An Association Rule Mining Analysis of Lifestyle Behavioral Risk Factors in Cancer Survivors with High Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Demographic and Disease Characteristics
2.2.2. Anthropometric Characteristics
2.2.3. Lifestyle Risk Behaviors
2.2.4. Cardiovascular Risk
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.2.6. Association Rule Mining
3. Results
3.1. Predictors of Lifestyle Risk Behaviors That Are Associated with High ASCVD Risk
3.2. Result of Association Rule Mining
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Information Center. Five Year Relative Survival Rate of Patients with Cancer in Korea 2017. Available online: https://www.cancer.go.kr (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Ning, Y.; Shen, Q.; Herrick, K.; Mikkelsen, R.; Anscher, M.; Houlihan, R.; Lapane, K. Abstract LB-339: Cause of Death in Cancer Survivors. In Proceedings of the AACR 103rd Annual Meeting 2012, Chicago, IL, USA, 31 March–4 April 2012; Volume 72 (Suppl. 8). Abstract nr LB-339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, A.C.; Liu, Q.; Neglia, J.P.; Wasilewski, K.; Leisenring, W.; Armstrong, G.T.; Robison, L.L.; Yasui, Y. Cause-specific late mortality among 5-year survivors of childhood cancer: The Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.; Xu, L.; Bhatia, S.; Cooper, R.; Brar, S.; Wong, F.L.; Armenian, S.H. Cardiovascular disease risk profiles in survivors of adolescent and young adult (AYA) cancer: The Kaiser Permanente AYA Cancer Survivors Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, P.T.; Stevens, J.; Khankari, N.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Neugut, A.I.; Gammon, M.D. Cardiovascular disease mortality among breast cancer survivors. Epidemiol. (Camb. Mass.) 2016, 27, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenian, S.H.; Xu, L.; Ky, B.; Sun, C.; Farol, L.T.; Pal, S.K.; Douglas, P.S.; Bhatia, S.; Chao, C. Cardiovascular disease among survivors of adult-onset cancer: A community-based retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, M.M.; Reulen, R.C.; Henson, K.; Kelly, J.; Cutter, D.; Levitt, G.A.; Frobisher, C.; Winter, D.L.; Hawkins, M.M.; British Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (BCCSS) Steering Group. Population-based long-term cardiac-specific mortality among 34 489 five-year survivors of childhood cancer in Great Britain. Circulation 2017, 135, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnasco, F.; Caruso, S.; Andreano, A.; Valsecchi, M.G.; Jankovic, M.; Biondi, A.; Miligi, L.; Casella, C.; Terenziani, M.; Massimino, M.; et al. Late mortality and causes of death among 5-year survivors of childhood cancer diagnosed in the period 1960–1999 and registered in the Italian Off-Therapy Registry. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 110, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, M.; Russell, R. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: Prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2011, 7, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, D.; Fallah-Rad, N.; Grenier, D.; Krahn, M.; Fang, T.; Ahmadie, R.; Walker, J.R.; Lister, D.; Arora, R.C.; Barac, I.; et al. Trastuzumab mediated cardiotoxicity in the setting of adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: A retrospective study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 117, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, E.; Jiang, H.; Ng, A.; Bashir, S.; Ahmed, S.; Tsang, R.; Sun, A.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Hodgson, D. Late cardiac toxicity after mediastinal radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma: Contributions of coronary artery and whole heart dose-volume variables to risk prediction. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giza, D.E.; Iliescu, G.; Hassan, S.; Marmagkiolis, K.; Iliescu, C. Cancer as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeffinger, K.C.; Mertens, A.C.; Sklar, C.A.; Yasui, Y.; Fears, T.; Stovall, M.; Vik, T.A.; Inskip, P.D.; Robison, L.L.; Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Obesity in adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, M.A. A New Perspective on the Health of Canadians: A Working Document; Government of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1974.
- Krokstad, S.; Ding, D.; Grunseit, A.C.; Sund, E.R.; Holmen, T.L.; Rangul, V.; Bauman, A. Multiple lifestyle behaviours and mortality, findings from a large population-based Norwegian cohort study-The HUNT Study. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, M.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Rodgers, A.; Lopez, A.D.; Mathers, C.D.; Murray, C.J.; Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Estimates of global and regional potential health gains from reducing muliple major risk factors. Lancet 2003, 362, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, C.; Okoro, C.A.; Li, J.; Wen, X.J.; White, A.; Balluz, L.S. Trends in modifiable lifestyle-related risk factors following diagnosis in breast cancer survivors. J. Cancer Surviv. 2013, 7, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, H.; Qiu, X.; Brown, M.C.; Eng, L.; Pringle, D.; Mahler, M.; Hon, H.; Tiessen, K.; Thai, H.; Ho, V.; et al. Socioeconomic status and lifestyle behaviours in cancer survivors: Smoking and physical activity. Curr. Oncol. 2016, 23, e546–e555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloc, N.B. Relationship of health practices and mortality. Prev. Med. 1973, 2, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.-W.; Sung, J.-H.; Kim, C.Y. High risk groups in health behavior defined by clustering of smoking, alcohol, and exercise habits: National Heath and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2010, 43, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Crespi, C.M.; Maxwell, A.E. Drinking patterns among Korean adults: Results of the 2009 Korean community health survey. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2013, 46, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, W.L.; Lee, I.M.; Pate, R.R.; Powell, K.E.; Blair, S.N.; Franklin, B.A.; Macera, C.A.; Heath, G.W.; Thompson, P.D.; Bauman, A. Physical activity and public health: Updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 116, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Jang, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.W. An association rule mining-based framework for understanding lifestyle risk behaviors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, O.M.; Marcelli, E. Short and long sleep are positively associated with obesity, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease among adults in the United States. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, D.C.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Bennett, G.; Coady, S.; D’agostino, R.B.; Gibbons, R.; Greenland, P.; Lackland, D.T.; Levy, D.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2935–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Imieliński, T.; Swami, A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD, International Conference on Management of Data; Association for Computing Machinery: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; Volume 22, pp. 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, W.; Shahbaz, M.; Guergachi, A. Applications of association rule mining in health informatics: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2017, 47, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harahap, M.; Husein, A.M.; Aisyah, S.; Lubis, F.R.; Wijaya, B.A. Mining association rule based on the diseases population for recommendation of medicine need. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1007, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, H.; Kahn, R.; Robertson, R.M.; American Cancer Society; American Diabetes Association; American Heart Association; Clark, N.G.; Doyle, C.; Hong, Y.; Gansler, T.; et al. Preventing cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes: A common agenda for the American Cancer Society, the American Diabetes Association, and the American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 109, 3244–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.K.; Terrin, N.C.; Menon, U.; Kreps, G.L.; McCance, K.; Parsons, S.K.; Mooney, K.H. Health behaviors in cancer survivors. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2007, 34, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallaway, M.S.; Glover-Kudon, R.; Momin, B.; Puckett, M.; Lunsford, N.B.; Ragan, K.R.; Rohan, E.A.; Babb, S. Smoking cessation attitudes and practices among cancer survivors-United States, 2015. J. Cancer Surviv. 2019, 13, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, M.L.; Buys, S.S.; Gren, L.H.; Simonsen, S.E.; Kirchhoff, A.C.; Hashibe, M. Do cancer survivors develop healthier lifestyle behaviors than the cancer-free population in the PLCO study? J. Cancer Surviv. 2017, 11, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, E.J.; Newton, C.C.; Carter, B.D.; Feskanich, D.; Freedman, N.D.; Prentice, R.L.; Flanders, W.D. What proportion of cancer deaths in the contemporary United States is attributable to cigarette smoking? Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreotti, G.; Freedman, N.D.; Silverman, D.T.; Lerro, C.C.; Koutros, S.; Hartge, P.; Alavanja, M.C.; Sandler, D.P.; Freeman, L.B. Tobacco use and cancer risk in the Agricultural Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Stevens, V.; Campbell, P.T. Active smoking and mortality among colorectal cancer survivors: The Cancer Prevention Study II nutrition cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. Smoking and cardiovascular disease: Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and early atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.; Miller, L.A.; Saad, A.; Abraham, J. Smoking behaviors among cancer survivors: An observational clinical study. J. Oncol. Pract. 2009, 5, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Aleixo, I.; Santos-Alves, E.; Mariani, D.; Rizo-Roca, D.; Padrão, A.I.; Rocha-Rodrigues, S.; Viscor, G.; Torrella, J.R.; Ferreira, R.; Oliveira, P.J.; et al. Physical exercise prior and during treatment reduces sub-chronic doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial toxicity and oxidative stress. Mitochondrion 2015, 20, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.W.; Liu, Q.; Armstrong, G.T.; Ness, K.K.; Yasui, Y.; Devine, K.; Tonorezos, E.; Soares-Miranda, L.; Sklar, C.A.; Douglas, P.S.; et al. Exercise and risk of major cardiovascular events in adult survivors of childhood hodgkin lymphoma: A report from the childhood cancer survivor study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3643–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.Y.; Tzeng, I.S.; Chou, H.H.; Jang, S.J.; Hsieh, C.A.; Ko, Y.L.; Huang, H.L. Association rule mining and prognostic stratification of 2-year longevity in octogenarians undergoing endovascular therapy for lower extremity arterial disease: Observational cohort study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e17487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, I.; Kaduszkiewicz, H.; Wagner, H.O.; Schön, G.; Scherer, M.; van den Bussche, H. Reducing complexity: A visualisation of multimorbidity by combining disease clusters and triads. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, H.; Xin, Y.; Shi, C. Mining association rules between stroke risk factors based on the apriori algorithm. Technol. Health Care 2017, 25, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.M.J.; Xu, S.; Kang, B.H.; Zhao, Z. A new multiple seeds based genetic algorithm for discovering a set of interesting Boolean association rules. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 74, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilou, S.; Bamidis, P.D.; Maglaveras, N.; Pappas, C. Mining association rules from clinical databases: An intelligent diagnostic process in healthcare. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2001, 84, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Key, T.J.; Allen, N.E.; Spencer, E.A.; Travis, R.C. The effect of diet on risk of cancer. Lancet 2002, 360, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Giovannucci, E.; Boffetta, P.; Fadnes, L.T.; Keum, N.; Norat, T.; Greenwood, D.C.; Riboli, E.; Vatten, L.J.; Tonstad, S. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer and all-cause mortality-a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int. J. Epdemiol. 2017, 46, 1029–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, A.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Spiegelman, D.; Chiuve, S.E.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.; Rexrode, K.M.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B. Healthful and Unhealthful Plant-Based Diets and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in U.S. Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satija, A.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Rimm, E.B.; Spiegelman, D.; Chiuve, S.E.; Borgi, L.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B. Plant-Based Dietary Patterns and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in US Men and Women: Results from Three Prospective Cohort Studies. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ASCVD Score | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (N = 520) | High (N = 377) | Total (N = 897) | ||
| Age | 54.8 ± 9.6 | 72.3 ± 5.6 | 62.2 ± 8.1 | <0.001 |
| Male | 113 (21.7%) | 245 (65.0%) | 358 (39.9%) | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.6 ± 3.2 | 23.8 ± 3.0 | 23.7 ± 3.1 | 0.267 |
| Household income | 0.368 | |||
| Lowest | 112 (21.5%) | 98 (26.0%) | 210 (23.4%) | |
| Lower middle | 129 (24.8%) | 94 (24.9%) | 223 (24.9%) | |
| Upper middle | 138 (26.5%) | 85 (22.5%) | 223 (24.9%) | |
| Highest | 141 (27.2%) | 100 (26.5%) | 241 (27.0%) | |
| Educational year | <0.001 | |||
| ≤6 years | 127 (24.4%) | 197 (52.3%) | 324 (36.1%) | |
| 7–9 years | 87 (16.7%) | 48 (12.7%) | 135 (15.1%) | |
| 10–12 years | 169 (32.5%) | 68 (18.0%) | 237 (26.4%) | |
| ≥13 years | 137 (26.4%) | 64 (17.0%) | 201 (22.4%) | |
| Marital status | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 426 (81.9%) | 271 (71.9%) | 697 (77.7%) | |
| No | 94 (18.1%) | 106 (28.1%) | 200 (22.3%) | |
| Hypertension | 31 (6.0%) | 32 (8.5%) | 63 (7.0%) | 0.184 |
| Diabetes | 4 (0.8%) | 21 (5.6%) | 25 (2.8%) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | ||||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 190.5 ± 36.6 | 182.3 ± 33.7 | 187 ± 35.6 | 0.001 |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 52.0 ± 12.5 | 46.7 ± 11.8 | 49.8 ± 12.5 | <0.001 |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 113.8 ± 33.2 | 108.3 ± 31.1 | 111.5 ± 32.5 | 0.012 |
| Blood pressure | ||||
| Systolic (mmHg) | 115.8 ± 14.9 | 129.7 ± 16.5 | 121.6 ± 17.0 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 74.9 ± 9.3 | 72.7 ± 9.7 | 74.0 ± 9.5 | <0.001 |
| Fasting blood glucose (mg/dL) | 100.6 ± 25.1 | 107.4 ± 26.6 | 103.5 ± 25.9 | <0.001 |
| Alameda’s heath risk behavior | ||||
| Current smoking | 31 (6.0%) | 55 (14.6%) | 86 (9.6%) | <0.001 |
| Heavy drinking | 54 (10.4%) | 54 (14.3%) | 108 (12.0%) | 0.092 |
| Physical inactivity | 474 (91.2%) | 361 (95.8%) | 835 (93.1%) | 0.011 |
| Obesity | 146 (28.1%) | 118 (31.3%) | 264 (29.4%) | 0.331 |
| Suboptimal sleep | 68 (13.1%) | 64 (17.0%) | 132 (14.7%) | 0.126 |
| Breakfast skipping | 142 (27.3%) | 87 (23.1%) | 229 (25.5%) | 0.175 |
| Frequent snacking | 53 (10.2%) | 5 (1.3%) | 58 (6.5%) | <0.001 |
| Crude Model | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | ||||
| Current smoking | 2.90 (1.77–4.75) | 11.79 (3.82–36.37) | 11.85 (3.84–36.51) | 11.19 (3.66–34.20) |
| Heavy drinking | 1.14 (0.75–1.75) | 2.84 (1.02–7.88) | 2.85 (1.02–7.92) | 2.79 (0.99–7.85) |
| Physical inactivity | 1.94 (1.02–3.71) | 0.26 (0.07–0.94) | 0.26 (0.07–0.97) | 0.23 (0.06–0.86) |
| Obesity | 1.12 (0.83–1.52) | 2.81 (1.49–5.32) | 2.84 (1.50–5.38) | 2.67 (1.40–5.08) |
| Suboptimal sleep | 1.44 (0.98–2.13) | 2.02 (0.87–4.70) | 2.06 (0.88–4.82) | 1.90 (0.79–4.57) |
| Breakfast skipping | 0.94 (0.66–1.33) | 1.14 (0.56–2.30) | 1.15 (0.57–2.32) | 1.12 (0.55–2.27) |
| Frequent snacking | 0.11 (0.04–0.27) | 0.57 (0.13–2.56) | 0.59 (0.13–2.67) | 0.54 (0.12–2.45) |
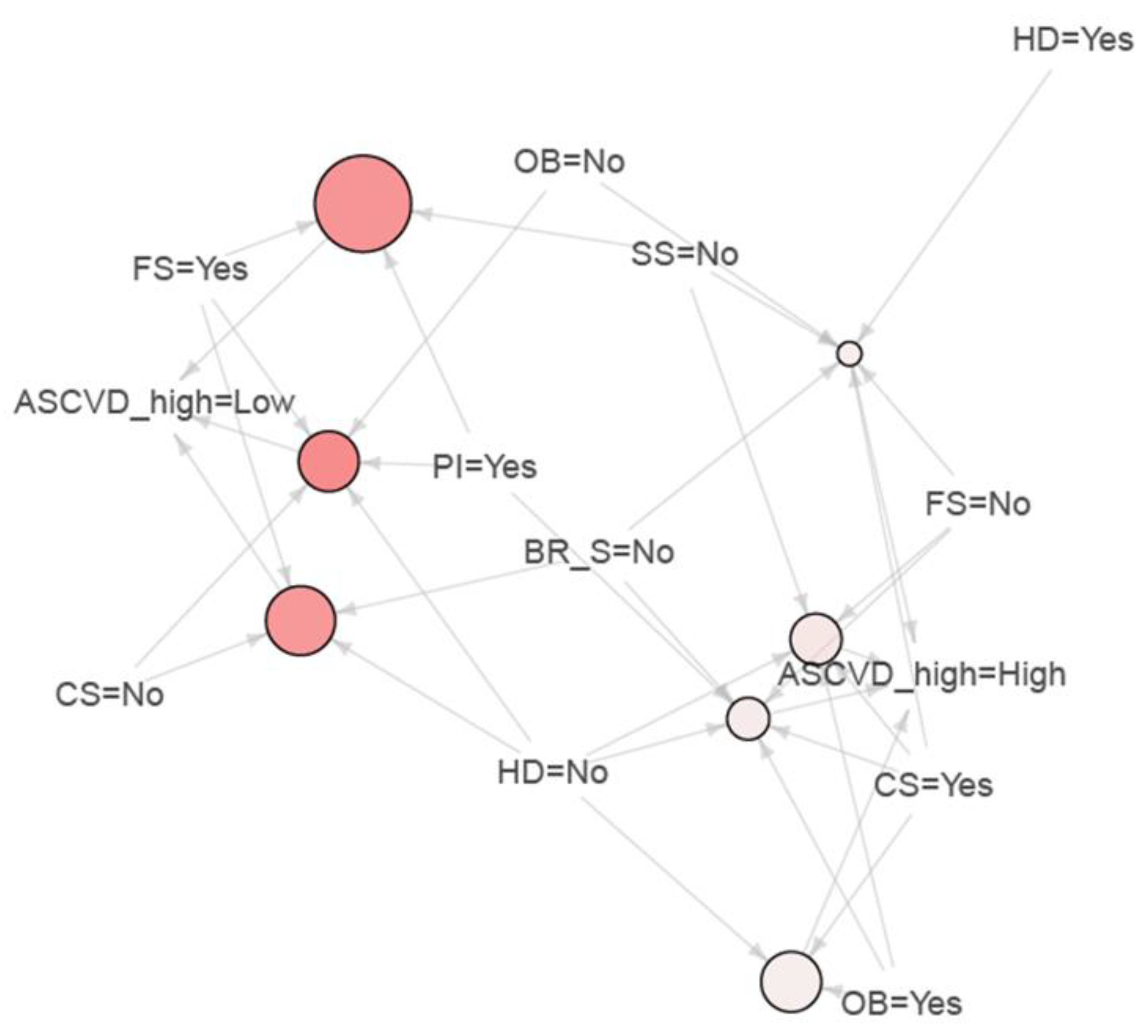
| LHS | RHS | Support | Confidence | Lift | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | {SS = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.052 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 28 |
| 2 | {PI = Yes, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.054 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 29 |
| 3 | {HD = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 33 |
| 4 | {CS = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.058 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 31 |
| 5 | {CS = No, PI = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.069 | 0.902 | 1.195 | 37 |
| 6 | {HD = No, PI = No, IA = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.067 | 0.900 | 1.192 | 36 |
| 7 | {CS = No, PI = No, IA = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.067 | 0.900 | 1.192 | 36 |
| 8 | {CS = No, PI = No, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 0.892 | 1.181 | 33 |
| 9 | {CS = No, HD = No, PI = No, IA = No, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 0.892 | 1.181 | 33 |
| 10 | {PI = No, IA = No, BS = Yes, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.058 | 0.886 | 1.173 | 31 |
| 11 | {HD = No, OB = No, BS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.135 | 0.820 | 1.086 | 73 |
| 12 | {CS = No, OB = No, IA = No, BS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.332 | 0.803 | 1.063 | 179 |
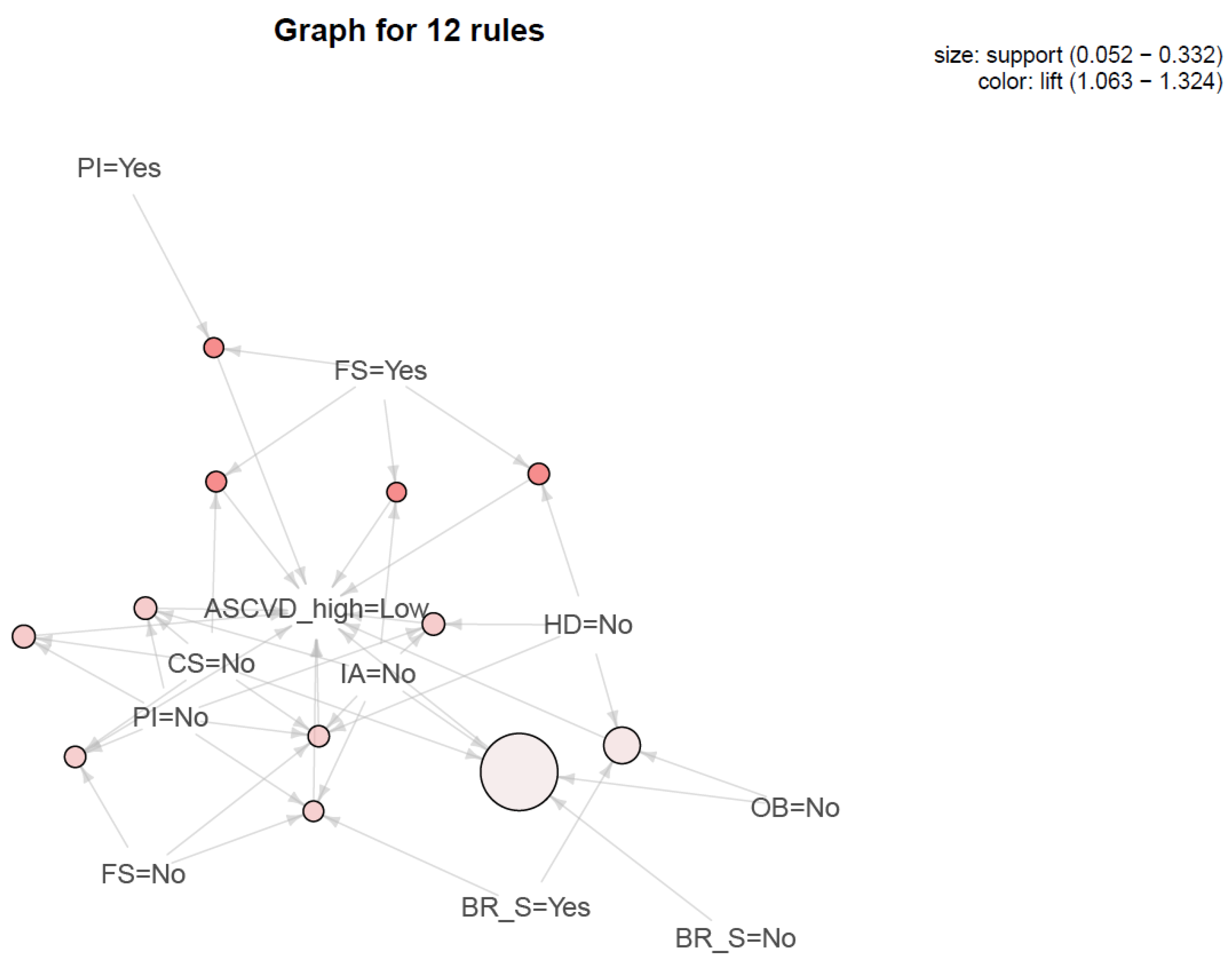
| LHS | RHS | Support | Confidence | Lift | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | {SS = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.052 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 28 |
| 2 | {PI = Yes, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.054 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 29 |
| 3 | {HD = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 33 |
| 4 | {CS = No, FS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.058 | 1.000 | 1.324 | 31 |
| 5 | {CS = No, PI = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.069 | 0.902 | 1.195 | 37 |
| 6 | {HD = No, PI = No, SS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.067 | 0.900 | 1.192 | 36 |
| 7 | {CS = No, PI = No, SS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.067 | 0.900 | 1.192 | 36 |
| 8 | {CS = No, PI = No, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 0.892 | 1.181 | 33 |
| 9 | {CS = No, HD = No, PI = No, SS = No, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.061 | 0.892 | 1.181 | 33 |
| 10 | {PI = No, SS = No, BS = Yes, FS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.058 | 0.886 | 1.173 | 31 |
| 11 | {HD = No, OB = No, BS = Yes} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.135 | 0.820 | 1.086 | 73 |
| 12 | {CS = No, OB = No, SS = No, BS = No} | {ASCVD_high = Low} | 0.332 | 0.803 | 1.063 | 179 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.J.; Cartmell, K.B. An Association Rule Mining Analysis of Lifestyle Behavioral Risk Factors in Cancer Survivors with High Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050366
Lee SJ, Cartmell KB. An Association Rule Mining Analysis of Lifestyle Behavioral Risk Factors in Cancer Survivors with High Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(5):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su Jung, and Kathleen B. Cartmell. 2021. "An Association Rule Mining Analysis of Lifestyle Behavioral Risk Factors in Cancer Survivors with High Cardiovascular Disease Risk" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 5: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050366
APA StyleLee, S. J., & Cartmell, K. B. (2021). An Association Rule Mining Analysis of Lifestyle Behavioral Risk Factors in Cancer Survivors with High Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(5), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11050366





