Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
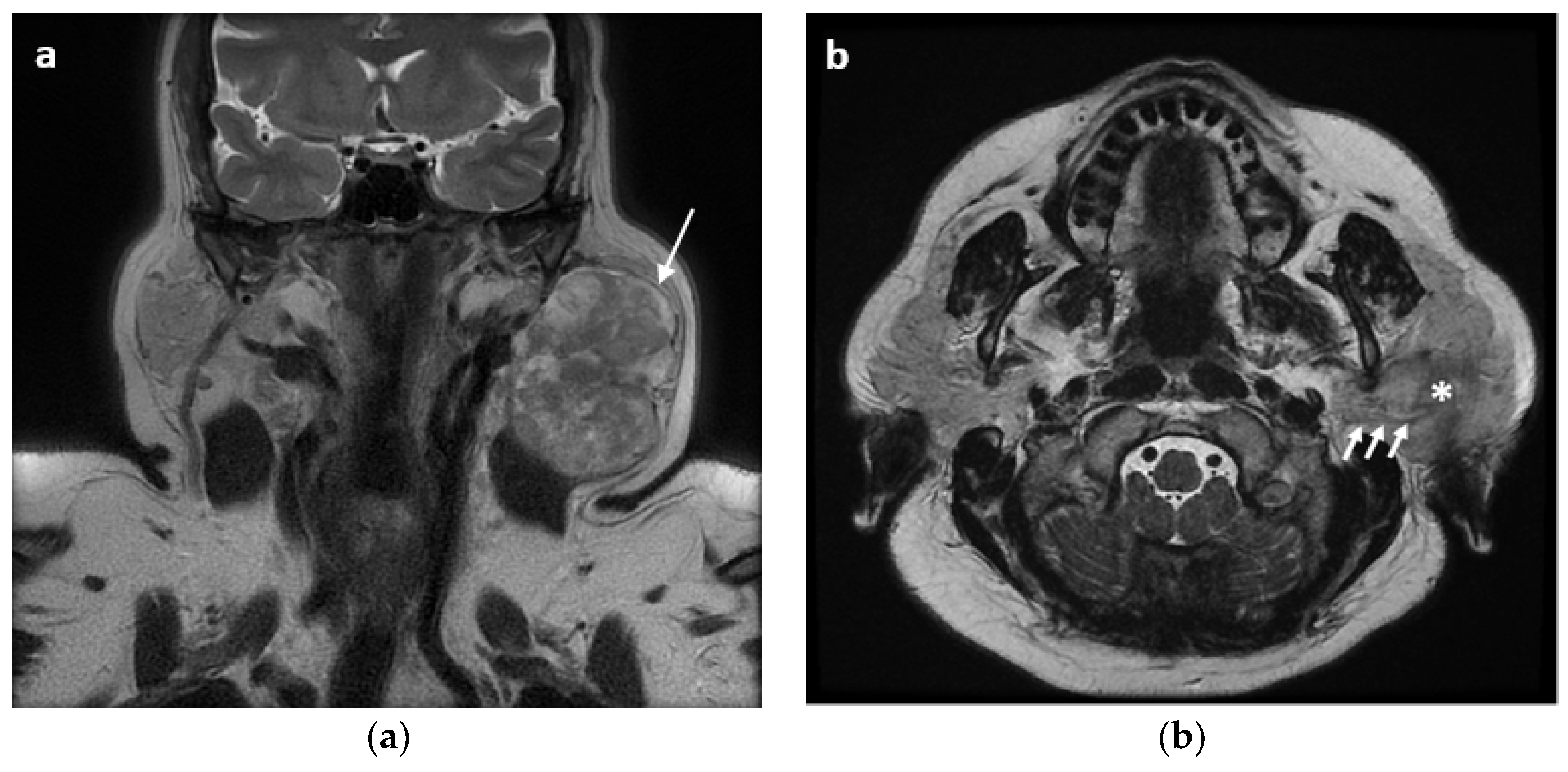
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surgical Technique
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradley, P.J.; McGurk, M. Incidence of salivary gland neoplasms in a defined UK population. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia-Sá, I.B.; Correia-Sá, M.; Costa-Ferreira, P.; Silva, Á.; Marques, M. Eleven years of parotid gland surgery in a plastic and reconstructive department. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, e26–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, R.M.; Laufer, D. Tumors of the major and minor salivary glands: Review of 25 years of experience. Anticancer Res. 1997, 17, 701–707. [Google Scholar]
- Spiro, R.H. Salivary neoplasms: Overview of a 35-year experience with 2807 patients. Head Neck Surg. 1986, 8, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.P.; Britt, C.J.; Saha, S.; McCulloch, T.M.; Wieland, A.M.; Harari, P.M.; Hartig, G.K. Patient and tumor characteristics predictive of primary parotid gland malignancy: A 20-year experience at the University of Wisconsin. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2015, 36, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, G.; Testa, D.; Montagnani, S.; Tafuri, D.; Salzano, F.A.; Rocca, A.; Amato, B.; Salzano, G.; Orabona, G.D.; Piombino, P.; et al. Surgical management of pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland in elderly patients: Role of morphological features. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12 (Suppl. S2), S12–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.; Nathan, C.-A. Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy for benign parotid tumors. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1039–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quer, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Marchal, F.; Vander Poorten, V.; Chevalier, D.; Leon, X.; Eisele, D.; Dulguerov, P. Classification of parotidectomies: A proposal of the European Salivary Gland Society. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quer, M.; Poorten, V.V.; Takes, R.P.; Silver, C.E.; Boedeker, C.C.; De Bree, R.; Rinaldo, A.; Sanabria, A.; Shaha, A.R.; Pujol, A.; et al. Surgical options in benign parotid tumors: A proposal for classification. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergotti, W.G.; Nguyen, S.A.; Zenk, J.; Gillespie, M.B. Extracapsular dissection for benign parotid tumors: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.G.; Erkul, E.; Nguyen, S.A.; Day, T.A.; Hornig, J.D.; Lentsch, E.J.; Gillespie, M.B. Extracapsular Dissection vs Superficial Parotidectomy of Benign Parotid Lesions. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Hua, R.X.; Li, T.Z.; Shan, X.F.; Cai, Z.G. PRISMA-Extracapsular Dissection Versus Superficial Parotidectomy in Treatment of Benign Parotid Tumors: Evidence from 3194 Patients. Medicine 2015, 94, e1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyle, F.M. Surgical consideration of parotid tumors. Am. J. Surg. 1956, 91, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, H.J., Jr.; Kambouris, A.; Pryzybylski, T.; Rachmaninoff, N. Salivary tumors: Clinicopathologic review of 190 patients. Am. J. Surg. 1964, 108, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Tomoda, K.; Kumazawa, T. The usefulness of partial parotidectomy for benign parotid gland tumors: A retrospective study of 306 cases. Acta Otolaryngol. 1993, 113 (Suppl. S500), 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leverstein, H.; van der Wal, J.E.; Tiwari, R.M.; van der Waal, I.; Snow, G.B. Surgical management of 246 previously untreated pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid gland. Br. J. Surg. 1997, 84, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- O’Brien, C.J.; Malka, V.B.; Mijailovic, M. Evaluation of 242 consecutive parotidectomies performed for benign and malignant disease. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1993, 63, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, R.L. Extracapsular Dissection with Facial Nerve Dissection for Benign Parotid Tumors. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 154, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial Nerve Grading System. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, S.R.; Kramer, D.E.; Hardy, B.; Jandali, D.; Stenson, K.; Kocak, M.; Al-Khudari, S. Functional outcomes after extracapsular dissection with partial facial nerve dissection for small and large parotid neoplasms. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laccourreye, H.; Laccourreye, O.; Cauchois, R.; Jouffre, V.; Menard, M.; Brasnu, D. Total conservative parotidectomy for primary benign pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: A 25-year experience with 229 patients. Laryngoscope 1994, 104, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, R.L. The significance of the margin in parotid surgery for pleomorphic adenoma. Laryngoscope 2002, 112, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernial, O.; Springer, I.N.; Warnke, P.; Härle, F.; Risick, C.; Wiltfang, J. Long-term recurrence rate of pleomorphic adenoma and postoperative facial nerve paresis (in parotid surgery). J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 35, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGurk, M.; Renehan, A.; Gleave, E.N.; Hancock, B.D. Clinical significance of the tumour capsule in the treatment of parotid pleomorphic adenomas. Br. J. Surg. 1996, 83, 1747–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Klussmann, J.P.; Wittekindt, C.; Stennert, E. Parotidectomy for Benign Parotid Disease at a University Teaching Hospital: Outcome of 963 Operations. Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klintworth, N.; Zenk, J.; Koch, M.; Iro, H. Postoperative complications after extracapsular dissection of benign parotid lesions with particular reference to facial nerve function. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Gurk, M.; Thomas, B.L.; Renehan, A.G. Extracapsular dissection for clinically benign parotid lumps: Reduced morbidity without oncological compromise. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Aversana, O.G.; Bonavolontà, P.; Iaconetta, G.; Forte, R.; Califano, L. Surgical management of benign tumors of the parotid gland: Extracapsular dissection vs superficial parotidectomy—Our experience in 232 cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, B.D. The management of salivary gland tumours. Surgery 1983, 73, 1620. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, B.D. Pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid: Removal without rupture. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1987, 69, 293–295. [Google Scholar]
- Dallera, P.; Marchetti, C.; Campobassi, A. Loyal capsular dissection of parotid pleomorphic adenomas. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1993, 22, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzan, L.; Pin, M. Extra-capsular dissection in benign parotid tumors. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, J.L.; Kim, H.S.; Park, C.I. Randomized clinical trial comparing partial parotidectomy versus superficial or total parotidectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2007, 94, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancock, B.D. Clinically benign parotid tumours: Local dissection as an alternative to superficial parotidectomy in selected cases. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1999, 81, 299–301. [Google Scholar]
- Martis, C. Parotid benign tumors: Comments on surgical treatment of 263 cases. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1983, 12, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, Y.; Caglak, F.; Keles, B.; Yildirim, G.; Salturk, Z. Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy in pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid gland. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis. Derg. 2011, 21, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witt, R.L. Facial nerve function after partial superficial parotidectomy: An 11-year review (1987–1997). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1999, 121, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, N.R.G.; Bse, B.J.A.; Dey, J.; Price, D.L.; Moore, E.J.; Janus, J.R. Analysis of Abdominal Dermal-Fat Grafting to Repair Parotidectomy Defects: An 18-Year Cohort Study. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 2144–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| N. of patients | 88 | |
| Age (mean) | 42.1 y (SD 15.9; range 21–65) | |
| sex | M | 31 |
| F | 57 | |
| Tumor size (mean) | 4.26 cm (SD 2,53; range 1.5–10) | |
| Depth | superficial | 64 (54 category I + 10 category III) |
| deep | 24 (14 category II + 2 category III + 8 category IV) | |
| Categories [9] | I | 54 |
| II | 14 | |
| III | 12 | |
| IV | 8 | |
| Istology | Pleomorphic Adenoma | 68 |
| Warthin tumor | 16 | |
| Mioepitelioma | 1 | |
| Basal cells Adenoma | 1 | |
| Lipoma | 2 | |
| complications | None | 84 |
| Transient Facial nerve weakness (resolution within 3 months) | 4 (4.54%) | |
| Permanent Facial nerve weakness | 0 | |
| Frey’s Sindrome | 0 | |
| sialocele | 0 |
| Categories [9] | N. of Patients | % |
|---|---|---|
| I | 54/88 | 61.4 |
| II | 14/88 | 15.9 |
| III | 12/88 | 13.6 |
| IV | 8/88 | 9.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massimilla, E.A.; Motta, G.; Magaldi, M.; Montella, M.; Messina, G.; Testa, D.; Cantone, E.; Motta, G. Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101641
Massimilla EA, Motta G, Magaldi M, Montella M, Messina G, Testa D, Cantone E, Motta G. Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(10):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101641
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassimilla, Eva Aurora, Giovanni Motta, Michelangelo Magaldi, Marco Montella, Gaetana Messina, Domenico Testa, Elena Cantone, and Gaetano Motta. 2022. "Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 10: 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101641
APA StyleMassimilla, E. A., Motta, G., Magaldi, M., Montella, M., Messina, G., Testa, D., Cantone, E., & Motta, G. (2022). Minimal Margin Surgery and Intraoperative Neuromonitoring in Benign Parotid Gland Tumors: Retrospective Clinical Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(10), 1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101641









