Reconstruction of Large Soft Tissue Defects in the Distal Lower Extremity: Free Chain-Linked Bilateral Anterolateral Thigh Perforator Flaps versus Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flaps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
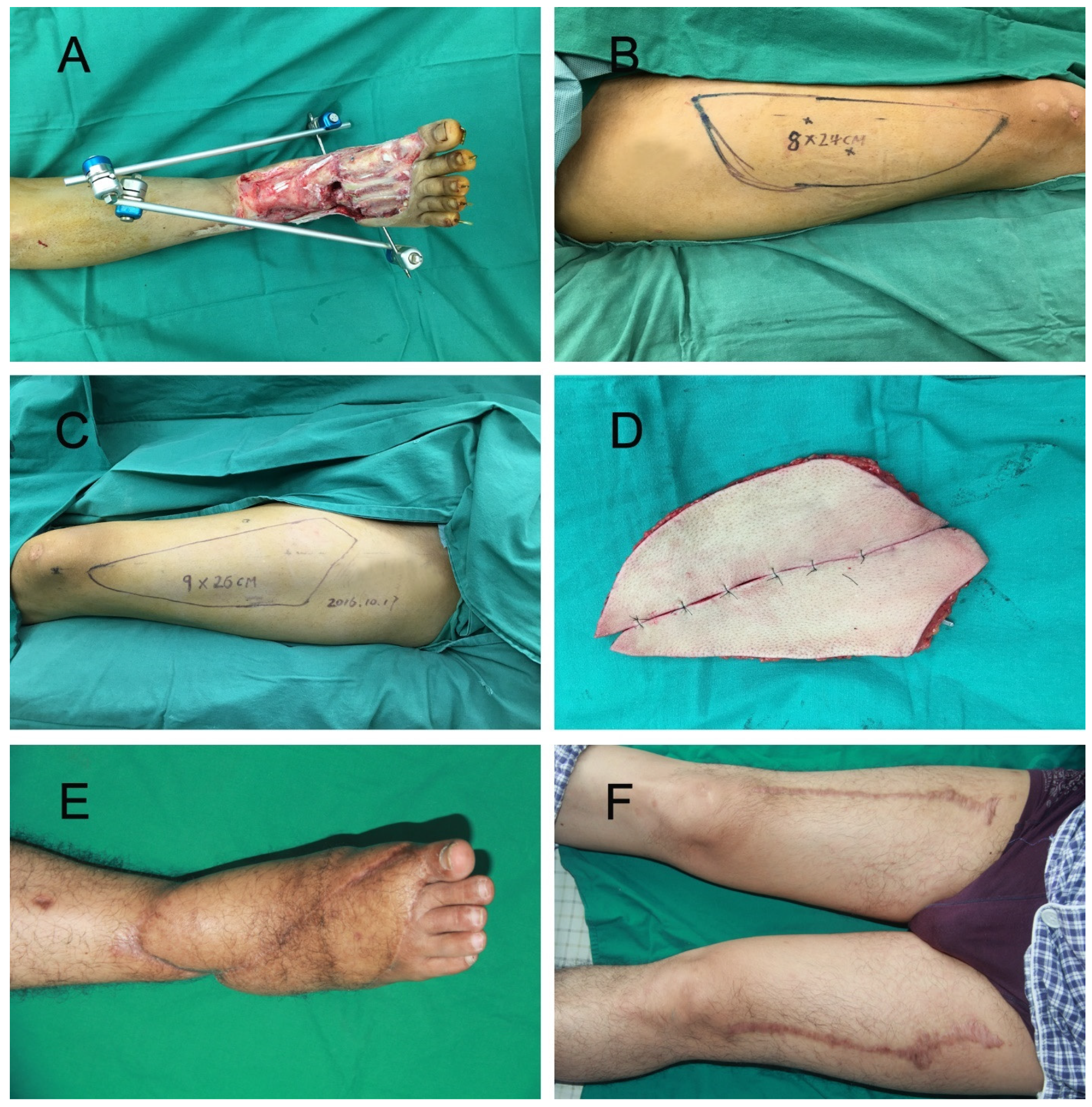
2.2. Surgical Method
2.3. Evaluation of Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Flap Characteristics and Intra-Operative Data
3.2. Flap Complications and Outcomes
3.3. Long-Term Follow-Up Results
3.4. Subjective Assessment of Donor Site Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.W.; Youn, S.; Kim, J.D.; Kim, J.T.; Hwang, K.T.; Kim, Y.H. Reconstruction of extensive lower limb defects with thoracodorsal axis chimeric flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, R.K.; Srinivasan, K.; Bhamre, A.; Singh, M.; Kumar, P.; Tambotra, A. A retrospective analysis of latissimus dorsi-serratus anterior chimeric flap reconstruction in 47 patients with extensive lower extremity trauma. Indian J. Plast. Surg. 2018, 51, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.L.; Van Waes, C.; D’Arpa, S.; Van Landuyt, K.; Blondeel, P.N.; Monstrey, S.; Stillaert, F.B. Bipedicled DIEAP flaps for reconstruction of limb soft tissue defects in male patients. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2016, 69, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Wartburg, U.; Kunzi, W.; Meuli, M. Reconstruction of skin and soft-tissue defects in crush-injuries of the lower leg in children. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1991, 1, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshima, I. A new classification of free combined or connected tissue transfers: Introduction to the concept of bridge, siamese, chimeric, mosaic, and chain-circle flaps. Acta Med. Okayama 2001, 55, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessler, G.A.; Schmidt, A.B.; Germann, G.; Pelzer, M. The role of fabricated chimeric free flaps in reconstruction of devastating hand and forearm injuries. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2011, 27, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Chen, J.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. The use of fabricated chimeric flap for reconstruction of extensive foot defects. Microsurgery 2016, 36, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.H.; Tu, Y.K.; Wu, C.H.; Yen, C.Y.; Yu, S.W.; Kao, F.C. Reconstruction of upper extremity large soft-tissue defects using pedicled latissimus dorsi muscle flaps--technique illustration and clinical outcomes. Injury 2008, 39 (Suppl. S4), 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.G.; Liu, Y.J.; He, X.; Ding, X.H.; Fang, G.G. Use of pedicled latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap to reconstruct the upper limb with large soft tissue defects. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2012, 15, 352–354. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Pan, D.; Wu, P.; Tang, J. Recurrent skin ulcer cross-repair and sensory reconstruction in a WRN gene mutational patient. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2018, 93, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlander, D.E.; Durand, P.; Couto, R.A.; Lamaris, G.A.; Kaza, A.G.; Swanson, M.; Gatherwright, J.; Kaufman, B.R. The Muscle-Sparing Descending Branch Latissimus Dorsi Free Flap for Lower Extremity Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 412e–420e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.P.; Fulton, A.; Quach, C.; Thistle, M.; Toledo, C.; Evans, N.A. Measurement Properties of the Lower Extremity Functional Scale: A Systematic Review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2016, 46, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwirth, M.; Hubmer, M.; Koch, H. The posterior interosseous artery flap: Clinical results with special emphasis on donor site morbidity. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2013, 66, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouz, S.M.; Castel, N.A.; Vijayasekaran, A.; Rebecca, A.M.; Lettieri, S.C. Lower-limb reconstruction with chimeric flaps: The quad flap. Microsurgery 2019, 39, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigdeli, A.K.; Thomas, B.; Schmidt, V.J.; Kotsougiani, D.; Hernekamp, F.J.; Hirche, C.; Kneser, U.; Gazyakan, E. The conjoined parascapular and latissimus dorsi free flap for reconstruction of extensive knee defects. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribuffo, D.; Cigna, E.; Gerald, G.L.; Houseman, N.; Seneviratne, S.; Lombardi, E.; Parisi, P.; Scuderi, N. Iginio Tansini revisited. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 2477–2481. [Google Scholar]
- Baudet, J.; Guimberteau, J.C.; Nascimento, E. Successful clinical transfer of two free thoraco-dorsal axillary flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1976, 58, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, M.; Decorte, T.; Demuynck, M.; Defrene, B.; Fredrickx, A.; Maele, G.V.; De Pypere, H.; Landuyt, K.V.; Blondeel, P.; Vanderstraeten, G.; et al. Shoulder function after harvesting a thoracodorsal artery perforator flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beris, A.E.; Soucacos, P.N.; Xenakis, T.A.; Zaravelas, S.; Mitsionis, G.; Dailiana, Z. Latissimus dorsi free tissue transfer for coverage of extensive soft tissue defects. Acta Orthop. Scand. Suppl. 1995, 264, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, O.; Ozgentas, H.E.; Dikici, M.B. Flow-through, functioning, free musculocutaneous flap transfer for restoration of a mangled extremity. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2005, 21, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.P., Jr.; Lipschitz, A.H.; Ansari, M.; Kenkel, J.M.; Rohrich, R.J. Functional donor site morbidity following latissimus dorsi muscle flap transfer. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2004, 53, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravvanis, A.; Deliconstantinou, I.; Tsoutsos, D. Reconstruction of the weight-bearing surface of the foot with integra-grafted latissimus dorsi muscle flap. Microsurgery 2011, 31, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.W., Jr.; Halls, M.J.; Simon, S.R. Free microvascular muscle flaps with skin graft reconstruction of extensive defects of the foot: A clinical and gait analysis study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1985, 75, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, B.; Laporta, R.; Pagnoni, M.; Campanale, A.; Grippaudo, F.R.; Santanelli Di Pompeo, F. Skin grafted latissimus dorsi flap for reconstruction of lateral aesthetic units of the face. Microsurgery 2015, 35, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.C.; Pribaz, J.; Zook, E.G.; Leighton, W.D.; Eriksson, E.; Smith, C.J. Functional evaluation of latissimus dorsi donor site. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 78, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.T.; Mun, G.H. A systematic review of functional donor-site morbidity after latissimus dorsi muscle transfer. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.G.; Chen, G.Z.; Song, Y.L. The free thigh flap: A new free flap concept based on the septocutaneous artery. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1984, 37, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Wu, P.; Yu, F.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, J. Use of a sequential chimeric perforator flap for one-stage reconstruction of complex soft tissue defects of the extremities. Microsurgery 2020, 40, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qing, L.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, F.; Cao, Z.; Tang, J. Individualized design of double skin paddle anterolateral thigh perforator flaps to repair complex soft tissue defects of the extremities: An anatomical study and retrospective cohort study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2021, 74, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qing, L.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, F.; Tang, J. Large wounds reconstruction of the lower extremity with combined latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap and flow-through anterolateral thigh perforator flap transfer. Microsurgery 2021, 41, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Qing, L.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J. Customized reconstruction of complex soft tissue defects in the upper extremities with variants of double skin paddle anterolateral thigh perforator flap. Injury 2021, 52, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, L.; Li, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, F.; Tang, J. Customized reconstruction of complex soft-tissue defect in the hand and forearm with individual design of chain-linked bilateral anterolateral thigh perforator flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2019, 72, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirtas, Y.; Kelahmetoglu, O.; Cifci, M.; Tayfur, V.; Demir, A.; Guneren, E. Comparison of free anterolateral thigh flaps and free muscle-musculocutaneous flaps in soft tissue reconstruction of lower extremity. Microsurgery 2010, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | Chain-Linked Bilateral ALT Group (N = 15) | Extended LD Group (N = 19) | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) # | |||
| Age (years) | 40.9 ± 12.0 | 42.5 ± 13.3 | 0.728 |
| Sex | 0.355 | ||
| Male | 14 | 15 | |
| Female | 1 | 4 | |
| Age ≥ 60 | 1 | 2 | 1.000 |
| Smokers | 7 | 6 | 0.484 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 2 | 8 | 0.128 |
| Atherosclerosis detected & | 3 | 6 | 0.697 |
| Wound size (cm2) # | 406.4 ± 91.9 | 359.4 ± 108.9 | 0.191 |
| Etiology | 1.000 | ||
| Traumatic | 14 | 16 | |
| Others * | 1 | 3 | |
| Follow-up, mo # | 18.8 ± 11.2 | 14.9 ± 6.0 | 0.207 |
| Variable | Chain-Linked Bilateral ALT Group (N = 15) | Extended LD Group (N = 19) | p Value # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flap size (cm2) | 440.3 ± 96.2 | 391.8 ± 113.8 | 0.196 |
| Flap elevation time, min | 152.7 ± 41.4 | 58.9 ± 24.8 | p < 0.001 |
| Vascular anastomosis time, min | 53.7 ± 8.1 | 27.2 ± 10.4 | p < 0.001 |
| Operation time, min | 429.6 ± 51.9 | 271.8 ± 59.5 | p < 0.001 |
| Recipients vessels † | 0.728 | ||
| Anterior tibial system | 10 | 11 | |
| Posterior tibial system | 5 | 8 |
| Variable | Chain-Linked Bilateral ALT Group (N = 15) | Extended LD Group (N = 19) | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flap success rate | 93.3% | 100% | 0.441 |
| Flap-related complications | 0.370 | ||
| Total flap necrosis | 1 | 0 | |
| Partial flap necrosis | 3 | 2 | |
| Factors of causing flap necrosis | |||
| Artery insufficiency | 2 | 0 | 0.187 |
| Venous congestion | 0 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Infection | 1 | 1 | 1.000 |
| Hematomas | 1 | 0 | 0.441 |
| Variable | Chain-Linked Bilateral ALT Group (N = 15) | Extended LD Group (N = 19) | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor site scar hyperplasia # | 4 | 10 | 0.171 |
| Cosmetic evaluation | |||
| Subjectively a | 0.288 c | ||
| Excellent | 3 | 2 | |
| Satisfactory | 4 | 3 | |
| Fair | 6 | 8 | |
| Unsatisfactory | 2 | 6 | |
| Objectively b | 0.165 c | ||
| Excellent | 4 | 2 | |
| Satisfactory | 5 | 4 | |
| Fair | 5 | 8 | |
| Unsatisfactory | 1 | 5 | |
| Lower extremity functional evaluation | 0.613 c | ||
| Excellent | 8 | 7 | |
| Satisfactory | 6 | 9 | |
| Fair | 1 | 3 | |
| Poor | 0 | 0 |
| Variable | Chain-Linked Bilateral ALT Group (N = 15) | Extended LD Group (N = 19) | p Value † |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporary muscular weakness | 3 | 13 | 0.007 |
| Permanent muscular weakness | 0 | 3 | 0.238 |
| Limitations of joint movement | 0 | 2 | 0.492 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Guliyeva, G.; Wu, P.; Qing, L.; Yu, F.; Tang, J. Reconstruction of Large Soft Tissue Defects in the Distal Lower Extremity: Free Chain-Linked Bilateral Anterolateral Thigh Perforator Flaps versus Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flaps. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091400
He J, Guliyeva G, Wu P, Qing L, Yu F, Tang J. Reconstruction of Large Soft Tissue Defects in the Distal Lower Extremity: Free Chain-Linked Bilateral Anterolateral Thigh Perforator Flaps versus Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flaps. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091400
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jiqiang, Gunel Guliyeva, Panfeng Wu, Liming Qing, Fang Yu, and Juyu Tang. 2022. "Reconstruction of Large Soft Tissue Defects in the Distal Lower Extremity: Free Chain-Linked Bilateral Anterolateral Thigh Perforator Flaps versus Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flaps" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091400
APA StyleHe, J., Guliyeva, G., Wu, P., Qing, L., Yu, F., & Tang, J. (2022). Reconstruction of Large Soft Tissue Defects in the Distal Lower Extremity: Free Chain-Linked Bilateral Anterolateral Thigh Perforator Flaps versus Extended Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flaps. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091400








