Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case–Control Subjects
Abstract
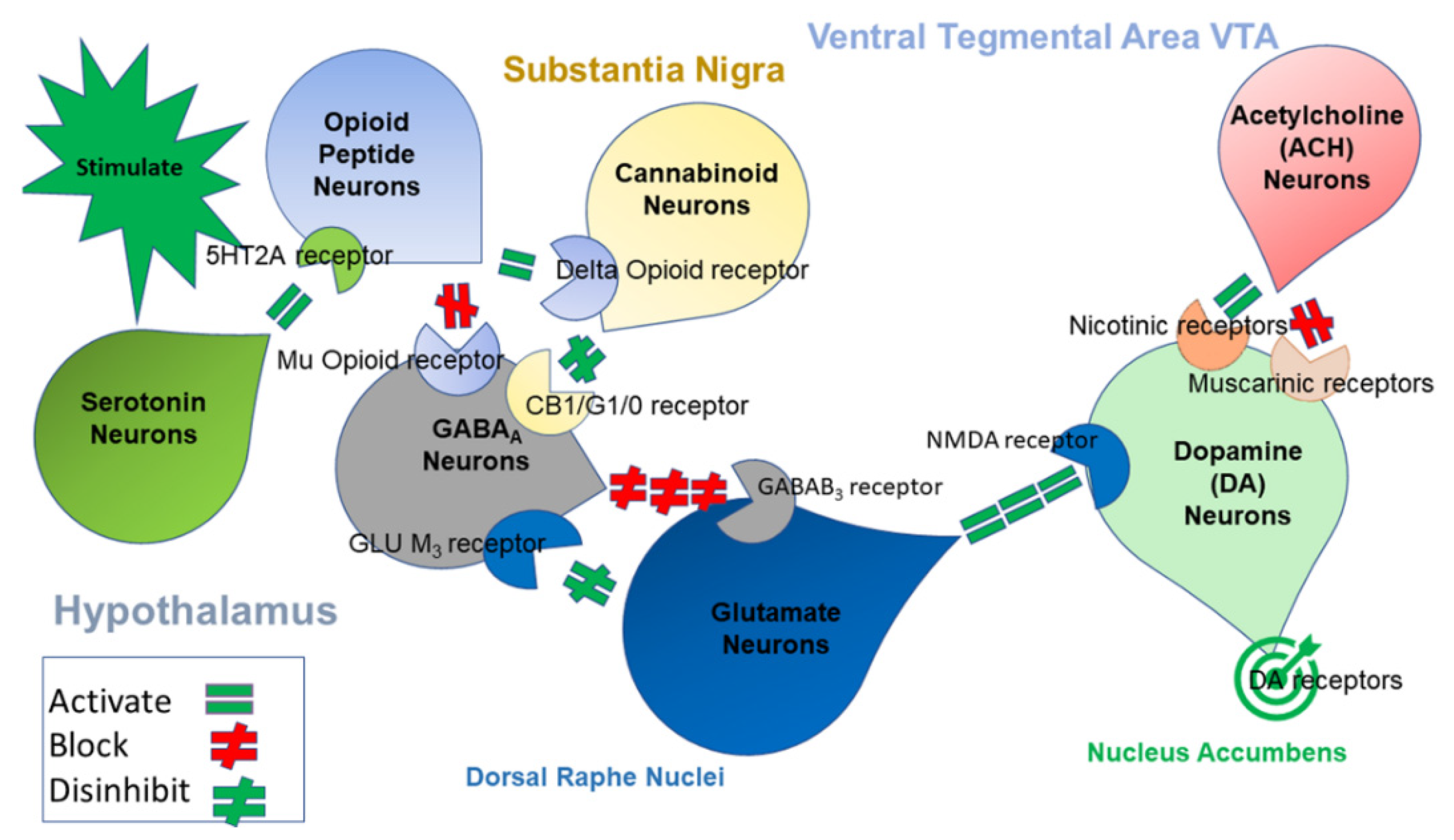
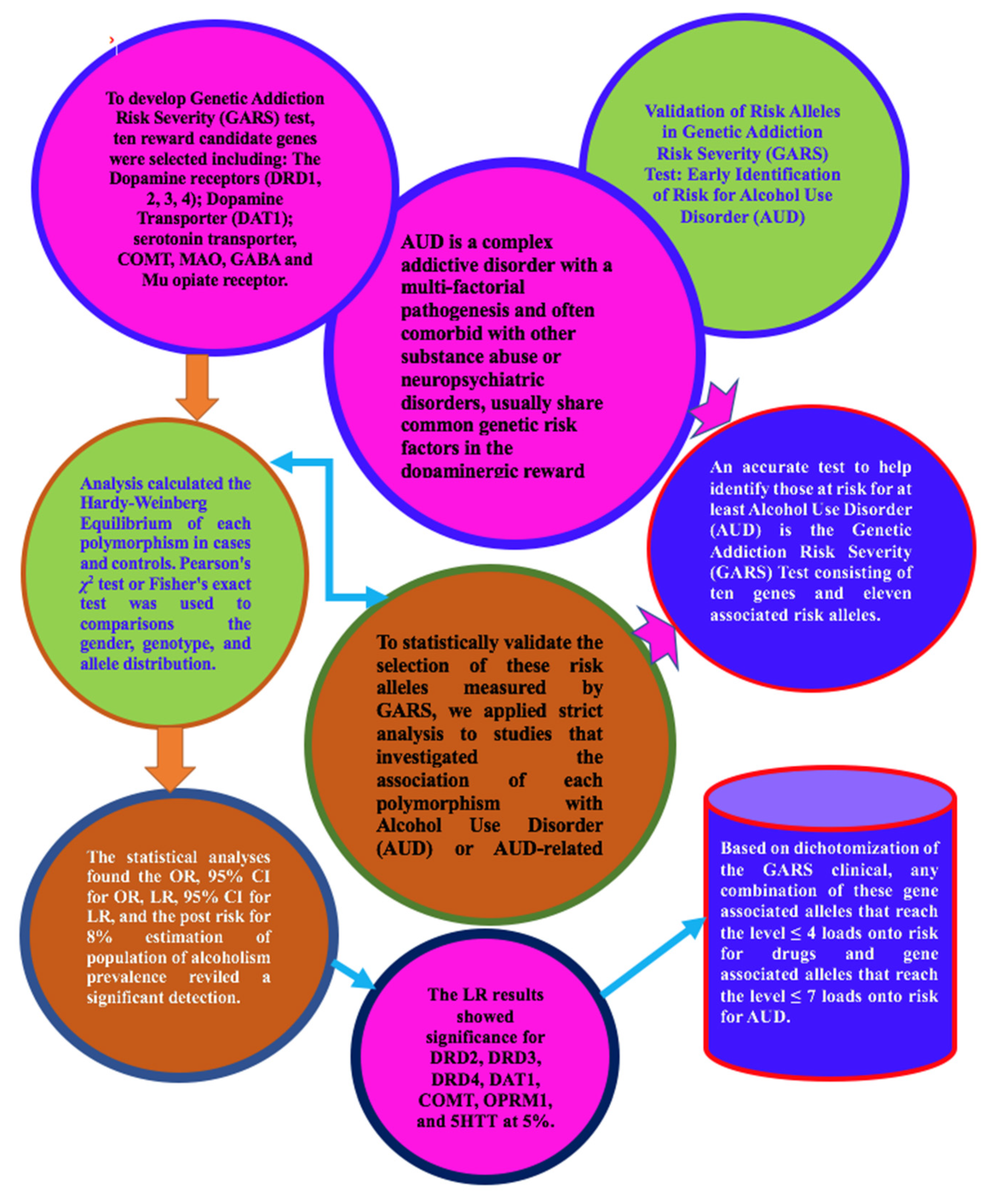
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Inclusion of Eligible Studies
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Study Limitations
Future Perspective
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oesterle, T.S.; Thusius, N.J.; Rummans, T.A.; Gold, M.S. Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opioid-Use Disorder. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 2072–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Baron, D.; McLaughlin, T.; Gold, M.S. Molecular neurological correlates of endorphinergic/dopaminergic mechanisms in reward circuitry linked to endorphinergic deficiency syndrome (EDS). J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 411, 116733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.A.P.S.; Gold, M. Treatment resistant opioid use disorder (TROUD): Definition, rationale, and recommendations. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 411, 116718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.S.; Baron, D.; Bowirrat, A.; Blum, K. Neurological correlates of brain reward circuitry linked to opioid use disorder (OUD): Do homo sapiens acquire or have a reward deficiency syndrome? J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 418, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, B.W.; Blum, K.; Baron, D.; Bowirrat, A.; Lott, L.; Brewer, R.; Boyett, B.; Siwicki, D.; Roy, A.K.; Podesta, A.; et al. Death by Opioids: Are there non-addictive scientific solutions? J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Lott, L.; Baron, D.; Smith, D.E.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Gold, M.S. Improving naltrexone compliance and outcomes with putative pro-dopamine regulator KB220, compared to treatment as usual. J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, J.R.; Schackman, B.R.; Leff, J.A.; Linas, B.P.; Walley, A.Y. Injectable naltrexone, oral naltrexone, and buprenorphine utilization and discontinuation among individuals treated for opioid use disorder in a United States commercially insured population. J. Subst. Abus. Treat. 2018, 85, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooteman, W.; Naassila, M.; Koeter, M.W.; Verheul, R.; Schippers, G.M.; Houchi, H.; Daoust, M.; van den Brink, W. Predicting the effect of naltrexone and acamprosate in alcohol-dependent patients using genetic indicators. Addict. Biol. 2009, 14, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, M.S.; Adams, C.; Kraehenbuehl, T.; Vengeliene, V.; Lawrence, A.J. The acute anti-craving effect of acamprosate in alcohol-preferring rats is associated with modulation of the mesolimbic dopamine system. Addict. Biol. 2005, 10, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.S.; Blum, K.; Febo, M.; Baron, D.; Modestino, E.J.; Elman, I.; Badgaiyan, R.D. Molecular role of dopamine in anhedonia linked to reward deficiency syndrome (RDS) and anti-reward systems. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Thanos, P.K.; Wang, G.J.; Febo, M.; Demetrovics, Z.; Modestino, E.J.; Braverman, E.R.; Baron, D.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Gold, M.S. The Food and Drug Addiction Epidemic: Targeting Dopamine Homeostasis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6050–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Baron, D.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Thanos, P.K.; Elman, I.; Braverman, E.R.; Gold, M.S. Understanding That Addiction Is a Brain Disorder Offers Help and Hope. Health 2022, 14, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Sheridan, P.; Wood, R.; Braverman, E.; Chen, T.; Phd, J.C.; Comings, D. The D2 dopamine receptor gene as a determinant of reward deficiency syndrome. J. R. Soc. Med. 1996, 89, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Wood, R.; Braverman, E.; Chen, T.; Sheridan, P. The D2 dopamine receptor gene as a predictor of compulsive disease: Bayes’ theorem. Funct. Neurol. 1995, 10, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, K.; Madigan, M.A.; Fried, L.; Braverman, E.R.; Giordano, J.; Badgaiyan, R.D. Coupling genetic addiction risk score (GARS) and pro dopamine regulation (KB220) to combat substance use disorder (SUD). Glob. J. Addict. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 1, 555556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Chen, A.L.; Thanos, P.K.; Febo, M.; Demetrovics, Z.; Dushaj, K.; Kovoor, A.; Baron, D.; Smith, D.E.; Lll, A.K.R.; et al. Genetic addiction risk score GARS trade a predictor of vulnerability to opioid dependence. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Downs, B.; Dushaj, K.; Li, M.; Braverman, E.R.; Fried, L.; Waite, R.; Demotrovics, Z.; Badgaiyan, R.D. The benefits of customized DNA directed nutrition to balance the brain reward circuitry and reduce addictive behaviors. Precis. Med. 2016, 1, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, K.; Oscar-Berman, M.; Demetrovics, Z.; Barh, D.; Gold, M.S. Genetic addiction risk score (GARS): Molecular neurogenetic evidence for predisposition to reward deficiency syndrome (RDS). Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 765–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Agan, G.; Fratantonio, J.; Simpatico, T.; Febo, M.; Haberstick, B.C.; Smolen, A.; Gold, M.S. Molecular Genetic Testing in Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS): Facts and Fiction. J. Reward Defic. Syndr. 2015, 1, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Butler, S.F.; McNaughton, E.C.; Black, R.A. Tapentadol abuse potential: A postmarketing evaluation using a sample of individuals evaluated for substance abuse treatment. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, B.; Anttila, V.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Finucane, H.K.; Walters, R.K.; Bras, J.; Duncan, L.; Escott-Price, V.; Falcone, G.J.; Gormley, P. Analysis of shared heritability in common disorders of the brain. Science 2018, 360, eaap8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laird, N.M.; Mosteller, F. Some statistical methods for combining experimental results. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Health Care 1990, 6, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Pigott, T.D. The power of statistical tests in meta-analysis. Psychol. Methods 2001, 6, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Pigott, T.D. The power of statistical tests for moderators in meta-analysis. Psychol. Methods 2004, 9, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Berlin, J.A. Publication bias: A problem in interpreting medical data. J. R. Stat. Soc. B Stat. Methodol. 1988, 151, 419–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple. Graph. Test. Br. Med. J. 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, R. Graphical display of estimates having differing standard errors. Technometrics 1988, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. A nonparametric “trim and fill” method of accounting for publication bias in meta-analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2000, 95, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, K. Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) test and Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS). In Proceedings of the 18th Annual Scientific Meeting of the Society for Brain Mapping & Therapeutics (SBMT), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gamma, F.; Faraone, S.V.; Glatt, S.J.; Yeh, Y.C.; Tsuang, M.T. Meta-analysis shows schizophrenia is not associated with the 40-base-pair repeat polymorphism of the dopamine transporter gene. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 73, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Noble, E.P.; Sheridan, P.J.; Montgomery, A.; Ritchie, T.; Jagadeeswaran, P.; Nogami, H.; Briggs, A.H.; Cohn, J.B. Allelic association of human dopamine D2 receptor gene in alcoholism. JAMA 1990, 263, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Border, R.; Johnson, E.C.; Evans, L.M.; Smolen, A.; Berley, N.; Sullivan, P.F.; Keller, M.C. No Support for Historical Candidate Gene or Candidate Gene-by-Interaction Hypotheses for Major Depression Across Multiple Large Samples. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, L.E.; Keller, M.C. A critical review of the first 10 years of candidate gene-by-environment interaction research in psychiatry. Am. J. Psychiatry 2011, 168, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatoum, A.S.; Wendt, F.R.; Galimberti, M.; Polimanti, R.; Neale, B.; Kranzler, H.R.; Gelernter, J.; Edenberg, H.J.; Agrawal, A. Ancestry may confound genetic machine learning: Candidate-gene prediction of opioid use disorder as an example. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 229, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.C.; Border, R.; Melroy-Greif, W.E.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Ehringer, M.A.; Keller, M.C. No Evidence that Schizophrenia Candidate Genes Are More Associated with Schizophrenia Than Noncandidate Genes. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 82, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sealock, J.M.; Sanchez-Roige, S.; Clarke, T.K.; Levey, D.F.; Cheng, Z.; Li, B.; Polimanti, R.; Kember, R.L.; Smith, R.V.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of problematic alcohol use in 435,563 individuals yields insights into biology and relationships with other traits. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wedow, R.; Li, Y.; Brazel, D.M.; Chen, F.; Datta, G.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; McGuire, D.; Tian, C.; et al. Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Baron, D.; Lott, L.; Ponce, J.V.; Siwicki, D.; Boyett, B.; Steinberg, B.; Modestino, E.J.; Fried, L.; Hauser, M.; et al. In Search of Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS)-Free Controls: The “Holy Grail” in Genetic Addiction Risk Testing. Curr. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 9, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, A.T.; Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Preaddiction—A Missing Concept for Treating Substance Use Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joutsa, J.; Moussawi, K.; Siddiqi, S.H.; Abdolahi, A.; Drew, W.; Cohen, A.L.; Ross, T.J.; Deshpande, H.U.; Wang, H.Z.; Bruss, J.; et al. Brain lesions disrupting addiction map to a common human brain circuit. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cdc.gov. Understanding the Epidemic. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html (accessed on 25 June 2022).
- Kótyuk, E.; Urbán, R.; Hende, B.; Richman, M.; Magi, A.; Király, O.; Barta, C.; Griffiths, M.D.; Potenza, M.N.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; et al. Development and validation of the Reward Deficiency Syndrome Questionnaire (RDSQ-29). J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene/Polymorphism | Number of Reference Sources | 95% CI Overall Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine D1 Receptor (DRD1): rs4532—risk allele G | 3 | The genetic variation in DRD1 and its relationship to a predisposition to alcoholism have been supported by various studies. A statistically significant association of DRD1 rs4532 polymorphism with alcohol dependence was found among Indian males (90 cases vs. 122 controls). Other studies also demonstrated that this could be associated with the impulsivity and aggressiveness of AUD patients. |
| Dopamine D2 Receptor (DRD2): rs1800497—risk allele A1 | 118 | From the meta-analysis of numerous case–control studies (total of 18,290 cases vs. 19,809 controls, including US Caucasian, native and African-American, British, French, Italian, Swedish, Finnish, Spanish, Mexican, Brazilian, Scandinavian, Japanese) pooled with the random effect models, the DRD2 rs1800497 was found to be associated with a risk of AUD and several AUD-related conditions. |
| Dopamine D3 Receptor (DRD3): rs6280—risk allele C (Ser9Gly) | 3 | Several case–control studies investigated the association between the DRD3 rs6280 polymorphism and alcohol dependence. In a Korean study (243 cases vs. 130 controls), the DRD3 rs6280 polymorphism was significantly associated with AUD development. |
| Dopamine D4 Receptor (DRD4): rs1800955—risk allele C (48bp repeat VNTR) | 35 | A meta-analysis of various case–control studies (total 2997 cases vs. 2588 controls, including US Caucasian, Mexican-American, Indian) pooled with the random effect models found that the DRD4 rs1800955 polymorphism was associated with the risk of developing AUD and AUD-related conditions. |
| Dopamine Transporter Receptor (DAT1): SLC6A3 3′-UTR—risk allele A9 (40bp repeat VNTR) | 43 | The central dopaminergic reward pathway is likely involved in alcohol intake and the progression of alcohol dependence. DAT1 is a primary mediator of dopaminergic neurotransmission. From the meta-analysis of numerous case–control studies (total 3790 cases vs. 3446 controls) pooled with the random effect models, the DAT1 SLC6A3 3′-UTR risk allele was found to be marginally associated with a risk of AUD and/AUD-related conditions. |
| Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT): rs4680—risk allele G (Val158Met) | 13 | A plethora of evidence supports COMT as a candidate gene that likely contributes to schizophrenia and substance use disorder. A meta-analysis of several case–control studies (total of 1212 cases vs. 933 controls, including US Caucasian, Finnish, Croatian, and Taiwanese) pooled with a random effect model, the association of COMPT rs4680 polymorphism with the risk of AUD and AUD-related conditions was found to have marginal statistical significance. |
| µ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1): rs1799971—risk allele G (A118G) | 28 | Opioid receptors play an essential role in ethanol reinforcement and alcohol dependence risk. Some features of alcohol dependence are likely associated with polymorphisms of the OPRM1 gene expressing µ-opioid receptors. From the meta-analysis of case–control studies (total of 3096 cases vs. 2896 controls, including US Caucasian, Spanish, Turkish, and Asian) pooled with the random effect model, the results indicated that the association of a functional OPRM variant and the risk of alcohol dependence was found to have marginal statistical significance. |
| γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) A Receptor, β-3 Subunit (GABRB3): CA repeat—risk allele 181 | 6 | The GABAergic system has been implicated in alcohol-related behaviors. From case–control studies (171 cases vs. 45 controls), the association of variants of the GABRB3 gene with alcohol dependence is, however, inconclusive. A more extensive controlled study is required for improved results. |
| Monoamine Oxidase A (MAO-A): 3′ 30bp VNTR -risk allele 4R DNRP | 6 | The function of monoamine oxidase (MAO) in alcoholism was determined using several case–control studies (170 cases vs. 177 controls). Although genetic heterogeneity is suspected of underlying alcoholism and MAO-A mutations may play a role in susceptibility to alcoholism, the overall results were not found to be statistically significant. A more extensive controlled study is required to obtain conclusive results. |
| Serotonin Transporter Receptor (5HTT) Linked Promoter Region (5HTTLPR) in SLC6A4: rs25531—risk allele S′ | 20 | Serotonin (5-HT) has been demonstrated to regulate alcohol consumption. Since the activity of the 5-HT transporter protein (5-HTT) regulates 5-HT levels, it may contribute to the risk of alcohol dependence. From the meta-analysis of some case–control studies (total 9996 cases vs. 9950 controls) pooled with the random effect models, the association between alcohol dependence and a polymorphism in the 5-HTTLPR was significant. |
| Gene/Polymorphism | OR | 95% CI for OR | Post Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dopamine D1 Receptor (DRD1): rs4532—risk allele G * | 1.77 | (1.01, 3.10) | - |
| Dopamine D2 Receptor (DRD2): rs1800497—risk allele A1 | 1.45 | (1.15, 1.90) | 0.12 |
| Dopamine D3 Receptor (DRD3): rs6280—risk allele C (Ser9Gly) | 3.37 | (1.54, 7.40) | 0.20 |
| Dopamine D4 Receptor (DRD4): rs1800955—risk allele C (48bp repeat VNTR) | 1.56 | (1.04, 2.36) | 0.10 |
| Dopamine Transporter Receptor (DAT1): SLC6A3 3′-UTR—risk allele A9 (40bp repeat VNTR) | 1.18 | (1.00, 1.45) | 0.10 |
| Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT): rs4680—risk allele G (Val158Met) | 1.43 | (0.98, 2.10) | 0.083 |
| µ-Opioid Receptor (OPRM1): rs1799971—risk allele G (A118G) | 1.47 | (1.00, 2.18) | 0.13 |
| γ-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) A Receptor, -3 Subunit (GABRB3): CA repeat—risk allele 181 | 0.33 | (0.14, 0.79) | 0.06 |
| Monoamine Oxidase A (MAO-A): 3′ 30bp VNTR-risk allele 4R DNRP | 0.62 | (0.15, 2.63) | 0.05 |
| Serotonin Transporter Receptor (5HTT) Linked Promoter Region (5HTTLPR) in SLC6A4: rs25531—risk allele S′ | 1.23 | (1.07, 1.40) | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blum, K.; Han, D.; Gupta, A.; Baron, D.; Braverman, E.R.; Dennen, C.A.; Kazmi, S.; Llanos-Gomez, L.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Elman, I.; et al. Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case–Control Subjects. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091385
Blum K, Han D, Gupta A, Baron D, Braverman ER, Dennen CA, Kazmi S, Llanos-Gomez L, Badgaiyan RD, Elman I, et al. Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case–Control Subjects. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091385
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlum, Kenneth, David Han, Ashim Gupta, David Baron, Eric R. Braverman, Catherine A. Dennen, Shan Kazmi, Luis Llanos-Gomez, Rajendra D. Badgaiyan, Igor Elman, and et al. 2022. "Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case–Control Subjects" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091385
APA StyleBlum, K., Han, D., Gupta, A., Baron, D., Braverman, E. R., Dennen, C. A., Kazmi, S., Llanos-Gomez, L., Badgaiyan, R. D., Elman, I., Thanos, P. K., Downs, B. W., Bagchi, D., Gondre-Lewis, M. C., Gold, M. S., & Bowirrat, A. (2022). Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case–Control Subjects. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091385












