Real-World Experience of the One-Year Efficacy of Rifaximin Add-On to Lactulose Is Superior to Lactulose Alone in Patients with Cirrhosis Complicated with Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Treatment Efficacy and Safety Assessments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
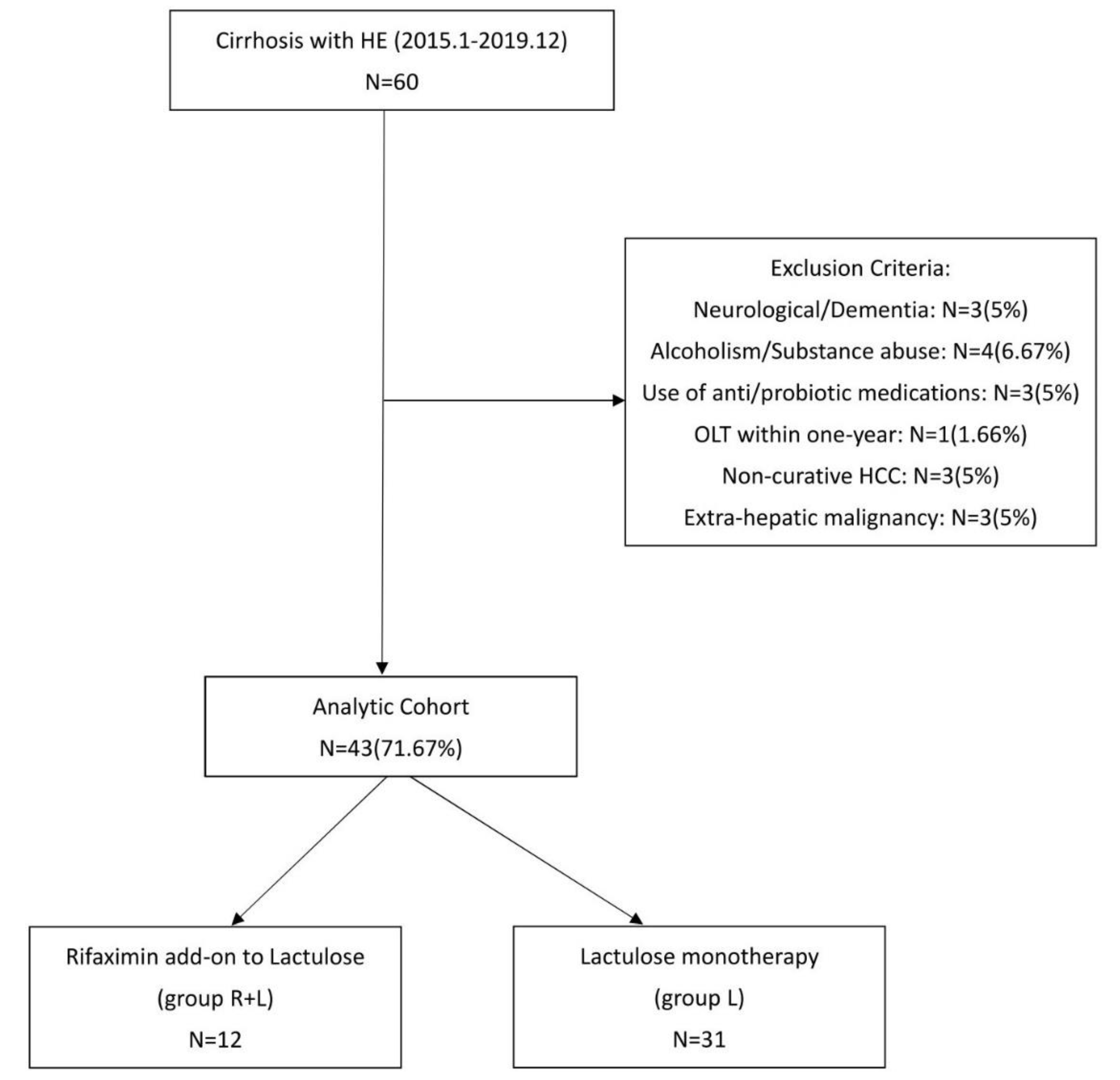
3.1. Flowchart and Patient Characteristics
3.2. Outcomes Analysis Between Group R + L Versus Group L Primary Outcome
3.3. Comparisons of Various Clinical and Laboratory Parameters between Group R + L vs. Group L after One-Year Follow-Up
3.4. Outcomes Analysis before and after Rifaximin Add-On within Group R+L
3.5. Side Effects of Rifaximin
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijdicks, E.F. Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnese, S.; Bajaj, J.S. Impact of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis on Quality-of-Life Issues. Drugs 2019, 79, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elwir, S.; Rahimi, R.S. Hepatic Encephalopathy: An Update on the Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Agrawal, A.; Sarin, S.K. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy: An open-label randomized controlled trial of lactulose versus placebo. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 885–891.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Perumpail, R.B.; Kumari, R.; Younossi, Z.M.; Wong, R.J.; Ahmed, A. Advances in cirrhosis: Optimizing the management of hepatic encephalopathy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongsamran, P.V.; Kim, J.W.; Cupo Abbott, J.; Rosenblatt, A. Pharmacotherapy for hepatic encephalopathy. Drugs 2010, 70, 1131–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpignato, C.; Pelosini, I. Rifaximin, a poorly absorbed antibiotic: Pharmacology and clinical potential. Chemotherapy 2005, 51, 36–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.J.; Bass, N.M.; Poordad, F.F.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Frederick, R.T.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin is safe and well tolerated for long-term maintenance of remission from overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1390–1397.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas, A.; Rodes, J.; Sunyer, L.; Rodrigo, L.; Planas, R.; Vargas, V.; Castells, L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, D.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.; Coll, I.; et al. Comparison of rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Zaidi, Y.A.; Alam, A.; Anjum, H.S. Efficacy of Rifaximin in prevention of recurrence of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of liver. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2014, 24, 269–273. Available online: https://www.jcpsp.pk/archive/2014/Apr2014/13.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, Y.B.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, J.Y.; Chang, Y.; Cho, H.; Yoo, J.J.; Cho, Y.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Yu, S.J.; et al. Rifaximin treatment is associated with reduced risk of cirrhotic complications and prolonged overall survival in patients experiencing hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 46, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahire, K.; Sonawale, A. Comparison of Rifaximin Plus Lactulose with the Lactulose Alone for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2017, 65, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Courson, A.; Jones, G.M.; Twilla, J.D. Treatment of Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy: Comparing the Effects of Adding Rifaximin to Lactulose on Patient Outcomes. J. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 29, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachogiannakos, J.; Viazis, N.; Vasianopoulou, P.; Vafiadis, I.; Karamanolis, D.G.; Ladas, S.D. Long-term administration of rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.R.; Kuo, C.W. Cost of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Taiwan. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 38, S148–S152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.A.; Tarn, Y.H.; Tang, S.L. Cost-utility analysis of different peg-interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin treatment strategies as initial therapy for naive Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khoury, A.C.; Wallace, C.; Klimack, W.K.; Razavi, H. Economic burden of hepatitis C-associated diseases: Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Americas. J. Med. Econ. 2012, 15, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D.R.; Tranah, E.J.; Shawcross, D.L. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: Role of ammonia and systemic inflammation. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, S7–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Arias, N.; Sheikh, M.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidhu, S.S.; Sharma, B.C.; Goyal, O.; Kishore, H.; Kaur, N. L-ornithine L-aspartate in bouts of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2018, 67, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahimi, R.S.; Singal, A.G.; Cuthbert, J.A.; Rockey, D.C. Lactulose vs polyethylene glycol 3350--electrolyte solution for treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy: The HELP randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, I.; Doval, E.; Garcia-Martinez, R.; Planas, M.; Cardenas, G.; Gomez, P.; Flavia, M.; Jacas, C.; Minguez, B.; Vergara, M.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acids supplementation in patients with cirrhosis and a previous episode of hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Sarin, S.K. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: An open-label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Kassam, Z.; Fagan, A.; Gavis, E.A.; Liu, E.; Cox, I.J.; Kheradman, R.; Heuman, D.; Wang, J.; Gurry, T.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplant from a rational stool donor improves hepatic encephalopathy: A randomized clinical trial. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanein, T.I.; Tofteng, F.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; McGuire, B.; Lynch, P.; Mehta, R.; Larsen, F.S.; Gornbein, J.; Stange, J.; Blei, A.T. Randomized controlled study of extracorporeal albumin dialysis for hepatic encephalopathy in advanced cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banares, R.; Nevens, F.; Larsen, F.S.; Jalan, R.; Albillos, A.; Dollinger, M.; Saliba, F.; Sauerbruch, T.; Klammt, S.; Ockenga, J.; et al. Extracorporeal albumin dialysis with the molecular adsorbent recirculating system in acute-on-chronic liver failure: The RELIEF trial. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, J.S.; Gavis, E.A.; Fagan, A.; Wade, J.B.; Thacker, L.R.; Fuchs, M.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.; Meador, J.; Puri, P.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Fecal Microbiota Transplant for Alcohol Use Disorder. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1688–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poordad, F.F. Review article: The burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, S.L. Considerations for the cost-effective management of hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Manag. Care 2018, 24, S51–S61. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, G.; Zachry, W., III. Systematic Review of the Economic Burden of Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy and Pharmacoeconomic Impact of Rifaximin. Pharmacoeconomics 2018, 36, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neff, G.W.; Kemmer, N.; Zacharias, V.C.; Kaiser, T.; Duncan, C.; McHenry, R.; Jonas, M.; Novick, D.; Williamson, C.; Hess, K.; et al. Analysis of hospitalizations comparing rifaximin versus lactulose in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Transplant. Proc. 2006, 38, 3552–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, G.; Morabito, A.; D’Amico, M.; Pasta, L.; Malizia, G.; Rebora, P.; Valsecchi, M.G. Clinical states of cirrhosis and competing risks. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salehi, S.; Tranah, T.H.; Lim, S.; Heaton, N.; Heneghan, M.; Aluvihare, V.; Patel, V.C.; Shawcross, D.L. Rifaximin reduces the incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal bleeding and all-cause admissions in patients on the liver transplant waiting list. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.Y.; Edwin, D.; Thuluvath, P.J. Relationship of the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) scale to hepatic encephalopathy, as defined by electroencephalography and neuropsychometric testing, and ascites. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 98, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Gargante, M.P.; Cristaldi, E.; Vacante, M.; Risino, C.; Cammalleri, L.; Pennisi, G.; Rampello, L. Acetyl-L-carnitine treatment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 3018–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziarska, D.; Wunsch, E.; Milkiewicz, M.; Wojcicki, M.; Nowacki, P.; Milkiewicz, P. Mini-Mental State Examination in patients with hepatic encephalopathy and liver cirrhosis: A prospective, quantified electroencephalography study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrias, M.; Turco, M.; Rui, M.D.; Gatta, A.; Angeli, P.; Merkel, C.; Amodio, P.; Schiff, S.; Montagnese, S. Covert hepatic encephalopathy: Does the mini-mental state examination help? J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neff, G.W.; Kemmer, N.; Duncan, C.; Alsina, A. Update on the management of cirrhosis—Focus on cost-effective preventative strategies. Clinicoecon. Outcomes Res. 2013, 5, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Group 1 Rifaximin + Lactulose | Group 2 Lactulose | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Parameter | N = 12 | N = 31 | |
| Clinical parameters | |||
| Age, mean ± SD | 67 ± 7.95 | 57.58 ± 12.28 | 0.007 |
| Males (%) | 6 (50%) | 20 (64.5%) | 0.388 |
| HE grade $ | 0.160 | ||
| Minimal/I/II/III/IV No. | 4/2/4/2/0 | 0/6/15/9/1 | |
| Ascites amount | 0.210 | ||
| Nil/Mild/Moderate/Severe No. | 7/2/2/1 | 13/4/6/8 | |
| EV | 0.052 | ||
| Nil/F1/F2/F3 No. | 1/3/3/5 | 10/8/8/5 | |
| EVB No. (%) | 6 (50%) | 7 (22.6%) | 0.108 |
| SBP No. (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| HRS No. (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
| HCC No. (%) | 4 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) | <0.001 |
| DM No. (%) | 5 (41.7%) | 7 (22.5%) | 0.216 |
| ESRD No. (%) | 1(8.3%) | 5 (16.1%) | 0.513 |
| Heart Failure No. (%) | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (3.2%) | 0.481 |
| Laboratory parameters Median (IQR) | |||
| Ammonia (μg/dL) | 226.0 (186.40–262.0) | 224.0 (174.75–317.0) | 0.895 |
| MELD | 14.05 (11.87–16.55) | 17.0 (14.0–22.0) | 0.048 |
| INR | 1.40 (1.30–1.60) | 1.50 (1.30–1.70) | 0.874 |
| WBC (103/uL) | 3.45 (2.75–5.37) | 4.85 (3.50–6.35) | 0.060 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.55 (8.82–10.30) | 10.0 (8.65–12.17) | 0.549 |
| PLT (103/uL) | 62.0 (37.0–79.75) | 81.0 (59.0–111.0) | 0.091 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.95 (0.83–1.09) | 1.13 (0.63–1.98) | 0.924 |
| Bilirubin, Total (mg/dL) | 1.85 (1.30–2.12) | 2.50 (1.30–3.30) | 0.095 |
| AST (U/L) | 40.0 (34.0–53.0) | 51.0 (37.0–73.0) | 0.188 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.0 (20.0–25.0) | 25.50 (18.75–31.50) | 0.461 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.0 (2.55–3.38) | 2.95 (2.40–3.36) | 0.987 |
| Univariable Logistic Reg. | Multivariable Logistic reg. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
| Group (rifaximin + lactulose vs. lactulose) | 0.148 (0.032, 0.694) | 0.015 | 0.214 (0.037, 0.925) | 0.045 |
| Age | 0.985 (0.927, 1.047) | 0.628 | ||
| Sex | 1.719 (0.377, 7.849) | 0.484 | ||
| MELD | 1.160 (0.969, 1.389) | 0.105 | ||
| HE grade (≥II vs. I and minimal) | 13.067 (2.5000, 68.291) | 0.002 | 10.182 (1.793, 57.802) | 0.009 |
| EVB (n, %) | 6 (50%) | 0.832 | ||
| HCC | 3.875 (0.471,31.912) | 0.208 | ||
| DM | 2.083 (0.467, 9.288) | 0.336 | ||
| ESRD | 1.812 (0.280, 11.750) | 0.533 | ||
| Heart Failure | 3.556 (0.202, 62.632) | 0.386 | ||
| Clinical Parameters | Group 1 Rifaximin + Lactulose | Group 2 Lactulose | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of hospitalizations due to HE | 1 (0.0, 2.0) | 3 (2.0, 4.0) | <0.001 |
| Days of hospitalizations | 11 (0.0, 27.0) | 37 (15.0, 97.0) | 0.003 |
| HE Recurrence | 6 (50%) | 27 (87.1%) | 0.011 |
| HE grade $ (n) | 7 | 23 | 0.003 |
| Minimal/I/II/III/IV/V: | 1/0/0/1/0/5 | 9/2/6/4/2/0 | |
| Death (n, %) | 2 (20%) | 13 (41.9%) | 0.216 |
| MMSE | 25.0 ± 4.1 | ||
| EVB (n, %) | 6 (50%) | 31 (100%) | 0.313 |
| Ascites (n) | 7 | 21 | 0.307 |
| Nil/Mild/moderate/Severe: | 5/1/0/1 | 10/5/1/5 | |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| Serum Ammonia | 132.2 (62.0, 222.0) | 201 (157.0, 239.0) | 0.179 |
| MELD | 14.6 (12.0, 20.1) | 20 (15.0, 22.0) | 0.115 |
| INR | 1.4 (1.4, 1.5) | 1.5 (1.3, 1.9) | 0.616 |
| WBC (103/uL) | 4.1 (3.6, 6.2) | 4.3 (2.9, 8.1) | 0.772 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 65 (47.0, 94.0) | 78 (49.0, 127.0) | 0.825 |
| PLT (103/uL) | 9.5 (8.9, 11.5) | 9.85 (8.5, 10.8) | 0.386 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.165 (0.8, 1.8) | 1.39 (0.9, 3.4) | 0.662 |
| Bilirubin Total (mg/dL) | 2.6 (1.0, 3.0) | 1.9 (1.0, 4.5) | 0.934 |
| AST (U/L) | 43 (29.0, 47.0) | 48 (36.0, 55.0) | 0.137 |
| ALT (U/L) | 26 (19.0, 46.0) | 26 (21.0, 37.0) | 1.0 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.805 (2.6, 3.0) | 2.94 (2.6, 3.4) | 0.861 |
| Baseline | 6 Months | 12 Months | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical parameters | ||||
| MMSE | 21.4 ± 2.2 | 27.4 ± 1.1 | 25.0 ± 1.8 | 0.02 |
| EVB | 50% | 0% | 0% | 0.011 |
| Ascites | 41.70% | 36.40% | 28.60% | 0.794 |
| Lab parameters | ||||
| MELD | 15.0 ± 1.6 | 14.9 ± 1.8 | 16.1 ± 1.6 | 0.524 |
| INR | 1.4 ± 0.03 | 1.4 ± 0.03 | 1.4 ± 0.05 | 0.484 |
| WBC | 4.0 ± 0.5 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 0.352 |
| Hb | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 10.0 ± 0.5 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 0.909 |
| Plt | 71.1 ± 10.8 | 79.0 ± 9.9 | 74.1 ± 12.4 | 0.566 |
| Cr | 2.3 ± 1.2 | 1.8 ± 1.0 | 3.0 ± 1.9 | 0.273 |
| Bilt | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 0.268 |
| Alb | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 0.45 |
| Serum Ammonia | 248.9 ± 47.0 | 133.1 ± 33.0 | 176.5 ± 61.6 | 0.187 † |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.; Huang, C.-H.; Tseng, H.-J.; Yang, F.-C.; Chien, R.-N. Real-World Experience of the One-Year Efficacy of Rifaximin Add-On to Lactulose Is Superior to Lactulose Alone in Patients with Cirrhosis Complicated with Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Taiwan. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060478
Chang C, Huang C-H, Tseng H-J, Yang F-C, Chien R-N. Real-World Experience of the One-Year Efficacy of Rifaximin Add-On to Lactulose Is Superior to Lactulose Alone in Patients with Cirrhosis Complicated with Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Taiwan. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(6):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060478
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Ching, Chien-Hao Huang, Hsiao-Jung Tseng, Fang-Chen Yang, and Rong-Nan Chien. 2021. "Real-World Experience of the One-Year Efficacy of Rifaximin Add-On to Lactulose Is Superior to Lactulose Alone in Patients with Cirrhosis Complicated with Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Taiwan" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 6: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060478
APA StyleChang, C., Huang, C.-H., Tseng, H.-J., Yang, F.-C., & Chien, R.-N. (2021). Real-World Experience of the One-Year Efficacy of Rifaximin Add-On to Lactulose Is Superior to Lactulose Alone in Patients with Cirrhosis Complicated with Recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy in Taiwan. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(6), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060478








