Efficacy of Incremental Next-Generation ALK Inhibitor Treatment in Oncogene-Addicted, ALK-Positive, TP53-Mutant NSCLC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
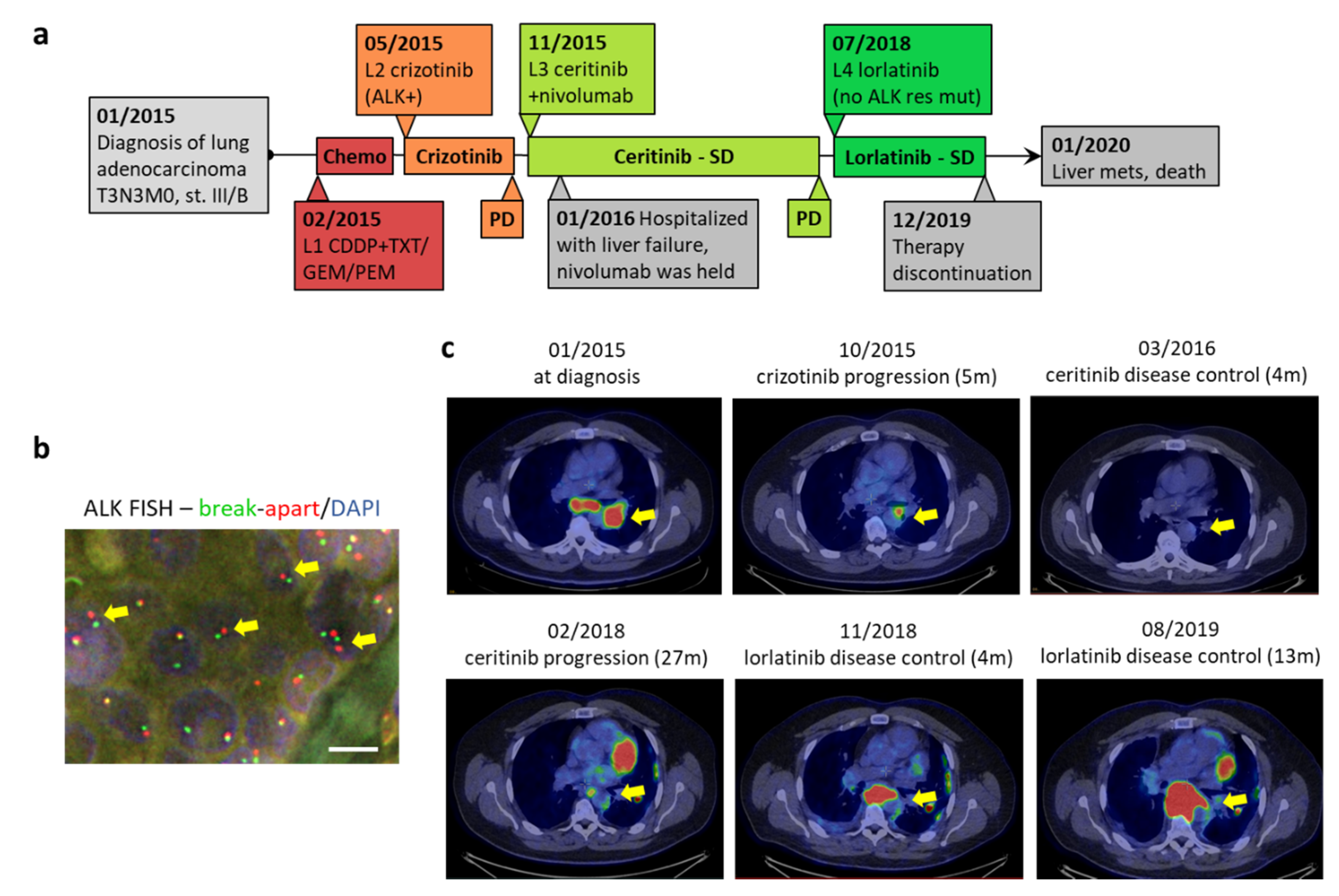
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statement
References
- Carpenter, E.L.; Mossé, Y.P. Targeting ALK in neuroblastoma-preclinical and clinical advancements. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, P. ALK in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) pathobiology, epidemiology, detection from tumor tissue and algorithm diagnosis in a daily practice. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christopoulos, P.; Budczies, J.; Kirchner, M.; Dietz, S.; Sültmann, H.; Thomas, M.; Stenzinger, A. Defining molecular risk in ALK + NSCLC. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 3093–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, B.J.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; Tang, Y.; et al. Final Overall Survival Analysis From a Study Comparing First-Line Crizotinib Versus Chemotherapy in ALK-Mutation-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iams, W.T.; Lovly, C.M. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase as a therapeutic target in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer J. (U. S.) 2015, 21, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soria, J.-C.; Tan, D.S.W.; Chiari, R.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L.; Wolf, J.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Cortinovis, D.; Yu, C.-J.; et al. First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced ALK -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.W.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; Riely, G.J.; et al. Activity and safety of ceritinib in patients with ALK -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-1): Updated results from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Gong, W. Lorlatinib for the treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Besse, B.; Bauer, T.M.; Felip, E.; Soo, R.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Chiari, R.; Bearz, A.; Lin, C.-C.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a global phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1654–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Crizotinib resistance: Implications for therapeutic strategies. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, iii42–iii50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patienten, S.; Therapie, N. PAKT Inhibitor May Promote Better Responses to Abiraterone in mCRPC. Onclive 2020, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, W.; Ying, J.; Gao, S. Concomitant TP53 mutations with response to crizotinib treatment in patients with ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blandino, G.; Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. Mutant p53 gain of function: Differential effects of different p53 mutants on resistance of cultured cells to chemotherapy. Oncogene 1999, 18, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, F.-L.; Lai, M.-D. Various forms of mutant p53 confer sensitivity to cisplatin and doxorubicin in bladder cancer cells. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kron, A.; Alidousty, C.; Scheffler, M.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Seidel, D.; Riedel, R.; Ihle, M.A.; Michels, S.; Nogova, L.; Fassunke, J.; et al. Impact of TP53 mutation status on systemic treatment outcome in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.I.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Kulig, K.; Boland, J.M.; Erickson-Johnson, M.R.; Oliveira, A.M.; Wampfler, J.; Jatoi, A.; Deschamps, C.; Marks, R.; Fortner, C.; et al. Worse disease-free survival in never-smokers with ALK+ lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rothenstein, J.M.; Chooback, N. ALK inhibitors, resistance development, clinical trials. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S59–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco, J.M.; Gao, D.; Smith, D.; Purcell, T.; Hancock, M.; Bunn, P.; Robin, T.; Liu, A.; Karam, S.; Gaspar, L.; et al. Natural History and Factors Associated with Overall Survival in Stage IV ALK-Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, S.; Arnould, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Coudert, B.; Fumoleau, P.; Boidot, R. Next-generation sequencing analysis of lung and colon carcinomas reveals a variety of genetic alterations. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glubb, D.M.; Cerri, E.; Giese, A.; Zhang, W.; Mirza, O.; Thompson, E.E.; Chen, P.; Das, S.; Jassem, J.; Rzyman, W.; et al. Novel functional germline variants in the VEGF receptor 2 gene and their effect on gene expression and microvessel density in lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5257–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Gaur, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y.C.; Li, H.; Hu, S.; Weng, Y.; Yen, Y. Mutants TP53 p.R273H and p.R273C but not p.R273G Enhance Cancer Cell Malignancy. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachova, P.; Thiel, K.W.; Leslie, K.K. The consequence of oncomorphic TP53 mutations in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19257–19275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Hollstein, M.; Xu, Y. p53 gain-of-function cancer mutants induce genetic instability by inactivating ATM. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.P.; Song, H.; Xu, Y. A common gain of function of p53 cancer mutants in inducing genetic instability. Oncogene 2010, 29, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbán, L.; Dóczi, R.; Vodicska, B.; Kormos, D.; Tóth, L.; Takács, I.; Várkondi, E.; Tihanyi, D.; Lakatos, D.; Dirner, A.; et al. Efficacy of Incremental Next-Generation ALK Inhibitor Treatment in Oncogene-Addicted, ALK-Positive, TP53-Mutant NSCLC. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030107
Urbán L, Dóczi R, Vodicska B, Kormos D, Tóth L, Takács I, Várkondi E, Tihanyi D, Lakatos D, Dirner A, et al. Efficacy of Incremental Next-Generation ALK Inhibitor Treatment in Oncogene-Addicted, ALK-Positive, TP53-Mutant NSCLC. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030107
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbán, László, Róbert Dóczi, Barbara Vodicska, Dóra Kormos, László Tóth, István Takács, Edit Várkondi, Dóra Tihanyi, Dóra Lakatos, Anna Dirner, and et al. 2020. "Efficacy of Incremental Next-Generation ALK Inhibitor Treatment in Oncogene-Addicted, ALK-Positive, TP53-Mutant NSCLC" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030107
APA StyleUrbán, L., Dóczi, R., Vodicska, B., Kormos, D., Tóth, L., Takács, I., Várkondi, E., Tihanyi, D., Lakatos, D., Dirner, A., Vályi-Nagy, I., & Peták, I. (2020). Efficacy of Incremental Next-Generation ALK Inhibitor Treatment in Oncogene-Addicted, ALK-Positive, TP53-Mutant NSCLC. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10030107



