The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Laboratory Assays
2.3. Clinical Assessment of SSc Patients
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. B-Cell Subset Distribution at t1 and Serum Anti-Spike IgG Levels in SSc Patients and HCs
3.2. B-Cell Subset Distribution 3 Months after Vaccination in SSc Patients
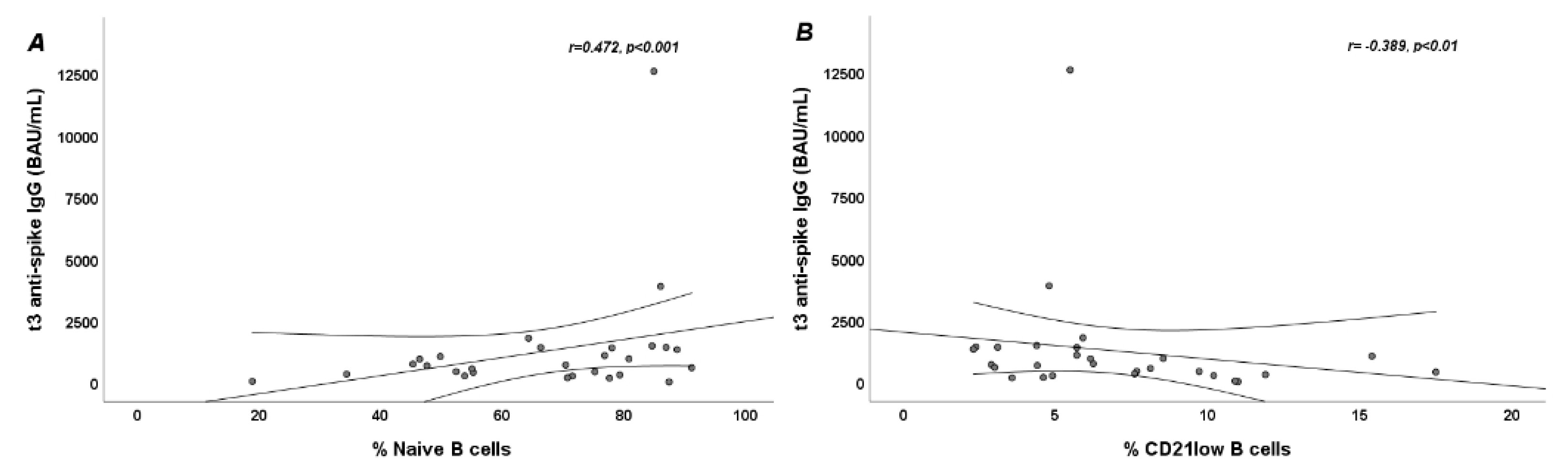
3.3. Anti-Spike IgG Serum Levels 3 Months after Vaccination and Their Correlation with B-Cell Subpopulations at Baseline
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Paz, Z.; Israeli, E.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vaccines and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondaan, C.; Furer, V.; Heijstek, M.W.; Agmon-Levin, N.; Bijl, M.; Breedveld, F.C.; D’Amelio, R.; Dougados, M.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; Van Laar, J.M. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases: A systematic literature review for the 2019 update of EULAR recommendations. RMD Open 2019, 5, e001035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Draft Landscape of COVID19 Candidate Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines (accessed on 5 March 2022).
- Lederer, K.; Castaño, D.; Atria, D.G.; Oguin, T.H., 3rd; Wang, S.; Manzoni, T.B.; Muramatsu, H.; Hogan, M.J.; Amanat, F.; Cherubin, P. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines Foster Potent Antigen-Specific Germinal Center Responses Associated with Neutralizing Antibody Generation. Immunity 2020, 53, 1281–1295.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velikova, T.; Georgiev, T. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and autoimmune diseases amidst the COVID-19 crisis. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 41, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furer, V.; Eviatar, T.; Zisman, D.; Peleg, H.; Paran, D.; Levartovsky, D.; Zisapel, M.; Elalouf, O.; Kaufman, I.; Meidan, R.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases and in the general population: A multicentre study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Kaplan, M.; Braun, M.; Markovits, D.; Giryes, S.; Toledano, K.; Tavor, Y.; Dolnikov, K.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Disease activity and humoral response in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases after two doses of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisen, U.M.; Berner, D.K.; Tran, F.; Sümbül, M.; Vullriede, L.; Ciripoi, M.; Reid, H.M.; Schaffarzyk, A.; Longardt, A.C.; Franzenburg, J. Immunogenicity and safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with chronic inflammatory conditions and immunosuppressive therapy in a monocentric cohort. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, C.; Ursini, F.; Gragnani, L.; Raimondo, V.; Giuggioli, D.; Foti, R.; Caminiti, M.; Olivo, D.; Cuomo, G.; Visentini, M. Impaired immunogenicity to COVID-19 vaccines in autoimmune systemic diseases. High prevalence of non-response in different patients’ subgroups. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 125, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, A. Pathogenic roles of B lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrapodi, R.; Pellicano, C.; Radicchio, G.; Leodori, G.; Colantuono, S.; Iacolare, A.; Gigante, A.; Visentini, M.; Rosato, E. CD21low B cells in systemic sclerosis: A possible marker of vascular complications. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 213, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentini, M.; Pellicano, C.; Leodori, G.; Marrapodi, R.; Colantuono, S.; Gigante, A.; Casato, M.; Rosato, E. CD21low B cells are predictive markers of new digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: An American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.R.; Johnson, S.R.; Anthony, D.D.; Arasaratnam, R.J.; Baden, L.R.; Bass, A.R.; Calabrese, C.; Gravallese, E.M.; Harpaz, R.; Kroger, A. American College of Rheumatology Guidance for COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases: Version 1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Bruni, C.; Allanore, Y.; Clementi, M.; Dagna, L.; Damjanov, N.S.; De Paulis, A.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Fox, D.; et al. Systemic sclerosis and the COVID-19 pandemic: World Scleroderma Foundation preliminary advice for patient management. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, G.; Iudici, M.; Walker, U.A.; Jaeger, V.K.; Baron, M.; Carreira, P.; Czirják, L.; Denton, C.P.; Distler, O.; Hachulla, E. The European Scleroderma Trials and Research group (EUSTAR) task force for the development of revised activity criteria for systemic sclerosis: Derivation and validation of a preliminarily revised EUSTAR activity index. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Sulli, A.; Secchi, M.E.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C. Nailfold capillaroscopy is useful for the diagnosis and follow-up of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. A future tool for the analysis of microvascular heart involvement? Rheumatology 2006, 45 (Suppl. S4), iv43–iv46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio-Barros, P.D.; Medeiros-Ribeiro, A.C.; Luppino-Assad, A.P.; Miossi, R.; da Silva, H.C.; Yuki, E.F.V.N.; Pasoto, S.G.; Saad, C.G.S.; A Silva, C.; Kupa, L.V.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with systemic sclerosis: Impact of disease subtype and therapy. Rheumatology 2021, 61, SI169–SI174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.; Tascilar, K.; Fagni, F.; Krönke, G.; Kleyer, A.; Meder, C.; Atreya, R.; Leppkes, M.; Kremer, A.E.; Ramming, A. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination responses in untreated, conventionally treated and anticytokine-treated patients with immunomediated inflammatory diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, C.; Campagna, R.; Oliva, A.; Leodori, G.; Miglionico, M.; Colalillo, A.; Mezzaroma, I.; Mastroianni, C.M.; Turriziani, O.; Rosato, E. Antibody response to BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in adult patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Núñez, J.J.; García-Chagollán, M.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Díaz-Pérez, S.A.; Torres-Hernández, P.C.; Rodríguez-Reyes, S.C.; Santoscoy-Ascencio, G.; de Quevedo, J.J.S.G.; Hernández-Bello, J. Differences in B-Cell Immunophenotypes and Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 After Administration of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccine in Individuals with and without Prior COVID-19—A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 4449–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, A.; Guerrier, T.; Jouvray, M.; Giovannelli, J.; Lefèvre, G.; Sobanski, V.; Hauspie, C.; Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.-Y.; Zéphir, H.; et al. Altered B lymphocyte homeostasis and functions in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Hodl, I.; Forstner, P.; Hatzl, S.; Sareban, N.; Moritz, M.; Fessler, J.; Dreo, B.; Uhl, B.; Url, C. CD19+ IgD+ CD27− Naïve B Cells as Predictors of Humoral Response to COVID 19 mRNA Vaccination in Immunocompromised Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 803742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentini, M.; Cagliuso, M.; Conti, V.; Carbonari, M.; Cibati, M.; Siciliano, G.; Cristofoletti, C.; Russo, G.; Casato, M.; Fiorilli, M. Clonal B cells of HCV—Associated mixed cryoglobulinemia patients contain exhausted marginal zone-like and CD21 low cells overexpressing Stra13. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancro, M.P. Age-Associated B Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reincke, M.E.; Payne, K.J.; Harder, I.; Strohmeier, V.; Voll, R.E.; Warnatz, K.; Keller, B. The Antige Presenting Potential of CD21 low B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 535784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, P.; Wullimann, D.; Gao, Y.; Wahren Borgström, E.; Norlin, A.-C.; Lind Enoksson, S.; Aleman, S.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Buggert, M.; Smith, C. Elevated CD21 low B Cell Frequency Is a Marker of Poor Immunity to Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Against SARS-CoV-2 in Patients with Common Variable Immunodeficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 42, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, C.; Callà, C.; Fiorita, A.; Marino, M.; Taddei, E.; Di Cesare, T.; Passali, G.; Di Santo, R.; Stefanile, A.; Fantoni, M.; et al. Salivary Biomarkers in COVID-19 Patients: Towards a Wide-Scale Test for Monitoring Disease Activity. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variables | SSc Patients | HCs | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, median and IQR | 51 (35–62) | 48 (33–60) | >0.05 |
| Female, n (%) | 24 (85.7) | 19 (90.5) | >0.05 |
| dcSSc, n (%) | 13 (46.4) | NA | NA |
| Disease duration, years, median and IQR | 14 (10–21) | NA | NA |
| mRSS, median and IQR | 13 (9–21) | NA | NA |
| SSc-specific autoantibodies | |||
| Anti-topoisomerase I, n (%) | 13 (46.4) | NA | NA |
| Anti-centromere, n (%) | 10 (35.7) | NA | NA |
| Anti-RNApolymerase III, n (%) | 1 (3.6) | NA | NA |
| None, n (%) | 4 (14.3) | NA | NA |
| Nailfold capillaroscopic pattern | |||
| Early, n (%) | 4 (14.3) | NA | NA |
| Active, n (%) | 5 (17.9) | NA | NA |
| Late, n (%) | 19 (67.9) | NA | NA |
| DAI, median and IQR | 1.38 (0.88–3.84) | NA | NA |
| DSS, median and IQR | 4 (3–6) | NA | NA |
| DUs’ history, n (%) | 14 (50) | NA | NA |
| Active DUs, n (%) | 3 (10.7) | NA | NA |
| ILD, n (%) | 22 (78.6) | NA | NA |
| PAH, n (%) | 2 (7.1) | NA | NA |
| Variables | SSc Patients | HCs | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-spike IgG levels, BAU/mL, median and IQR | 635 (285–1135) | 358 (177–1021) | >0.05 |
| B cells, %, median and IQR | 7.53 (5.87–11.5) | 7.6 (6.86–10.2) | >0.05 |
| Naive B cells, %, median and IQR | 70.55 (47.15–80.2) | 55.4 (44.5–62.7) | <0.05 |
| IgM-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 8.57 (4.62–19.15) | 21.3 (15.8–29.8) | <0.001 |
| Switched-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 14.15 (8.5–20.2) | 19.5 (16.1–21.9) | <0.05 |
| Double-negative B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.16 (3.78–7.76) | 3.96 (3.03–5.1) | <0.05 |
| CD21low B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.59 (3.84–9.13) | 3.65 (3.11–4.69) | <0.05 |
| Increased naive B cells, n (%) | 8 (28.6) | 0 (0) | <0.01 |
| Increased IgM-memory B cells, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NA |
| Increased switched-memory B cells, n (%) | 1 (3.6) | 2 (9.5) | >0.05 |
| Increased double-negative B cells, n (%) | 10 (35.7) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Increased CD21low B cells, n (%) | 6 (21.4) | 0 (0) | <0.01 |
| Variables | t1 | t3 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| B cells, %, median and IQR | 7.53 (5.87–11.5) | 8.1 (5.75–12.5) | >0.05 |
| Naive B cells, %, median and IQR | 70.55 (47.15–80.2) | 60.2 (41.95–77.25) | <0.05 |
| IgM-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 8.57 (4.62–19.15) | 11.45 (4.9–22.75) | <0.001 |
| Switched-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 14.15 (8.5–20.2) | 18.25 (9.85–25.85) | <0.05 |
| Double-negative B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.16 (3.78–7.76) | 5.2 (4.1–7.6) | >0.05 |
| CD21low B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.59 (3.84–9.13) | 9.75 (6.77–15.9) | <0.05 |
| Anti-Topoisomerase I and Anti-RNA Polymerase III (n = 14) | Anti-Centromere and ANA (n = 14) | p | ILD (n = 22) | No ILD (n = 6) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-spike IgG levels, BAU/mL, median and IQR | 575 (266–946) | 1003 (335–1400) | >0.05 | 575 (266–1050) | 1245 (706–1420) | >0.05 | |
| t1 | Naive B cells, %, median and IQR | 68.35 (52.4–75.2) | 77.8 (55.2–84.6) | >0.05 | 71.1 (52.4–84.6) | 73.6 (64.3–78) | >0.05 |
| IgM-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 11.85 (4.44–18.9) | 6.61 (4.28–14.7) | >0.05 | 8.29 (4.35–18.9) | 9.64 (6.44–14.7) | >0.05 | |
| Switched-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 15.4 (9.07–18.7) | 12.25 (7.46–17.5) | >0.05 | 13.25 (7.46–18.7) | 12.45 (8.78–14.3) | >0.05 | |
| Double-negative B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.72 (3.67–8.51) | 4.96 (3.88–6.43) | >0.05 | 5.16 (3.06–7.98) | 4.72 (4.25–6.43) | >0.05 | |
| CD21low B cells, %, median and IQR | 5.19 (4.4–8.12) | 6.07 (4.38–11) | >0.05 | 6.2 (4.4–10.2) | 5.7 (2.89–5.9) | >0.05 | |
| t3 | Naive B cells, %, median and IQR | 55.35 (44.8–77) | 64.35 (41.2–77.5) | >0.05 | 66.95 (44.8–77.5) | 44.6 (33–61.5) | >0.05 |
| IgM-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 14.15 (4.7–26.6) | 10.8 (5.1–19.4) | >0.05 | 11.3 (4.6–20.6) | 16.9 (10.4–29) | >0.05 | |
| Switched-memory B cells, %, median and IQR | 18.45 (9.7–25.8) | 17.7 (11.4–32) | >0.05 | 17 (9.7–25.8) | 27.65 (18.4–32.8) | >0.05 | |
| Double-negative B cells, %, median and IQR | 4.3 (3.2–8.7) | 5.85 (5–6.8) | >0.05 | 5 (4–6.8) | 6.4 (5.3–9.7) | >0.05 | |
| CD21low B cells, %, median and IQR | 9.65 (6.35–13.8) | 10.95 (7.18–16) | >0.05 | 9.65 (6.35–16) | 10.55 (8–13.7) | >0.05 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellicano, C.; Colalillo, A.; Basile, V.; Marino, M.; Basile, U.; La Gualana, F.; Mezzaroma, I.; Visentini, M.; Rosato, E. The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091420
Pellicano C, Colalillo A, Basile V, Marino M, Basile U, La Gualana F, Mezzaroma I, Visentini M, Rosato E. The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091420
Chicago/Turabian StylePellicano, Chiara, Amalia Colalillo, Valerio Basile, Mariapaola Marino, Umberto Basile, Francesca La Gualana, Ivano Mezzaroma, Marcella Visentini, and Edoardo Rosato. 2022. "The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091420
APA StylePellicano, C., Colalillo, A., Basile, V., Marino, M., Basile, U., La Gualana, F., Mezzaroma, I., Visentini, M., & Rosato, E. (2022). The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091420










