Abstract
This study focuses on the application of a non-immersive virtual reality (VR)-based neurocognitive intervention in critically ill patients. Our aim was to assess the feasibility of direct outcome measures to detect the impact of this digital therapy on patients’ cognitive and emotional outcomes. Seventy-two mechanically ventilated adult patients were randomly assigned to the “treatment as usual” (TAU, n = 38) or the “early neurocognitive stimulation” (ENRIC, n = 34) groups. All patients received standard intensive care unit (ICU) care. Patients in the ENRIC group also received adjuvant neurocognitive stimulation during the ICU stay. Outcome measures were a full neuropsychological battery and two mental health questionnaires. A total of 42 patients (21 ENRIC) completed assessment one month after ICU discharge, and 24 (10 ENRIC) one year later. At one-month follow-up, ENRIC patients had better working memory scores (p = 0.009, d = 0.363) and showed up to 50% less non-specific anxiety (11.8% vs. 21.1%) and depression (5.9% vs. 10.5%) than TAU patients. A general linear model of repeated measures reported a main effect of group, but not of time or group–time interaction, on working memory, with ENRIC patients outperforming TAU patients (p = 0.008, ηp2 = 0.282). Our results suggest that non-immersive VR-based neurocognitive stimulation may help improve short-term working memory outcomes in survivors of critical illness. Moreover, this advantage could be maintained in the long term. An efficacy trial in a larger sample of participants is feasible and must be conducted.
1. Introduction
Approximately half of intensive care unit (ICU) survivors develop post-intensive care syndrome (PICS) [1], which comprises a set of acquired physical, cognitive, and emotional deficits that negatively affect the quality of life of patients and their families [2]. These disorders can drastically alter the ability to perform activities of daily living normally [3] and even prevent patients from returning to work [4]. In addition, they are associated with high medical and financial costs [5]. However, there is evidence that their severity can be mitigated by preventive interventions during the early stages of critical illness [1].
The cognitive impairment associated with PICS resembles that of mild-to-moderate dementia [6] and may persist for years after discharge [7]. This impairment can adopt different phenotypes depending on the severity of dysfunction and the cognitive domains affected, being especially pronounced in memory, executive functions, and processing speed [8]. Several variables, such as older age, female gender, mechanical ventilation (MV), delirium, and deep sedation have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive sequelae. Conversely, greater cognitive reserve, i.e., the brain’s resistance to pathological changes [9], may be a protective factor [10,11,12].
ICUs are places for the care of critically ill, unstable, and recoverable patients who are at risk of dying. Therefore, they are a potentially hostile environment for a vulnerable patient. In addition to the physical stress associated with critical illness and interventions (e.g., MV), there are physiological (e.g., delirium) and psychosocial factors (e.g., noise, ambient light, restricted mobility, and social isolation) that can adversely affect patient comfort and well-being. Consequently, patients can also experience a strong emotional impact related to the ICU environment, their critical illness, and associated sequelae, and suffer non-specific anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and depression [13]. Stressors such as longer ICU and hospital stay, prolonged MV, negative or delusional experiences during ICU admission, and functional disability after discharge are risk factors for the development of these disorders [5,14].
Interest in post-ICU sequelae and how to prevent them has increased markedly in recent years [15,16]. The ABCDEF bundle is an evidence-based clinical guideline that provides recommendations to improve patient recovery and outcomes during the ICU stay [17]. Common measures to mitigate PICS include optimized delirium management [18]; early mobilization [19]; and, in some cases, occupational therapy [20]. Over the years, these measures have expanded to include in situ neurocognitive stimulation [21] and stress and anxiety reduction [22]. However, ICU patients are usually bedridden and often unable to communicate verbally, especially when undergoing MV. In these cases, classical neurocognitive and psychotherapeutic interventions are particularly difficult to apply. To address this limitation, several technology-based solutions have been proposed [23].
Virtual reality (VR) refers to immersive, multisensory, viewer-centered, 3D computer-generated, interactive environments created by combining different technologies. Cognitive and emotional therapies based on VR techniques have achieved promising results in patients with neurocognitive and mental health disorders [24,25], but reports on their use in critically ill patients are scarce [26,27,28,29]. Thus far, most studies in critically ill patients have used immersive systems that provide a full stereoscopic experience through the use of various sensory output devices, such as head-mounted displays [26,28,29]. Other studies have used non-immersive systems that employ computer displays or large projection screens that are less expensive but do not provide a full stereoscopic experience [27]. Despite these differences, all have used simulated environments inspired by the real world and based on images and sounds from nature, as these are considered the most appropriate scenarios to help patients abstract from the ICU environment and their critical illness. However, none have been designed specifically for MV patients, who are at high risk of post-ICU sequelae due to the cross-talks between lung and brain [2,11,13,14].
Patient-centered care aims to make patients feel known, respected, and well-informed, actively involved in their own care and in decisions related to their illness and recovery process. With this in mind, we developed the Early Neurocognitive Rehabilitation in Intensive Care (ENRIC) platform, an innovative non-immersive VR-based early neurocognitive intervention designed specifically for the ICU environment and the MV patient. In a first proof-of-concept (PoC) study, we already demonstrated the feasibility of this intervention in terms of safety, tolerability, and potential efficacy in stimulating the brain using a surrogate outcome measure, such as heart rate variability [30]. However, its potential efficacy in mitigating post-ICU sequelae using direct outcome measures, such as neuropsychological testing and mental health questionnaires, has yet to be evaluated. A more precise understanding of how and to what extent ENRIC therapy helps improve cognitive and emotional outcomes in survivors of critical illness may contribute to a better approach to disease management that also addresses comfort and well-being.
Following CONSORT guidelines for non-pharmacological [31] and pilot trials [32], the overall purpose of this second PoC study was to assess the feasibility of direct outcome measures to detect differences between stimulated vs. non-stimulated groups and to provide data (e.g., mean, standard deviation, 95% confidence interval) for the design of future efficacy trials in larger samples of participants. To this end, we set two specific objectives: first, to evaluate the impact of ENRIC therapy on patients’ cognitive and emotional outcomes one month after ICU discharge, and second, to analyze whether or not the effect of this intervention is maintained one year later.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This is a prospective, randomized, non-blind, two-arm, pilot clinical trial that was conducted between November 2015 and September 2020. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Parc Taulí University Hospital (Catalonia, Spain; #2013/067), registered in ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02078206) and carried out in accordance with the latest version of the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.2. Sample Size
The minimum sample size for a pilot randomized clinical trial (RCT) should be 9% of the number required in the main study [33]. The sample size of a full RCT calculated with the G*Power software v3.1.9.4, assuming a conservative effect size of 0.20 at a study power of 0.80 and with an alpha error of 0.05 would be 778 subjects (786 according to [33]). Therefore, 72 critically ill patients were recruited for this pilot RCT (Figure 1).
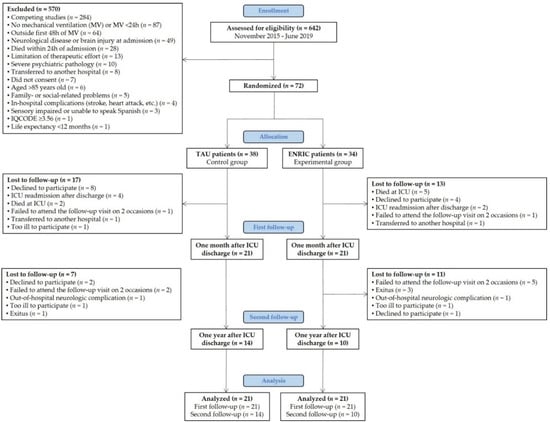
Figure 1.
Flow diagram. TAU—treatment as usual, ENRIC—early neurocognitive stimulation, ICU—intensive care unit, IQCODE—informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly. Over a four-year period, 642 ICU patients were screened for eligibility, but 570 met at least one exclusion criterion. Of the 72 eligible patients, 38 (52.8%) were randomly assigned to the TAU group and 34 (47.2%) to the ENRIC group. Forty-two patients (58.3%) completed the cognitive and emotional evaluation one month after ICU discharge. Twenty-four patients (57.1%) were re-evaluated one year later.
2.3. ENRIC Technology Features
The ENRIC platform, designed by a multidisciplinary team of neuropsychologists, critical care physicians, nurses, and other biomedical researchers [30], features stimulation software with various cognitive exercises, including passive, guided observation, selective attention, and working memory exercises, specifically designed or adapted to the ICU environment and MV patient. All cognitive exercises are based on previous cognitive rehabilitation programs that have proven effective in improving cognitive outcomes in patients with neurocognitive and mental health disorders [34,35]. Using a central processing unit, a flat screen TV, and a Kinect® motion sensor to detect the movement of the patient’s arms and hands, the stimulation software places patients in a relaxing environment (tropical island) composed of 4 scenarios with real nature sounds (wheat field, beach, forest, and mountain landscape) in which they can walk accompanied by a virtual avatar. All scenarios are similar to previous environments that have proven effective in reducing stress and anxiety in critically ill patients [26,27,28,29]. The route through the virtual world and the order of the cognitive exercises is initially predefined; however, the therapist can modify the route, reconfigure the order of appearance of the exercises, or jump from one exercise to another using commands. Together with the therapist, the virtual avatar orientates the patients in time and delivers instructions, while encouraging them to do the cognitive exercises and to relax (see Supplementary Files S1 and S2).
2.4. Participants and Procedure
Patients were recruited from the ICU of the Parc Taulí University Hospital, a mixed medical/surgical ICU with 16 beds in single rooms. All subjects were aged 18–85 years old and had undergone ≥24 h of invasive MV. Exclusion criteria were prior cognitive impairment or dementia [36] (see Supplementary File S3), a history of neurological disease (including brain injury at admission), a history of severe mental illness (including intellectual disability), being non-Spanish speaking, and a life expectancy of <12 months. Patients who were readmitted to the ICU in the month following discharge, those who following the physician’s clinical indications were too ill to participate in follow-up visits because of severe frailty, and those who suffered out-of-hospital neurological complications were also excluded. Patients who did not participate in the one-month follow-up visit were not scheduled for the one-year follow-up visit.
Eligible patients were screened daily by an ICU research nurse and invited to participate when they reached a minimum level of consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale ≥ 13) and sedation/alertness (Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS) −1 to +1). Patients were randomly assigned (ratio 1:1) to the “treatment as usual” (TAU) or “early neurocognitive stimulation” (ENRIC) group using a simple randomization method (blind envelope system) (Figure 1). At enrollment, we obtained written informed consent from patients or their authorized surrogates. If consent was initially obtained from a surrogate (e.g., in case of delirium or deep sedation), we ratified the patient’s consent once they were deemed mentally competent. Patients whose relatives refused to participate, those who did not sign the informed consent form, or those who refused to participate even when their relatives gave prior consent were excluded.
Demographic data, medical comorbidities (Charlson Comorbidity Index, CCI), disease severity (Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation-II, APACHE-II), and organ failure (Sequential Organ Failure Assessment, SOFA) were collected at admission. Delirium was assessed daily using the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU). Daily doses of opioids and sedatives were also recorded [37]. Sequential data, including delirium and medication, were collected daily from ICU admission until ICU discharge, or for a maximum of 28 days, by experienced ICU clinical and research staff.
During the study, both groups of patients were managed with similar processes of care and only patients in the ENRIC group received adjuvant neurocognitive stimulation every morning in their own beds until ICU discharge when they were alert and calm (RASS −1 to +1). All sessions were guided by a neuropsychologist (therapist) and a virtual avatar (co-therapist) and were supervised by an ICU research nurse or critical care physician. The main objective of the intervention was to provide early neurocognitive stimulation and promote participation in the cognitive exercises, regardless of the accuracy of the responses. The type of cognitive exercises included in each session and their workload were determined daily on the basis of both the patients’ health status [38] and their ability to interact with the ENRIC software (i.e., patients’ alertness) and Kinect® technology (i.e., patients’ ability to raise each arm against gravity). Delirium did not prevent the session from being conducted unless RASS ≥2 (e.g., agitation). The clinical team predefined a session length of 15–20 min, but patients were encouraged to continue as long as they could without fatigue. A detailed description of the protocol of the intervention can be found in the first PoC study [30].
To assess the feasibility of direct outcome measures to detect differences between stimulated vs. non-stimulated groups, we examined PICS-related cognitive and emotional deficits one month and one year after ICU discharge using a comprehensive neuropsychological battery and two mental health questionnaires.
2.5. Cognitive and Emotional Assessment
Patients were administered a battery of nine cognitive tests that provided 14 neuropsychological measures [39,40,41,42] and an estimate of intelligence quotient [43]. The raw scores of all neuropsychological measures were converted to z-scores using the normative data set provided by each test and then averaged to create a global neurocognitive score and 6 cognitive indexes: attention, working memory, learning and memory, memory retrieval, executive functions, and processing speed (see Supplementary File S4). These cognitive indexes have already proven effective in detecting cognitive deficits in survivors of critical illness [8].
Patients were also administered 2 mental health questionnaires. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to assess non-specific anxiety and depression [44]. The Davidson Trauma Scale (DTS) was used to assess PTSD [45]. The results of these questionnaires can be interpreted dichotomously or continuously. While the HADS Anxiety and Depression scales ranging from 0 to 7 are considered non-pathological, the range of 8 to 21 is pathological. As for the DTS, the non-pathological range is 0 to 39, while the pathological range is 40 to 136. When interpreted on a continuum, higher scores mean more severe symptoms.
2.6. Primary and Secondary Outcome Measures
The primary outcome measure was patients’ cognitive functioning and emotional state one month after ICU discharge, measured by the global neurocognitive score, the six cognitive indexes, and the two mental health questionnaires. How these variables changed over a 12 month period was our secondary outcome measure.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Some variables, such as cognitive reserve, were preprocessed prior to statistical analysis (see Supplementary Files S4 and S5). The analysis was performed using SPSS v25. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Data normality was checked using skewness, kurtosis, and Shapiro–Wilk tests. Results are presented as means (standard deviation, SD), medians [interquartile range, IQR], or n (%). Effect sizes based on Cohen’s d (small = 0.2; medium = 0.5; large = 0.8) and partial eta-squared (ηp2; small = 0.01; medium = 0.06; large = 0.14) and 95% confidence intervals are reported for all outcome measures.
The differences between the TAU and ENRIC groups in continuous variables one month after ICU discharge were analyzed using the Student’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test. For categorical variables, the chi-squared (X2) test was used. To examine how patients’ cognitive and emotional outcomes changed over a 12 month period, we used a general linear model for repeated measures, with factors group (TAU vs. ENRIC), time (one month vs. one year), and group–time interaction.
The possible confounding effect of demographic and clinical variables on patients’ cognitive and emotional outcomes one month after ICU discharge was explored using bivariate regressions. The possible confounders were selected on the basis of their potential to influence cognitive and emotional outcomes according to the previous literature [5,8,14,46]. All variables that reached statistical significance in these screening analyses were included in a multiple linear regression model (one for each cognitive and emotional outcome in which the TAU and ENRIC groups differed). To obtain more consistent models, non-significant variables were excluded step-by-step, starting with the parameters with the highest p-value. A final model was constructed including all variables that independently influenced the test score.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
Seventy-two patients were enrolled and randomly assigned to the TAU (n = 38) or ENRIC group (n = 34). One month after ICU discharge, 21 TAU patients (55.3%) and 21 ENRIC patients (61.8%) completed the first follow-up visit. One year later, 14 TAU patients (66.7%) and 10 ENRIC patients (47.6%) were re-evaluated at a second follow-up visit (Figure 1).
Table 1 summarizes the demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients who completed the first follow-up visit (n = 42). No significant differences were observed between the two groups.

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients evaluated one month after ICU discharge. Mean (SD) or Median [IQR] are reported, unless otherwise specified.
Considering only patients who completed both follow-up visits (n = 24), we found that ENRIC patients were hospitalized for more days than TAU patients and that, at hospital discharge, the former were mostly transferred to a social-health center (60.0%), whereas the latter were mostly discharged home (85.7%) (see Supplementary File S6).
3.2. Characteristics of Early Neurocognitive Stimulation
ENRIC patients received neurocognitive stimulation on at least 2 study days. The first session was administered 9 (IQR: 2–22) days after ICU admission. Sessions were administered on 70.2% (IQR: 22–100%) of the eligible study days until ICU discharge. In total, 106 sessions were administered (mean number of sessions per patient, 5.1 (IQR: 2–14); mean duration of each session, 13.8 (IQR: 5–31) minutes). Patients completed 86.8% (n = 92) of the sessions. Reasons for discontinuing a session were fatigue (50.0%), extreme sleepiness (14.3%), dizziness (14.3%), anxiety (14.3%), and confusion (7.1%). No sessions were interrupted early for safety reasons, and no adverse events occurred. Discontinuation did not prevent participation in subsequent sessions. The composition of the first five sessions, with progressively more challenging cognitive exercises, is shown in Supplementary File S7. More details on the safety and tolerability of this intervention can be found in the first PoC study [30].
3.3. Cognitive and Emotional Outcomes One Month after ICU Discharge
Table 2 shows that ENRIC patients outperformed TAU patients on the working memory index (p = 0.009, d = 0.363) but not on the other cognitive outcomes, including global neurocognition, attention, learning and memory, memory retrieval, executive functions, and processing speed.

Table 2.
Cognitive and emotional outcomes one month after ICU discharge (Student’s t-test). Mean (SD) is reported.
Regarding emotional state, 16.7% of patients scored within the pathological range for non-specific anxiety (HADS Anxiety: TAU = 21.1% vs. ENRIC = 11.8%, p = 0.455, V = 0.124), 8.3% for depression (HADS Depression: TAU = 10.5% vs. ENRIC = 5.9%, p = 0.615, V = 0.084), and 5.7% for PTSD (DTS: TAU = 5.6% vs. ENRIC = 5.9%, p = 0.967, V = 0.007). For more details, see Table 2 and Supplementary File S8.
3.4. Change in Cognitive and Emotional Outcomes over a 12 Month Period
Table 3 summarizes the means, main effects, and interaction effects of group (TAU vs. ENRIC) and time (one month vs. one year) on cognitive and emotional outcomes for patients who completed both follow-up visits (n = 24). We only found a main effect of group in the working memory index, with ENRIC patients outperforming TAU patients (p = 0.008, ηp2 = 0.282). We did not find any effect of group on emotional outcomes, or any effect of time or group–time interaction on cognitive and emotional outcomes. For more details, see Supplementary File S8.

Table 3.
Change in cognitive and emotional outcomes over a 12 month period (general linear model of repeated measures). Mean (SD) is reported.
3.5. Impact of Demographic and Clinical Variables on Working Memory Performance
Bivariate regressions (Table 4) show that early neurocognitive stimulation, greater cognitive reserve, and higher dose of morphine equivalents had statistically significant effects on working memory performance one month after ICU discharge. All other variables had p > 0.05 and were discarded. In the multiple regression model (Table 4), early neurocognitive stimulation and cognitive reserve, but not the dose of morphine equivalents, remained significant factors. Therefore, the final model only included early neurocognitive stimulation (B = 0.558, 95% CI: 0.15–0.97, p = 0.008) and cognitive reserve (B = 0.028, 95% CI: 0.01–0.05, p = 0.005) and explained 28.2% of the variance of the working memory index (unadjusted R2 = 0.317, F = 9.041, p = 0.001). Several properties of interest, such as normal distribution of the residuals, were checked to confirm the goodness of fit of the model.

Table 4.
Influence of demographic and clinical variables on working memory performance one month after ICU discharge.
In view of this result, we re-ran the general linear model of repeated measures for the working memory index adjusting the analysis for cognitive reserve. The results show that the effect of group was maintained (F = 7.105, p = 0.014, ηp2 = 0.253), with ENRIC patients outperforming TAU patients. No effect of time (F = 0.000, p = 0.997, ηp2 = 0.000) or group-time interaction (F = 0.360, p = 0.555, ηp2 = 0.017) was found. Cognitive reserve was significant for working memory performance (F = 8.298, p = 0.009, ηp2 = 0.283).
4. Discussion
We have demonstrated for the first time that non-immersive VR-based neurocognitive interventions can be useful solutions to mitigate certain PICS-related sequelae in critically ill patients undergoing MV. Specifically, we found that patients who received neurocognitive stimulation in the ICU had better outcomes in the working memory domain one month and one year after discharge compared to patients who received only standard ICU care. This result suggests two preliminary conclusions: first, that these types of digital therapies could have a positive impact on certain short-term cognitive outcomes in survivors of critical illness and, second, that their benefits could persist over time.
Deep sedation is one of the main barriers to early physical and occupational therapy in the ICU [47]. In our study, neurocognitive stimulation began when patients reached RASS −1 to +1 and was successfully applied during 70.2% of their time in the ICU, reflecting a wide therapeutic window. Only 13.2% of sessions were interrupted due to sudden patient indisposition, in no case related to safety reasons or adverse events (e.g., inadvertent removal of catheters or endotracheal tubes). Therefore, the present findings are consistent with those of the first PoC study in which we already demonstrated that ENRIC therapy is a safe and well-tolerated intervention [30]. However, the mean duration of the sessions [13.8 min] was shorter than expected [15–20 min], suggesting that sessions lasting 12–15 min may be more appropriate than longer ones in critically ill patients, as is also the case in a recently published study in stroke patients [48].
One of the main findings of this study is that ENRIC therapy may help improve working memory outcomes in survivors of critical illness. The neural substrate of working memory primarily involves the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex [49]. This is in line with previous findings from our group, using heart rate variability as a surrogate outcome measure, in which we already demonstrated that ENRIC therapy effectively stimulates the prefrontal regions of the brain [30]. Indeed, working memory is supported by a broader network of fronto-parietal brain regions that provide the temporary storage and manipulation of information necessary for the proper functioning of other cognitive domains, such as language understanding, learning, and reasoning [50]. Therefore, although our results do not reveal any direct impact of ENRIC therapy beyond the domain of working memory, it is conceivable that the better performance observed in this cognitive function positively influences general cognition and, in particular, memory and executive functions. Nevertheless, whether this effect is transferred to real world skills is a controversial issue that needs to be explored further [51].
Brummel et al. [21] were the first to evaluate the feasibility and safety of a combined intervention of early physical therapy and neurocognitive stimulation. However, they found no difference between the control and the experimental groups in cognitive outcomes three months after ICU discharge. The use of classic paper-and-pencil neuropsychological exercises in the intervention of Brummel et al. may help explain their different results in comparison with those of ENRIC therapy. It is possible that VR environments and Kinect® technology offer advantages in terms of motivation and engagement with neurocognitive stimulation. Another explanation could be that we have used a broader neuropsychological battery than the one used in the study by Brummel et al., allowing us to detect subtler differences in cognitive outcomes [8].
Cognitive reserve has been identified as a protective factor against cognitive decline in several studies in patients with neurocognitive and mental health disorders [52,53,54]. In our study, along with the significant impact of early neurocognitive stimulation, greater cognitive reserve was also associated with better working memory outcomes in survivors of critical illness. In contrast, we found no impact of age, gender, and duration of MV [55,56]. Patients in our study had a shorter duration of delirium than patients in other cohorts [6,10]; perhaps for this reason we found no relationship between this variable and cognitive performance.
Unlike other studies that found reduced levels of anxiety and depression following VR-based emotional interventions [26,27,28,29], we found no significant differences in emotional outcomes between the stimulated and non-stimulated groups. However, at one-month follow-up, 50% fewer patients in the ENRIC group experienced pathological levels of non-specific anxiety (11.8% vs. 21.1%) and depression (5.9% vs. 10.5%) compared with patients who received only standard ICU care. This difference, although not statistically significant, is clinically relevant and should be borne in mind. Surprisingly, patients who received early neurocognitive stimulation showed a trend towards a worsening of depressive symptoms at one-year follow-up. The longer hospital stay and discharge destination in this subgroup of patients, both probably related to a slower functional recovery or to other variables not considered in our study (e.g., ICU acquired weakness), may help explain this result [5,14].
In our study, the one-year follow-up is limited to a small number of patients at a single center, and therefore the results related to these data should be interpreted with caution. It is also worth mentioning that the research staff was not blinded to group assignment and that the same neuropsychologists who administered the neurocognitive stimulation also assessed its impact on cognitive and emotional outcomes at the two follow-up visits. However, our results are strengthened by the study’s RCT design, the inclusion of both medical and surgical patients, and the daily monitoring of delirium and medication. Moreover, the wide therapeutic window of the intervention, its specific design and tailoring to the ICU environment and MV patient, and the use of a comprehensive neuropsychological battery all add value to our results. Nevertheless, the use of a broader psychopathological assessment might have increased our sensitivity to detect subtler differences in patients’ emotional state. Other issues that should be addressed in future trials are the personalization of the intervention to the patient’s health status (including the frequency of the sessions and the type, duration, and difficulty of cognitive exercises) and its impact on functionality and quality of life.
In line with the challenges and perspectives in the field of e-health and m-health, our results support the introduction of new technologies based on the principles of cognitive rehabilitation as a complement to standard ICU care. These novel interventions should always focus on personalized management and patient-centered decision making, empowering patients to be active players in their recovery process.
5. Conclusions
Non-immersive VR-based early neurocognitive interventions can be a useful solution to improve short- and long-term working memory outcomes in ICU survivors. Further studies with larger samples are now needed to corroborate these results in a definitive efficacy trial. If confirmed, ENRIC therapy and other VR-based technological tools may become cost-effective solutions for hospitals and, in particular, ICUs, as they could help reduce the medical and financial costs associated with PICS. The present findings can foster the introduction of digital therapies as adjuvant, feasible, and safe interventional tools in the ICU. This is of particular interest in the context of the paradigm shift from face-to-face healthcare to telemedicine and telerehabilitation, as well as in the adoption of new technological environments highly adaptable to patients’ needs.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jpm11121260/s1, File S1: ENRIC Technology Features, File S2: ENRIC Platform Video, File S3: Participants and Procedure, File S4: Cognitive Assessment, File S5: Data Preprocessing, File S6: Sample Characteristics, File S7: Characteristics of Early Neurocognitive Stimulation, File S8: Cognitive and Emotional Outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J., A.O., L.B., J.L.-A., and S.F.-G.; data curation, G.N.-V., G.G., C.d.H., L.S., D.H., R.B., and S.F.-G.; formal analysis, G.N.-V., C.d.H., D.H., R.B., J.L.-A., and S.F.-G.; funding acquisition, G.N.-V., L.B., and S.F.-G.; investigation, G.N.-V., G.G., C.d.H., D.H., R.B., and S.F.-G.; methodology, C.d.H., M.J., L.B., J.L.-A., and S.F.-G.; project administration, S.F.-G.; resources, M.J., L.S., A.O., and L.B.; supervision, A.O., L.B., and J.L.-A.; writing—original draft, G.N.-V., J.L.-A., and S.F.-G.; writing—review and editing, G.N.-V., G.G., C.d.H., M.J., L.S., D.H., R.B., A.O., L.B., J.L.-A., and S.F.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by NeuroContent 2.0 (Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Gobierno de España, grant number IPT-300000-2010-30), Fundació La Marató de TV3 (Corporació Catalana de Mitjans Audiovisuals, Generalitat de Catalunya, grant number 181/U/2011), AGAUR-Producte 2019 (Departament d’Empresa i Coneixement, Generalitat de Catalunya, grant number 2019PROD00108), and the European Regional Development Fund (European Comission). L.S. was supported by PERIS program from the Health Department of la Generalitat de Catalunya. The funders played no role in study design, data collection and analysis, manuscript preparation, or decision to publish.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Parc Taulí University Hospital (protocol code 2013/067 and date of approval 19 December 2013).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Marc Turon for his help in carrying out the study, Carles Forné for his contribution to the statistical analysis, and Michael Maudsley for his support in editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
G.N.-V., M.J., L.B., J.L.-A., S.F.-G., and Marc Turon are authors of the Early Neurocognitive Rehabilitation in Intensive Care (ENRIC) platform (source code protected under copyright and duly registered at SafeTheProof with registration number 960-951, 848, 947, 944-940). C.d.H., L.S., L.B., J.L.-A., and José Aquino-Esperanza have been named in a provisional European patent application number EP19383116 owned by Corporació Sanitària Parc Taulí: “A device and method for respiratory monitoring in mechanically ventilated patients”. L.B. is inventor of a U.S. patent owned by Corporació Sanitària Parc Taulí: “Method and system for managed related patient parameters provided by a monitoring device”, U.S. Patent No. 12/538,940. L.B. owns stock options of BetterCare SL, a research and development spinoff of Corporació Sanitària Parc Taulí. The rest of the authors declare no potential conflict of interests in connection with the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- Inoue, S.; Hatakeyama, J.; Kondo, Y.; Hifumi, T.; Sakuramoto, H.; Kawasaki, T.; Taito, S.; Nakamura, K.; Unoki, T.; Kawai, Y.; et al. Post-intensive care syndrome: Its pathophysiology, prevention, and future directions. Acute Med. Surg. 2019, 6, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.C.; Mitchell, N.; Hopkins, R.O. Cognitive Functioning, Mental Health, and Quality of Life in ICU Survivors: An Overview. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 38, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashyna, T.J.; Ely, E.W.; Smith, D.M.; Langa, K.M. Long-term Cognitive Impairment and Functional Disability Among Survivors of Severe Sepsis. JAMA 2010, 304, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herridge, M.S.; Tansey, C.M.; Matté, A.; Tomlinson, G.; Diaz-Granados, N.; Cooper, A.; Guest, C.B.; Mazer, C.D.; Mehta, S.; Stewart, T.E.; et al. Functional Disability 5 Years after Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, R.; Girard, T. Medical and Economic Implications of Cognitive and Psychiatric Disability of Survivorship. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandharipande, P.P.; Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Morandi, A.; Thompson, J.L.; Pun, B.T.; Brummel, N.E.; Hughes, C.G.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Shintani, A.K.; et al. Long-Term Cognitive Impairment after Critical Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulte, P.J.; Warner, D.O.; Martin, D.P.; Deljou, A.; Mielke, M.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Weingarten, T.N.; Warner, M.A.; Rabinstein, A.A.; et al. Association Between Critical Care Admissions and Cognitive Trajectories in Older Adults. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gonzalo, S.; Navarra-Ventura, G.; Bacardit, N.; Gomà Fernández, G.; de Haro, C.; Subirà, C.; López-Aguilar, J.; Magrans, R.; Sarlabous, L.; Aquino Esperanza, J.; et al. Cognitive phenotypes 1 month after ICU discharge in mechanically ventilated patients: A prospective observational cohort study. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, Y. Cognitive reserve. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, T.D.; Jackson, J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Pun, B.T.; Thompson, J.L.; Shintani, A.K.; Gordon, S.M.; Canonico, A.E.; Dittus, R.S.; Bernard, G.R.; et al. Delirium as a predictor of long-term cognitive impairment in survivors of critical illness. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, M.; Fernández-Gonzalo, S.; de Haro, C.; Magrans, R.; López-Aguilar, J.; Blanch, L. Mechanisms involved in brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: Implications and therapeutics. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gonzalo, S.; Turon, M.; De Haro, C.; López-Aguilar, J.; Jodar, M.; Blanch, L. Do sedation and analgesia contribute to long-term cognitive dysfunction in critical care survivors? Med. Intensiva 2018, 42, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Girard, T.D.; Brummel, N.E.; Thompson, J.L.; Hughes, C.G.; Pun, B.T.; Vasilevskis, E.E.; Morandi, A.; Shintani, A.K.; et al. Depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN-ICU study: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Kang, J.; Jeong, Y.J. Risk factors for post–intensive care syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aust. Crit. Care 2020, 33, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarra-Ventura, G.; López-Aguilar, J.; Blanch, L.; Fernández-Gonzalo, S. Characterization and management of cognitive and emotional alterations in COVID-19 critically ill patients after ICU discharge. Med. Intensiva 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaiceta, G.M.; Brochard, L.; Dos Santos, C.C.; Fernández, R.; Georgopoulos, D.; Girard, T.; Jubran, A.; López-Aguilar, J.; Mancebo, J.; Pelosi, P.; et al. The central nervous system during lung injury and mechanical ventilation: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 127, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Ely, E.W.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Patel, M.B. The ABCDEF Bundle in Critical Care. Crit. Care Clin. 2017, 33, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barr, J.; Fraser, G.L.; Puntillo, K.; Ely, E.W.; Gélinas, C.; Dasta, J.F.; Davidson, J.E.; Devlin, J.W.; Kress, J.P.; Joffe, A.M.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Pain, Agitation, and Delirium in Adult Patients in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 263–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.E.; Goad, A.; Thompson, C.; Taylor, K.; Harry, B.; Passmore, L.; Ross, A.; Anderson, L.; Baker, S.; Sanchez, M.; et al. Early intensive care unit mobility therapy in the treatment of acute respiratory failure. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costigan, F.A.; Duffett, M.; Harris, J.E.; Baptiste, S.; Kho, M.E. Occupational Therapy in the ICU. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, e1014–e1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummel, N.E.; Girard, T.D.; Ely, E.W.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Morandi, A.; Hughes, C.G.; Graves, A.J.; Shintani, A.; Murphy, E.; Work, B.; et al. Feasibility and safety of early combined cognitive and physical therapy for critically ill medical and surgical patients: The Activity and Cognitive Therapy in ICU (ACT-ICU) trial. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McIlroy, P.A.; King, R.S.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; Tabah, A.; Ramanan, M. The Effect of ICU Diaries on Psychological Outcomes and Quality of Life of Survivors of Critical Illness and Their Relatives. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, N.A.; Anderson, D.C.; Kesecioglu, J. ICU design in 2050: Looking into the crystal ball! Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.; Wall, K.J.; Thangavelu, K.; Craven, L.; Ward, E.; Dissanayaka, N.N. A systematic review of the use of virtual reality and its effects on cognition in individuals with neurocognitive disorders. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2019, 5, 834–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.; Reeve, S.; Robinson, A.; Ehlers, A.; Clark, D.; Spanlang, B.; Slater, M. Virtual reality in the assessment, understanding, and treatment of mental health disorders. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, G.J.; Kapil, S.; Cole, S.P.; Rodriguez, S. Virtual reality use in adult ICU to mitigate anxiety for a patient on V-V ECMO. J. Clin. Anesth. 2019, 55, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.G.; Rodriguez, R.A.; Gonzalez, M.; Bernardy, M.; Peña, R.; Beck, W.; Patterson, D.R.; Meyer, W.J. Immersive Virtual Reality as an Adjunctive Non-opioid Analgesic for Pre-dominantly Latin American Children with Large Severe Burn Wounds During Burn Wound Cleaning in the Intensive Care Unit: A Pilot Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerber, S.M.; Jeitziner, M.-M.; Knobel, S.E.J.; Mosimann, U.P.; Müri, R.M.; Jakob, S.M.; Nef, T. Perception and Performance on a Virtual Reality Cognitive Stimulation for Use in the Intensive Care Unit: A Non-randomized Trial in Critically Ill Patients. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.; Jones, G. Feasibility and Potential Benefits of Immersive Virtual Reality in the Intensive Care Unit. ICU Manag. Pract. 2020, 20, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Turon, M.; Fernandez-Gonzalo, S.; Jodar, M.; Gomà, G.; Montanya, J.; Hernando, D.; Bailón, R.; de Haro, C.; Gomez-Simon, V.; Lopez-Aguilar, J.; et al. Feasibility and safety of virtual-reality-based early neurocognitive stimulation in critically ill patients. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutron, I.; Moher, D.; Altman, D.G.; Schulz, K.F.; Ravaud, P. Extending the CONSORT Statement to Randomized Trials of Nonpharmacologic Treatment: Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldridge, S.M.; Chan, C.L.; Campbell, M.J.; Bond, C.M.; Hopewell, S.; Thabane, L.; Lancaster, G.A.; PAFS Consensus Group. CONSORT 2010 statement: Extension to randomised pilot and feasibility trials. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2016, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cocks, K.; Torgerson, D.J. Sample size calculations for pilot randomized trials: A confidence interval approach. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Gonzalo, S.; Turon, M.; Jodar, M.; Pousa, E.; Hernandez Rambla, C.; García, R.; Palao, D. A new computerized cognitive and social cognition training specifically designed for patients with schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder in early stages of illness: A pilot study. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, Y.; Yee, M.K.; Ho, V.T.; Cicerone, K.D. Computerized Cognitive Rehabilitation of Attention and Executive Function in Acquired Brain Injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2016, 31, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorm, A.F. The Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE): A review. Int. Psychogeriatrics 2004, 16, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haro, C.; Magrans, R.; López-Aguilar, J.; Montanyà, J.; Lena, E.; Subirà, C.; Fernandez-Gonzalo, S.; Gomà, G.; Fernández, R.; Albaiceta, G.M.; et al. Effects of sedatives and opioids on trigger and cycling asynchronies throughout mechanical ventilation: An observational study in a large dataset from critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanch, L.; Sales, B.; Montanya, J.; Lucangelo, U.; Garcia-Esquirol, O.; Villagra, A.; Chacon, E.; Estruga, A.; Borelli, M.; Burgueño, M.J.; et al. Validation of the Better Care® system to detect ineffective efforts during expiration in mechanically ventilated patients: A pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2012, 38, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 3rd Edition: WAIS-III; TEA Ediciones: Barcelona, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Memory Scale, 3rd Edition: WMS-III; TEA Ediciones: Barcelona, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, E.; Sherman, E.M.S.; Spreen, O. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Tests: Administration, Norms, and Commentary, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lezak, M.D.; Howieson, D.B.; Bigler, E.D.; Daniel, T. Neuropsychological Assessment, 5th ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gomar, J.J.; Ortiz-Gil, J.; McKenna, P.J.; Salvador, R.; Sans-Sansa, B.; Sarró, S.; Guerrero, A.; Pomarol-Clotet, E. Validation of the Word Accentuation Test (TAP) as a means of estimating premorbid IQ in Spanish speakers. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 128, 175–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, J.R.T.; Tharwani, H.M.; Connor, K.M. Davidson Trauma Scale (DTS): Normative scores in the general population and effect sizes in placebo-controlled SSRI trials. Depress. Anxiety 2002, 15, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, L.; Quintel, M. Lung–brain cross talk in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanni, J.M.; Korupolu, R.; Fan, E.; Pradhan, P.; Janjua, K.; Palmer, J.B.; Brower, R.G.; Needham, D.M. Rehabilitation therapy and outcomes in acute respiratory failure: An observational pilot project. J. Crit. Care 2010, 25, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.R.; Ward, N.S.; Brander, F.; Maier, M.; Kelly, K.; Verschure, P.F.M.J. Relationship between intensity and recovery in post-stroke rehabilitation: A retrospective analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.J.; Abd Hamid, A.I.; Abdullah, J.M. Working Memory from the Psychological and Neurosciences Perspectives: A Review. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baddeley, A. Working memory. Science 1992, 255, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Santos, A.C.; Moreira, C.S.; Magalhães, R.; Magalhães, C.; Pereira, D.R.; Leite, J.; Carvalho, S.; Sampaio, A. Reviewing working memory training gains in healthy older adults: A meta-analytic review of transfer for cognitive outcomes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 103, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.J.; Weaver, L.K.; Hopkins, R.O. Cognitive sequelae in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with and without recall of the intensive care unit. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2007, 13, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tow, A.; Holtzer, R.; Wang, C.; Sharan, A.; Kim, S.J.; Gladstein, A.; Blum, Y.; Verghese, J. Cognitive Reserve and Postoperative Delirium in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colangeli, S.; Boccia, M.; Verde, P.; Guariglia, P.; Bianchini, F.; Piccardi, L. Cognitive Reserve in Healthy Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dementiasr 2016, 31, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Khan, A.; Afridi, M.; Saeed, A.; Jan, A.; Amjad, N. Frequency and predictors of cognitive decline in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2014, 24, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hope, A.A.; Morrison, R.S.; Du, Q.; Wallenstein, S.; Nelson, J.E. Risk Factors for Long-Term Brain Dysfunction after Chronic Critical Illness. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).