Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Quality (subjectively assessed and divided into “good” or “poor” sleep);
- Duration (time slept over 24 h);
- Efficacy (sleep latency, wake after sleep onset);
- Timing (chronotype—morning vs. evening type);
- Alertness vs. sleepiness.
2. Materials and Methods
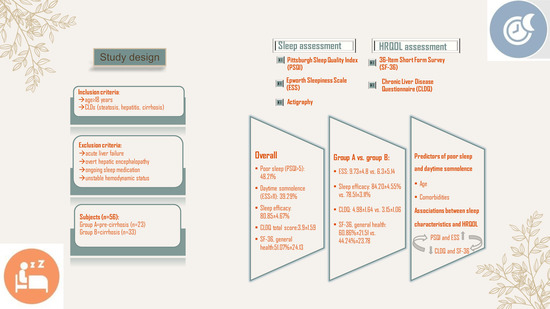
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Sleep Health Assessment
2.4. HRQOL Assessment
2.5. Ethics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Background Patients’ Caracteristics
- Group 1: 23 patients with pre-cirrhosis (patients with steatosis and chronic hepatitis with Fibro Scan results that revealed no/mild/moderate fibrosis (F ≤ 3);
- Group 2: 33 patients with cirrhosis (F = 4).
3.2. Sleep Assessment–Patients’ Characteristics
3.3. Predictors of Poor Sleep and Daytime Sleepiness
3.4. HRQOL Assessment—Patients’ Characteristics
3.5. Associations between Sleep Characteristics and HRQOL among Enrolled Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haraldstad, K.; Wahl, A.; Andenæs, R.; Andersen, J.R.; Andersen, M.H.; Beisland, E.; Borge, C.R.; Engebretsen, E.; Eisemann, M.; Halvorsrud, L.; et al. A systematic review of quality of life research in medicine and health sciences. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Megari, K. Quality of life in chronic disease patients. Health Psychol. Res. 2013, 1, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, N. Dictionary of Quality of Life and Health Outcomes Measurement; International Society for Quality of Life Research: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Katulka, E.K.; Berube, F.R.; D’Agata, M.N. Dreaming of better health: Quantifying the many dimensions of sleep. Sleep 2019, 43, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J. Sleep Health: Can We Define It? Does It Matter? Sleep 2014, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, A.M.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotogea, O.-M.; Ilie, M.; Bungau, S.; Chiotoroiu, A.; Stanescu, A.; Diaconu, C. Comprehensive Overview of Sleep Disorders in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formentin, C.; Garrido, M.; Montagnese, S. Assessment and Management of Sleep Disturbance in Cirrhosis. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2018, 17, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.M.; Malhotra, A.M.; Kaltsakas, G. Sleep disorder in patients with chronic liver disease: A narrative review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12 (Suppl. S2), S248–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umbro, I.; Fabiani, V.; Fabiani, M.; Angelico, F.; Del Ben, M. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and obstructive sleep apnea. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabril, M.; Jackson, M.; Gotur, R.; Weber, R.; Orman, E.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Most Individuals with Advanced Cirrhosis Have Sleep Disturbances, Which Are Associated with Poor Quality of Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1271–1278.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. A New Method for Measuring Daytime Sleepiness: The Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosca, L.E.; Todea, A.A.; Rusu, A. Reliability and validity of the Romanian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38 (Suppl. S55), 3924. [Google Scholar]
- Blanariu, G.-E.G.; Ștefănescu, G.; Trifan, A.V.; Moscalu, M.; Dimofte, M.-G.; Ștefănescu, C.; Drug, V.L.; Afrăsânie, V.-A.; Ciocoiu, M. Sleep Impairment and Psychological Distress among Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease—Beyond the Obvious. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Middleton, B.; Skene, D.; Morgan, M.Y. Night-time sleep disturbance does not correlate with neuropsychiatric impairment in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2009, 29, 1372–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, J.; Harper, R.; Jones, N.M.; O’Cathain, A.; Thomas, K.J.; Usherwood, T.; Westlake, L. Validating the SF-36 health survey questionnaire: New outcome measure for primary care. BMJ 1992, 305, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taru, V.; Indre, M.G.; Ignat, M.D.; Forgione, A.; Racs, T.; Olar, B.A.; Farcau, O.; Chereches, R.; Stefanescu, H.; Procopet, B. Validation and Performance of Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (CLDQ-RO) in the Romanian Population. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2021, 30, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research in-volving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Córdoba, J.; Cabrera, J.; Lataif, L.; Penev, P.; Zee, P.; Blei, A.T. High prevalence of sleep disturbance in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998, 27, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Jahdali, H.; Al Enezi, A.; Anwar, A.E.; AL-Harbi, A.; Baharoon, S.; Aljumah, A.; Shimemeri, A.; Abudallah, K. Preva-lence of insomnia and sleep patterns among liver cirrhosis patients. J. Circadian Rhythm. 2014, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.E.; Al-Jahdali, F.; Ahmed, A.E.; Shirbini, N.; Salim, B.; Ali, Y.Z.; Abdulrahman, A.; Khan, M.; Khaleid, A.; Hamdan, A.-J. Symptoms of Daytime Sleepiness and Sleep Apnea in Liver Cirrhosis Patients. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, J.; Dhiman, R.K.; Khatri, A.; Thumburu, K.K.; Grover, S.; Duseja, A.; Chawla, Y. Correlation between degree and quality of sleep disturbance and the level of neuropsychiatric impairment in patients with liver cirrhosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rui, M.; Schiff, S.; Aprile, D.; Angeli, P.; Bombonato, G.; Bolognesi, M.; Sacerdoti, D.; Gatta, A.; Merkel, C.; Amodio, P.; et al. Excessive daytime sleepiness and hepatic encephalopathy: It is worth asking. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostacci, B.; Ferlisi, M.; Antognini, A.B.; Sama, C.; Morelli, C.; Mondini, S.; Cirignotta, F. Sleep Disturbance and Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Case Control Study. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 29, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnese, S.; Middleton, B.; Mani, A.R.; Skene, D.J.; Morgan, M.Y. Sleep and circadian abnormalities in patients with cir-rhosis: Features of delayed sleep phase syndrome? Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, A.; Escheik, C.; Gerber, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Quality of Life in Cirrhosis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2012, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Demographic and Clinical Data | All Patients (n = 56) | Pre-Cirrhosis (n =23) | Cirrhosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 33) | Compensated (n = 11) | Decompensated (n = 22) | |||
| Age (mean ± SD) | 59.75 ± 10.06 | 55.96 ± 11.50 * | 62.39 ± 8.05 * | 59.27 ± 7.24 | 63.95 ± 8.13 |
| Gender (males), n (%) | 41 (73.20%) | 16 (69.60%) | 25 (75.80%) | 8 (72.70%) | 17 (77.30%) |
| Etiology, n (%) | |||||
| Alcoholic | 21 (37.50%) | 7 (30.40%) | 14 (42.40%) | 5 (45.40%) | 9 (40.90%) |
| Viral hepatitis | 17 (30.40%) | 9 (39.10%) | 8 (24.20%) | 4 (36.30%) | 4 (18.20%) |
| Alcoholic + Viral Hepatitis | 11 (19.60%) | 2 (8.70%) | 9 (27.30%) | 2 (18.20%) | 7 (31.80%) |
| NAFLD | 7 (12.50%) | 5 (21.70%) | 2 (6.10%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (9.10%) |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 17 (30.40%) | 6 (26.10%) | 11 (33.30%) | 2 (18.20%) | 9 (40.90%) |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 19 (33.90%) | 9 (39.10%) | 10 (30.30%) | 2 (18.20%) | 8 (36.40%) |
| Sleep Parameters | All Patients (n = 56) | Pre-Cirrhosis (n = 23) | Cirrhosis (n = 33) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSQI (mean ± SD) | 6.50 ± 3.90 | 5.65 ± 3.57 | 7.09 ± 4.06 | 0.177 |
| Good sleepers (≤5), n (%) Poor sleepers (>5), n (%) | 29 (51.79%) | 14 (60.87%) | 15 (45.45%) | 0.194 |
| 27 (48.21%) | 9 (39.13%) | 18 (54.55%) | ||
| ESS (mean ± SD) | 8.32 ± 5.18 | 6.30 ± 5.14 | 9.73 ± 4.80 | 0.014 * |
| ≥11, n (%) <11, n (%) | 22 (39.29%) | 7 (30.43%) | 15 (45.45%) | 0.197 |
| 34 (60.71%) | 16 (69.57%) | 18 (54.55%) | ||
| Bed time (hour: minutes ± SD) | 22:26 ± 0:48 | 22:09 ± 0:47 | 22:38 ± 0:45 | 0.025 * |
| Get-up time (hour: minutes ± SD) | 7:46 ± 0:55 | 7:04 ± 0:37 | 8:15 ± 0:45 | <0.001 * |
| Time in bed (hour: minutes ± SD) | 9:19 ± 0:51 | 8:54 ± 0:47 | 9:36 ± 0:46 | 0.002 * |
| Total sleep time (hour: minutes ± SD) | 7:36 ± 0:40 | 7:34 ± 0:40 | 7:38 ± 0:40 | 0.752 |
| Onset latency (minutes ± SD) | 19.43 ± 8.27 | 17.91 ± 9.09 | 20.49 ± 7.61 | 0.253 |
| Sleep efficacy (% ± SD) | 80.85 ± 4.67 | 84.20 ± 4.55 | 78.51 ± 3.11 | <0.001 * |
| WASO (minutes ± SD) | 38.69 ± 8.22 | 38.74 ± 9.60 | 38.65 ± 7.27 | 0.966 |
| Number of awakenings per night (mean ± SD) | 35.42 ± 12.33 | 28.18 ± 11.88 | 40.47 ± 10.01 | <0.001 * |
| Sleep Parameters | Compensated (n = 11) | Decompensated (n = 22) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSQI (mean ± SD) | 4 ± 2 | 8.64± 3.97 | 0.001 * |
| Good sleepers (≤5), n (%) | 9 (81.82%) | 6 (27.27%) | 0.004 ** |
| Poor sleepers (>5), n (%) | 2 (18.18%) | 16 (72.73%) | |
| ESS (mean ± SD) | 6 ± 3 | 11.59 ± 4.46 | 0.001 * |
| ≥11, n (%) | 1 (9.10%) | 14 (63.64%) | 0.004 ** |
| <11, n (%) | 10 (90.90%) | 8 (36.36%) | |
| Bedtime (hour: minutes ± SD) | 22:35 ± 0:45 | 22:40 ± 0:45 | 0.811 |
| Get-up time (hour: minutes ± SD) | 8:05 ± 0:39 | 8:20 ± 0:48 | 0.391 |
| Time in bed (hour: minutes ± SD) | 9:29 ± 0:40 | 9:40 ± 0:50 | 0.544 |
| Total sleep time (hour: minutes ± SD) | 7:46 ± 0:38 | 7:34 ± 0:42 | 0.421 |
| Onset latency (minutes ± SD) | 18.34 ± 5.83 | 21.57 ± 8.26 | 0.256 |
| Sleep efficacy (%± SD) | 80.82 ± 3.33 | 77.36 ± 2.29 | 0.001 * |
| WASO (minutes) | 37.48 ± 7.11 | 39.23 ± 7.44 | 0.524 |
| Number of awakenings per night (mean ± SD) | 31.55 ± 9.60 | 44.93 ± 6.80 | <0.001 * |
| Logistic Regression Analysis for Predictors of Poor Sleep (PSQI > 5) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Regression | Multiple Regression | |||||
| Variables | Poor Sleepers (n = 27) | Good Sleepers (n = 29) | p-Value | OR [95% CI] | β Coef. | p-Value |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 66.59 ± 7.02 | 53.38 ± 8.13 | <0.001 * | 0.828 [0.725–0.945] | −0.189 | 0.003 *** |
| Gender (males), n (%) | 19 (70.40%) | 22 (75.90%) | 0.765 | - | - | - |
| Etiology, n (%) | 0.027 ** | |||||
| Alcoholic | 10 (37%) | 11 (37.90%) | REF | |||
| Viral Hepatitis | 4 (14.80%) | 13 (44.80%) | 2.687 [0.096−75.017] | 0.988 | 0.561 | |
| Alcoholic+Viral Hepatitis | 7 (25.90%) | 4 (13.80%) | 3.913 [0.156–98.37] | 1.364 | 0.407 | |
| NAFLD | 6 (22.20%) | 1 (3.40) | 3.024 [0.101–90.437] | 1.107 | 0.523 | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 15 (55.60%) | 2 (6.90%) | <0.001 ** | 4.531 [0.458–42.354] | 1.511 | 0.185 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 16 (59.30%) | 3 (10.30%) | <0.001 ** | 0.930 [0.103–8.419] | −0.073 | 0.948 |
| Logistic Regression Analysis for Predictors of Daytime Somnolence (ESS ≥ 11) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple | Multiple | |||||
| Variables | ESS ≥ 11 (n = 22) | ESS < 11 (n = 34) | p-Value | OR [95% CI] | β Coef. | p-Value |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 68.32 ± 5.28 | 54.21 ± 8.40 | <0.001 * | 0.776 [0.641–0.940] | −0.254 | 0.009 *** |
| Gender (males), n (%) | 15 (68.20%) | 26 (76.50%) | 0.351 | - | - | - |
| Etiology, n (%) | 0.059 | |||||
| Alcoholic | 8 (36.20%) | 13 (38.20%) | - | - | - | |
| Viral hepatitis | 3 (13.60%) | 14 (41.20%) | - | - | - | |
| Alcoholic+Viral Hepatitis | 6 (27.30%) | 5 (14.70%) | - | - | - | |
| NAFLD | 5 (22.70%) | 2 (5.90%) | - | - | - | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 15 (68.20%) | 2 (5.90%) | <0.001 ** | 13,311 [1.253–141.4] | 2.589 | 0.032 *** |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) | 16 (59.30%) | 3 (10.30%) | <0.001 ** | 2.525 [0.321–19.86] | 0.926 | 0.379 |
| HRQOL Parameters | All Patients (n = 56) | Pre-Cirrhosis (n = 23) | Cirrhosis (n = 33) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDQ (mean ± SD) | ||||
| Total score | 3.90 ± 1.59 | 4.98 ± 1.64 | 3.15 ± 1.06 | <0.001 * |
| Abdominal symptoms | 3.55 ± 1.66 | 4.67 ± 1.71 | 2.77 ± 1.10 | <0.001 * |
| Fatigue | 3.86 ± 1.70 | 4.96 ± 1.81 | 3.09 ± 1.10 | <0.001 * |
| Systemic symptoms | 3.93 ± 1.76 | 5.21 ± 1.81 | 3.04 ± 1.03 | <0.001 * |
| Activity | 4.03 ± 1.81 | 5.27 ± 1.71 | 3.17 ± 1.33 | <0.001 * |
| Emotional function | 4.35 ± 1.53 | 5.18 ± 1.56 | 3.78 ± 1.24 | <0.001 * |
| Worry | 3.70 ± 1.71 | 4.60 ± 1.86 | 3.07 ± 1.28 | 0.001 * |
| SF-36 (%, mean ± SD) | ||||
| Physical functioning | 74.10 ± 21.76 | 85.00 ± 21.05 | 66.51 ± 19.10 | 0.001 * |
| Role limitations due to physical health problems | 65.71 ± 26.10 | 75.00 ± 23.83 | 59.24 ± 25.98 | 0.025 * |
| Role limitations due to emotional problems | 61.91 ± 23.30 | 66.67 ± 24.63 | 58.59 ± 22.11 | 0.205 |
| Energy fatigue | 61.16 ± 23.58 | 65.21 ± 21.76 | 58.33 ± 24.70 | 0.287 |
| Emotional wellbeing | 67.76 ± 15.46 | 70.26 ± 15.10 | 66.03 ± 15.70 | 0.318 |
| Social functioning | 73.97 ± 21.37 | 79.34 ± 20.50 | 70.22 ± 21.46 | 0.117 |
| Pain | 72.63 ± 19.50 | 82.50 ± 18.01 | 65.75 ± 17.67 | 0.001 * |
| General health | 51.07 ± 24.13 | 60.86 ± 21.51 | 44.24 ± 23.78 | 0.010 * |
| HRQOL Parameters | Compensated (n = 11) | Decompensated (n = 22) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CLDQ (mean ± SD) | |||
| Total score | 4.19 ± 0.89 | 2.63 ± 0.69 | <0.001 * |
| Abdominal symptoms | 3.87 ± 1.03 | 2.22 ± 0.63 | <0.001 * |
| Fatigue | 4.07 ± 1.09 | 2.60 ± 0.73 | <0.001 * |
| Systemic symptoms | 3.91 ± 0.92 | 2.61 ± 0.79 | <0.001 * |
| Activity | 4.35 ± 1.09 | 2.58 ± 1.01 | <0.001 * |
| Emotional function | 4.89 ± 1.14 | 3.22 ± 0.87 | <0.001 * |
| Worry | 4.07 ± 1.20 | 2.57 ± 1.01 | 0.001 * |
| SF-36 (%, mean ± SD) | |||
| Physical functioning | 84.09 ± 7.68 | 57.72 ± 16.88 | <0.001 * |
| Role limitations due to physical health problems | 84.09 ± 12.61 | 46.81 ± 21.63 | <0.001 * |
| Role limitations due to emotional problems | 75.78 ± 15.55 | 49.99 ± 19.94 | 0.001 * |
| Energy fatigue | 76.36 ± 14.33 | 49.31 ± 24.01 | 0.002 * |
| Emotional wellbeing | 78.81 ± 12.71 | 59.63 ± 13.05 | <0.001 * |
| Social functioning | 90.22 ± 10.33 | 60.22 ± 18.35 | <0.001 * |
| Pain | 83.40 ± 11.02 | 56.93 ± 13.15 | <0.001 * |
| General health | 61.36 ± 18.31 | 35.68 ± 21.72 | 0.001 * |
| HRQOL | PSQI | ESS | Sleep Efficacy | Number of Awakenings/Nights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLDQ (mean ± SD) | ||||
| Total score | −0.671 | −0.729 | 0.785 | −0.769 |
| Abdominal symptoms | −0.608 | −0.671 | 0.724 | −0.735 |
| Fatigue | −0.670 | −0.711 | 0.763 | −0.768 |
| Systemic symptoms | −0.644 | −0.705 | 0.746 | −0.741 |
| Activity | −0.691 | −0.751 | 0.819 | −0.753 |
| Emotional function | −0.571 | −0.625 | 0.688 | −0.674 |
| Worry | −0.597 | −0.650 | 0.689 | −0.665 |
| SF-36 (mean %) | ||||
| Physical functioning | −0.804 | −0.809 | 0.711 | −0.693 |
| Role limitations due to physical health problems | −0.741 | −0.825 | 0.634 | −0.732 |
| Role limitations due to emotional problems | −0.653 | −0.669 | 0.566 | −0.565 |
| Energy fatigue | −0.667 | −0.632 | 0.488 | −0.502 |
| Emotional wellbeing | −0.648 | −0.595 | 0.517 | −0.519 |
| Social functioning | −0.735 | −0.732 | 0.637 | −0.63 |
| Pain | −0.735 | −0.752 | 0.716 | −0.612 |
| General health | −0.690 | −0.682 | 0.585 | −0.635 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plotogea, O.-M.; Gheorghe, G.; Stan-Ilie, M.; Constantinescu, G.; Bacalbasa, N.; Bungau, S.; Diaconu, C.C. Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121387
Plotogea O-M, Gheorghe G, Stan-Ilie M, Constantinescu G, Bacalbasa N, Bungau S, Diaconu CC. Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121387
Chicago/Turabian StylePlotogea, Oana-Mihaela, Gina Gheorghe, Madalina Stan-Ilie, Gabriel Constantinescu, Nicolae Bacalbasa, Simona Bungau, and Camelia Cristina Diaconu. 2021. "Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121387
APA StylePlotogea, O.-M., Gheorghe, G., Stan-Ilie, M., Constantinescu, G., Bacalbasa, N., Bungau, S., & Diaconu, C. C. (2021). Assessment of Sleep among Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: Association with Quality of Life. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121387