Abstract
The pulse CO-Oximetry allows continuous, noninvasive monitoring of hemoglobin (SpHb). We assessed the impact of increased end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2) on the accuracy and trending ability of SpHb in laparoscopic surgery. Participants (n = 64) were randomly allocated to the low carbon dioxide (CO2) group (EtCO2: 30–35 mmHg) or the high CO2 group (EtCO2: 40–45 mmHg). The SpHb and laboratory hemoglobin (tHb) were obtained during surgery. The correlation coefficient (r) between SpHb and tHb showed greater tendency in the low CO2 group (r = 0.68) than in the high CO2 group (r = 0.43). The bias (precision) was −1.18 (1.09) with a limit of agreement (LOA) of −3.31 to 0.95 in low CO2 group and −1.02 (1.24) with a LOA of −3.45 to 1.42 in high CO2 group; they did not differ significantly between the groups (p = 0.246). The low CO2 group showed a high concordance rate of 95.9% and a moderate correlation between ΔSpHb and ΔtHb (r = 0.53). However, the high CO2 group showed a concordance rate of 77.8% and no correlation between ΔSpHb and ΔtHb (r = 0.11). In conclusion, increased EtCO2 significantly reduced the trending ability of SpHb during laparoscopic surgery. Caution should be executed when interpreting SpHb values during laparoscopic surgery in patients with hypercapnia.
1. Introduction
To date, laparoscopic surgery has expanded to various surgeries because of its minimal invasiveness, few complications, and rapid recovery. Despite numerous benefits, pneumoperitoneum is required during laparoscopic surgery to secure the surgical view; however, it is associated with some disadvantages, such as excessive carbon dioxide (CO2) retention and underestimated blood loss because of the limited view through the scope [1]. Moreover, pneumoperitoneum stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, leading to hemodynamic changes [2], which may be confused with changes of vital signs related to blood loss. Thus, rapid assessment of the hemoglobin (Hb) concentration is essential even in laparoscopy.
The Radical-7 pulse CO-Oximetry is a device that allows monitoring of continuous, noninvasive hemoglobin (SpHb). It was developed in the process of overcoming pulse oximetry’s shortcomings and uses 8-wavelength spectrometry, whereas pulse oximetry uses 2-wavelength spectrometry [3]. Compared to a laboratory Hb (tHb), SpHb enables real-time monitoring of Hb changes without invasiveness, time-delay, unnecessary labor, and collection of serial blood samples. Considering that one-third of transfusions in the operation room are administered without first obtaining tHb value [4], SpHb can help to minimize unnecessary blood sampling and transfusions along with reducing the associated costs and improving the quality of care, which is a major public health issue [5,6].
Several clinical studies have investigated the accuracy, precision, and trending ability of SpHb in various conditions including indigo carmine, anemia, cardiopulmonary bypass, transplantation, trauma, dark-skinned and hemodilution [7,8,9,10,11,12]. In a previous study, altered arterial CO2 pressure (PaCO2) impaired the agreement between oxygen saturation calculated from arterial blood analyzers and that measured with pulse oximetry [13]. Pulse oximetry and pulse CO-Oximetry have technological similarity based on light absorption through a finger sensor. Recently, an observational pilot study suggested that the values of SpHb may be affected by the presence of CO2 insufflation [14]. Therefore, we hypothesized that increased end-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) would affect sensing of SpHb and reduce the accuracy and trending ability of SpHb during laparoscopic surgery. This study aimed to assess the impact of increased EtCO2 on the accuracy and trending ability of SpHb in patients undergoing laparoscopic gastrectomy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
This randomized, double-blinded, controlled study was conducted at Ajou University Health System. The present study was approved by the Ajou Hospital Institutional Review Board (AJIRB-MED-OBS-17-339, 8 January 2018) and registered prior to patient enrollment at ClinicalTrial.gov (NCT03430778, principal investigator: JEK, registration date: 13 February 2018). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. This manuscript adheres to the applicable CONSORT guidelines.
Patients undergoing elective laparoscopic gastrectomy with an American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I-III, aged 19–85 years, were included. Exclusion criteria were prior surgery involving the hand, infection, hematologic diseases, or refusal to participate in this study.
2.2. Interventions
Participants were randomly allocated to one of the two groups by computer-generated randomization (http://www.random.org, 14 February 2018): the low CO2 group or the high CO2 group. The low CO2 group participants were maintained at an EtCO2 level of 30–35 mmHg by adjusting the tidal volume and inspiratory rate within a peak inspiratory pressure ≤ 29 cmH2O during surgery. The high CO2 group participants were maintained at an EtCO2 level of 40–45 mmHg during surgery. Group assignment information was concealed in a sealed, opaque envelope. Before anesthesia induction, the envelope was opened by an independent investigator who performed all interventions but was not involved in outcome assessment (J.B.C.). He adjusted the respiratory rate according to the group assignment in all patients. The outcome assessor who did not perceive the concept of study conducted the blood sampling and data recording (K.L.). The other investigators who did not know the patient’s group assignment collected the data of the blood analyzer from electrical medical records (H.Y.K. and J.E.K).
On patients’ arrival to the operating room, basic monitoring (pulse oximetry, electrocardiography, and non-invasive blood pressure measurement) was performed. A spectrophotometric adhesive SpHb sensor (Rainbow R1 25, Rev E; Masimo, Irvine, CA, USA) was applied to the patients’ fourth finger and was covered with an impermeable black shield. SpHb levels were continuously monitored with a Radical-7 Pulse CO-Oximetry (Masimo, Irvine, CA, USA; software version 1451). Anesthesia was induced with intravenous (IV) propofol (2 mg/kg) and remifentanil (3.0–4.0 ng/mL) using a target-controlled infusion, followed by rocuronium (1 mg/kg). After endotracheal intubation, mechanical ventilation was initiated with a tidal volume of 8 mL/kg and an inspired oxygen fraction (FiO2) of 0.5. Anesthesia was maintained with a remifentanil (target concentration, 0.5–4.0 ng/mL), sevoflurane (2–2.5%), and rocuronium infusion within a surgical pleth index of 30–50, bispectral index score of 40–60, and train-of-four of 1–2. Lactate Ringer’s solution was infused at a rate of 5–10 mL/kg/h. A radial arterial catheter was placed on the contralateral side of patients as the SpHb sensor. The arterial blood was sampled to measure tHb using the satellite CO-Oximetry (Stat Profile pHOx Ultra; Nova Biomedical, Waltham, MA, USA). In case of the mean arterial pressure (MAP) < 60 mmHg, an IV bolus of ephedrine (4 mg) was primarily administered, and infusion of norepinephrine was administered as needed. At the end of the surgery, an IV of propacetamol (1 g) and ramosetron (0.3 mg) was administered for postoperative analgesia and antiemetic treatment. After confirming the train-of-four ≥ 2 using a nerve stimulator, an IV of sugammadex (2 mg/kg) was administered for reversal of the neuromuscular block. After confirming an adequate tidal volume, patients were extubated and transferred to a post-anesthesia care unit.
2.3. Data Collection
Arterial blood sampling was obtained after confirming that SpHb was unchanged for 30 s. Simultaneous SpHb and the perfusion index (PI) were recorded within 10 s after arterial blood sampling. In vivo adjustment (calibration) was not conducted. Hemodynamics (heart rate [HR] and MAP), data on the monitor (SpHb, PI, and EtCO2), and data from the blood analyzer (pH, PaCO2, arterial oxygen pressure [PaO2], tHb, and bicarbonate) were collected at five time points: after anesthesia induction; at 30, 60, and 90 min after pneumoperitoneum; and at the end of the surgery. Intraoperative vasopressor use was also recorded.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The primary end point was the bias (=SpHb–tHb). The sample size was calculated based on the bias. In a previous study, the standard deviation (SD) of bias during use of pulse CO-Oximetry was 0.92 g/dL [15]. Considering that a mean difference of 0.8 in bias was significant, 28 participants were required in each group for a significance level of 5% and a power of 90%. Considering the dropout rate of 25%, 70 patients were included.
All paired data (SpHb–tHb) and changes in SpHb (ΔSpHb) and tHb (ΔtHb) between two consecutive measurements were analyzed. SpHb values were excluded in the analysis when the PI was <1, because a low PI affects the accuracy.
Correlation between simultaneous SpHb and tHb measurement pairs was depicted in a scatter plot, and coefficients of determination (r values) were calculated by Pearson correlation analysis. For the accuracy of SpHb, a modified Bland—Altman’s method was used with consideration of multiple measurements per individual. The precision was defined as 1 SD of the bias. The 95% limits of agreement (LOA) were presented by calculating the interval defined by the bias ± 1.96 SD. The correlation coefficient between SpHb and tHb with repeated observations for each patient was estimated by using a mixed-effects model. For trend analysis, the four-quadrant plot was used with differences of ΔSpHb and ΔtHb. A central exclusion zone of 1 g/dL was applied to compensate for intrinsic SpHb bias. The effect of PaCO2 on the bias and SD was analyzed using the F test and t test. The relationship between bias and PaCO2 was analyzed with a mixed-effects model for different PaCO2 ranges (PaCO2 < 35 mmHg, 35 mmHg ≤ PaCO2 < 40 mmHg, and PaCO2 ≥ 40 mmHg).
Data are presented as mean ± SD [range], median [range], or number of patients (%). Normality of distribution was assessed with the Shapiro–Wilk test. Parametric and nonparametric data were analyzed using the Student’s t-test and Mann–Whitney test. Categorical data were compared using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Repeated measured data were analyzed using the linear mixed model and post-hoc analysis. When the interaction was statistically significant, the p-value was adjusted with Bonferroni correction. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS for Windows (version 25.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and SAS (version 9.4; SAS Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Intraoperative Characteristics
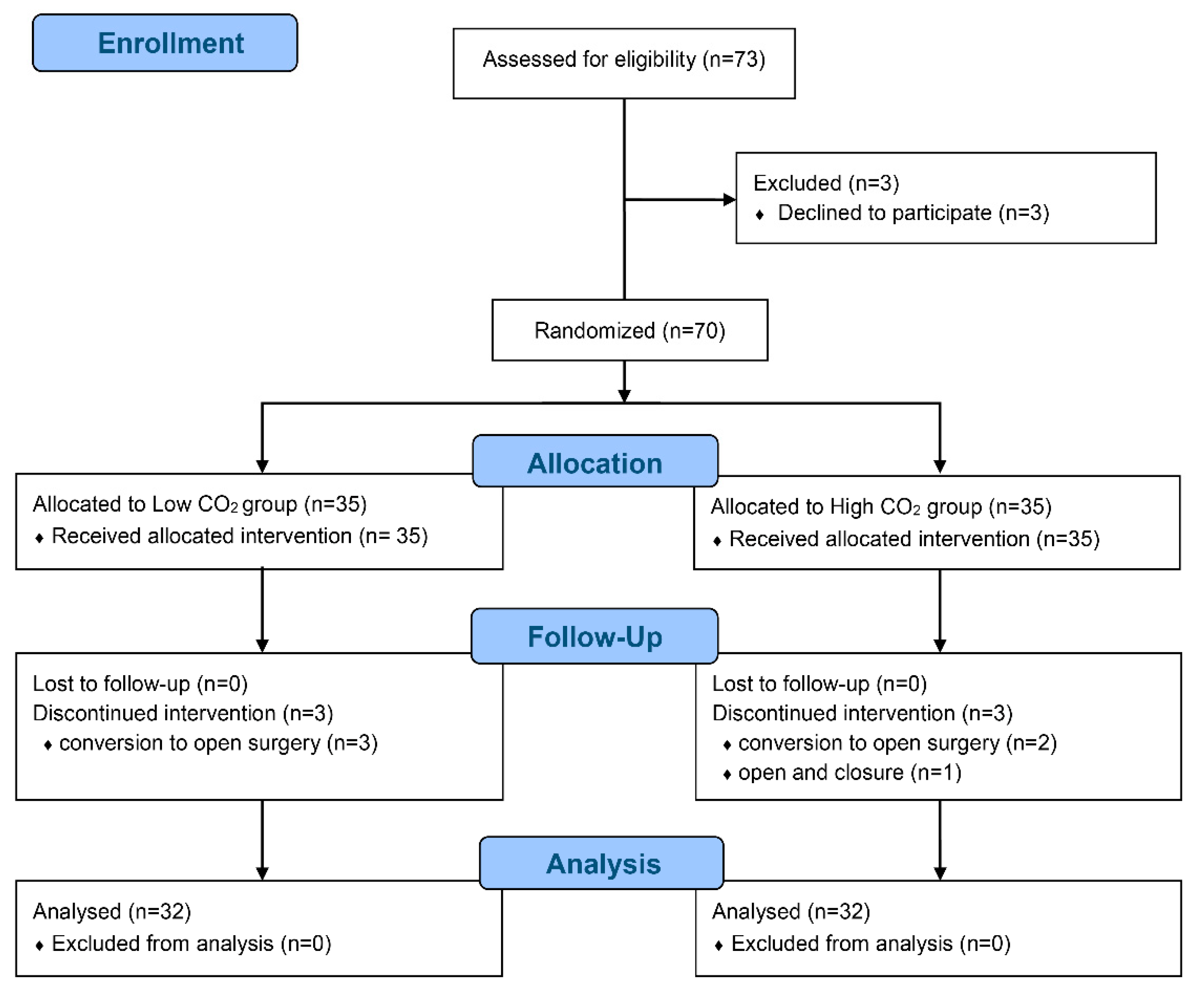
Seventy patients were enrolled and randomized between January 2019 and May 2019, but six patients withdrawn because of conversion to open surgery (n = 5) and closure due to abdominal seeding (n = 1) (Figure 1).
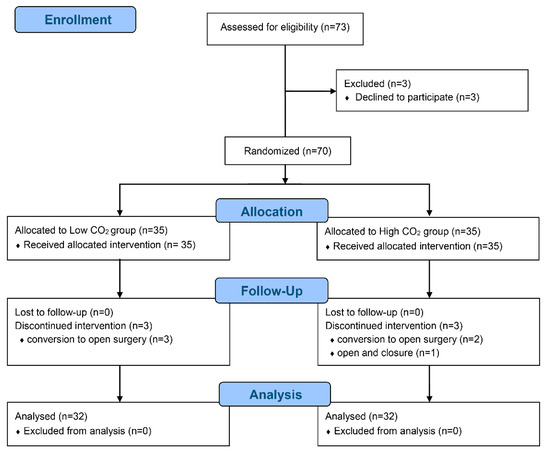
Figure 1.
CONSORT flow diagram.
There were no significant differences in patient characteristics and surgical data between the high and low CO2 groups (Table 1). No patient received a transfusion during surgery. Both HR and MAP were adequately maintained and comparable between the groups (Pgroup×time = 0.787 and Pgroup×time = 0.423, respectively). The PaO2 and pH were also comparable between the groups (Pgroup×time = 0.423 and Pgroup×time = 0.138); however, PaCO2 and bicarbonate were significantly higher in the high CO2 group than in the low CO2 group at all time points (Pgroup×time < 0.001 and Pgroup×time = 0.020, respectively).

Table 1.
Patient characteristics and perioperative profiles.
3.2. Collection of SpHb and tHb Values
In total, 320 paired measurements of SpHb and tHb were collected from 64 patients. Twenty-five SpHb measurements (7.8%, 13 in the low CO2 group and 12 in the high CO2 group) were excluded because the PI was <1.0. The mean PI values for the remaining SpHb measurements were 3.9 ± 2.0 [1–8.2]% in the low CO2 group and 4.2 ± 2.5 [1–12]% in the high CO2 group (Table 1). Finally, 295 paired measurements of SpHb and tHb were analyzed (92.2%, 147 in the low CO2 group and 148 in the high CO2 group). The SpHb and tHb values were significantly lower in the low CO2 group than in the high CO2 group (p < 0.001 and p = 0.003, respectively, Table 1).
3.3. Accuracy and Trending Ability of SpHb
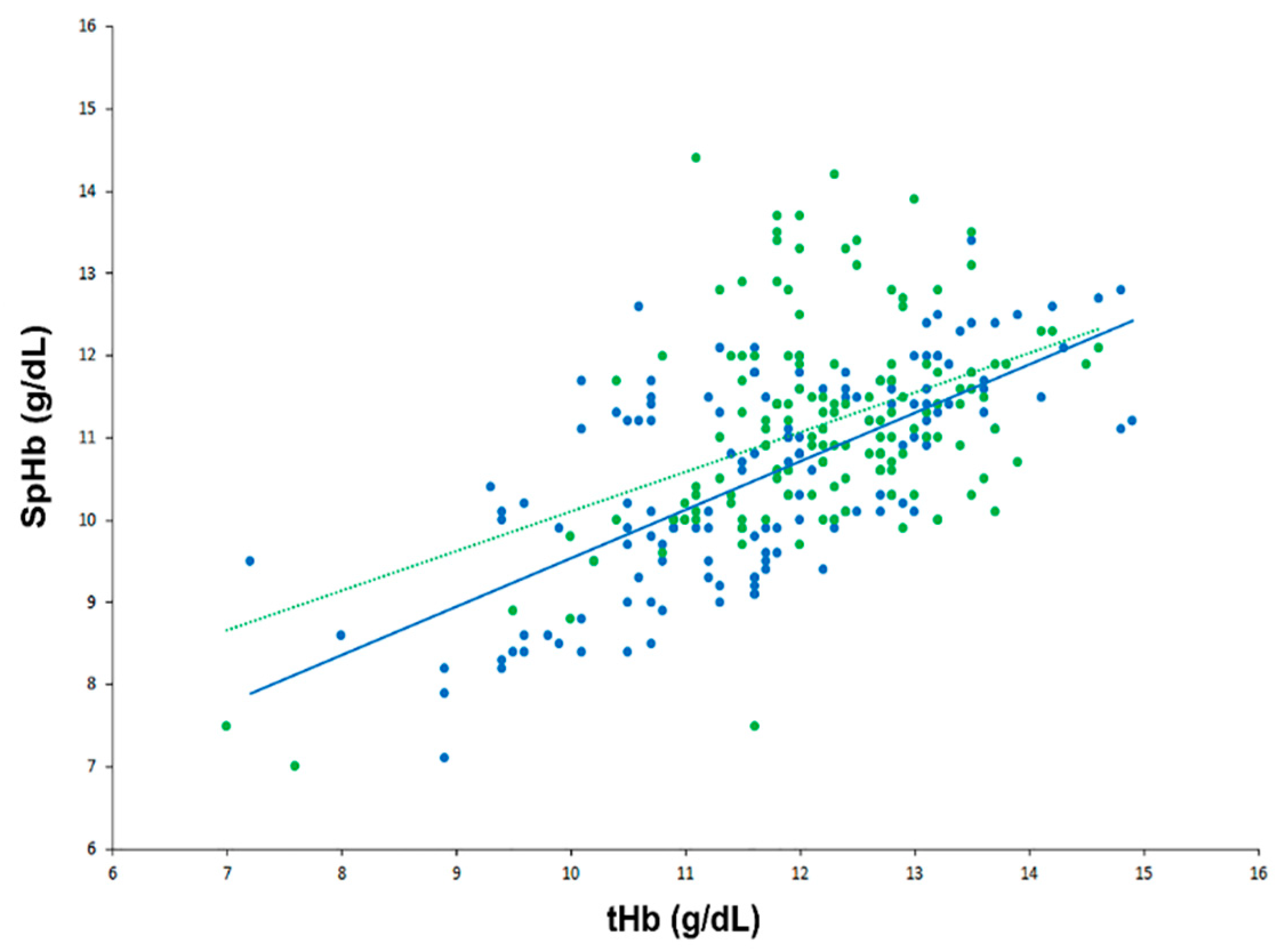
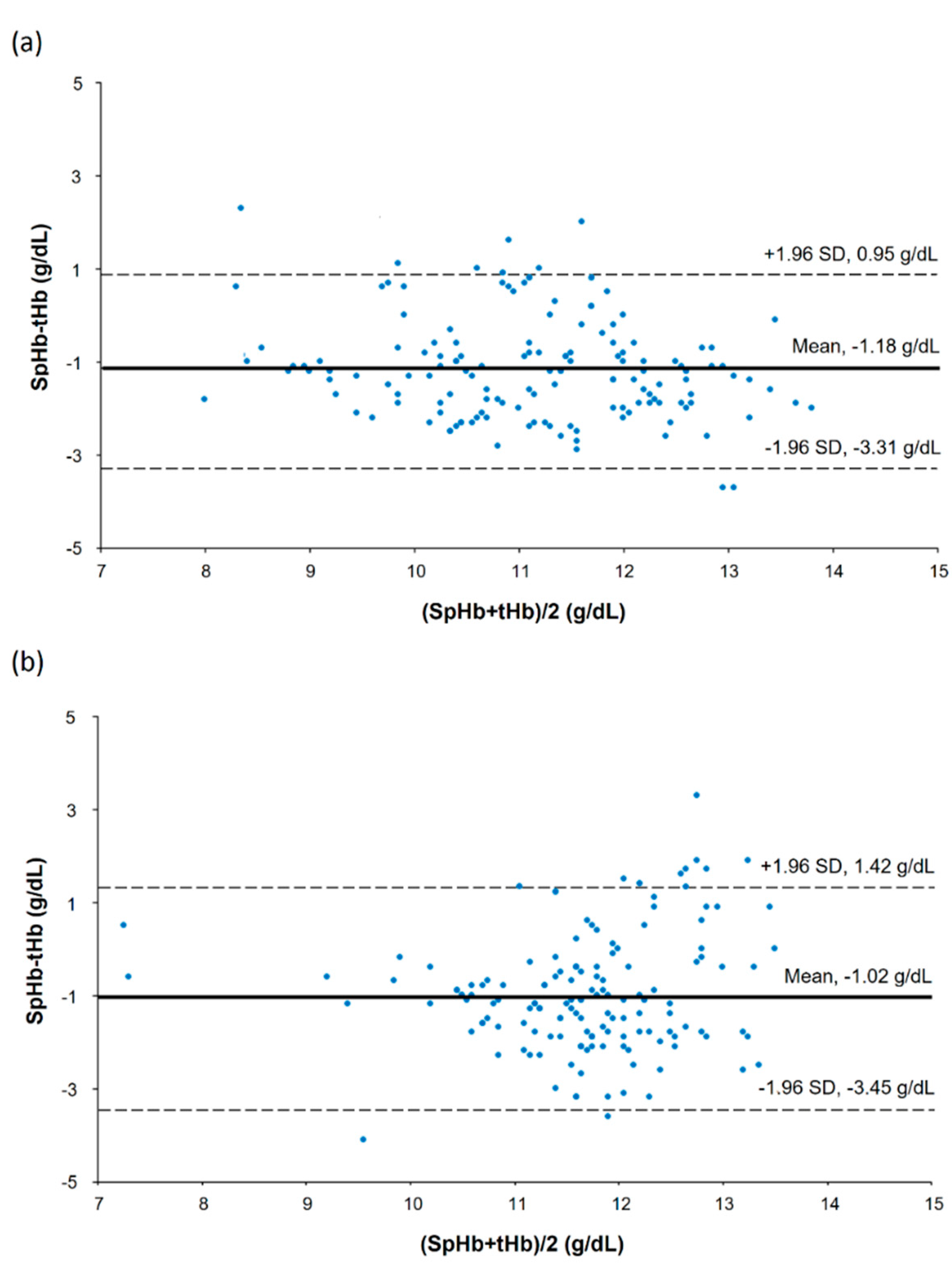
In a scatter plot with all SpHb and tHb data points, there was a strong positive correlation between SpHb and tHb in the low CO2 group but a moderate positive correlation in the high CO2 group (Figure 2): the r values were 0.68 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.58 to 0.76) and 0.43 (95% CI 0.29 to 0.55) for the low and high CO2 groups, respectively (p = 0.153). Results of the modified Bland–Altman’s analysis for repeated measurements are shown in Figure 3. The bias (precision) values were −1.18 (1.09) with an LOA of −3.31 to 0.95 in the low CO2 group and −1.02 (1.24) with an LOA of −3.45 to 1.42 in the high CO2 group, and they did not differ significantly between the groups (p = 0.246).

Figure 2.
Scatter plot showing real-time continuous hemoglobin and laboratory hemoglobin data in the low carbon dioxide (CO2) (blue) and high CO2 groups (green).
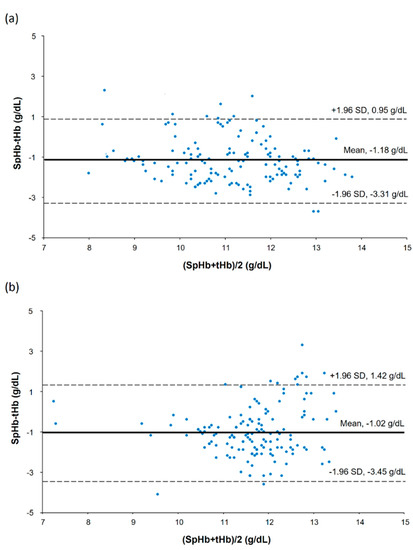
Figure 3.
Bland—Altman’s plot showing repeated measurements in the low carbon dioxide (CO2) (a) and high CO2 groups (b).
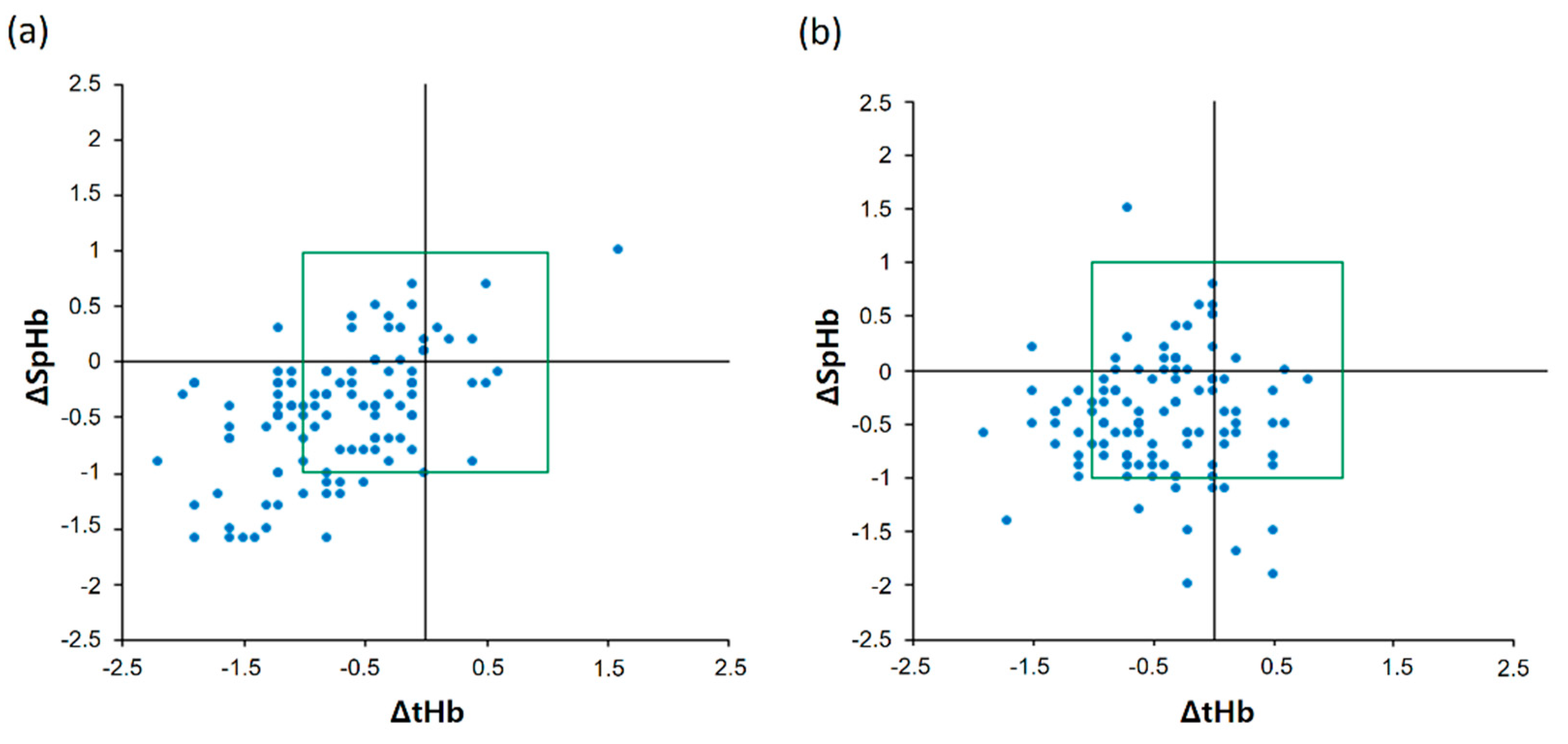
The four-quadrant plot of ΔSpHb and ΔtHb is shown in Figure 4. The low CO2 group showed a highly acceptable concordance rate of 95.9% (47 of 49) and a moderate positive correlation between ΔSpHb and ΔtHb (Figure 4a): the r value was 0.53 (95% CI 0.38 to 0.65). However, the high CO2 group showed a lower acceptable concordance rate of 77.8% (28 of 36) than the low CO2 group and no correlation between ΔSpHb and ΔtHb (Figure 4b): the r value was 0.11 (95% CI −0.08 to 0.29).

Figure 4.
Four-quadrant plot showing changes in real-time continuous hemoglobin values and laboratory hemoglobin values in the low carbon dioxide (CO2) (a) and high CO2 groups (b).
3.4. Comparisons According to the PaCO2 Ranges
According to the PaCO2 ranges, bias was significantly increased in the PaCO2 ≥ 45 mmHg range compared with those in the PaCO2 < 35 mmHg and 35 ≤ PaCO2 < 45 mmHg ranges (p = 0.020 and p = 0.004, respectively; Table 2).

Table 2.
Accuracy of SpHb by PaCO2 range.
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this randomized controlled study is the first to assess the impact of increased EtCO2 on SpHb during laparoscopic surgery. The bias did not differ between the groups. However, the correlation between SpHb and tHb was strong in the low CO2 group but moderate in the high CO2 group. In addition, the concordance rate between SpHb and tHb was more acceptable in the low CO2 group than in the high CO2 group. Moreover, the correlation between ∆SpHb and ∆tHb was moderate in the low CO2 group but negligible in the high CO2 group. Lastly, the bias was significantly increased in the range of PaCO2 ≥ 45 mmHg.
Pulse oximetry and pulse CO-Oximetry are based on the measurement of the differential optical density of light that pass through the tissue. The accuracy of pulse oximetry, when being evaluated by the difference between the oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry and that in the arterial blood, was affected by several factors [16,17]. Similarly, the accuracy of pulse CO-Oximetry has been evaluated using the SpHb and tHb values. In there, SpHb has shown clinical usefulness but was affected by various factors [7,8,9,10,11,12]. In previous studies, altered PaCO2 levels affected the accuracy and reliability of oxygen saturation in pulse oximetry [13]. Hence, we differentiated the EtCO2 levels between the groups and assessed the SpHb values.
In our study, increased EtCO2 did not affect the accuracy of SpHb in terms of the similar bias between the groups, although the low CO2 group showed a lower precision and a narrower LOA than the high CO2 group. The bias values in the low and high CO2 groups seem to be adequate in terms of accuracy, by being within ≤1.5 g/dL of the tHb as proposed by Miller et al. [18], but they were slightly high compared to a meta-analysis result of −0.27 g/dL performed in the operating room [19]. This may be because we did not conduct the calibration (in-vivo adjustment). If SpHb was calibrated with the initial tHb, the bias in our study would be deceased, because a previous study reported that after calibration, bias and the SD of SpHb were reduced by 0.5 g/dL compared to tHb in surgical patients [20].
In contrast to accuracy, increased EtCO2 reduced the trending ability of SpHb in our study, in which the levels of concordance and correlation between SpHb and tHb were strong enough to reduce the number of invasive blood samplings by pulse CO-Oximetry in the low CO2 group but less in the high CO2 group. Since inception of pulse CO-Oximetry in 2008, numerous studies investigating its ability have focused on the accuracy of SpHb as the absolute difference of Hb compared to conventional methods [21,22]. These studies showed reasonable accuracy for SpHb, but certain patient conditions limited this. For example, Riess et al. investigated the use of SpHb during cardiac surgery and found SpHb to be accurate before but not after cardiopulmonary bypass. They concluded that sole reliance on SpHb for deciding transfusion is inappropriate [8]. A few SpHb studies have evaluated the trending ability and accuracy of SpHb [9,10,12]. Barker et al. suggested that the primary value of SpHb is derived from a continuous, real-time measurement and trending rather than accuracy, and that SpHb is not an alternative to tHb but an additional trend monitor [23]. Downward, stable, or upward SpHb trends enable clinicians to quickly decide whether to transfuse a patient. Thus, altered trending ability of SpHb leads to time-delayed or unnecessary red blood cell transfusion. In our study, it may be clinically more meaningful that increased EtCO2 during laparoscopic surgery reduced the ability of trending in SpHb rather than not affecting the accuracy of SpHb.
Several possibilities may explain the reduced ability of trending in SpHb in our study. First, pulse CO-Oximetry measures the concentrations of four Hb types: oxyhemoglobin, deoxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, and carboxyhemoglobin. Thus, increased PaCO2 may alter the wavelength reading because of increases in the amount of carbaminohemoglobin, considering that about 10% of the CO2 is carried as carbaminohemoglobin [24]. Second, PaCO2-related vasodilation causes dynamic circulation (opening) in an arteriovenous shunt at the fingertip [25,26], which may lead to venous pulsation and spurious detection by pulse CO-Oximetry of venous blood as arterial. It is notable because deoxyhemoglobin can carry more CO2 than the oxygenated form (the Haldane effect) [24]. Third, increased PaCO2 causes a reduction in CO2-medicated extracellular pH [25], which can induce changes in red blood cell morphology [27].
There are several limitations to our study. First, tHb was measured using satellite CO-Oximetry, which has been the common method to measure tHb in the operating room. However, the International Committee for Standardization in Hematology recommends a central laboratory hematology analyzer that uses the cyanide method for tHb measurement [28]. Second, the study groups were divided according to EtCO2, and not PaCO2. Although EtCO2 measurement is a good non-invasive method to estimate PaCO2, EtCO2 may not predict the actual PaCO2 in certain circumstances. Third, we used an older version of SpHb sensors (Rev E), but updated SpHb sensors may show the different results. Fourth, all patients were transferred to the operating room for a scheduled surgery with stable hemodynamics and a Hb level within the normal range. Further studies are needed considering special conditions, such as low Hb levels or critical illness. Fifth, all adhesive SpHb sensors were applied to the fourth finger of each patient’s left hand. Since differences in oxygen saturation among fingers or between dominant and non-dominant hands have been reported, this may have affected our results, although arterial catheterization was performed in the right arm and SpHb values with a PI < 1.0 were excluded [29]. Sixth, we did not calibrate the SpHb with initial tHb. However, for the assessment of ΔSpHb and ΔtHb, calibration could have been beneficial to assess a drift over the increased EtCO2 or the time.
5. Conclusions
An increased EtCO2 significantly reduced the trending ability of SpHb in patients undergoing laparoscopic gastrectomy. Caution should be executed during decision-making regarding transfusion based on the SpHb value in patients with hypercapnia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-Y.K. and J.-E.K.; methodology, K.L.; validation, J.-B.C. and S.-U.H.; formal analysis, H.-S.L.; investigation, H.-Y.K., K.L. and J.-E.K.; resources, J.-E.K.; data curation, H.-Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-Y.K.; writing—review and editing, J.-E.K.; visualization, H.-S.L.; supervision, H.-Y.K. and J.-E.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the National Institutes of Health of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2017R1C1B5074930).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Ajou University Hospital (No. AJIRB-MED-OBS-17-339).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tomimaru, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Morita, S.; Imamura, H.; Iwazawa, T.; Dono, K. Is intraoperative blood loss underestimated in patients undergoing laparoscopic hepatectomy? World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 3685–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, T.M.; Giraud, G.D.; Togioka, B.M.; Jones, D.B.; Cigarroa, J.E. Cardiovascular and ventilatory consequences of laparoscopic surgery. Circulation 2017, 135, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamir, M.Y.; Avramovich, A.; Smaka, T. The current status of continuous noninvasive measurement of total, carboxy, and methemoglobin concentration. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, S.M.; Savage, W.J.; Rothschild, J.A.; Rivers, R.J.; Ness, P.M.; Paul, S.L.; Ulatowski, J.A. Variability in blood and blood component utilization as assessed by an anesthesia information management system. Anesthesiology 2012, 117, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribed-Sanchez, B.; Gonzalez-Gaya, C.; Varea-Diaz, S.; Corbacho-Fabregat, C.; Perez-Oteyza, J.; Belda-Iniesta, C. Economic analysis of the reduction of blood transfusions during surgical procedures while continuous hemoglobin monitoring is used. Sensors 2018, 18, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodnough, L.T.; Shander, A. Patient blood management. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isosu, T.; Satoh, T.; Oishi, R.; Imaizumi, T.; Hakozaki, T.; Obara, S.; Ikegami, Y.; Kurosawa, S.; Murakawa, M. Effects of indigo carmine intravenous injection on noninvasive and continuous total hemoglobin measurement. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2016, 30, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, M.L.; Pagel, P.S. Noninvasively measured hemoglobin concentration reflects arterial hemoglobin concentration before but not after cardiopulmonary bypass in patients undergoing coronary artery or valve surgery. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2016, 30, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdogan Kayhan, G.; Colak, Y.Z.; Sanli, M.; Ucar, M.; Toprak, H.I. Accuracy of non-invasive hemoglobin monitoring by pulse CO-oximeter during liver transplantation. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017, 83, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, P.F.; Anazodo, A.; Gao, C.; Chen, H.; Wade, C.; Hartsky, L.; Miller, C.; Imle, C.; Fang, R.; et al. Trends of hemoglobin oximetry: Do they help predict blood transfusion during trauma patient resuscitation? Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Omar, S. The clinical utility of noninvasive pulse co-oximetry hemoglobin measurements in dark-skinned critically ill patients. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubenek-Turconi, Ş.I.; Văleanu, L.; Popescu, M.; Panaitescu, E.; Tomescu, D.; Cacoveanu, M.C.; Perel, A. Continuous noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring reflects the development of acute hemodilution after consecutive fluid challenges. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, X.; Torres, F.; Sampol, G.; Rios, J.; Marti, S.; Escrich, E. Accuracy and reliability of pulse oximetry at different arterial carbon dioxide pressure levels. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.S.; Yoo, J.W.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, J.E. Accuracy of continuous and noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring in the presence of CO2 insufflation: An observational pilot study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e933027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macknet, M.R.; Allard, M.; Applegate, R.L., 2nd; Rook, J. The accuracy of noninvasive and continuous total hemoglobin measurement by pulse CO-Oximetry in human subjects undergoing hemodilution. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.D.; Chan, M.M.; Chan, M.M. Pulse oximetry: Understanding its basic principles facilitates appreciation of its limitations. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitzan, M.; Romem, A.; Koppel, R. Pulse oximetry: Fundamentals and technology update. Med. Devices 2014, 7, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.D.; Ward, T.A.; Shiboski, S.C.; Cohen, N.H. A Comparison of three methods of hemoglobin monitoring in patients undergoing spine surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 112, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaninejad, H.; Ghadimi, N.; Sayehmiri, K.; Hosseinifard, H.; Azarfarin, R.; Gorji, H.A. Comparison of invasive and noninvasive blood hemoglobin measurement in the operating room: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isosu, T.; Obara, S.; Hosono, A.; Ohashi, S.; Nakano, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Mogami, M.; Murakawa, M. Validation of continuous and noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring by pulse CO-oximetry in Japanese surgical patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2013, 27, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lilot, M.; Murphy, L.S.; Sidhu, K.S.; Yu, Z.; Rinehart, J.; Cannesson, M. Accuracy of continuous noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2014, 119, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.V.; Vincent, J.L.; Nowak, E.; Coat, M.; Paleiron, N.; Gouny, P.; Ould-Ahmed, M.; Guillouet, M.; Arvieux, C.C.; Gueret, G. The accuracy of noninvasive hemoglobin measurement by multiwavelength pulse oximetry after cardiac surgery. Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.J.; Shander, A.; Ramsay, M.A. Continuous noninvasive hemoglobin monitoring: A measured response to a critical review. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- James, W.; Iain, C. Respiration: Gas transfer. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2005, 6, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova, D.V.; Kulikov, V.P. Cerebrovascular and systemic hemodynamic response to carbon dioxide in humans. Blood Press. Monit. 2014, 19, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walløe, L. Arterio-venous anastomoses in the human skin and their role in temperature control. Temperature 2016, 3, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cicha, I.; Suzuki, Y.; Tateishi, N.; Maeda, N. Changes of RBC aggregation in oxygenation-deoxygenation: pH dependency and cell morphology. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H2335–H2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, L. Factors affecting hemoglobin measurement. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2013, 27, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaranoglu, G.; Bakan, M.; Umutoglu, T.; Zengin, S.U.; Idin, K.; Salihoglu, Z. Comparison of SpO2 values from different fingers of the hands. Springerplus 2015, 4, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).