Association Study of BDNF, SLC6A4, and FTO Genetic Variants with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
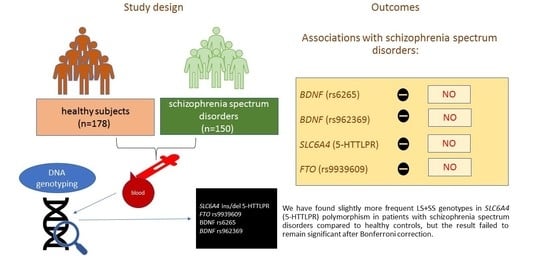
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Schizophrenia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/schizophrenia (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Kendler, K.S.; Gallagher, T.J.; Abelson, J.M.; Kessler, R.C. Lifetime Prevalence, Demographic Risk Factors, and Diagnostic Validity of Nonaffective Psychosis as Assessed in a US Community Sample: The National Comorbidity Survey. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1996, 53, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Birnbaum, H.; Demler, O.; Falloon, I.R.H.; Gagnon, E.; Guyer, M.; Howes, M.J.; Kendler, K.S.; Shi, L.; Walters, E.; et al. The Prevalence and Correlates of Nonaffective Psychosis in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication (NCS-R). Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 58, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vicente, B.; Kohn, R.; Rioseco, P.; Saldivia, S.; Levav, I.; Torres, S. Lifetime and 12-Month Prevalence of DSM-III-R Disorders in the Chile Psychiatric Prevalence Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perälä, J.; Suvisaari, J.; Saarni, S.I.; Kuoppasalmi, K.; Isometsä, E.; Pirkola, S.; Partonen, T.; Tuulio-Henriksson, A.; Hintikka, J.; Kieseppä, T.; et al. Lifetime Prevalence of Psychotic and Bipolar I Disorders in a General Population. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ochoa, S.; Haro, J.M.; Torres, J.V.; Pinto-Meza, A.; Palacín, C.; Bernal, M.; Brugha, T.; Prat, B.; Usall, J.; Alonso, J.; et al. What Is the Relative Importance of Self Reported Psychotic Symptoms in Epidemiological Studies? Results from the ESEMeD-Catalonia Study. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 102, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureje, O.; Olowosegun, O.; Adebayo, K.; Stein, D.J. The Prevalence and Profile of Non-Affective Psychosis in the Nigerian Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing. World Psychiatry 2010, 9, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO Mental Disorders. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Brazinova, A.; Hasto, J.; Levav, I.; Pathare, S. Mental Health Care Gap: The Case of the Slovak Republic. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2019, 46, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoy, V.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Qi, T.; Panagiotaropoulou, G.; Awasthi, S.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Bryois, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Dennison, C.A.; Hall, L.S.; et al. Mapping Genomic Loci Implicates Genes and Synaptic Biology in Schizophrenia. Nature 2022, 604, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklar, P.; Purcell, S. Common Polygenic Variation Contributes to Risk of Schizophrenia That Overlaps with Bipolar Disorder International Schizophrenia Consortium. Nature 2009, 460, 748–752. [Google Scholar]
- Pocklington, A.J.; Rees, E.; Walters, J.T.R.; Han, J.; Kavanagh, D.H.; Chambert, K.D.; Holmans, P.; Moran, J.L.; McCarroll, S.A.; Kirov, G.; et al. Novel Findings from CNVs Implicate Inhibitory and Excitatory Signaling Complexes in Schizophrenia. Neuron 2015, 86, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, T.; Walters, J.T.R.; Johnstone, M.; Curtis, D.; Suvisaari, J.; Torniainen, M.; Rees, E.; Iyegbe, C.; Blackwood, D.; McIntosh, A.M.; et al. The Contribution of Rare Variants to Risk of Schizophrenia in Individuals with and without Intellectual Disability. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rees, E.; Han, J.; Morgan, J.; Carrera, N.; Escott-Price, V.; Pocklington, A.J.; Duffield, M.; Hall, L.S.; Legge, S.E.; Pardiñas, A.F.; et al. De Novo Mutations Identified by Exome Sequencing Implicate Rare Missense Variants in SLC6A1 in Schizophrenia. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Martinowich, K. Cell Biology of BDNF and Its Relevance to Schizophrenia. Novartis Found. Symp. 2008, 289, 119–195. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9780470751251.ch10 (accessed on 10 March 2023). [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gratacòs, M.; González, J.R.; Mercader, J.M.; de Cid, R.; Urretavizcaya, M.; Estivill, X. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met and Psychiatric Disorders: Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies Confirm Association to Substance-Related Disorders, Eating Disorders, and Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirollahi, M.; Kazemi, E.; Ashouri, S. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Val66Met Polymorphism and Risk of Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis of Case-Control Studies. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naoe, Y.; Shinkai, T.; Hori, H.; Fukunaka, Y.; Utsunomiya, K.; Sakata, S.; Matsumoto, C.; Shimizu, K.; Hwang, R.; Ohmori, O.; et al. No Association between the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Val66Met Polymorphism and Schizophrenia in Asian Populations: Evidence from a Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 415, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Glatt, S.J.; Kia-Keating, B.; Yoneda, H.; Tsuang, M.T. Meta-Analysis Reveals No Association of the Val66Met Polymorphism of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Either Schizophrenia or Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatr. Genet. 2007, 17, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhao, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Feng, G.; Xu, F.; Zhu, S.; He, L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Risk of Schizophrenia: An Association Study and Meta-Analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 353, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zintzaras, E. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Polymorphisms and Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Psychiatr. Genet. 2007, 17, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Rashidi, E.; Amooeian, V.G. Brain, Blood, Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Serum Biomarkers in Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 265, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Son, Y.D.; Joo, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Woo, M.K. Altered Interregional Correlations between Serotonin Transporter Availability and Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in Schizophrenia: A High-Resolution PET Study Using [11C]DASB and [18F]FDG. Schizophr. Res. 2017, 182, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.Y.; Numata, S.; Iga, J.I.; Kinoshita, M.; Umehara, H.; Ishii, K.; Ohmori, T. Gene Expression-Based Biological Test for Major Depressive Disorder: An Advanced Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brusov, O.S.; Faktor, M.I.; Zlobina, G.P.; Bologov, P.V.; Kaleda, V.G.; Oleichik, I.V.; Korenev, A.N.; Piatnitskii, A.N.; Dupin, A.M.; Katasonov, A.B.; et al. Levels and Molecular Heterogeneity of Serotonin Transporter Protein in Platelets of Patients with Different Mental Diseases: A Comparative Analysis with the Use of Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies. Vestn. Ross. Akad. Meditsinskikh Nauk./Ross. Akad. Meditsinskikh Nauk. 2001, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Terzić, T.; Kastelic, M.; Dolžan, V.; Plesničar, B.K. Influence of 5-HTIA and 5-HTTLPR Genetic Variants on the Schizophrenia Symptoms and Occurrence of Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Huang, X.; Ruan, L.; Yu, T.; Li, X.; Jesse, F.F.; Cao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, F.; et al. No Association of SLC6A3 and SLC6A4 Gene Polymorphisms with Schizophrenia in the Han Chinese Population. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 579, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, R.; Tremblay, P.B.; Schmider, J.; Henneken, M.; Dettling, M.; Müller-Oerlinghausen, B.; Uebelhack, R.; Roots, I.; Brockmöller, J. Serotonin Transporter Polymorphisms: No Association with Response to Antipsychotic Treatment, but Associations with the Schizoparanoid and Subtypes of Schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.; Moylan, S.; Harvey, B.H.; Maes, M.; Berk, M. Neuroprogression in Schizophrenia: Pathways Underpinning Clinical Staging and Therapeutic Corollaries. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, L.G.P.; Nunes, S.O.V.; Anderson, G.; Vargas, H.O.; Barbosa, D.S.; Galecki, P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M. Shared Metabolic and Immune-Inflammatory, Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress Pathways in the Metabolic Syndrome and Mood Disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 78, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Puri, B.K.; Walker, A.J.; Maes, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Walder, K.; Berk, M. Shared Pathways for Neuroprogression and Somatoprogression in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 862–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macekova, Z.; Fazekas, T.; Stanko, P.; Vyhnalek, M.; Dragasek, J.; Krivosova, M.; Krenek, P.; Snopkova, M.; Klimas, J. Cognitive Screening within Advanced Pharmaceutical Care in Elderly Patients with Suspected Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Gerontol. 2022, 16, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Tonhajzerova, I.; Visnovcova, Z.; Ondrejka, I.; Funakova, D.; Hrtanek, I.; Ferencova, N. Major Depressive Disorder at Adolescent Age Is Associated with Impaired Cardiovascular Autonomic Regulation and Vasculature Functioning. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2022, 181, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivosova, M.; Gondas, E.; Murin, R.; Dohal, M.; Ondrejka, I.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Hutka, P.; Ferencova, N.; Visnovcova, Z.; Hrtanek, I.; et al. The Plasma Levels of 3-Hydroxybutyrate, Dityrosine, and Other Markers of Oxidative Stress and Energy Metabolism in Major Depressive Disorder. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferencova, N.; Visnovcova, Z.; Kelcikova, S.; Tonhajzerova, I.; Ondrejka, I.; Funakova, D.; Hrtanek, I. Evaluation of Inflammatory Response System (IRS) and Compensatory Immune Response System (CIRS) in Adolescent Major Depression. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 5959–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, M.; Locke, A.E.; Corre, T.; Czamara, D.; Wolf, C.; Ching-Lopez, A.; Milaneschi, Y.; Kloiber, S.; Cohen-Woods, S.; Rucker, J.; et al. Interaction between the FTO Gene, Body Mass Index and Depression: Meta-Analysis of 13701 Individuals. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 211, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bednarova, A.; Habalova, V.; Farkasova Iannaccone, S.; Tkac, I.; Jarcuskova, D.; Krivosova, M.; Marcatili, M.; Hlavacova, N. Association of HTTLPR, BDNF, and FTO Genetic Variants with Completed Suicide in Slovakia. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, F.; Shimomura, T.; Kotani, K.; Ikawa, S.; Nanba, E.; Adachi, K. Anxiety Traits Associated with a Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene Regulatory Region in the Japanese. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 44, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé, X.; Guinó, E.; Valls, J.; Iniesta, R.; Moreno, V. SNPStats: A Web Tool for the Analysis of Association Studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1928–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghamari, R.; Yazarlou, F.; Khosravizadeh, Z.; Moradkhani, A.; Abdollahi, E.; Alizadeh, F. Serotonin Transporter Functional Polymorphisms Potentially Increase Risk of Schizophrenia Separately and as a Haplotype. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serretti, A.; Catalano, M.; Smeraldi, E. Serotonin Transporter Gene Is Not Associated with Symptomatology of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 1999, 35, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, C.U.; Serretti, A.; Artioli, P.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, C.U.; Lee, S.J.; Paik, I.H.; Lee, C. Interaction Analysis between 5-HTTLPR and TNFA -238/-308 Polymorphisms in Schizophrenia. J. Neural Transm. 2006, 113, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, L.; Dean, B.; Pereira, A.; Mackinnon, A.; Kouzmenko, A.; Copolov, D. No Association between the Serotonin Transporter-Linked Promoter Region Polymorphism and Either Schizophrenia or Density of the Serotonin Transporter in Human Hippocampus. Mol. Med. 1998, 4, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.J.; Hong, C.J.; Yu, Y.W.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Song, H.L.; Lai, H.C.; Yang, K.H. Association Study of a Functional Serotonin Transporter Gene Polymorphism with Schizophrenia, Psychopathology and Clozapine Response. Schizophr. Res. 2000, 44, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, Y.K. No Association of Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism (5-HTTVNTR and 5-HTTLPR) with Characteristics and Treatment Response to Atypical Antipsychotic Agents in Schizophrenic Patients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáiz, P.A.; García-Portilla, M.P.; Arango, C.; Morales, B.; Alvarez, V.; Coto, E.; Fernández, J.M.; Bascarán, M.T.; Bousoño, M.; Bobes, J. Association Study of Serotonin 2A Receptor (5-HT2A) and Serotonin Transporter (5-HTT) Gene Polymorphisms with Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubertret, C.; Hanoun, N.; Adès, J.; Hamon, M.; Gorwood, P. Family-Based Association Study of the 5-HT Transporter Gene and Schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2005, 8, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golimbet, V.; Korovaitseva, G.; Lezheiko, T.; Abramova, L.I.; Kaleda, V.G. The Serotonin Transporter Gene 5-HTTLPR Polymorphism Is Associated with Affective Psychoses but Not with Schizophrenia: A Large-Scale Study in the Russian Population. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 208, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelski, P.; Hauser, J.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Skibińska, M.; Kaczmarkiewicz-Fass, M.; Rajewska, A.; Gattner, K.; Czerski, P.M. Lack of Association between the Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism in the Serotonin Transporter Gene and Schizophrenia. Psychiatr. Pol. 2006, 40, 925–935. [Google Scholar]
- Peitl, V.; Štefanović, M.; Karlović, D. Depressive Symptoms in Schizophrenia and Dopamine and Serotonin Gene Polymorphisms. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 77, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konneker, T.I.; Crowley, J.J.; Quackenbush, C.R.; Keefe, R.S.E.; Perkins, D.O.; Stroup, T.S.; Lieberman, J.A.; van den Oord, E.; Sullivan, P.F. No Association of the Serotonin Transporter Polymorphisms 5-HTTLPR and Rs25531 with Schizophrenia or Neurocognition. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2010, 153B, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.B.; Sklar, P. Meta-Analysis Reveals Association between Serotonin Transporter Gene STin2 VNTR Polymorphism and Schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.L.; Wang, B.J.; Yao, J. Association between the SLC6A4 Gene and Schizophrenia: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malan-Müller, S.; Kilian, S.; van den Heuvel, L.L.; Bardien, S.; Asmal, L.; Warnich, L.; Emsley, R.A.; Hemmings, S.M.J.; Seedat, S. A Systematic Review of Genetic Variants Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2016, 170, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffeei, S.N.; Mohamed, Z.; Reynolds, G.P.; Said, M.A.; Hatim, A.; Mohamed, E.H.M.; Aida, S.A.; Zainal, N.Z. Association of FTO, LEPR and MTHFR Gene Polymorphisms with Metabolic Syndrome in Schizophrenia Patients Receiving Antipsychotics. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, G.P.; Yevtushenko, O.O.; Gordon, S.; Arranz, B.; San, L.; Cooper, S.J. The Obesity Risk Gene FTO Influences Body Mass in Chronic Schizophrenia but Not Initial Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Weight Gain in First-Episode Patients. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Pang, L.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Nemani, K.; Zhang, H.; et al. Fat-Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene Polymorphisms and Weight Gain after Risperidone Treatment in First Episode Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Funct. 2014, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terzić, T.; Kastelic, M.; Dolžan, V.; Plesničar, B.K. Genetic Variability Testing of Neurodevelopmental Genes in Schizophrenic Patients. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 56, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peka-Wysiecka, J.; Wroñski, M.; Jasiewicz, A.; Grzywacz, A.; Tybura, P.; Kucharska-Mazur, J.; Bieñkowski, P.; Samochowiec, J. BDNF Rs 6265 Polymorphism and COMT Rs 4680 Polymorphism in Deficit Schizophrenia in Polish Sample. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharyan, R.; Boyajyan, A.; Arakelyan, A.; Gevorgyan, A.; Mrazek, F.; Petrek, M. Functional Variants of the Genes Involved in Neurodevelopment and Susceptibility to Schizophrenia in an Armenian Population. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, E.N.; Siafakas, N.; Stefanis, N.; Douzenis, A.; Kontaxakis, V.; Laskos, E.; Kastania, A.; Zoumbourlis, V.; Lykouras, L. Association of Serum BDNF and Val66met Polymorphism of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in a Sample of First Psychotic Episode Patients. Psychiatriki 2009, 20, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Pivac, N.; Nikolac, M.; Nedic, G.; Mustapic, M.; Borovecki, F.; Hajnsek, S.; Presecki, P.; Pavlovic, M.; Mimica, N.; Muck Seler, D. Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met Polymorphism and Psychotic Symptoms in Alzheimer’s Disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galderisi, S.; Maj, M.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Piccardi, P.; Mucci, A.; Invernizzi, G.; Rossi, A.; Pini, S.; Vita, A.; Cassano, P.; et al. COMT Val(158)Met and BDNF C(270)T Polymorphisms in Schizophrenia: A Case-Control Study. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 73, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squassina, A.; Piccardi, P.; del Zompo, M.; Rossi, A.; Vita, A.; Pini, S.; Mucci, A.; Galderisi, S. NRG1 and BDNF Genes in Schizophrenia: An Association Study in an Italian Case-Control Sample. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 176, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.K.; Mitra, P.; Ghosh, R.; Sharma, S.; Nebhinani, N.; Sharma, P. Association of Circulating BDNF Levels with BDNF Rs6265 Polymorphism in Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 394, 112832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, X.; Fan, W.; Tang, W.; Cai, J.; Song, L.; Zhang, C. Interaction between BDNF and TNF-α Genes in Schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, C.U.; Chiesa, A.; Porcelli, S.; Han, C.; Patkar, A.A.; Lee, S.J.; Park, M.H.; Serretti, A.; de Ronchi, D. Influence of BDNF Variants on Diagnosis and Response to Treatment in Patients with Major Depression, Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 2012, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zai, C.C.; Manchia, M.; de Luca, V.; Tiwari, A.K.; Squassina, A.; Zai, G.C.; Strauss, J.; Shaikh, S.A.; Freeman, N.; Meltzer, H.Y.; et al. Association Study of BDNF and DRD3 Genes in Schizophrenia Diagnosis Using Matched Case–Control and Family Based Study Designs. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencz, T.; Lipsky, R.H.; DeRosse, P.; Burdick, K.E.; Kane, J.M.; Malhotra, A.K. Molecular Differentiation of Schizoaffective Disorder from Schizophrenia Using BDNF Haplotypes. Br. J. Psychiatry 2009, 194, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Numata, S.; Ueno, S.-I.; Iga, J.-I.; Yamauchi, K.; Hongwei, S.; Ohta, K.; Kinouchi, S.; Shibuya-Tayoshi, S.; Tayoshi, S.; Aono, M.; et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Val66Met Polymorphism in Schizophrenia Is Associated with Age at Onset and Symptoms. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 401, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mané, A.; Bergé, D.; Penzol, M.J.; Parellada, M.; Bioque, M.; Lobo, A.; González-Pinto, A.; Corripio, I.; Cabrera, B.; Sánchez-Torres, A.M.; et al. Cannabis Use, COMT, BDNF and Age at First-Episode Psychosis. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 250, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Hong, W.; Li, Z.; Fang, Y.; Yu, S. Lack of Effect of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Val66Met Polymorphism on Early Onset Schizophrenia in Chinese Han Population. Brain Res. 2011, 1417, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.H.; Yan, Q.Z.; Yan, X.M.; Li, C.B.; Fang, H.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Yao, H.J.; Chen, D.C.; Xiu, M.H.; et al. The Study of BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism in Chinese Schizophrenic Patients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age | Controls | Patients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Males | Female | Total | Males | Females | |
| Number (%) | 178 | 97 (54.5) | 81 (45.5) | 150 | 82 (54.6) | 68 (45.4) |
| Average ± SD | 46.7 ± 15.2 | 43.9 ± 16.0 | 51.3 ± 15.0 | 45.6 ± 13.1 | 42.2 ± 14.0 | 49.6 ± 10.6 |
| min–max | 21–80 | 21–73 | 23–80 | 20–71 | 20–71 | 31–71 |
| Code | Diagnosis | Total | Males | Females | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| F20 | Schizophrenia | 73 | 48.7 | 45 | 54.9 | 28 | 41.2 |
| F21 | Schizotypal disorder | 1 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1.5 |
| F22 | Persistent delusional disorders | 8 | 5.3 | 4 | 4.9 | 4 | 5.9 |
| F23 | Acute and transient psychotic disorders | 22 | 14.7 | 16 | 19.5 | 6 | 8.8 |
| F25 | Schizoaffective disorders | 45 | 30.0 | 17 | 20.7 | 28 | 41.2 |
| F29 | Unspecified nonorganic psychosis | 1 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Allele | Patients | Controls | Controls HWE p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Frequency | n | Frequency | |||
| SLC6A4 5-HTTLPR | L | 178 | 0.59 | 190 | 0.53 | 1.00 |
| S | 122 | 0.41 | 166 | 0.47 | ||
| FTO rs9939609 | T | 170 | 0.57 | 187 | 0.53 | 0.88 |
| A | 130 | 0.43 | 169 | 0.47 | ||
| BDNF rs6265 | C | 243 | 0.81 | 288 | 0.81 | 0.47 |
| T | 57 | 0.19 | 68 | 0.19 | ||
| BDNF rs962369 | T | 229 | 0.76 | 278 | 0.78 | 0.19 |
| C | 71 | 0.24 | 78 | 0.22 | ||
| Genotype | Controls | Patients | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | (%) | n | (%) | ||||
| SLC6A4 5-HTTLPR | LL | 51 | (28.6) | 59 | (39.3) | 1.00 | 0.11 |
| LS | 88 | (49.4) | 60 | (40.0) | 0.59 (0.36–0.97) | ||
| SS | 39 | (21.9) | 31 | (20.7) | 0.69 (0.38–1.25) | ||
| FTO rs9939609 | TT | 48 | (27.0) | 47 | (31.3) | 1.00 | 0.56 |
| TA | 91 | (51.1) | 76 | (50.7) | 0.85 (0.52–1.41) | ||
| AA | 39 | (21.9) | 27 | (18.0) | 0.71 (0.37–1.33) | ||
| BDNF rs6265 | CC | 118 | (66.3) | 101 | (67.3) | 1.00 | 0.89 |
| CT | 52 | (29.2) | 41 | (27.3) | 0.92 (0.57–1.50) | ||
| TT | 8 | (4.5) | 8 | (5.3) | 1.17 (0.42–3.23) | ||
| BDNF rs962369 | TT | 105 | (59.0) | 87 | (58.0) | 1.00 | 0.5 |
| TC | 68 | (38.2) | 55 | (36.7) | 0.98 (0.62–1.54) | ||
| CC | 5 | (2.8) | 8 | (5.3) | 1.93 (0.61–6.12) | ||
| Genotype | Controls n (%) | Patients n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | LL | 51 (28.6) | 59 (39.3) | 1.00 | 0.04 |
| LS + SS | 127 (71.3) | 91 (60.7) | 0.62 (0.39–0.98) | ||
| Males | LL | 25 (25.8) | 26 (31.7) | 1.00 | 0.38 |
| LS + SS | 72 (74.2) | 56 (68.3) | 0.75 (0.39–1.43) | ||
| Females | LL | 26 (32.1) | 33 (48.5) | 1.00 | 0.04 |
| LS + SS | 55 (67.9) | 35 (51.5) | 0.50 (0.26–0.98) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bednarova, A.; Habalova, V.; Krivosova, M.; Marcatili, M.; Tkac, I. Association Study of BDNF, SLC6A4, and FTO Genetic Variants with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040658
Bednarova A, Habalova V, Krivosova M, Marcatili M, Tkac I. Association Study of BDNF, SLC6A4, and FTO Genetic Variants with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(4):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040658
Chicago/Turabian StyleBednarova, Aneta, Viera Habalova, Michaela Krivosova, Matteo Marcatili, and Ivan Tkac. 2023. "Association Study of BDNF, SLC6A4, and FTO Genetic Variants with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 4: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040658
APA StyleBednarova, A., Habalova, V., Krivosova, M., Marcatili, M., & Tkac, I. (2023). Association Study of BDNF, SLC6A4, and FTO Genetic Variants with Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(4), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13040658