Controller Design for Parallel Mechanism Solar Tracker
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- By using the Stewart platform, which has a high load-carrying capacity, precise positioning ability, and high rigidity due to its structure, we designed a solar tracker that will operate with high accuracy in challenging working conditions.
- We set up the mathematical and graphical model of the Stewart platform, whose mechanical design is complex and whose control algorithms are exceedingly difficult, in a Simulink environment.
- We designed an embedded PID controller that eliminates wind disturbance and follows the solar trajectory with high accuracy.
2. Materials and Methods
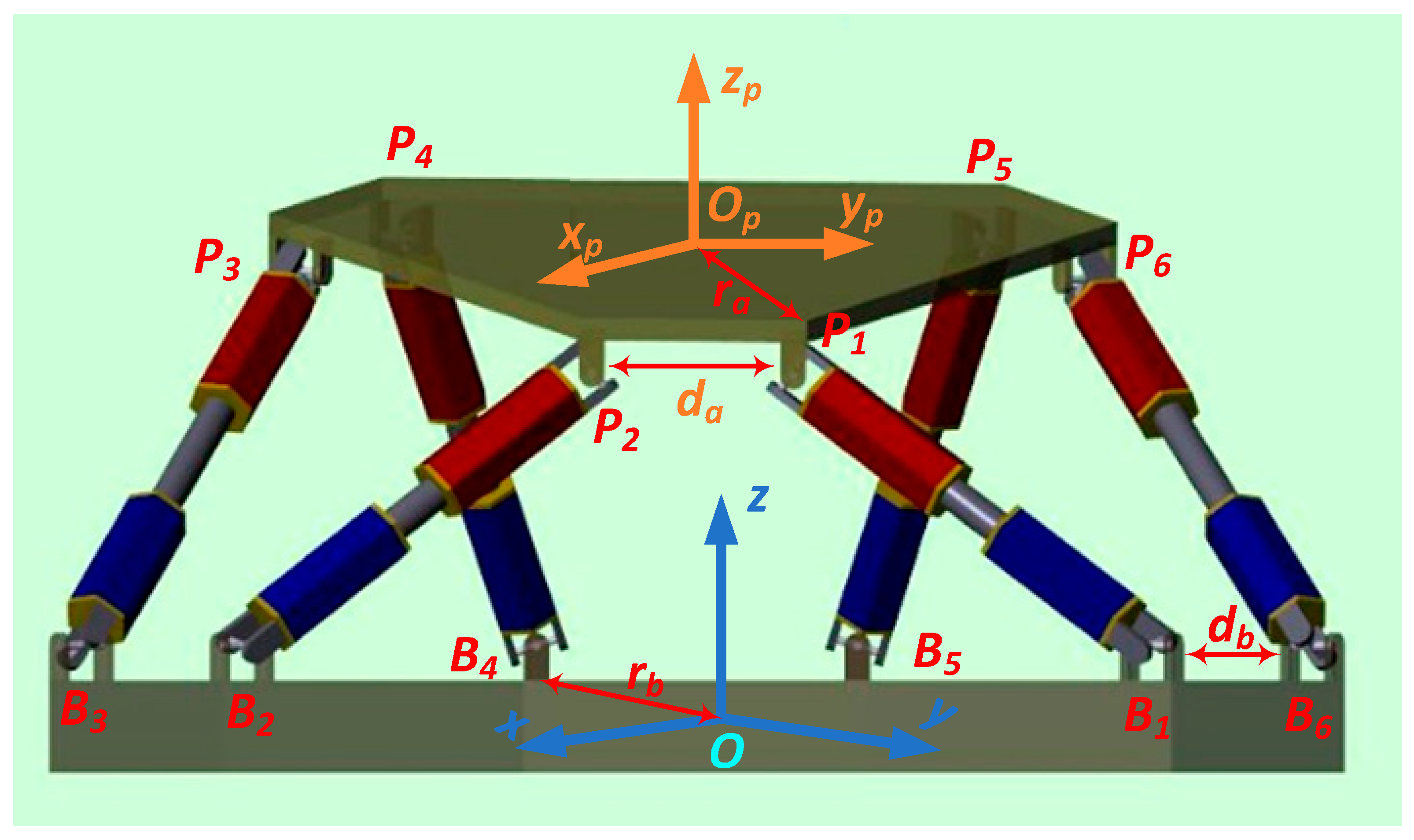
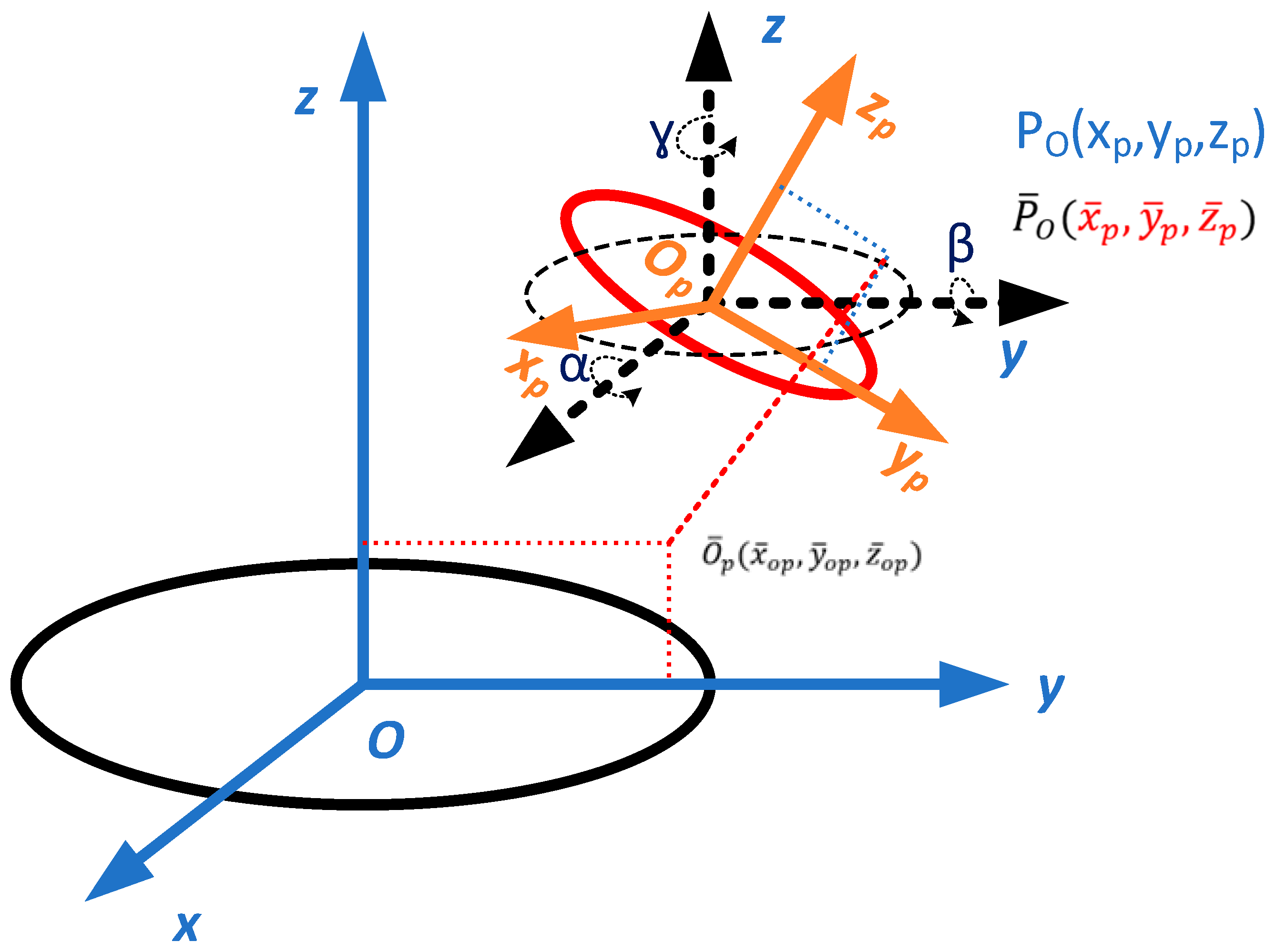
2.1. Stewart Platform
2.2. Definition of Sun Attitude
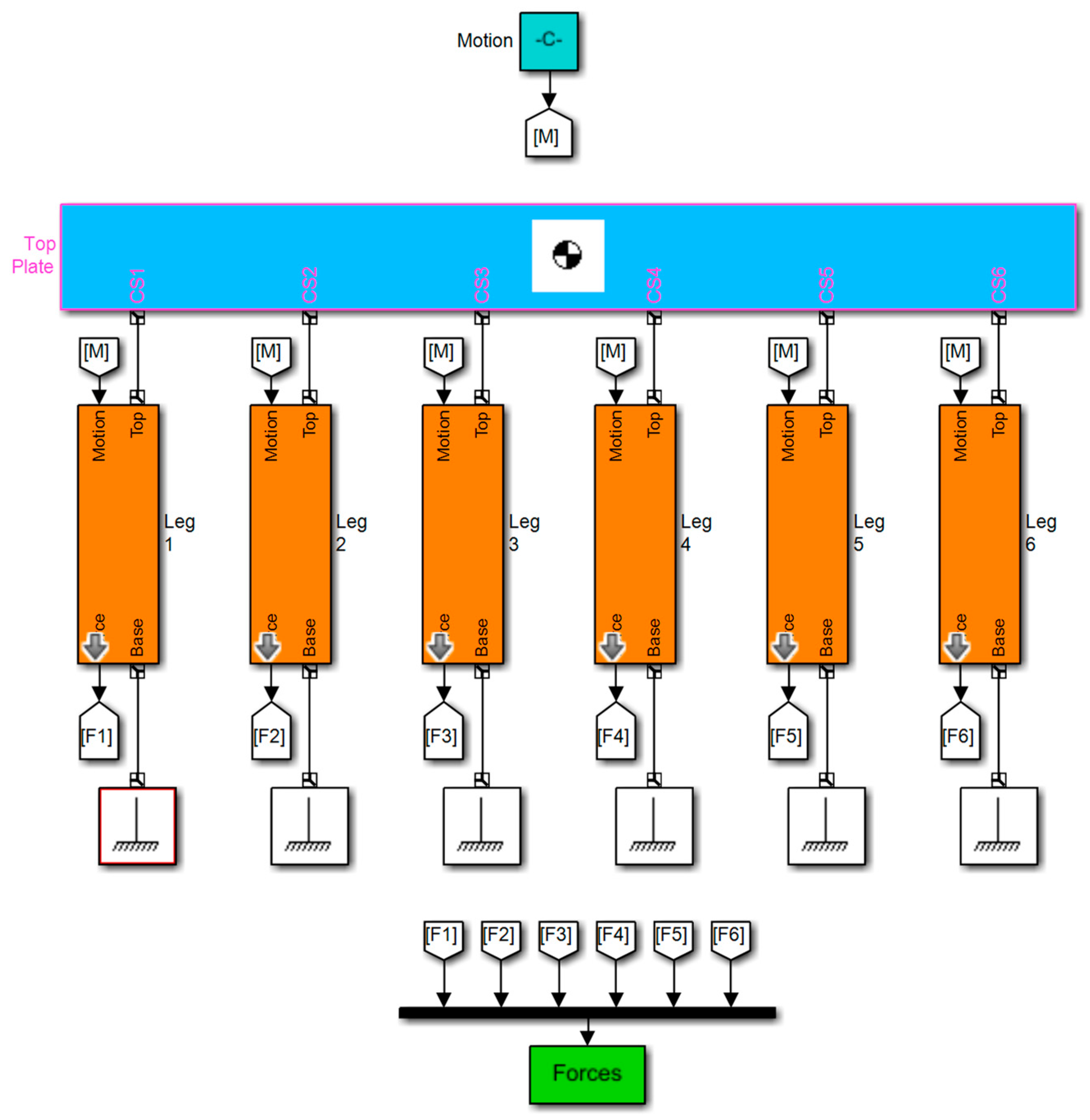
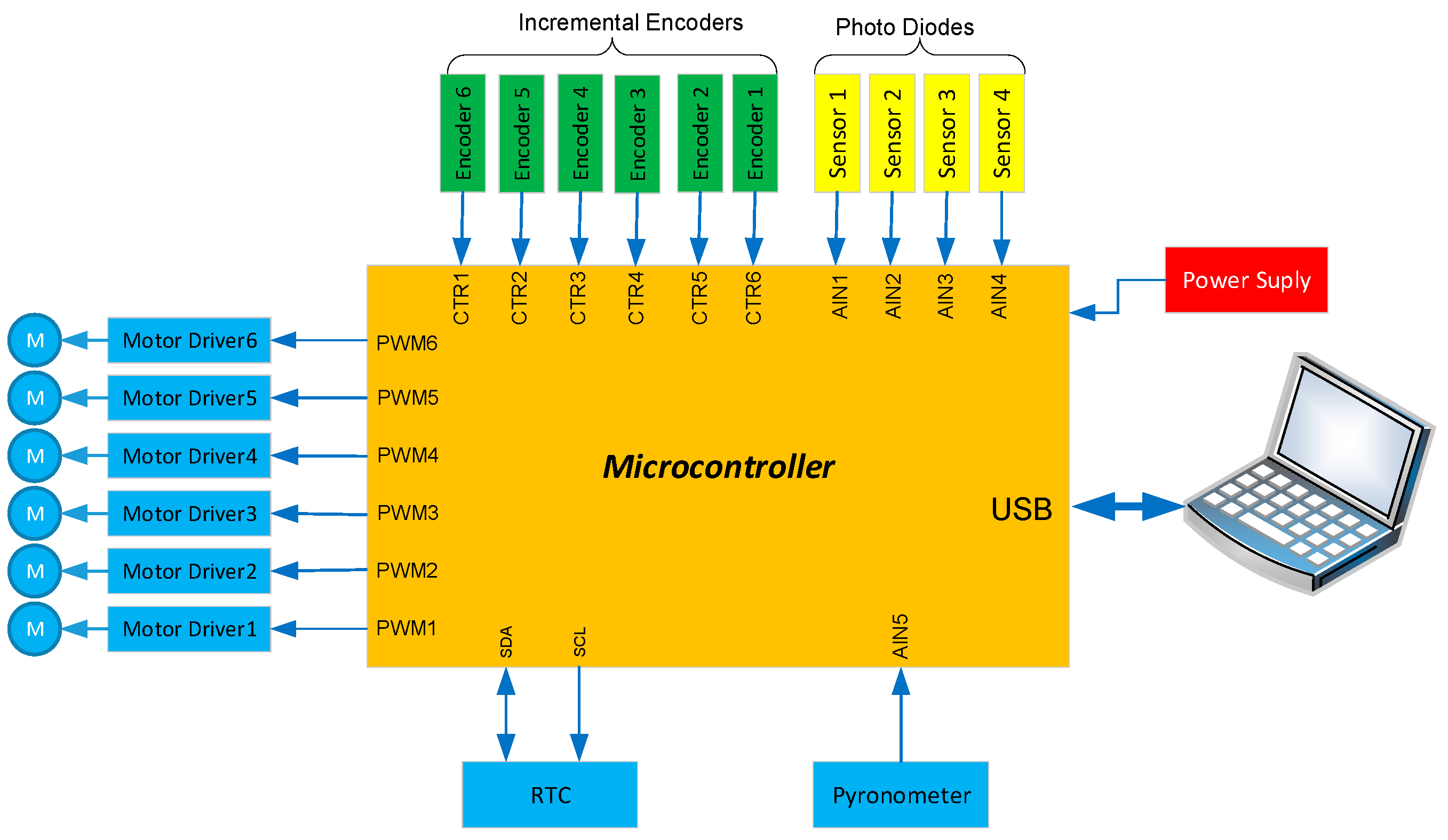
2.3. Real-Time Embedded Controller
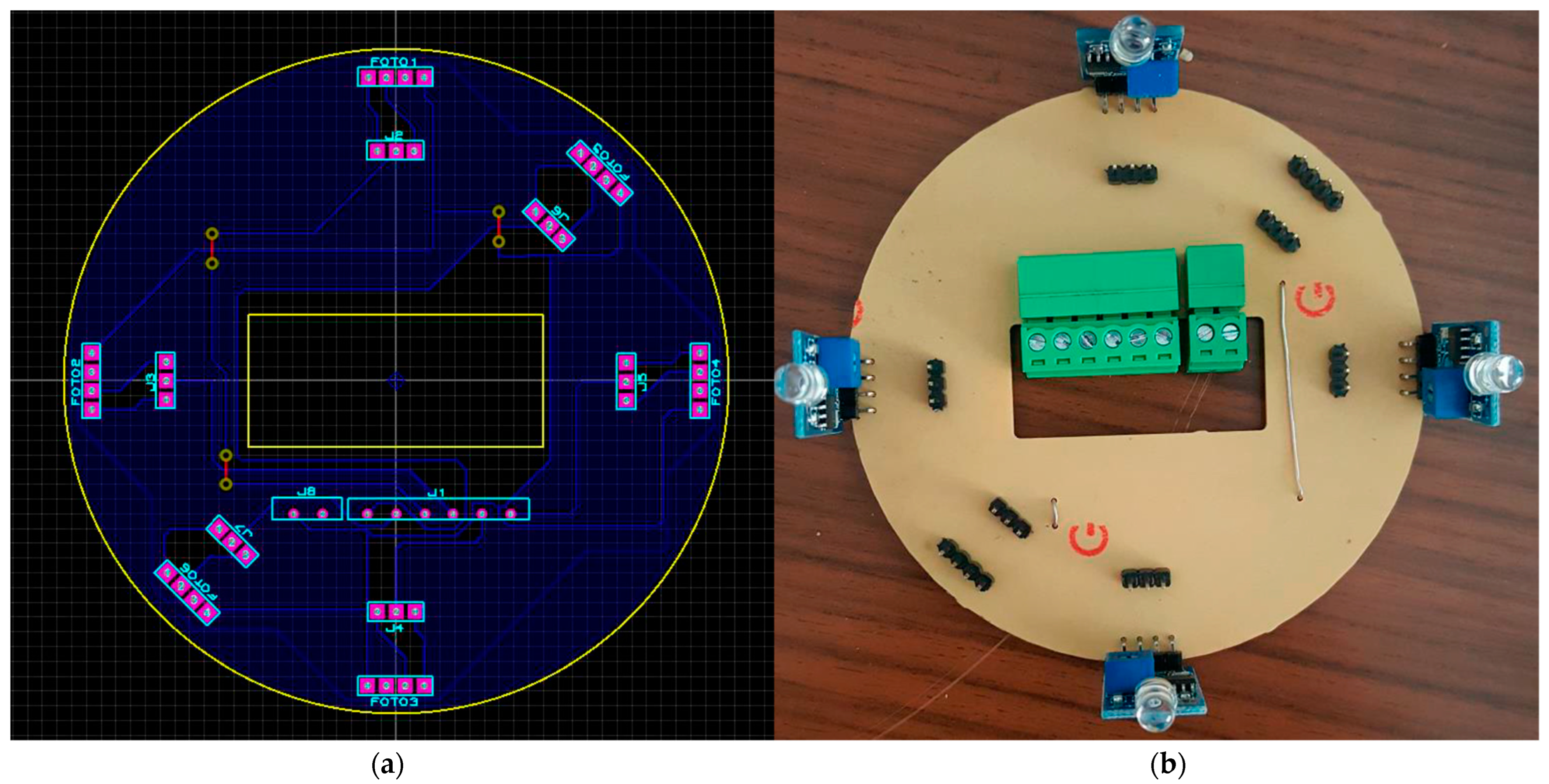
2.4. Hardware Architecture
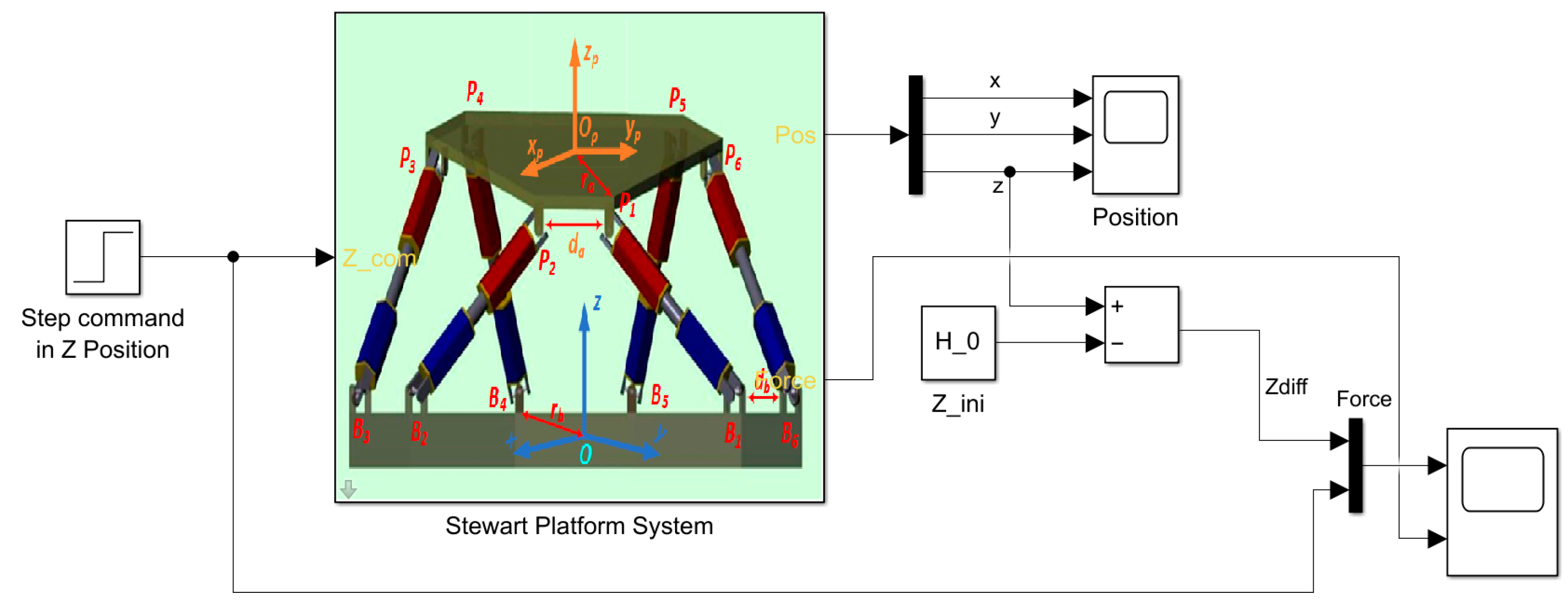
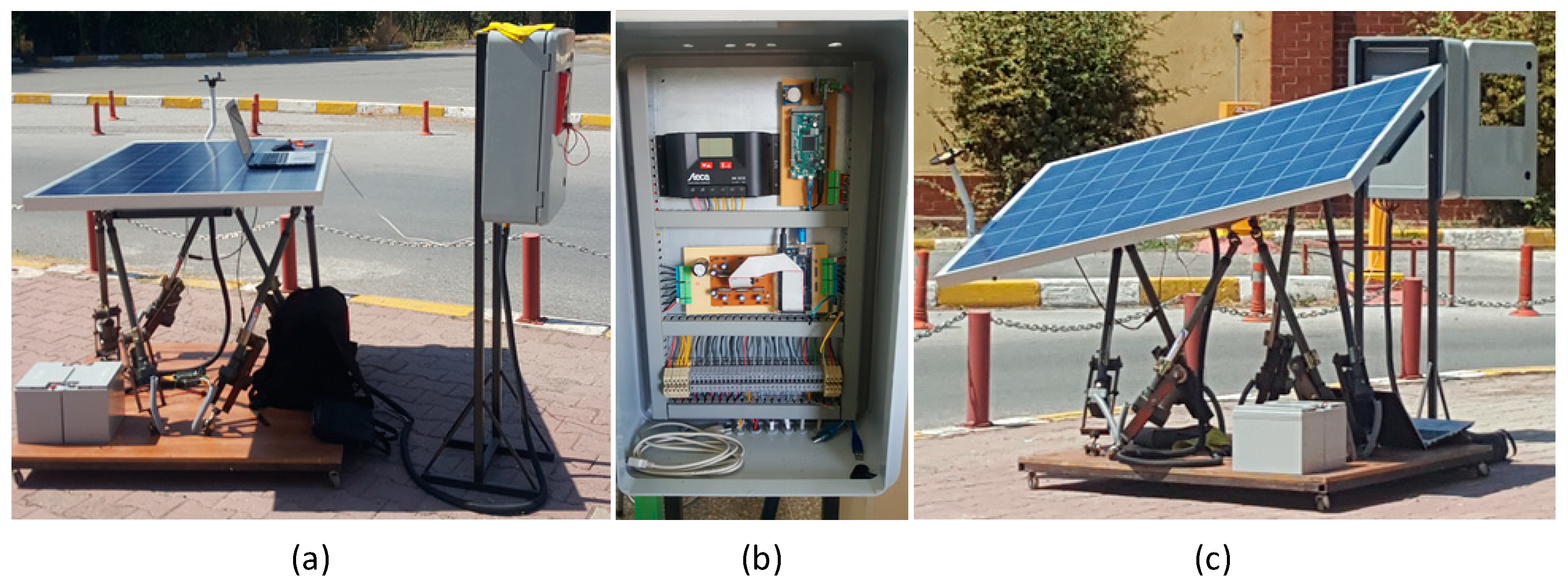
3. Experimental Works
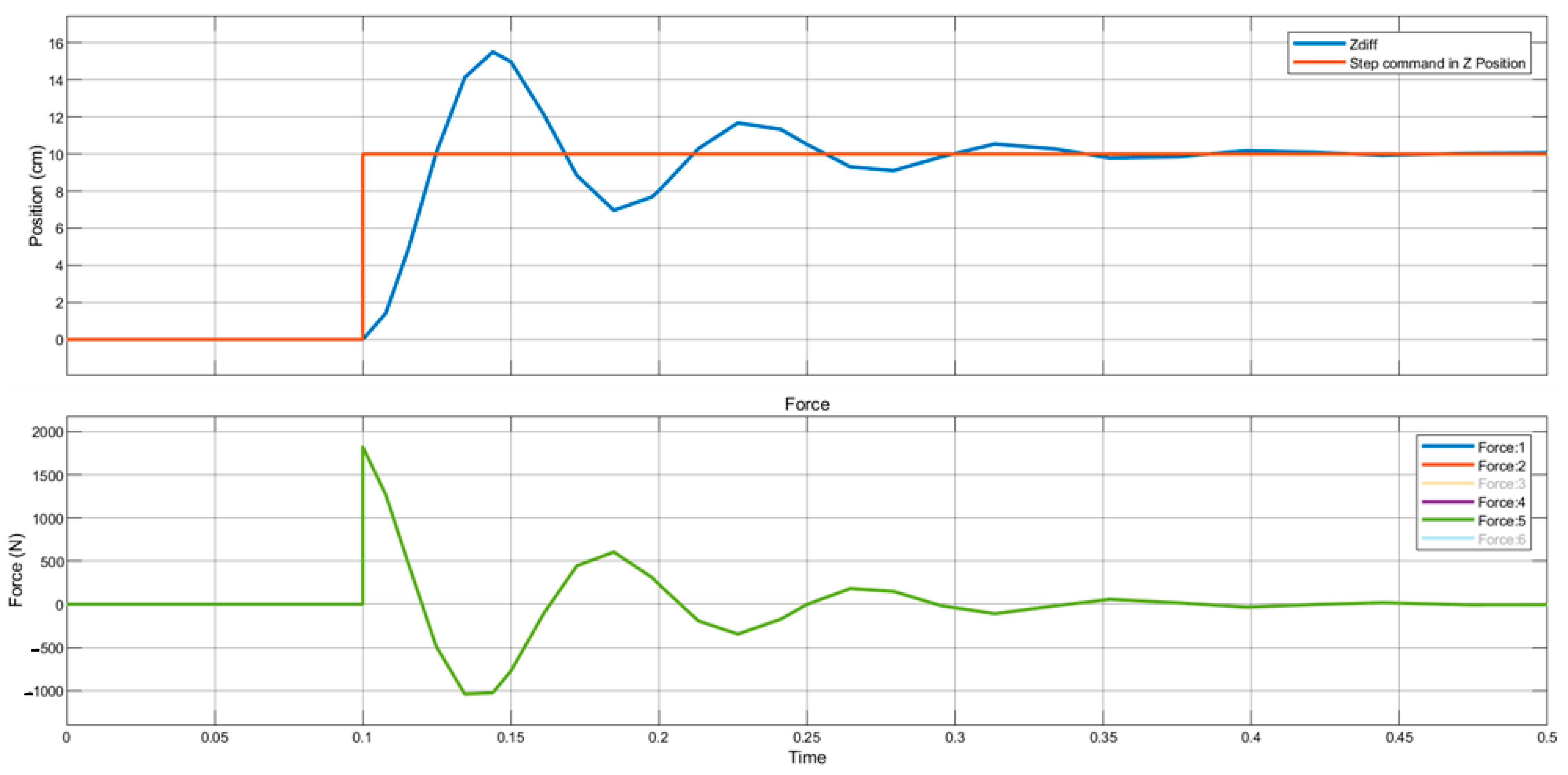
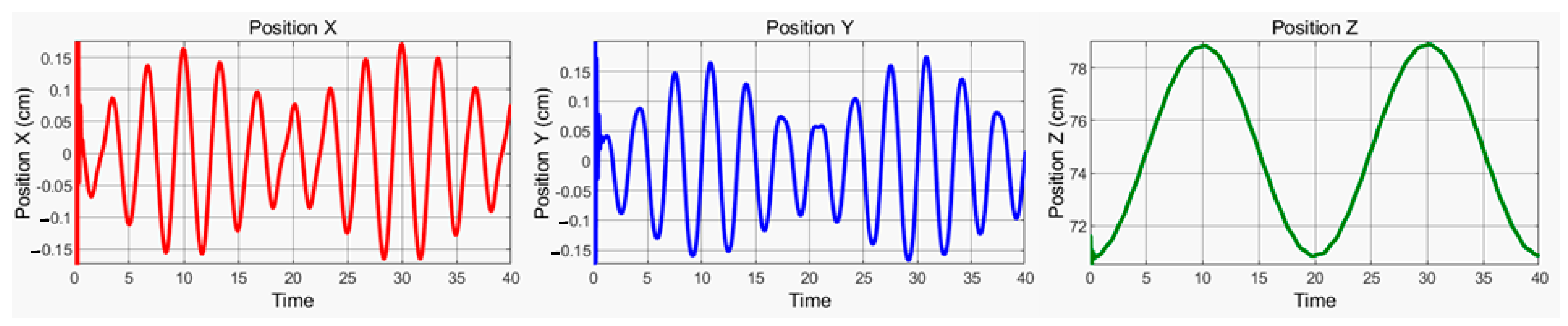
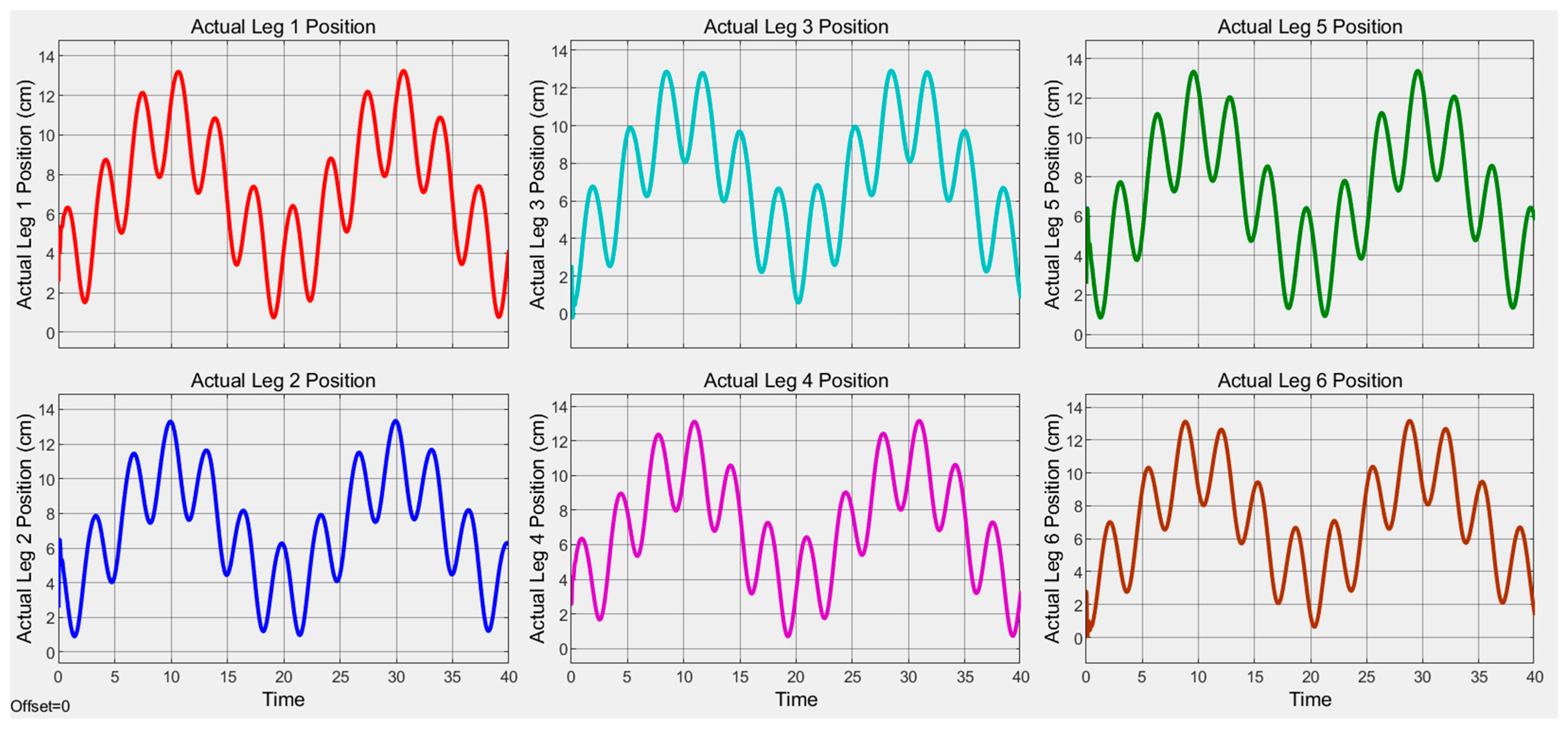
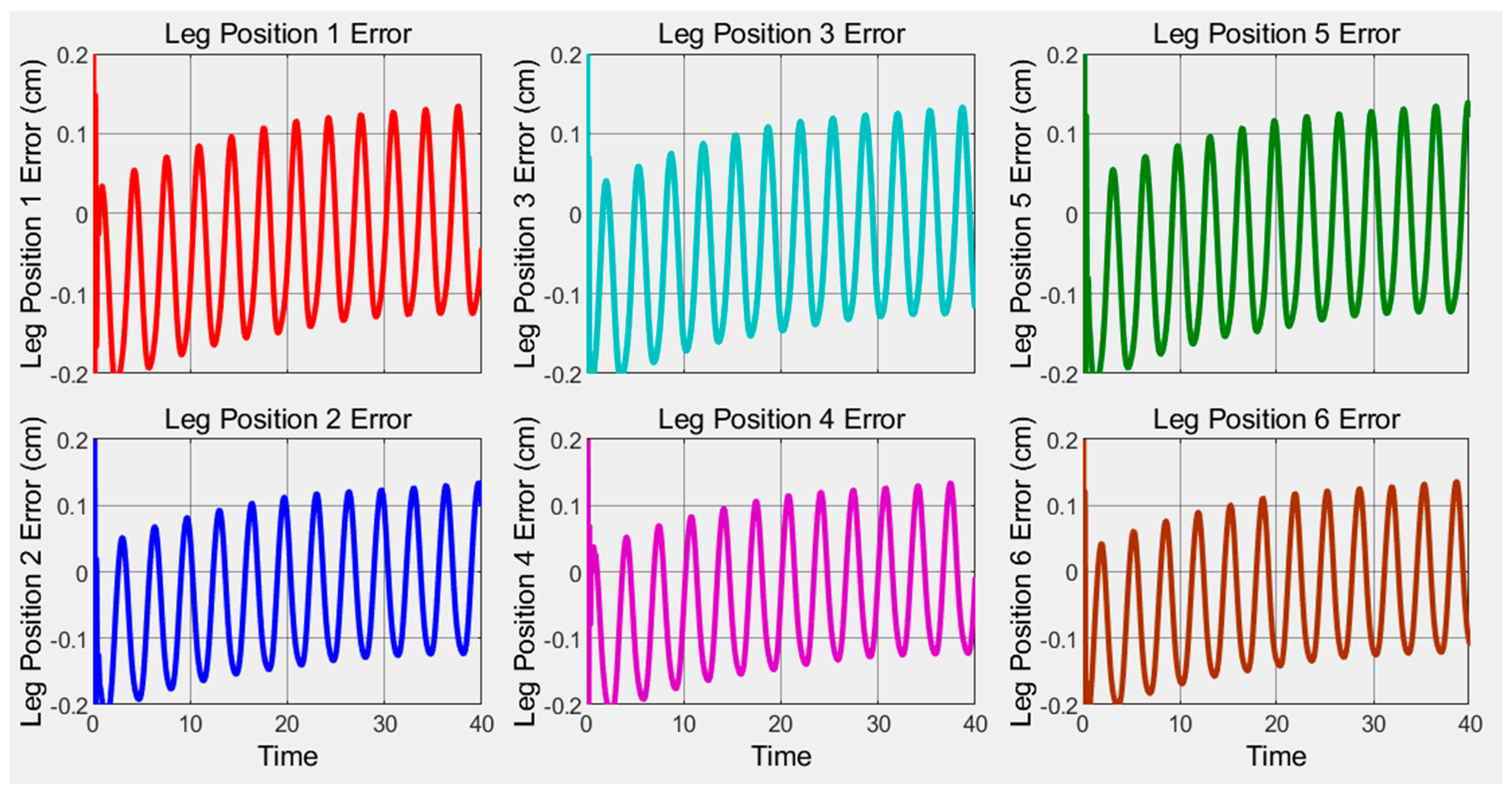
4. Result and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clifford, M.; Eastwood, D. Design of a novel passive solar tracker. Sol. Energy 2004, 77, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.S.; Carvalho, M. Design, Greenhouse Emissions, and Environmental Payback of a Photovoltaic Solar Energy System. Energies 2022, 15, 6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigo, P.D.; Siluk, J.C.M.; Lacerda, D.P.; Spellmeier, J.P. Competitive business model of photovoltaic solar energy installers in Brazil. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukdir, Y.; El Omari, H. Characterization of cadmium sulfide light dependent resistors sensors for optical solar trackers. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2023, 13, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, A.-H.I.; Shareef, H.; Ameen, N.; Alhammadi, A.H.; Iratni, M.; Alkaabi, A.S. A state-of-the-art review: Solar trackers. In Proceedings of the 2022 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences, ASET 2022, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 21–24 February 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amayreh, M.I.; Alahmer, A. On improving the efficiency of hybrid solar lighting and thermal system using dual-axis solar tracking system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsengiyumva, W.; Chen, S.G.; Hu, L.; Chen, X. Recent advancements and challenges in Solar Tracking Systems (STS): A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 250–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Wang, H.-C.; Chang, H.-Y. Dual-axis solar tracker with satellite compass and inclinometer for automatic positioning and tracking. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2022, 66, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.N.; Francisco, G.R.; Montezuma, M.A.; Sampaio, L.P.; Acho, L. Low-cost dual-axis solar tracker with photovoltaic energy processing for education. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazezkhan, G.; Xiang, B.; Wang, N.; Yusup, A. Dynamic modeling of the Stewart platform for the NanShan Radio Telescope. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2020, 12, 1687814020940072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, G.; Jones, T. Position analysis of a two DOF parallel mechanism—the Canterbury tracker. Mech. Mach. Theory 1999, 34, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Xu, Y.; Yao, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Design and analysis of a scissors double-ring truss deployable mechanism for space antennas. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 105357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Practical Wind-Disturbance Rejection for Large Deep Space Observatory Antenna. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itul, T.; Pisla, D. Dynamics of a 3-DOF parallel mechanism used for orientation applications. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics, AQTR 2008-THETA 16th Edition-Proceedings, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 22–25 May 2008; Volume 2, pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qi, Y.; Dong, G.; Sun, T. Type synthesis of 2-DoF rotational parallel mechanisms actuating the inter-satellite link antenna. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2016, 29, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Shao, L.; Fu, L.; Han, X.; Li, S. Kinematic analysis and optimal design of a novel parallel pointing mechanism. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Ma, Z.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Design and optimization of solar tracker with U-PRU-PUS parallel mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 155, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yao, J.; Dong, Z. Neuroadaptive learning algorithm for constrained nonlinear systems with disturbance rejection. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2022, 32, 6127–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadavari, H.; Aghaei, V.T.; Ikizoglu, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning based Control of Stewart Platform with Parametric Simulation in ROS and Gazebo. J. Mech. Robot. 2023, 15, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furqan, M.; Suhaib, M.; Ahmad, N. Studies on Stewart platform manipulator: A review. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 4459–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Lee, S.; Joo, S.; Seo, J. Denavit-Hartenberg Notation-Based Kinematic Constraint Equations for Forward Kinematics of the 3–6 Stewart Platform. J. Mech. Robot. 2022, 14, 054505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D. A Platform with Six Degrees of Freedom. In Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London, UK, 1 June 1965; Volume 180, pp. 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.K.S.; Vundavilli, P.R. Forward Kinematics of the Stewart Parallel Manipulator Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Comput. Methods 2022, 19, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xu, W.; Yu, B.; Ding, F.; Cheng, L.; Huang, J. A Novel Hybrid Algorithm for the Forward Kinematics Problem of 6 DOF Based on Neural Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Su, J.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H.; Xu, G. Efficient hybrid method for forward kinematics analysis of parallel robots based on signal decomposition and reconstruction. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017699094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navvabi, H.; Markazi, A.H. Hybrid position/force control of Stewart Manipulator using Extended Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding Mode Controller (E-AFSMC). ISA Trans. 2018, 88, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; She, J.; Wang, F.; Iwasaki, M. Disturbance Rejection for Stewart Platform Based on Integration of Equivalent-Input-Disturbance and Sliding-Mode Control Methods. In IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, D.; Beckman, W.; Duffie, J. Evaluation of hourly tilted surface radiation models. Sol. Energy 1990, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, P.; Georgiev, A.; Boudinov, H. Cheap two axis sun following device. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, C.; Yao, J. Dynamic Decoupling Based Robust Synchronous Control for a Hydraulic Parallel Manipulator. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 30548–30562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B. Creating a Stewart Platform Model Using SimMechanics—MATLAB & Simulink. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/company/newsletters/articles/creating-a-stewart-platform-model-using-simmechanics.html (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Poulek, V.; Libra, M. New solar tracker. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1998, 51, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Dai, S.; Liu, H. Wind loading characteristics and roof zoning of solar arrays mounted on flat-roofed tall buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawashdeh, H.; Stathopoulos, T. Wind loads on solar panels mounted on flat roofs: Effect of geometric scale. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 206, 104339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H. Calculation of Wind Load on Photovoltaic Panel of Solar Power Plant. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Power and Renewable Energy, ICPRE 2020, Shanghai, China, 12–14 September 2020; pp. 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Engin, M. Controller Design for Parallel Mechanism Solar Tracker. Machines 2023, 11, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030372
Engin M. Controller Design for Parallel Mechanism Solar Tracker. Machines. 2023; 11(3):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030372
Chicago/Turabian StyleEngin, Mustafa. 2023. "Controller Design for Parallel Mechanism Solar Tracker" Machines 11, no. 3: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030372
APA StyleEngin, M. (2023). Controller Design for Parallel Mechanism Solar Tracker. Machines, 11(3), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11030372





