Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Collection Process and Data Items
2.6. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Synthesis Methods
2.8. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Meta-Analyses
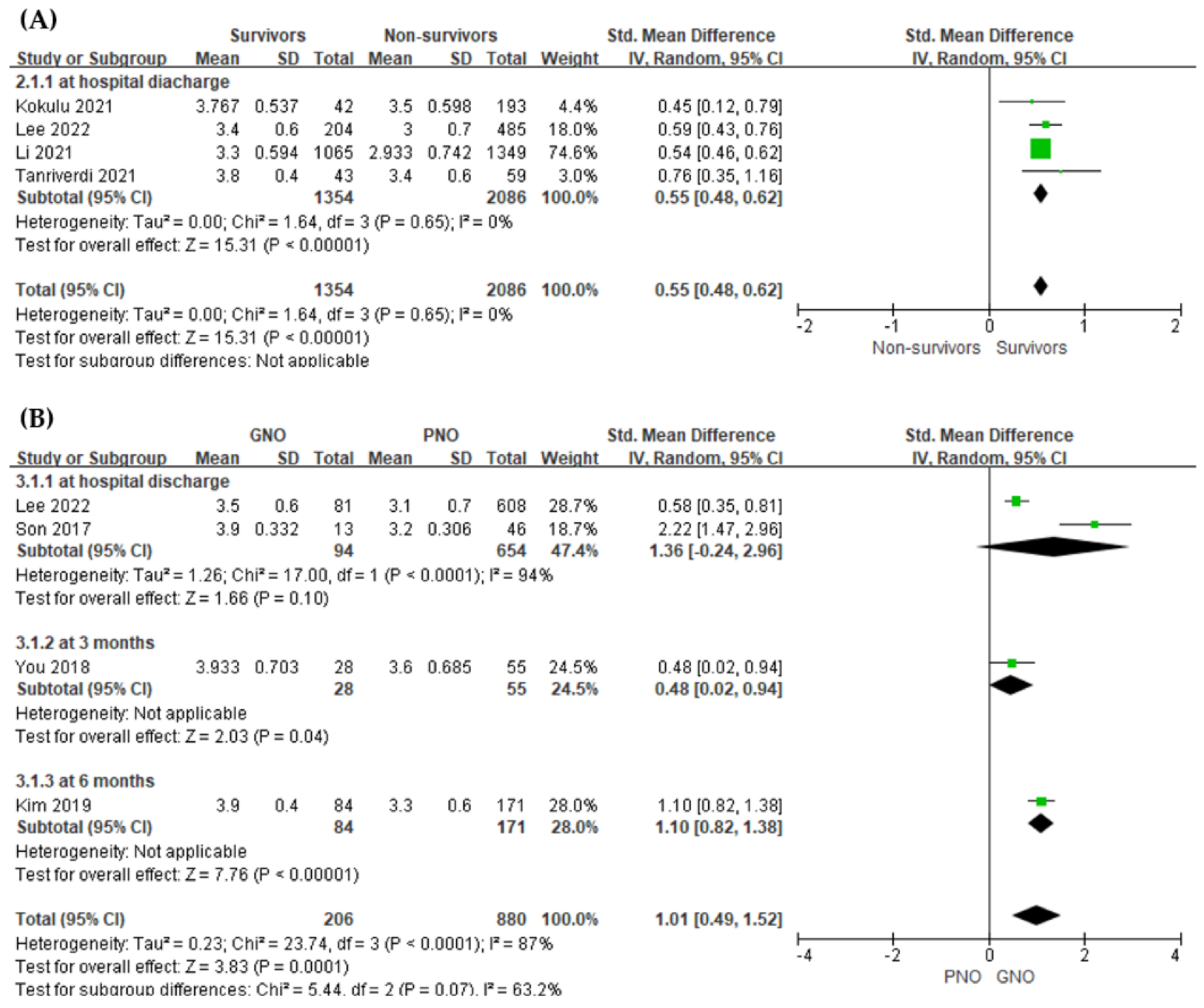
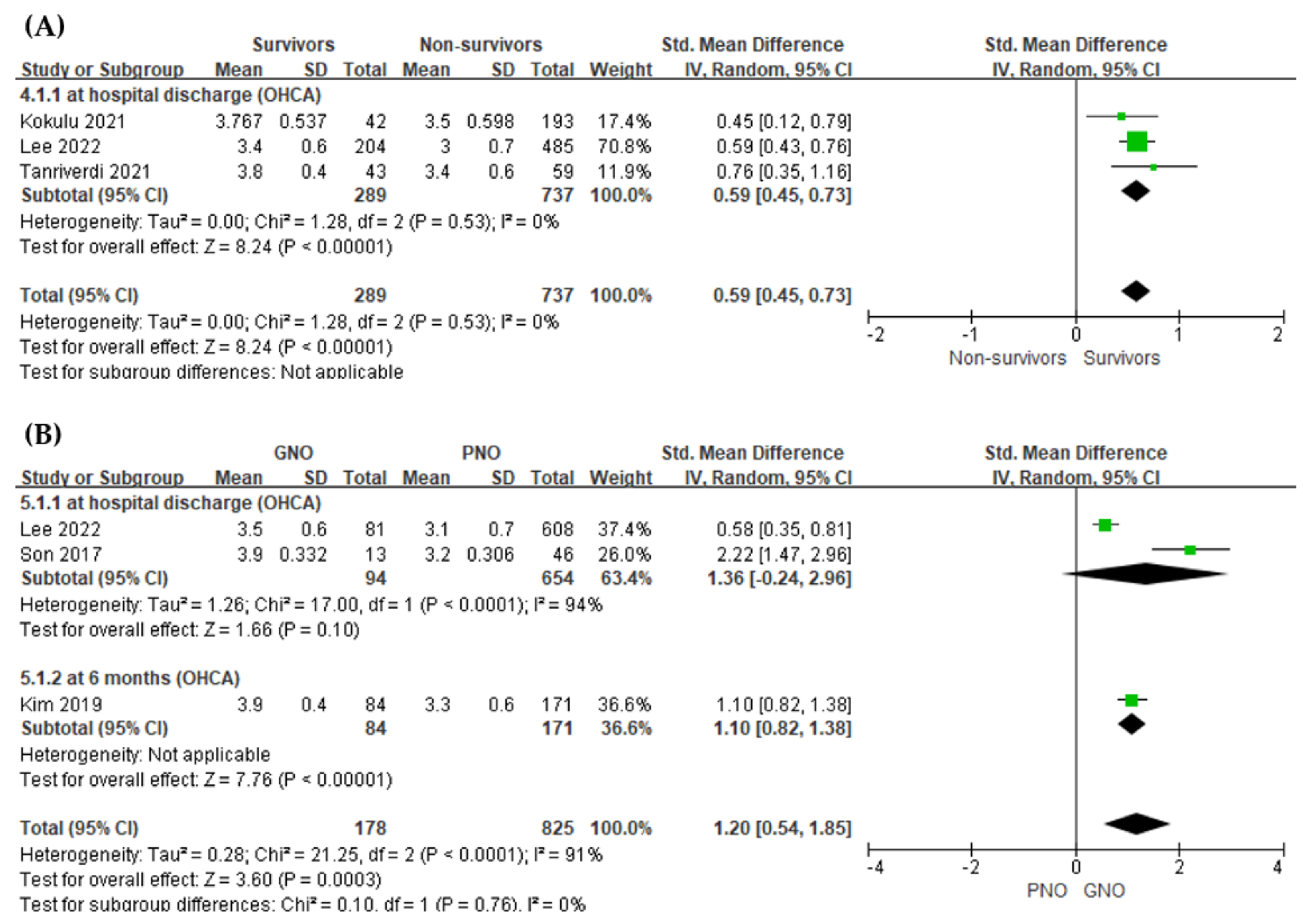
3.4.1. Value of the Serum Albumin Level for Predicting In-Hospital Mortality
3.4.2. Value of the Serum Albumin Level for Predicting Poor Neurological Outcome
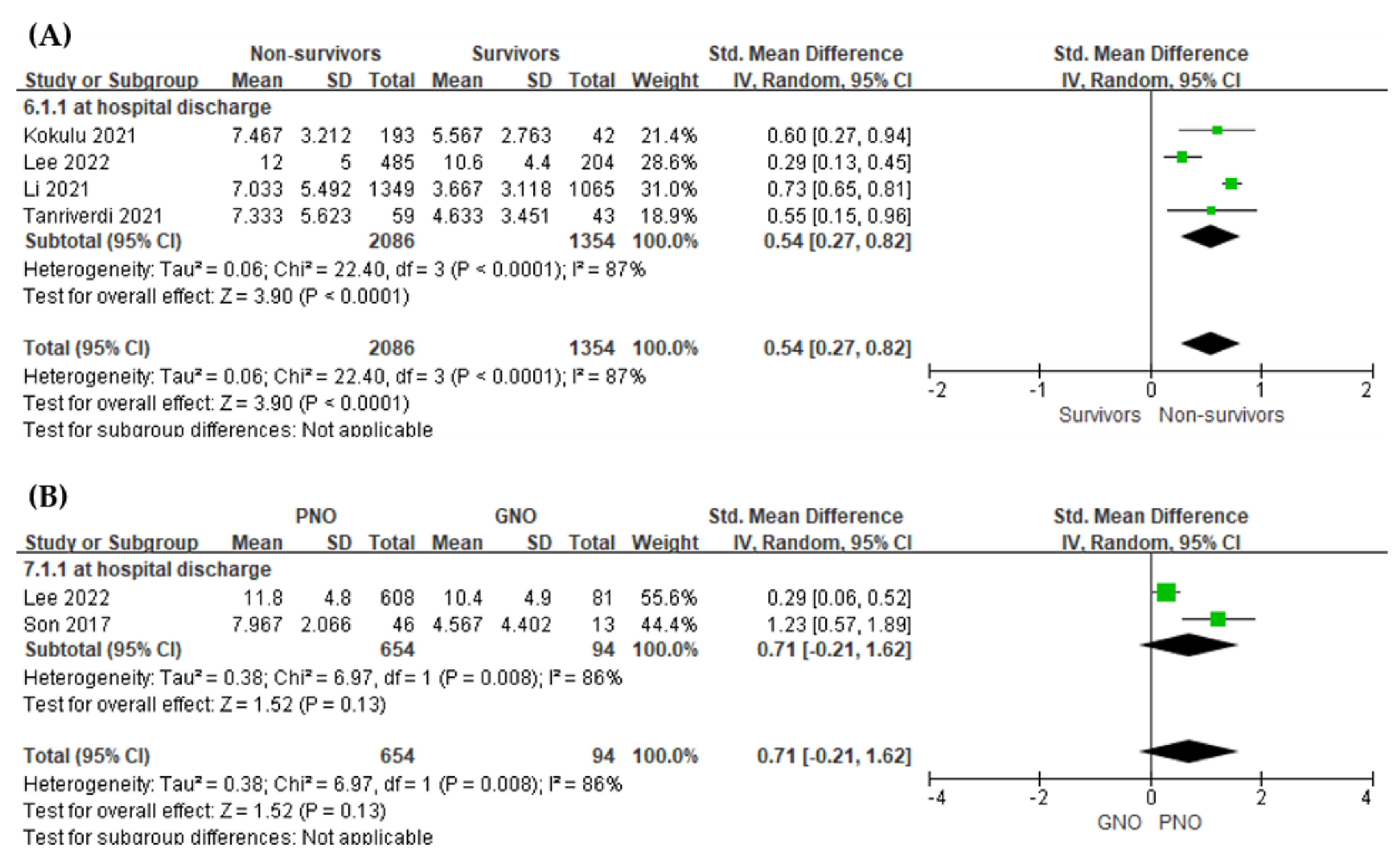
3.4.3. Value of the Serum Lactate Level for Predicting In-Hospital Mortality
3.4.4. Value of the Serum Lactate Level for Predicting Poor Neurological Outcome
3.5. Additional Analysis for Identifying and Measuring Heterogeneity
3.6. Risk of Bias across Studies
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adrie, C.; Monchi, M.; Laurent, I.; Um, S.; Yan, S.B.; Thuong, M.; Cariou, A.; Charpentier, J.; Dhainaut, J.F. Coagulopathy after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation following cardiac arrest: Implication of the protein C anticoagulant pathway. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witten, L.; Gardner, R.; Holmberg, M.J.; Wiberg, S.; Moskowitz, A.; Mehta, S.; Grossestreuer, A.V.; Yankama, T.; Donnino, M.W.; Berg, K.M. Reasons for death in patients successfully resuscitated from out-of-hospital and in-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 136, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, S.; Farrow, C.; Turner, D.; Nolan, J. Mode of death after admission to an Intensive Care Unit following cardiac arrest. Intensiv. Care Med. 2004, 30, 2126–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geocadin, R.G.; Callaway, C.W.; Fink, E.L.; Golan, E.; Greer, D.M.; Ko, N.U.; Lang, E.; Licht, D.J.; Marino, B.S.; McNair, N.D.; et al. Standards for studies of neurological prognostication in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e517–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, A.R.; Bartos, J.A.; Cabañas, J.G.; Donnino, M.W.; Drennan, I.R.; Hirsch, K.G.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Kurz, M.C.; Lavonas, E.J.; Morley, P.T.; et al. Part 3: Adult basic and advanced life support: 2020 American Heart Association guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2020, 142, S366–S468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, C.; Cariou, A.; Cavallaro, F.; Cronberg, T.; Friberg, H.; Hoedemaekers, C.; Horn, J.; Nolan, J.P.; Rossetti, A.O.; Soar, J. Prognostication in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest: An advisory statement from the European Resuscitation Council and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Resuscitation 2014, 85, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, R.; Börner, A.; Krack, A.; Sigusch, H.H.; Surber, R.; Figulla, H.R. Outcome after cardiac arrest: Predictive values and limitations of the neuroproteins neuron-specific enolase and protein S-100 and the Glasgow Coma Scale. Resuscitation 2005, 65, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, N.R.; Simpson, C.; Sherwood, R.A.; Abraha, H.D.; Cobbe, S.M.; O’Carroll, R.E.; Deary, I.; Fox, K.A.A. Prediction of cognitive dysfunction after resuscitation from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest using serum neuron-specific enolase and protein S-100. Heart 2007, 93, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arques, S. Human serum albumin in cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 52, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnau-Barrés, I.; Güerri-Fernández, R.; Luque, S.; Sorli, L.; Vázquez, O.; Miralles, R. Serum albumin is a strong predictor of sepsis outcome in elderly patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 38, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.N.; Kundu, S.K.; Islam, M.Z.; Bhuiyan, A.S.; Haque, M.M.; Malek, M.S.; Paul, P.K.; Shaha, B.; Thakur, A.K.; et al. Serum albumin level and in-hospital outcome of patients with first attack acute myocardial infarction. Mymensingh Med. J. 2019, 28, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Moja, L.; Moschetti, I.; Gensini, G.F.; Gusinu, R. Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2006, 1, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Youn, C.S.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, S.P. Prognostic value of serum albumin at admission for neurologic outcome with targeted temperature management after cardiac arrest. Emerg. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 6132542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; She, Y.; Mo, W.; Jin, B.; Xiang, W.; Luo, L. Albumin level at admission to the Intensive Care Unit is associated with prognosis in cardiac arrest patients. Cureus 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Park, J.; Min, J.; Yoo, I.; Jeong, W.; Cho, Y.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, S.; et al. Relationship between time related serum albumin concentration, optic nerve sheath diameter, cerebrospinal fluid pressure, and neurological prognosis in cardiac arrest survivors. Resuscitation 2018, 131, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, W65–W94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the Sample Mean and standard deviation from the sample size, Median, Range and/or Interquartile Range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.A.; van der Windt, D.A.; Cartwright, J.L.; Côté, P.; Bombardier, C. Assessing bias in studies of prognostic factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.E.; Kunz, R.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Schünemann, H.J.; GRADE Working Group. GRADE: An emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008, 336, 924–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingol Tanriverdi, T.; Patmano, G.; Bozkurt, F.T.; Kaya, B.C.; Tercan, M. Prognostic value of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2021, 75, e14227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokulu, K.; Sert, E.T. The role of the lactate/albumin ratio in predicting survival outcomes in patients resuscitated after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A preliminary report. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 50, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.S.; Kim, K.S.; Suh, G.J.; Kwon, W.Y.; Park, M.J.; Ko, J.I.; Kim, T. Admission levels of high-density lipoprotein and apolipoprotein A-1 are associated with the neurologic outcome in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2017, 4, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Oh, J.; Lim, T.H.; Kang, H.; Ko, B.S.; Cho, Y.; The Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium KoCARC Investigators. Association between Initial Serum cholesterol Levels and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized after Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Retrospective Multicenter Registry Study. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.; Kasayama, S.; Kanehara, H.; Bando, Y. CLD (chronic liver diseases)-HbA1c as a suitable indicator for estimation of mean plasma glucose in patients with chronic liver diseases. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2008, 81, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, P.; Bunn, F.; Lefebvre, C.; Li, W.P.A.; Li, L.; Roberts, I.; Schierhout, G.; Albumin Reviewers. Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franch-Arcas, G. The meaning of hypoalbuminaemia in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.P.; Wolmarans, M.R.; Park, G.R. The role of albumin in critical illness. Br. J. Anaesth. 2000, 85, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziani, F.; Kremer, H.; Tesse, A.; Baron-Menguy, C.; Mathien, C.; Mostefai, H.A.; Carusio, N.; Schneider, F.; Asfar, P.; Andriantsitohaina, R. Human serum albumin improves arterial dysfunction during early resuscitation in mouse endotoxic model via reduced oxidative and nitrosative stresses. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Miao, W.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Miao, L.; Feng, H. Protective effect of albumin on VEGF and brain edema in acute ischemia in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 472, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshage, H.J.; Janssen, J.A.; Franssen, J.H.; Hafkenscheid, J.C.; Yap, S.H. Study of the molecular mechanism of decreased liver synthesis of albumin in inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 1987, 79, 1635–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takegawa, R.; Kabata, D.; Shimizu, K.; Hisano, S.; Ogura, H.; Shintani, A.; Shimazu, T. Serum albumin as a risk factor for death in patients with prolonged sepsis: An observational study. J. Crit. Care 2019, 51, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougouin, W.; Lamhaut, L.; Marijon, E.; Jost, D.; Dumas, F.; Deye, N.; Beganton, F.; Empana, J.P.; Chazelle, E.; Cariou, A.; et al. Characteristics and prognosis of sudden cardiac death in Greater Paris: Population-based approach from the Paris sudden death expertise center (Paris-SDEC). Intensiv. Care Med. 2014, 40, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Jo, Y.H.; Rhee, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Na, S.H.; Hwang, S.S. Albumin and C-reactive protein have prognostic significance in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Chung, S.P.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.O.; Shin, S.D.; Song, K.J.; Cha, K.C.; You, J.S.; et al. The prognostic usefulness of the lactate/albumin ratio for predicting clinical outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A prospective, multicenter observational study (KoCARC) study. Shock 2020, 53, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Quintairos, E.; Silva, A.; Couto, L.; Taccone, F.S. The value of blood lactate kinetics in critically ill patients: A systematic review. Crit. Care. 2016, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, M.H.; Afifi, A.A. Experimental and clinical studies on lactate and pyruvate as indicators of the severity of acute circulatory failure (shock). Circulation 1970, 41, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, M.S.; Grossestreuer, A.V.; Patel, H.; Ntshinga, L.; Coker, A.; Yankama, T.; Donnino, M.W.; Berg, K.M. Lactate and Hypotension as Predictors of Mortality after In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest. Resuscitation 2021, 158, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.J.; Liu, L.J.; Liu, C.F. Blood lactate or lactate clearance: Which is robust to predict the neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BioMed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8014213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author (Year) | Country | Inclusion Period | Study Type | Sample Size, n | In-Hospital Mortality, n (%) | PNO *, n (%) | Serum Sampling Time | Outcome Measurement Timepoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim (2019) | Korea | 2009–2016 | sPOS | 255 OHCA | 107 (42.0) | 171 (67.1) | within 1 h after ROSC | at 6 months |
| Kokulu (2021) | Turkey | January 2018–December 2020 | sPOS | 235 OHCA | 193 (82.1) | NR | within 10 min on admission | at hospital discharge |
| Lee (2022) | Korea | October 2015–June 2020 | mPOS | 689 OHCA | 485 (70.4) | 608 (88.2) | immediately after ROSC | at hospital discharge |
| Li (2021) | China | 2014–2015 | mROS | 2414 CA | 1349 (55.9) | NR | within 24 h on admission | at hospital discharge |
| Son (2017) | Korea | March 2013–December 2015 | sROS | 59 OHCA | 21 (35.6) | 46 (78.0) | within 24 h after ROSC | at hospital discharge |
| Tanriverdi (2021) | Turkey | NR | sROS | 102 OHCA | 59 (57.8) | NR | immediately on admission | at hospital discharge |
| You (2018) | Korea | January 2014–January 2018 | sROS | 83 CA | NR | 55 (66.3) | immediately on admission | at 3 months |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Lim, T.-H.; Jang, B.-H.; Cho, Y.; Kim, W.; Kim, J.-G.; Choi, K.-S.; Na, M.-K.; et al. Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111787
Lee H, Lee J, Shin H, Lim T-H, Jang B-H, Cho Y, Kim W, Kim J-G, Choi K-S, Na M-K, et al. Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(11):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Heekyung, Juncheol Lee, Hyungoo Shin, Tae-Ho Lim, Bo-Hyoung Jang, Youngsuk Cho, Wonhee Kim, Jae-Guk Kim, Kyu-Sun Choi, Min-Kyun Na, and et al. 2022. "Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 11: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111787
APA StyleLee, H., Lee, J., Shin, H., Lim, T.-H., Jang, B.-H., Cho, Y., Kim, W., Kim, J.-G., Choi, K.-S., Na, M.-K., Ahn, C., & Kwon, S.-M. (2022). Association between Early Phase Serum Albumin Levels and Outcomes of Post-Cardiac Arrest Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12111787







