Real-Life Experience on Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
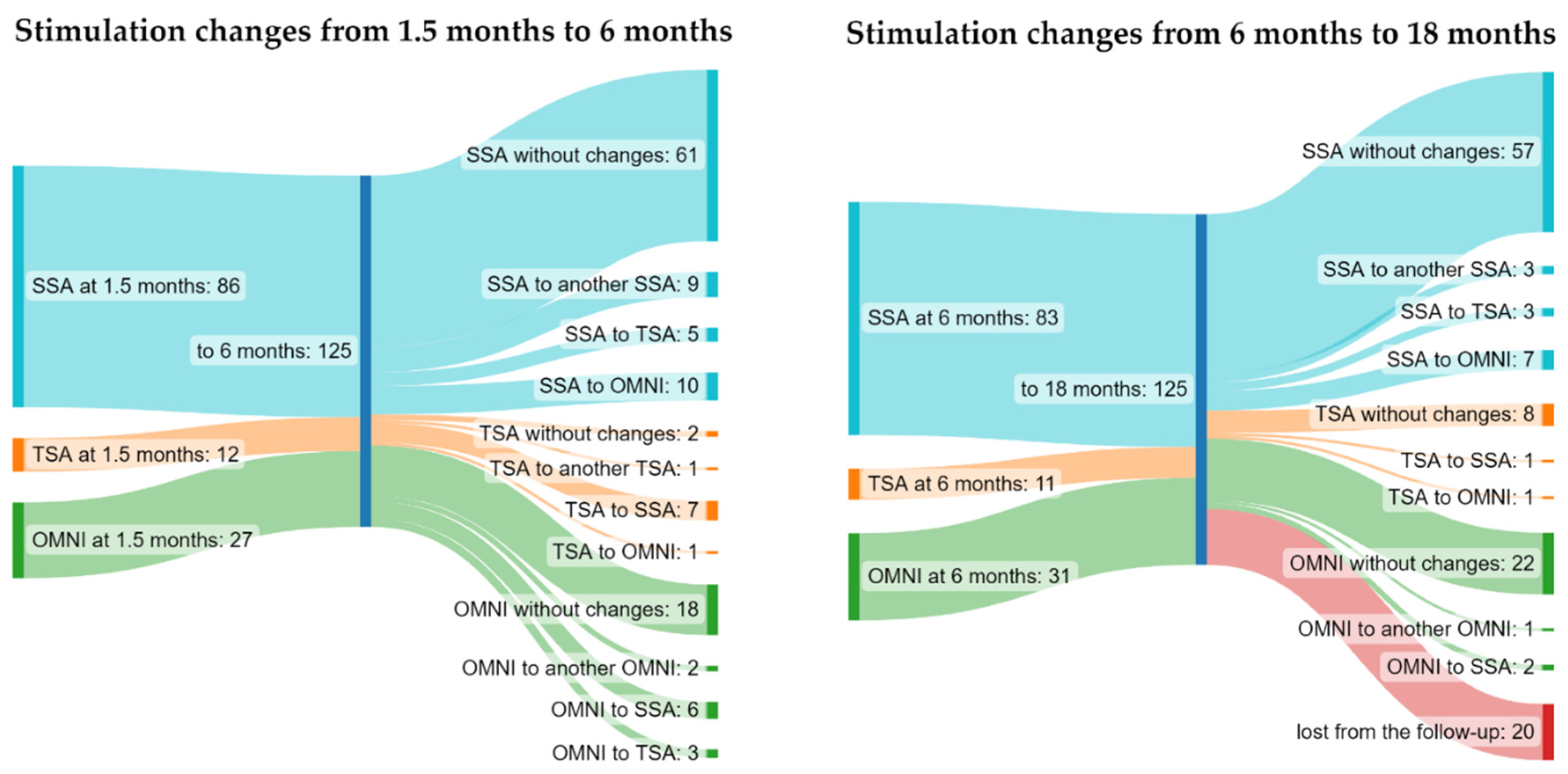
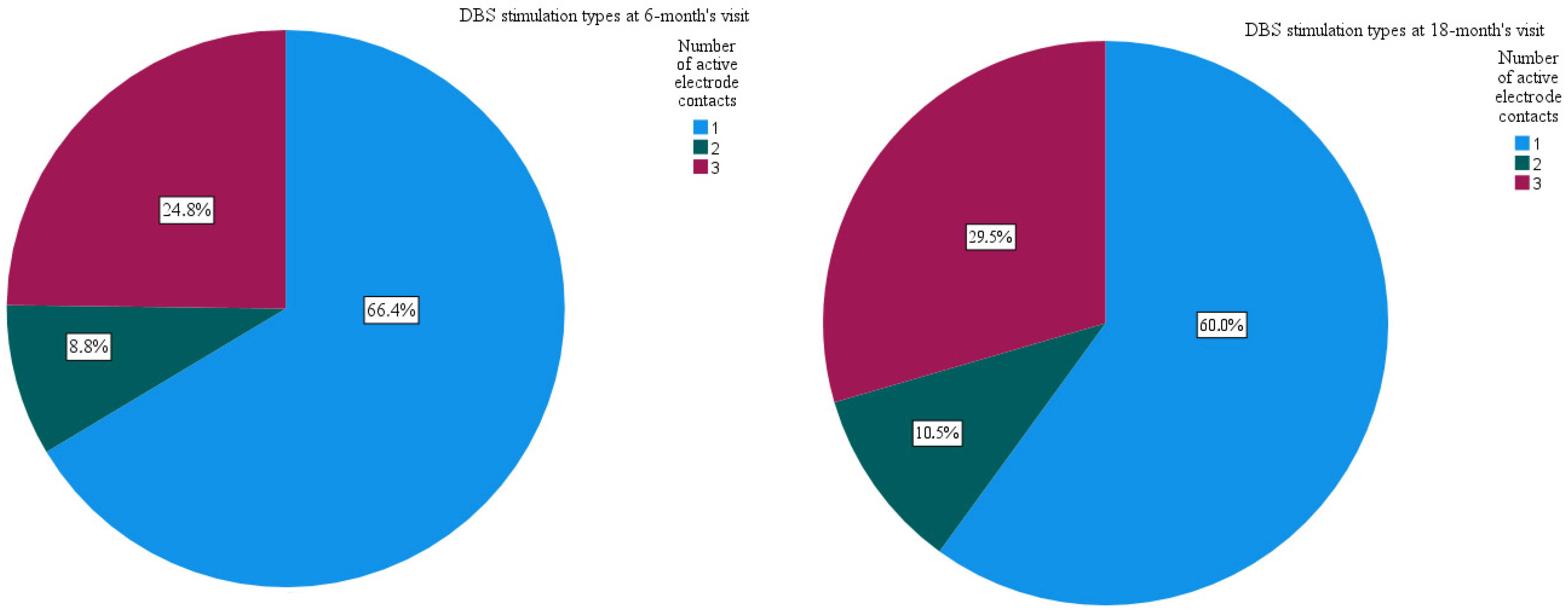
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Odin, P.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Slevin, J.; Volkmann, J.; Dietrichs, E.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Krauss, J.K.; Valldeoriola, F.; Barcelona, H.; Puente, V.; et al. Collective physician perspectives on non-oral medication approaches for the management of clinically relevant unresolved issues in Parkinson’s disease: Consensus from an international survey and discussion program. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 10, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deuschl, G.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Krack, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schäfer, H.; Bötzel, K.; Daniels, C.; Deutschländer, A.; Dillmann, U.; Eisner, W.; et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fox, S.H.; Katzenschlager, R.; Lim, S.-Y.; Barton, B.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Seppi, K.; Coelho, M.; Sampaio, C.; Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Committee. International Parkinson and movement disorder society evidence-based medicine review: Update on treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1248–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Liu, D.; Shi, L.; Meng, F.; Fang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, A.; Zhang, J. Differential Effects of Subthalamic Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Internus Deep Brain Stimulation on Motor Subtypes in Parkinson’s Disease. World Neurosurg. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitzler, A.; Mir, P.; Brodsky, M.A.; Verhagen, L.; Groppa, S.; Alvarez, R.; Evans, A.; Blazquez, M.; Nagel, S.; Pilitsis, J.G.; et al. Directional Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease: Results of an International Crossover Study with Randomized, Double-Blind Primary Endpoint. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aum, D.J.; Tierney, T.S. Deep brain stimulation: Foundations and future trends. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Schöneberg, N.; Esposito, M.S.; Geiger, J.R.P.; Sharott, A.; Tovote, P. Current approaches to characterize micro- and macroscale circuit mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease in rodent models. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 351, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, A.M.; Lipsman, N.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P.; Chabardes, S.; Chang, J.W.; Matthews, K.; McIntyre, C.C.; Schlaepfer, T.E.; Schulder, M.; et al. Deep brain stimulation: Current challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitman, F.M.P.; Janssen, A.; van der Gaag, N.A.; Hoffmann, C.F.E.; Zutt, R.; Contarino, M.F. The actual use of directional steering and shorter pulse width in selected patients undergoing deep brain stimulation. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 93, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Brinke, T.R.; Odekerken, V.J.J.; Dijk, J.M.; van den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R.; de Bie, R.M.A. Directional Deep Brain Stimulation: First experiences in centers across the globe. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 949–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, A.; Alesch, F. Systems for deep brain stimulation: Review of technical features. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna Austria 1996) 2017, 124, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contarino, M.F.; Bour, L.J.; Verhagen, R.; Lourens, M.A.; de Bie, R.M.; van den Munckhof, P.; Schuurman, P.R. Directional steering: A novel approach to deep brain stimulation. Neurology 2014, 83, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigerwald, F.; Müller, L.; Johannes, S.; Matthies, C.; Volkmann, J. Directional deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus: A pilot study using a novel neurostimulation device. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2016, 31, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembek, T.A.; Reker, P.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Wirths, J.; Treuer, H.; Klehr, M.; Roediger, J.; Dafsari, H.S.; Barbe, M.T.; Timmermann, L. Directional DBS increases side-effect thresholds-A prospective, double-blind trial. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2017, 32, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollo, C.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Oertel, M.F.; Stieglitz, L.; Taub, E.; Fuhr, P.; Lozano, A.M.; Raabe, A.; Schüpbach, M. Directional deep brain stimulation: An intraoperative double-blind pilot study. Brain A J. Neurol. 2014, 137, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Nikolov, P.; Hartmann, C.J.; Trenado, C.; Slotty, P.J.; Vesper, J.; Schnitzler, A.; Groiss, S.J. Directional Deep Brain Stimulation of the Thalamic Ventral Intermediate Area for Essential Tremor Increases Therapeutic Window. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2021, 24, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.M.; Liss, A.; Park, Y.L.; DiMarzio, M.; Prusik, J.; Hobson, E.; Adam, O.; Durphy, J.; Sukul, V.; Danisi, F.; et al. Early Experience with New Generation Deep Brain Stimulation Leads in Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor Patients. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2020, 23, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintér, D.; Járdaházi, E.; Balás, I.; Harmat, M.; Makó, T.; Juhász, A.; Janszky, J.; Kovács, N. Antiparkinsonian Drug Reduction After Directional Versus Omnidirectional Bilateral Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, G.; Jain, R.; Scholtes, H.; Wang, A.; Barbe, M.; Paschen, S.; Kuehn, A.; Volkmann, J.; Pötter-Nerger, M.; Vesper, J. Real-World Clinical Outcomes Using a Novel Directional Lead from a DBS Registry for Parkinson’s Disease (1385). Neurology 2020, 94, 1385. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson, C.L.; Stowe, R.; Patel, S.; Rick, C.; Gray, R.; Clarke, C.E. Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2010, 25, 2649–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuschl, G.; Paschen, S.; Witt, K. Clinical outcome of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2013, 116, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steigerwald, F.; Matthies, C.; Volkmann, J. Directional Deep Brain Stimulation. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shub, A.; Bezchlibnyk, Y.B.; Smith, D.A.; Malapira, T.; Miller, W.W.; Huang, Y.; Aradi, S.; Zesiewicz, T. Clinical Outcomes from Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Retrospective Analysis (1018). Neurology 2020, 94, 1018. [Google Scholar]
- Rammo, R.A.; Ozinga, S.J.; White, A.; Nagel, S.J.; Machado, A.G.; Pallavaram, S.; Cheeran, B.J.; Walter, B.L. Directional Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease and Essential Tremor: The Cleveland Clinic Experience. Neuromodul. J. Int. Neuromodul. Soc. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veerappan, V.; Anderson, S.; Safarpour, D.; Hiller, A.L. Role of Directional Configuration in Deep Brain Stimulation for Essential Tremor: A Single Center Experience. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. (N. Y.) 2021, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krack, P.; Batir, A.; Van Blercom, N.; Chabardes, S.; Fraix, V.; Ardouin, C.; Koudsie, A.; Limousin, P.D.; Benazzouz, A.; LeBas, J.F.; et al. Five-year follow-up of bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eghlidos, Z.; Rahimian, Z.; Vadiee, G.; Jahangiri, S. Effects of subthalamic deep brain stimulation on non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2022, 146, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, D.; Mencinger, M.; Rajnar, R.; Mušič, P.; Benedičič, M.; Flisar, D.; Bošnjak, R.; Mehrkens, J.; Pirtošek, Z.; Boetzel, K.; et al. Long-term effect of bilateral STN-DBS on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: A four-year observational, prospective study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 89, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Silverdale, M.; Strack, M.; Rizos, A.; Ashkan, K.; Mahlstedt, P.; Sachse, L.; Steffen, J.; Dembek, T.A.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; et al. Nonmotor symptoms evolution during 24 months of bilateral subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flouty, O.; Yamamoto, K.; Germann, J.; Harmsen, I.E.; Jung, H.H.; Cheyuo, C.; Zemmar, A.; Milano, V.; Sarica, C.; Lozano, A.M. Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease and chronic pain in the era of deep brain stimulation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Kim, H.-J.; Jeon, B.S.; Park, H.; Lee, W.-W.; Paek, S.H. An 8-Year Follow-up on the Effect of Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation on Pain in Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Bruno, V.; Arena, J.; Cammarota, Á.; Merello, M. Challenges in PD Patient Management After DBS: A Pragmatic Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2018, 5, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Silburn, P.; Pouratian, N.; Cheeran, B.; Venkatesan, L.; Kent, A.; Schnitzler, A. Comparing Current Steering Technologies for Directional Deep Brain Stimulation Using a Computational Model That Incorporates Heterogeneous Tissue Properties. Neuromodul. Technol. Neural. Interface 2020, 23, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rebelo, P.; Green, A.L.; Aziz, T.Z.; Kent, A.; Schafer, D.; Venkatesan, L.; Cheeran, B. Thalamic Directional Deep Brain Stimulation for tremor: Spend less, get more. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, P.; Nickl, R.; Breun, M.; Volkmann, J.; Kirsch, D.; Ernestus, R.I.; Steigerwald, F.; Matthies, C. Directional Leads for Deep Brain Stimulation: Technical Notes and Experiences. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2021, 99, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Nagel, S.J.; Agarwal, R.; Pötter-Nerger, M.; Hamel, W.; Sharan, A.D.; Connolly, A.T.; Cheeran, B.; Larson, P.S. Reduced Risk of Reoperations With Modern Deep Brain Stimulator Systems: Big Data Analysis From a United States Claims Database. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 785280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramme, J.; Dembek, T.A.; Treuer, H.; Dafsari, H.S.; Barbe, M.T.; Wirths, J.; Visser-Vandewalle, V. Potentials and Limitations of Directional Deep Brain Stimulation: A Simulation Approach. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2021, 99, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mean (SD) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | 35 (56%) male/28 (44%) female |
| Age | 61.6 yrs (1.1 yrs) |
| Time from PD diagnosis to the DBS operation | 11.1 yrs (3.9 yrs) |
| Time from the patient reported onset of motor fluctuations and/or dyskinesia to the DBS operation | 3.0 yrs (0.3 yrs) |
| Comorbidities | 64% know comorbidity 4% hypertension 5% atrial fibrillation 3% coronary artery disease 2% DM II |
| Concurrent medication | 6% antithrombotic drug 5% anticoagulant 5% antidepressant |
| Baseline, Median (IQR) | 6-Month Programming Visit, Median (IQR) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| UPDRS part III, medication OFF state | 34.6 | 20.7 (Stimulation ON) | p < 0.001 * |
| UPDRS part III, medication on | 15.0 (8.0) | ||
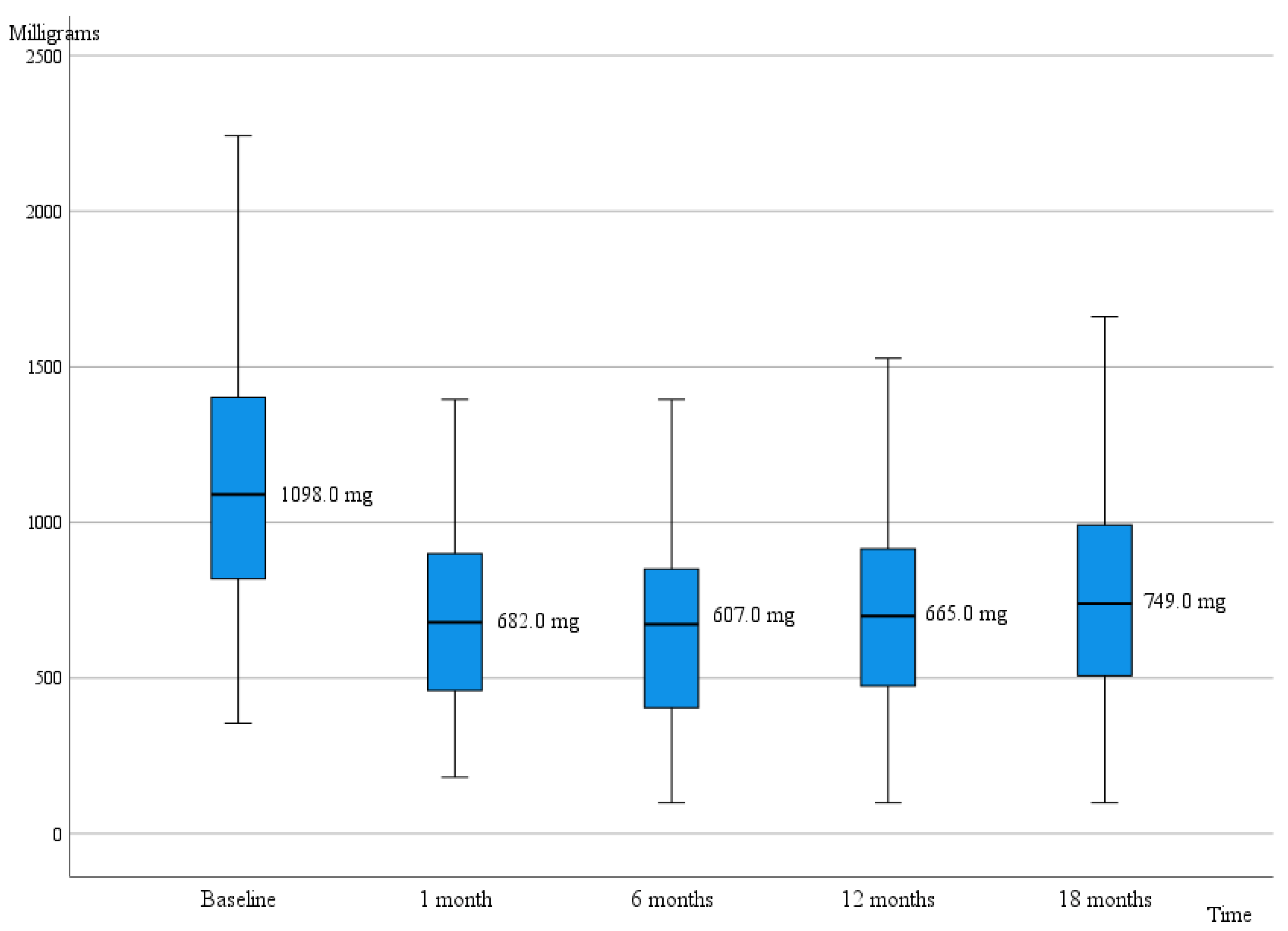
| LEDD | 1098.0 (660.0) | 673.0 (540.0) | p < 0.001 * |
| AIMS | 10.0 (11.0) | 1.0 (2.0) | p < 0.001 * |
| Hoehn and Yahr stage | 3.0 (0.5) | 2.0 (0.5) | p < 0.001 * |
| NMS-Quest | 9.0 (5.0) | 7.5 (7.0) | p = 0.021 * |
| PDQ-SI | 23.8 (16.6) | 24.4 (18.5) | p = 0.652 |
| BDI | 7.0 (5.0) | 7.0 (8.0) | p = 0.860 |
| MMSE | 28.0 (3.0) | 29.0 (4.0) | p = 0.032 * |
| 1-Month Visit Median, (IQR) | 6-Month Visit, Median (IQR) | 12-Month Visit, Median (IQR) | 18-Month Visit, Median (IQR) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All stimulation types | ||||
| 1.4 (0.5) | 2.2 (1.1) | 2.5 (1.4) | 2.7 (1.4) |
| 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) |
| 130.0 (0.0) | 130.0 (30.0) | 130.0 (30.0) | 130.0 (30.0) |
| 737.0 (182.0) | 1693.5 (872.0) | 1437.0 (762.0) | 1350.0 (712.0) |
| SSA | ||||
| 2.1 (1.3) ¶ | 2.2 (1.0) | 2.3 (1.0) | 2.2 (1.2) |
| 60.0 (0.0) ¶ | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) |
| 130.0 (0.0) ¶ | 130.0 (30.0) | 130.0 (30.0) | 130.0 (30.0) |
| 2099.0 (597.0) ¶ | 1950.0 (538.0) | 1725.0 (563) | 1637.0 (625.0) |
| TSA/Omnipolar | ||||
| 2.4 (0.5) ¶ | 2.6 (1.4) | 3.1 (2.0) | 3.1 (1.7) |
| 60.0 (0.0) ¶ | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) | 60.0 (0.0) |
| 130.0 (0.0) ¶ | 130.0 (15.0) | 130.0 (38.0) | 130.0 (43.0) |
| 1387.0 (538) ¶ | 1100.0 (305.0) | 1062.5 (431.0) | 994.0 (325.0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koivu, M.; Scheperjans, F.; Eerola-Rautio, J.; Vartiainen, N.; Resendiz-Nieves, J.; Kivisaari, R.; Pekkonen, E. Real-Life Experience on Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081224
Koivu M, Scheperjans F, Eerola-Rautio J, Vartiainen N, Resendiz-Nieves J, Kivisaari R, Pekkonen E. Real-Life Experience on Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(8):1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081224
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoivu, Maija, Filip Scheperjans, Johanna Eerola-Rautio, Nuutti Vartiainen, Julio Resendiz-Nieves, Riku Kivisaari, and Eero Pekkonen. 2022. "Real-Life Experience on Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 8: 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081224
APA StyleKoivu, M., Scheperjans, F., Eerola-Rautio, J., Vartiainen, N., Resendiz-Nieves, J., Kivisaari, R., & Pekkonen, E. (2022). Real-Life Experience on Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(8), 1224. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081224






