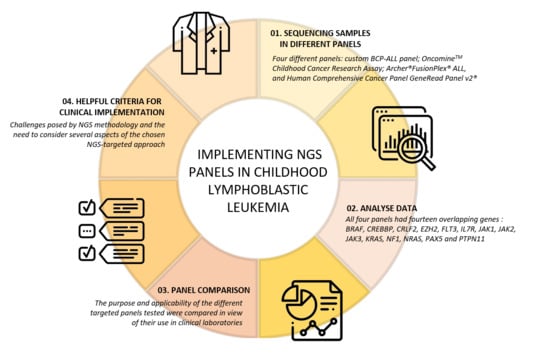
Helpful Criteria When Implementing NGS Panels in Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Issues
2.2. Design of the Study
2.3. NGS-Targeted Panels Included in the Study
2.3.1. BCP-ALL Custom Panel
2.3.2. Archer® FusionPlex® ALL Kit
2.3.3. OncomineTM Childhood Cancer Research Assay (OCCRA)
2.3.4. Human Comprehensive Cancer GeneRead Panel v2®
2.4. Sequencing and Variant Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dissection of the NGS Panels
3.1.1. BCP-ALL Custom Panel
3.1.2. Archer® FusionPlex® ALL Kit
3.1.3. OncomineTM Childhood Cancer Research Assay (OCCRA)
3.1.4. Human Comprehensive Cancer GeneRead Panel v2®
3.2. Panel Dissection
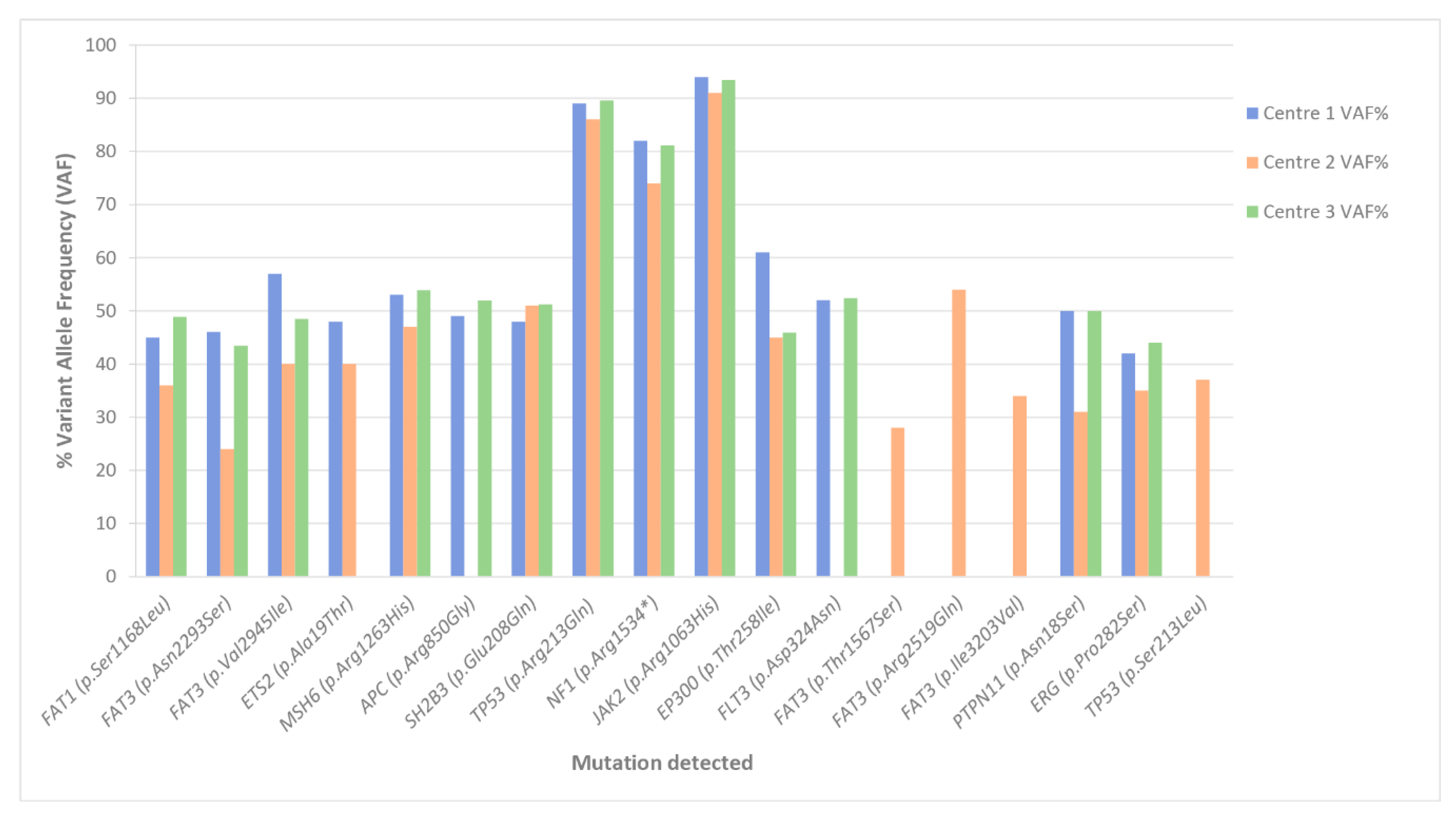
3.2.1. SNV Detection
3.2.2. CNV Detection
3.2.3. RNA Fusion Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Panel Discussion
4.2. Implementing NGS in Pediatric BCP-ALL
4.2.1. The Panel Choice
4.2.2. Technical Challenges of Each Analyzed Panel for BCP-ALL Diagnosis
4.2.3. Data Analysis for Variant Detection
4.2.4. Variant Prioritization and Reporting
5. Conclusions: Lessons Learned and the Future Ahead
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunger, S.P.; Mullighan, C.G. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pui, C.-H.; Yang, J.J.; Hunger, S.P.; Pieters, R.; Schrappe, M.; Biondi, A.; Vora, A.; Baruchel, A.; Silverman, L.B.; Schmiegelow, K.; et al. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: Progress Through Collaboration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2938–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, M. A causal mechanism for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.-H.; Gaynon, P.S.; Boyett, J.M.; Chessells, J.M.; Baruchel, A.; Kamps, W.; Silverman, L.B.; Biondi, A.; Harms, D.O.; Vilmer, E.; et al. Outcome of treatment in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with rearrangements of the 11q23 chromosomal region. Lancet 2002, 359, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Rossi, S.; Foschi, R.; Trama, A.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Pastore, G.; Peris-Bonet, R.; Stiller, C.; Capocaccia, R. Survival and cure trends for European children, adolescents and young adults diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from 1982 to 2002. Haematologica 2013, 98, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, K.; Catherwood, M.A.; Dobbin, E.; Sproul, A.; Langabeer, S.E.; Mills, K.I. Inter-Laboratory Evaluation of a Next-Generation Sequencing Panel for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burghel, G.J.; Hurst, C.D.; Watson, C.M.; Chambers, P.A.; Dickinson, H.; Roberts, P.; Knowles, M.A. Towards a Next-Generation Sequencing Diagnostic Service for Tumour Genotyping: A Comparison of Panels and Platforms. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 478017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathology, M.; Area, H.; Service, P.; Dna, N.; Meldrum, C.; Doyle, M.A.; Tothill, R.W. Next-Generation Sequencing for Cancer Diagnostics: A Practical Perspective. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2011, 32, 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bastida, J.M.; Lozano, M.L.; Benito, R.; Janusz, K.; Palma-Barqueros, V.; Del Rey, M.; Hernández-Sánchez, J.M.; Riesco, S.; Bermejo, N.; González-García, H.; et al. Introducing high-throughput sequencing into mainstream genetic diagnosis practice in inherited platelet disorders. Haematologica 2018, 103, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoppers, B.M.; Nguyen, M.T.; Sénécal, K.; Tassé, A.M.; Zawati, M.H. Next-generation sequencing and the return of results. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Churchman, M.L.; Roberts, K.G.; Moore, I.; Zhou, X.; Nakitandwe, J.; Hagiwara, K.; Pelletier, S.; Gingras, S.; Berns, H.; et al. PAX5-driven subtypes of B-progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, C.; Harrison, C.J. Advances in B-cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Genomics. HemaSphere 2018, 2, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilljebjörn, H.; Fioretos, T. New oncogenic subtypes in pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, U.; Shumilov, E.; Flach, J.; Porret, N.; Joncourt, R.; Wiedemann, G.; Fiedler, M.; Novak, U.; Amstutz, U.; Pabst, T. Challenges in the introduction of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for diagnostics of myeloid malignancies into clinical routine use. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sujobert, P.; Le Bris, Y.; de Leval, L.; Gros, A.; Merlio, J.P.; Pastoret, C.; Huet, S.; Sarkozy, C.; Davi, F.; Callanan, M.; et al. The Need for a Consensus Next-generation Sequencing Panel for Mature Lymphoid Malignancies. HemaSphere 2019, 3, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, D.J.; Humburg, P.; Kanapin, A.; Rivas, M.A.; Gaulton, K.; Cazier, J.-B.; Donnelly, P. Choice of transcripts and software has a large effect on variant annotation. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leng, W.W.J.; Gadellaa-Van Hooijdonk, C.G.; Barendregt-Smouter, F.A.S.; Koudijs, M.J.; Nijman, I.; Hinrichs, J.W.J.; Cuppen, E.; Van Lieshout, S.; Loberg, R.D.; De Jonge, M.; et al. Targeted next generation sequencing as a reliable diagnostic assay for the detection of somatic mutations in tumours using minimal DNA amounts from formalin fixed paraffin embedded material. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, G.; Baux, D.; Faugère, V.; Moclyn, M.; Koenig, M.; Claustres, M.; Roux, A.F. Assessment of the latest NGS enrichment capture methods in clinical context. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alonso, C.M.; Llop, M.; Sargas, C.; Pedrola, L.; Panadero, J.; Hervás, D.; Cervera, J.; Such, E.; Ibáñez, M.; Ayala, R.; et al. Clinical Utility of a Next-Generation Sequencing Panel for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Diagnostics. J. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 21, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Press, R.D.; Eickelberg, G.; Froman, A.; Yang, F.; Stentz, A.; Flatley, E.M.; Fan, G.; Lim, J.Y.; Meyers, G.; Maziarz, R.T.; et al. NGS-Defined Minimal Residual Disease Before Stem Cell Transplantation Predicts Acute Myeloid Leukemia Relapse. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotrova, M.; Trka, J.; Kneba, M.; Brüggemann, M. Is Next-Generation Sequencing the way to go for Residual Disease Monitoring in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia? Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 21, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Liu, W.-J. Application of minimal residual disease monitoring in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 6885–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, L.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Corless, C.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Lubin, I.M.; Pfeifer, J.; Temple-Smolkin, R.L.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Nikiforova, M.N. Guidelines for Validation of Next-Generation Sequencing–Based Oncology Panels: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vega-Garcia, N.; Benito, R.; Esperanza-Cebollada, E.; Llop, M.; Robledo, C.; Vicente-Garcés, C.; Alonso, J.; Barragán, E.; Fernández, G.; Hernández-Sánchez, J.M.; et al. Helpful Criteria When Implementing NGS Panels in Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040244
Vega-Garcia N, Benito R, Esperanza-Cebollada E, Llop M, Robledo C, Vicente-Garcés C, Alonso J, Barragán E, Fernández G, Hernández-Sánchez JM, et al. Helpful Criteria When Implementing NGS Panels in Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040244
Chicago/Turabian StyleVega-Garcia, Nerea, Rocío Benito, Elena Esperanza-Cebollada, Marta Llop, Cristina Robledo, Clara Vicente-Garcés, Javier Alonso, Eva Barragán, Guerau Fernández, Jesús M. Hernández-Sánchez, and et al. 2020. "Helpful Criteria When Implementing NGS Panels in Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040244
APA StyleVega-Garcia, N., Benito, R., Esperanza-Cebollada, E., Llop, M., Robledo, C., Vicente-Garcés, C., Alonso, J., Barragán, E., Fernández, G., Hernández-Sánchez, J. M., Martín-Izquierdo, M., Maynou, J., Minguela, A., Montaño, A., Ortega, M., Torrebadell, M., Cervera, J., Sánchez, J., Jiménez-Velasco, A., ... on behalf of the Group of Leukemia of the Spanish Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (SEHOP). (2020). Helpful Criteria When Implementing NGS Panels in Childhood Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040244