Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s disease and Healthy Comparators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Data Availability Statement
2.4. Neurological and Psychiatric Evaluation
2.5. Cognitive Assessment
2.6. MRS Acquisition and Processing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic, Neuropsychiatric and Cognitive Features
3.2. Cerebellar GABA, Glx Levels and Excitation/Inhibition Balance
3.3. Comparisons between PD and HC Correlation Coefficients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murueta-Goyena, A.; Andikoetxea, A.; Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Gabilondo, I. Contribution of the GABAergic system to non-motor manifestations in premotor and early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, S.; Kim, T.; Yoon, I.Y.; Jeong, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, K.W. Progression of cognitive impairments in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, H.J.; Byblow, W.D. Does response inhibition have pre- and postdiagnostic utility in Parkinson’s disease? J. Mot. Behav. 2015, 47, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Gorman Tuura, R.L.; Baumann, C.R.; Baumann-Vogel, H. Beyond dopamine: GABA, glutamate, and the axial symptoms of Parkinson disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, M.M.; Galley, S.; Johnson, S.; Stevenson, J.; Huang, X.; McKeown, M.J. The role of the cerebellum in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 40, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.J.; McKeown, M.J. Joint amplitude and connectivity compensatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmahmann, J.D.; Guell, X.; Stoodley, C.J.; Halko, M.A. The Theory and Neuroscience of Cerebellar Cognition. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 337–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.E.; Lees, A.J. Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank, London: Overview and research. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1993, 39, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Counsell, C.; Giladi, N.; Holloway, R.G.; Moore, C.G.; Wenning, G.K.; et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: Status and recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, C.L.; Stowe, R.; Patel, S.; Rick, C.; Gray, R.; Clarke, C.E. Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.; Williams, J.; Karg, R.; Spitzer, R. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5—Research Version (SCID-5 for DSM-5, Research Version; SCID-5-RV); American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B. SCID-5-PD: Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Personality Disorders: Includes the Self-Report Screener Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Screening Personality Questionnaire (SCID-5-SPQ); American Psychiatric Association: Arlington, VA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781585624744. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, G.; Colombo, L.; Vallar, G.; Rusconi, M.L.; Pinarello, A. TIB. Test di intelligenza breve per la valutazione del quoziente intellettivo attuale e pre-morboso. Prof. Psicol. 1997, 1, 2–24. [Google Scholar]
- Emre, M.; Aarsland, D.; Brown, R.; Burn, D.J.; Duyckaerts, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Broe, G.A.; Cummings, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.; Spalletta, G.; Chiapponi, C.; Luccichenti, G.; Cacciari, C.; Orfei, M.D.; Caltagirone, C.; Piras, F. White matter hyperintensities segmentation: A new semi-automated method. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-Sponsored Revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkstein, S.E. Apathy and Withdrawal. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2000, 12, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesimo, G.A.; Caltagirone, C.; Gainotti, G. The Mental Deterioration Battery: normative data, diagnostic reliability and qualitative analyses of cognitive impairment. Eur. Neurol. 1996, 36, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalletta, G.; Robinson, R.G.; Cravello, L.; Pontieri, F.E.; Pierantozzi, M.; Stefani, A.; Long, J.D.; Caltagirone, C.; Assogna, F. The early course of affective and cognitive symptoms in de novo patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.E. A Modified Card Sorting Test Sensitive to Frontal Lobe Defects. Cortex 1976, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarra, P.; Vezzadini, G.; Dieci, F.; Zonato, F.; Venneri, A. A short version of the Stroop test: Normative data in an Italian population sample. Nuova Riv. Neurol. 2002, 12, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, P.G.; McGonigle, D.J.; O’Gorman, R.L.; Puts, N.A.J.; Vidyasagar, R.; Evans, C.J.; Edden, R.A.E. Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA. Neuroimage 2014, 86, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edden, R.A.E.; Puts, N.A.J.; Harris, A.D.; Barker, P.B.; Evans, C.J. Gannet: A batch-processing tool for the quantitative analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid–edited MR spectroscopy spectra. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondot, P.; de Recondo, J.; Coignet, A.; Ziegler, M. Mental disorders in Parkinson’s disease after treatment with L-DOPA. Adv. Neurol. 1984, 40, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dyke, K.; Pépés, S.E.; Chen, C.; Kim, S.; Sigurdsson, H.P.; Draper, A.; Husain, M.; Nachev, P.; Gowland, P.A.; Morris, P.G.; et al. Comparing GABA-dependent physiological measures of inhibition with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy measurement of GABA using ultra-high-field MRI. Neuroimage 2017, 152, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Altena, E.; Nombela, C.; Housden, C.R.; Maxwell, H.; Rittman, T.; Huddleston, C.; Rae, C.L.; Regenthal, R.; Sahakian, B.J.; et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibition modulates response inhibition in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2014, 137, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piras, F.; Piras, F.; Banaj, N.; Ciullo, V.; Vecchio, D.; Edden, R.A.E.; Spalletta, G. Cerebellar GABAergic correlates of cognition-mediated verbal fluency in physiology and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 139, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, Y.; Hirayama, K.; Takeda, A.; Hosokai, Y.; Ishioka, T.; Suzuki, K.; Itoyama, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Mori, E. Corticolimbic gray matter loss in Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazuel, L.; Chassain, C.; Jean, B.; Pereira, B.; Cladière, A.; Speziale, C.; Durif, F. Proton MR spectroscopy for diagnosis and evaluation of treatment efficacy in Parkinson disease. Radiology 2016, 278, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, K.; Leentjens, A.F.G.; Langlois, C.; Moonen, A.J.H.; Duits, A.A.; Carette, A.S.; Duhamel, A. The spectrum of cognitive disorders in Parkinson’s disease: A data-driven approach. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Min, J.O.; Kang, D.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, G.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, S.; An, H.; Known, J.; Kim, J.; et al. Control of motor coordination by astrocytic tonic GABA release through modulation of excitation/inhibition balance in cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5004–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmahmann, J.D. The cerebrocerebellar system. In Essentials of Cerebellum and Cerebellar Disorders: A Primer for Graduate Students; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 101–115. ISBN 9783319245515. [Google Scholar]
- Bellebaum, C.; Daum, I. Cerebellar involvement in executive control. Cerebellum 2007, 6, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguid, I.; Branco, T.; London, M.; Chadderton, P.; Häusser, M. Tonic inhibition enhances fidelity of sensory information transmission in the cerebellar cortex. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11132–11143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Purmann, S.; Pollmann, S. Adaptation to recent conflict in the classical color-word Stroop-task mainly involves facilitation of processing of task-relevant information. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milham, M.P.; Banich, M.T.; Webb, A.; Barad, V.; Cohen, N.J.; Wszalek, T.; Kramer, A.F. The relative involvement of anterior cingulate and prefrontal cortex in attentional control depends on nature of conflict. Cogn. Brain Res. 2001, 12, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel-Cresswell, S.; De La Fuente-Fernandez, R.; Galley, S.; McKeown, M.J. Imaging of compensatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010, 23, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, N.S.; Rodnitzky, R.L.; Uc, E.Y. Prefrontal dopamine signaling and cognitive symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 24, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Kareken, D.A.; Christian, B.T.; Dzemidzic, M.; Yoder, K.K. Cortical dopamine release during a behavioral response inhibition task. Synapse 2014, 68, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandam, L.S.; Hester, R.; Wagner, J.; Cummins, T.D.R.; Garner, K.; Dean, A.J.; Kim, B.N.; Nathan, P.J.; Mattingley, J.B.; Bellgrove, M.A. Methylphenidate but not atomoxetine or citalopram modulates inhibitory control and response time variability. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 902–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manza, P.; Amandola, M.; Tatineni, V.; Li, C.R.; Leung, H.-C. Response inhibition in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of dopaminergic medication and disease duration effects. NPJ Park. Dis. 2017, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittleman, G.; Goldowitz, D.; Heck, D.H.; Blaha, C.D. Cerebellar modulation of frontal cortex dopamine efflux in mice: Relevance to autism and schizophrenia. Synapse 2008, 62, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanoue, A.C.; Blatt, G.J.; Soghomonian, J.J. Decreased parvalbumin mRNA expression in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in Parkinson′s disease. Brain Res. 2013, 1531, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanoue, A.C.; Dumitriu, A.; Myers, R.H.; Soghomonian, J.J. Decreased glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA expression in prefrontal cortex in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 226, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kühn, S.; Schubert, F.; Mekle, R.; Wenger, E.; Ittermann, B.; Lindenberger, U.; Gallinat, J. Neurotransmitter changes during interference task in anterior cingulate cortex: Evidence from fMRI-guided functional MRS at 3 T. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinu, K.; Degroot, C.; Madjar, C.; Strafella, A.P.; Monchi, O. Levodopa influences striatal activity but does not affect cortical hyper-activity in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2012, 35, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, K.; Jech, R.; Ballarini, T.; Holiga, Š.; Růžička, F.; Piecha, F.A.; Möller, H.E.; Vymazal, J.; Růžička, E.; Schroeter, M.L. Modulatory Effects of Levodopa on Cerebellar Connectivity in Parkinson’s Disease. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boecker, H.; Weindl, A.; Brooks, D.J.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Liedtke, C.; Miederer, M.; Sprenger, T.; Wagner, K.J.; Miederer, I. GABAergic dysfunction in essential tremor: An11C-flumazenil PET study. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gironell, A.; Figueiras, F.P.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Herance, J.R.; Pascual-Sedano, B.; Trampal, C.; Gispert, J.D. Gaba and serotonin molecular neuroimaging in essential tremor: A clinical correlation study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Santaniello, S. Role of cerebellar GABAergic dysfunctions in the origins of essential tremor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13592–13601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Nuland, A.J.M.; den Ouden, H.E.M.; Zach, H.; Dirkx, M.F.M.; van Asten, J.J.A.; Scheenen, T.W.J.; Toni, I.; Cools, R.; Helmich, R.C. GABAergic changes in the thalamocortical circuit in Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.D.; Prokic, E.J.; McAllister, C.J.; Ronnqvist, K.C.; Williams, A.C.; Yamawaki, N.; Witton, C.; Woodhall, G.L.; Stanford, I.M. GABA-mediated changes in inter-hemispheric beta frequency activity in early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2014, 281, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
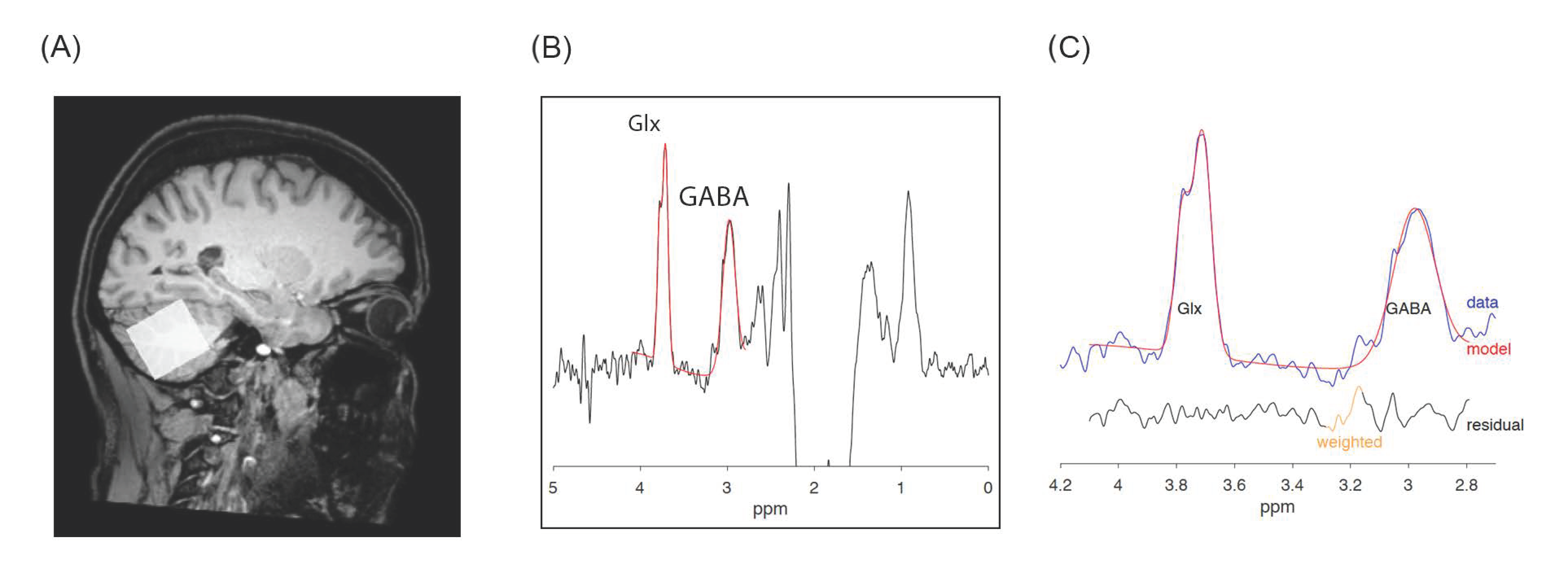
| Characteristics (Standard Deviation) | HC (n = 20) | PD (n = 20) | t or χ2 | d.f. | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years/sd) | 54.25 (16.62) | 58.55 (9.6) | 1.09 | 38 | 0.27 |
| Males n (%) | 12 (60) | 10 (50) | 0.4 | 1 | 0.52 |
| Educational level (years/sd) | 14.00 (3.21) | 12.65 (3.97) | −1.18 | 38 | 0.24 |
| Age at onset (years/sd) | - | 55.4 (9.59) | - | - | - |
| Duration of illness (years/sd) | - | 3.51 (1.78) | - | - | - |
| H&Y score | - | 1.47 (0.47) | - | - | - |
| UPDRS-III score (sd) | - | 12.30 (6.01) | - | - | - |
| Levodopa equivalents (mg/day-sd) | - | 335.0 (260.99) | - | - | - |
| Combined dopamine agonists/levodopa treatment n (%) | - | 7 (35) | - | - | - |
| Dopamine agonists monotherapy n (%) | - | 6 (30) | - | - | - |
| Levodopa monotherapy n (%) | - | 3 (15) | - | - | - |
| non medicated | - | 4 (20) | - | - | - |
| Apathy diagnosis n (%) | - | 1 (5) | - | - | - |
| AS tot. (score/sd) | - | 8.75 (5.38) | - | - | - |
| AS motivation | - | 0.60 (0.68) | - | - | - |
| AS interest | - | 1.65 (1.66) | - | - | - |
| AS effort | - | 0.45 (0.75) | - | - | - |
| AS indifference | - | 0.65 (1.22) | - | - | - |
| HARS tot. (score/sd) | - | 7.25 (4.54) | - | - | - |
| BDI tot. (score/sd) | - | 9.10 (6.62) | - | - | - |
| BDI psychic | - | 5.45 (4.51) | - | - | - |
| BDI somatic | - | 3.65 (2.34) | - | - | - |
| PPRS tot. (score/sd) | - | 6.55 (0.82) | - | - | - |
| PPRS hallucinations | - | 1.10 (0.30) | - | - | - |
| PPRS illusions | - | 1.05 (0.22) | - | - | - |
| PPRS paranoid ideation | - | 1.0 (0.0) | - | - | - |
| PPRS sleep disturbance | - | 1.30 (0.57) | - | - | - |
| PPRS confusion | - | 1.0 (0.0) | - | - | - |
| PPRS sexual preoccupation | - | 1.10 (0.45) | - | - | - |
| MMSE (raw score/sd) | 29.50 (1.0) | 28.80 (1.05) | 2.15 | 38 | 0.04 |
| M-WCST-sf C | 5.95 (0.22) | 5.95 (0.22) | 0.0 | 38 | 1.0 |
| M-WCST-sf P | 0.15 (0.36) | 1.0 (1.77) | -2.09 | 38 | 0.04 |
| M-WCST-sf NP | 0.60 (0.82) | 1.0 (0.97) | −1.40 | 38 | 0.38 |
| SWCT-sv IE-T (sec/sd) | 31.40 (9.01) | 34.55 (10.66) | −1.0 | 38 | 0.43 |
| SWCT-sv IE-E | 0.20 (0.69) | 0.45 (1.05) | −0.88 | 38 | 0.09 |
| Mean cerebellar GABA (ppm/sd) | 3.48 (0.46) | 3.59 (0.61) | −0.60 | 38 | 0.55 |
| Cerebellar GABA left | 3.53 (0.56) | 3.55 (0.76) | −0.11 | 38 | 0.91 |
| Cerebellar GABA right | 3.44 (0.54) | 3.62 (0.82) | −0.82 | 38 | 0.41 |
| Mean cerebellar Glx | 10.17 (0.99) | 10.21 (1.0) | −0.12 | 38 | 0.90 |
| Cerebellar Glx left | 10.29 (1.31) | 10.42 (1.16) | −0.35 | 38 | 0.73 |
| Cerebellar Glx right | 10.05 (1.29) | 9.99 (1.34) | 0.14 | 38 | 0.89 |
| Mean cerebellar E/I balance (Glx/GABA) | 2.97 (0.48) | 2.91 (0.56) | 0.31 | 38 | 0.75 |
| Cerebellar E/I balance (Glx/GABA) left | 2.99 (0.60) | 3.04 (0.63) | −0.26 | 38 | 0.80 |
| Cerebellar E/I balance (Glx/GABA) right | 2.99 (0.60) | 2.87 (0.70) | 0.56 | 38 | 0.58 |
| Levodopa eq. r to z (p level) | M-WCST-sf P r to z (p level) | SWCT-sv IE-T r to z (p level) | SWCT-sv IE-E r to z (p level) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS tot | −0.06 (0.81) | 0.14 (0.55) | 0.10 (0.68) | 0.16 (0.50) |
| HARS tot | −0.52 (0.02) | −0.11 (0.64) | −0.16 (0.49) | 0.06 (0.79) |
| BDI tot | −0.13 (0.58) | 0.03 (0.90) | −0.04 (0.85) | −0.11(0.64) |
| PPRS tot | 0.37 (0.10) | 0.04 (0.88) | −0.06 (0.80) | 0.25 (0.30) |
| Mean GABA r to z (p level) | GABA left r to z (p level) | GABA right r to z (p level) | |||||||
| HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC=20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | |
| levodopa eq. (mg/day) | - | 0.007 (.98) | - | - | 0.06 (0.80) | - | - | −0.05 (0.85) | - |
| M-WCST-sf P | 0.05 (0.82) | 0.31 (0.19) | −0.79(ns) | 0.11 (0.64) | 0.11 (0.63) | 0 (ns) | −0.03 (0.91) | 0.35 (0.12) | −1.15(ns) |
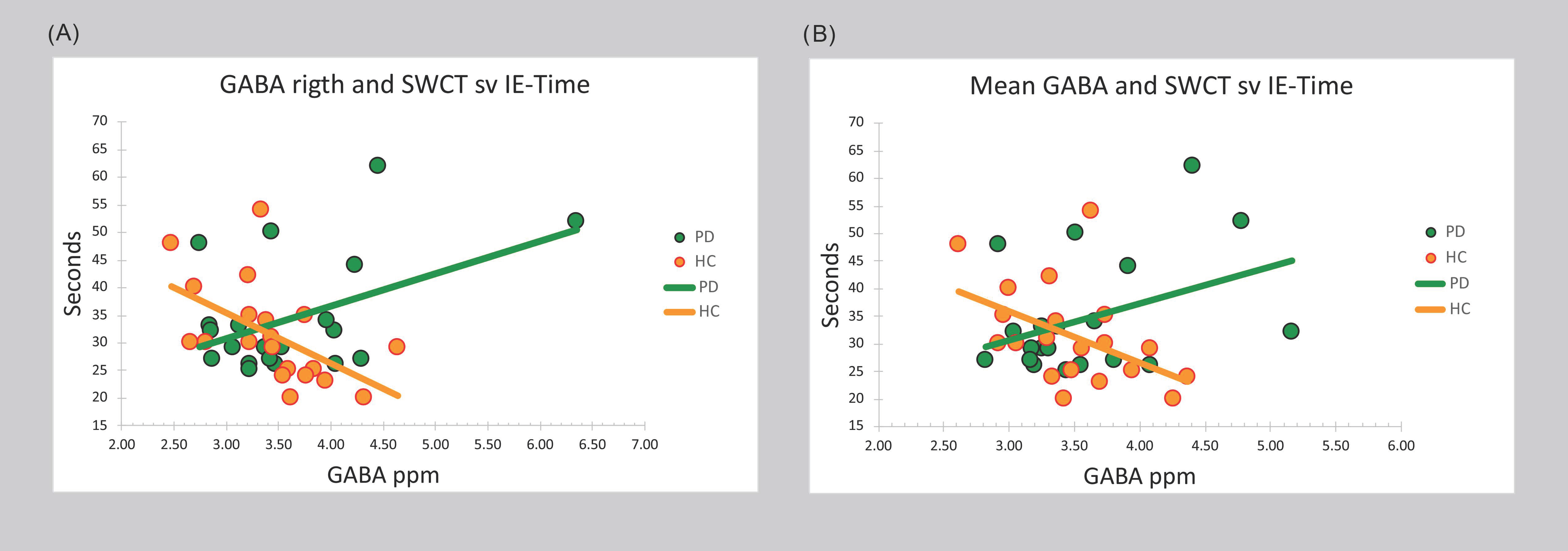
| SWCT-sv IE-T | −0.47 (0.03) | 0.39 (0.09) | −2.69 (0.007) * | −0.25 (0.29) | 0.13 (0.59) | −1.13 (ns) | −0.55 (0.01) | 0.45 (0.04) | −3.22 (0.001) * |
| SWCT-sv IE-E | −0.42(0.06) | 0.48 (0.03) | −2.83 (0.005) * | −0.30 (0.20) | 0.53 (0.01) | −2.62 (0.009) * | −0.40 (0.08) | 0.21 (0.36) | −1.86 (ns) |
| Mean Glx r to z (p level) | Glx left r to z (p level)) | Glx right r to z (p level)) | |||||||
| HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | |
| levodopa eq. (mg/day) | - | −0.50 (0.02) | - | - | −0.36 (0.11) | - | - | −0.43 (0.06) | - |
| M-WCST-sf P | 0.06 (0.80) | 0.31 (0.18) | −0.76 (ns) | −0.28 (0.24) | 0.21 (0.36) | −1.46 (ns) | 0.37 (0.10) | 0.28 (0.24) | 0.29 (ns) |
| SWCT-sv IE-T | 0.07 (0.78) | 0.09 (0.71) | −0.06 (ns) | −0.002 (0.1) | −0.01 (0.96) | 0.02 (ns) | 0.10 (0.67) | 0.14 (0.54) | −0.12 (ns) |
| SWCT-sv IE-E | −0.18 (0.44) | 0.30 (0.19) | −1.43 (ns) | −0.25 (0.28) | 0.06 (0.79) | −0.92 (ns) | −0.02 (0.94) | 0.40 (0.08) | −1.29 (ns) |
| Mean E/I (Glx/GABA) r to z (p level)) | E/I (Glx/GABA) left r to z (p level)) | E/I (Glx/GABA) right r to z (p level)) | |||||||
| HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | HC = 20 | PD = 20 | Z-test z (p level) | |
| levodopa eq. (mg/day) | - | −0.29 (0.21) | - | - | −0.32 (0.17) | - | - | −0.21 (0.37) | - |
| M-WCST-sf P | −0.03 (0.89) | −0.12 (0.61) | 0.26 (ns) | −0.28 (0.23) | −0.06 (0.79) | −0.66 (ns) | 0.25 (0.29) | −0.13 (0.58) | 1.13 (ns) |
| SWCT-sv IE-T | 0.40 (0.07) | −0.28 (0.23) | 2.07 (0.03) | 0.13 (0.59) | −0.19 (0.42) | 0.94 (ns) | 0.51 (0.02) | −0.22 (0.35) | 2.29 (0.02) |
| SWCT-sv IE-E | 0.27 (0.25) | −0.22 (.36) | 1.46 (ns) | 0.06 (0.81) | −0.35 (0.13) | 1.24 (ns) | 0.37 (0.10) | −0.03 (0.90) | 1.22 (ns) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piras, F.; Vecchio, D.; Assogna, F.; Pellicano, C.; Ciullo, V.; Banaj, N.; Edden, R.A.E.; Pontieri, F.E.; Piras, F.; Spalletta, G. Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s disease and Healthy Comparators. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010016
Piras F, Vecchio D, Assogna F, Pellicano C, Ciullo V, Banaj N, Edden RAE, Pontieri FE, Piras F, Spalletta G. Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s disease and Healthy Comparators. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010016
Chicago/Turabian StylePiras, Federica, Daniela Vecchio, Francesca Assogna, Clelia Pellicano, Valentina Ciullo, Nerisa Banaj, Richard A. E. Edden, Francesco E. Pontieri, Fabrizio Piras, and Gianfranco Spalletta. 2021. "Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s disease and Healthy Comparators" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010016
APA StylePiras, F., Vecchio, D., Assogna, F., Pellicano, C., Ciullo, V., Banaj, N., Edden, R. A. E., Pontieri, F. E., Piras, F., & Spalletta, G. (2021). Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s disease and Healthy Comparators. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010016









