First Results of Concurrent Chemoradiation with Two Courses of 5 × 25 mg/m2 Cisplatin for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lacas, B.; Carmel, A.; Landais, C.; Wong, S.J.; Licitra, L.; Tobias, J.S.; Burtness, B.; Ghi, M.G.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Grau, C.; et al. Meta-analysis of chemotherapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): An update on 107 randomized trials and 19,805 patients, on behalf of MACH-NC Group. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 156, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelstein, D.J.; Lavertu, P.; Saxton, J.P.; Secic, M.; Wood, B.G.; Wanamaker, J.R.; Eliachar, I.; Strome, M.; Larto, M.A. Mature results of a phase III randomized trial comparing concurrent chemoradiotherapy with radiation therapy alone in patients with stage III and IV squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 2000, 88, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, J.; Domenge, C.; Ozsahin, M.; Matuszewska, K.; Lefèbvre, J.L.; Greiner, R.H.; Giralt, J.; Maingon, P.; Rolland, F.; Bolla, M.; et al. Postoperative irradiation with or without concomitant chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.S.; Pajak, T.F.; Forastiere, A.A.; Jacobs, J.; Campbell, B.H.; Saxman, S.B.; Kish, J.A.; Kim, H.E.; Cmelak, A.J.; Rotman, M.; et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremic, B.; Shibamoto, Y.; Stanisavljevic, B.; Milojevic, L.; Milicic, B.; Nikolic, N. Radiation therapy alone or with concurrent low-dose daily either cisplatin or carboplatin in locally advanced unresectable squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: A prospective randomized trial. Radiother. Oncol. 1997, 43, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaan, I.; Soror, T.; Bruchhage, K.L.; Hakim, S.G.; Schild, S.E.; Rades, D. Comparison of two cisplatin regimens for chemoradiation in patients with squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Castro, G., Jr.; Snitcovsky, I.M.; Gebrim, E.M.; Leitão, G.M.; Nadalin, W.; Ferraz, A.R.; Federico, M.H. High-dose cisplatin concurrent to conventionally delivered radiotherapy is associated with unacceptable toxicity in unresectable, non-metastatic stage IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strojan, P.; Vermorken, J.B.; Beitler, J.J.; Saba, N.F.; Haigentz, M., Jr.; Bossi, P.; Worden, F.P.; Langendijk, J.A.; Eisbruch, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; et al. Cumulative cisplatin dose in concurrent chemoradiotherapy for head and neck cancer: A systematic review. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E2151–E2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, M.; Huang, S.H.; Xu, W.; Su, J.; Hansen, A.R.; Bratman, S.V.; Ringash, J.; Jang, R.; Cho, J.; Bayley, A.; et al. Impact of cisplatin dose and smoking pack-years in human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with chemoradiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 118, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babar, A.; Woody, N.M.; Ghanem, A.I.; Tsai, J.; Dunlap, N.E.; Schymick, M.; Liu, H.Y.; Burkey, B.B.; Lamarre, E.D.; Ku, J.A.; et al. Outcomes of post-operative treatment with concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) in high-risk resected oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma (OCSCC): A multi-institutional collaboration. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 2409–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundog, M.; Basaran, H.; Bozkurt, O.; Eroglu, C. A comparison of cisplatin cumulative dose and cisplatin schedule in patients treated with concurrent chemo-radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 86, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Seidl, D.; Janssen, S.; Bajrovic, A.; Hakim, S.G.; Wollenberg, B.; Karner, K.; Strojan, P.; Schild, S.E. Chemoradiation of locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head-and-neck (LASCCHN): Is 20mg/m(2) cisplatin on five days every four weeks an alternative to 100 mg/m(2) cisplatin every three weeks? Oral Oncol. 2016, 59, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Seidl, D.; Janssen, S.; Bajrovic, A.; Karner, K.; Strojan, P.; Schild, S.E. Comparison of weekly administration of cisplatin versus three courses of cisplatin 100 mg/m(2) for definitive radiochemotherapy of locally advanced head-and-neck cancers. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha, V.; Joshi, A.; Patil, V.M.; Agarwal, J.; Ghosh-Laskar, S.; Budrukkar, A.; Murthy, V.; Gupta, T.; D’Cruz, A.K.; Banavali, S.; et al. Once-a-week versus once-every-3-weeks cisplatin chemoradiation for locally advanced head and neck cancer: A phase III randomized noninferiority trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyota, N.; Tahara, M.; Mizusawa, J.; Kodaira, T.; Fujii, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Mitani, H.; Iwae, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Onozawa, Y.; et al. Weekly cisplatin plus radiation for postoperative head and neck cancer (JCOG1008): A multicenter, noninferiority, phase II/III randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rades, D.; Stoehr, M.; Kazic, N.; Hakim, S.G.; Walz, A.; Schild, S.E.; Dunst, J. Locally advanced stage IV squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Impact of pre-radiotherapy hemoglobin level and interruptions during radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 70, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Xu, C.; Chen, Y.P.; Guo, R.; Mao, Y.P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J.; Tang, L.L. Optimizing the cumulative cisplatin dose during radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Dose-effect analysis for a large cohort. Oral Oncol. 2019, 89, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Kou, J.; Zhou, G.Q.; Wu, C.F.; Sun, Y.; Lin, L. Cisplatin-based concurrent chemoradiotherapy improved the survival of locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma after induction chemotherapy by reducing early treatment failure. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Group A n Patients (%) | Group B n Patients (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.74 | ||
| ≤63 years | 4 (40) | 49 (50) | |
| ≥64 years | 6 (60) | 49 (50) | |
| Gender | 1.00 | ||
| Female | 1 (10) | 16 (16) | |
| Male | 9 (90) | 82 (84) | |
| Karnofsky performance status | 0.75 | ||
| ≤80 | 6 (60) | 52 (53) | |
| 90–100 | 4 (40) | 46 (47) | |
| Main tumor site | 1.00 | ||
| Oropharynx/oral cavity | 7 (70) | 72 (73) | |
| Hypopharynx/larynx | 3 (30) | 26 (27) | |
| Primary tumor stage | 1.00 | ||
| T1-2 | 4 (40) | 36 (37) | |
| T3-4 | 6 (60) | 62 (63) | |
| Nodal stage | 1.00 | ||
| N0-1 | 3 (30) | 34 (35) | |
| N2-3 | 7 (70) | 64 (65) | |
| Histologic grade a | 1.00 | ||
| G1-2 | 5 (50) | 46 (49) | |
| G3 | 5 (50) | 47 (51) | |
| HPV status b | 1.00 | ||
| Negative | 4 (50) | 36 (49) | |
| Positive | 4 (50) | 37 (51) | |
| Upfront surgery | 1.00 | ||
| No | 4 (40) | 44 (45) | |
| Yes | 6 (60) | 54 (55) | |
| Pre-treatment history of smoking c | 1.00 | ||
| No | 1 (10) | 16 (18) | |
| Yes | 9 (90) | 73 (82) | |
| Smoking during chemoradiation d | 0.31 | ||
| No | 4 (40) | 54 (60) | |
| Yes | 6 (60) | 36 (40) | |
| Pre-treatment hemoglobin level e | 0.74 | ||
| <12 g/dL | 3 (30) | 39 (40) | |
| ≥12 g/dL | 7 (70) | 58 (60) |
| Characteristic | Loco-Regional Control (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At 6 Months | At 12 Months | ||
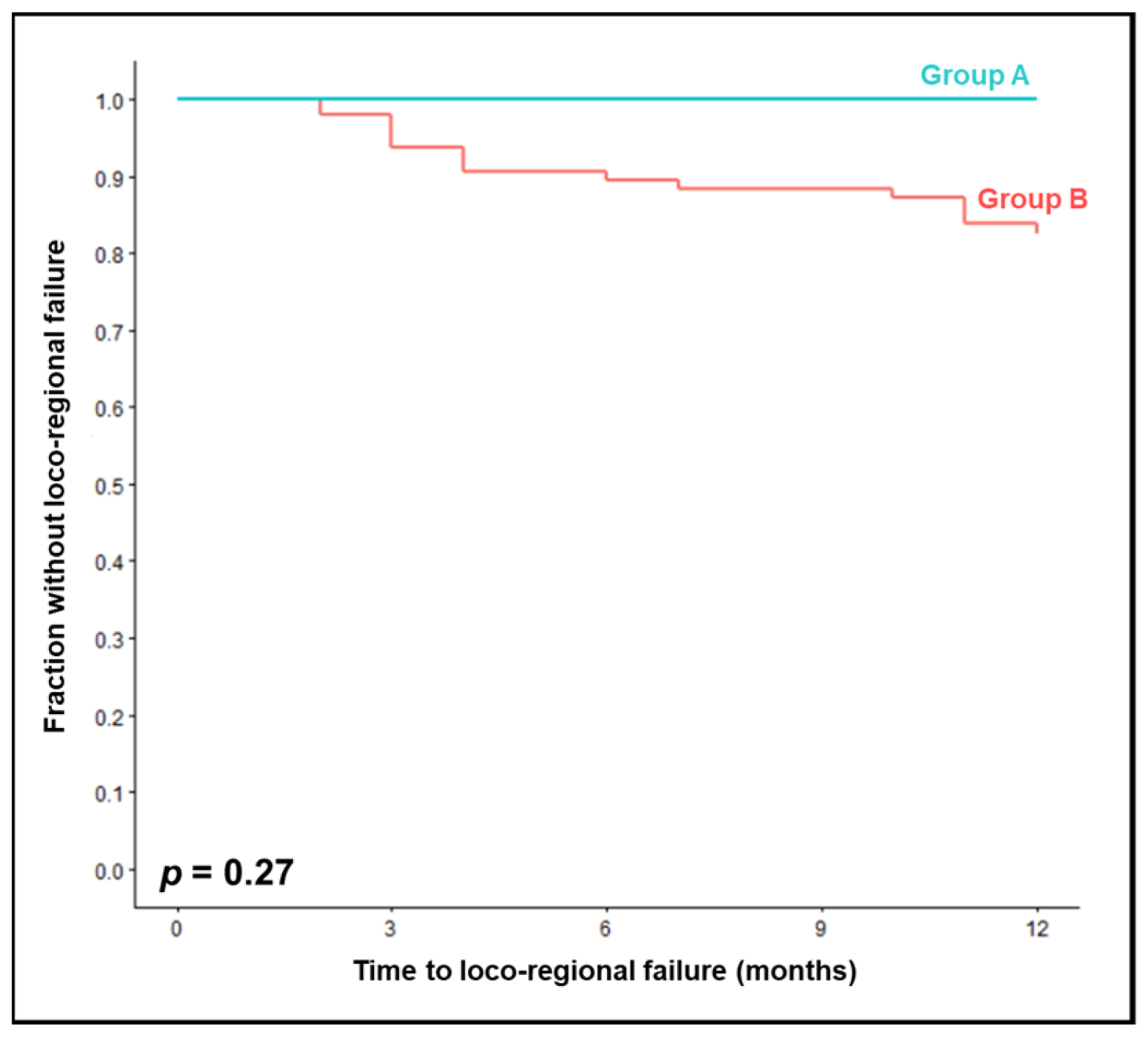
| Planned cumulative cisplatin dose | 0.27 | ||
| 250 mg/m2 (group A) | 100 | 100 | |
| 200 mg/m2 (group B) | 89 | 83 | |
| Age | 0.27 | ||
| ≤63 years | 84 | 80 | |
| ≥64 years | 96 | 87 | |
| Gender | 0.25 | ||
| Female | 94 | 94 | |
| Male | 90 | 82 | |
| Karnofsky performance status | 0.026 | ||
| ≤80 | 83 | 76 | |
| 90–100 | 98 | 92 | |
| Main tumor site | 0.093 | ||
| Oropharynx/oral cavity | 91 | 88 | |
| Hypopharynx/larynx | 89 | 72 | |
| Primary tumor stage | 0.098 | ||
| T1-2 | 95 | 92 | |
| T3-4 | 88 | 79 | |
| Nodal stage | 0.013 | ||
| N0-1 | 97 | 97 | |
| N2-3 | 87 | 77 | |
| Histologic grade a | 0.60 | ||
| G1-2 | 88 | 81 | |
| G3 | 92 | 85 | |
| HPV status b | 0.009 | ||
| Negative | 84 | 78 | |
| Positive | 100 | 97 | |
| Upfront surgery | 0.11 | ||
| No | 89 | 76 | |
| Yes | 91 | 89 | |
| Pre-treatment history of smoking c | 0.73 | ||
| No | 93 | 86 | |
| Yes | 90 | 82 | |
| Smoking during chemoradiation d | 0.27 | ||
| No | 93 | 87 | |
| Yes | 87 | 77 | |
| Pre-treatment hemoglobin level e | 0.074 | ||
| <12 g/dL | 80 | 76 | |
| ≥12 g/dL | 97 | 88 | |
| Characteristic | Metastases-Free Survival (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At 6 Months | At 12 Months | ||
| Planned cumulative cisplatin dose | 0.38 | ||
| 250 mg/m2 (group A) | 100 | 100 | |
| 200 mg/m2 (group B) | 94 | 88 | |
| Age | 0.35 | ||
| ≤63 years | 92 | 86 | |
| ≥64 years | 96 | 92 | |
| Gender | 0.48 | ||
| Female | 94 | 94 | |
| Male | 94 | 87 | |
| Karnofsky performance status | 0.094 | ||
| ≤80 | 89 | 84 | |
| 90–100 | 100 | 94 | |
| Main tumor site | 0.14 | ||
| Oropharynx/oral cavity | 95 | 92 | |
| Hypopharynx/larynx | 93 | 80 | |
| Primary tumor stage | 0.16 | ||
| T1-2 | 97 | 95 | |
| T3-4 | 92 | 85 | |
| Nodal stage | 0.62 | ||
| N0-1 | 100 | 90 | |
| N2-3 | 91 | 88 | |
| Histologic grade a | 0.77 | ||
| G1-2 | 92 | 87 | |
| G3 | 96 | 89 | |
| HPV status b | 0.55 | ||
| Negative | 95 | 91 | |
| Positive | 100 | 94 | |
| Upfront surgery | 0.61 | ||
| No | 96 | 91 | |
| Yes | 93 | 87 | |
| Pre-treatment history of smoking c | 0.66 | ||
| No | 100 | 85 | |
| Yes | 95 | 90 | |
| Smoking during chemoradiation d | 0.073 | ||
| No | 100 | 94 | |
| Yes | 90 | 84 | |
| Pre-treatment hemoglobin level e | 0.49 | ||
| <12 g/dL | 90 | 87 | |
| ≥12 g/dL | 97 | 90 | |
| Characteristic | Overall Survival (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At 6 Months | At 12 Months | ||
| Planned cumulative cisplatin dose | 0.90 | ||
| 250 mg/m2 (group A) | 89 | 89 | |
| 200 mg/m2 (group B) | 92 | 88 | |
| Age | 0.17 | ||
| ≤63 years | 92 | 92 | |
| ≥64 years | 91 | 83 | |
| Gender | 0.11 | ||
| Female | 100 | 100 | |
| Male | 90 | 85 | |
| Karnofsky performance status | 0.051 | ||
| ≤80 | 86 | 82 | |
| 90–100 | 98 | 94 | |
| Main tumor site | 0.34 | ||
| Oropharynx/oral cavity | 90 | 86 | |
| Hypopharynx/larynx | 97 | 93 | |
| Primary tumor stage | 0.62 | ||
| T1-2 | 95 | 89 | |
| T3-4 | 90 | 86 | |
| Nodal stage | 0.71 | ||
| N0-1 | 86 | 86 | |
| N2-3 | 94 | 88 | |
| Histologic grade a | 0.23 | ||
| G1-2 | 94 | 92 | |
| G3 | 90 | 84 | |
| HPV status b | 0.11 | ||
| Negative | 85 | 80 | |
| Positive | 92 | 92 | |
| Upfront surgery | 0.89 | ||
| No | 90 | 87 | |
| Yes | 93 | 88 | |
| Pre-treatment history of smoking c | 0.12 | ||
| No | 82 | 76 | |
| Yes | 93 | 90 | |
| Smoking during chemoradiation d | 0.49 | ||
| No | 91 | 90 | |
| Yes | 90 | 84 | |
| Pre-treatment hemoglobin level e | 0.014 | ||
| <12 g/dL | 83 | 78 | |
| ≥12 g/dL | 97 | 94 | |
| Toxicity | Group A | Group B | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n Patients (%) | n Patients (%) | ||
| Oral mucositis a | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 5 (50) | 70 (75) | 0.13 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 2 (20) | 24 (26) | 1.00 |
| Radiation dermatitis b | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 9 (90) | 77 (84) | 1.00 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 1 (10) | 31 (34) | 0.17 |
| Xerostomia c | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 3 (30) | 28 (29) | 1.00 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 1 (10) | 5 (5) | 0.46 |
| Cervical lymphedema d | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 1 (11) | 10 (11) | 1.00 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| Nausea e | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 0 (0) | 13 (14) | 0.60 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 0 (0) | 2 (2) | 1.00 |
| Hearing problems f | |||
| Grade ≥ 1 | 2 (22) | 21 (22) | 1.00 |
| Decreased renal function g | |||
| Grade ≥ 1 | 4 (40) | 31 (32) | 0.73 |
| Grade ≥ 2 | 1 (10) | 6 (6) | 0.51 |
| Hematotoxicity h | |||
| Grade ≥ 2 | 9 (90) | 70 (73) | 0.45 |
| Grade ≥ 3 | 4 (40) | 29 (30) | 0.50 |
| Grade 4 | 1 (10) | 3 (3) | 0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zwaan, I.; Soror, T.; Idel, C.; Pries, R.; Bruchhage, K.L.; Hakim, S.G.; Yu, N.Y.; Rades, D. First Results of Concurrent Chemoradiation with Two Courses of 5 × 25 mg/m2 Cisplatin for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13061006
Zwaan I, Soror T, Idel C, Pries R, Bruchhage KL, Hakim SG, Yu NY, Rades D. First Results of Concurrent Chemoradiation with Two Courses of 5 × 25 mg/m2 Cisplatin for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(6):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13061006
Chicago/Turabian StyleZwaan, Inga, Tamer Soror, Christian Idel, Ralph Pries, Karl L. Bruchhage, Samer G. Hakim, Nathan Y. Yu, and Dirk Rades. 2023. "First Results of Concurrent Chemoradiation with Two Courses of 5 × 25 mg/m2 Cisplatin for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 6: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13061006
APA StyleZwaan, I., Soror, T., Idel, C., Pries, R., Bruchhage, K. L., Hakim, S. G., Yu, N. Y., & Rades, D. (2023). First Results of Concurrent Chemoradiation with Two Courses of 5 × 25 mg/m2 Cisplatin for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(6), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13061006






