Equivalent Dynamic Modeling for the Relative Rotation of Bolted Joint Interface Using Valanis Model of Hysteresis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
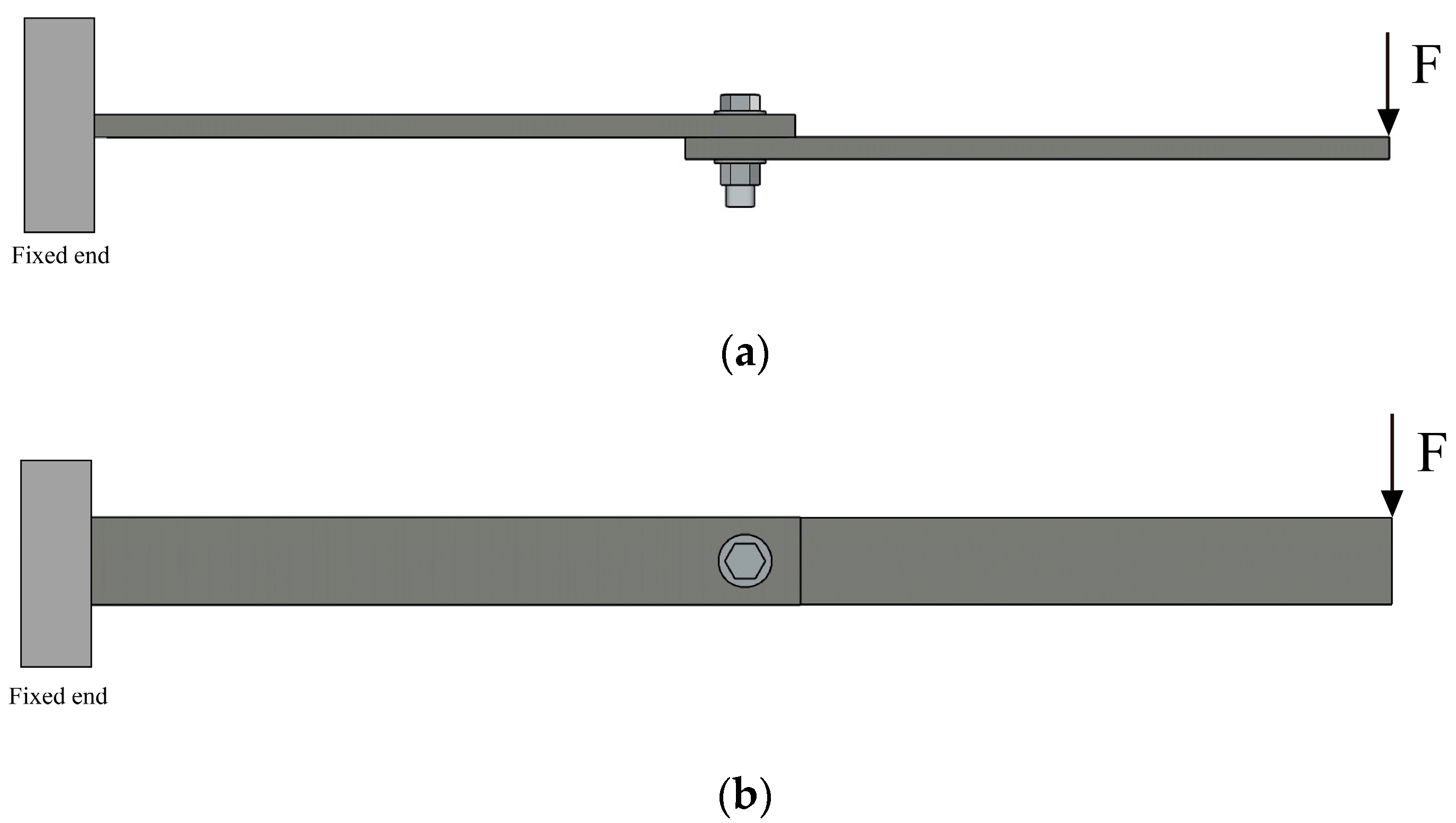
2. Equivalent Modeling of the Bolt-Jointed Beam Structure
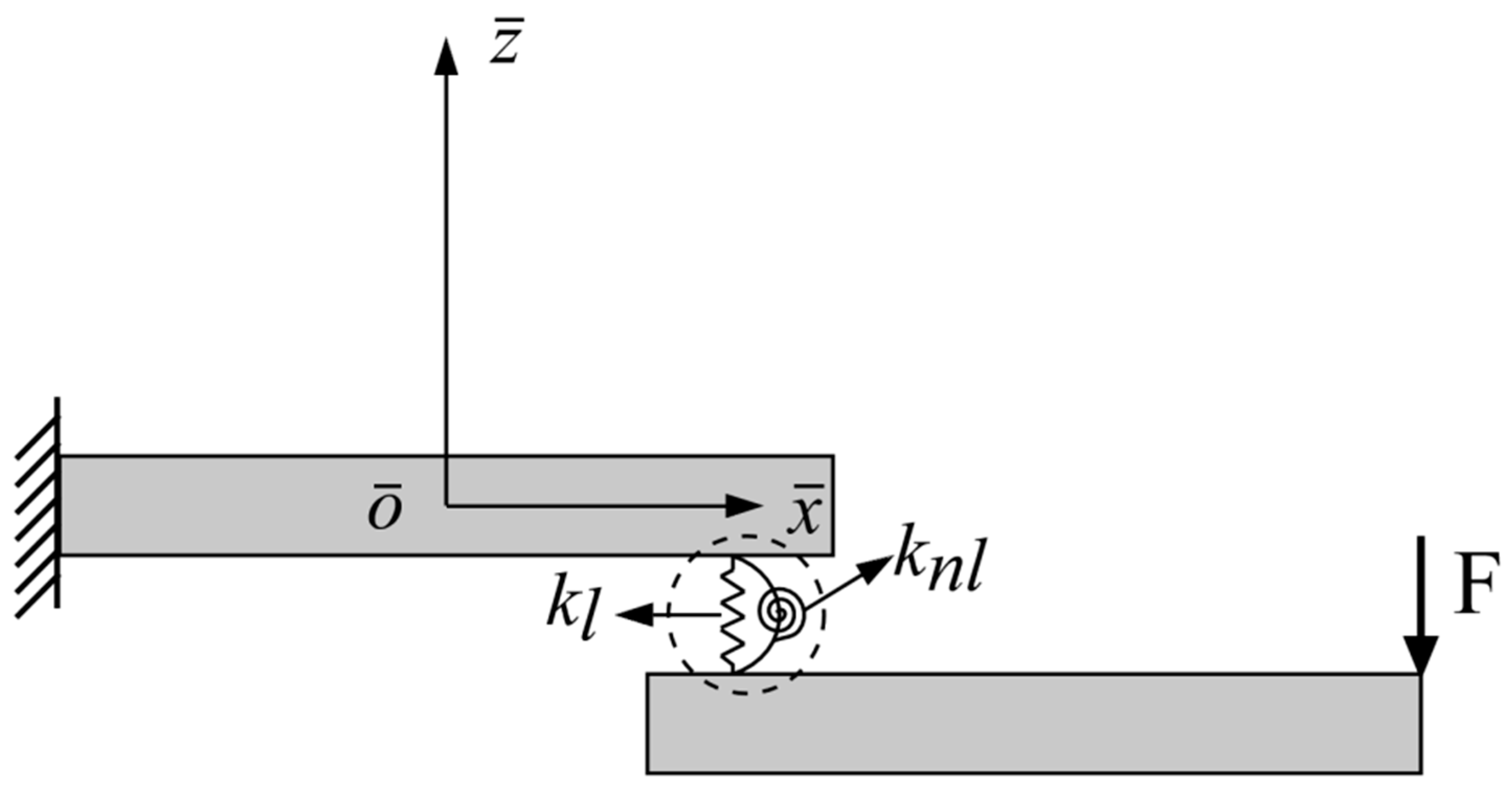
2.1. Equivalent Dynamic Model of the Bolt-Jointed Beam
2.2. Calculation of the Beam Deformation Using Timoshenko Beam Elements
3. FEM Contact Mechanics Analysis of the Bolted Joint
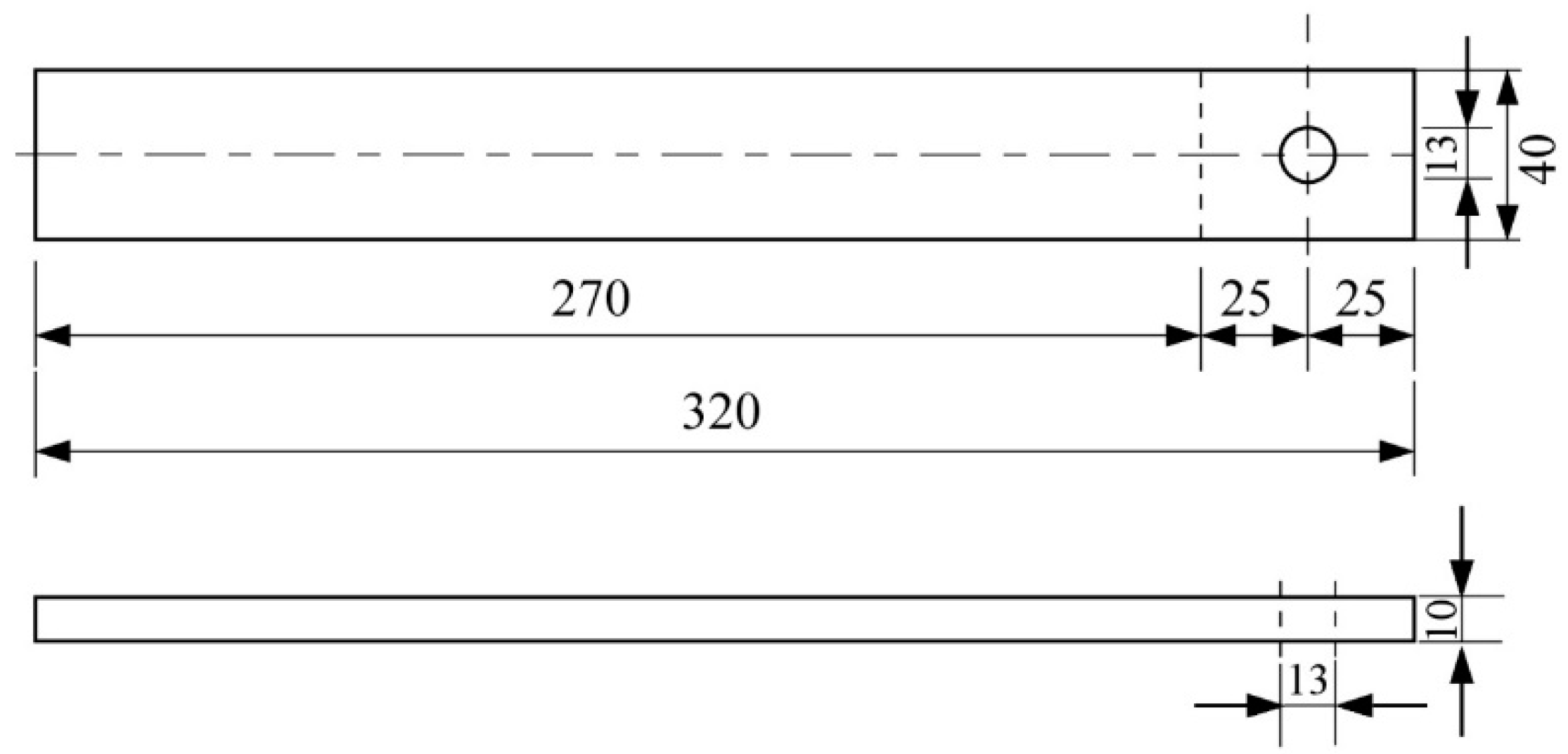
3.1. Solid FEM Model
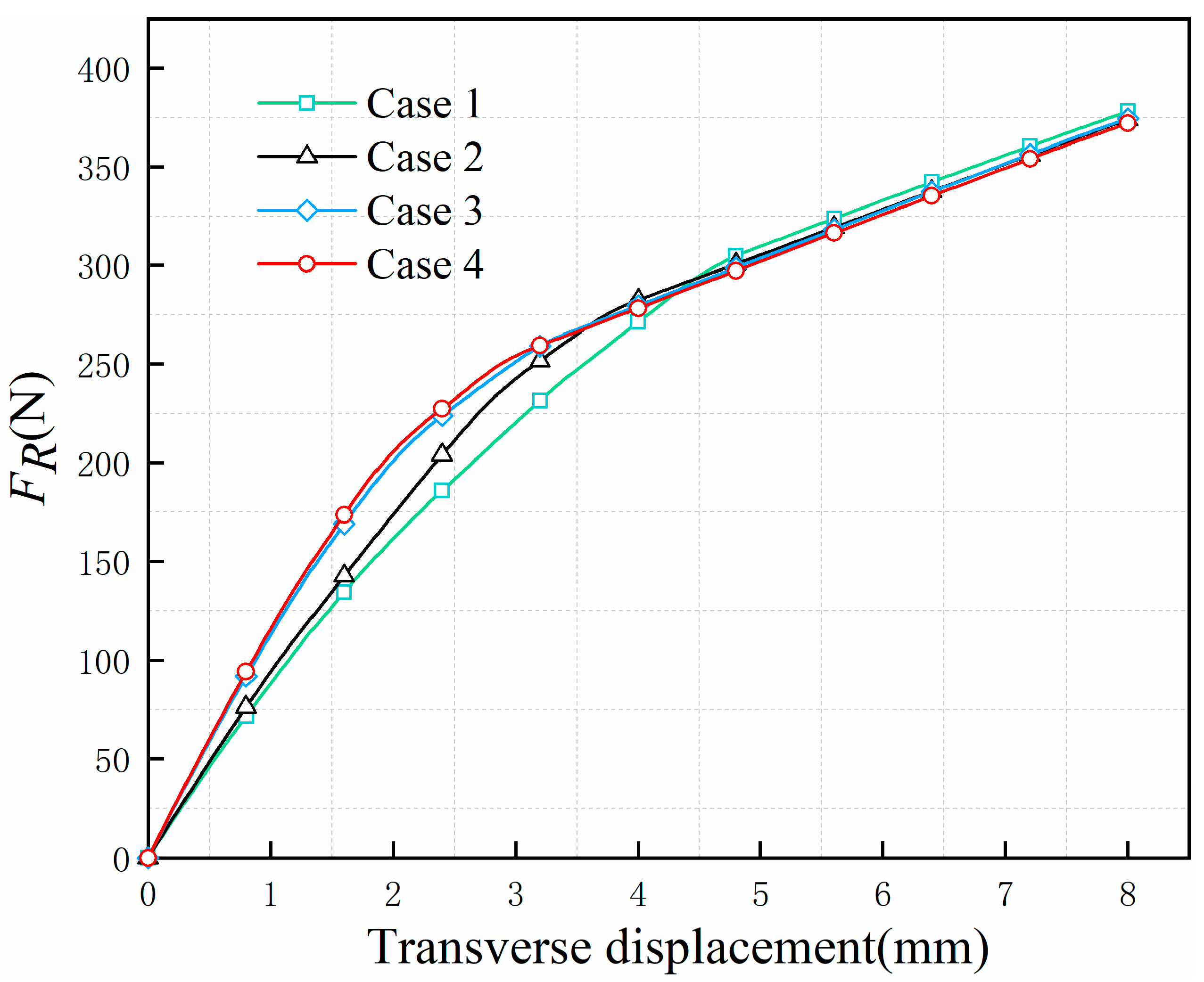
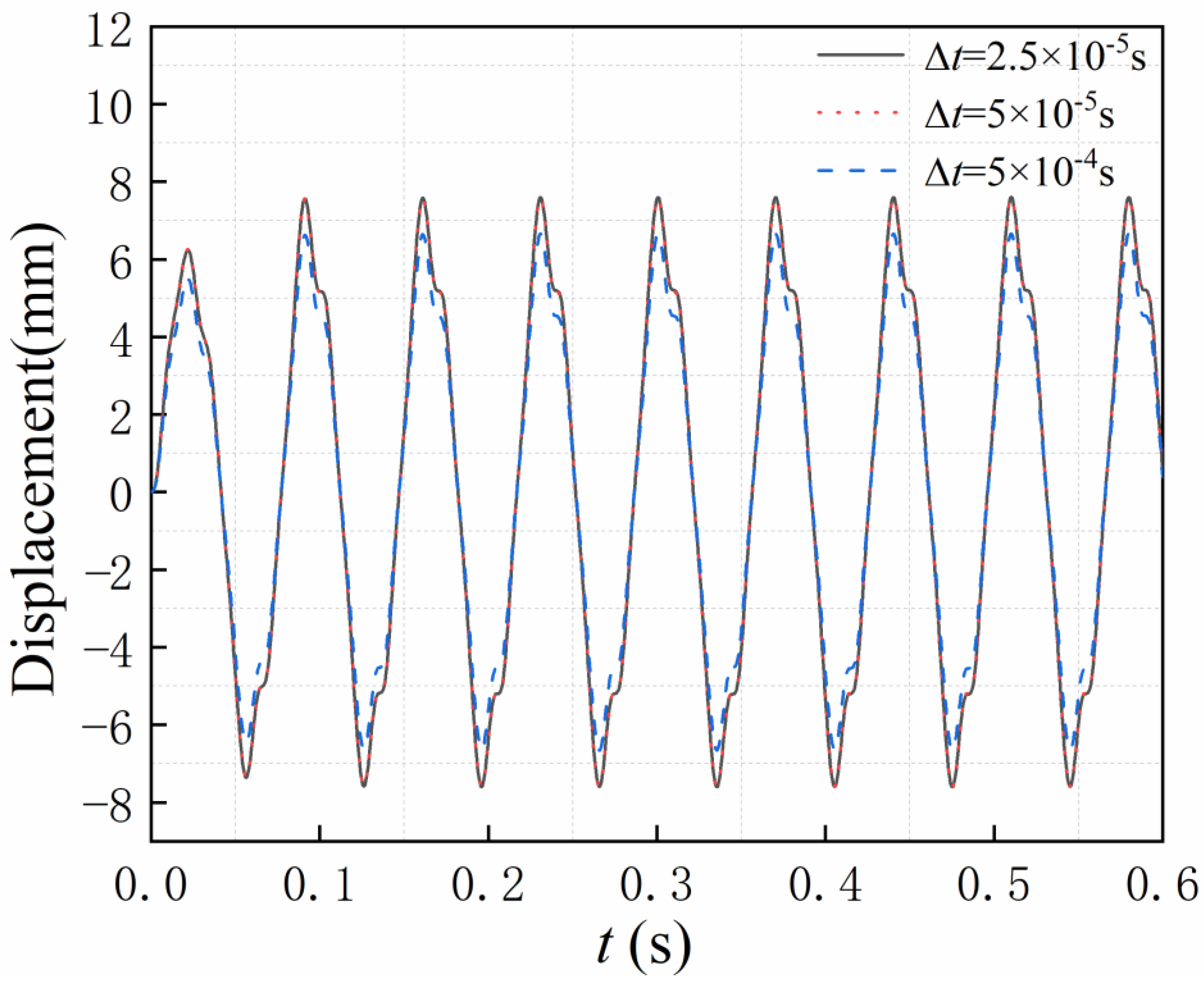
3.2. Influence of the Mesh Density
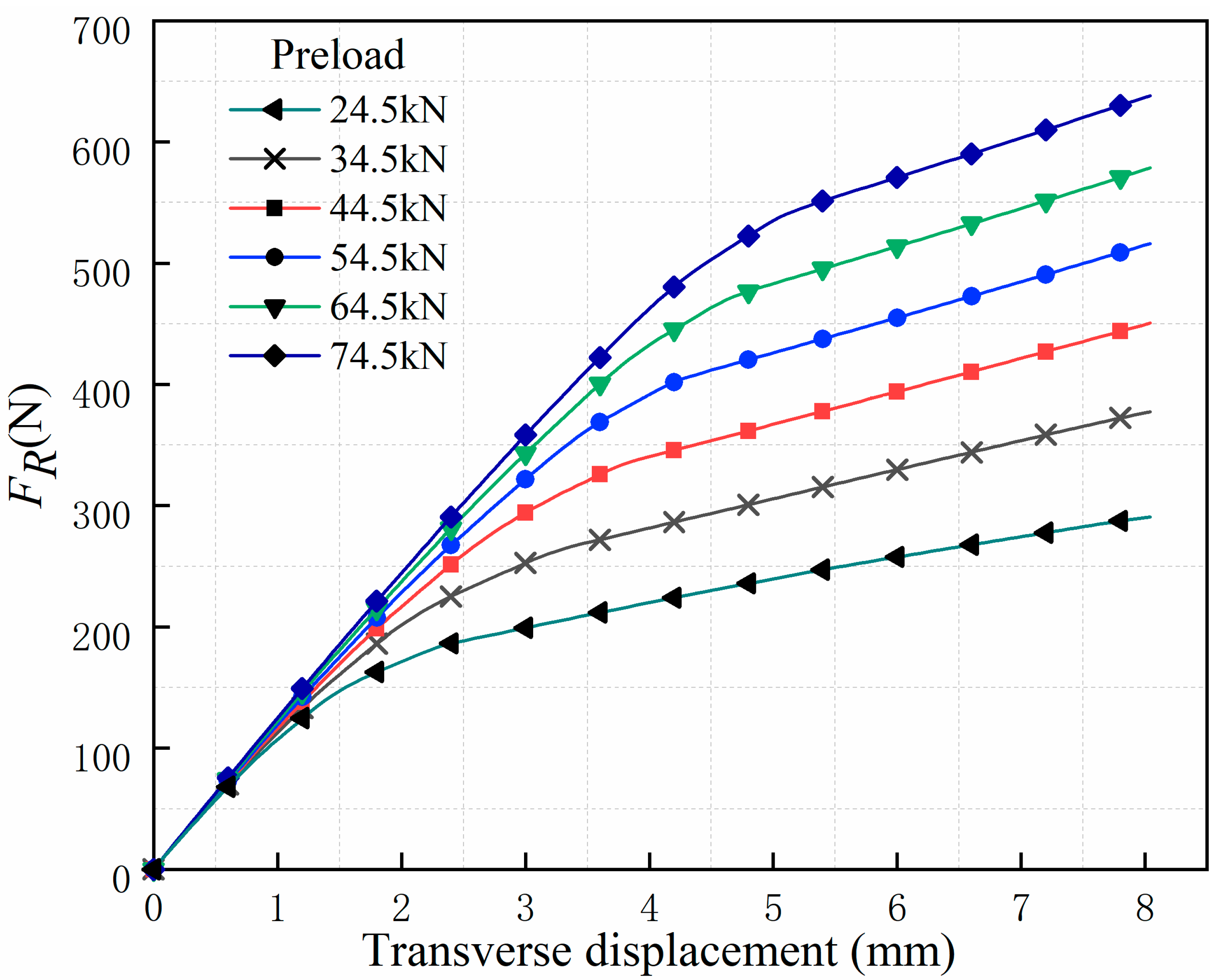
3.3. Static Analysis of the Solid FEM Model
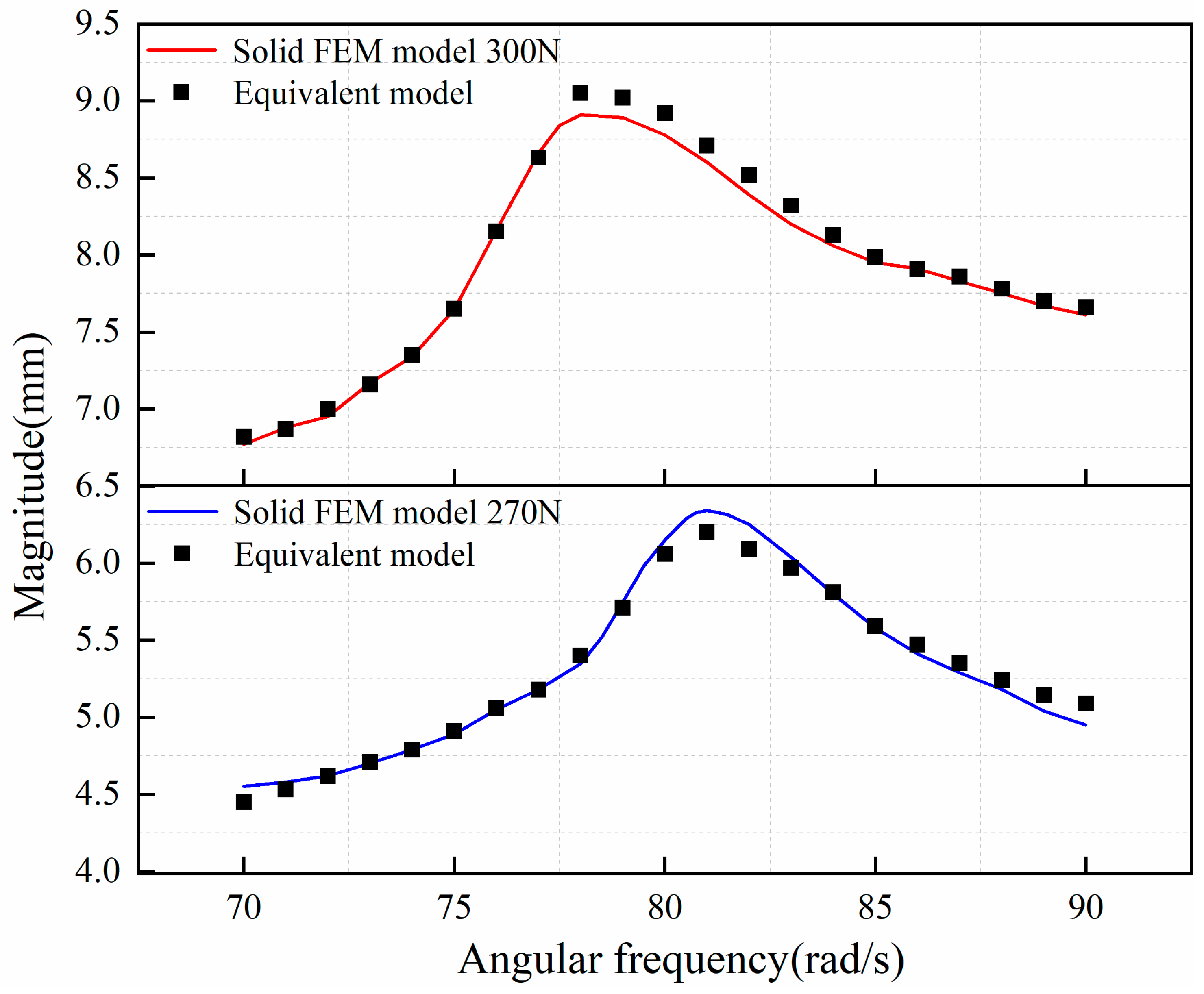
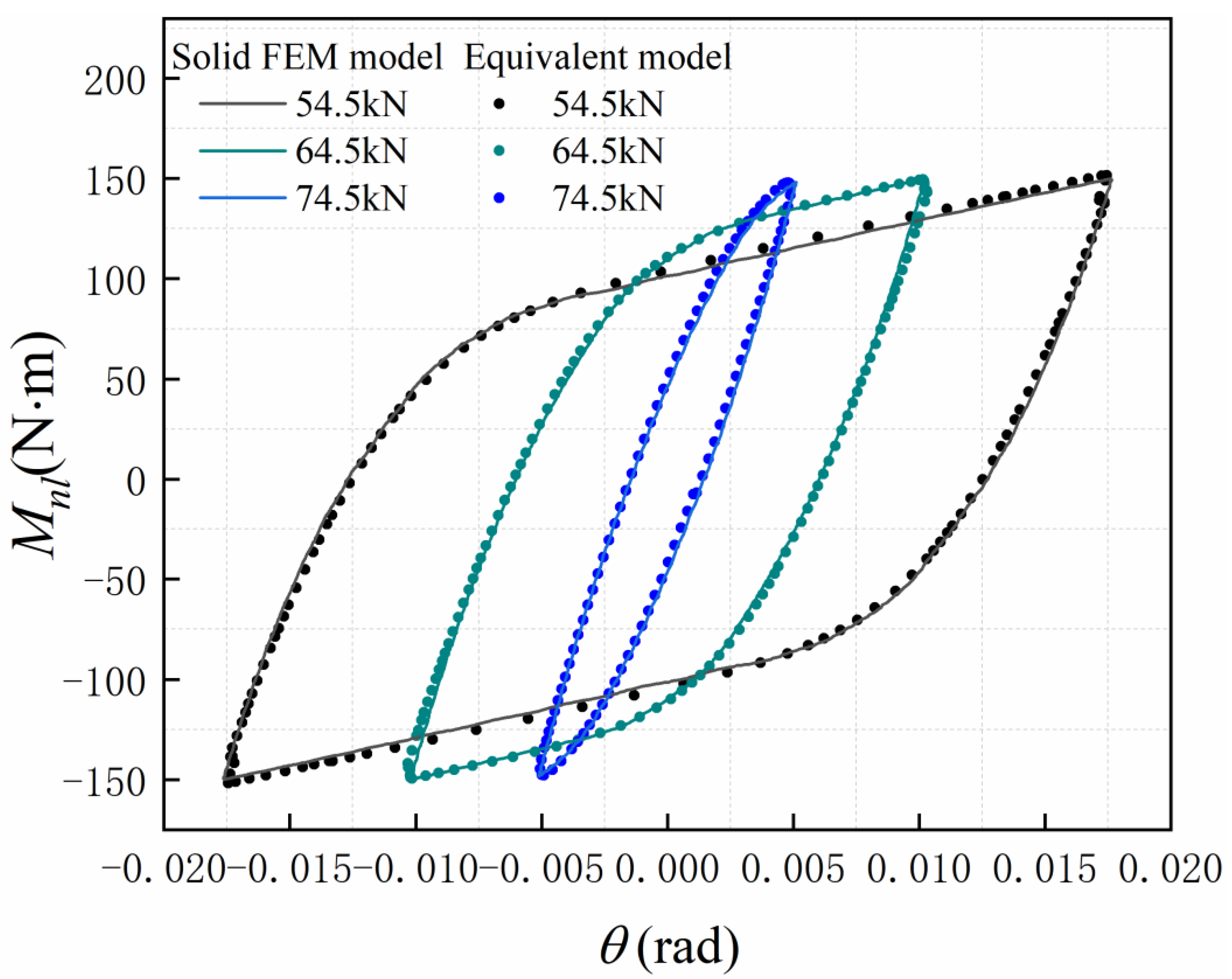
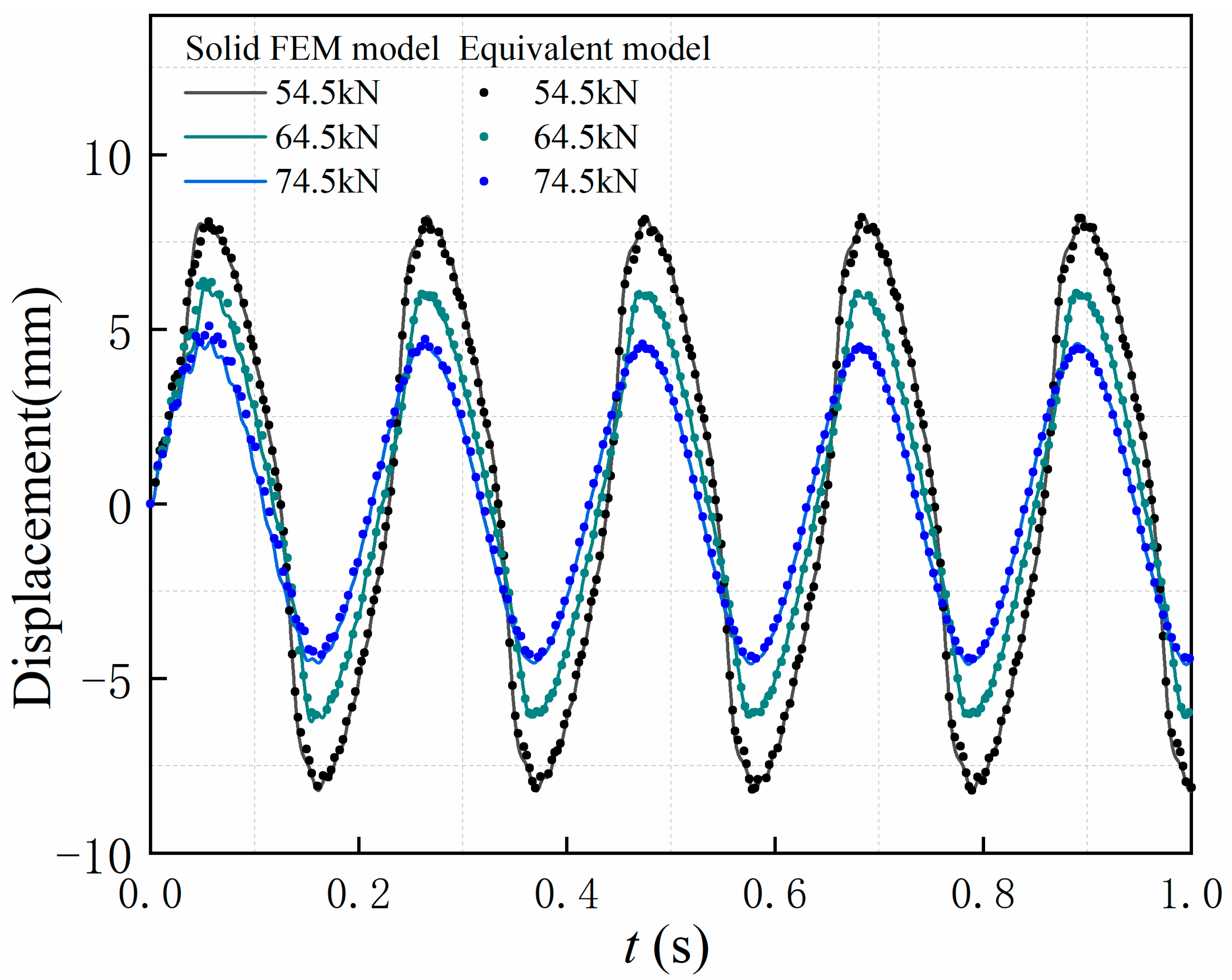
4. Results and Discussion
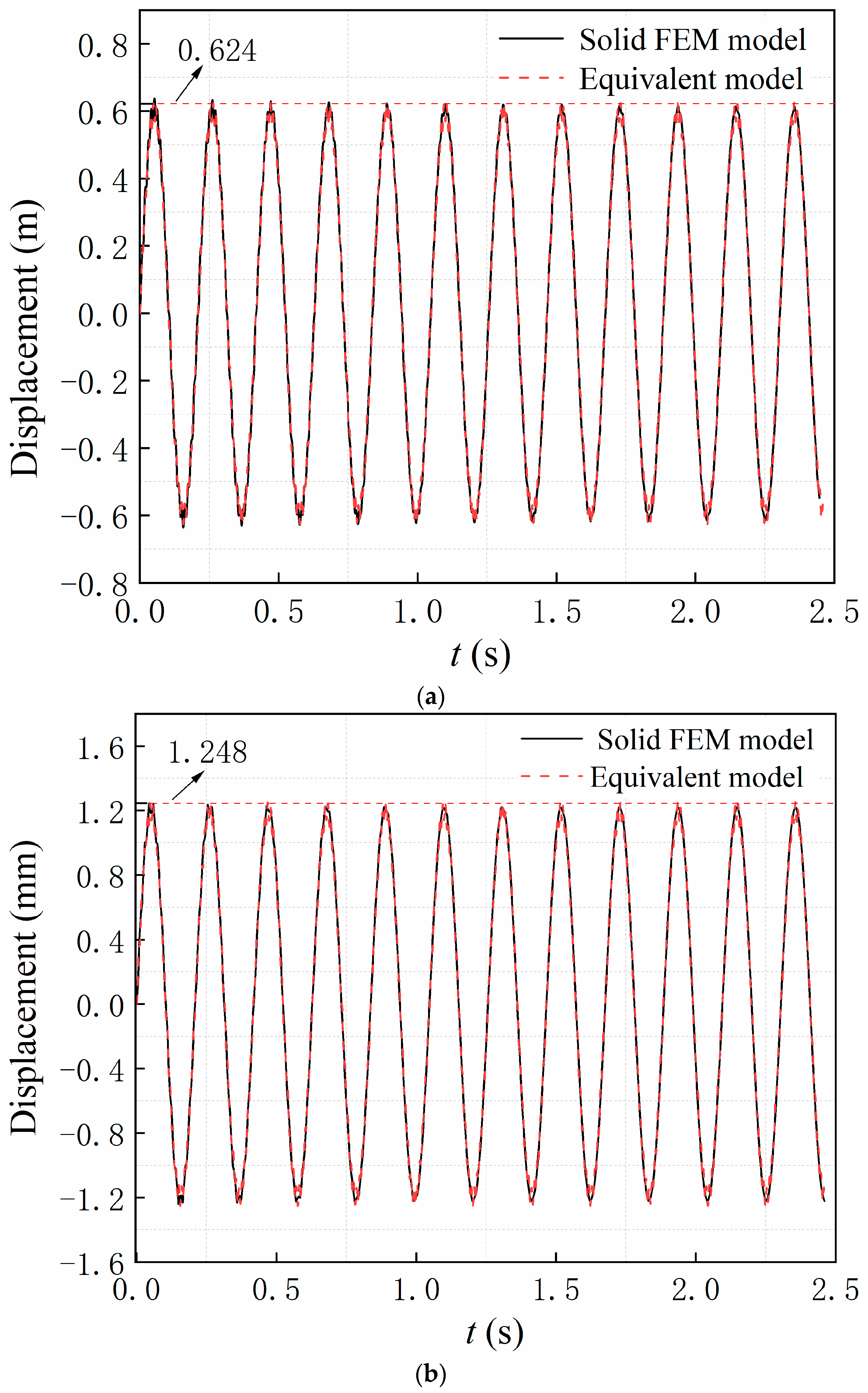
4.1. Validation of the Deformation of the Timoshenko Beam Model
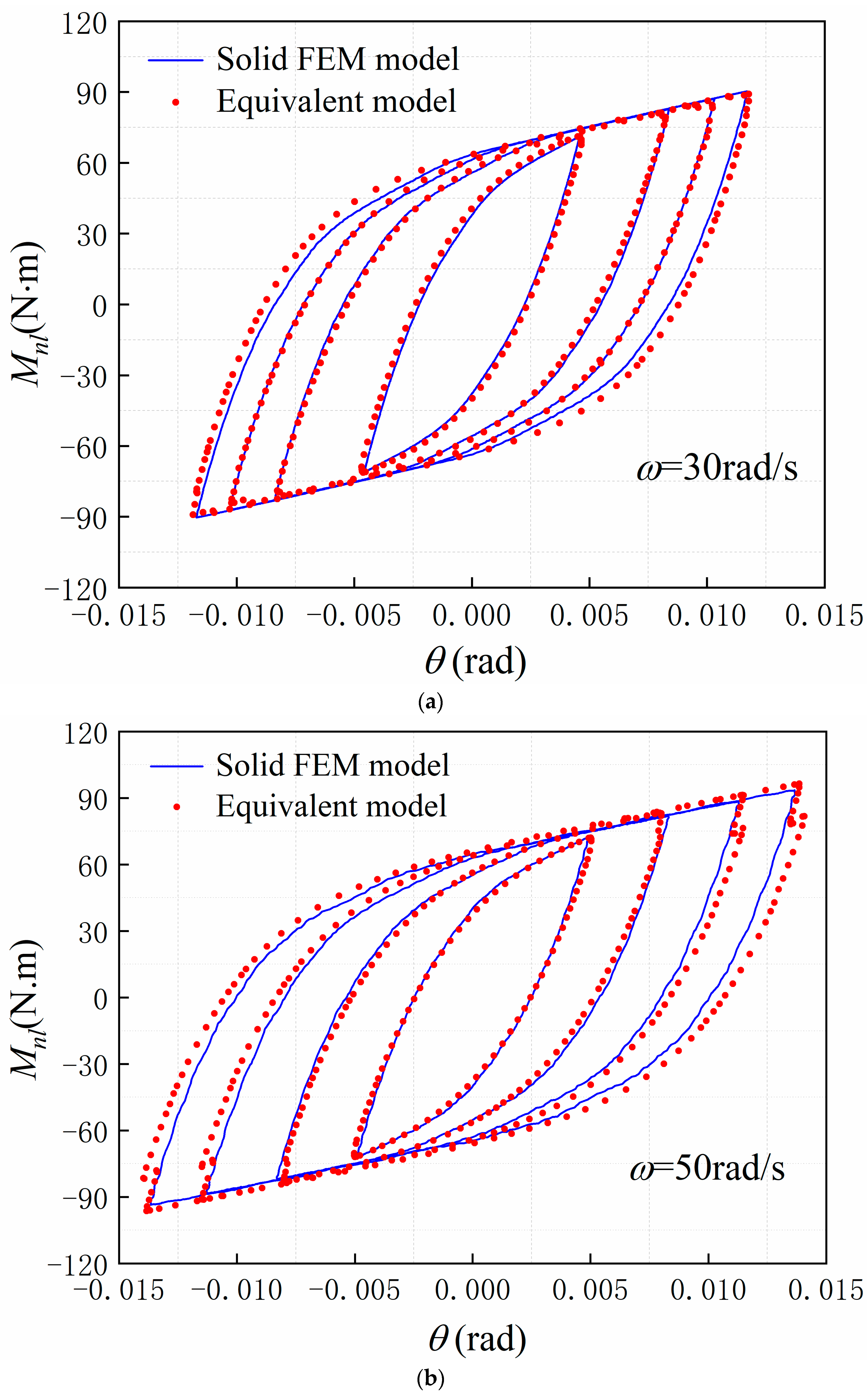
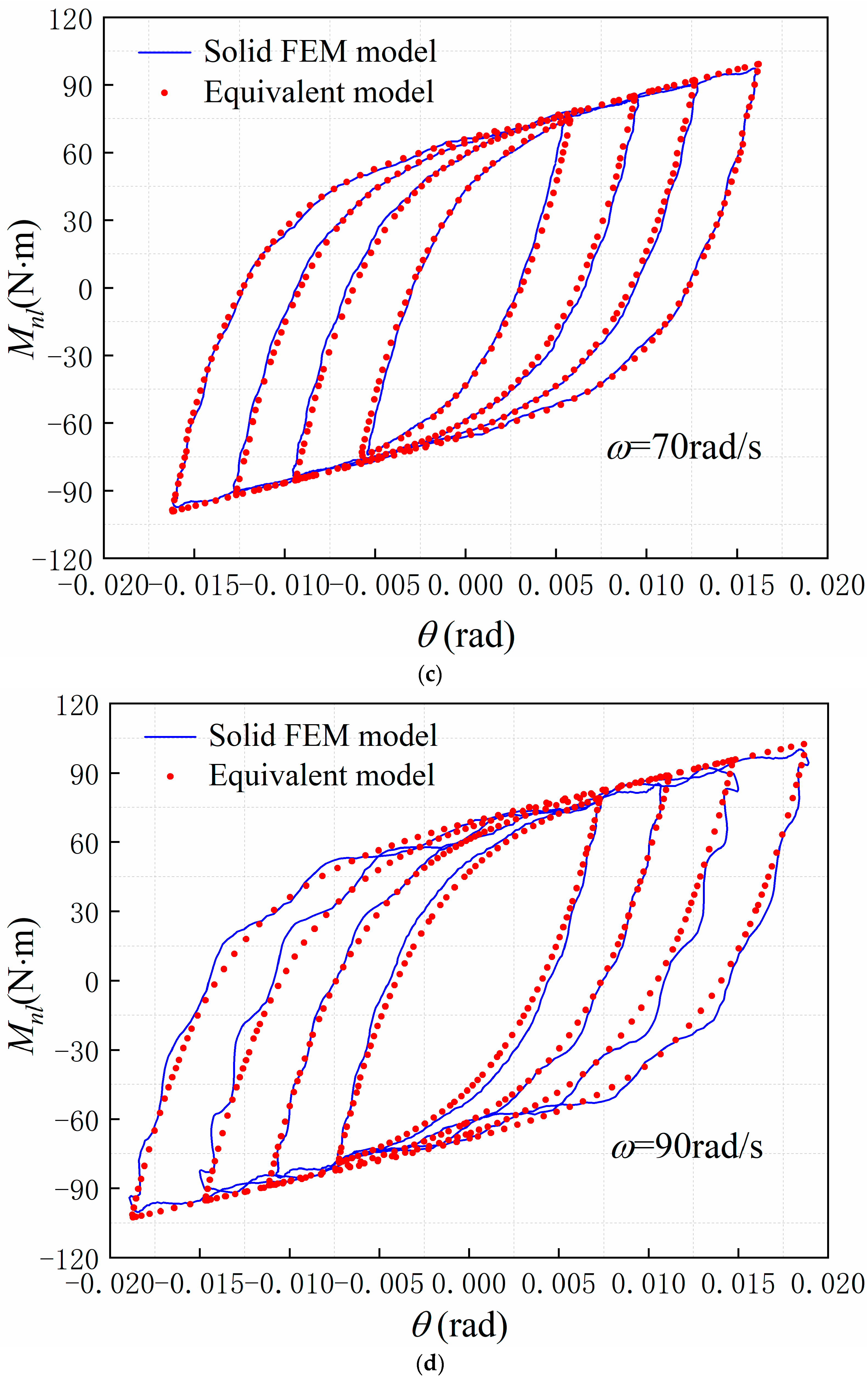
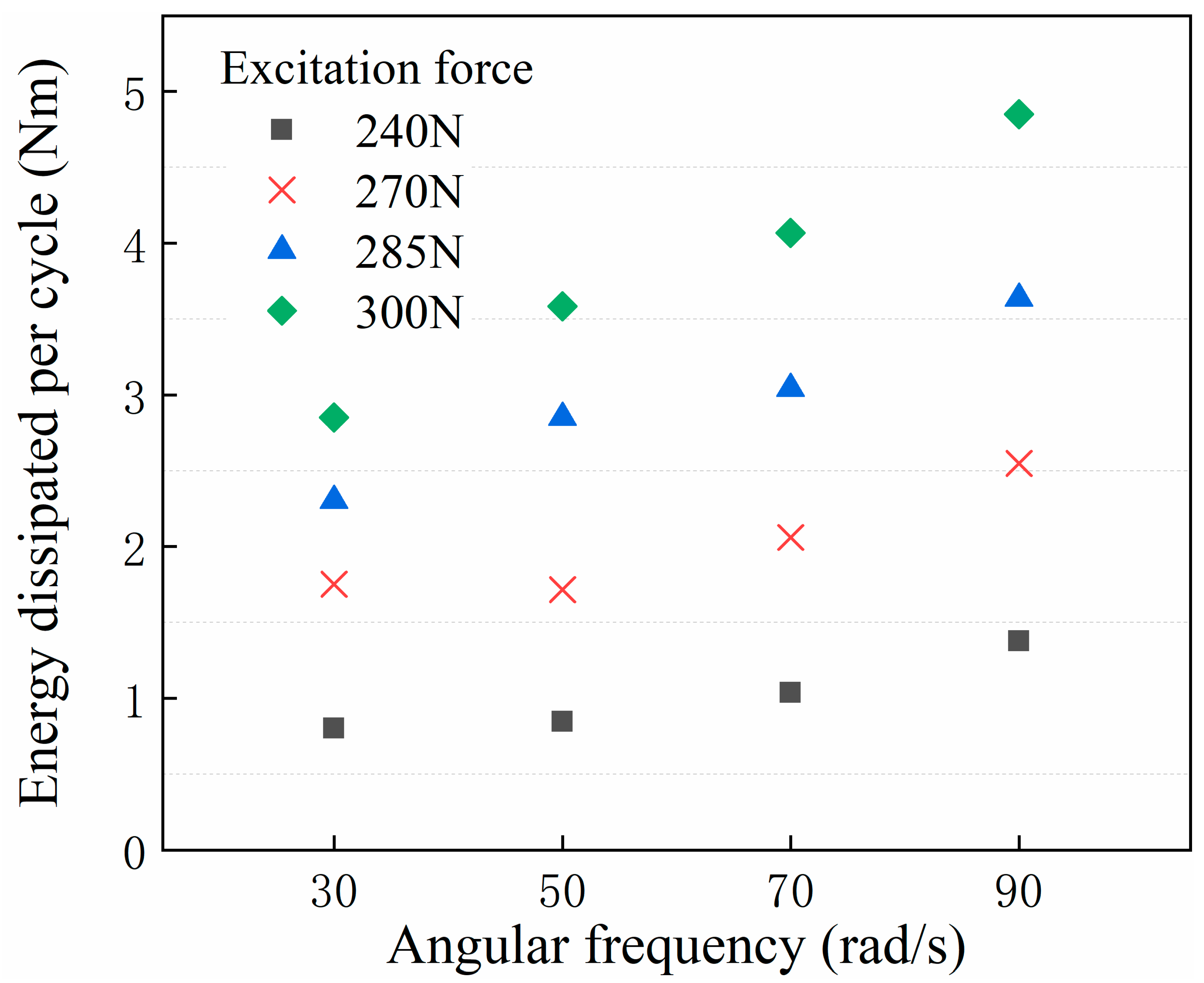
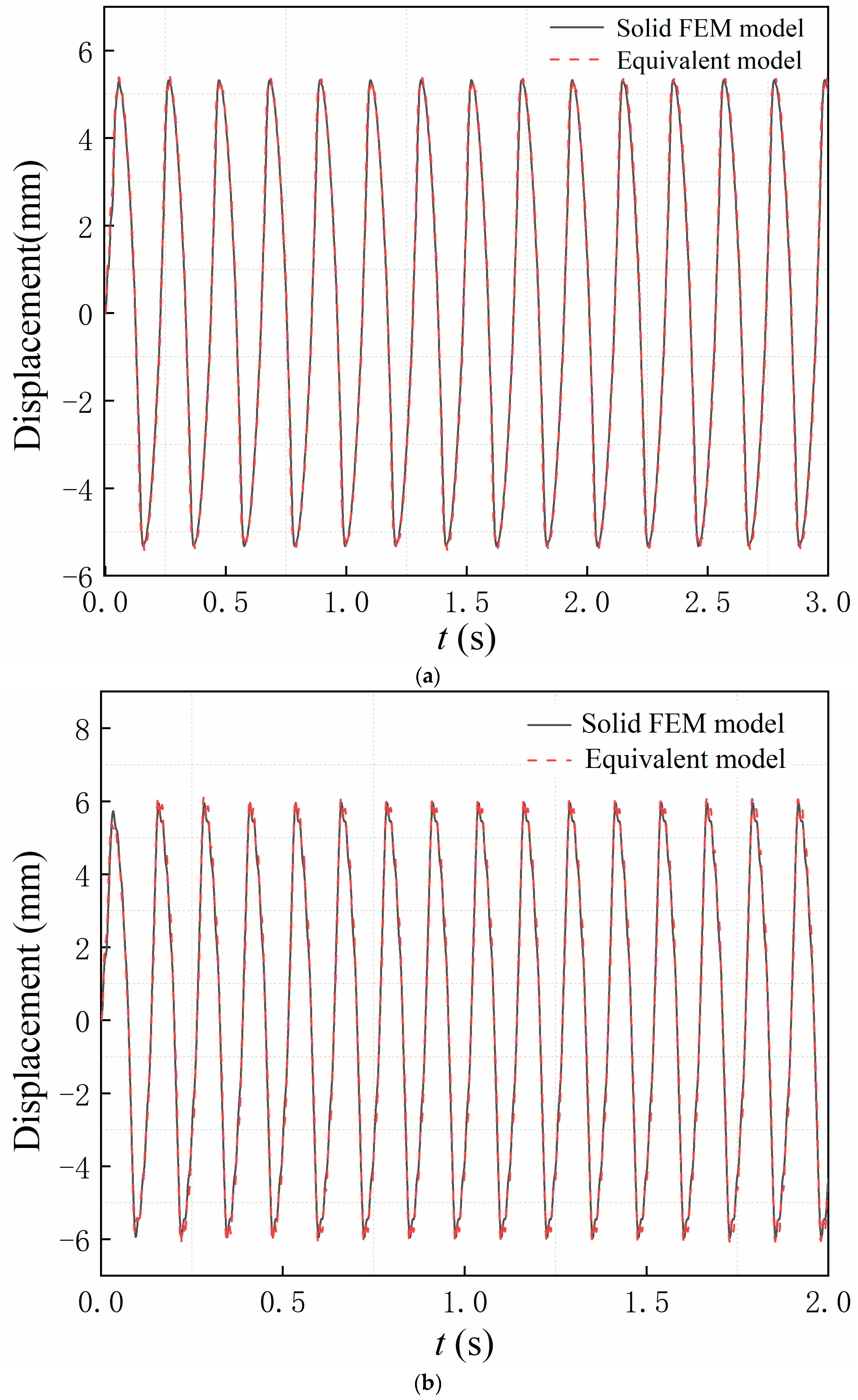
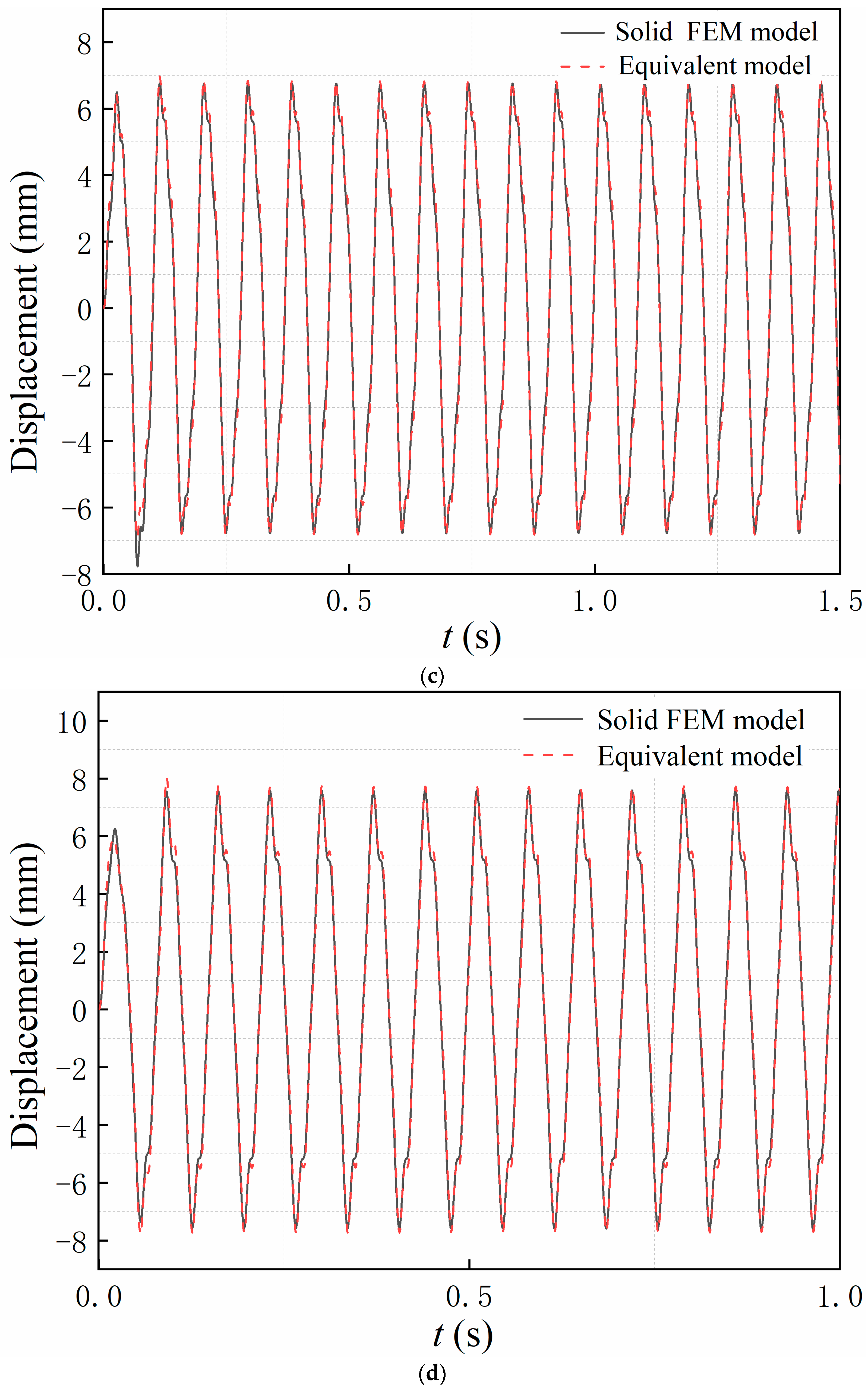
4.2. Validation of the Equivalent Model of the Bolt-Jointed Beam
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaul, L.; Nitsche, R. The role of friction in mechanical joints. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.F.; Shao, Y.M.; Xu, J.W. Investigation into the energy dissipation of a lap joint using the one-dimensional microslip friction model. Eur. J. Mech. A -Solids 2014, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Z. Research on process planning method of aerospace engine bolt tightening based on digital twin. Machines 2022, 10, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, M.; Lawal, I.; Brake, M.R.W.; Song, H. Measurement of slip and separation in jointed structures with non-flat interfaces. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 134, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Z. A six-parameter Iwan model and its application. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 68, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, A.T.; Balaji, N.N.; Kuether, R.J.; Brink, A.R.; Brake, M.R.W.; Quinn, D.D. A review of damping models for structures with mechanical joints. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2020, 72, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, J. Linear damping models for structural vibration. J. Sound Vib. 1998, 215, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.W.; Maietta, D.M.; Chang, L. An asperity microcontact model incorporating the transition from elastic deformation to fully plastic flow. J. Tribol. 2000, 122, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Etsion, I. Elastic-plastic contact analysis of a sphere and a rigid flat. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. A model for contact and static friction of nominally flat rough surfaces under full stick contact condition. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Mao, K.; Tian, W.; Li, L. A Three-dimensional transition interface model for bolt joint. Machines 2022, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hartwigsen, C.J.; McFarland, D.M.; Vakakis, A.F.; Bergman, L.A. Simulation of Dynamics of Beam Structures With Bolted Joints Using Adjusted Iwan Beam Elements. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 273, 249–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouc, R. A mathematical model for hysteresis. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1971, 24, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.K. Method for random vibration of hysteretic systems. J. Eng. Mech. 1976, 102, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valanis, K.C. Fundamental consequences of a new intrinsic time measure. plasticity as a limit of the endochcronic theory. Archiv. Mech. 1980, 32, 171–191. [Google Scholar]
- Segalman, D.J. A four-parameter Iwan model for lap-type joints. J. Appl. Mech. 2005, 72, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, M.; Ikhouane, F.; Rodellar, J. The hysteresis Bouc-Wen model, a survey. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2009, 16, 161–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, J.E.; Barbat, A.H. Equivalent linearization of the Bouc–Wen hysteretic model. Eng. Struct. 2000, 22, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, H. An alternative linearization approach applicable to hysteretic systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2014, 19, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, G. Equivalent linearization of Bouc–Wen hysteretic model with harmonic input. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 2019, 100, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacayo, R.M.; Allen, M.S. Updating structural models containing nonlinear Iwan joints using quasi-static modal analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 118, 133–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, H.; Rajaei, M. Identification of Iwan distribution density function in frictional contacts. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 3382–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.A.; Sikder, U. Bouc–Wen hysteresis model identification using modified firefly algorithm. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 395, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, G.A.; Alvarez, D.A.; Bedoya-Ruíz, D. Identification of Bouc-Wen type models using the transitional Markov chain Monte Carlo method. Comput. Struct. 2015, 146, 252–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, M.; Ouyang, H.; Mottershead, J.E. Simplified models of bolted joints under harmonic loading. Comput. Struct. 2005, 84, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.W.; Ni, Y.Q.; Ko, J.M. Steady-state oscillation of hysteretic differential model-II: Performance analysis. J. Eng. Mech. 1994, 120, 2299–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiana, N.; Sessa, S.; Rosati, L. A generalized class of uniaxial rate-independent models for simulating asymmetric mechanical hysteresis phenomena. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 146, 106984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiana, N.; Rosati, L. Classification and unified phenomenological modeling of complex uniaxial rate-independent hysteretic responses. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 182, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamia, N.; Jalali, H.; Taghipour, J.; Friswell, M.I.; Khodaparast, H.H. An equivalent model of a nonlinear bolted flange joint. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 153, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, L.; Lenz, J. Nonlinear dynamics of structures assembled by bolted joints. Acta Mech. 1997, 125, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.S.; Wang, L.B.; Jin, D.P.; Liu, X.D.; Lu, P.L. Equivalent beam model for spatial repetitive lattice structures with hysteretic nonlinear joints. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 200, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, H.W.; Liu, R.Q.; Liu, K. Equivalent dynamic model for triangular prism mast with the tape-spring hinges. AIAA J. 2021, 59, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cao, Q.D.; Wei, J. Survey on equivalent continuum modeling for truss structures and their nonlinear dynamics and vibration control. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourahmadian, F.; Ahmadian, H.; Jalali, H. Modeling and identification of frictional forces at a contact interface experiencing micro-vibro-impacts. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 2874–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, L.; Armand, J.; Schwingshackl, C.W.; Salles, L.; Wong, C. An advanced underplatform damper modelling approach based on a microslip contact model. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 436, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abad, J.; Medel, F.J.; Franco, J.M. Determination of Valanis model parameters in a bolted lap joint: Experimental and numerical analyses of frictional dissipation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 89, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jalali, H.; Jamia, N.; Friswell, M.I.; Khodaparast, H.H.; Taghipour, J. A generalization of the Valanis model for friction modelling. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 179, 109339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.A.; Lawlor, V.P.; Stanley, W.F.; McCarthy, C.T. Bolt-hole clearance effects and strength criteria in single-bolt, single-lap, composite bolted joints. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, Y.; Sakai, T. Rotating loosening mechanism of a nut connecting a rotary disk under rotating-bending force. J. Mech. Des. 2005, 127, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Olsson, M.; Izumi, S.; Sakai, S. Investigation into the self-loosening behavior of bolted joint subjected to rotational loading. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2012, 23, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.T.; McCarthy, M.A. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of single-bolt, single-lap composite bolted joints: Part II––effects of bolt-hole clearance. Compos. Struct. 2005, 71, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.-Y.; Han, Q.-K.; Chu, F.-L. Bolt loosening at rotating joint interface and its influence on rotor dynamics. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2016, 59, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi-Shoore, M.R.; Mofid, M. New modeling for moment–rotation behavior of bolted endplate connections. Sci. Iran. 2011, 18, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graves, G.; Ross, M.; Abdelkefi, A. Joint interface modeling and characterization of lap-jointed beams. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 1–28, on line. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göge, D.; Sinapius, M.; Füllekrug, U.; Link, M. Detection and description of non-linear phenomena in experimental modal analysis via linearity plots. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2005, 40, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, S.S.; Wu, Z.M.; Chan, S.L. Vibration control study of a suspension footbridge using hybrid slotted bolted connection elements. Eng. Struct. 2004, 26, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bograd, S.; Reuss, P.; Schmidt, A.; Gaul, L.; Mayer, M. Modeling the dynamics of mechanical joints. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 2801–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, D.D.; Segalman, D.J. Using series-series Iwan-type models for understanding joint dynamics. J. Appl. Mech. 2005, 72, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abad, J.; Franco, J.M.; Celorrio, R.; Lezáun, L. Design of experiments and energy dissipation analysis for a contact mechanics 3D model of frictional bolted lap joints. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 45, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, F.; Jamal-Omidi, M. Vibration of nonlinear bolted lap-jointed beams using Timoshenko theory. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2018, 88, 981–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.P.; Wen, H.; Chen, T. Identification using Valanis model for beams with nonlinear bolted joint and boundary connection. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference Vibroengineering, Shanghai, China, 7–8 December 2016; pp. 185–191. Available online: https://www.extrica.com/article/17951 (accessed on 8 December 2016).
- Yokoyama, T. Vibrations of a hanging Timoshenko beam under gravity. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 141, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, Z.; Kosmatka, J.B. An improved two-node Timoshenko beam finite element. Comput. Struct. 1993, 47, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, F.; Sun, K.; Mu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q. Study on tangential stiffness nonlinear softening of bolted joint in friction-sliding process. Tribol. Int. 2021, 156, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, J.C.; Kang, B.S. Finite element analysis and modeling of structure with bolted joints. Appl. Math. Model. 2007, 31, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Xu, H.W. ANSYS Structural Analysis Unit and Application, 1st ed.; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 384–386. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 20273; Fasteners; Clearance Holes for Bolts and Screws. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1992; pp. 2–3.
- Hu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, S.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, W. Experimental Study on Timber−Lightweight Concrete Composite Beams with Ductile Bolt Connectors. Materials 2021, 14, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN-ISO 898; Mechanical Properties of Fasteners Made of Carbon Steel-Part 2: Nuts with Specified Property Classed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 7–9.
- Weggel, D.C.; Boyajian, D.M.; Chen, S. Modelling structures as systems of springs. World Trans. Eng. Technol. Educ. 2007, 6, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Vaiana, N.; Capuano, R.; Rosati, L. Evaluation of path-dependent work and internal energy change for hysteretic mechanical systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 186, 109862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


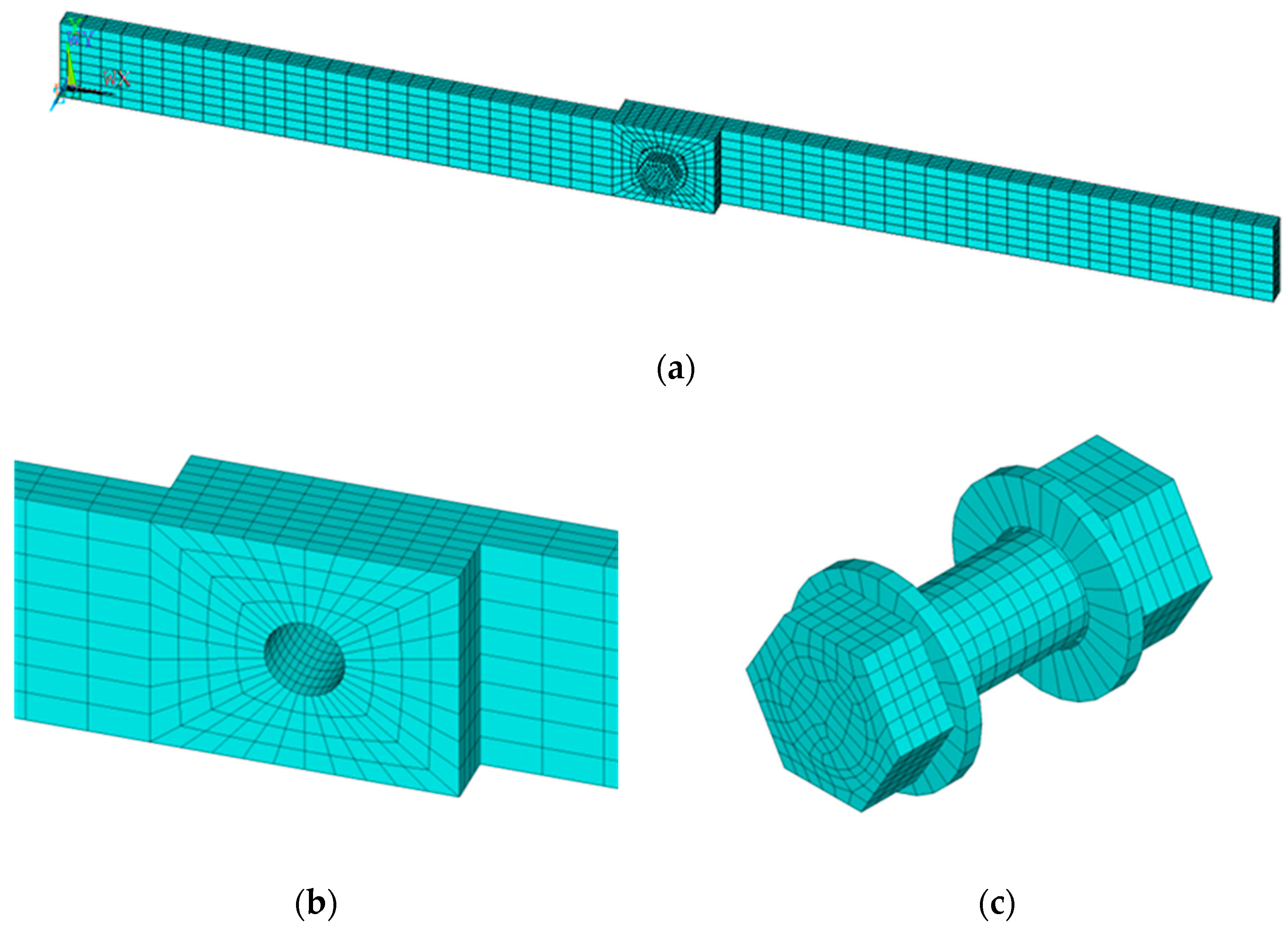
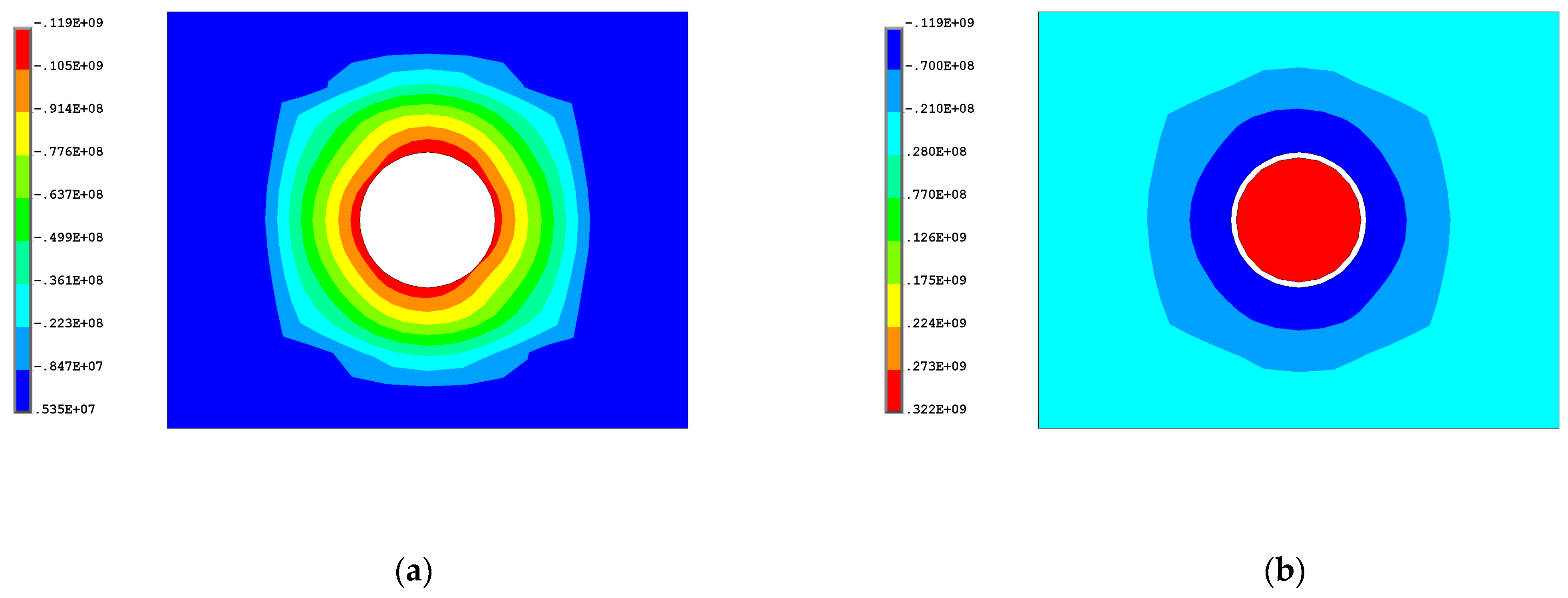
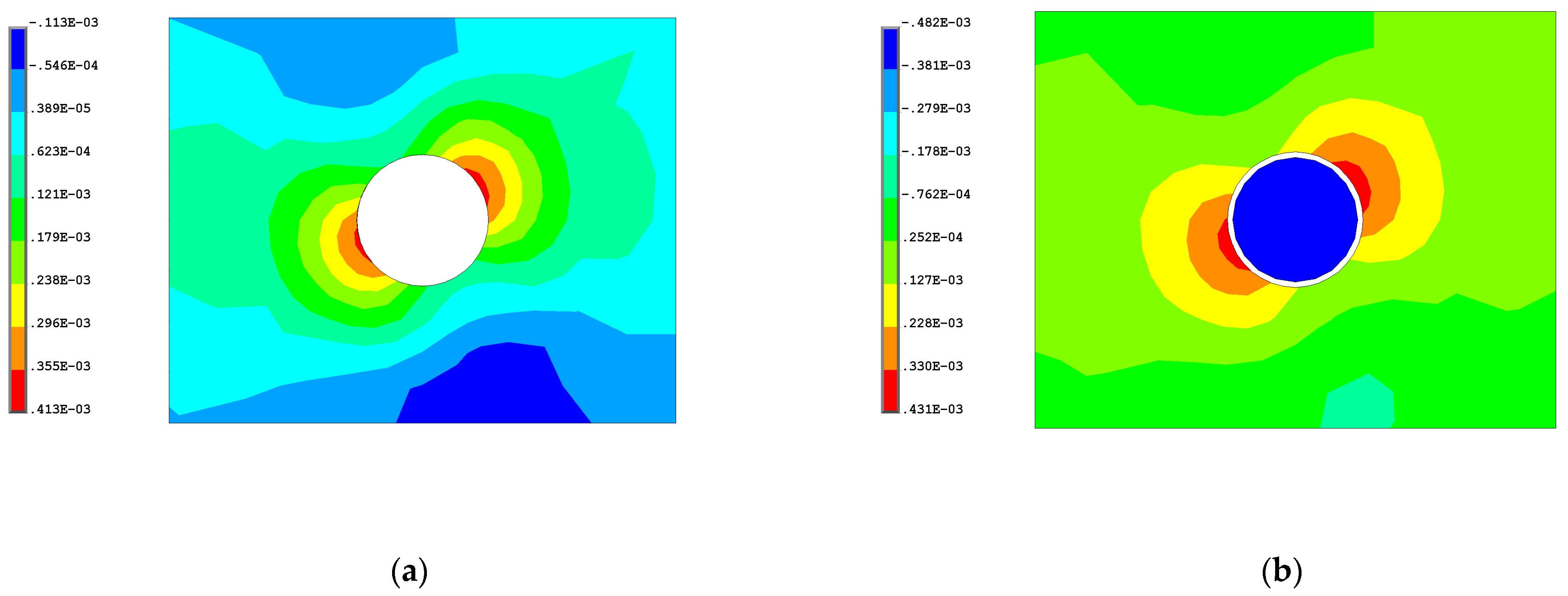
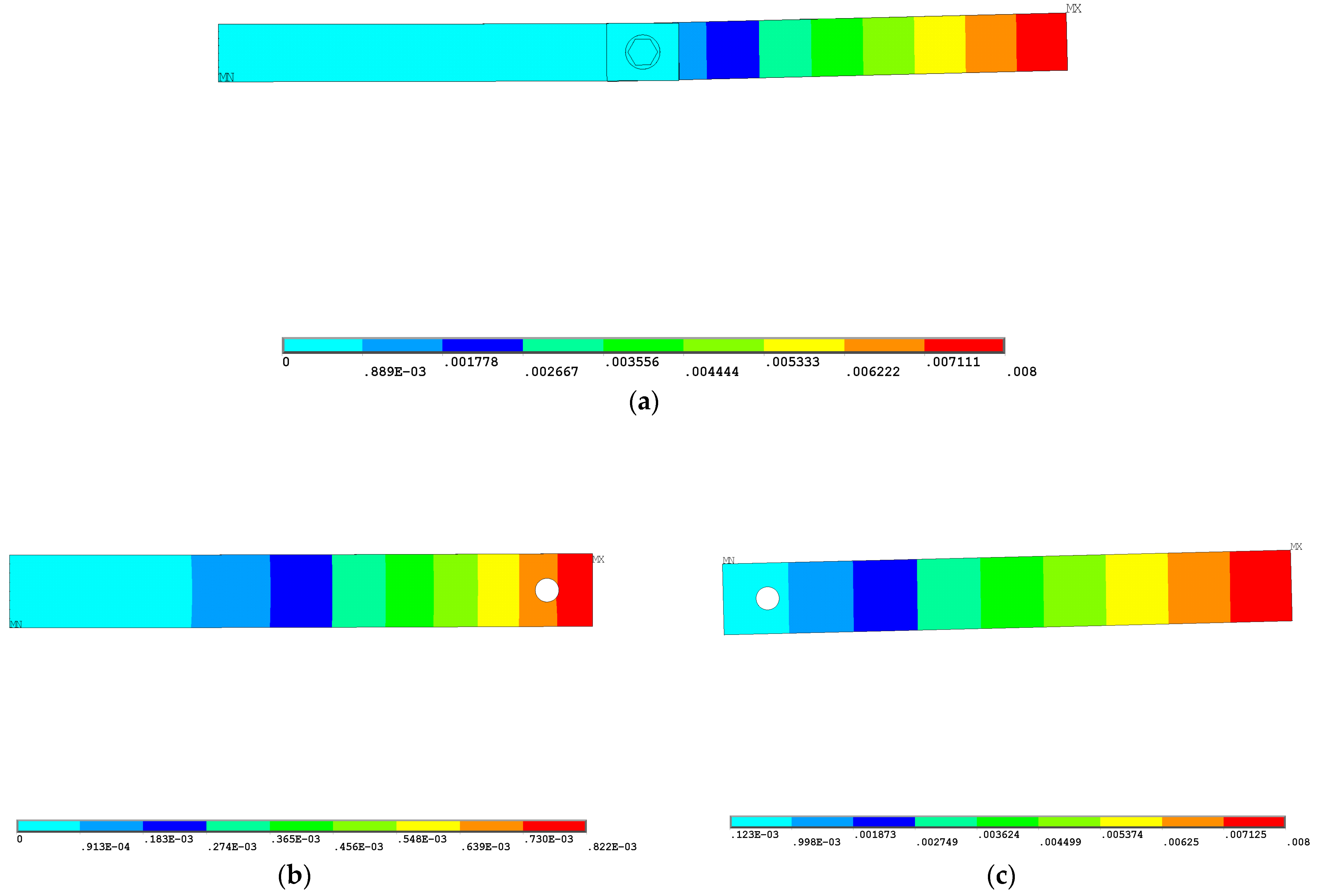


| Contact Surface (CONTA174 Element) | Target Surface (TARGE170 Element) | Number of Contact Pairs |
|---|---|---|
| Free beam | Fixed beam | 1 |
| Head of bolt | Washer | 1 |
| beams | Washer | 1 |
| Nut | Washer | 2 |
| Bolt shank | Inner surface of the nut | 1 |
| Bolt shank | Inner surfaces of washers | 2 |
| Bolt shank | Bolt hole of beams | 2 |
| Parameter | ANSYS Real Constant | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| kn | FKN | Normal penalty stiffness factor | 1.61 |
| kτ | FKT | Tangent penalty stiffness factor | 0.277 |
| b(N) | CHOE | Contact cohesion | 0 |
| c | DC | Exponential decay coefficient | 41,278 |
| MU | Dynamic coefficient of friction | 0.183 | |
| FACT | Static/dynamic ratio | 1.21 | |
| (mm) | SLTO | Allowable elastic slip | −1.7 × 10−5 |
| Mesh | Number of Elements | Number of Nodes | Elapsed CPU Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 1201 | 1962 | 816 |
| Case 2 | 2355 | 3424 | 1298 |
| Case 3 | 4494 | 6138 | 2280 |
| Case 4 | 20,910 | 26,748 | 8719 |
| Frequency (Rad/s) | E0 (kNm/Rad) | Et (kNm/Rad) | σ0 (Nm) | κ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 22.0 | 2.15 | 71.1 | 0.3 |
| 50 | 21.2 | 2.11 | 74.7 | 0.2 |
| 70 | 21.1 | 2.02 | 73.6 | 0.2 |
| 90 | 18.5 | 1.75 | 77 | 0.1 |
| Frequency (Rad/s) | Applied Loads (N) | Steady-State Response Amplitude (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid FEM Model | Equivalent Model | Error (%) | ||
| 30 | 240 | 2.82 | 2.80 | +0.71 |
| 270 | 4.18 | 3.95 | −5.50 | |
| 285 | 4.84 | 4.72 | −2.48 | |
| 300 | 5.32 | 5.36 | +0.75 | |
| 50 | 240 | 2.94 | 2.94 | +0.01 |
| 270 | 4.14 | 4.06 | −1.93 | |
| 285 | 5.15 | 5.26 | +2.14 | |
| 300 | 5.96 | 6.07 | +1.84 | |
| 70 | 240 | 3.15 | 3.22 | +2.22 |
| 270 | 4.55 | 4.50 | −1.10 | |
| 285 | 5.66 | 5.63 | −0.53 | |
| 300 | 6.77 | 6.83 | +0.89 | |
| 90 | 240 | 3.77 | 3.78 | +0.27 |
| 270 | 4.95 | 5.14 | +3.84 | |
| 285 | 6.27 | 6.16 | −1.75 | |
| 300 | 7.59 | 7.71 | +1.58 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Liu, F. Equivalent Dynamic Modeling for the Relative Rotation of Bolted Joint Interface Using Valanis Model of Hysteresis. Machines 2023, 11, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030342
Zhang G, Liu F. Equivalent Dynamic Modeling for the Relative Rotation of Bolted Joint Interface Using Valanis Model of Hysteresis. Machines. 2023; 11(3):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guowei, and Fushou Liu. 2023. "Equivalent Dynamic Modeling for the Relative Rotation of Bolted Joint Interface Using Valanis Model of Hysteresis" Machines 11, no. 3: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030342
APA StyleZhang, G., & Liu, F. (2023). Equivalent Dynamic Modeling for the Relative Rotation of Bolted Joint Interface Using Valanis Model of Hysteresis. Machines, 11(3), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030342






