The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Background: The Essential Role of Biomarkers in Breast Cancer
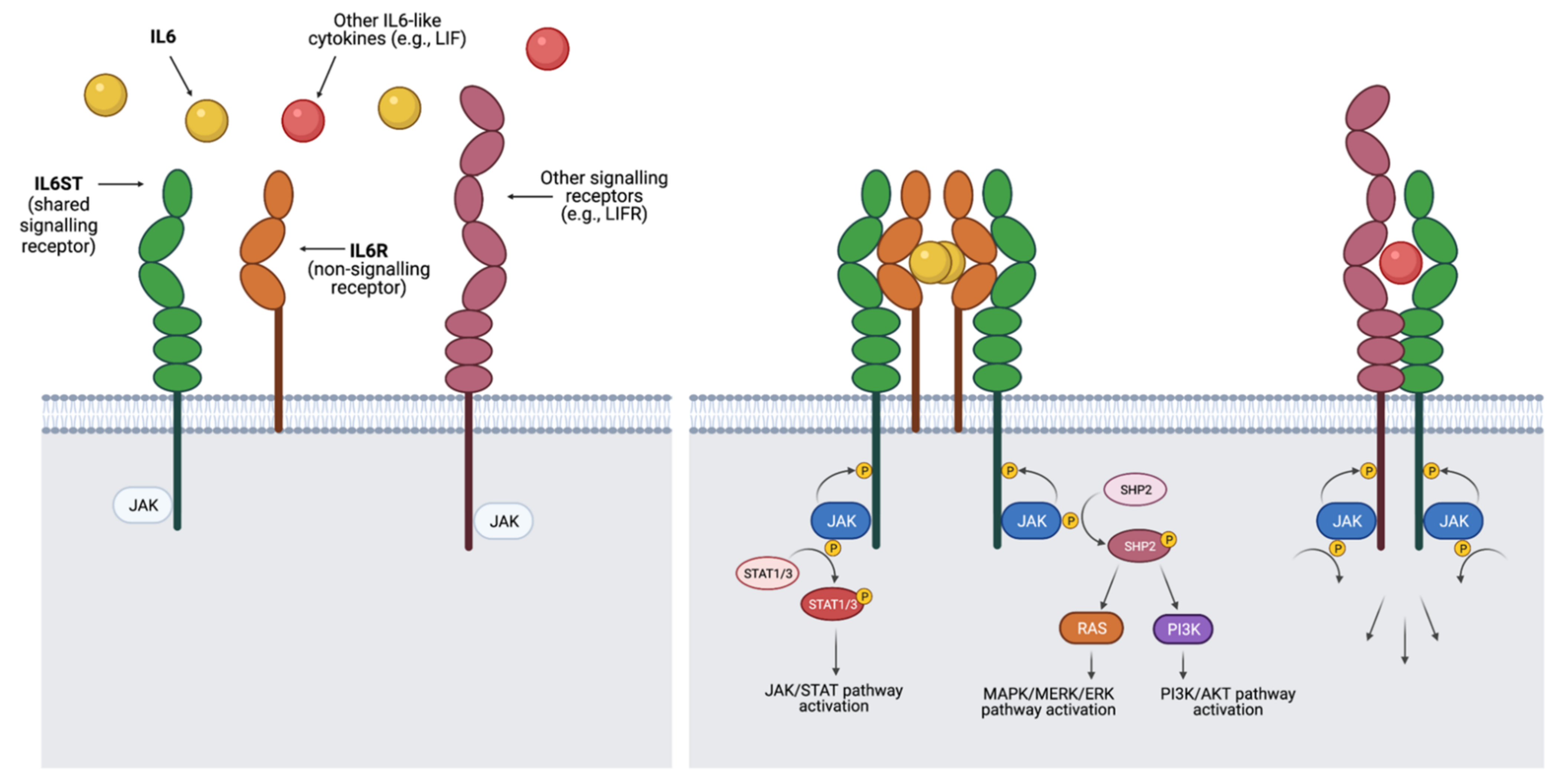
2. The IL6-Like Cytokine Family and Its Signalling in Breast Cancer
3. IL6ST as an Independent Predictor in BC
| Original Publication | Study Type | Study Cohorts | Associations Reported | Main Predictive or Prognostic Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karczewska et al. (2000) [38] | Independent biomarker | 75 PBCs who received surgery +/− adjuvant therapy. | IL6ST expression strongly correlates with earlier disease stages. In advanced stages, IL6ST expression is associated with better prognosis and higher OS and DFS rates. IL6ST negatively correlates with lymph node status and tumour size. IL6ST is independent from other well established clinicopathological factors. | IL6ST is a positive prognostic factor. |
| Tozlu et al. (2006) [43] | Independent biomarker | PBCs who received surgery (+ ET for ER+):
| IL6ST is a perfect discriminator of ER+ status. | IL6ST is predictive for ER status and likely endocrine responsiveness. |
| Filipits et al. (2011) [44] | Molecular signatures: EP and EPclin | Original cohorts of ER+/HER2- BCs treated with ET:
| EP and EPclin scores (linked to lower IL6ST expression) are continuous predictors of the risk of distant recurrence. EPclin is also prognostic for disease recurrence in patients who received chemotherapy, regardless of menopausal status. Patients with higher EPclin score derive benefit from the addition of chemotherapy to ET. | EP and EPclin stratify into risk groups that are prognostic for risk of distant recurrence at 5, 10 and 15 years in ER+/HER2- patients. EPclin is also prognostic for LRFS. EPclin high-risk group is predictive for chemotherapy benefit in pre- and postmenopausal ER+/HER2- patients. |
| Sota et al. (2014) [49] | Molecular signature: IRSN-23 | PBCs who received NAC:
| Higher IL6ST is associated with lack of pCR from NAC. IRSN-23 classifies into Gp-R and Gp-NR groups, with differential response to NAC. | IRSN-23 signature stratifies into groups predictive of response to NAC, regardless of BC subtype of chemotherapy regimen. |
| Andres et al. (2014) [50] | Independent biomarker | Tumour marker analysis:
| IL6ST expression is significantly elevated in male BCs compared to female malignancies. IL6ST correlates with ER expression. | |
| Mathe et al. (2015) [40] | Independent biomarker | Screening set:
| IL6ST expression is associated with longer survival. IL6ST expression is lower in TNBC than ER+ tumours. | IL6ST is prognostic for OS and RFS in TNBC. |
| Fertig et al. (2015) [42] | Independent biomarker | 638 + 897 PBCs from publicly-available sets. | IL6ST expression is higher in luminal tumours (ER+/PR+) than in other BC subtypes. Positive trend towards longer survival in IL6ST+ luminal A tumours. | |
| Turnbull et al. (2015) [51] | Molecular signatures: EER4, EA2 and EA2clin | EER4 cohort of ER+ postmenopausal IBCs treated with NET & ET:
| IL6ST alone is an independent predictor of response to AIs. EER4 predicts response to AIs with greater accuracy and also predict RFS and BCSS. EA2 and EA2clin predict outcome from adjuvant ET with greater accuracy and also predict RFS and BCSS. EA2 also predicts outcome in premenopausal women. EA2clin predicts treatment response regardless of ET regimen. | IL6ST is an independent predictive marker for AI response in ER+/HER2- patients. EER4 further improves on this predictive ability. Models are prognostic of outcome (RFS, BCSS) from adjuvant ET response, regardless of menopausal status or ET regimen in ER+/HER2- patients. |
| Klahan et al. (2017) [39] | Independent biomarker | 108 pretreated IBCs:
| IL6ST correlates with LVI in samples without lymph node metastasis and perineural invasion. | |
| Tsunashima et al. (2018) [54] | Molecular signature: 42GC | ER+ BCs treated with ET who recurred:
| Higher IL6ST is associated with lower risk of early recurrence but higher risk of late recurrence. 42GC classified intro LR and NLR groups, with differential risk of recurrence over time. could predict late recurrence | 42GC stratifies into prognostic groups for risk of early and late recurrence in ER+ BC intervals. |
4. Molecular Signatures Incorporating IL6ST
4.1. EndoPredict and EPclin Scores for Prediction of Risk of Distant Recurrence
4.2. Immune-Related 23-Gene Signature for Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
4.3. Edinburgh EndoResponse4, EndoAdjuvant2 and EA2clin for Prediction of Response to and Outcome from Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy
4.4. 42-Gene Classifier for Prediction Risk of Late Recurrence
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, A.J.; Colburn, W.A.; DeGruttola, V.G.; DeMets, D.L.; Downing, G.J.; Hoth, D.F.; Oates, J.A.; Peck, C.C.; Schooley, R.T.; Spilker, B.A.; et al. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and Other Tools); National Institute of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017.
- Nicolini, A.; Carpi, A.; Rossi, G. Cytokines in breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Harbeck, N.; Nap, M.; Molina, R.; Nicolini, A.; Senkus, E.; Cardoso, F. Clinical use of biomarkers in breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pérez, C.; Turnbull, A.K.; Dixon, J.M. The evolving role of receptors as predictive biomarkers for metastatic breast cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2019, 19, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinert, T.; Saad, E.D.; Barrios, C.H.; Bines, J. Clinical Implications of ESR1 Mutations in Hormone Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angus, L.; Beije, N.; Jager, A.; Martens, J.W.M.; Sleijfer, S. ESR1 mutations: Moving towards guiding treatment decision-making in metastatic breast cancer patients. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Sun, X.; He, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, H. Elevated levels of serum tumor markers CEA and CA15-3 are prognostic parameters for different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazarian, A.; Blyuss, O.; Metodieva, G.; Gentry-Maharaj, A.; Ryan, A.; Kiseleva, E.M.; Prytomanova, O.M.; Jacobs, I.J.; Widschwendter, M.; Menon, U.; et al. Testing breast cancer serum biomarkers for early detection and prognosis in pre-diagnosis samples. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabel, A.M. Tumor markers of breast cancer: New prospectives. J. Oncol. Sci. 2017, 3, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughran, G.; Aggarwal, N.; Shadbolt, B.; Stuart-Harris, R. The utility of the tumor markers CA15.3, CEA, CA-125 and CA19.9 in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Manag. 2020, 9, BMT50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.F.; Nathanson, K.L.; Couch, F.J.; Offit, K. Genomic biomarkers for breast cancer risk. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer New York LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 882, pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Akcakanat, A.; Zheng, X.; Cruz Pico, C.X.; Kim, T.-B.; Chen, K.; Korkut, A.; Sahin, A.; Holla, V.; Tarco, E.; Singh, G.; et al. Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Proteomic Profiling of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Grimaldi, M.; Celentano, E.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Libra, M. Identification of Modulated MicroRNAs Associated with Breast Cancer, Diet, and Physical Activity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, H.Y.; Norman, B.P.; Lai, K.S.; Rahman, N.M.A.N.A.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Osman, M.A. The regulatory role of microRNAs in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abolghasemi, M.; Tehrani, S.S.; Yousefi, T.; Karimian, A.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Ghamari, A.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Yousefi, M.; Kafil, H.S.; Bastami, M.; et al. MicroRNAs in breast cancer: Roles, functions, and mechanism of actions. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5008–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 family cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, J.S.; Hunter, C.A. gp130 at the nexus of inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, K.; Taga, T.; Saito, M.; Suematsu, S.; Kumanogoh, A.; Tanaka, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Hirata, M.; Yamagami, T.; Nakahata, T.; et al. Targeted disruption of gp130, a common signal transducer for the interleukin 6 family of cytokines, leads to myocardial and hematological disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bravo, J.; Heath, J. Receptor recognition by gp130 cytokines. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omokehinde, T.; Johnson, R.W. GP130 Cytokines in Breast Cancer and Bone. Cancers 2020, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.A.; Jenkins, B.J. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Bansal, Y.; Kumar, R.; Bansal, G. A panoramic review of IL-6: Structure, pathophysiological roles and inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiß, R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, M.Y.; Davies, D.M.; Maher, J. The role of the interleukin (IL)-6/IL-6 receptor axis in cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1449–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Nagao, K.; Miyayama, H.; Matsuda, M.; Baba, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Fukuda, M.; Mizumoto, T.; Hamamoto, R. An Analysis of Serum Interleukin-6 Levels to Predict Benefits of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate in Advanced or Recurrent Breast Cancer. Oncology 2000, 59, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoe, T.; Lino, Y.; Morishita, Y. Trends of IL-6 and IL-8 levels in patients with recurrent breast cancer: Preliminary report. Breast Cancer 2000, 7, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelot, T.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Menetrier-Caux, C.; Rastkha, M.; Duc, A.; Blay, J.Y. Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, C.N.; Chand, A.; Putoczki, T.L.; Ernst, M. Emerging roles for IL-11 signaling in cancer development and progression: Focus on breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M.; Kamimura, D.; Hirano, T. Pleiotropy and Specificity: Insights from the Interleukin 6 Family of Cytokines. Immunity 2019, 50, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirano, T.; Matsuda, T.; Nakajima, K. Signal transduction through gp130 that is shared among the receptors for the interleukin 6 related cytokine subfamily. Stem Cells 1994, 12, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ernst, M.; Jenkins, B.J. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, T.H.T.-H.; Wahler, J.; Suh, N. Potential therapeutic implications of IL-6/IL-6R/gp130-targeting agents in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15460–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masjedi, A.; Hashemi, V.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Azizi, G.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewska, A.; Nawrocki, S.; Brȩborowicz, D.; Filas, V.; Mackiewicz, A. Expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor, and glycoprotein 130 correlates with good prognoses for patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 88, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klahan, S.; Wong, H.S.C.; Tu, S.H.; Chou, W.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Ho, T.F.; Liu, C.Y.; Yih, S.Y.; Lu, H.F.; Chen, S.C.C.; et al. Identification of genes and pathways related to lymphovascular invasion in breast cancer patients: A bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profiles. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathe, A.; Wong-Brown, M.; Morten, B.; Forbes, J.F.; Braye, S.G.; Avery-Kiejda, K.A.; Scott, R.J. Novel genes associated with lymph node metastasis in triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariyar, M.; Scott, R.; Avery-Kiejda, K. OR20 Validation of Four Triple Negative Breast Cancer–Specific Genes and their Association with Prognosis. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 13 (Suppl. 5), 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fertig, E.J.; Lee, E.; Pandey, N.B.; Popel, A.S. Analysis of gene expression of secreted factors associated with breast cancer metastases in breast cancer subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tozlu, S.; Girault, I.; Vacher, S.; Vendrell, J.; Andrieu, C.; Spyratos, F.; Cohen, P.; Lidereau, R.; Bieche, I. Identification of novel genes that co-cluster with estrogen receptor alpha in breast tumor biopsy specimens, using a large-scale real-time reverse transcription-PCR approach. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipits, M.; Rudas, M.; Jakesz, R.; Dubsky, P.; Fitzal, F.; Singer, C.F.; Dietze, O.; Greil, R.; Jelen, A.; Sevelda, P.; et al. A new molecular predictor of distant recurrence in ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer adds independent information to conventional clinical risk factors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6012–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M.; Brase, J.C.; Calvo, L.; Krappmann, K.; Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Fisch, K.; Ruiz, A.; Weber, K.E.; Munarriz, B.; Petry, C.; et al. Clinical validation of the EndoPredict test in node-positive, chemotherapy-treated ER+/HER2- breast cancer patients: Results from the GEICAM 9906 trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubsky, P.; Brase, J.C.; Jakesz, R.; Rudas, M.; Singer, C.F.; Greil, R.; Dietze, O.; Luisser, I.; Klug, E.; Sedivy, R.; et al. The EndoPredict score provides prognostic information on late distant metastases in ER+/HER2-breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filipits, M.; Dubsky, P.; Rudas, M.; Greil, R.; Balic, M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Singer, C.; Hlauschek, D.; Brown, K.; Bernhisel, R.; et al. Prediction of distant recurrence using EndoPredict among women with ER+, HER2-node-positive and node-negative breast cancer treated with endocrine therapy only. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sestak, I.; Martín, M.; Dubsky, P.; Kronenwett, R.; Rojo, F.; Cuzick, J.; Filipits, M.; Ruiz, A.; Gradishar, W.; Soliman, H.; et al. Prediction of chemotherapy benefit by EndoPredict in patients with breast cancer who received adjuvant endocrine therapy plus chemotherapy or endocrine therapy alone. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sota, Y.; Naoi, Y.; Tsunashima, R.; Kagara, N.; Shimazu, K.; Maruyama, N.; Shimomura, A.; Shimoda, M.; Kishi, K.; Baba, Y.; et al. Construction of novel immune-related signature for prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in human breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, S.A.; Smolenkova, I.A.; Wittliff, J.L. Gender-associated expression of tumor markers and a small gene set in breast carcinoma. Breast 2014, 23, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.K.; Arthur, L.M.; Renshaw, L.; Larionov, A.A.; Kay, C.; Dunbier, A.K.; Thomas, J.S.; Dowsett, M.; Sims, A.H.; Dixon, J.M. Accurate Prediction and Validation of Response to Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2270–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.; Lee, Y.; Pearce, D.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Uddin, S.; Webb, H.; Fernando, A.; Thomas, J.; Renshaw, L.; Sims, A.; et al. A test utilising diagnostic and on-treatment biomarkers to improve prediction of response to endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, A.; Fernando, A.; Renshaw, L.; Keys, J.; Thomas, J.; Sims, A. EA2Clin: A novel immunohistochemical prognostic and predictive test for patients with estrogen receptor-Positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, P6-09-27. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunashima, R.; Naoi, Y.; Shimazu, K.; Kagara, N.; Shimoda, M.; Tanei, T.; Miyake, T.; Kim, S.J.; Noguchi, S. Construction of a novel multi-gene assay (42-gene classifier) for prediction of late recurrence in ER-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzal, F.; Filipits, M.; Rudas, M.; Greil, R.; Dietze, O.; Samonigg, H.; Lax, S.; Herz, W.; Dubsky, P.; Bartsch, R.; et al. The genomic expression test EndoPredict is a prognostic tool for identifying risk of local recurrence in postmenopausal endocrine receptor-positive, her2neu-negative breast cancer patients randomised within the prospective ABCSG 8 trial. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warf, M.B.; Rajamani, S.; Krappmann, K.; Doedt, J.; Cassiano, J.; Brown, K.; Reid, J.E.; Kronenwett, R.; Roa, B.B. Analytical validation of a 12-gene molecular test for the prediction of distant recurrence in breast cancer. Futur. Sci. OA 2017, 3, FSO221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kronenwett, R.; Bohmann, K.; Prinzler, J.; Sinn, B.V.; Haufe, F.; Roth, C.; Averdick, M.; Ropers, T.; Windbergs, C.; Brase, J.C.; et al. Decentral gene expression analysis: Analytical validation of the Endopredict genomic multianalyte breast cancer prognosis test. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denkert, C.; Kronenwett, R.; Schlake, W.; Bohmann, K.; Penzel, R.; Weber, K.E.; Höfler, H.; Lehmann, U.; Schirmacher, P.; Specht, K.; et al. Decentral gene expression analysis for ER+/Her2− breast cancer: Results of a proficiency testing program for the EndoPredict assay. Virchows Arch. 2012, 460, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haybittle, J.L.; Blamey, R.W.; Elston, C.W.; Johnson, J.; Doyle, P.J.; Campbell, F.C.; Nicholson, R.I.; Griffiths, K. A prognostic index in primary breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1982, 45, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Tuñón, I.; Ricote, M.; Ruiz, A.; Fraile, B.; Paniagua, R.; Royuela, M. OSM, LIF, Its Receptors, and Its Relationship with the Malignance in Human Breast Carcinoma (In Situ and in Infiltrative). Cancer Investig. 2008, 26, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkus, E.; Kyriakides, S.; Ohno, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Poortmans, P.; Rutgers, E.; Zackrisson, S.; Cardoso, F. Primary breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v8–v30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krop, I.; Ismaila, N.; Andre, F.; Bast, R.C.; Barlow, W.; Collyar, D.E.; Hammond, M.E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Liu, M.C.; Mennel, R.G.; et al. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline focused update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.F.; Schmitt, F. An update on breast cancer multigene prognostic tests-emergent clinical biomarkers. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NCCN. 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast Cancer; National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Plymouth Meeting, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- NICE. Tumour Profiling Tests to Guide Adjuvant Chemotherapy Decisions in Early Breast Cancer; National Institute of Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ontario Health (Quality). Gene Expression Profiling Tests for Early-Stage Invasive Breast Cancer: A Health Technology Assessment; Ontario Health (Quality): Toronto, ON, Canada, 2020; Volume 20. [Google Scholar]
- Almstedt, K.; Mendoza, S.; Otto, M.; Battista, M.J.; Steetskamp, J.; Heimes, A.S.; Krajnak, S.; Poplawski, A.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Hasenburg, A.; et al. EndoPredict® in early hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 182, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.M.; Keil, E.; Lehmann, A.; Winzer, K.-J.; Richter-Ehrenstein, C.; Prinzler, J.; Bangemann, N.; Reles, A.; Stadie, S.; Schoenegg, W.; et al. The EndoPredict Gene-Expression Assay in Clinical Practice—Performance and Impact on Clinical Decisions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thangarajah, F.; Eichler, C.; Fromme, J.; Malter, W.; Caroline Radosa, J.; Ludwig, S.; Puppe, J.; Paepke, S.; Warm, M.; Caroline Radosa JuliaRadosa, J.; et al. The impact of EndoPredict® on decision making with increasing oncological work experience: Can overtreatment be avoided? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 299, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buus, R.; Sestak, I.; Kronenwett, R.; Denkert, C.; Dubsky, P.; Krappmann, K.; Scheer, M.; Petry, C.; Cuzick, J.; Dowsett, M. Comparison of EndoPredict and EPclin with Cncotype DX recurrence score for prediction of risk of distant recurrence after endocrine therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schnabel, C.A.; Schroeder, B.E.; Jerevall, P.L.; Jankowitz, R.C.; Fornander, T.; Stäl, O.; Brufsky, A.M.; Sgroi, D.; Erlander, M.G. Breast cancer index identifies early-stage estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients at risk for early- and late-distant recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4196–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sgroi, D.C.; Sestak, I.; Cuzick, J.; Zhang, Y.; Schnabel, C.A.; Schroeder, B.; Erlander, M.G.; Dunbier, A.; Sidhu, K.; Lopez-Knowles, E.; et al. Prediction of late distant recurrence in patients with oestrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer: A prospective comparison of the breast-cancer index (BCI) assay, 21-gene recurrence score, and IHC4 in the TransATAC study population. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, B.; Zhang, Y.; Stål, O.; Fornander, T.; Brufsky, A.; Sgroi, D.C.; Schnabel, C.A. Risk stratification with Breast Cancer Index for late distant recurrence in patients with clinically low-risk (T1N0) estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filipits, M.; Nielsen, T.O.; Rudas, M.; Greil, R.; Stoger, H.; Jakesz, R.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Dietze, O.; Regitnig, P.; Gruber-Rossipal, C.; et al. The PAM50 risk-of-recurrence score predicts risk for late distant recurrence after endocrine therapy in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive early breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrios, C.H.; Sampaio, C.; Vinholes, J.; Caponero, R. What is the role of chemotherapy in estrogen receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer? Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, D.; Wischnewsky, M.; Joukhadar, R.; Chow, O.; Janni, W.; Leinert, E.; Fink, V.; Stüber, T.; Curtaz, C.; Kreienberg, R.; et al. Does chemotherapy improve survival in patients with nodal positive luminal A breast cancer? A retrospective Multicenter Study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbull, A.; Webber, V.; McStay, D.; Arthur, L.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Fernando, A.; Renshaw, L.; Keys, J.; Clarke, R.; Sims, A. Predicting benefit from HER2-targeted therapies in patients with ER+/HER2+ breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, P3-10-26. [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull, A.K.; Webber, V.; McStay, D.; Arthur, L.M.; Martinez-Perez, C.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Kay, C.; Renshaw, L.; Keys, J.; et al. Abstract P1-18-07: Can some ER+/HER2+ patients be safely spared from treatment with chemotherapy plus herceptin? Cancer Res. 2020, 80, P1-18-07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Perez, C.; Kay, C.; Swan, R.; Ekatah, G.E.; Arthur, L.M.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Sims, A.H.; Oikonomidou, O.; Turnbull, A.K.; et al. Abstract P6-16-04: IL6ST, a biomarker of endocrine therapy response, has potential in identifying a subgroup of women with ER+ DCIS who are more likely to benefit from adjuvant endocrine therapy. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, P6-16-04. [Google Scholar]


| Original Publication | Signature | Biomarkers Incorporated in the Signature | Clinical Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filipits et al. (2011) [44] | EndoPredict | Low risk-associated (surrogates for ER signalling/cell differentiation): RBBP8, IL6ST, AZGP1, MGP, STC2 |
| |
| High risk-associated (surrogates for proliferation/cell cycle): BIRC5, UBE2C, DHCR7 | ||||
| Housekeeper genes: CALM2, OAZ1, RPL37A | ||||
| Control gene: HBB | ||||
| EPclin | Clinical factors: Lymph node status, tumour size | |||
| Molecular factors: EndoPredict genes | ||||
| LR-associated:IL6ST (5 probes), NPY1R, ELOVL5, ASAH1 (2 probes), ALDH6A1, SYBU, RAB5C, PTP4A2, HSPA2, SLC7A8 ADRA2A, MYCBP, CX3CR1, ERCC1, DNAJA3, NINJ1, C4orf43, IFI35, ZNF688, SNX1, CREBL2, HPN, NME3, PDHB, NKX3-1, DEXI, GSTM3, LCMT1 | ||||
| Sota et al. (2014) [49] | IRSN-23 | Non-pCR-associated: IL6ST (3 probes), CX3CR1, ZEB1 (2 probes), SEMA3C, HFE, EDA |
| |
| pCR-associated: CARD9, IDO1, CXCL9, PNP, CXCL11 (2 probes), CEBPB, CD83, CD1D, CTSC, CXCL10, IGHG1, VEGFA, CR2 | ||||
| Turnbull et al. (2016) [51] | EER4 | Pretreatment levels: IL6ST, NGFRAP1 |
| |
| 2-week levels: ASPM, MCM4 | ||||
| EA2 | Pretreatment levels:IL6ST |
| ||
| 2-week levels: MCM4 | ||||
| EA2clin | Clinical factors | Lymph node involvement, tumour size and tumour grade |
| |
| Molecular factors | Pretreament level: IL6ST 2-week level: MCM4 | |||
| Tsunashima et al. (2018) [54] | 42GC | NLR-associated: KLF7, STS, RALA, SMURF2, OXTR, ABCC10, ASAP2, CALB2, OPA1 |
| |
| LR-associated: IL6ST (5 probes), NPY1R, ELOVL5, ASAH1 (2 probes), ALDH6A1, SYBU, RAB5C, PTP4A2, HSPA2, SLC7A8 ADRA2A, MYCBP, CX3CR1, ERCC1, DNAJA3, NINJ1, C4orf43, IFI35, ZNF688, SNX1, CREBL2, HPN, NME3, PDHB, NKX3-1, DEXI, GSTM3, LCMT1 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Pérez, C.; Leung, J.; Kay, C.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Dixon, J.M.; Turnbull, A.K. The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070618
Martínez-Pérez C, Leung J, Kay C, Meehan J, Gray M, Dixon JM, Turnbull AK. The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(7):618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070618
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Pérez, Carlos, Jess Leung, Charlene Kay, James Meehan, Mark Gray, J Michael Dixon, and Arran K Turnbull. 2021. "The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 7: 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070618
APA StyleMartínez-Pérez, C., Leung, J., Kay, C., Meehan, J., Gray, M., Dixon, J. M., & Turnbull, A. K. (2021). The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(7), 618. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11070618









