The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Psychosocial Questionnaires
2.4. Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Psychosocial and GARS Data
3.3. Risk Alleles and Association with Weight Loss and Inventory Scores
3.4. Heterosis
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Carpaij, O.A.; van den Berge, M. The asthma-obesity relationship: Underlying mechanisms and treatment implications. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2018, 24, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, T.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.S.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Praxedes, D.R.; Silva-Júnior, A.E.; Macena, M.L.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Bueno, N.B. Prevalence of food addiction among patients undergoing metabolic/bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2022, 24, e13529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, B.M.; Kvach, E.; Eckel, R.H. Treatment of Obesity: Weight Loss and Bariatric Surgery. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönroos, S.; Helmiö, M.; Juuti, A.; Tiusanen, R.; Hurme, S.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Ovaska, J.; Leivonen, M.; Peromaa-Haavisto, P.; Mäklin, S.; et al. Effect of Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy vs. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Weight Loss and Quality of Life at 7 Years in Patients With Morbid Obesity: The SLEEVEPASS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, C.A.; Christiansen, P. Psychological issues and alcohol misuse following bariatric surgery. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezaj, V.; Benoit, S.C.; Davis, J.; Engel, S.; Lloret-Linares, C.; Mitchell, J.E.; Pepino, M.Y.; Rogers, A.M.; Steffen, K.; Sogg, S. Changes in Alcohol Use after Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery: Predictors and Mechanisms. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Thanos, P.K.; Wang, G.-J.; Febo, M.; Demetrovics, Z.; Modestino, E.J.; Braverman, E.R.; Baron, D.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Gold, M.S. The Food and Drug Addiction Epidemic: Targeting Dopamine Homeostasis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6050–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, M.S.; Blum, K.; Febo, M.; Baron, D.; Modestino, E.J.; Elman, I.; Badgaiyan, R.D. Molecular role of dopamine in anhedonia linked to reward deficiency syndrome (RDS) and anti- reward systems. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 309–325. [Google Scholar]
- Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; Bassey, R.; Blum, K. Pre-clinical models of reward deficiency syndrome: A behavioral octopus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 115, 164–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Blum, K.; Ponce, J.V.; Lott, L.; Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; Badgaiyan, S.; Brewer, R.; Downs, B.W.; Fynman, P.; Weingarten, A.; et al. High Genetic Addiction Risk Score (GARS) in Chronically Prescribed Severe Chronic Opioid Probands Attending Multi-pain Clinics: An Open Clinical Pilot Trial. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3335–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Baron, D.; Lott, L.; Ponce, J.V.; Siwicki, D.; Boyett, B.; Steinberg, B.; Modestino, E.J.; Fried, L.; Hauser, M.; et al. In Search of Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS)-free Controls: The “Holy Grail” in Genetic Addiction Risk Testing. Curr. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 9, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Baron, D.; Lott, L.; Ponce, J.V.; Brewer, R.; Siwicki, D.; Boyett, B.; Gondre-Lewis, M.C.; Smith, D.E.; et al. Biotechnical development of genetic addiction risk score (GARS) and selective evidence for inclusion of polymorphic allelic risk in substance use disorder (SUD). J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Modestino, E.J.; Gondre-Lewis, M.; Chapman, E.J.; Neary, J.; Siwicki, D.; Baron, D.; Hauser, M.; Smith, D.E.; Roy, A.K.; et al. The Benefits of Genetic Addiction Risk Score (GARS™) Testing in Substance Use Disorder (SUD). Int. J. Genom. Data Min. 2018, 2018, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Simpatico, T.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Demetrovics, Z.; Fratantonio, J.; Agan, G.; Febo, M.; Gold, M.S. Coupling Neurogenetics (GARS™) and a Nutrigenomic Based Dopaminergic Agonist to Treat Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS): Targeting Polymorphic Reward Genes for Carbohydrate Addiction Algorithms. J. Reward Defic. Syndr. 2015, 1, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fried, L.; Modestino, E.J.; Siwicki, D.; Lott, L.; Thanos, P.K.; Baron, D.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Ponce, J.V.; Giordano, J.; Downs, W.B.; et al. Hypodopaminergia and “Precision Behavioral Management” (PBM): It is a Generational Family Affair. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwer, D.B.; Allison, K.C.; Wadden, T.A.; Ashare, R.; Spitzer, J.C.; McCuen-Wurst, C.; LaGrotte, C.; Williams, N.N.; Edwards, M.; Tewksbury, C.; et al. Psychopathology, disordered eating, and impulsivity as predictors of outcomes of bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, I.R.; Fuchs, O.; Hansen, G.; von Mutius, E.; Kopp, M.V. What is precision medicine? Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotyuk, E.; Magi, A.; Eisinger, A.; Király, O.; Vereczkei, A.; Barta, C.; Griffiths, M.D.; Székely, A.; Kökönyei, G.; Farkas, J.; et al. Co-occurrences of substance use and other potentially addictive behaviors: Epidemiological results from the Psychological and Genetic Factors of the Addictive Behaviors (PGA) Study. J. Behav. Addict. 2020, 9, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belligoli, A.; Bettini, S.; Segato, G.; Busetto, L. Predicting Responses to Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brethauer, S.A.; Kim, J.; el Chaar, M.; Papasavas, P.; Eisenberg, D.; Rogers, A.; Ballem, N.; Kligman, M.; Kothari, S. Standardized outcomes reporting in metabolic and bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. Med. 2015, 11, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, D.M.; Olmsted, M.P.; Bohr, Y.; Garfinkel, P.E. The eating attitudes test: Psychometric features and clinical correlates. Psychol. Med. 1982, 12, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Hermann, T.; Kübler, A. A short version of the Food Cravings Questionnaire-Trait: The FCQ-T-reduced. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzsimmons-Craft, E.E.; Keatts, D.A.; Bardone-Cone, A.M. Eating Expectancies in Relation to Eating Disorder Recovery. Cognit. Ther. Res. 2013, 37, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Development of the Yale Food Addiction Scale Version 2.0. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2016, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trottier, K.; McFarlane, T.; Olmsted, M.P.; McCabe, R.E. The Weight Influenced Self-Esteem Questionnaire (WISE-Q): Factor structure and psychometric properties. Body Image 2013, 10, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, E.A.; Xia, M.; Fosco, G.; Yaptangco, M.; Skidmore, C.R.; Crowell, S.E. The Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale Short Form (DERS-SF): Validation and Replication in Adolescent and Adult Samples. J. Psychopathol. Behav. Assess. 2016, 38, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarr, K.L.; Keefer, A.L. Measures of depression and depressive symptoms: Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II), Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. 11), S454–S466. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, A.J.; Israel, B.A.; Zenk, S.N.; Parker, E.A.; Lichtenstein, R.; Shellman-Weir, S.; Klem, A.B. Psychosocial stress and social support as mediators of relationships between income, length of residence and depressive symptoms among African American women on Detroit’s eastside. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, A.J.; Mentz, G.; Lachance, L.; Johnson, J.; Gaines, C.; Israel, B.A. Associations between socioeconomic status and allostatic load: Effects of neighborhood poverty and tests of mediating pathways. Am. J. Public Health 2012, 102, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boór, K.; Rónai, Z.; Nemoda, Z.; Gaszner, P.; Sasvári-Székely, M.; Guttman, A.; Kalász, H. Noninvasive genotyping of dopamine receptor D4 (DRD4) using nanograms of DNA from substance-dependent patients. Curr. Chem. 2002, 9, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Oscar-Berman, M.; Demetrovics, Z.; Barh, D.; Gold, M.S. Genetic Addiction Risk Score (GARS): Molecular neurogenetic evidence for predisposition to Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS). Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 50, 765–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedram, P.; Wadden, D.; Amini, P.; Gulliver, W.; Randell, E.; Cahill, F.; Vasdev, S.; Goodridge, A.; Carter, J.C.; Zhai, G.; et al. Food addiction: Its prevalence and significant association with obesity in the general population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulte, E.M.; Gearhardt, A.N. Associations of Food Addiction in a Sample Recruited to Be Nationally Representative of the United States. Eur. Eat Disord. Rev. 2018, 26, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comings, D.E. Molecular heterosis as the explanation for the controversy about the effect of the DRD2 gene on dopamine D2 receptor density. Mol. Psychiatry 1999, 4, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.T.; Lee, H.-Y.; Han, C.; Pae, C.-U.; Tae, W.S.; Lee, M.-S.; Joe, S.-H.; Jung, I.-K.; Ham, B.-J. DRD2/ANKK1 TaqI A polymorphism affects corticostriatal activity in response to negative affective facial stimuli. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 223, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleator, J.; Abbott, J.; Judd, P.; Wilding, J.P.; Sutton, C.J. Correlations between night eating, sleep quality, and excessive daytime sleepiness in a severely obese UK population. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.G.; Wei, C.; Bartlett, S.J.; Lang, J.; Wise, R.A.; Dixon, A.E. Obesity and symptoms of depression contribute independently to the poor asthma control of obesity. Respir. Med. 2014, 108, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauri, M.; Rucci, P.; Calderone, A.; Santini, F.; Oppo, A.; Romano, A.; Rinaldi, S.; Armani, A.; Polini, M.; Pinchera, A.; et al. Axis I and II disorders and quality of life in bariatric surgery candidates. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 69, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Kerver, G.A.; Schaefer, L.M.; Hawkins, M.A.W.; Crowther, J.H.; Duncan, J. Eating expectancies before bariatric surgery: Assessment and associations with weight loss trajectories. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abilés, V.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, S.; Abilés, J.; Mellado, C.; García, A.; de la Cruz, A.P.; Fernández-Santaella, M.C. Psychological characteristics of morbidly obese candidates for bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, N.; Tanaka, S.; Hirata, N.; Ogino, S.; Ozaki, N. A battery of self-screening instruments and self-reported body frame could not detect eating disorders among college students. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashino, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Takegami, M.; Nakayama, T.; Sokejima, S.; Fukuhara, S. Association between number of comorbid conditions, depression, and sleep quality using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: Results from a population-based survey. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapaport, M.H.; Clary, C.; Fayyad, R.; Endicott, J. Quality-of-life impairment in depressive and anxiety disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.M.; Tweardy, S.; Geliebter, A.; Avena, N.M. A Longitudinal Preliminary Study of Addiction-Like Responses to Food and Alcohol Consumption Among Individuals Undergoing Weight Loss Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 2700–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sham, P.C.; Owen, M.J.; He, L. Meta-analysis shows significant association between dopamine system genes and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2276–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ptácek, R.; Kuzelová, H.; Stefano, G.B. Dopamine D4 receptor gene DRD4 and its association with psychiatric disorders. Med. Sci. Monit. 2011, 17, Ra215–Ra220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patte, K.A.; Davis, C.A.; Levitan, R.D.; Kaplan, A.S.; Carter-Major, J.; Kennedy, J.L. A Behavioral Genetic Model of the Mechanisms Underlying the Link Between Obesity and Symptoms of ADHD. J. Atten. Disord. 2020, 24, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza, M.; Garolera, M.; Jurado, M.A.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Hernan, I.; Sánchez-Garre, C.; Vernet-Vernet, M.; Sender-Palacios, M.J.; Marques-Iturria, I.; Pueyo, R.; et al. Dopamine genes (DRD2/ANKK1-TaqA1 and DRD4-7R) and executive function: Their interaction with obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avsar, O.; Kuskucu, A.; Sancak, S.; Genc, E. Are dopaminergic genotypes risk factors for eating behavior and obesity in adults? Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 654, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallgatter, A.J.; Lesch, K.P. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome as a natural model for COMT haploinsufficiency-related dopaminergic dysfunction in ADHD. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 10, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leehr, E.J.; Schag, K.; Brückmann, C.; Plewnia, C.; Zipfel, S.; Nieratschker, V.; Giel, K.E. A Putative Association of COMT Val(108/158)Met with Impulsivity in Binge Eating Disorder. Eur. Eat Disord. Rev. 2016, 24, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Ding, M.; Liu, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.-C.; Pang, H.; Xing, J.X.; Xuan, J.F.; Xia, X.; Wang, B.J.; et al. The GABRB3 Polymorphism and its Association with Schizophrenia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Tafti, M.; Landolt, H.P. Catechol-O-methyltransferase, dopamine, and sleep-wake regulation. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 22, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawinski, P.; Tegelkamp, S.; Sander, C.; Häntzsch, M.; Huang, J.; Mauche, N.; Scholz, M.; Spada, J.; Ulke, C.; Burkhardt, R.; et al. Time to wake up: No impact of COMT Val158Met gene variation on circadian preferences, arousal regulation and sleep. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, S.; Carola, V.; Cerniglia, L.; Bussone, S.; Bevilacqua, A.; Tambelli, R. The μ-opioid receptor gene A118G polymorphism is associated with insecure attachment in children with disruptive mood regulation disorder and their mothers. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.M.; Rushing, B.G.; Tapia Menchaca, K.Y. Variation of the human mu-opioid receptor (OPRM1) gene predicts vulnerability to frustration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peciña, M.; Love, T.; Stohler, C.S.; Goldman, D.; Zubieta, J.K. Effects of the Mu opioid receptor polymorphism (OPRM1 A118G) on pain regulation, placebo effects and associated personality trait measures. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanos, P.K.; Zhuo, J.; Robison, L.; Kim, R.; Ananth, M.; Choai, I.; Grunseich, A.; Grissom, N.M.; George, R.; Delis, F.; et al. Suboptimal maternal diets alter mu opioid receptor and dopamine type 1 receptor binding but exert no effect on dopamine transporters in the offspring brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2018, 64, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzerouk, F.; Djerada, Z.; Bertin, E.; Barrière, S.; Gierski, F.; Kaladjian, A. Contributions of Emotional Overload, Emotion Dysregulation, and Impulsivity to Eating Patterns in Obese Patients with Binge Eating Disorder and Seeking Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, M.; Boncompagni, I.; Forte, G.; Guarino, A.; Favieri, F. Emotion and overeating behavior: Effects of alexithymia and emotional regulation on overweight and obesity. Eat Weight Disord. 2020, 25, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereidouni, F.; Atef-Vahid, M.K.; Fathali Lavasani, F.; Jamshidi Orak, R.; Klonsky, E.D.; Pazooki, A. Are Iranian obese women candidate for bariatric surgery different cognitively, emotionally and behaviorally from their normal weight counterparts? Eat Weight Disord. 2015, 20, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavender, J.M.; King, W.C.; Kalarchian, M.A.; Devlin, M.J.; Hinerman, A.; Gunstad, J.; Marcus, M.D.; Mitchell, J.E. Examining emotion-, personality-, and reward-related dispositional tendencies in relation to eating pathology and weight change over seven years in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS) study. J. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 120, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Brodie, M.S.; Pandey, S.C.; Cadet, J.L.; Gupta, A.; Elman, I.; Thanos, P.K.; Gondre-Lewis, M.C.; Baron, D.; Kazmi, S.; et al. Researching Mitigation of Alcohol Binge Drinking in Polydrug Abuse: KCNK13 and RASGRF2 Gene(s) Risk Polymorphisms Coupled with Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Guiding Precision Pro-Dopamine Regulation. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bowirrat, A.; Gomez, L.L.; Baron, D.; Elman, I.; Giordano, J.; Jalali, R.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Modestino, E.J.; Gold, M.S.; et al. Hypothesizing in the Face of the Opioid Crisis Coupling Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Testing with Electrotherapeutic Nonopioid Modalities Such as H-Wave Could Attenuate Both Pain and Hedonic Addictive Behaviors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereczkei, A.; Barta, C.; Magi, A.; Farkas, J.; Eisinger, A.; Király, O.; Belik, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Szekely, A.; Sasvári-Székely, M.; et al. FOXN3 and GDNF Polymorphisms as Common Genetic Factors of Substance Use and Addictive Behaviors. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Han, D.; Gupta, A.; Baron, D.; Braverman, E.R.; Dennen, C.A.; Kazmi, S.; Llanos-Gomez, L.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Elman, I.; et al. Statistical Validation of Risk Alleles in Genetic Addiction Risk Severity (GARS) Test: Early Identification of Risk for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) in 74,566 Case-Control Subjects. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Gondre Lewis, M.C.; Simpatico, T.A.; Ceccanti, M.; Steinberg, B.; Modestino, E.J.; Thanos, P.K.; Baron, D.; McLaughlin, T.; et al. Exploration of Epigenetic State Hyperdopaminergia (Surfeit) and Genetic Trait Hypodopaminergia (Deficit) During Adolescent Brain Development. Curr. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 10, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, E.D.; Bowirrat, A.; Gupta, A.; Giordano, J.; A Dennen, C.; R Braverman, E.; D Badgaiyan, R.; McLaughlin, T.; Baron, D.; Blum, K. The Future is Now for Precision Genomic Addiction Medicine as a Frontline Modality for Inducing “Dopamine Homeostasis” in Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS). Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennen, C.A.; Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Thanos, P.K.; Elman, I.; Ceccanti, M.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; McLaughlin, T.; Gupta, A.; Bajaj, A.; et al. Genetic Addiction Risk Severity Assessment Identifies Polymorphic Reward Genes as Antecedents to Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS) Hypodopaminergia’s Effect on Addictive and Non-Addictive Behaviors in a Nuclear Family. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, K.; Oscar-Berman, M.; Femino, J.; Waite, R.L.; Benya, L.; Giordano, J.; Borsten, J.; Downs, W.B.; Braverman, E.R.; Loehmann, R.; et al. Withdrawal from Buprenorphine/Naloxone and Maintenance with a Natural Dopaminergic Agonist: A Cautionary Note. J. Addict. Res. Ther. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blum, K.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Agan, G.; Fratantonio, J.; Simpatico, T.; Febo, M.; Haberstick, B.C.; Smolen, A.; Gold, M.S. Molecular Genetic Testing in Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS): Facts and Fiction. J. Reward Defic. Syndr. 2015, 1, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; Elman, I.; Alim, T.; Chapman, E.; Settles-Reaves, B.; Galvao, C.; Gold, M.S.; Baron, D.; Kazmi, S.; Gardner, E.; et al. Frequency of the Dopamine Receptor D3 (rs6280) vs. Opioid Receptor µ1 (rs1799971) Polymorphic Risk Alleles in Patients with Opioid Use Disorder: A Preponderance of Dopaminergic Mechanisms? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Lott, L.; Siwicki, D.; Fried, L.; Hauser, M.; Simpatico, T.; Baron, D.; Howeedy, A.; Badgaiyan, R.D. Genetic Addiction Risk Score (GARS™) as a Predictor of Substance Use Disorder: Identifying Predisposition Not Diagnosis. Curr. Trends Med. Diagn. Methods 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, A.; Blum, K.; Bowirrat, A.; Gupta, A.; Baron, D.; Fugel, D.; Nicholson, A.; Fitch, T.; Downs, B.W.; Bagchi, D.; et al. DNA Directed Pro-Dopamine Regulation Coupling Subluxation Repair, H-Wave® and Other Neurobiologically Based Modalities to Address Complexities of Chronic Pain in a Female Diagnosed with Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS): Emergence of Induction of “Dopamine Homeostasis” in the Face of the Opioid Crisis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, K.; Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; Baron, D.; Thanos, P.K.; Braverman, E.R.; Neary, J.; Elman, I.; Badgaiyan, R.D. Introducing Precision Addiction Management of Reward Deficiency Syndrome, the Construct That Underpins All Addictive Behaviors. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blum, K.; Baron, D.; Hauser, M.; Henriksen, S.; Thanos, P.K.; Black, C.; Siwicki, D.; Modestino, E.J.; Downs, B.W.; Badgaiyan, S.; et al. Americas’ opioid/psychostimulant epidemic would benefit from general population early identification of genetic addiction risk especially in children of alcoholics (COAs). J. Syst. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, D.F.; Stein, M.B.; Wendt, F.R.; Pathak, G.A.; Zhou, H.; Aslan, M.; Quaden, R.; Harrington, K.M.; Nuñez, Y.Z.; Overstreet, C.; et al. Bi-ancestral depression GWAS in the Million Veteran Program and meta-analysis in >1.2 million individuals highlight new therapeutic directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoum, A.S.; Colbert, S.M.C.; Johnson, E.C.; Huggett, S.B.; Deak, J.D.; Pathak, G.A.; Jennings, M.V.; Paul, S.E.; Karcher, N.R.; Hansen, I.; et al. Multivariate genome-wide association meta-analysis of over 1 million subjects identifies loci underlying multiple substance use disorders. Nat. Ment. Health 2023, 1, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


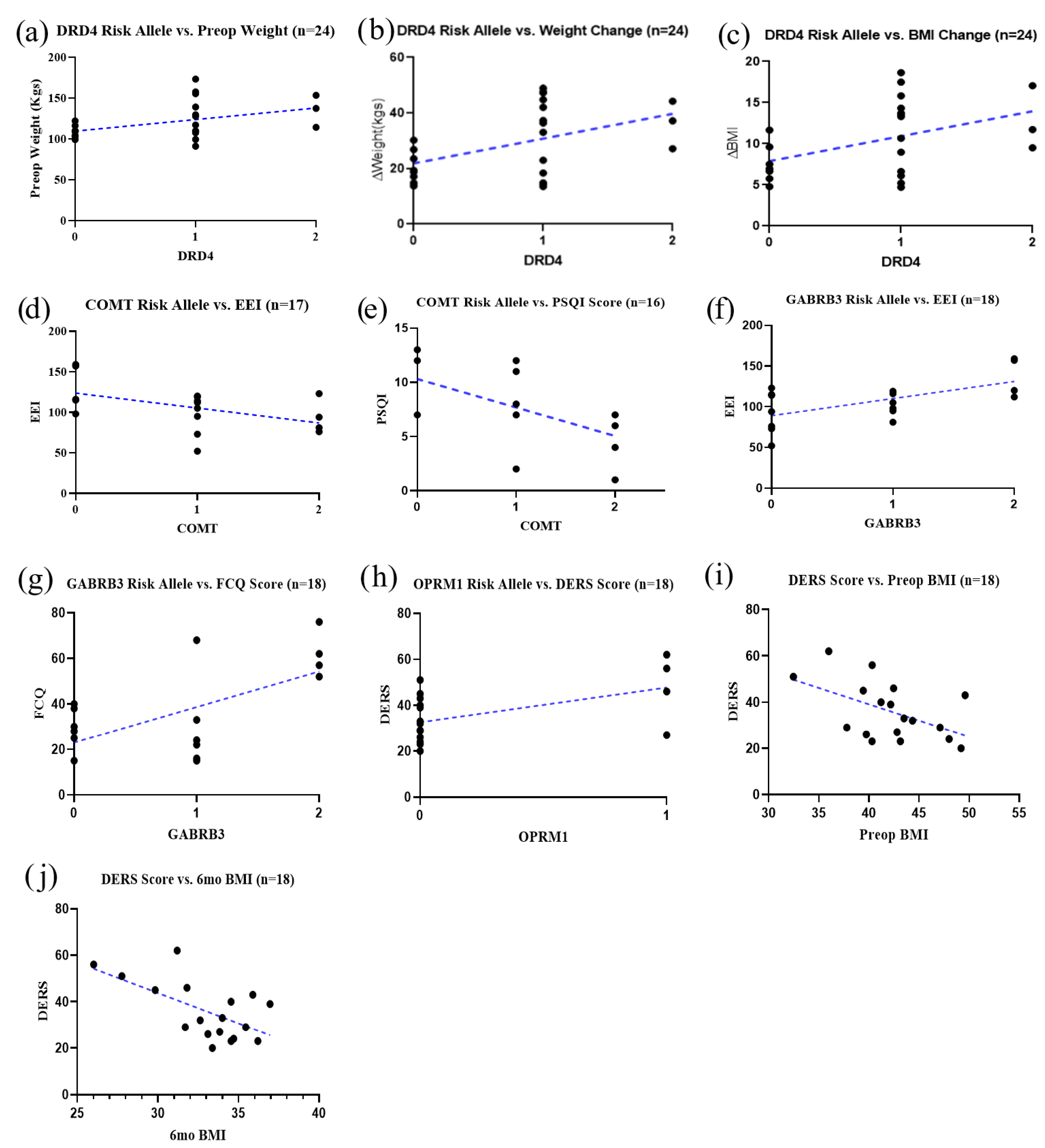
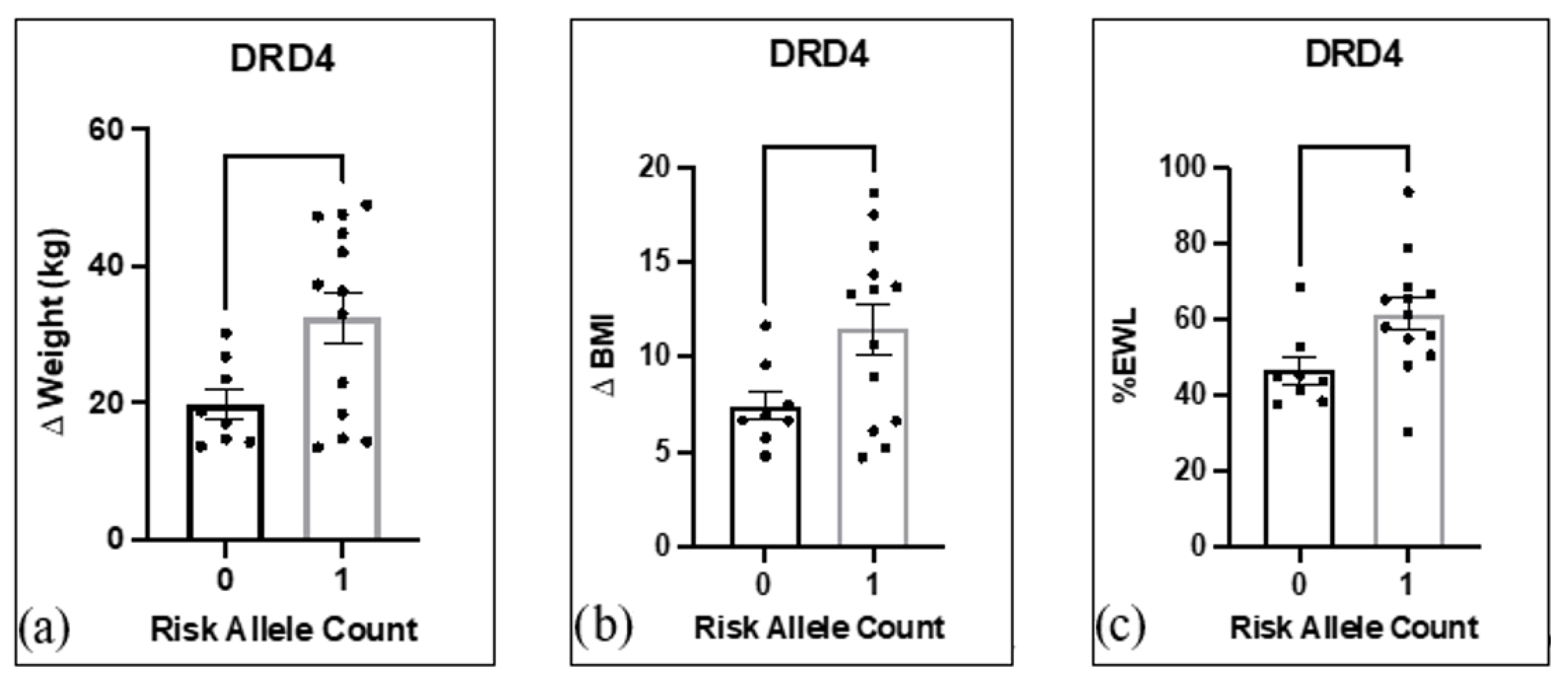
| Age (years) | M = 47 ± 12, range: 22–72 |
| Sex | 90% Female |
| Race | 85% White |
| Weight (kgs) | M = 118, SD = 20.8 |
| BMI | M = 43, SD = 6.0 |
| Surgery | 26% RYGB (bypass) 74% Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy |
| Childhood Weight Status | 8% Underweight; 38% Healthy Weight; 42% Overweight 12% Obese |
| Marital Status | 27% Single/Never Married; 41% Married/Living with Spouse; 11% Living with Intimate Partner 14% Divorced 7% Widowed |
| Employment | 51% Full-time; 11% Part-time 11% Not employed, but looking 27% Not employed, not looking |
| Education | 96% Graduated from High School/GED 50% College Degree (Associates/Bachelors) 15% College Degree (Masters) |
| Income Last Year | 27% Less Than $10,000 27% $1500–$55,000 23% $55,000–$99,000 12% $100,000 and over |
| Total Population (n = 24) | VSG (n = 19) | RYGB (n = 5) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean BMI ± SD | 33.3 ± 3.7 | 32.7 ± 3.6 | 35.5 ± 4.2 |
| Mean△BMI ± SD | 10.3 ± 4.3 | 9.8 ± 4.3 | 12.1 ± 4.4 |
| %EWL ± SD | 56.0 ± 13.8 | 56.3 ± 14.3 | 54.5 ± 14.7 |
| Eating Attitudes Test-26 | Total: 14.9 (8.1) |
|---|---|
| Food Cravings Questionnaire—Trait Reduced (FCQ-T) |
|
| Eating Expectancies Inventory |
|
| Modified Yale Food Addiction Scale 2.0 | Mean Symptom Count (SD): 1.32 (1.23) No Food Addiction (%): 61 Mild (%): 31 Moderate (%): 4 Severe (%): 4 |
| Weight-Influenced Self Esteem Questionnaire | M (SD): 1.6 (1.3) |
| Difficulties in Emotion Regulation Scale—Short Form | Total Mean (SD): 33.81 (10.96)
|
| Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale | Total Score (Mean, range): 12.7, 0–35 No Depression (%): 69 Mild Depression (%): 8 Probable Depression (%): 23 |
| Chronic Stress Index | Perceived Everyday Unfair Treatment (Mean Score): 1.8 Major Negative Life Events in Past Year: 1.13 |
| Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire | M (SD): 3.24 (0.89) |
| Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index | M (SD): 8.0 (3.74) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thanos, P.K.; Hanna, C.; Mihalkovic, A.; Hoffman, A.B.; Posner, A.R.; Busch, J.; Smith, C.; Badgaiyan, R.D.; Blum, K.; Baron, D.; et al. The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13071164
Thanos PK, Hanna C, Mihalkovic A, Hoffman AB, Posner AR, Busch J, Smith C, Badgaiyan RD, Blum K, Baron D, et al. The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(7):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13071164
Chicago/Turabian StyleThanos, Panayotis K., Colin Hanna, Abrianna Mihalkovic, Aaron B. Hoffman, Alan R. Posner, John Busch, Caroline Smith, Rajendra D. Badgaiyan, Kenneth Blum, David Baron, and et al. 2023. "The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 7: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13071164
APA StyleThanos, P. K., Hanna, C., Mihalkovic, A., Hoffman, A. B., Posner, A. R., Busch, J., Smith, C., Badgaiyan, R. D., Blum, K., Baron, D., Mastrandrea, L. D., & Quattrin, T. (2023). The First Exploratory Personalized Medicine Approach to Improve Bariatric Surgery Outcomes Utilizing Psychosocial and Genetic Risk Assessments: Encouraging Clinical Research. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(7), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13071164










