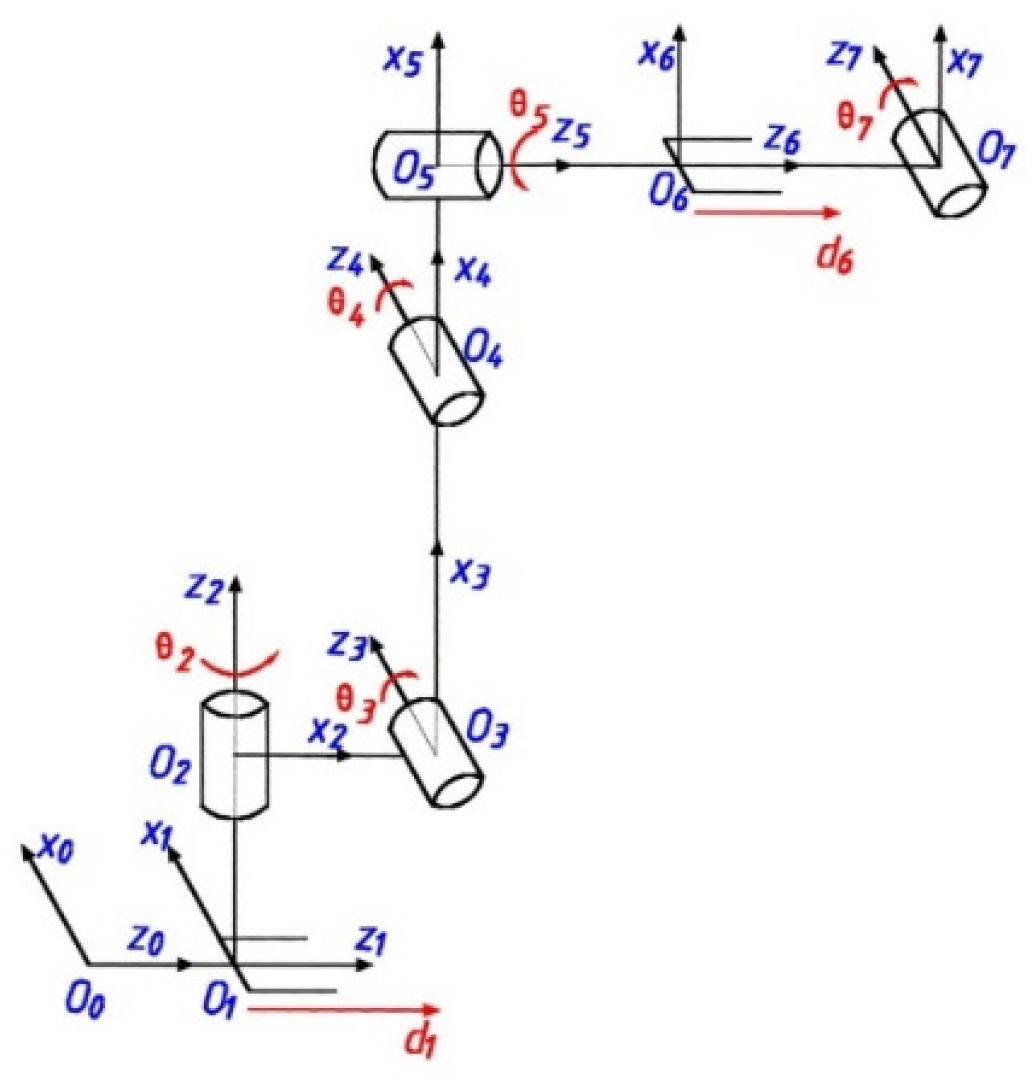
3.2. Forward Kinematic Modeling
3.3. The MD-H Error Model
4. Rigid-Flexible Coupling Error Model
4.1. Kinematic Error Model
Kinematic Error Model
4.2. Analysis of Redundancy Kinematic Error of Robots
- If αi−1 ≠ 0, a redundancy error is present;
- If αi−1 = 0 and ai−1 ≠ 0, δdi−1* and δdi* are mutually redundant, and either shall be eliminated, and δβi shall be introduced for identification.
- If αi−1 = 0 and ai−1 = 0, δdi−1* and δdi* are mutually redundant, and δθi−1 and δθi are mutually redundant, and some parameters shall be eliminated.
- If θi = 0 and di* ≠ 0, δai−1 and δai are mutually redundant, and some parameters shall be eliminated.
- If θi = 0 and di* = 0, δαi−1 and δαi are mutually redundant and δai−1 and δai are mutually redundant, and some parameters shall be eliminated.
- After eliminating redundant parameters, the D-H parameter error still contains 24 errors.
5. Static Stiffness Error Model
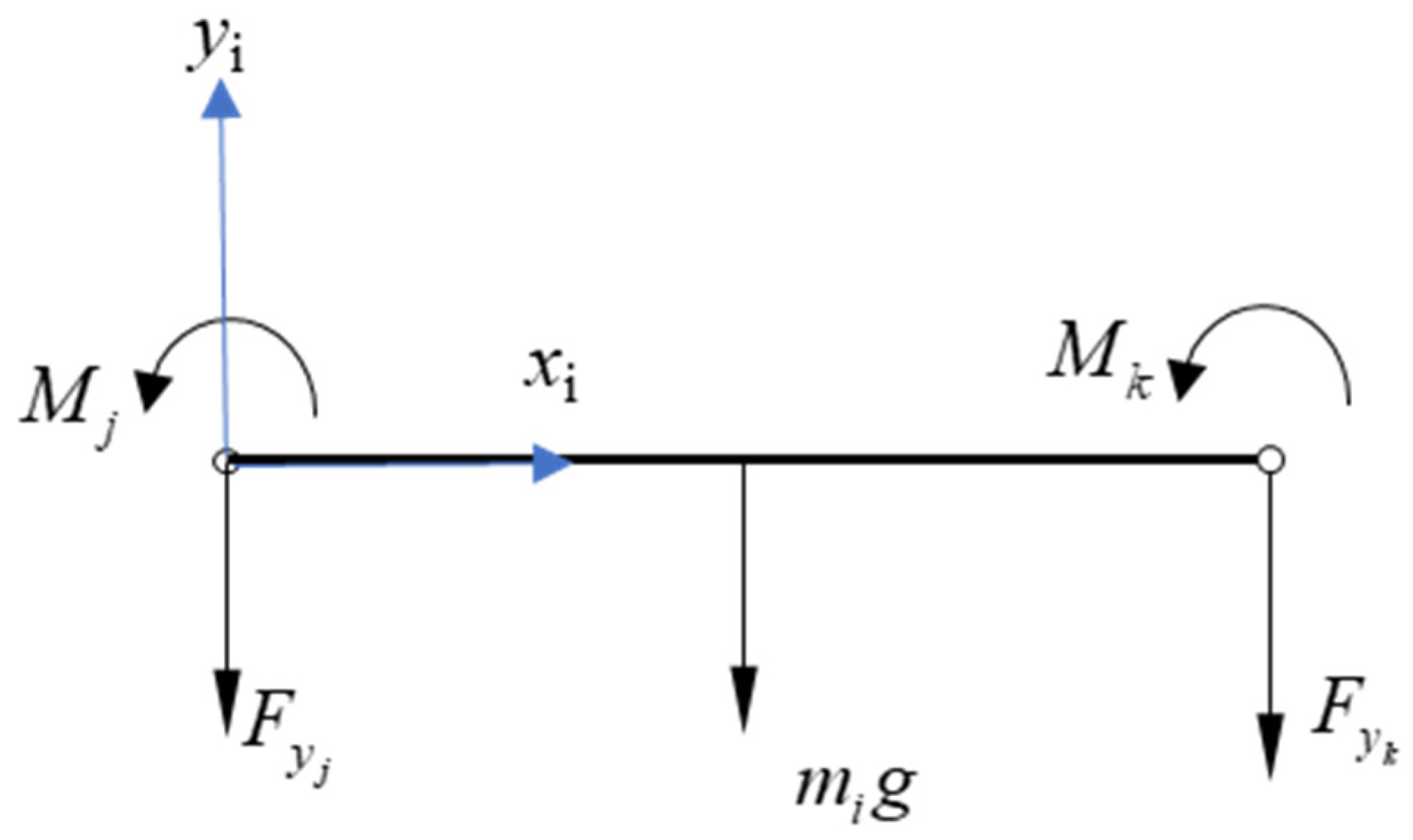
5.1. Static Stiffness Model
5.2. Rigid-Flexible Coupling Kinematic Error Model
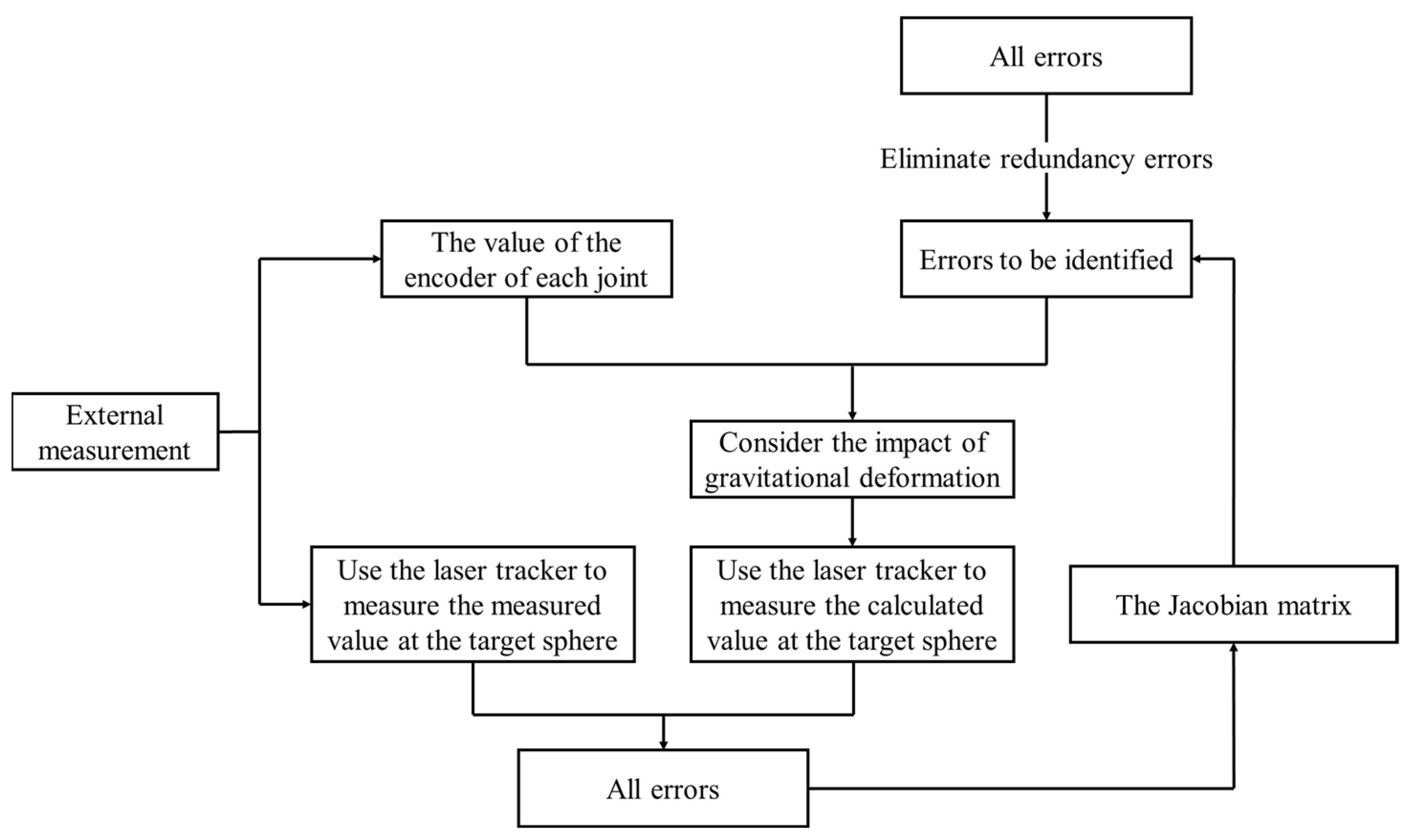
6. Error Compensation Strategy for 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots
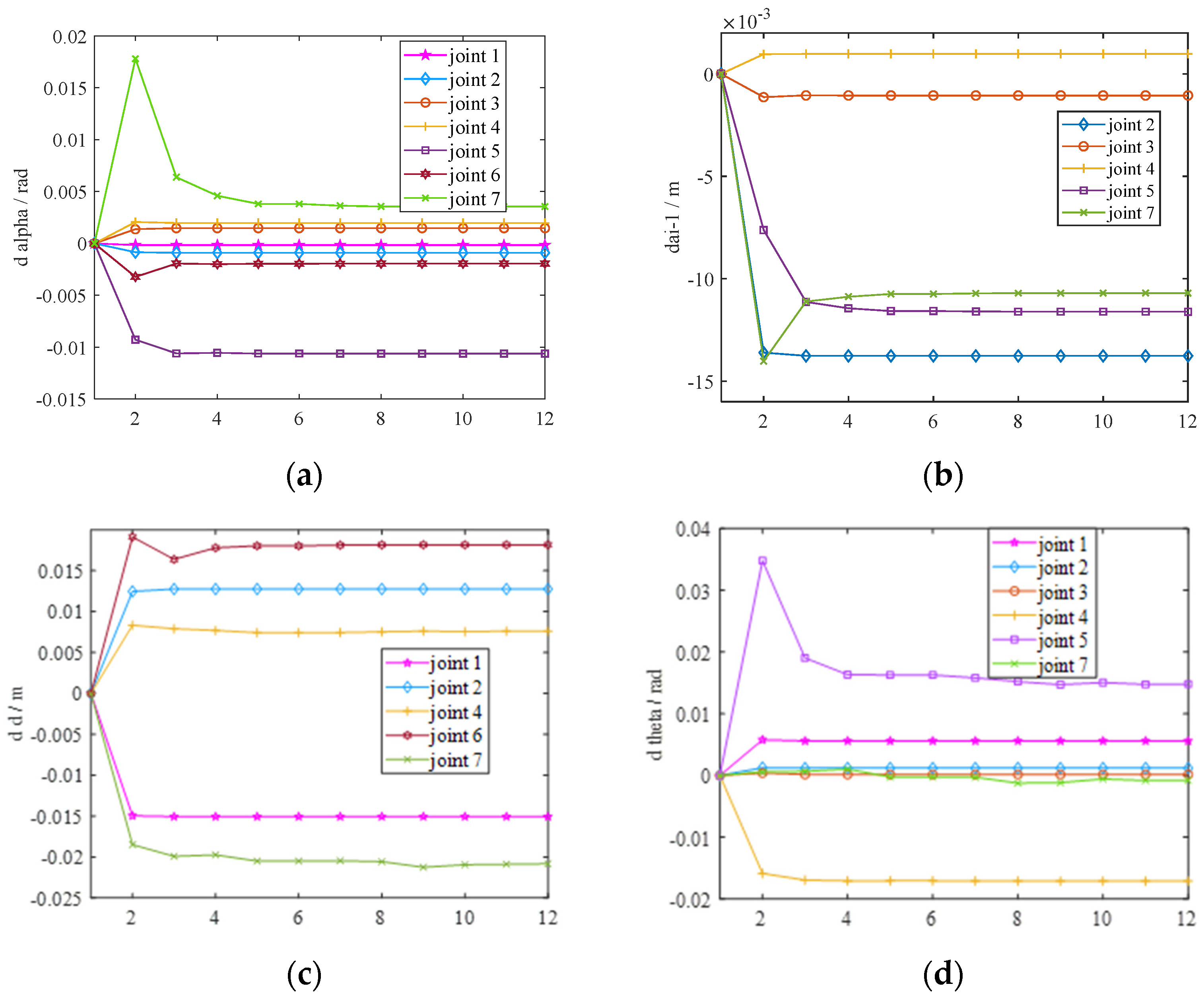
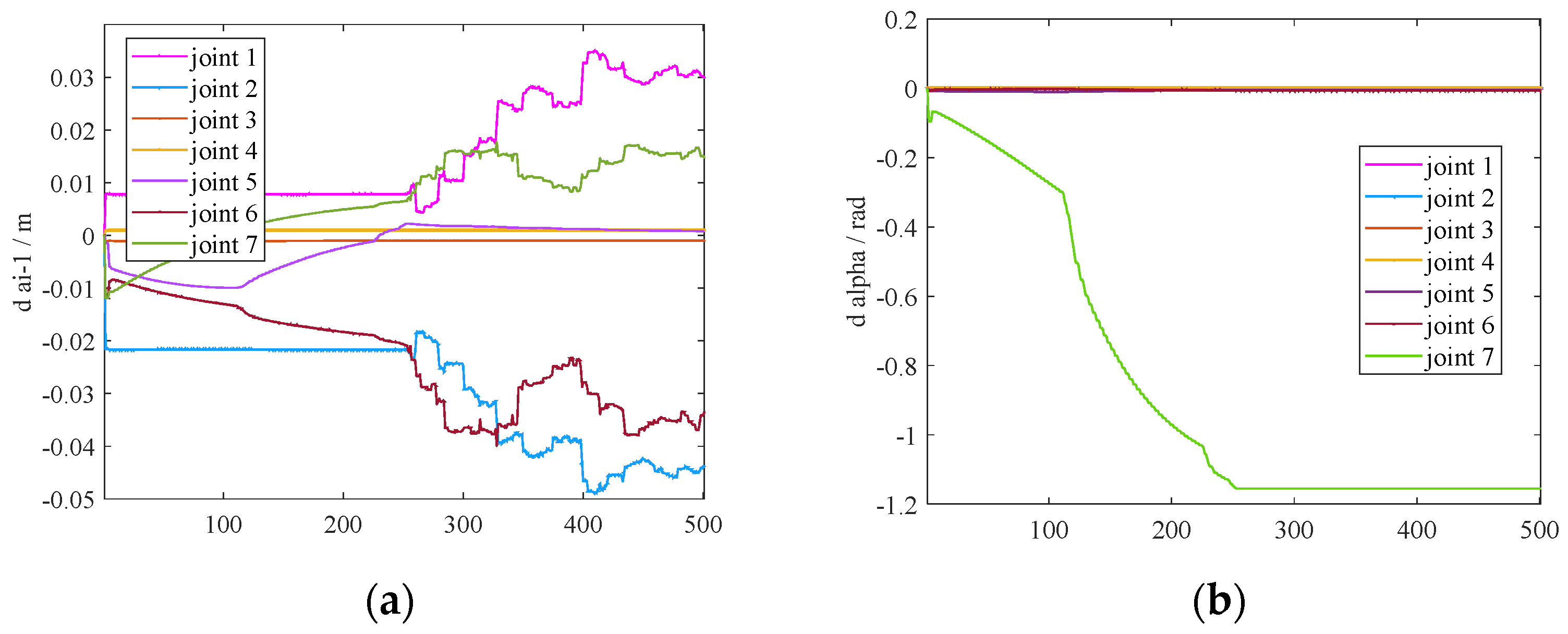
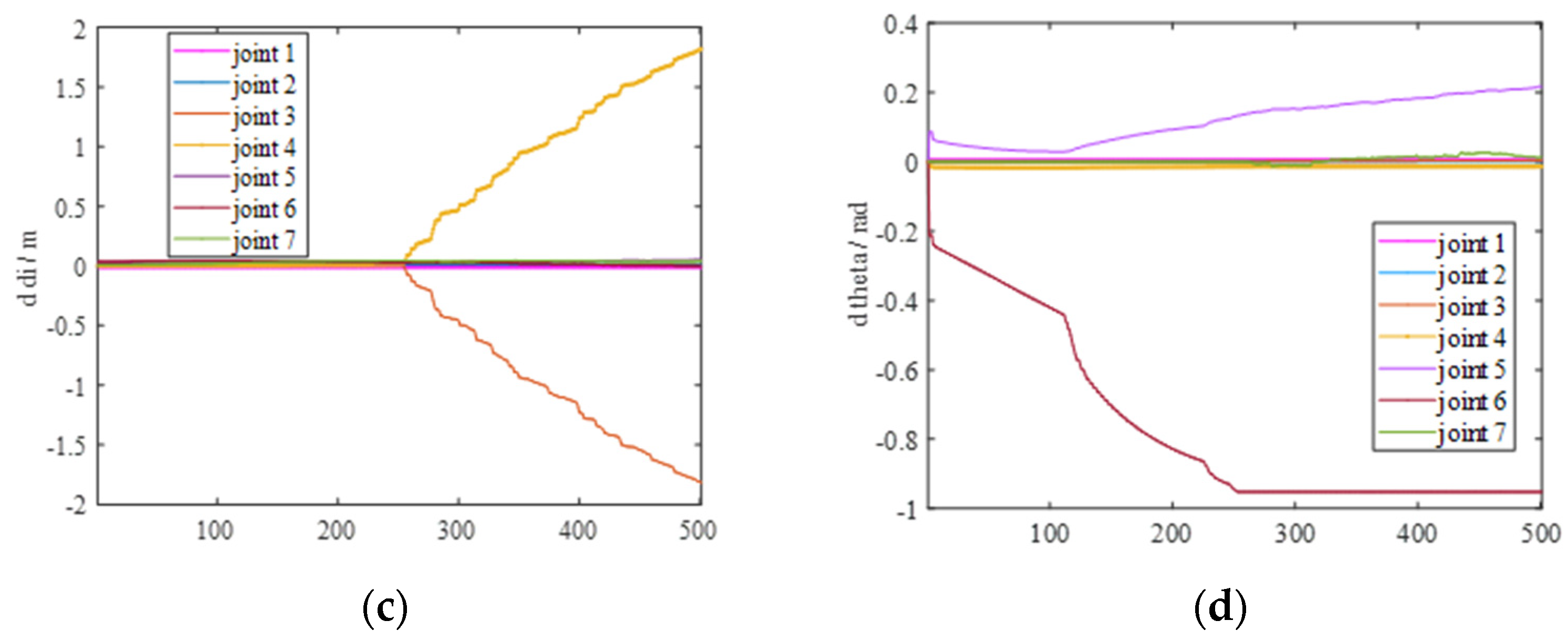
7. Experimental Methods and Data Analysis
7.1. Procedures
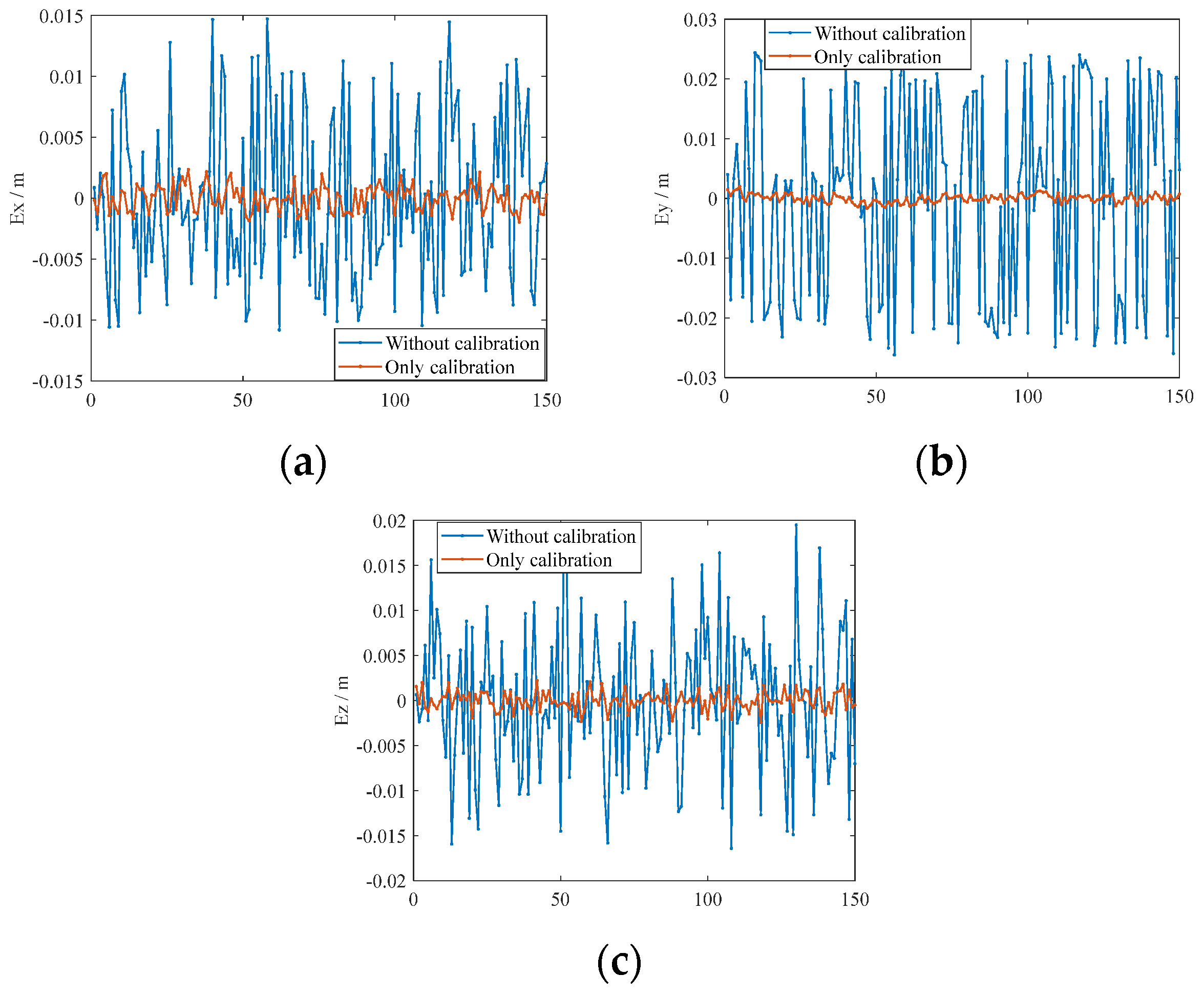
7.2. Validation of Error Elimination Effectiveness
7.3. Experimental Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; You, Z. Study on the stiffness of a 5-DOF hybrid machine tool with actuation redundancy. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L. A brief discussion about the factors that affect the quality of aircraft parts spraying. Mod. Paint. Finish. 2014, 17, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.W. Design and Control of Spraying Robot in Large Car Product Line. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zi, B.; Wang, Z.Y.; You, W.; Zheng, L. Research Progress and Trend of Key Technology of Intelligent Spraying Robot. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 58, 53–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Cheung, C.-F.; Li, B.; Ho, L.-T.; Zhang, J.-F. Kinematics analysis of a hybrid manipulator for computer controlled ultra-precision freeform polishing. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2017, 44, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucuk, S. Dexterous working space optimization of a new hybrid parallel robot manipulator. J. Mech. Robot. 2018, 10, 064503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, Z.; Mooring, B.; Ravani, B. An overview of robot calibration. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 1987, 3, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, R.P.; Knasinski, A.B. A technique to calibrate industrial robots with experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Mannan, M.A.; Poo, A.N. Error compensation in machine tools—A review: Part I: Geometric, cutting-force induced and fixture-dependent errors. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2000, 40, 1235–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Mannan, M.A.; Poo, A.N. Error compensation in machine tools—A review: Part II: Thermal errors. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2000, 40, 1257–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N. Calibration for accuracy improvement of serial manipulators based on compressed sensing. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 820–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elatta, A.Y.; Gen, L.P.; Zhi, F.L.; Yu, D.Y.; Luo, F. An overview of robot calibration. Inf. Technol. J. 2004, 3, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubiola, A.; Bonev, I.A. Absolute calibration of an ABB IRB 1600 robot using a laser tracker. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2013, 29, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denavit, J.; Hartenberg, R.S. A Kinematic Notation for Lower-Pair Mechanisms Based on Matrices. J. Appl. Mech. 1955, 22, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, S.A. Robot arm geometric link parameter estimation. In The 22nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1477–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, H.W. Kinematic Modeling, Identification, and Control of Robotic Manipulators; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, H.; Roth, Z.; Hamano, F. A complete and parametrically continuous kinematic model for robot manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1992, 8, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, W.; Gautier, M.; Enguehard, C. Identifiable Parameters and Optimum Configurations for Robots Calibration. Robotica 1991, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubair, A.; Slamani, M.; Bonev, I.A. Kinematic calibration of a five-bar planar parallel robot using all working modes. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2013, 29, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nubiola, A.; Slamani, M.; Joubair, A.; Bonev, I.A. Comparison of two calibration methods for a small industrial robot based on an optical CMM and a laser tracker. Robotica 2014, 32, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, P.; Andreff, N.; Lavest, J.-M.; Dhome, M. Simplifying the kinematic calibration of parallel mechanisms using vision-based metrology. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Yu, G. Kinematic calibration of a 3-DOF parallel tool head. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2017, 44, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liao, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Wei, S. Simulation and experimentation for calibration of general 7R serial robots. Robot 2006, 28, 483–487. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Majarena, A.C.; Santolaria, J.; Samper, D.; Aguilar, J.J. Analysis and evaluation of objective functions in kinematic calibration of parallel mechanisms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renders, J.-M.; Rossignol, E.; Becquet, M.; Hanus, R. Kinematic calibration and geometrical parameter identification for robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1991, 7, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Application of genetic algorithms to robot kinematics calibration. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2009, 40, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, C.; Xue, L.; Hu, S.; Jiang, Y. Calibration of a steward parallel robot using genetic algorithm. In IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 2495–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.; Ehmann, K. Volumetric Error Analysis of a Stewart Platform-Based Machine Tool. CIRP Ann. 1997, 46, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear inequalities. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.Y.; Lin, S.G.; Liu, W. Measurement method of six-axis load sharing based on the Stewart platform. Measurement 2010, 43, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboubkhah, M.; Nategh, M.J.; Khadem, S.E. A comprehensive study on the free vibration of machine tools’ hexapod table. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 40, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, L.-W.; Joshi, S. Kinematics and Optimization of a Spatial 3-UPU Parallel Manipulator. J. Mech. Des. 2000, 122, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashkevich, A.; Chablat, D.; Wenger, P. Stiffness analysis of overconstrained parallel manipulators. Mech. Mach. Theory 2009, 44, 966–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhao, X.; Whitehouse, D. Stiffness estimation of a tripod-based parallel kinematic machine. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2002, 18, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarata, A. Unified formulation for the stiffness analysis of spatial mechanisms. Mech. Mach. Theory 2016, 105, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C. Stiffness mapping for parallel manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1990, 6, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, C.M.; Zhang, D. Stiffness analysis of parallel mechanisms using a lumped model. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2002, 17, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Klimchik, A.; Pashkevich, A.; Caro, S.; Chablat, D. Stiffness Matrix of Manipulators With Passive Joints: Computational Aspects. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimchi, A.; Pashkevich, A.; Chablat, D. CAD-based approach for identification of elastostatics parameters of robotic manipulators. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2013, 75, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, B.; Xie, F.G.; Liu, X.J.; Yang, C.B. Elasto-geometrical error modeling and compensation of a five-axis parallel machining robot. Precis. Eng. J. Int. Soc. Precis. Eng. Nanotechnol. 2021, 69, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimchi, A.; Bondarenko, D.; Pashkevich, A.; Briot, S.; Furet, B. Compliance error compensation in robotic-based milling. Inform. Control. Autom. Robot. 2014, 283, 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- ASME B89.4.19-2006; Performance Evaluation of Laser-Based Spherical Coordinate Measurement Systems. ASME Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Huang, T.; Zhao, D.; Yin, F.; Tian, W.; Chetwynd, D.G. Kinematic calibration of a 6-DoF hybrid robot by considering multicollinearity in the identification Jacobian. Mech. Mach. Theor. 2019, 131, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Inverse Kinematics of a 7-DOF Spray-Painting Robot with a Telescopic Forearm. In 14th International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications (ICIRA); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, G.; Li, W. A new calibration method for hybrid machine tools using virtual tool center point position constraint. Measurement 2021, 181, 109582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Joint No. | /mm | /° | /mm | /° | βi/° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| #2 | 0 | −90 | - | ||
| #3 | −90 | 0 | - | ||
| #4 | 0 | 0 | β4 | ||
| #5 | −90 | 0 | - | ||
| #6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | |
| #7 | 0 | 90 | 0 | - |
| /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 1350 | 246 | 0–4000 | 626 | 1700–2300 |
| X-Direction/m | Y-Direction/m | Z-Direction/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Mean | Maximum | Mean | Maximum | Mean | |
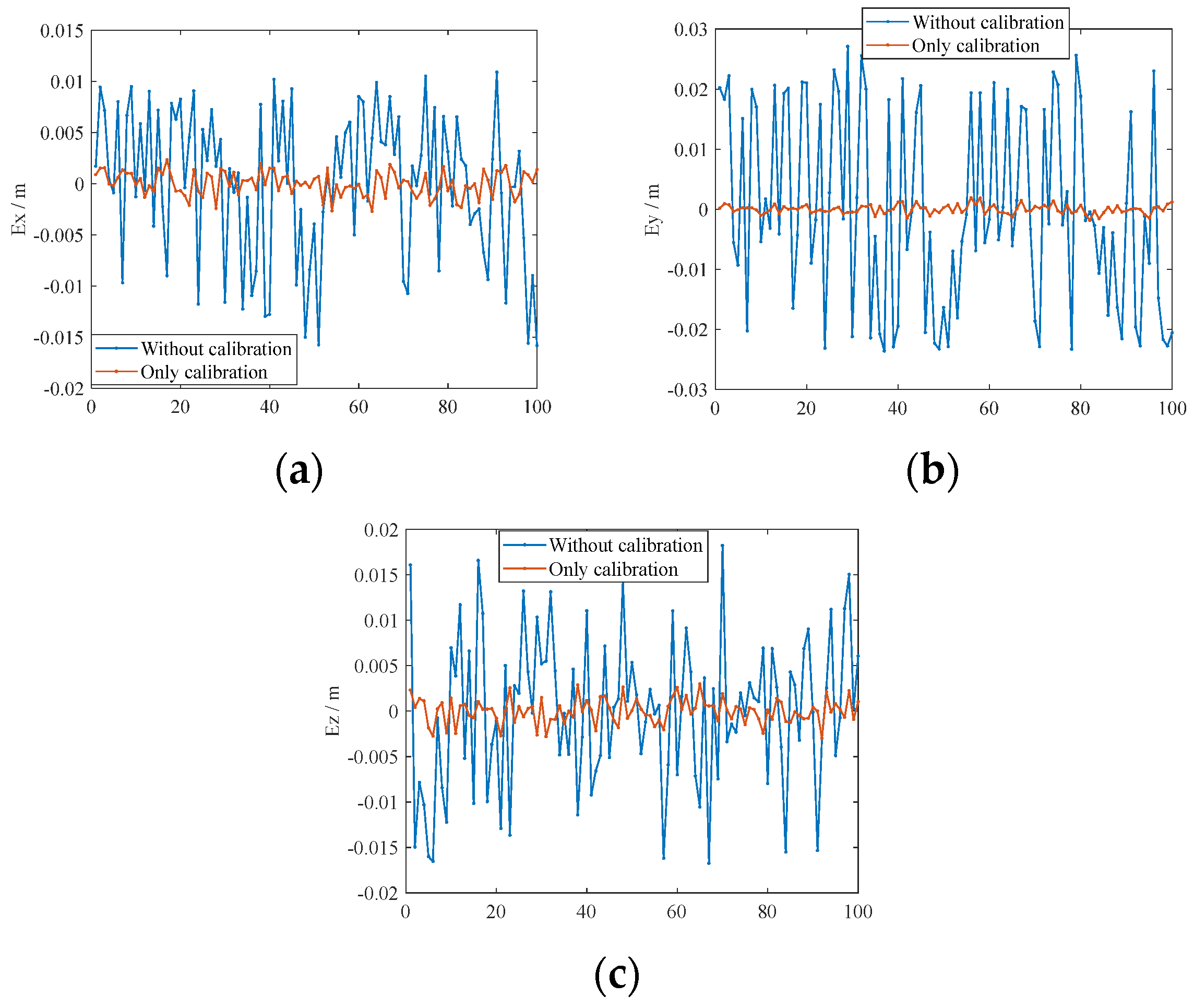
| Without calibration | 0.0147 | 0.0057 | 0.0262 | 0.0144 | 0.0195 | 0.0063 |
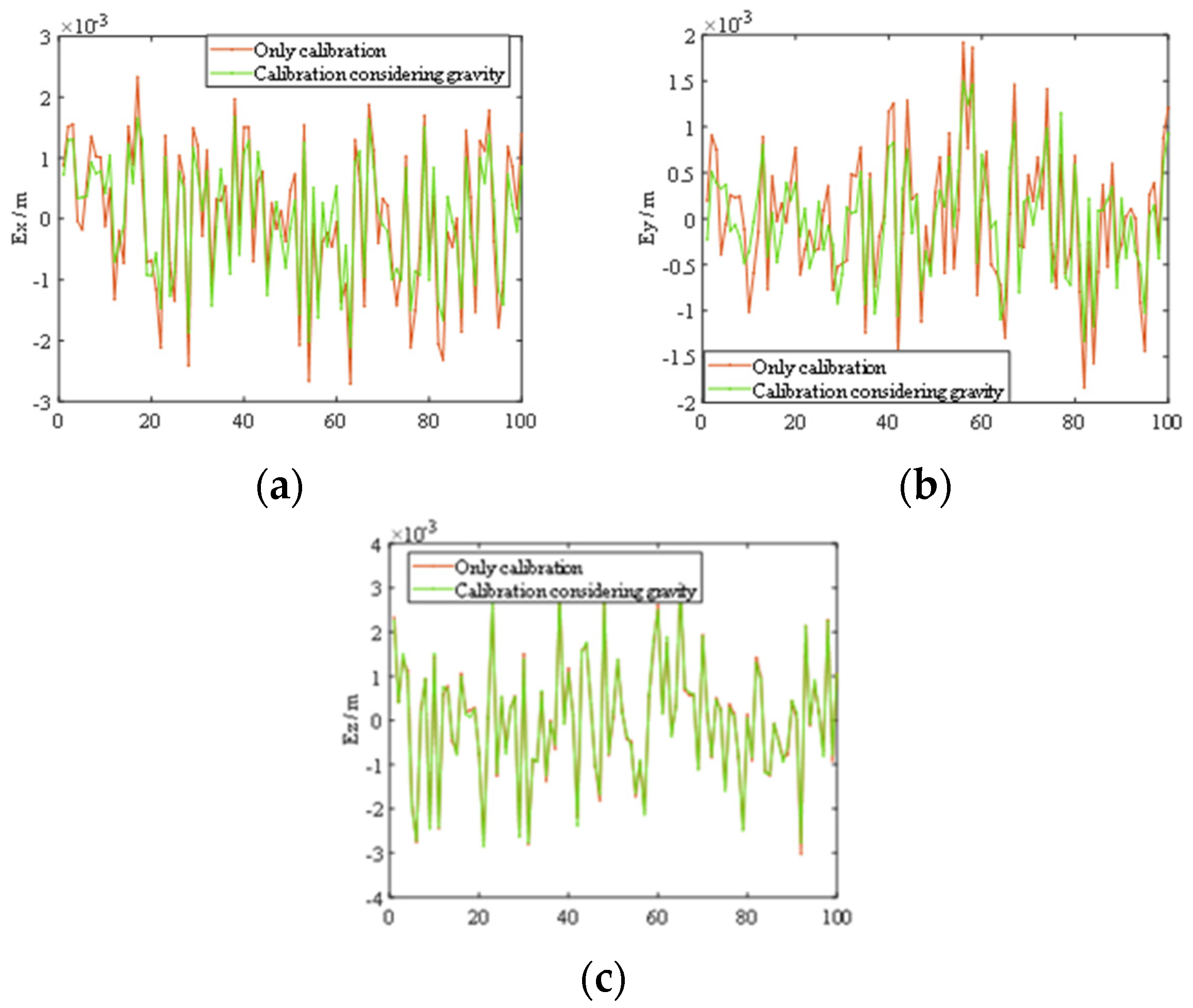
| Only calibration | 0.0024 | 0.0009 | 0.0020 | 0.0006 | 0.0024 | 0.0008 |
| Calibration considering gravity | 0.0017 | 0.0007 | 0.0015 | 0.0004 | 0.0023 | 0.0007 |
| Joint No. | /m | /rad | /m | /rad | δβi/rad |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | −0.0002 | −0.0151 | 0.0056 | - |
| 2 | −0.0138 | −0.0009 | 0.0128 | 0.0012 | - |
| 3 | −0.0011 | 0.0015 | - | 0.0002 | - |
| 4 | 0.0009 | 0.0020 | 0.0076 | −0.0171 | 0.0148 |
| 5 | −0.0116 | −0.0106 | - | 0.0148 | - |
| 6 | - | −0.0019 | 0.0182 | - | - |
| 7 | −0.0107 | 0.0035 | −0.0208 | −0.0001 | - |
| X-Direction/m | Y-Direction/m | Z-Direction/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Mean | Maximum | Mean | Maximum | Mean | |
| Without calibration | 0.0158 | 0.0059 | 0.0271 | 0.0139 | 0.0182 | 0.0067 |
| Only calibration | 0.0027 | 0.0010 | 0.0019 | 0.0006 | 0.0030 | 0.0011 |
| Calibration considering gravity | 0.0021 | 0.0008 | 0.0015 | 0.0005 | 0.0029 | 0.0011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Kinematic Calibration Method for Large-Sized 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots. Machines 2023, 11, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010020
Wang Y, Li M, Wang J, Zhao Q, Wu J, Wang J. Kinematic Calibration Method for Large-Sized 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots. Machines. 2023; 11(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yutian, Mengyu Li, Junjian Wang, Qinzhi Zhao, Jun Wu, and Jinsong Wang. 2023. "Kinematic Calibration Method for Large-Sized 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots" Machines 11, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010020
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, M., Wang, J., Zhao, Q., Wu, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Kinematic Calibration Method for Large-Sized 7-DoF Hybrid Spray-Painting Robots. Machines, 11(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11010020








