Genomic Portrait of a Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Case in a Large Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The SCA1 Family with a Member Affected by ALS
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing and Data Processing
2.4. Variant Prioritization and Assessment of Pathogenicity
2.5. NeuroArray aCGH Processing and Data Analysis
2.6. CNV Validation
2.7. Functional Enrichment Analysis of the CNV-Associated Gene Sets
2.8. Genomic Scale Profiling of ALS by Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.9. Visualization of the Protein–Protein Interaction Network
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Potentially Disease-Causing Sequence Variants in ALS Associated Genes
3.2. Identification of Copy Number Variants Related to ALS Phenotype
3.3. Functional and Pathway Enrichment Analysis of CNV-Driven Genes Identified Disease-Specific Molecular Signatures
3.4. WES-Based Mutation Profile Confirms the Functional Impact of Axon Guidance, Cell Adhesion and Immune Response in ALS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ATXN-1 | ataxin-1 |
| ATXN-2 | ataxin-2 |
| ATXN-3 | Ataxin 3 |
| ATXN7 | Ataxin 7 |
| ATXN2L | Ataxin 2 Like |
| SCA1 | spinocerebellar ataxia type I |
| SCA2 | spinocerebellar ataxia type II |
| aCGH | comparative genomic hybridization array |
| WES | whole-exome sequencing |
| NGS | next-generation sequencing |
| SOD1 | Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase-1 |
| FUS | fused in sarcoma/translocated in liposarcoma |
| TARDBP/TDP-43 | transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa |
| C9ORF72 | chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 |
| ANG | Angiogenin |
| SNV | single-nucleotide variant |
| CNV | copy number variant |
| MN | motor neuron |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| MUPs | motor unit potentials |
| PSWs | positive sharp waves |
| DSF | disease-free survival |
| Cy5 | cyanine 5 |
| Cy3 | cyanine 3 |
| dUTP | deoxyuridine triphosphate |
| ADM-2 | aberration detection method II algorithm |
| FDR | Flase Discovery Rate |
| CNVD | Copy Number Variation in Disease |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics |
| DGV | Database of Genomic Variants |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| ncRNA | non coding RNA |
| LoF | loss-of-function |
| MAF | minor allele frequency |
| EVS | Exome Variant Server |
| HGMD | Human Gene Mutation Database |
| LOVD | Leiden Open Variation Database |
| OMIM | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| BP | biological process |
| MF | molecular function |
| CC | Cellular Component |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| SCN1A | sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 1 |
| WRN | Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase |
| LPA | Lipoprotein(A) |
| SCN7A | sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 7 |
| EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 |
| EPHA1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 |
| EPHA2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 |
| EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 |
| EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 |
| EPHA6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 |
| EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 |
| EPHX1 | Epoxide Hydrolase 1 |
| CHMP2B | Charged Multivesicular Body Protein 2B |
| MAPT | Microtubule Associated Protein Tau |
| VPS54 | Vacuolar Protein Sorting-Associated Protein 54 |
| TTN | Titin |
| AHR | Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor |
| NSF | N-Ethylmaleimide Sensitive Factor, Vesicle Fusing ATPase |
| ARL13B | ADP Ribosylation Factor Like GTPase 13B |
| MNVs | Multiple nucleotide variants |
| INDEL | Insertion/Deletion |
| CAPN2 | Calpain 2 |
| DCC | DCC netrin 1 receptor |
| LRRK1 | Leucine Rich Repeat Kinase 1 |
| MMRN1 | Multimerin 1 |
| NOS2 | Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 |
| ARSB | Arylsulfatase B |
| TMEM216 | Transmembrane Protein 216 |
| LRP2 | LDL Receptor Related Protein 2 |
| NOTCH4 | Notch Receptor 4 |
| PCK1 | Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase 1 |
| TNK1 | Tyrosine Kinase Non Receptor 1 |
| CNTN4 | Contactin 4 |
| DIAPH3 | Diaphanous Related Formin 3 |
| CDH13 | Cadherin 13 |
| DYNC1H1 | Dynein Cytoplasmic 1 Heavy Chain 1; |
| CPZ | Carboxypeptidase Z |
| NEFH | Neurofilament Heavy |
| TRPM7 | Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily M Member 7 |
| VPS26A | Vacuolar Protein Sorting-Associated Protein 26, Retromer Complex Component A |
| KIF1A | Kinesin Family Member 1A |
| CYP2D6 | Cytochrome P450 Family 2 Subfamily D Member 6 |
| GLE1 | GLE1 RNA Export Mediator |
| SETX | Senataxin |
| TAF15 | TATA-Box Binding Protein Associated Factor 15 |
| ALS2 | Alsin Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor ALS2 |
| CCNF | Cyclin F |
| PFN1 | Profilin 1 |
| CEP112 | Centrosomal Protein 112 |
| VAPB | Vesicle-Associated Membrane Protein Associated Protein B and C |
| AVS | ALS variant server |
| DPYD | Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase |
| SNARE | soluble NSF attachment protein receptor |
| MATR3 | Matrin 3 |
| ERBB4 | Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4 |
| NEK1 | NIMA Related Kinase 1 |
| OPTN | Optineurin |
| SQSTM1 | Sequestosome 1 |
| TBK1 | TANK Binding Kinase 1 |
| TUBA4A | Tubulin Alpha 4a |
| VCP | Valosin Containing Protein |
| VEGFA | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A |
| RPS27A | Ribosomal Protein S27a |
| UBA52 | Ubiquitin A-52 Residue Ribosomal Protein Fusion Product 1 |
| UBC | Ubiquitin C |
| UBB | Ubiquitin B |
| ANO2 | Anoctamin 2 |
| CHCHD10 | Coiled-Coil-Helix-Coiled-Coil-Helix Domain Containing 10 |
| ELAVL4 | Embryonic Lethal, Abnormal Vision, Drosophila (ELAV)-Like 4 |
| GRIN1 | Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor NMDA Type Subunit 1 |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| ZNF280A | Zinc Finger Protein 280A |
| C22orf46 | Chromosome 22 Open Reading Frame 46 |
| APEH | Acylaminoacyl-Peptide Hydrolase |
| MST1 | Macrophage Stimulating 1 |
| DCHS2 | Dachsous Cadherin-Related 2 |
| FAT1 | FAT Atypical Cadherin 1 |
| BACE1 | Beta-Secretase 1 |
References
- Mathis, S.; Goizet, C.; Soulages, A.; Vallat, J.-M.; Masson, G.L. Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 399, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, A.E.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Andersen, P.M.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kubisch, C. Current knowledge and recent insights into the genetic basis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Medizinische Genetik 2018, 30, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renton, A.E.; Chiò, A.; Traynor, B.J. State of play in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis genetics. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatelli, M.; Marangi, G.; Conte, A.; Tasca, G.; Zollino, M.; Lattante, S. New ALS-Related Genes Expand the Spectrum Paradigm of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.F.; Ferrucci, L.; Singleton, A.B.; Tienari, P.J.; Laaksovirta, H.; Restagno, G.; Chio, A.; Traynor, B.J.; Nalls, M.A. Genome-wide analysis of the heritability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, S.B.; Downie, J.M.; Tsetsou, S.; Feusier, J.E.; Figueroa, K.P.; Bromberg, M.B.; Jorde, L.B.; Pulst, S.M. The evolving genetic risk for sporadic ALS. Neurology 2017, 89, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, S.; Battke, F.; Sprecher, A.; Munz, M.; Synofzik, M.; Schöls, L.; Gasser, T.; Grehl, T.; Prudlo, J.; Biskup, S. Rare Variants in Neurodegeneration Associated Genes Revealed by Targeted Panel Sequencing in a German ALS Cohort. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conforti, F.L.; Spataro, R.; Sproviero, W.; Mazzei, R.; Cavalcanti, F.; Condino, F.; Simone, I.L.; Logroscino, G.; Patitucci, A.; Magariello, A.; et al. Ataxin-1 and ataxin-2 intermediate-length PolyQ expansions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2012, 79, 2315–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüb, U.; Bürk, K.; Timmann, D.; den Dunnen, W.; Seidel, K.; Farrag, K.; Brunt, E.; Heinsen, H.; Egensperger, R.; Bornemann, A.; et al. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1): New pathoanatomical and clinico-pathological insights. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2012, 38, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spataro, R.; La Bella, V. A case of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with intermediate ATXN-1 CAG repeat expansion in a large family with spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1442–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungaro, C.; Citrigno, L.; Trojsi, F.; Sprovieri, T.; Gentile, G.; Muglia, M.; Monsurro, M.R.; Tedeschi, G.; Cavallaro, S.; Conforti, F.S. ALS and CHARGE syndrome: A clinical and genetic study. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 118, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- La Cognata, V.; Morello, G.; Gentile, G.; Cavalcanti, F.; Cittadella, R.; Conforti, F.L.; De Marco, E.V.; Magariello, A.; Muglia, M.; Patitucci, A.; et al. NeuroArray: A Customized aCGH for the Analysis of Copy Number Variations in Neurological Disorders. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cognata, V.; Morello, G.; Gentile, G.; D’Agata, V.; Criscuolo, C.; Cavalcanti, F.; Cavallaro, S. A customized high-resolution array-comparative genomic hybridization to explore copy number variations in Parkinson’s disease. Neurogenetics 2016, 17, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Serra, H.G.; Zoghbi, H.Y.; Orr, H.T. The spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 protein, ataxin-1, has RNA-binding activity that is inversely affected by the length of its polyglutamine tract. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravanidis, S.; Kattan, F.G.; Doxakis, E. Unraveling the pathways to neuronal homeostasis and disease: Mechanistic insights into the role of RNA-binding proteins and associated factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Therrien, M.; Rouleau, G.A.; Dion, P.A.; Parker, J.A. Deletion of C9ORF72 Results in Motor Neuron Degeneration and Stress Sensitivity in C. elegans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babić Leko, M.; Župunski, V.; Kirincich, J.; Smilović, D.; Hortobágyi, T.; Hof, P.R.; Šimić, G. Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration Related to C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion. Behav. Neurol. 2019, 2019, 2909168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellier, C.; Campanari, M.; Julie Corbier, C.; Gaucherot, A.; Kolb-Cheynel, I.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Ruffenach, F.; Page, A.; Ciura, S.; Kabashi, E.; et al. Loss of C9ORF72 impairs autophagy and synergizes with polyQ Ataxin-2 to induce motor neuron dysfunction and cell death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1276–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; Kwak, S. Excitotoxicity and ALS: What is unique about the AMPA receptors expressed on spinal motor neurons? Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2005, 6, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederer, C.W.; Torrisi, A.; Pantelidou, M.; Santama, N.; Cavallaro, S. Pathways and genes differentially expressed in the motor cortex of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. BMC Genom. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, B. Dysfunction of Membrane Trafficking Leads to Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury After Transient Cerebral Ischemia. Transl. Stroke Res. 2018, 9, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.A.; Yeaman, E.J.; Blizzard, C.A.; Chuckowree, J.A.; Dickson, T.C. A case for microtubule vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Altered dynamics during disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burk, K.; Pasterkamp, R.J. Disrupted neuronal trafficking in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morello, G.; Guarnaccia, M.; Spampinato, A.G.; Salomone, S.; D’Agata, V.; Conforti, F.L.; Aronica, E.; Cavallaro, S. Integrative multi-omic analysis identifies new drivers and pathways in molecularly distinct subtypes of ALS. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax, M.; McKenna, J.; Do-Ha, D.; Stevens, C.H.; Higginbottom, S.; Balez, R.; Cabral-da-Silva, M.C.; Farrawell, N.E.; Engel, M.; Poronnik, P.; et al. The Ubiquitin Proteasome System Is a Key Regulator of Pluripotent Stem Cell Survival and Motor Neuron Differentiation. Cells 2019, 8, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahheydari, H.; Ragagnin, A.; Walker, A.K.; Toth, R.P.; Vidal, M.; Jagaraj, C.J.; Perri, E.R.; Konopka, A.; Sultana, J.M.; Atkin, J.D. Protein Quality Control and the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Frontotemporal Dementia Continuum. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.P.; Smith, E.F.; Shaw, P.J.; De Vos, K.J. Protein Homeostasis in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Therapeutic Opportunities? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
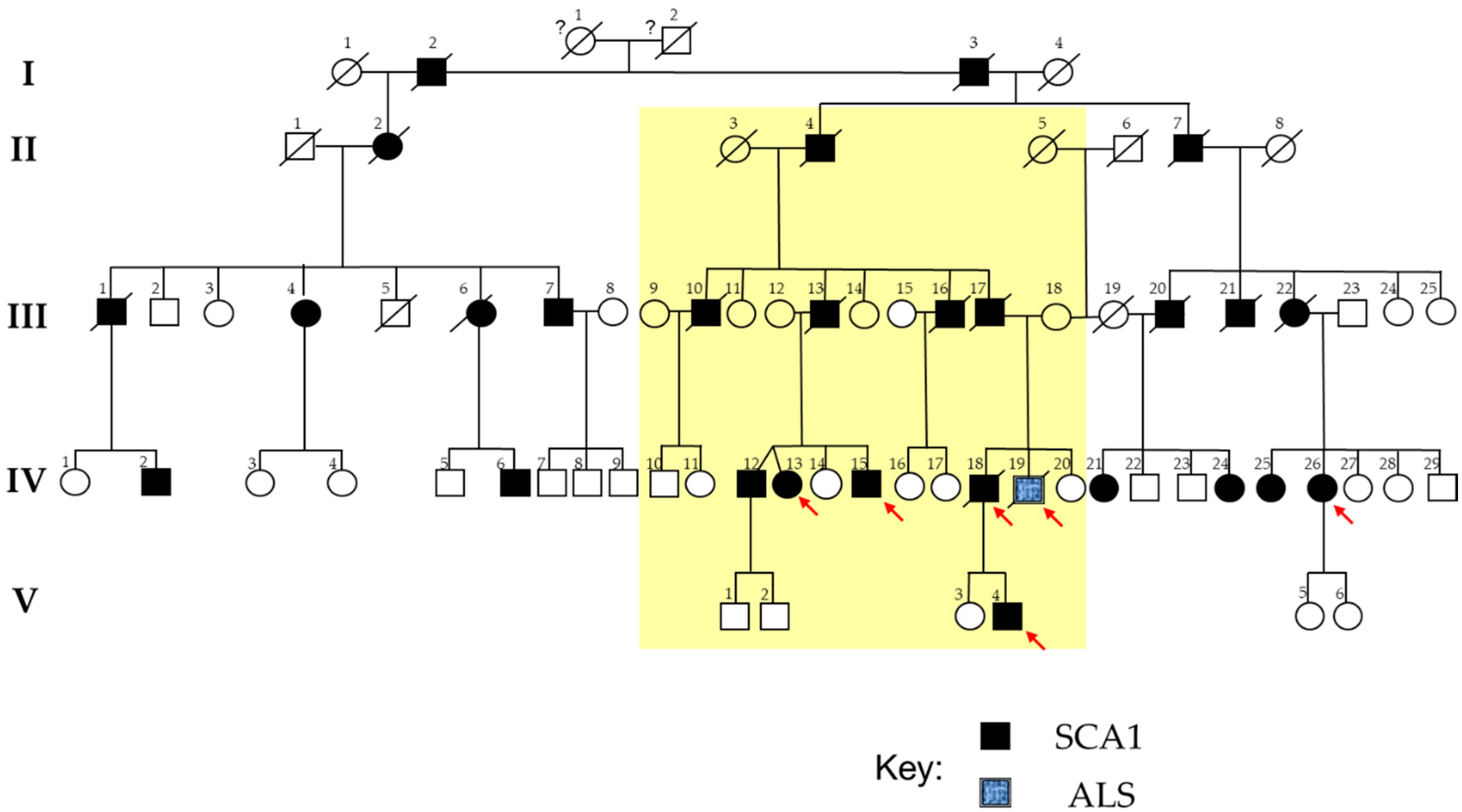
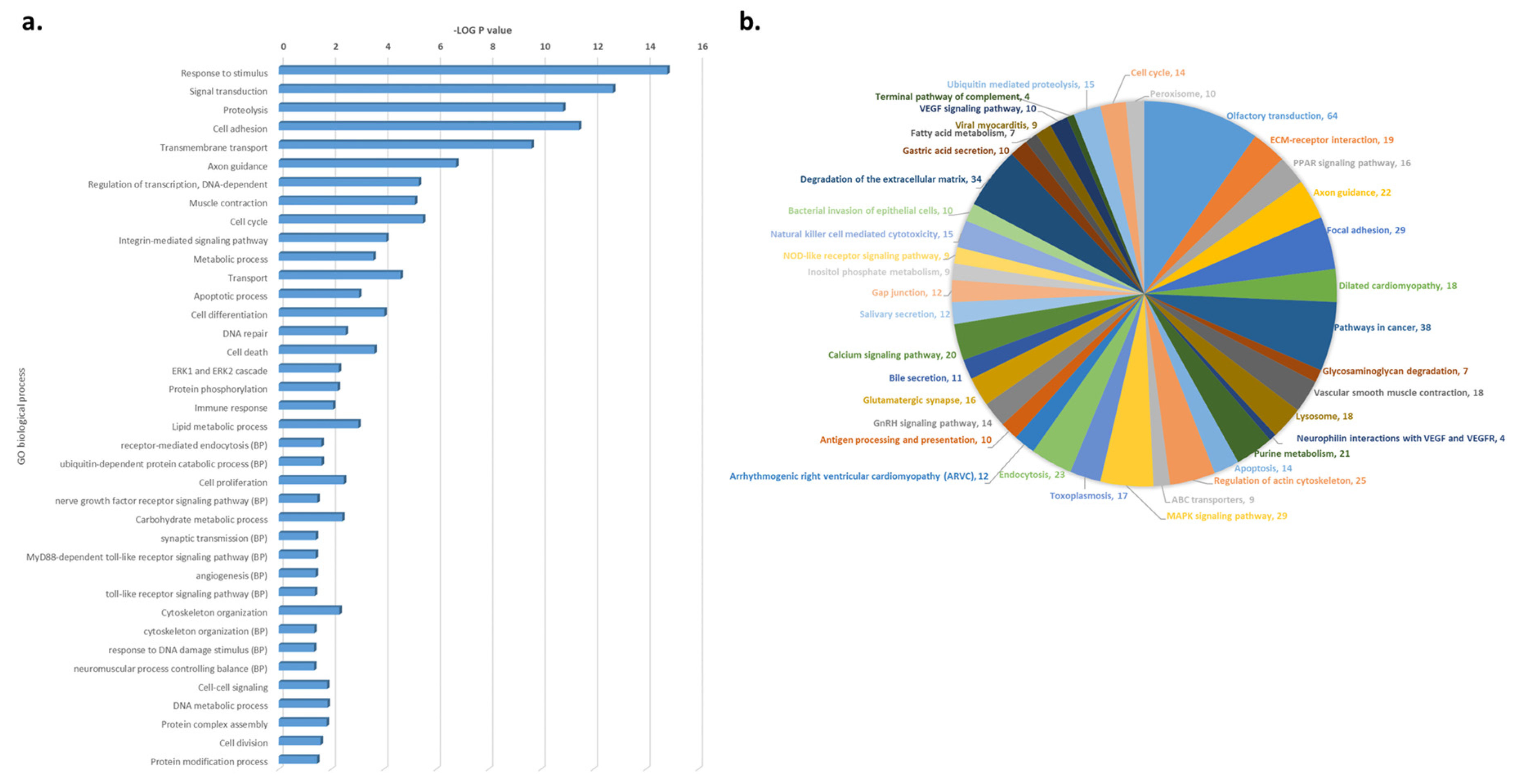
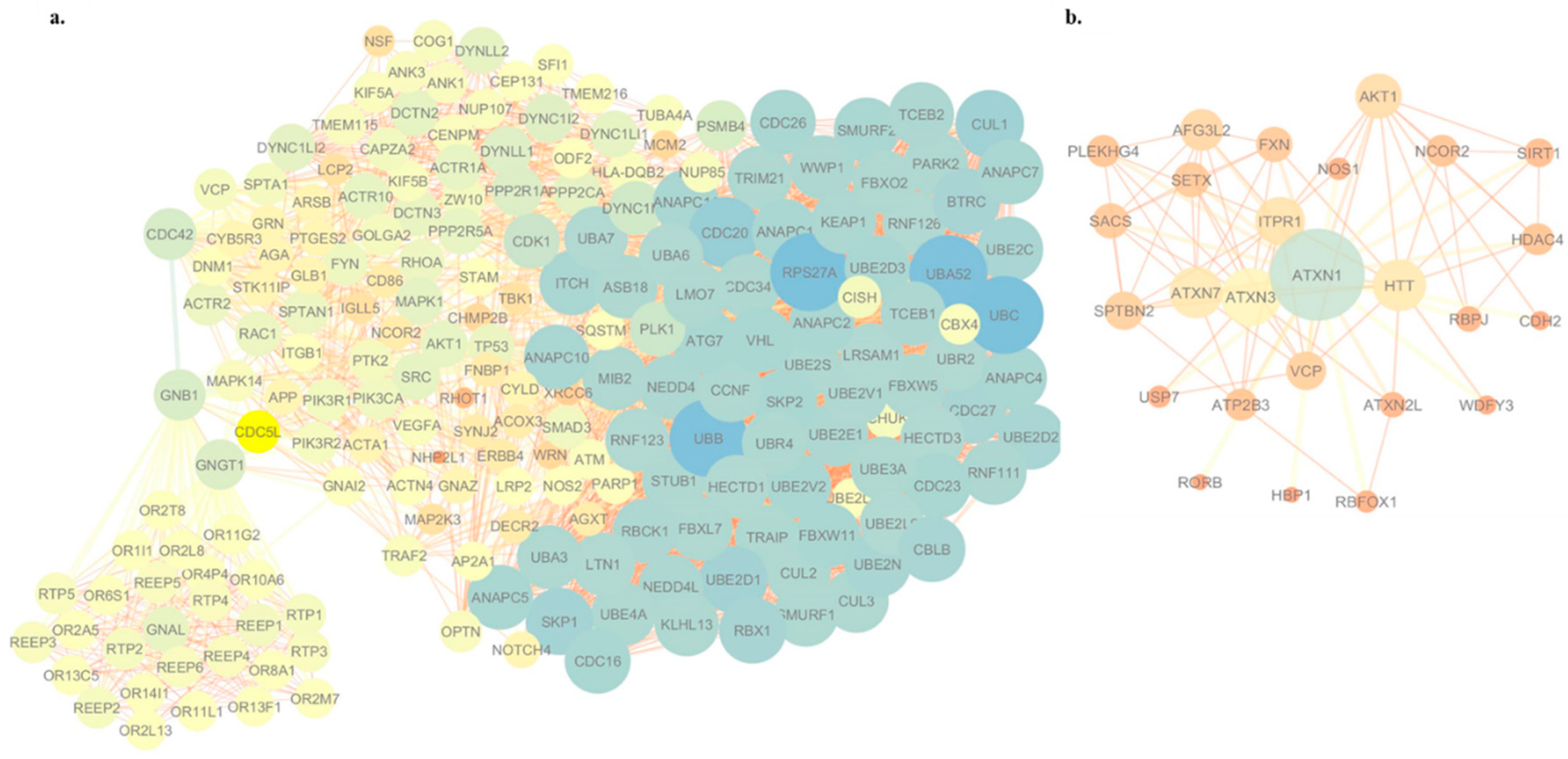
| Genotype | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr | Pos | Reference | Gene Symbol | Variant Class | Exonic | AA Change (Reference Gene) | ExAC_Freq | dbSNP | Polyphen/SIFT Prediction | IV-19 (ALS) | IV-15 (SCA1-MN) | V-4 (SCA1-MN) | V-26 (SCA1) |
| 2 | 202626479 | T | ALS2 | nonsynonymous SNV | 4 | p.Ser80Arg (NM_00113574) | . | . | Damaging/Pathogenic | T/G | T/G | - | - |
| 16 | 2498978 | G | CCNF | nonsynonymous SNV | 10 | p.Arg406Gln (NM_001323538) | 0.00 | rs146438723 | Damaging/Pathogenic | G/A | G/A | - | G/A |
| 22 | 29885908 | A | NEFH | nonsynonymous SNV | 4 | p.Asp760Gly (NM_021076) | . | . | Damaging/Pathogenic | A/G | A/G | - | - |
| 4 | 170428901 | C | NEK1 | nonsynonymous SNV | 22 | p.Ala626Thr (NM_001199397.1) | 0.05 | rs33933790 | Damaging/Pathogenic | C/T | - | C/T | - |
| 9 | 135204010 | T | SETX | nonsynonymous SNV | 10 | p.Lys992Arg (NM_001351527) | 0.02 | rs61742937 | Damaging/Pathogenic | T/C | - | T/C | - |
| 17 | 34171599 | - | TAF15 | frameshift insertion | 15 | p.Ser433fs (NM_139215) | . | . | Damaging/Pathogenic | C/CG | - | - | - |
| Chr | Start | Stop | Probes | Log2 Ratio (Test/Control) | p-Value | Gene | Common CNV (DGV Frequency) | qPCR Validation | Clinical Interpretation | Detected in SCA1-MN Family Members (Patient Code) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98,164,881.00 | 98,187,177.00 | 6 | −0.63967 | 1.54 × 10−10 | DPYD | Yes (0.005–0.04%) | Likely pathogenic | No | |
| 2 | 64,146,992 | 64,211,176.00 | 25 | −0.3406 | 5.01 × 10−13 | VPS54 | Yes (0.003%) | X | Likely pathogenic | Yes (IV-18 *, IV-13, IV-15) |
| 2 | 166,852,501 | 166,870,328.00 | 14 | −0.5323 | 4.49 × 10−14 | SCN1A | Not | Likely pathogenic | No | |
| 2 | 166,911,120 | 166,913,035.00 | 5 | −0.67504 | 5.51 × 10−11 | SCN1A | Yes (0.1%) | Likely pathogenic | No | |
| 2 | 167,328,904 | 167,334,011.00 | 6 | −0.75482 | 4.24 × 10−11 | SCN7A | Yes (0.005–1%) | X | Likely pathogenic | No |
| 2 | 179,536,740 | 179,540,750.00 | 9 | −0.57381 | 1.35 × 10−10 | TTN | Yes (0.4%) | Likely pathogenic | No | |
| 3 | 87,299,007 | 89,814,870.00 | 10 | −0.45231 | 1.51 × 10−10 | CHMP2B, EPHA3 | Yes (0.003–1%) | X | Uncertain clinical significance | No |
| 3 | 93,772,085 | 113,652,487.00 | 20 | −0.28537 | 4.68 × 10−11 | ARL13B | Yes (0.006–0.03%) | Uncertain clinical significance | No | |
| 6 | 161,026,135 | 161,067,305.00 | 17 | 0.477799 | 2.80 × 10−21 | LPA | Yes (>70%) | Likely benign | No | |
| 7 | 17,362,101 | 17,375,411.00 | 12 | −0.64847 | 3.43 × 10−22 | AHR | Yes (0.0034–0.04%) | Likely pathogenic | Yes (IV-13) | |
| 8 | 30,947,985 | 30,999,316.00 | 23 | −0.30766 | 1.60 × 10−11 | WRN | Not | Likely pathogenic | No | |
| 9 | 27,558,554 | 27,573,862.00 | 13 | −0.39928 | 2.08 × 10−11 | C9orf72 | Not | X | Likely pathogenic | No |
| 10 | 70,892,631 | 70,931,418.00 | 15 | −0.36405 | 4.32 × 10−10 | VPS26A | Yes (>10%) | Likely benign | No | |
| 17 | 44,301,037 | 44,771,900.00 | 16 | −0.61264 | 4.50 × 10−29 | NSF | Yes | X | Likely benign | Yes (IV-18, IV-13, IV-15) |
| 21 | 38,791,571 | 38,865,493.00 | 15 | −0.35809 | 8.53 × 10−11 | DYRK1A | Yes (0.003–5%) | Uncertain clinical significance | Yes (IV-13) | |
| X | 108,902,635 | 108,906,573.00 | 6 | −0.73236 | 5.03 × 10−10 | ACSL4 | Yes (2%) | Likely benign | No |
| GO Biological Processes | ALS | SCA IV-18 | SCA IV-13 | SCA IV-15 |
| growth | ||||
| vacuolar transport | ||||
| circadian rhythm | ||||
| peptidyl-tyrosine modification, phosphorylation | ||||
| regulation of hydrolase activity | ||||
| cell morphogenesis | ||||
| regulation of endocytosis | ||||
| regulation of growth rate | ||||
| lysosomal transport | ||||
| membrane depolarization during action potential | ||||
| regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization | ||||
| neuronal action potential | ||||
| regulation of microtubule-based process | ||||
| endosomal transport | ||||
| Golgi vesicle transport | ||||
| autophagy | ||||
| regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization | ||||
| Pathway Name | ALS | SCA IV-18 | SCA IV-13 | SCA IV-15 |
| Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins | ||||
| Phase 0 - rapid depolarization | ||||
| Retrograde transport at the Trans-Golgi-Network | ||||
| Muscle contraction | ||||
| L1CAM interactions | ||||
| Cardiac conduction | ||||
| Intra-Golgi and retrograde Golgi-to-ER traffic | ||||
| Axon guidance | ||||
| Membrane Trafficking | ||||
| Fatty acid, triacylglycerol, and ketone body metabolism | ||||
| Endocytosis | ||||
| Vesicle-mediated transport |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morello, G.; Gentile, G.; Spataro, R.; Spampinato, A.G.; Guarnaccia, M.; Salomone, S.; La Bella, V.; Conforti, F.L.; Cavallaro, S. Genomic Portrait of a Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Case in a Large Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 Family. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040262
Morello G, Gentile G, Spataro R, Spampinato AG, Guarnaccia M, Salomone S, La Bella V, Conforti FL, Cavallaro S. Genomic Portrait of a Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Case in a Large Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 Family. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040262
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorello, Giovanna, Giulia Gentile, Rossella Spataro, Antonio Gianmaria Spampinato, Maria Guarnaccia, Salvatore Salomone, Vincenzo La Bella, Francesca Luisa Conforti, and Sebastiano Cavallaro. 2020. "Genomic Portrait of a Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Case in a Large Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 Family" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040262
APA StyleMorello, G., Gentile, G., Spataro, R., Spampinato, A. G., Guarnaccia, M., Salomone, S., La Bella, V., Conforti, F. L., & Cavallaro, S. (2020). Genomic Portrait of a Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Case in a Large Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 1 Family. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040262








