Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Selection and Eligibility
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Subgroups in Celiac Disease
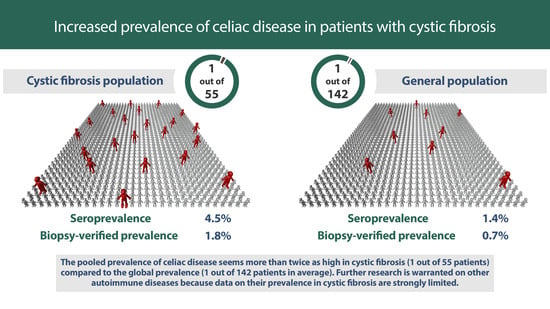
3. Results
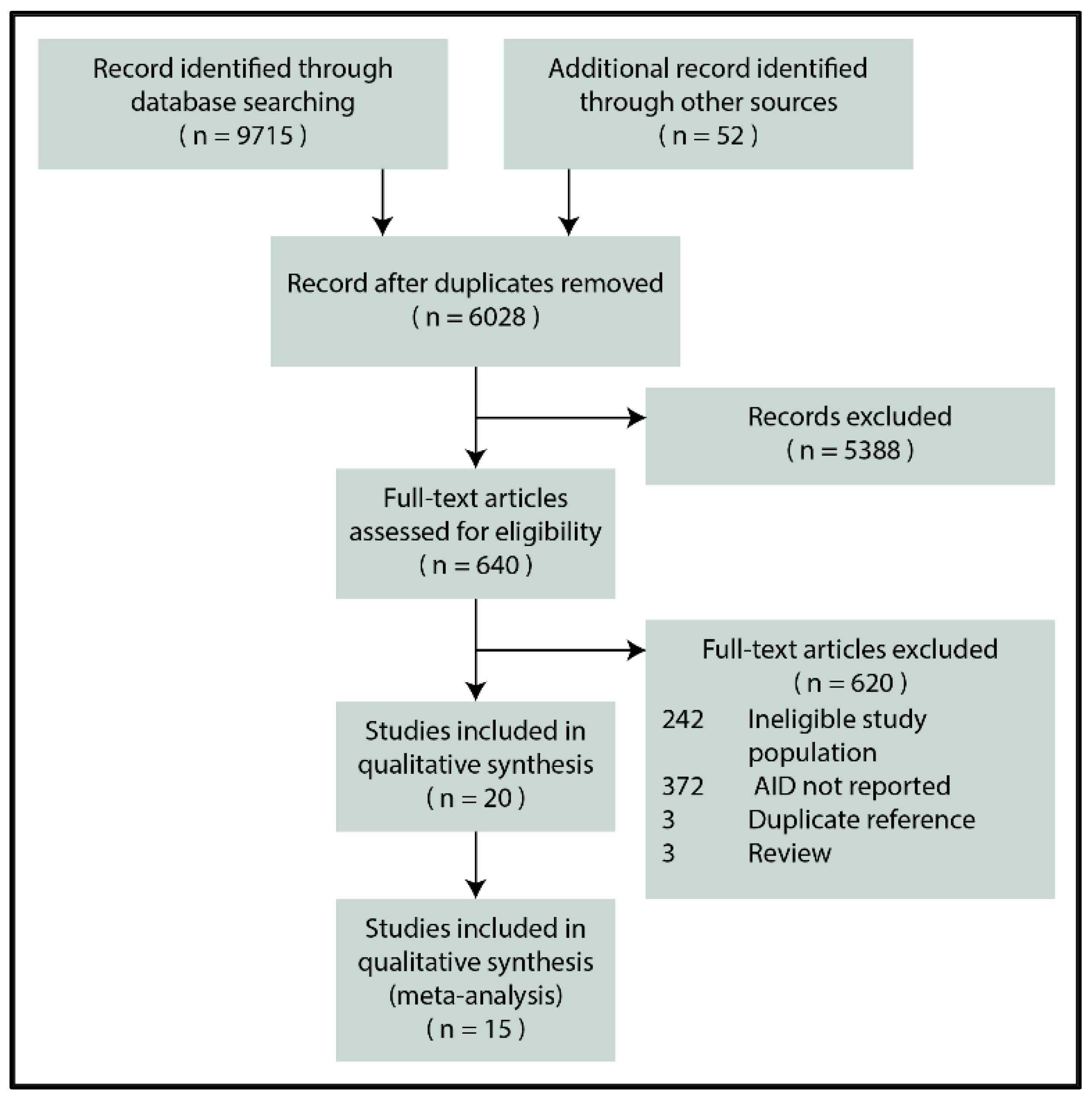
3.1. Search and Selection
3.2. Celiac Disease
3.2.1. Characteristics of the Studies Included
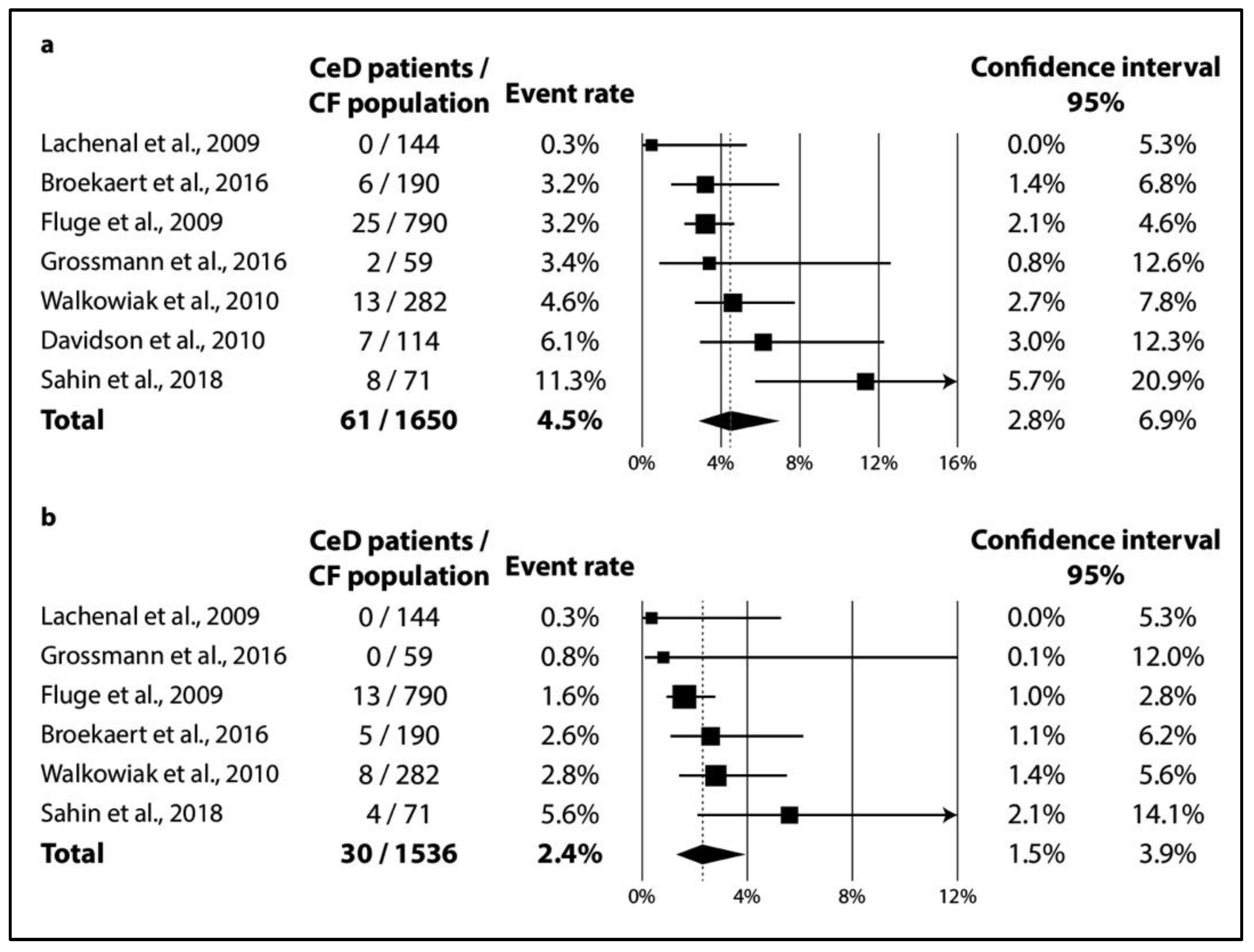
3.2.2. Results of Meta-Analysis
3.2.3. Publication Bias
3.3. Systematic Review on Autoimmune Diseases Other Than Celiac Disease
3.4. Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Explanation and Elaboration
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
5.1. Implications for Practice
5.2. Implications for Research and Cost-Effectiveness
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Sullivan, B.P.; Freedman, S.D. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.M. The prevalence of cystic fibrosis in the European Union. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walters, S.M.A. Epidemiology of cystic fibrosis. In Cystic Fibrosis, 3rd ed.; Hodson, M., Geddes, D.M., Bush, A., Eds.; Edward Arnold Ltd.: London, UK, 2007; pp. 21–45. [Google Scholar]
- Burgel, P.-R.; Bell, S.; Olesen, H.V.; Viviani, L.; Zolin, A.; Blasi, F.; Elborn, J. Future trends in cystic fibrosis demography in 34 European countries. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saint-Criq, V.; Gray, M.A. Role of CFTR in epithelial physiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Law, S.M.; Gray, R.D. Neutrophil extracellular traps and the dysfunctional innate immune response of cystic fibrosis lung disease: A review. J. Inflamm. 2017, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghasafari, P.; George, U.; Pidaparti, R. A review of inflammatory mechanism in airway diseases. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, G.; Pouyani, M.R.; Abolhassani, H.; Sharifi, L.; Dizaji, M.Z.; Mohammadi, J.; Mirshafiey, A.; Aghamohammadi, A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of immune dysregulation and autoimmunity. Cell. Immunol. 2016, 310, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaravalloti, G.; Baracchini, A.; Rossomando, V.; Ughi, C.; Ceccarelli, M. Celiac disease and cystic fibrosis: Casual association? Minerva Pediatrica 1995, 47, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.C.; Nelson, R.; Anderson, C.M. Cystic fibrosis and coeliac disease: Coexistence in two children. Arch. Dis. Child. 1973, 48, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demeyer, S.; De Boeck, K.; Witters, P.; Cosaert, K. Beyond pancreatic insufficiency and liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 175, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitz, D.; Durie, P.R.; Clarke, L.L.; Werlin, S.L.; Taylor, C.J.; Semler, J.; De Lisle, R.C.; Lewindon, P.; Lichtman, S.M.; Sinaasappel, M.; et al. Gastrointestinal Outcomes and Confounders in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, H.J.E.; Van Kreel, B.; Forget, P.P. Effects of Therapy With Lansoprazole on Intestinal Permeability and Inflammation in Young Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2001, 33, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lampert, S.; Pour Schahin, S.; Wiest, G.; Hahn, E.; Ficker, J.H. 56-jähriger Patient mit zystischer Fibrose und Sprue. Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie 2007, 45, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, C.; Duff, A.J.; Bell, S.; Heijerman, H.G.; Munck, A.; Ratjen, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Southern, K.W.; Barben, J.; Flume, P.A.; et al. ECFS best practice guidelines: The 2018 revision. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2018, 17, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahiri, T.; Hempstead, S.E.; Brady, C.; Cannon, C.; Clark, K.; Condren, M.E.; Guill, M.F.; Guillerman, R.P.; Leone, C.G.; Maguiness, K.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation for Preschoolers with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20151784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Toma, A.; Volta, U.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; Sanders, D.S.; Cellier, C.; Mulder, C.J.; Lundin, K.E.A. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 583–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, I.D.; Fasano, A.; Guandalini, S.; Hoffenberg, E.; Levy, J.; Reilly, N.; Verma, R. NASPGHAN Clinical Report on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gluten-related Disorders. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.; Kurppa, K.; Mearin, M.L.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, R.; Castillejo, G.; et al. European Society Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Kelly, C.P.; Calderwood, A.H.; Murray, J.A. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 656–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passot, F.M.; Calderon, V.; Fichant, G.; Lane, D.; Pasta, F. Centromere Binding and Evolution of Chromosomal Partition Systems in the Burkholderiales. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3426–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kerem, B.; Rommens, J.M.; Buchanan, J.A.; Markiewicz, D.; Cox, T.K.; Chakravarti, A.; Buchwald, M.; Tsui, L.C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Genetic analysis. Science 1989, 245, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riordan, J.; Rommens, J.; Kerem, B.; Alon, N.; Rozmahel, R.; Grzelczak, Z.; Zielenski, J.; Lok, S.; Plavsic, N.; Chou, J.; et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science 1989, 245, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommens, J.M.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Kerem, B.; Drumm, M.L.; Melmer, G.; Dean, M.; Rozmahel, R.; Cole, J.; Kennedy, D.; Hidaka, N.; et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: Chromosome walking and jumping. Science 1989, 245, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.M.S.; Lisy, K.; Riitano, D.; Tufanaru, C. Methodological guidance for systematic reviews of observational epidemiological studies reporting prevalence and incidence data. Int. J. Evid. Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.0 (Updated July 2019); Cochrane: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, D.T. Nutritional status and treatment in children with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Nutr. Suppl. 2011, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanyar, S.; Ekbom, A.; Askling, J.; Johannesson, M.; Montgomery, S. Cystic fibrosis gene mutations and gastrointestinal diseases. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2010, 9, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broekaert, I.J.; Radojska, S.M.; Gathof, B.; Rietschel, E.; Koningsbruggen-Rietschel, S.V. Cystic Fibrosis and Celiac Disease: Mere Coincidence? JSM Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, A.; Martinez, A.; MacMahon, V.; Gonzalez, T.; Lillquis, Y.; Jenkins, S. Cystic fibrosis and celiac disease: TTG screening results indicate a common association. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, E.S.C.; Nogueira, H.B.R.; Catunda, A.V.; Gifoni, D.P.; Padilha, P.S.; Soares, V.G. Cistic fibroses in children and adolescents in Fortaleza-CE: A epidemiology study and comorbidities. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2016, 51, S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluge, G.; Olesen, H.; Gilljam, M.; Meyer, P.; Pressler, T.; Storrösten, O.; Karpati, F.; Hjelte, L. Co-morbidity of cystic fibrosis and celiac disease in Scandinavian cystic fibrosis patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2009, 8, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grossmann, K.; Röber, N.; Hiemann, R.; Rödiger, S.; Schierack, P.; Reinhold, D.; Laass, M.W.; Conrad, K.; Roggenbuck, D. Simultaneous detection of celiac disease-specific IgA antibodies and total IgA. Autoimmun. Highlights 2016, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lachenal, F.; Nkana, K.; Nove-Josserand, R.; Fabien, N.; Durieu, I. Prevalence and clinical significance of auto-antibodies in adults with cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Littlewood, J.M. Abdominal pain in cystic fibrosis. J. R. Soc. Med. 1995, 88 (Suppl. S25), 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masip, E.; Calvo, J.; Donat, E.; Polo, B.; Martinez, S.; Ribes-Koninckx, C. Association between cystic fibrosis and celiac disease, how much is that frequent? J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, F.; Accomando, A.; D’Antoni, M.; Abbate, C.; Iapichino, L.; Balsamo, V. Coesistenza di malattia celiaca (MC) e di fibrosi cistica (FC). Descrizione di un caso clinico. Riv. Ital. Pediatr. 1991, 17, 614–617. [Google Scholar]
- Ras, J.E.; Vreugdenhil, A.C.E.; Houwen, R.H.J.; Van den Neucker, A.M. Zijn we tevreden met e´e´n diagnose? Tijdschr. Kindergeneeskd 2012, 80, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Y.; Erkan, T.; Kutlu, T.; Kepil, N.; Kilinc, A.A.; Cokugras, F.C.; Cokugras, H. The Frequency of Celiac Disease in Turkish Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. J. Ther. 2019, 25, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valletta, E.A.; Mastella, G. Incidence of Celiac Disease in a Cystic Fibrosis Population. Acta Paediatr. 1989, 78, 784–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowiak, J.; Blask-Osipa, A.; Lisowska, A.; Oralewska, B.; Pogorzelski, A.; Cichy, W.; Sapiejka, E.; Kowalska, M.; Korzon, M.; Szaflarska-Popławska, A. Cystic fibrosis is a risk factor for celiac disease. Acta Biochimica Polonica 2010, 57, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesler, A.M.; Kroner, P.T.; Abader, P.; Afsh, M.; Lewis, M.D. Tu2053—Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Cystic Fibrosis: Is It More Prevalent? Gastroenterology 2019, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Still, J.D. Cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, biliary abnormalities, and cancer. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1990, 11, 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Sowa, M.; Kolenda, R.; Baumgart, D.C.; Pratschke, J.; Papp, M.; Tornai, T.; Suchanski, J.; Bogdanos, D.; Mytilinaiou, M.G.; Hammermann, J.; et al. Mucosal Autoimmunity to Cell-Bound GP2 Isoforms Is a Sensitive Marker in PSC and Associated With the Clinical Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, H.P.; Benda, N.; Fitzke, G.; Lang, A.; Langenberg, M.; Riethmuller, J.; Stern, M. Colonic wall thickness measured by ultrasound: Striking differences in patients with cystic fibrosis versus healthy controls. Gut 1997, 40, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strandvik, B.; Hjelte, L.; Gabrielsson, N.; Glaumann, H. Sclerosing Cholangitis in Cystic Fibrosis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1988, 23, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arora, A.; Strand, T.A.; Leffler, D.A.; Catassi, C.; Green, P.H.; Kelly, C.P.; Ahuja, V.; Makharia, G.K. Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 823–836.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruscia, E.M.; Zhang, P.-X.; Satoh, A.; Caputo, C.; Medzhitov, R.; Shenoy, A.; Egan, M.E.; Krause, D.S. Abnormal Trafficking and Degradation of TLR4 Underlie the Elevated Inflammatory Response in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6990–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaman, M.M.; Gelrud, A.; Junaidi, O.; Regan, M.M.; Warny, M.; Shea, J.C.; Kelly, C.; O’Sullivan, B.P.; Freedman, S.D. Interleukin 8 Secretion from Monocytes of Subjects Heterozygous for the ΔF508 Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Gene Mutation Is Altered. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2004, 11, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersson, C.; Zaman, M.M.; Jones, A.B.; Freedman, S.D. Alterations in immune response and PPAR/LXR regulation in cystic fibrosis macrophages. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKeon, D.J.; Condliffe, A.M.; Cowburn, A.; Cadwallader, K.C.; Farahi, N.; Bilton, D.; Chilvers, E. Prolonged survival of neutrophils from patients with F508 CFTR mutations. Thorax 2008, 63, 660–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriceau, S.; Lenoir, G.; Witko-Sarsat, V. In Cystic Fibrosis Homozygotes and Heterozygotes, Neutrophil Apoptosis Is Delayed and Modulated by Diamide or Roscovitine: Evidence for an Innate Neutrophil Disturbance. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.R.; Costelloe, E.A.; Lunn, D.P.; Stacey, K.; Delaney, S.J.; Passey, R.; McGlinn, E.; McMorran, B.; Ahadizadeh, A.; Geczy, C.L.; et al. G551D Cystic Fibrosis Mice Exhibit Abnormal Regulation of Inflammation in Lungs and Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 3870–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubin, P.J.; Kolls, J.K. IL-17 in cystic fibrosis: More than just Th17 cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, F.; Henry, A.; Kreindler, J.L.; Dubin, P.J.; Ulrich, L.; Steele, C.; Finder, J.D.; Pilewski, J.M.; Carreno, B.M.; Goldman, S.J.; et al. Role of IL-17A, IL-17F, and the IL-17 Receptor in Regulating Growth-Related Oncogene-α and Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor in Bronchial Epithelium: Implications for Airway Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronborg, G.; Hansen, M.B.; Svenson, M.; Fomsgaard, A.; Hsiby, N.; Bendtzen, K. Cytokines in sputum and serum from patients with cystic fibrosis and chronicpseudomonas aeruginosa infection as markers of destructive inflammation in the lungs. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 1993, 15, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElvaney, N.G.; Nakamura, H.; Birrer, P.; Hébert, C.A.; Wong, W.L.; Alphonso, M.; Baker, J.B.; Catalano, M.A.; Crystal, R.G. Modulation of airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. In vivo suppression of interleukin-8 levels on the respiratory epithelial surface by aerosolization of recombinant secretory leukoprotease inhibitor. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miossec, P. IL-17 and Th17 cells in human inflammatory diseases. Microbes Infect. 2009, 11, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adib-Conquy, M.; Pedron, T.; Petit-Bertron, A.-F.; Tabary, O.; Corvol, H.; Jacquot, J.; Clément, A.; Cavaillon, J.-M. Neutrophils in Cystic Fibrosis Display a Distinct Gene Expression Pattern. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, L.; Villella, V.R.; Raia, V.; Kroemer, G. The gliadin-CFTR connection: New perspectives for the treatment of celiac disease. Ital. J. Pediatrics 2019, 45, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenna, R.; Tiberti, C.; Petrarca, L.; Lucantoni, F.; Mennini, M.; Luparia, R.P.L.; Panimolle, F.; Mastrogiorgio, G.; Pietropaoli, N.; Magliocca, F.M.; et al. The Celiac Iceberg. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.K.; Schwarzenberg, S.J. Pancreatic insufficiency in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2017, 16, S70–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Mearin, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Coeliac Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, I.D.; Dirks, M.H.; Liptak, G.S.; Colletti, R.B.; Fasano, A.; Guandalini, S.; Hoffenberg, E.; Horvath, K.; Murray, J.; Pivor, M.; et al. Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Celiac Disease in Children: Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 40, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yel, L. Selective IgA Deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbonas, V.; Sadauskaite, J.; Cerkauskiene, R.; Kaminskas, A.; Mäki, M.; Kurppa, K. Population-Based Screening for Selective Immunoglobulin A (IgA) Deficiency in Lithuanian Children Using a Rapid Antibody-Based Fingertip Test. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgic, B.; Sari, S.; Basturk, B.; Ensari, A.; Egritas, O.; Bukulmez, A.; Baris, Z. Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Healthy Turkish School Children. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Lachenal et al., 2009 [36] | Broekaert et al., 2016 [31] | Fluge et al., 2009 [34] | Walkowiak et al., 2010 [43] | Sahin et al., 2019 [41] | Davidson et al., 2009 [32] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting | |||||||
| Country (centers) | France (Lyon) | Germany (Cologne) | Denmark, Norway, and Sweden | Poland | Turkey (Istanbul) | Canada (Vancouver) | |
| Recruitment period | Jan 2000–Jan 2007 | N/A | 2004–2005 | 2006–2009 | Oct 2015–Mar 2017 | N/A | |
| Prospective | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| Age group | adults | adults and children | adults and children | adults and children | children | children | |
| Age (mean (SD) | 25 (5.9) | 25.5 (19.6) | N/A | 17.3 (11.3) | 9.9 (5.5) | N/A | |
| Total number of patients with CF | 144 | 190 | 790 | 282 | 71 | 114 | |
| Number of patients with known CeD | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (0.8%) | 2 (0.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | |
| Number of patients with de novo diagnosed CeD | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (1.1%) | 4 (0.5%) | 4 (1.4%) | 2 (2.8%) | 4 (3.5%) | |
| Total prevalence of CeD | 0/144 (0.0%) | 2/190 (1.1%) | 10/790 (1.3%) | 6/282 (2.1%) | 2/71 (2.8%) | 4/114 (3.5%) | |
| Diagnostic criteria of CF | sweat test + genetics | sweat test + genetics | N/A | sweat test + genetics | sweat test + genetics | N/A | |
| Diagnostic criteria of CeD | serology | histology | histology | histology | histology | histology | |
| Littlewood et al., 1995 [37] | Valletta et al., 1989 [42] | Pardo et al., 1991 [39] | Ras et al., 2012 [40] | Bahmanyar et al., 2010 [30] | De Castro et al., 2016 [33] | Anton et al., 2011 [29] | Masip et al., 2017 [38] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting | |||||||||
| Country (centers) | UK (Leeds) | Italy (Verona) | Italy (Palermo) | the Netherlands | Sweden | Brazil (Fortaleza) | Romania (Iasi) | Spain (Valencia) | |
| Recruitment period | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1968–2003 | N/A | N/A | 2005–2015 | |
| Prospective | no | yes | no | yes | no | no | no | no | |
| Age group | children | children | children | children | adults and children | children | children | children | |
| Age (mean (SD) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 10 (5.2) | N/A | 4.7 (4.3) | N/A | N/A | |
| Total number of patients with CF | 500 | 1100 | 146 | 281 | 865 | 55 | 15 | 70 | |
| Total prevalence of CeD | 2/500 (0.4%) | 5/1100 (0.5%) | 2/146 (1.4%) | 7/281 (2.5%) | 30/865 (3.5%) | 3/55 (5.5%) | 1/15 (6.7%) | 6/70 (8.6%) | |
| Diagnostic criteria of CF | N/A | sweat test | sweat test | sweat test + genetics | sweat test + genetics | N/A | N/A | sweat test + genetics | |
| Diagnostic criteria of CeD | N/A | histology | histology | ESPGHAN | N/A | N/A | N/A | ESPGHAN | |
| Lachenal et al., 2009 [36] | Grossmann et al., 2016 [35] | Broekaert et al., 2016 [31] | Fluge et al., 2009 [34] | Walkowiak et al., 2010 [43] | Sahin et al., 2019 [41] | Davidson et al., 2009 [32] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Setting | ||||||||
| Country (centers) | France (Lyon) | Germany (Dresden) | Germany (Cologne) | Denmark, Norway, and Sweden | Poland | Turkey (Istanbul) | Canada (Vancouver) | |
| Recruitment period | Jan 2000– Jan 2007 | N/A | N/A | 2004–2005 | 2006–2009 | Oct 2015– Mar 2017 | N/A | |
| Prospective | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | |
| Age (mean (SD)) | 25 (5.9) | 12 (17) | 25.5 (19.6) | N/A | 17.3 (11.3) | 9.9 (5.5) | N/A | |
| Total number of patients with CF | 144 | 59 | 190 | 790 | 282 | 71 | 114 | |
| TGA-IgA positivity | ||||||||
| % | 0.0% (0) | 3.4% (2) | 3.2% (6) | N/A | 3.9% (11) | 11.3% (8) | 6.1% (2) | |
| Method | ELISA | ELISA | ELISA | ELISA | nephelometry | ELISA | N/A | |
| Cut-off | N/A | 3.91 U/ml | 20 U/ml | 50 U/ml | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| EMA-IgA positivity | ||||||||
| % | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 3.2% (6) | 0.9% (7) | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Method | IIF (monkey esophagus) | IIF (monkey esophagus) | IIF (monkey liver) | IIF (monkey esophagus) | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Cut-off | N/A | 1:10 | 1:10 | 1:5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| TGA-IgA and EMA-IgA positivity | 0% (0) | 0% (0) | 2.6% (5) | 0.9% (7) | 2.1% (6) | 5.6% (4) | N/A | |
| IgA deficiency | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2.2% (17) | 1.8% (5) | N/A | 2.6% (3) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imrei, M.; Németh, D.; Szakács, Z.; Hegyi, P.; Kiss, S.; Alizadeh, H.; Dembrovszky, F.; Pázmány, P.; Bajor, J.; Párniczky, A. Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090859
Imrei M, Németh D, Szakács Z, Hegyi P, Kiss S, Alizadeh H, Dembrovszky F, Pázmány P, Bajor J, Párniczky A. Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(9):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090859
Chicago/Turabian StyleImrei, Marcell, Dávid Németh, Zsolt Szakács, Péter Hegyi, Szabolcs Kiss, Hussain Alizadeh, Fanni Dembrovszky, Piroska Pázmány, Judit Bajor, and Andrea Párniczky. 2021. "Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 9: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090859
APA StyleImrei, M., Németh, D., Szakács, Z., Hegyi, P., Kiss, S., Alizadeh, H., Dembrovszky, F., Pázmány, P., Bajor, J., & Párniczky, A. (2021). Increased Prevalence of Celiac Disease in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(9), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11090859