A Handcrafted Radiomics-Based Model for the Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
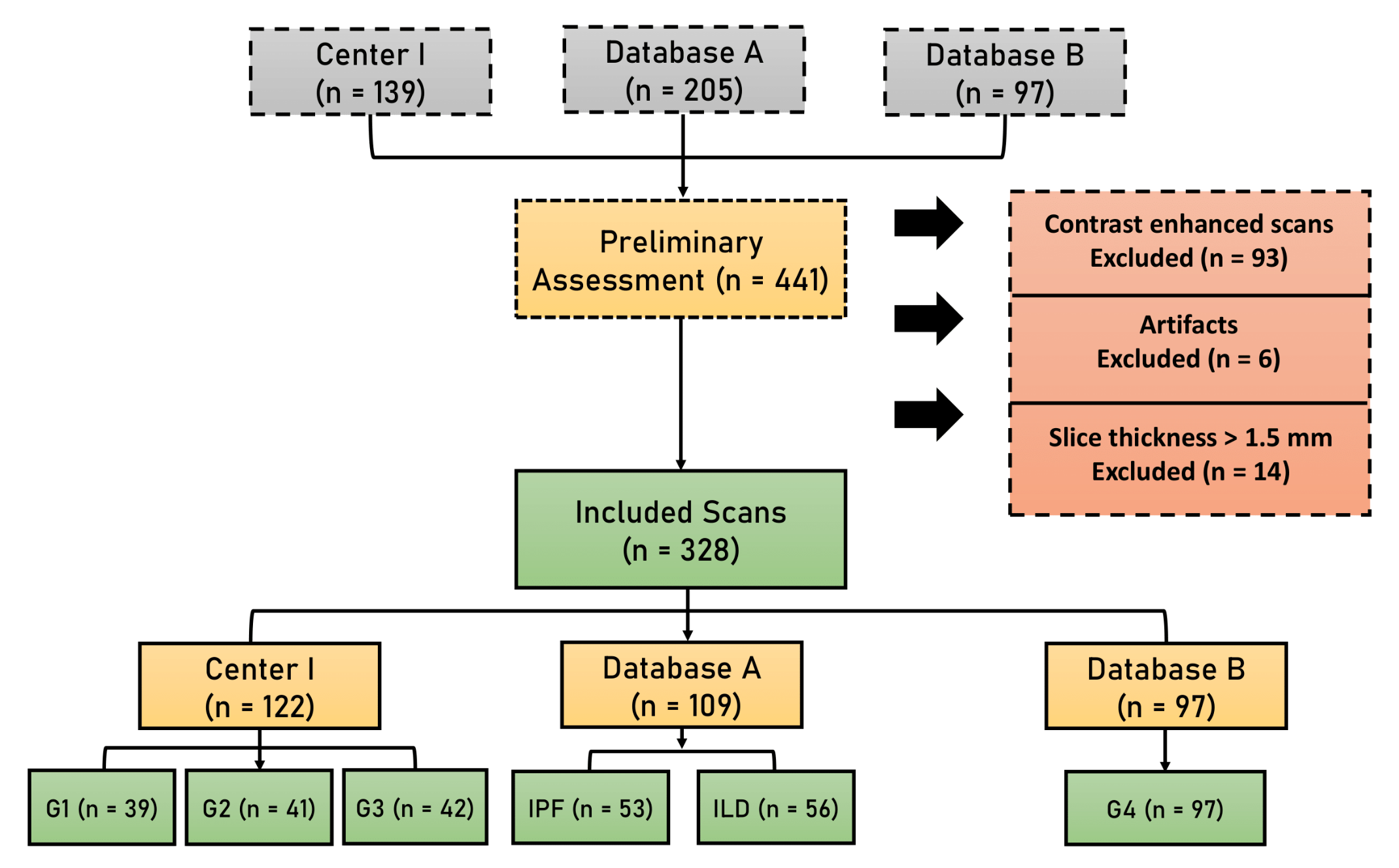
2.1. Study Population
2.2. High-Resolution CT (HRCT) Scanning
2.3. Segmentation
2.4. Radiomic Features Extraction
2.5. Data Splitting
2.6. Feature Selection and Modeling
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. Feature Extraction and Feature Selection
3.3. Performance of the Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Model | Features Name |
|---|---|
| M1 | GLSZM_SZNN, GLDZM_LISDE, GLSZM_HISAE, GLSZM_HILAE, GLCM_diffVar, GLRLM_GLV, GLCM_infoCorr2, GLSZM_LILAE, IH_medianD, GLDZM_LILDE |
| M2 | NGLDM_LGSDE, GLDZM_DZN, GLDZM_LISDE, Trachea_Volume, NGLDM_HGLDE, GLRLM_GLV, GLCM_clusShade, IH_qcod, GLDZM_HILDE, GLCM_contrast |
| M3 | GLCM_infoCorr2, Fractal_sd, Trachea_Volume, GLCM_maxCorr, GLDZM_SDE, GLRLM_GLV, IH_energy, GLDZM_LISDE, NGLDM_DV, Stats_kurtosis |
| M4 | Trachea_Volume, GLDZM_DZN, NGLDM_LGSDE, GLCM_infoCorr2, GLDZM_SDE, GLCM_sumVar, NGTDM_strength, NGLDM_HGLDE, GLDZM_LISDE, GLCM_maxCorr |
| M4.1 | |
| M5 | Trachea_Volume, GLRLM_GLV, GLCM_diffVar, GLSZM_HILAE, NGLDM_LGSDE, GLSZM_SAE, IH_qcod, GLSZM_ZE, GLSZM_IV, Stats_kurtosis |
| ILD Names |
|---|
| Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) |
| Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) |
| Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (other than systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD)) (CTD-ILD) |
| Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) |
| Unclassifiable ILD |
| Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) |
| Pleuro-parenchymal fibroelastosis |
| Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) |
| Eosinophilic pneumonia |
| systemic sclerosis SSc-ILD |
| Respiratory bronchiolitis (RB-ILD) |
References
- Kishaba, T. Evaluation and Management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Investig. 2019, 57, 300–311. [Google Scholar]
- Sgalla, G.; Biffi, A.; Richeldi, L. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis, Epidemiology and Natural History. Respirology 2016, 21, 427–437. [Google Scholar]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Mang, C.; Grosse, C.; Schmid, K.; Stiebellehner, L.; Bankier, A.A. What Every Radiologist Should Know about Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Radiographics 2007, 27, 595–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lynch, D.A.; Sverzellati, N.; Travis, W.D.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Goldin, J.G.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; Johkoh, T.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Fleischner Society White Paper. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 138–153. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.D.; Costabel, U.; Hansell, D.M.; King, T.E., Jr.; Lynch, D.A.; Nicholson, A.G.; Ryerson, C.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Selman, M.; Wells, A.U.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Luo, Q.; Xie, J.-X.; Wu, L.-L.; Liao, L.-Y.; Zhang, X.-X.; Chen, R.-C. Diagnostic Yield and Postoperative Mortality Associated with Surgical Lung Biopsy for Evaluation of Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 149, 1394.e1–1401.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, D.; Zamvar, V. The Efficacy of Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery Lung Biopsies in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease: A Retrospective Study of 66 Patients. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonobe, M.; Handa, T.; Tanizawa, K.; Sato, M.; Sato, T.; Chen, F.; Omasa, M.; Bando, T.; Date, H.; Mishima, M. Videothoracoscopy-Assisted Surgical Lung Biopsy for Interstitial Lung Diseases. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 62, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglia, C.; Bonifazi, M.; Wells, A.U.; Tomassetti, S.; Gurioli, C.; Piciucchi, S.; Dubini, A.; Tantalocco, P.; Sanna, S.; Negri, E.; et al. Safety and Diagnostic Yield of Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy in Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Diseases: A Comparative Study versus Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Respiration 2016, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.; McKeever, T.; Fogarty, A.; Navaratnam, V.; Hubbard, R. Surgical Lung Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease in England: 1997–2008. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durheim, M.T.; Kim, S.; Gulack, B.C.; Burfeind, W.R.; Gaissert, H.A.; Kosinski, A.S.; Hartwig, M.G. Mortality and Respiratory Failure After Thoracoscopic Lung Biopsy for Interstitial Lung Disease. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 104, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richeldi, L.; Scholand, M.B.; Lynch, D.A.; Colby, T.V.; Myers, J.L.; Groshong, S.D.; Chung, J.H.; Benzaquen, S.; Nathan, S.D.; Davis, J.R.; et al. Utility of a Molecular Classifier as a Complement to High-Resolution Computed Tomography to Identify Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruden, J.F. CT in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Beyond. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, J.; Sakai, F.; Johkoh, T.; Noma, S.; Akira, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Colby, T.V.; Ogura, T.; Inoue, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Diagnostic Certainty of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis/usual Interstitial Pneumonia: The Effect of the Integrated Clinico-Radiological Assessment. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2640–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Calandriello, L.; Sverzellati, N.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. UIP Observer Consort Interobserver Agreement for the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Criteria for a UIP Pattern on CT. Thorax 2016, 71, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Wells, A.U.; Desai, S.R.; Poletti, V.; Piciucchi, S.; Dubini, A.; Nunes, H.; Valeyre, D.; Brillet, P.Y.; Kambouchner, M.; et al. Multicentre Evaluation of Multidisciplinary Team Meeting Agreement on Diagnosis in Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease: A Case-Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting More Information from Medical Images Using Advanced Feature Analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The Bridge between Medical Imaging and Personalized Medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding Tumour Phenotype by Noninvasive Imaging Using a Quantitative Radiomics Approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, M.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.E.; Pieters, T.; Ghaye, B.; Geets, X. Radiomics Applied to Lung Cancer: A Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogowicz, M.; Vuong, D.; Huellner, M.W.; Pavic, M.; Andratschke, N.; Gabrys, H.S.; Guckenberger, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S. CT Radiomics and PET Radiomics: Ready for Clinical Implementation? Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 63, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogowicz, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Guckenberger, M.; Riesterer, O. Combined CT Radiomics of Primary Tumor and Metastatic Lymph Nodes Improves Prediction of Loco-Regional Control in Head and Neck Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parmar, C.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Grossmann, P.; Rios Velazquez, E.; Bussink, J.; Rietveld, D.; Rietbergen, M.M.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Lambin, P.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Radiomic Feature Clusters and Prognostic Signatures Specific for Lung and Head & Neck Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11044. [Google Scholar]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Grossmann, P.; Tan, Y.; Oxnard, G.R.; Rizvi, N.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zhao, B. Corrigendum: Defining a Radiomic Response Phenotype: A Pilot Study Using Targeted Therapy in NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martini, K.; Baessler, B.; Bogowicz, M.; Blüthgen, C.; Mannil, M.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Schniering, J.; Maurer, B.; Frauenfelder, T. Applicability of Radiomics in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Systemic Sclerosis: Proof of Concept. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 31, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaee, T.; Wu, G.; Ibrahim, A.; Halilaj, I.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Rogers, W.; Gietema, H.A.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; Lambin, P.; Woodruff, H.C. The Emerging Role of Radiomics in COPD and Lung Cancer. Respiration 2020, 99, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Occhipinti, M.; Paoletti, M.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Karwoski, R.A.; Nardi, C.; Inchingolo, R.; Larici, A.R.; Camiciottoli, G.; Lavorini, F.; et al. Spirometric Assessment of Emphysema Presence and Severity as Measured by Quantitative CT and CT-Based Radiomics in COPD. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratwani, A.; King, C.; Brown, W.; Shlobin, O.; Weir, N.; Nathan, S. Tracheobronchial Tree Size as a Predictor of Disease Severity and Outcomes in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Chest 2017, 152, A487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Ryerson, C.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Tomassetti, S.; Lee, J.S.; Poletti, V.; Buccioli, M.; Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; et al. A Multidimensional Index and Staging System for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-ul-Hassan, M.; Zhang, G.G.; Latifi, K.; Ullah, G.; Hunt, D.C.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Abdalah, M.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Goldgof, D.G.; Mackin, D.; et al. Intrinsic Dependencies of CT Radiomic Features on Voxel Size and Number of Gray Levels. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Refaee, T.; Primakov, S.; Barufaldi, B.; Acciavatti, R.J.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Hustinx, R.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Woodruff, H.C.; Wildberger, J.E.; et al. The Effects of In-Plane Spatial Resolution on CT-Based Radiomic Features’ Stability with and without ComBat Harmonization. Cancers 2021, 13, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Vallières, M.; Abdalah, M.A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Andrearczyk, V.; Apte, A.; Ashrafinia, S.; Bakas, S.; Beukinga, R.J.; Boellaard, R.; et al. The Image Biomarker Standardization Initiative: Standardized Quantitative Radiomics for High-Throughput Image-Based Phenotyping. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackin, D.; Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Fried, D.; Yang, J.; Taylor, B.; Rodriguez-Rivera, E.; Dodge, C.; Jones, A.K.; Court, L. Measuring Computed Tomography Scanner Variability of Radiomics Features. Invest. Radiol. 2015, 50, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Others Feature Selection with the Boruta Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zavaletta, V.A.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Robb, R.A. High Resolution Multidetector CT-Aided Tissue Analysis and Quantification of Lung Fibrosis. Acad. Radiol. 2007, 14, 772–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhegger, B.; Marchiori, E.; Zanon, M.; Rubin, A.S.; Fragomeni, R.; Altmayer, S.; Carvalho, C.R.R.; Baldi, B.G. Imaging in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Mimics. Clinics 2019, 74, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, F.; Moua, T.; Rajagopalan, S.; Karwoski, R.A.; Raghunath, S.; Decker, P.A.; Hartman, T.E.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Robb, R.A.; Ryu, J.H. Automated Quantification of Radiological Patterns Predicts Survival in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, J.; Bartholmai, B.J.; Rajagopalan, S.; Kokosi, M.; Nair, A.; Karwoski, R.; Walsh, S.L.F.; Wells, A.U.; Hansell, D.M. Mortality Prediction in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evaluation of Computer-Based CT Analysis with Conventional Severity Measures. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uppaluri, R.; Hoffman, E.A.; Sonka, M.; Hunninghake, G.W.; McLennan, G. Interstitial Lung Disease: A Quantitative Study Using the Adaptive Multiple Feature Method. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, S.; Keller-Reichenbecher, M.A.; Zuna, I.; Schlegel, W.; Van Kaick, G. Usual Interstitial Pneumonia. Quantitative Assessment of High-Resolution Computed Tomography Findings by Computer-Assisted Texture-Based Image Analysis. Invest. Radiol. 1997, 32, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.H.; Vargas, P.F.; Raff, U.; Lynch, D.A.; Rojas, G.M.; Moxley, D.M.; Newell, J.D. Automated Discrimination and Quantification of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis from Normal Lung Parenchyma Using Generalized Fractal Dimensions in High-Resolution Computed Tomography Images. Acad. Radiol. 1995, 2, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, S.M.; Yagihashi, K.; Huckleberry, J.; Rho, B.-H.; Schroeder, J.D.; Strand, M.; Schwarz, M.I.; Flaherty, K.R.; Kazerooni, E.A.; van Beek, E.J.R.; et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Data-Driven Textural Analysis of Extent of Fibrosis at Baseline and 15-Month Follow-Up. Radiology 2017, 285, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Brown, M.S.; Chong, D.; Gjertson, D.W.; Lu, P.; Kim, H.J.; Coy, H.; Goldin, J.G. Comparison of the Quantitative CT Imaging Biomarkers of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis at Baseline and Early Change with an Interval of 7 Months. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Calandriello, L.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N. Deep Learning for Classifying Fibrotic Lung Disease on High-Resolution Computed Tomography: A Case-Cohort Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumossalam, A.M.; Elshafeey, M.M.; Abdelsalam, E.M. Tracheoechography versus CT Tracheography for Assessment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Related Tracheopathy. Egypt. J. Chest Dis. Tuberc. 2015, 64, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, A.; Refaee, T.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Primakov, S.; Hustinx, R.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Woodruff, H.C.; Maidment, A.D.A.; Lambin, P. The Application of a Workflow Integrating the Variable Reproducibility and Harmonizability of Radiomic Features on a Phantom Dataset. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Refaee, T.; Primakov, S.; Barufaldi, B.; Acciavatti, R.J.; Granzier, R.W.Y.; Hustinx, R.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Woodruff, H.C.; Wildberger, J.E.; et al. Reply to Orlhac, F.; Buvat, I. Comment on “Ibrahim et Al. The Effects of In-Plane Spatial Resolution on CT-Based Radiomic Features’ Stability with and without ComBat Harmonization. Cancers 2021, 13, 1848”. Cancers 2021, 13, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | IPF\UIP (HRCT & Biopsy) | Non-IPF ILD (Biopsy) | Normal | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median (IQR) | 65 (60, 71) | 63 (57, 72) | 62 (56, 67) | 0.06 |
| Sex = M (%) | 104 (78.8) | 51 (51.5) | 56 (57.7) | <0.001 |
| FEV1 (mean (SD)) | 71.08 (18.34) | 71.77 (21.94) | - | 0.8 |
| FVC (mean (SD)) | 67.39 (19.53) | 71.07 (22.17) | - | 0.18 |
| DLCO (mean (SD)) | 38.92 (11.62) | 36.73 (16.12) | - | 0.23 |
| BMI (mean (SD)) | 28.06 (4.42) | 28.69 (5.59) | - | 0.34 |
| Model (M) | AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (95% CI) | % | % | % | |
| M1 | 1.0 (1.0–1.0) | 99 | 98 | 98 |
| M2 | 0.96 (0.90–1.0) | 91 | 88 | 94 |
| M3 | 0.87 (0.74–1.0) | 72 | 65 | 90 |
| M4 | 0.82 (0.68–0.95) | 70 | 66 | 79 |
| M4.1 | 0.66 (0.59–0.73) | 65 | 60 | 69 |
| M5 | 0.77 (0.69–0.85 | 69 | 64 | 75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Refaee, T.; Bondue, B.; Van Simaeys, G.; Wu, G.; Yan, C.; Woodruff, H.C.; Goldman, S.; Lambin, P. A Handcrafted Radiomics-Based Model for the Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030373
Refaee T, Bondue B, Van Simaeys G, Wu G, Yan C, Woodruff HC, Goldman S, Lambin P. A Handcrafted Radiomics-Based Model for the Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(3):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030373
Chicago/Turabian StyleRefaee, Turkey, Benjamin Bondue, Gaetan Van Simaeys, Guangyao Wu, Chenggong Yan, Henry C. Woodruff, Serge Goldman, and Philippe Lambin. 2022. "A Handcrafted Radiomics-Based Model for the Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 3: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030373
APA StyleRefaee, T., Bondue, B., Van Simaeys, G., Wu, G., Yan, C., Woodruff, H. C., Goldman, S., & Lambin, P. (2022). A Handcrafted Radiomics-Based Model for the Diagnosis of Usual Interstitial Pneumonia in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030373







