Active Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot Based on Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Adjustment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mechanical Design and Sensor Systems for of Lebot
2.2. Active Training Based on Fixed Parameters of SDM
2.2.1. Virtual Spring-Damping Model
- (1)
- . The solution of the characteristic equation is a pair of imaginary conjugate roots. The system is underdamped.
- (2)
- . The roots of the characteristic equation are a pair of real weight roots and the damping of the system is in the form of critical damping.
- (3)
- . The roots of the characteristic equation are mutually exclusive real roots and the damping of the system is in an overdamped state.
- (4)
- . The number of roots of the characteristic equation is greater than 0. The system is unstable.
2.2.2. Research on Trajectory Tracking Disturbance Suppression Method Based on SMC
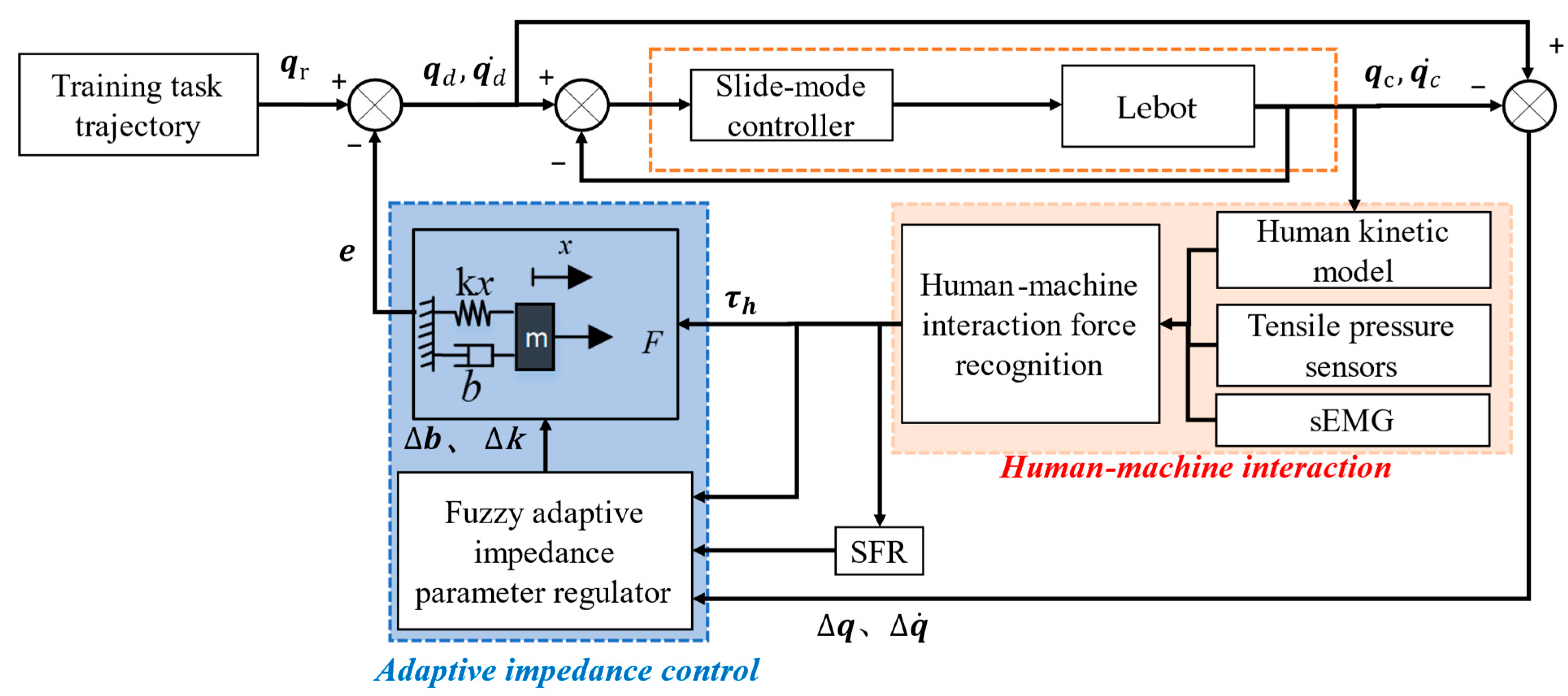
2.3. Active Training by Adding a Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Parameter Regulator
- (1)
- Design of fuzzy variable stiffness adaptive regulator
- (2)
- Design of fuzzy variable damping adaptive regulator
3. Results
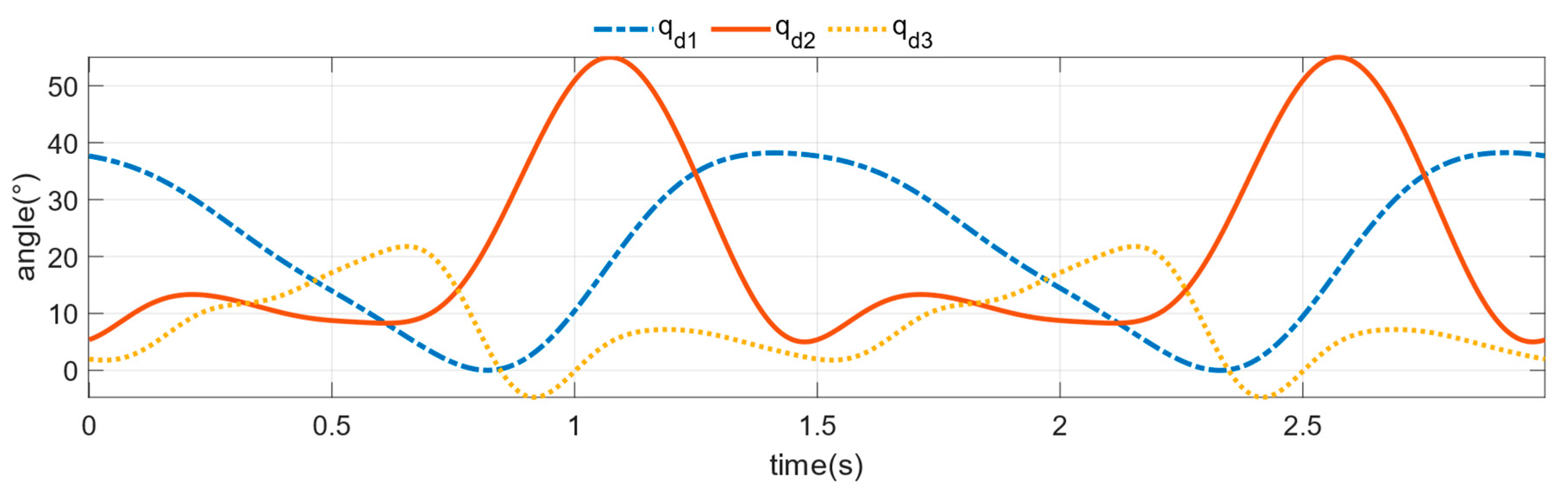
3.1. Simulation Verification Experiments
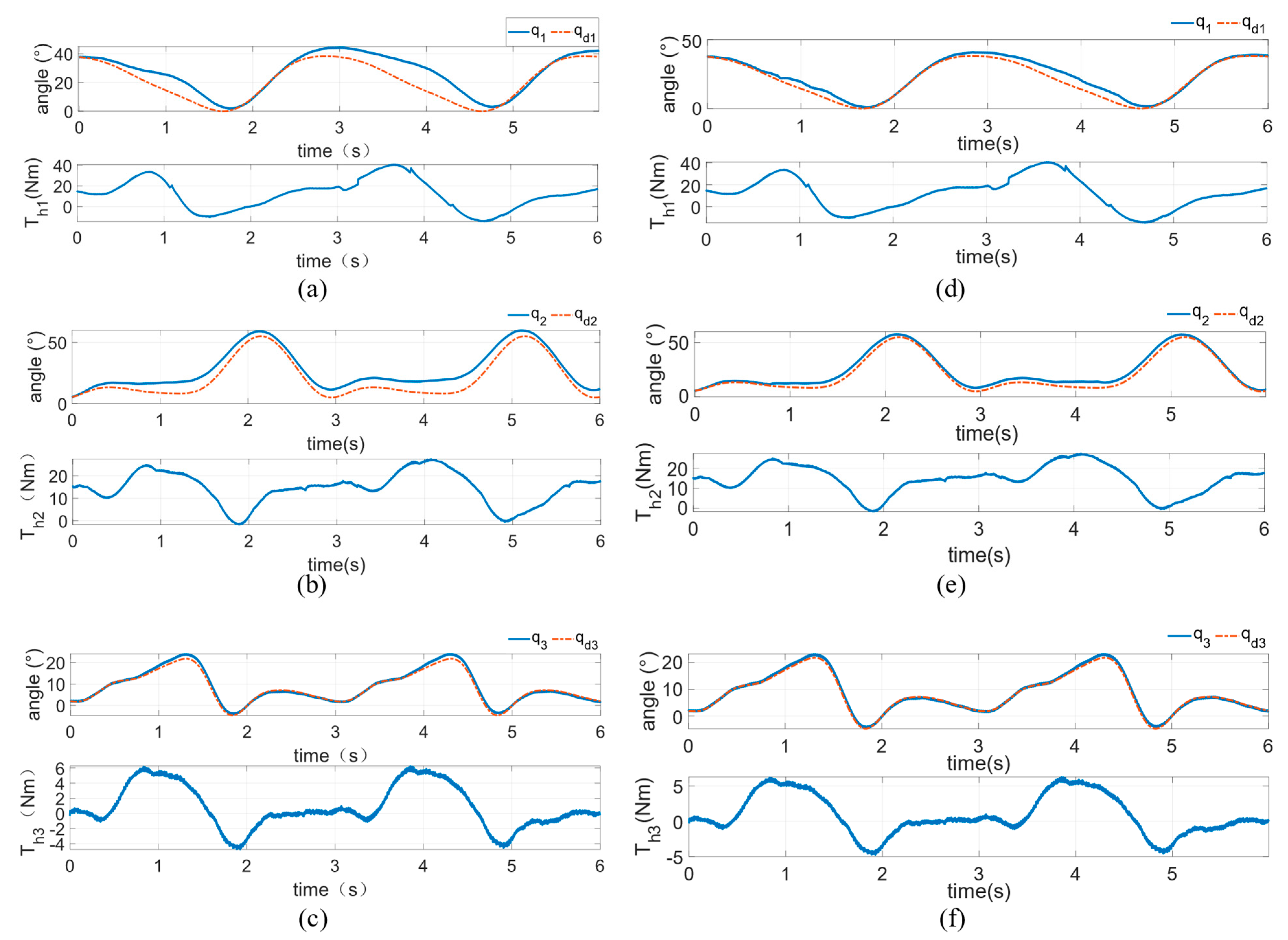
3.2. Actual Verification Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soltani Sharif Abadi, A.; Alinaghi Hosseinabadi, P.; Hameed, A.; Ordys, A.; Pierscionek, B. Fixed-Time Observer-Based Controller for the Human–Robot Collaboration with Interaction Force Estimation. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Chen, T.; Zhu, H.; Fu, M.; Xu, J. Fuzzy Variable Impedance-Based Adaptive Neural Network Control in Physical Human–Robot Interaction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2023, 237, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Cao, J.; Xie, S. Reviewing High-Level Control Techniques on Robot-Assisted Upper-Limb Rehabilitation. Adv. Robot. 2018, 32, 1253–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X. A Review on Lower Limb Rehabilitation Exoskeleton Robots. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Ju, L.; Ding, X. Human-Centred Adaptive Control of Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot Based on Human–Robot Interaction Dynamic Model. Mech. Mach. Theory 2021, 162, 104340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadiyadkuri, F.; Popal, A.M.; Paiwand, S.S.; Zhang, X. Interaction Dynamics Modeling and Adaptive Impedance Control of Robotic Exoskeleton for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Song, Q.; Yin, C.; Cao, D. Adaptive Impedance Control Method for Dynamic Contact Force Tracking of Robotic Excavators. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2022, 148, 04022124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, J.; Moghaddam, M.M. Nonlinear Time Delay Estimation Based Model Reference Adaptive Impedance Control for an Upper-Limb Human-Robot Interaction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2022, 236, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, A. Human-Robot Interaction in Rehabilitation and Assistance: A Review. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harandi, M.R.J. Comments on “Novel Adaptive Impedance Control for Exoskeleton Robot for Rehabilitation Using a Nonlinear Time-Delay Disturbance Observer”. ISA Trans. 2022, 136, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Su, C.-Y. Adaptive Impedance Control of Robotic Exoskeletons Using Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), Macau, China, 18–20 August 2016; pp. 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, W.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y.; Kong, K. Active Impedance Control of a Lower Limb Exoskeleton to Assist Sit-to-Stand Movement. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3530–3536. [Google Scholar]
- Jamwal, P.K.; Hussain, S.; Ghayesh, M.H.; Rogozina, S.V. Impedance Control of an Intrinsically Compliant Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3638–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.; van Asseldonk, E.H.; van der Kooij, H. Selective Control of Gait Subtasks in Robotic Gait Training: Foot Clearance Support in Stroke Survivors with a Powered Exoskeleton. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2013, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YFeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Vladareanu, L. Research on Safety and Compliance of a New Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1523068. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yu, H. Intelligent Parametric Adaptive Hybrid Active–Passive Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot. Machines 2022, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Yu, H. Spring Damping Based Control for a Novel Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot with Active Flexible Training Planning. Technol. Healthc. Care 2022, 31, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ai, Q.; Sheng, B.; Xie, S. Recent Development of Mechanisms and Control Strategies for Robot-Assisted Lower Limb Rehabilitation. Mechatronics 2015, 31, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Su, H.; Li, Z.; Ao, D.; Song, R. Adaptive Control with a Fuzzy Tuner for Cable-Based Rehabilitation Robot. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2016, 14, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlivan, A.U.; Losey, D.P.; O’Malley, M.K. Minimal Assist-as-Needed Controller for Upper Limb Robotic Rehabilitation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 32, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

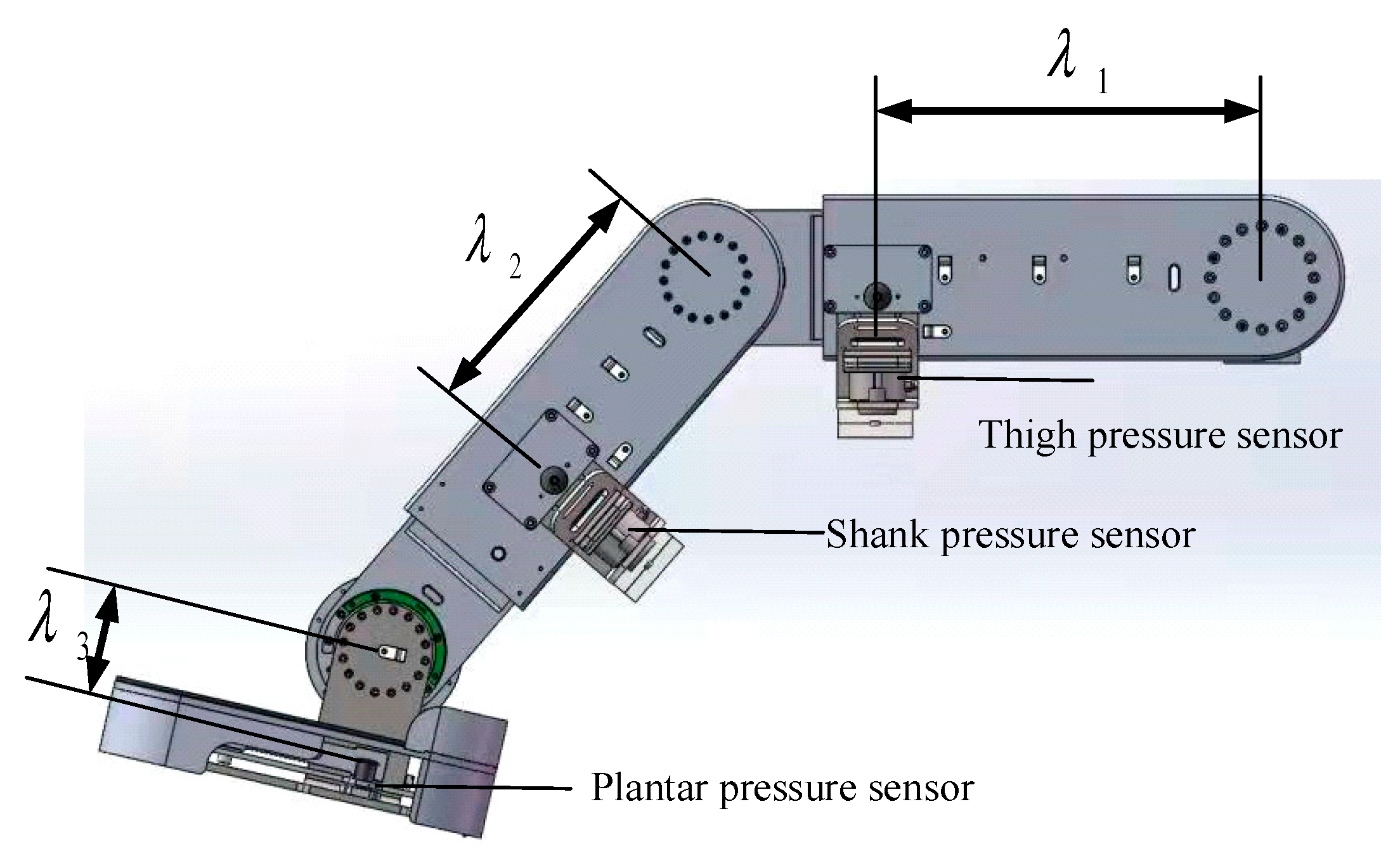





| Lower Limb Segments | Length | Center of Mass Position | Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper trunk | L0 = 0.470H | R0 = 0.264H | M0 = 0.607M |
| Thighs | L1 = 0.245H | R1 = 0.106H | M1 = 0.107M |
| Calf | L2 = 0.246H | R2 = 0.107H | M2 = 0.046M |
| Foot | L3 = 0.074H | R3 = 0.018H | M3 = 0.016M |
| NB | NS | ZO | PS | PB | |
| NB | NB | NS | NS | ZO | ZO |
| NS | NS | NS | ZO | ZO | PS |
| ZO | NS | ZO | ZO | ZO | PS |
| PS | ZO | ZO | ZO | PS | PB |
| PB | ZO | ZO | ZO | PB | PB |
| NB | NS | ZO | PS | PB | |
| NB | NB | NS | NS | ZO | ZO |
| NS | NS | NS | ZO | ZO | PS |
| ZO | NS | ZO | ZO | ZO | PS |
| PS | ZO | ZO | ZO | PS | PB |
| PB | ZO | ZO | ZO | PB | PB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Yu, H. Active Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot Based on Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Adjustment. Machines 2023, 11, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050565
Hu J, Zhuang Y, Meng Q, Yu H. Active Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot Based on Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Adjustment. Machines. 2023; 11(5):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050565
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jie, Yuantao Zhuang, Qiaoling Meng, and Hongliu Yu. 2023. "Active Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot Based on Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Adjustment" Machines 11, no. 5: 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050565
APA StyleHu, J., Zhuang, Y., Meng, Q., & Yu, H. (2023). Active Training Control Method for Rehabilitation Robot Based on Fuzzy Adaptive Impedance Adjustment. Machines, 11(5), 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines11050565






