REAC Antalgic Neuro Modulation in Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Power Analysis
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Population
2.4. Pain Assessments before Treatment
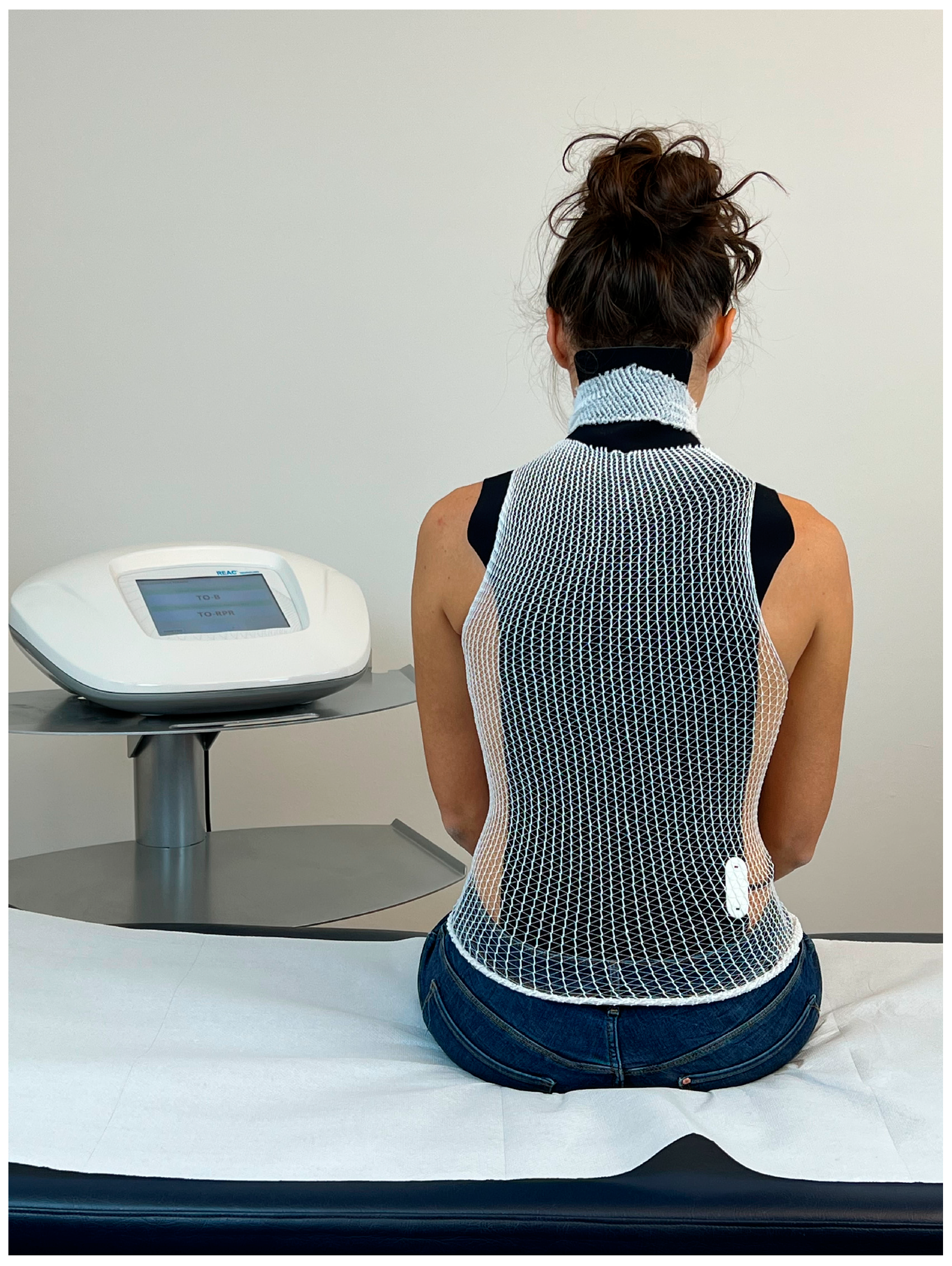
2.5. REAC Technology
2.6. Treatments
2.7. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. NAS Results
3.2. SDS Results
3.3. Results of Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grose, C.; Carpenter, J.E. Varicella zoster virus. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, N.H.; Gilden, D.H.; Cohrs, R.J.; Mahalingam, R.; Nagel, M.A. Varicella zoster virus infection: Clinical features, molecular pathogenesis of disease, and latency. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 675–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.I. Herpesvirus latency. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3361–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFeely, A.; Doyle, R.; O’Riordan, S.; Connolly, S.; O’Dwyer, C. Severe brachial plexopathy secondary to shingles (herpes zoster). Age Ageing 2021, 50, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monib, S.; Pakdemirli, E. Shingles (herpes zoster) mimicking acute abdomen. Cureus 2020, 12, e10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, D.J.; Curtis, M.P.; Kratzer, A. Shingles. Home Healthc. Now 2020, 38, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.R.; Canaday, D.H. Herpes zoster in the older adult. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 31, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; Rice, A.S. Clinical practice. Postherpetic neuralgia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.H. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: Practical consideration for prevention and treatment. Korean J. Pain 2015, 28, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalamachu, S.; Morley-Forster, P. Diagnosing and managing postherpetic neuralgia. Drugs Aging 2012, 29, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic pain: From mechanisms to treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zippo, A.G.; Rinaldi, S.; Pellegata, G.; Caramenti, G.C.; Valente, M.; Fontani, V.; Biella, G.E. Electrophysiological effects of non-invasive radio electric asymmetric conveyor (reac) on thalamocortical neural activities and perturbed experimental conditions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boonstra, A.M.; Stewart, R.E.; Koke, A.J.; Oosterwijk, R.F.; Swaan, J.L.; Schreurs, K.M.; Schiphorst Preuper, H.R. Cut-off points for mild, moderate, and severe pain on the numeric rating scale for pain in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain: Variability and influence of sex and catastrophizing. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriwatanakul, K.; Kelvie, W.; Lasagna, L.; Calimlim, J.F.; Weis, O.F.; Mehta, G. Studies with different types of visual analog scales for measurement of pain. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1983, 34, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Ang, H.-G. Comparison of two pain rating scales among chinese cancer patients. Chin. Med. J. 1992, 105, 953–956. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, A.; Parle-McDermott, A. DNA methylation: A timeline of methods and applications. Front. Genet. 2011, 2, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elio, C.; Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S.; Gasbarro, V. Reac-induced endogenous bioelectric currents in the treatment of venous ulcers: A three-arm randomized controlled prospective study. Acta Dermatovenerol. Alp. Pannonica Adriat. 2020, 29, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.; Selberg, J.; Rolandi, M. Endogenous bioelectrics in development, cancer, and regeneration: Drugs and bioelectronic devices as electroceuticals for regenerative medicine. iScience 2019, 22, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levin, M. Molecular bioelectricity: How endogenous voltage potentials control cell behavior and instruct pattern regulation in vivo. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 3835–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Q.; Biswas, A.; Liu, W. Soliton interaction control through dispersion and nonlinear effects for the fifth-order nonlinear schrödinger equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 2479–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznanski, R.R.; Cacha, L.A.; Al-Wesabi, Y.M.S.; Ali, J.; Bahadoran, M.; Yupapin, P.P.; Yunus, J. Solitonic conduction of electrotonic signals in neuronal branchlets with polarized microstructure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, G.; Rani, R.; Emadifar, H. Soliton: A dispersion-less solution with existence and its types. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-F. Neural synergetics, lorenz model of brain, soliton-chaos double solutions and physical neurobiology. NeuroQuantology 2012, 11, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, A.S.; Winlow, W. The soliton and the action potential—Primary elements underlying sentience. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, S.; Fontani, V.; Castagna, A. Brain activity modification produced by a single radioelectric asymmetric brain stimulation pulse: A new tool for neuropsychiatric treatments. Preliminary fmri study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2011, 7, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinaldi, S.; Mura, M.; Castagna, A.; Fontani, V. Long-lasting changes in brain activation induced by a single reac technology pulse in wi-fi bands. Randomized double-blind fmri qualitative study. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, A.; Rinaldi, C.; Araldi, L.; Azzara, A.; Carta, A.M.; Casale, N.; Castagna, A.; Del Medico, M.; Di Stasio, M.; et al. Long-lasting efficacy of radio electric asymmetric conveyer neuromodulation treatment on functional dysmetria, an adaptive motor behavior. Cureus 2022, 14, e25768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontani, V.; Rinaldi, S.; Aravagli, L.; Mannu, P.; Castagna, A.; Margotti, M.L. Noninvasive radioelectric asymmetric brain stimulation in the treatment of stress-related pain and physical problems: Psychometric evaluation in a randomized, single-blind placebo-controlled, naturalistic study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2011, 4, 681–686. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegata, G.; Caracci, S.; Medaglini, S. Radio electric asymmetric conveyer neurobiological treatments in non-specific neck pain: A retrospective study. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.C.D.; Maglioni, C.B.; Machado, G.B.; Araújo, J.E.D.; Silva, J.R.T.D.; Silva, M.L.D. Prevalence and characteristics of chronic pain in brazil: A national internet-based survey study. Braz. J. Pain 2018, 1, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breivik, H.; Collett, B.; Ventafridda, V.; Cohen, R.; Gallacher, D. Survey of chronic pain in europe: Prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur. J. Pain 2006, 10, 287–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Chronic pain: Structural and functional changes in brain structures and associated negative affective states. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B. Chronic pain: Emerging evidence for the involvement of epigenetics. Neuron 2012, 73, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crow, M.; Denk, F.; McMahon, S.B. Genes and epigenetic processes as prospective pain targets. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penas, C.; Navarro, X. Epigenetic modifications associated to neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain after neural trauma. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortuno-Sahagun, D.; Schliebs, R.; Pallas, M. Editorial: Epigenetic mechanisms regulating neural plasticity. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, N.; Yu, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, L.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, D.S.; Xie, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Mecp2 epigenetic silencing of oprm1 gene in primary sensory neurons under neuropathic pain conditions. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 743207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Hao, M.L.; Cheng, X.T.; Hua, Z. Bioinformatics analysis of genes and mechanisms in postherpetic neuralgia. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 1380504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ing, M.R.; Hellreich, P.D.; Johnson, D.W.; Chen, J.J. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for chronic post-herpetic neuralgia. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, G.; Del Re, B. Epigenetic dysregulation in various types of cells exposed to extremely low-frequency magnetic fields. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 386, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, A.; Tai, W.L.; Lennikov, A.; Cho, K.-S.; Utheim, T.; Chen, D. Epigenetic modulation following electrical stimulation in neurons. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 2969-F0210. [Google Scholar]


| NAS Scale | SDS Scale | |
|---|---|---|
| Wilcoxon test | Z = −6.429 Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) = 0.000 | Z = −6.547 Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) = 0.000 |
| Sign test | Z = −7.143 Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) = 0.000 | Z = −7.143 Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) = 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barcessat, A.R.P.; Nunes, L.d.S.; Gonçalves, R.G.; Darienso, D. REAC Antalgic Neuro Modulation in Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040653
Barcessat ARP, Nunes LdS, Gonçalves RG, Darienso D. REAC Antalgic Neuro Modulation in Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(4):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040653
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarcessat, Ana Rita Pinheiro, Lucas dos Santos Nunes, Rebeca Góes Gonçalves, and Danyela Darienso. 2023. "REAC Antalgic Neuro Modulation in Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 4: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040653
APA StyleBarcessat, A. R. P., Nunes, L. d. S., Gonçalves, R. G., & Darienso, D. (2023). REAC Antalgic Neuro Modulation in Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(4), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040653





