The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Personalized Management of Diabetic Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Preclinical Studies
4. Clinical Studies
5. Studies Onnon-Diabetic Patients
6. ARBs and Erectile Dysfunction
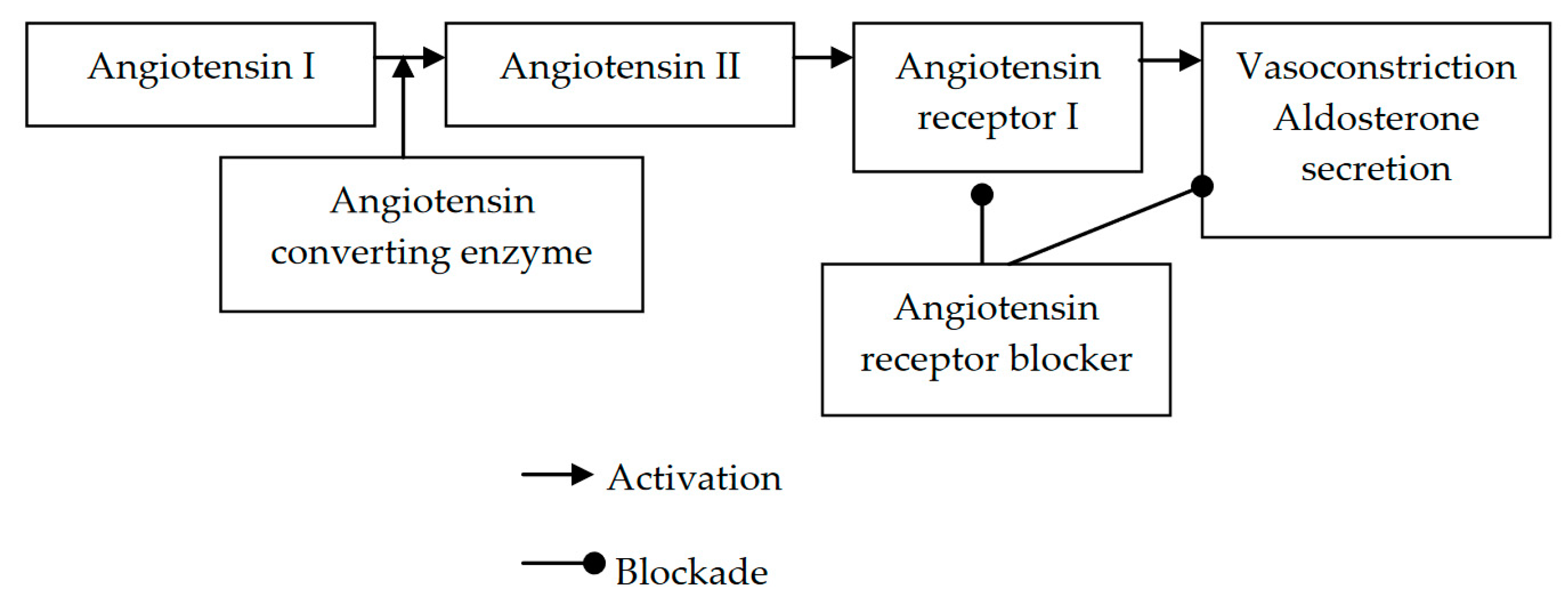
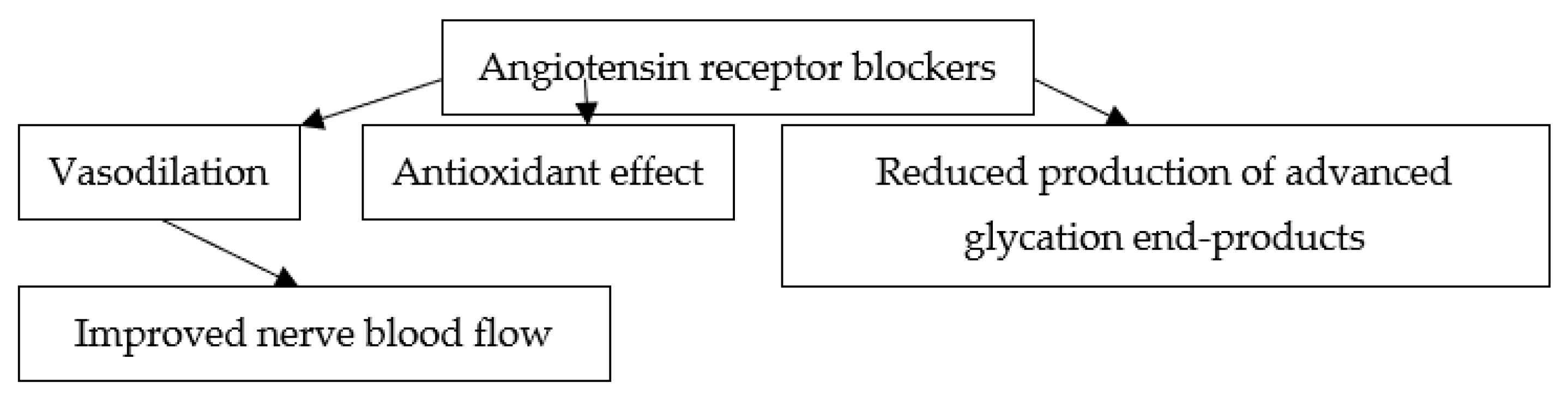
7. Putative Mechanisms of the Effects of ARBs on Diabetic Neuropathy
8. Indications for ARB Therapy
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Menke, A.; Casagrande, S.S.; Geiss, L.S.; Cowie, C.C. Prevalence of and Trends in Diabetes Among Adults in the United States, 1988–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizokami-Stout, K.R.; Boyle, C.T.; Shah, V.N.; Aleppo, G.; Mcgill, J.B.; Pratley, R.; Toschi, E.; Ang, L.; Pop-Busui, R. Contemporary Prevalence of Diabetic Neuropathy in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D)—Findings from the T1D Exchange. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; He, H. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the development and progression of neuropathy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1995, 122, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Low, P.A.; Waberski, B.H.; Martin, C.L.; Albers, J.W.; Feldman, E.L.; Sommer, C.; Cleary, P.A.; Lachin, J.M.; Herman, W.H.; et al. Effects of prior intensive insulin therapy on cardiac autonomic nervous system function in type 1 diabetes mellitus: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complica-tions study (DCCT/EDIC). Circulation 2009, 119, 2886–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Park, S.A.; Cho, J.H.; Song, K.H.; Yoon, K.H.; Cha, B.Y.; Son, H.Y.; Yoo, K.D.; Moon, K.W.; Park, Y.M.; et al. Progression of car-diovascular autonomic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: A 7-year follow-up study. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1832–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.R.; Fuller, J.H.; EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, K.Y.; Maser, R.E.; Pambianco, G.; Becker, D.J.; Orchard, T.J. Hypertension as a risk factor for diabetic neuropathy: A prospective study. Diabetes 1997, 46, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Niskanen, L.; Lehtinen, J.; Mervaala, E.; Siitonen, O.; Uusitupa, M. Natural History of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, C.A.; Carrington, A.L.; Ashe, H.; Bath, S.; Every, L.C.; Griffiths, J.; Hann, A.W.; Hussein, A.; Jackson, N.; Johnson, K.E.; et al. The North-West Diabetes Foot Care Study: Incidence of, and risk factors for, new diabetic foot ulceration in a community-based patient cohort. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.J.; Breddy, J.L.; Veves, A.; Boulton, A.J.M. The Prediction of Diabetic Neuropathic Foot Ulceration Using Vibration Perception Thresholds: A prospective study. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppini, D.; Bowtell, P.; Weng, C.; Young, P.; Sönksen, P. Showing neuropathy is related to increased mortality in diabetic patients—A survival analysis using an accelerated failure time model. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy. Circulation 2007, 115, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.S.; Tarnow, L.; Rossing, P.; Hansen, B.V.; Hilsted, J.; Parving, H.-H. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Type 1 Diabetic Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.; Nevitt, S.; Eleftheriadou, A.; Kanagala, P.; Esa, H.; Cuthbertson, D.J.; Tahrani, A.; Alam, U. Cardiac autonomic neu-ropathy and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.; Dekker, J.M.; TenVoorde, B.J.; Kostense, P.J.; Heine, R.J.; Bouter, L.M.; Heethaar, R.M.; Stehouwer, C.D. Impaired Autonomic Function Is Associated with Increased Mortality, Especially in Subjects with Diabetes, Hypertension, or a History of Cardiovascular Disease: The Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.L.; Albers, J.; Herman, W.H.; Cleary, P.; Waberski, B.; Greene, D.A.; Stevens, M.J.; Feldman, E.L.; DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Neuropathy Among the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Cohort 8 Years After Trial Completion. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insu-lin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on measures of autonomic nervous system function in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Diabetologia 1998, 41, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of compli-cations in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichiri, M.; Kishikawa, H.; Ohkubo, Y.; Wake, N. Long-term results of the Kumamoto Study on optimal diabetes control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2000, 23 (Suppl. S2), B21–B29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohkubo, Y.; Kishikawa, H.; Araki, E.; Miyata, T.; Isami, S.; Motoyoshi, S.; Kojima, Y.; Furuyoshi, N.; Shichiri, M. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: A randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 1995, 28, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advance Collaborative Group; Patel, A.; MacMahon, S.; Chalmers, J.; Neal, B.; Billot, L.; Woodward, M.; Marre, M.; Cooper, M.; Glasziou, P.; et al. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth, W.; Abraira, C.; Moritz, T.; Reda, D.; Emanuele, N.; Reaven, P.D.; Zieve, F.J.; Marks, J.; Davis, S.N.; Hayward, R.; et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Cardiovascular Disease and Risk Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018. Diabetes Care 2022, 45 (Suppl. S1), S144–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.M.; Kodali, R. Should Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Ever Be Used for the Management of Hypertension? Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxfield, E.K.; Cameron, N.E.; Cotter, M.A.; Dines, K.C. Angiotensin II receptor blockade improves nerve function, modulates nerve blood flow and stimulates endoneurial angiogenesis in streptozotocin-diabetic rats and nerve function. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxfield, E.K.; Love, A.; Cotter, M.A.; Cameron, N.E. Nerve function and regeneration in diabetic rats: Effects of ZD-7155, an AT1 receptor antagonist. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1995, 269, E530–E537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Domon, Y.; Inoue, T.; Arakawa, N.; Yokoyama, T. Olmesartan medoxomil ameliorates sciatic nerve regeneration in diabetic rats. NeuroReport 2009, 20, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Ichikawa, Y.; Igarashi, O.; Kinoshita, M.; Ikeda, K. Trophic effect of olmesartan, a novel AT1R antagonist, on spinal motor neurons in vitro and in vivo. Neurol. Res. 2002, 24, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahveisi, K.; Mousavi, S.H.; Hosseini, M.; Rad, A.K.; Jalali, S.A.; Rajaei, Z.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Hadjzadeh, M.A. The role of local ren-in-angiotensin system on high glucose-induced cell toxicity, apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production in PC12 cells. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavusoglu, T.; Karadeniz, T.; Cagiltay, E.; Karadeniz, M.; Yigitturk, G.; Acikgoz, E.; Uyanikgil, Y.; Ates, U.; Tuglu, M.I.; Erbas, O. The Protective Effect of Losartan on Diabetic Neuropathy in a Diabetic Rat Model. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2015, 123, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rejaie, S.S.; Abuohashish, H.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Arrejaie, A.; Aleisa, A.M.; AlSharari, S.D. Telmisartan inhibits hyperalgesia and inflammatory progression in a diabetic neuropathic pain model of Wistar rats. Neurosciences 2015, 20, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubba, S.; Agarwal, S.K.; Prakash, A.; Puri, V.; Babbar, R.; Anuradha, S. Effect of losartan on albuminuria, peripheral and autonomic neuropathy in normotensive microalbuminuric type 2 diabetics. Neurol. India 2003, 51, 355–358. [Google Scholar]
- Maser, R.E.; Lenhard, M. Effect of treatment with losartan on cardiovascular autonomic and large sensory nerve fiber function in individuals with diabetes mellitus: A 1-year randomized, controlled trial. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2003, 17, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didangelos, T.P.; Arsos, G.A.; Karamitsos, D.T.; Athyros, V.G.; Georga, S.D.; Karatzas, N.D. Effect of quinapril or losartan alone and in combination on left ventricular systolic and diastolic functions in asymptomatic patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2006, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athyros, V.G.; Didangelos, T.P.; Karamitsos, D.T.; Papageorgiou, A.A.; Boudoulas, H.; Kontopoulos, A.G. Long-term effect of conver-ting enzyme inhibition on circadian sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation in patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Acta Cardiol. 1998, 53, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kontopoulos, A.G.; Athyros, V.G.; Didangelos, T.P.; Papageorgiou, A.A.; Avramidis, M.J.; Mayroudi, M.C.; Karamitsos, D.T. Effect of Chronic Quinapril Administration on Heart Rate Variability in Patients with Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, S.; Tamura, K.; Wakui, H.; Kanaoka, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Maeda, A.; Dejima, T.; Yanagi, M.; Azuma, K.; Umemura, S. Effects of an-giotensin II type 1 receptor blocker on ambulatory blood pressure variability in hypertensive patients with overt diabetic nephropathy. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambara, K.; Fujita, M.; Sumita, Y.; Miyamoto, S.; Sekiguchi, H.; Eiho, S.; Komeda, M. Beneficial effect of candesartan treatment on cardiac autonomic nervous activity in patients with chronic heart failure: Simultaneous recording of ambulatory electro-cardiogram and posture. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 27, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Béchir, M.; Enseleit, F.; Chenevard, R.; Lüscher, T.F.; Noll, G. Effect of losartan on muscle sympathetic activity and baroreceptor function in systemic hypertension. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 95, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amador, N.; Encarnación, J.J.; Guízar, J.M.; Rodríguez, L.; Lopez, M. Effect of losartan and spironolactone on left ventricular mass and heart sympathetic activity in prehypertensive obese subjects: A 16-week randomized trial. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2005, 19, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galetta, F.; Franzoni, F.; Fallahi, P.; Tocchini, L.; Graci, F.; Carpi, A.; Antonelli, A.; Santoro, G. Effect of telmisartan on QT interval variability and autonomic control in hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, M.; Arslan, U.; Türkoğlu, S.; Balcioğlu, S.; Çengel, A. Losartan Improves Heart Rate Variability and Heart Rate Turbulence in Heart Failure Due to Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. J. Card. Fail. 2007, 13, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petretta, M.; Spinelli, L.; Marciano, F.; Apicella, C.; Vicario, M.L.E.; Testa, G.; Volpe, M.; Bonaduce, D. Effects of losartan treatment on cardiac autonomic control during volume loading in patients with DCM. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H86–H92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Lacourcière, Y.; LeBlanc, A.R.; Nadeau, R.; Dubé, B.; Florescu, M.; Lamarre-Cliche, M.; Poirier, L.; Larochelle, P.; de Champlain, J. Effect of the renin-angiotensin system or calcium channel blockade on the circadian variation of heart rate variability, blood pressure and circulating catecholamines in hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Ligtenberg, G.; Oey, L.; Koomans, H.A.; Blankestijn, P.J. Moxonidine Normalizes Sympathetic Hyperactivity in Patients with Eprosartan-Treated Chronic Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2902–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusser, K.; Vitkovsky, J.; Schmieder, R.E.; Schobel, H.P. AT1 antagonism by eprosartan lowers heart rate variability and baro-reflex gain. Auton. Neurosci. 2003, 107, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.H.; Ligtenberg, G.; Oey, P.L.; Koomans, H.A.; Blankestijn, P.J. Enalapril and Losartan Reduce Sympathetic Hyperactivity in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasti, L.; Petrozzino, M.R.; Mainardi, L.T.; Grimoldi, P.; Zanotta, D.; Garganico, D.; Diolisi, A.; Simoni, C.; Grandi, A.M.; Gaudio, G.; et al. Autonomic function and baroreflex sensitivity during angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition or angiotensin II AT-1 receptor blockade in essential hypertensive patients. Acta Cardiol. 2001, 56, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, K.U.; Wysocki, M.; Friberg, P.R.; Andersson, O.K. Candesartan cilexetil in hypertension: Effects of six weeks’ treatment on haemodynamics, baroreceptor sensitivity and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Blood Press 1999, 8, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Rongen, G.A.; Brooks, S.; Ando, S.-I.; Dajani, H.R.; Abramson, B.L.; Floras, J.S. Neural and Hypotensive Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade. Hypertension 1998, 31, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaile, J.; Chowdhary, S.; Osman, F.; Ross, H.; Fletcher, J.; Littler, W.; Coote, J.; Townend, J. Effects of angiotensin II (AT1) receptor blockade on cardiac vagal control in heart failure. Clin. Sci. 2001, 101, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbia, F.; Silke, B.; Carra, R.; Milan, A.; Del Colle, S.; Pugni, C.; Mulatero, P.; Chiandussi, L.; Veglio, F. Heart Rate Variability and Baroreflex Sensitivity during Fosinopril, Irbesartan and Atenolol Therapy in Hypertension. Clin. Drug Investig. 2004, 24, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, C.-M.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Hu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Hsu, L.-C.; Chao, A.-C. Effects of Atenolol and Losartan on Baroreflex Sensitivity and Heart Rate Variability in Uncomplicated Essential Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, F.; Lazzeri, C.; Foschi, M.; Tosti-Guerra, C.; Barletta, G. Cardiac autonomic tone during trandolapril-irbesartan low-dose combined therapy in hypertension: A pilot project. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2002, 16, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sakata, K.; Yoshida, H.; Obayashi, K.; Ishikawa, J.; Tamekiyo, H.; Nawada, R.; Doi, O. Effects of losartan and its combination with quinapril on the cardiac sympathetic nervous system and neurohormonal status in essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, K.M.; Struthers, A. Endogenous angiotensin II and baroreceptor dysfunction: A comparative study of losartan and enalapril in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 46, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tommasi, E.; Iacoviello, M.; Romito, R.; Ceconi, C.; Guida, P.; Massari, F.; Francolini, G.; Bertocchi, F.; Ferrari, R.; Rizzon, P.; et al. Comparison of the effect of valsartan and lisinopril on autonomic nervous system activity in chronic heart failure. Am. Heart J. 2003, 146, E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachet, S.; Danigo, A.; Labriffe, M.; Bessaguet, F.; Quinchard, B.; Deny, N.; Baffert, K.-A.; Deluche, E.; Sturtz, F.; Demiot, C.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin-System Inhibitors for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: OncoToxSRA, a Preliminary Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, C.G.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.; Glasser, D.B.; Mittleman, M.A.; Rimm, E.B. Association of Type and Duration of Diabetes with Erectile Dysfunction in a Large Cohort of Men. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, G.; Franciosi, M.; Belfiglio, M.; Di Nardo, B.; Greenfield, S.; Kaplan, S.H.; Pellegrini, F.; Sacco, M.; Tognoni, G.; Valentini, M.; et al. Quality of Care and Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes (QuED) Study Group. Erectile dysfunction and quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: A serious problem too often overlooked. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.X.; Yao, L.S.; Wang, R.; Dai, Y.T. Valsartan treatment reverses erectile dysfunction in diabetic rats. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2006, 19, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Yang, B.; Wen, Y.; Fang, F.; Cui, S.; Lin, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, R.; Dai, Y. Losartan, an Angiotensin Type I Receptor, Restores Erectile Function by Downregulation of Cavernous Renin-Angiotensin System in Streptozocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Sex. Med. 2009, 6, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Shin, J.W.; Oh, J.K.; Ryu, K.S.; Kim, S.W.; Paick, J.-S. Restoration of erectile capacity in normotensive aged rats by modulation of angiotensin receptor type 1. J. Androl. 2004, 26, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Baumhäkel, M.; Schlimmer, N.; Böhm, M.; on behalf of the DO-IT Investigators. Effect of irbesartan on erectile function in patients with hypertension and metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2008, 20, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llisterri, J.L.; Vidal, J.V.L.; Vicente, J.A.; Roca, M.A.; Bravo, C.P.; Zamorano, M.A.S.; Ferrario, C.M. Sexual Dysfunction in Hypertensive Patients Treated with Losartan. Am. J. Med Sci. 2001, 321, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düsing, R. Effect of the angiotensin II antagonist valsartan on sexual function in hypertensive men. Blood Press. Suppl. 2003, 2, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, R.E.; Lenhard, M.J. Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Due to Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical Manifestations, Consequences, and Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, M.; Mitsui, M.K.; Mitsui, Y.; Okuda, K.; Nakasaka, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Schmelzer, J.D. Altered vasoreactivity to angiotensin II in experimental diabetic neuropathy: Role of nitric oxide. Muscle Nerve 1999, 22, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkove, S.B. A 52-year-old woman with disabling peripheral neuropathy: Review of diabetic polyneuropathy. JAMA 2009, 302, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D. Treatment of diabetic neuropathy and neuropathic pain: How far have we come? Diabetes Care 2008, 31 (Suppl. S2), S255–S261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A.; Assaloni, R.; Da Ros, R.; Maier, A.; Piconi, L.; Quagliaro, L.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D. Effect of Atorvastatin and Irbesartan, Alone and in Combination, on Postprandial Endothelial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Circulation 2005, 111, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriello, A.; Assaloni, R.; Da Ros, R.; Maier, A.; Quagliaro, L.; Piconi, L.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D. Effect of irbesartan on nitrotyrosine generation in non-hypertensive diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 1535–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, T.; van Ypersele de Strihou, C.; Ueda, Y.; Ichimori, K.; Inagi, R.; Onogi, H.; Ishikawa, N.; Nangaku, M.; Kurokawa, K. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors lower in vitro the formation of advanced glycation end products: Biochemical mechanisms. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, N. Metabolic memory in the autonomic neuropathy of diabetes: Implications for pathogenesis and patient care. Circulation 2009, 119, 2865–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Patel, A.; MacMahon, S.; Advance Collaborative Group; Chalmers, J.; Neal, B.; Woodward, M.; Billot, L.; Harrap, S.; Poulter, N.; Marre, M.; et al. Effects of a fixed combination of perindopril and indapamide on macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (the ADVANCE trial): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, R.W.; Estacio, R.O.; Esler, A.; Mehler, P. Effects of aggressive blood pressure control in normotensive type 2 diabetic patients on albuminuria, retinopathy and strokes. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estacio, R.O.; Jeffers, B.W.; Gifford, N.; Schrier, R.W. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, B54–B64. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes UKPDS UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2. BMJ 1998, 317, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Levy, P. Sexual dysfunction in patients with hypertension: Implications for therapy. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2002, 4, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kifor, I.; Williams, G.H.; Vickers, M.A.; Sullivan, M.P.; Jodbert, P.; Dluhy, R.G. Tissue angiotensin II as a modulator of erectile function. I. Angiotensin peptide content, secretion and effects in the corpus cavernosum. J. Urol. 1997, 157, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.J.; Ückert, S.; Stief, C.G.; Truss, M.C.; Machtens, S.; Scheller, F.; Knapp, W.H.; Hartmann, U.; Jonas, U. Possible role of bradykinin and angiotensin II in the regulation of penile erection and detumescence. Urology 2001, 57, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gæde, P.; Vedel, P.; Larsen, N.; Jensen, G.V.; Parving, H.-H.; Pedersen, O. Multifactorial Intervention and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | ARB | Animal Model | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| [28] | ZD 8731 | Streptozotocin-diabetic rats | ZD 8731 ameliorated motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity and increased nerve capillary density |
| [29] | ZD 7155 | Streptozotocin-diabetic rats | ZD 7155 ameliorated motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity, improved nerve regeneration, and increased nerve capillary density and endoneurial blood flow |
| [30] | Olmesartan | Diabetic rats | Olmesartan improved nerve regeneration and increased the production of the ciliary neurotrophic factor |
| Ref. | n | Study Population | ARB | Treatment Duration (Months) | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [35] | 25 | Normotensive patients with T2DM and microalbuminuria | Losartan | 1 | Losartan had no effect on peripheral or autonomic neuropathy |
| [36] | 44 | Patients with T1DM or T2DM | Losartan | 12 | Losartan had no effect on cardiovascular autonomic function or vibration-perception threshold |
| [37] | 62 | Normotensive patients with T1DM or T2DM and autonomic neuropathy | Losartan | 12 | Losartan improved autonomic nervous function but did not affect vibration-perception threshold |
| Ref. | n | Study Population | ARB | Treatment Duration (Months) | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | 50 | Prehypertensive obese patients | Losartan | 4 | Losartan decreased heart sympathetic activity |
| [47] | 57 | Hypertensive patients | Telmisartan | 2 | Telmisartan increased heart parasympathetic activity |
| [49] | 25 | Young males | Eprosartan | 7 days | Eprosartan lowered heart rate variability and baroreflex gain |
| Ref. | n | Study Population | ARB | Treatment Duration (Months) | Major Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [67] | 1069 | Hypertensive males with metabolic syndrome | Irbesartan | 6 | Irbesartan improved erectile function, orgasmic function, and intercourse satisfaction |
| [68] | 164 | Hypertensive males | Losartan | 3 | Losartan improved sexual satisfaction and increased the frequency of sexual activity |
| [69] | 3502 | Hypertensive males | Valsartan | 6 | Valsartan improved erectile function, orgasmic function, and intercourse satisfaction; increased sexual desire |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostourou, D.-T.; Milonas, D.; Polychronopoulos, G.; Sofogianni, A.; Tziomalos, K. The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Personalized Management of Diabetic Neuropathy. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081253
Kostourou D-T, Milonas D, Polychronopoulos G, Sofogianni A, Tziomalos K. The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Personalized Management of Diabetic Neuropathy. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(8):1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081253
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostourou, Danai-Thomais, Dimitrios Milonas, Georgios Polychronopoulos, Areti Sofogianni, and Konstantinos Tziomalos. 2022. "The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Personalized Management of Diabetic Neuropathy" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 8: 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081253
APA StyleKostourou, D.-T., Milonas, D., Polychronopoulos, G., Sofogianni, A., & Tziomalos, K. (2022). The Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Personalized Management of Diabetic Neuropathy. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(8), 1253. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12081253







