Resveratrol Inhibits Activation of Microglia after Stroke through Triggering Translocation of Smo to Primary Cilia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of N9 Microglia
2.2. Experimental Animals
2.3. MCAO/R Model
2.4. OGD/R Model
2.5. Drugs Treatment
2.6. Analysis of Neurologic Deficit Scores
2.7. Determination of Cerebral Infarct Volume
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
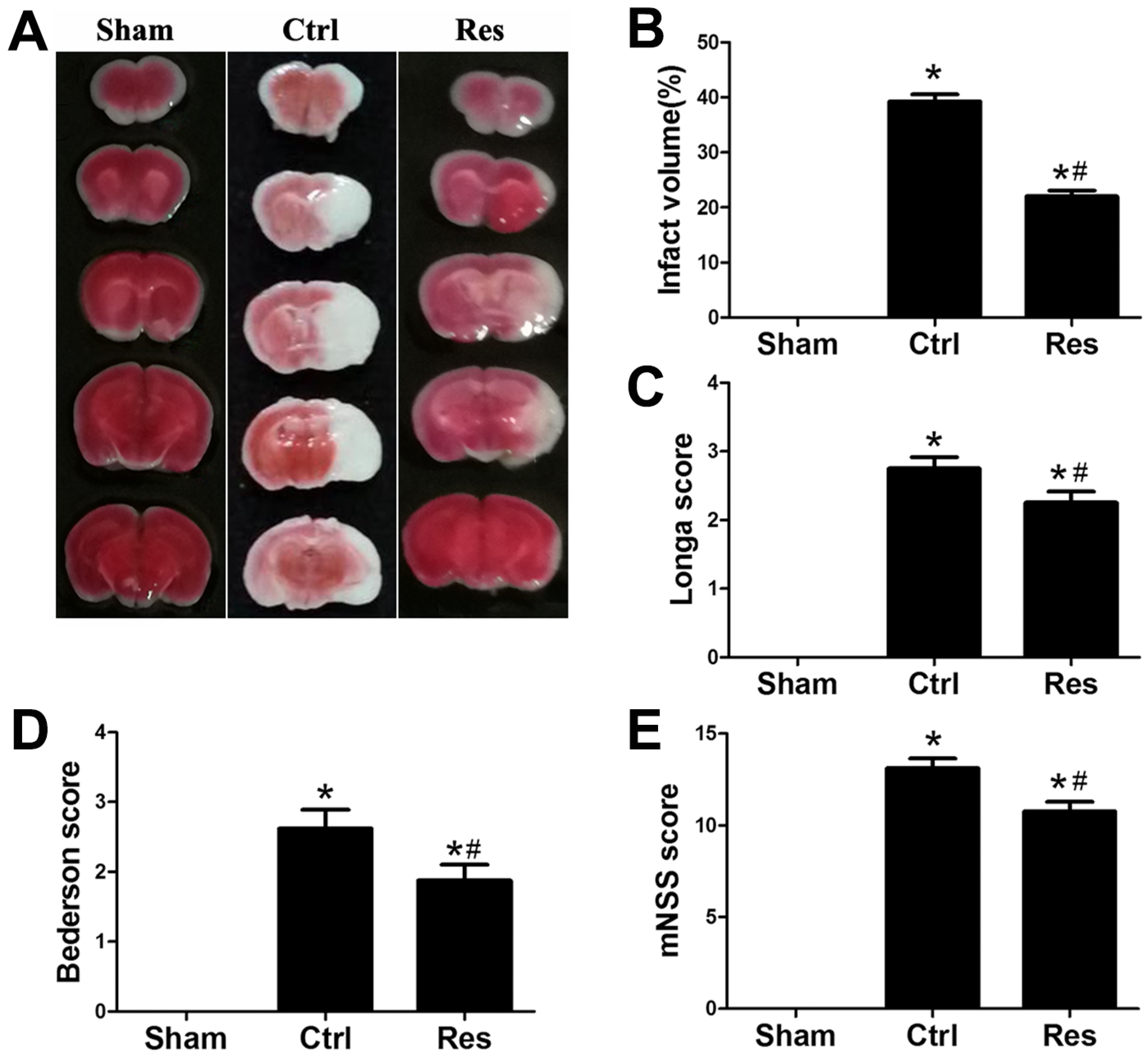
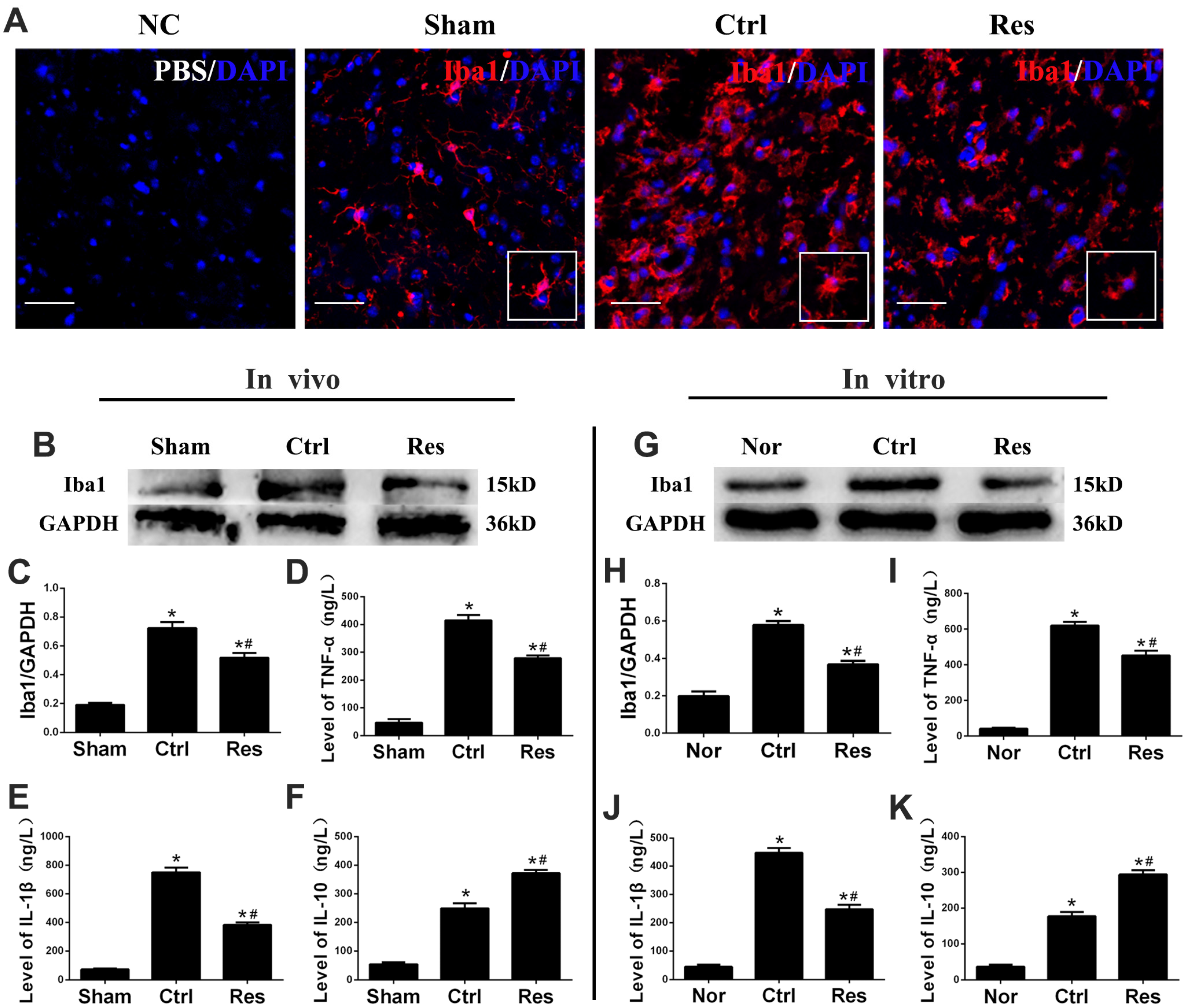
3.1. Resveratrol Decreased Infarct Volume, Improved Neurological Function, and Inhibited Activation of Microglia and Inflammation after Stroke
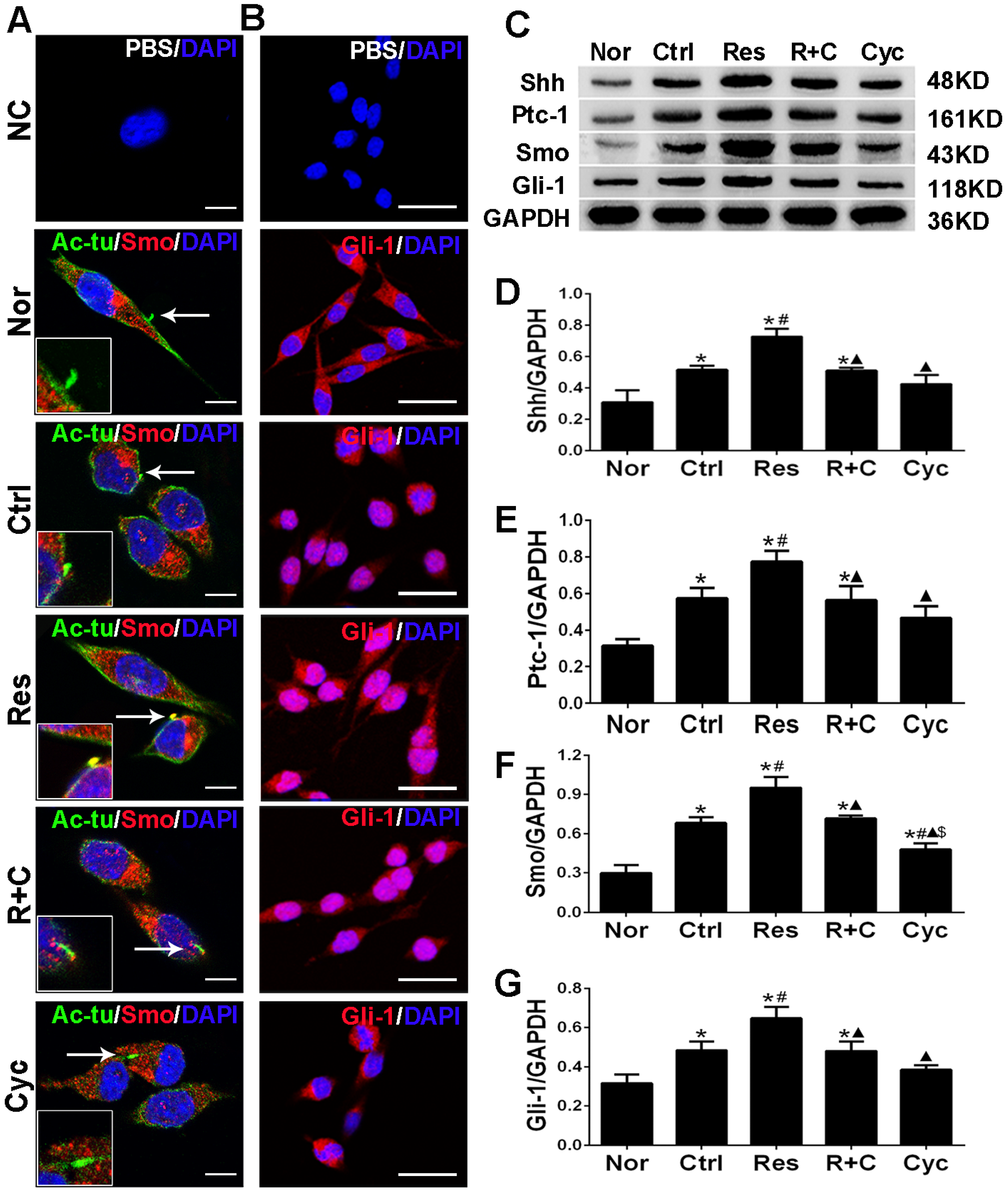
3.2. Resveratrol Triggered the Translocation of Smo/Gli-1 Molecules and Upregulated the Expression of Shh, Ptc-1, Smo, and Gli-1 after OGD/R Injury of N9 Microglia In Vitro
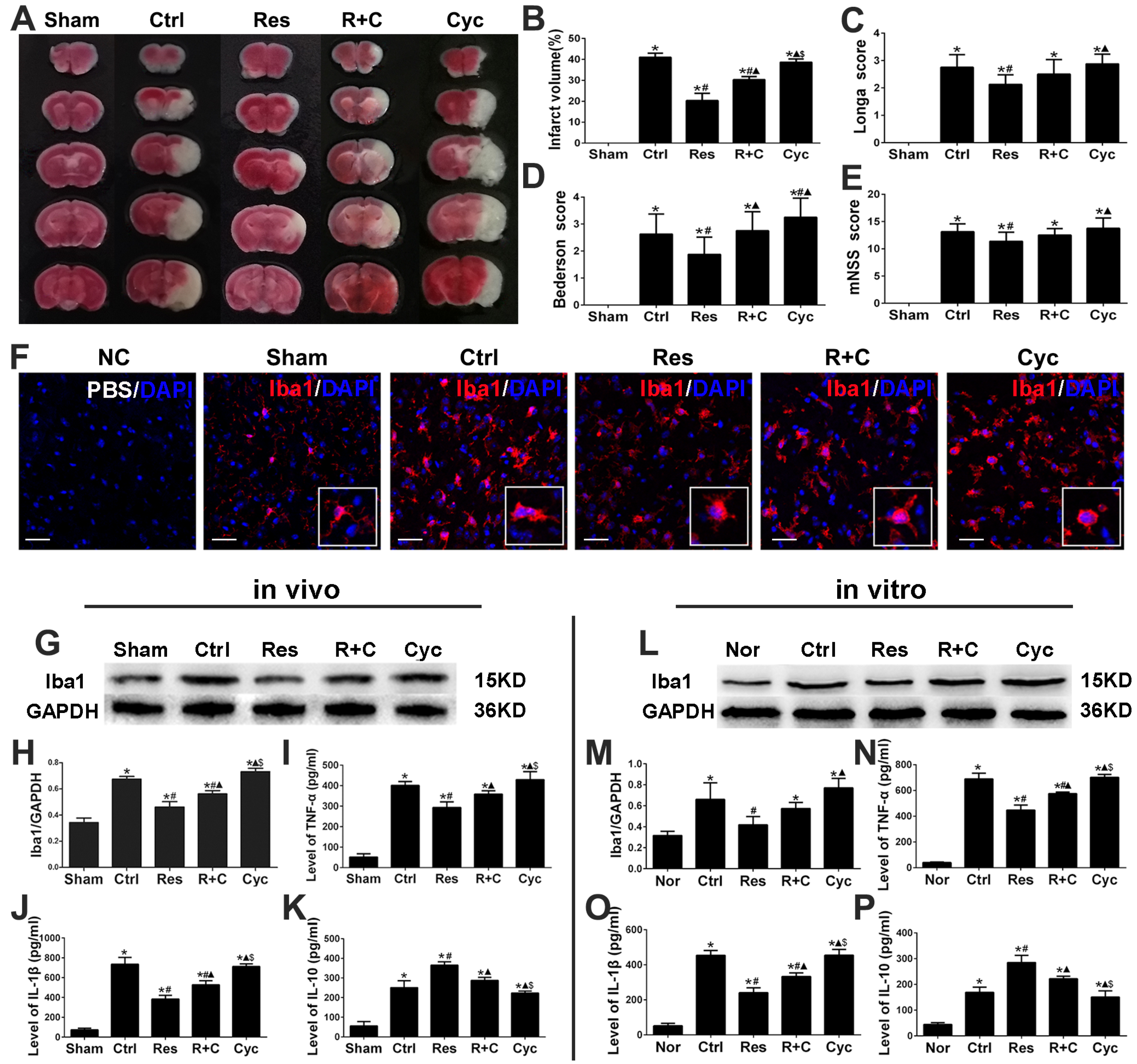
3.3. Cyclopamine Increased Infarct Volume, Deteriorated Neurological Function, and Promoted Activation of Microglia and Inflammation after Stroke
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Cho, S. Microglia and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.-Y. The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 157, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Xiao, D.; Muhammed, A.; Deng, J.; Chen, L.; He, J. Anti-Inflammatory Action and Mechanisms of Resveratrol. Molecules 2021, 26, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Javed, S.; Javed, S.; Tariq, A.; Šamec, D.; Tejada, S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Resveratrol and Alzheimer’s Disease: Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 2622–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Agrawal, M.; Doré, S. Neuroprotective Properties and Mechanisms of Resveratrol in in Vitro and in Vivo Experimental Cerebral Stroke Models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, J.-H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.-Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The Role of Resveratrol in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Shen, C.; Song, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, F.; Yang, Q. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Mediates Resveratrol to Increase Proliferation of Neural Stem Cells after Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Injury in Vitro. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 2019–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Guo, S.; Liao, H.; Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol Enhances Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptogenesis Via Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Following Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Tang, F.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, L.; Song, X.; Jia, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol Pretreatment Decreases Ischemic Injury and Improves Neurological Function Via Sonic Hedgehog Signaling After Stroke in Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Fan, C.; Chen, N.; Huang, J.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by upregulating ex-pression of transcription factor Nrf2 and HO-1 in rats. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jiang, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, G.; Liu, W.; Jamangulova, N.; Wu, X.; Song, X. Resveratrol reduces morphine tol-erance by inhibiting microglial activation via AMPK signalling. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 1458–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Hu, L.; Xia, Y.-P.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Miao, C.; Yang, C.-Q.; Yuan, M.; Wang, L. Resveratrol suppresses glial activation and alleviates trigeminal neuralgia via activation of AMPK. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Lu, T.; Xie, C.; Jia, J. Resveratrol Attenuates Microglial Activation via SIRT1-SOCS1 Pathway. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 8791832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Lv, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Hang, C. Resveratrol Attenuates Early Brain Injury after Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.S.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; Wu, L.Y.; Ye, Z.N.; Liu, J.P.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, M.L.; Zhang, X.; Hang, C.H. Resveratrol Attenuates Acute In-flammatory Injury in Experimental Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats via Inhibition of TLR4 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, B.; Shi, C.; Meng, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, J. Resveratrol alleviates ethanol-induced neuroinflammation in vivo and in vitro: Involvement of TLR2-MyD88-NF-kappaB pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 103, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Inhibitive Effect of Resveratrol on the Inflammation in Cultured Astrocytes and Microglia Induced by Abeta1-42. Neuroscience 2018, 379, 390–404. [Google Scholar]
- Arensdorf, A.M.; Dillard, M.E.; Menke, J.M.; Frank, M.W.; Rock, C.O.; Ogden, S.K. Sonic Hedgehog Activates Phospholipase A2 to Enhance Smoothened Ciliary Translocation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2074–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, J.A.; Kobayashi, M.; Krishnan, A.; Webber, C.; Christie, K.; Guo, G.; Singh, V.; Zochodne, D.W. Intrinsic facilitation of adult peripheral nerve regeneration by the Sonic hedgehog morphogen. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 271, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.S.; Tomar, S.; Sharma, D.; Mahindroo, N.; Udayabanu, M. Targeting sonic hedgehog signaling in neurological disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 76–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briscoe, J.; Thérond, P.P. The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, P.W.; Nakano, Y.; Seger, C. Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.G.; Shen, C.B.; Wu, W.B.; Ren, J.W.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, Q. Primary cilia mediate sonic hedgehog signaling to regulate neu-ronal-like differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells for resveratrol induction in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-S.; Cheng, H.; Tang, C.-M.; Nien, M.-W.; Huang, Y.-S.; Lee, I.-H.; Yin, J.-H.; Kuo, T.B.; Yang, C.C.; Tsai, S.-K.; et al. Anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic, and pro-angiogenic effects mediate functional improvement by sonic hedgehog against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 247, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.C.; Hsiao, Y.H.; Gean, P.W. Learning induces sonic hedgehog signaling in the amygdala which promotes neurogenesis and long-term memory formation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18, pyu071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, M.A.; Armstrong, R.C. Postnatal Sonic hedgehog (Shh) responsive cells give rise to oligodendrocyte lineage cells during myelination and in adulthood contribute to remyelination. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 299, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.J.; Petralia, R.S.; Ott, C.; Wang, Y.X.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Mattson, M.P. Dendrosomatic Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Hip-pocampal Neurons Regulates Axon Elongation. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 16126–16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Lu, M.; Borneman, J.; Buller, B.; Savant-Bhonsale, S.; Elias, S.B.; Chopp, M. Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Increase Oligodendrogenesis after Stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Jin, J.-X.; Taweechaipaisankul, A.; Kim, G.A.; Ahn, C.; Lee, B.C. Sonic hedgehog signaling mediates resveratrol to improve maturation of pig oocytes in vitro and subsequent preimplantation embryo development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 233, 5023–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Kriz, J.; Seidah, N.G. Mouse model of intraluminal MCAO. Cerebral infarct evaluation by cresyl violet staining. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 69, 4038. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Cheng, W.; Yu, P.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates injury and promotes prolif-eration of neural stem cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation by upregulating the expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and NQO1 in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3646–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bederson, J.B.; Pitts, L.H.; Tsuji, M.; Nishimura, M.C.; Davis, R.L.; Bartkowski, H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986, 17, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, D.; Lu, M.; Chopp, M. Therapeutic Benefit of Intravenous Administration of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells After Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Stroke 2001, 32, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaito, A.; Posadino, A.M.; Younes, N.; Hasan, H.; Halabi, S.; Alhababi, D.; Al-Mohannadi, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Eid, A.H.; Nasrallah, G.K.; et al. Potential Adverse Effects of Resveratrol: A Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Meng, N.; Yao, N.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Q.; Han, K.; Song, J.; et al. Resveratrol Exerts Dos-age-Dependent Effects on the Self-Renewal and Neural Differentiation of hUC-MSCs. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhu, F.; Han, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, K. The Cytotoxicity Effect of Resveratrol: Cell Cycle Arrest and Induced Apoptosis of Breast Cancer 4T1 Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamim, U.; Hanif, S.; Albanyan, A.; Beck, F.W.; Bao, B.; Wang, Z.; Banerjee, S.; Sarkar, F.H.; Mohammad, R.M.; Hadi, S.M.; et al. Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is enhanced in low pH environments associated with cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 227, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuda, M.; Ogasawara, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Inoue, K.; Sakashita, H. Resveratrol Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Autophagy by Blocking SREBP1 Expression in Oral Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Zhang, M.; Guan, E.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Long, X.; Long, F.; Zhao, R.C.-H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of keloid fibroblasts by targeting HIF-1α. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2020, 54, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintus, G.; Shaito, A.; Al-Mansoob, M.; Ahmad, S.M.; Haider, M.Z.; Eid, A.H.; Posadino, A.M.; Giordo, R. Resveratrol-mediated regulation of mitochondria biogenesis-associated pathways in neurodegenerative diseases: Molecular insights and potential therapeutic applications. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Yan, Y.; He, X.-Y.; Yang, H.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yu, H. Effects of Resveratrol on the Mechanisms of Antioxidants and Estrogen in Alzheimer’s Disease. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8983752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, R.C.; Franco, F.N.; de Araújo, G.R.; Silva, B.N.M.; Chaves, M.M. The preventive use of resveratrol increases its antioxidant effect by SIRT1 and subclinical anti-inflammatory action in Neuro-2A cells. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2022, 58, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Song, Y.; Yu, X.; Deng, B.; Zhou, X. Resveratrol inhibits neural apoptosis and regulates RAX/P-PKR expression in retina of diabetic rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 25, 2560–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, K.; Wan, W.; Cheng, Y.; Pu, X.; Ye, X. Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by regulating the JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway after stroke in rats. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, R.; Alomari, N.; Nauli, S.M. Primary Cilium-Dependent Signaling Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breunig, J.J.; Sarkisian, M.R.; Arellano, J.I.; Morozov, Y.M.; Ayoub, A.E.; Sojitra, S.; Wang, B.; Flavell, R.A.; Rakic, P.; Town, T. Primary cilia regulate hippocampal neurogenesis by mediating sonic hedgehog signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13127–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.-G.; Spassky, N.; Romaguera-Ros, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.-M.; Aguilar, A.; Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luesma, M.J.; Cantarero, I.; Castiella, T.; Soriano, M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Junquera, C. Enteric neurons show a primary cilium. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 17, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, É.; Komoly, S.; Ács, P. Quantitative Comparison of Primary Cilia Marker Expression and Length in the Mouse Brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raleigh, D.R.; Sever, N.; Choksi, P.K.; Sigg, M.A.; Hines, K.M.; Thompson, B.M.; Elnatan, D.; Jaishankar, P.; Bisignano, P.; Garcia-Gonzalo, F.R.; et al. Cilia-Associated Oxysterols Activate Smoothened. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 316–327.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, I.; Liang, J.; Hedeen, D.; Roberts, K.J.; Zhang, Y.; Ha, B.; Latorraca, N.R.; Faust, B.; Dror, R.O.; Beachy, P.A.; et al. Smoothened stimulation by membrane sterols drives Hedgehog pathway activity. Nature 2019, 571, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, F.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol Activated Sonic Hedgehog Signaling to Enhance Viability of NIH3T3 Cells in Vitro via Regulation of Sirt1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Xiang, Q.; Yang, Q. Resveratrol Inhibits Activation of Microglia after Stroke through Triggering Translocation of Smo to Primary Cilia. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020268
Liao H, Huang J, Liu J, Chen Y, Zhu H, Li X, Wen J, Xiang Q, Yang Q. Resveratrol Inhibits Activation of Microglia after Stroke through Triggering Translocation of Smo to Primary Cilia. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(2):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020268
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Hongyan, Jiagui Huang, Jie Liu, Yue Chen, Huimin Zhu, Xuemei Li, Jun Wen, Qin Xiang, and Qin Yang. 2023. "Resveratrol Inhibits Activation of Microglia after Stroke through Triggering Translocation of Smo to Primary Cilia" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 2: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020268
APA StyleLiao, H., Huang, J., Liu, J., Chen, Y., Zhu, H., Li, X., Wen, J., Xiang, Q., & Yang, Q. (2023). Resveratrol Inhibits Activation of Microglia after Stroke through Triggering Translocation of Smo to Primary Cilia. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(2), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020268









