Study of Angiogenic, Pro-Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Congenital and Acquired Cholesteatomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Selection
2.2. Immunofluorescence Analyses
2.3. Fluorescence Spectrum Intensity Analysis
2.4. Western Blot
2.5. Statistical Data
3. Results
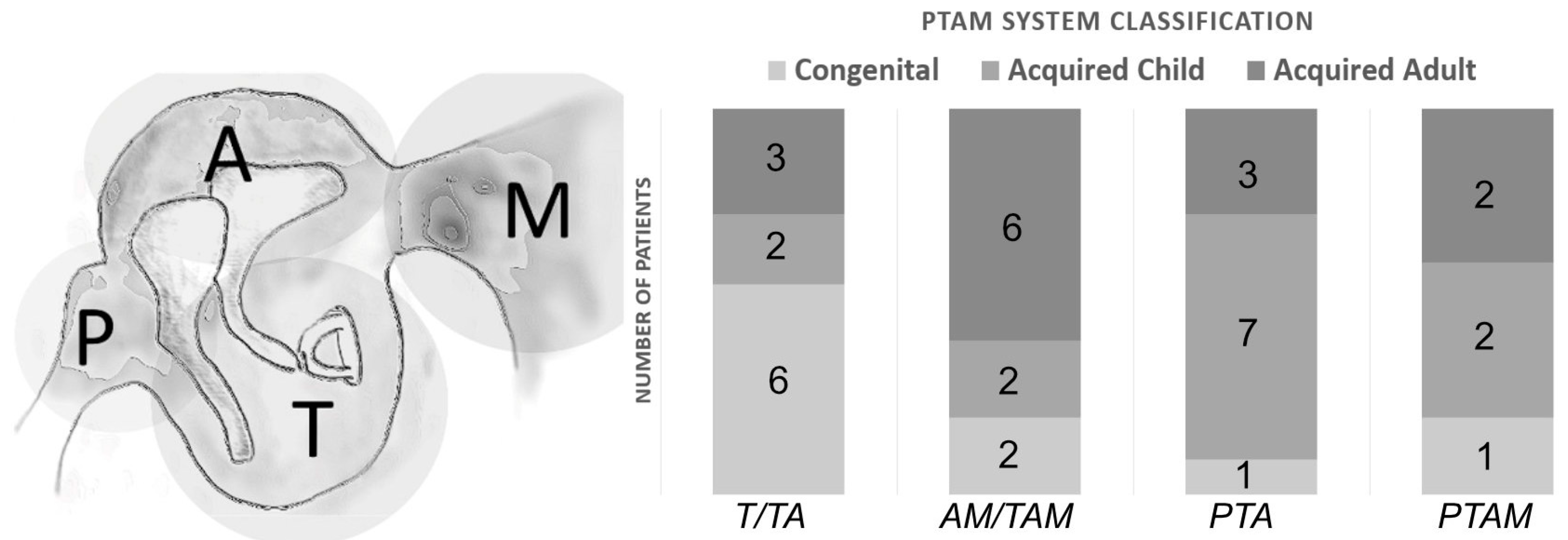
3.1. Patients
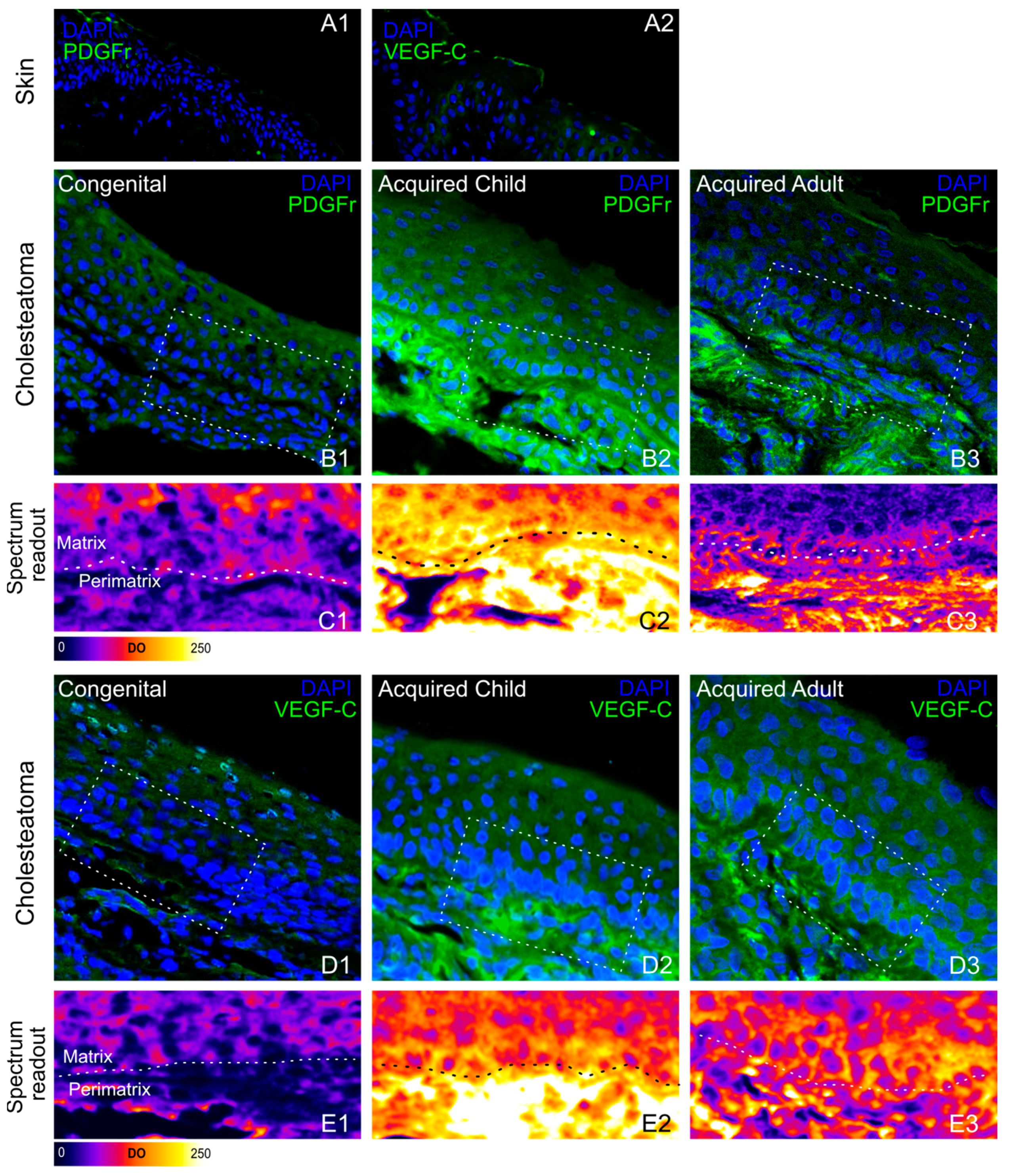
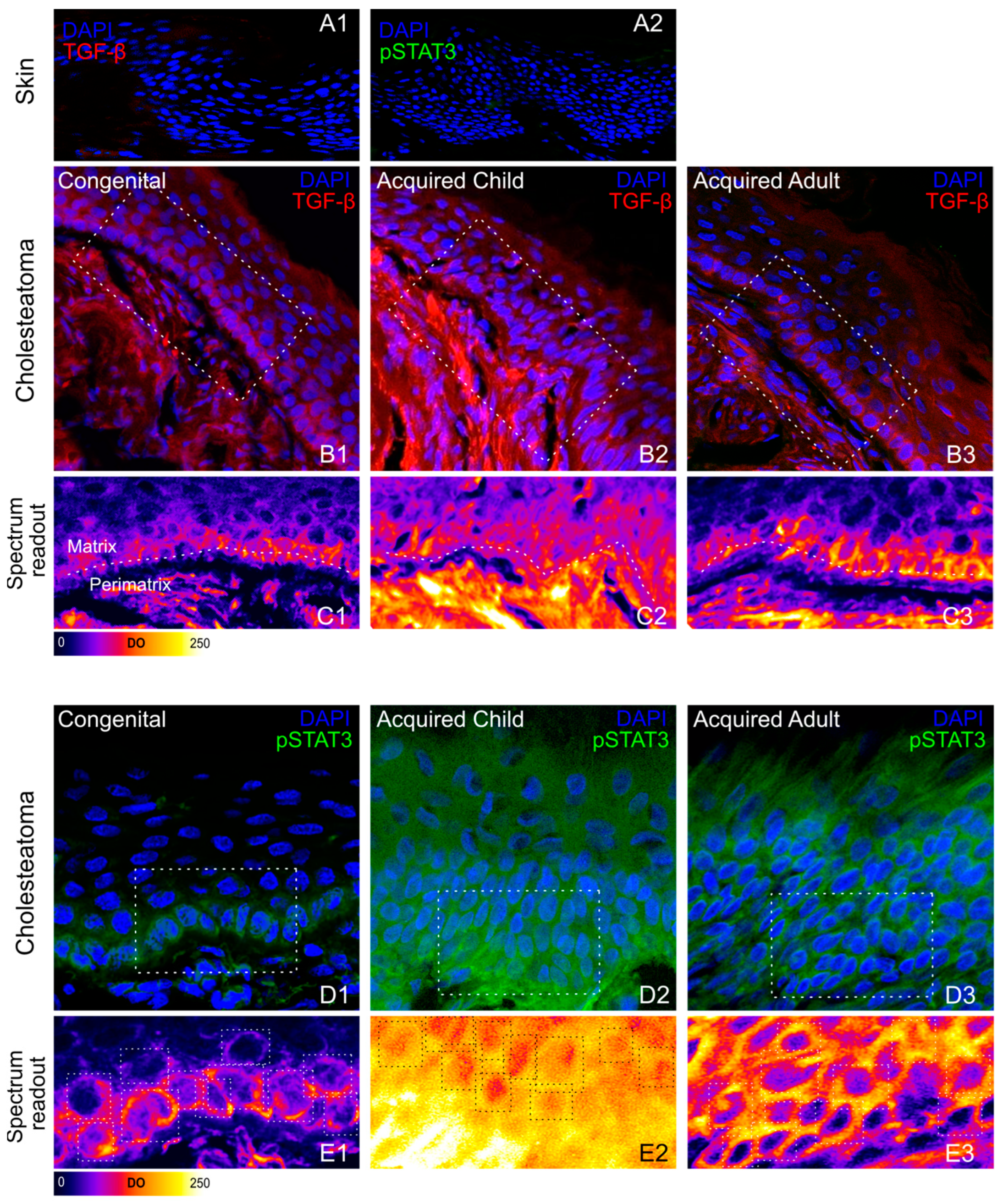
3.2. Immunohistochemical Phenotyping of Cholesteatoma
3.3. Western Blot Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuo, C.-L.; Shiao, A.-S.; Yung, M.; Sakagami, M.; Sudhoff, H.; Wang, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Lien, C.-F. Updates and Knowledge Gaps in Cholesteatoma Research. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 854024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashishth, A.; Nagar, T.R.S.; Mandal, S.; Venkatachalam, V.P. Extensive intratemporal cholesteatomas: Presentation, complications and surgical outcomes. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 272, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.S.; Kim, H.G.; Jung, D.J.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.-Y. Clinical Aspects and Surgical Outcomes of Congenital Cholesteatoma in 93 Children: Increasing Trends of Congenital Cholesteatoma from 1997 through 2012. J. Audiol. Otol. 2016, 20, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tos, M. A New Pathogenesis of Mesotympanic (Congenital) Cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, B. Tubal closing failure in retraction type cholesteatoma and adhesive middle ear lesions. Acta Otolaryngol. 1978, 86, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, B.; Magnuson, B. Evacuation of the Middle Ear by Sniffing: A Cause of High Negative Pressure and Development of Middle Ear Disease. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1984, 92, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, P.; Holmquist, J. Mastoid volume and eustachian tube function in ears with cholesteatoma. Am. J. Otol. 1987, 8, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sadé, J. Cellular Differentiation of the Middle Ear Lining. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1971, 80, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhoff, H.; Tos, M. Pathogenesis of attic cholesteatoma: Clinical and immunohistochemical support for combination of retraction theory and proliferation theory. Am. J. Otol. 2000, 21, 786–792. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.L. Etiopathogenesis of Acquired Cholesteatoma: Prominent Theoriesand Recent Advances in Biomolecular Research. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Oshima, S.; Takahashi, K.; Takahashi, S. Pediatric middle ear cholesteatoma: The comparative study of congenital cholesteatoma and acquired cholesteatoma. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2015, 273, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikka, K.; Sharma, S.C.; Thakar, A.; Dattagupta, S. Evaluation of epithelial proliferation in paediatric and adult cholesteatomas using the Ki-67 proliferation marker. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 126, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Zhan, H.; Peng, S. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor Ki67 and p16 in human middle ear cholesteatoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008, 22, 987–991. [Google Scholar]
- Maniu, A.; Harabagiu, O.; Perde Schrepler, M.; Catana, A.; Fanuta, B.; Mogoanta, C.A. Molecular biology of cholesteatoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzei, M.; Ventriglia, G.; Hagnia, M.; Antonopolous, A.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Dazert, S.; Hildmann, H.; Sudhoff, H. Osteoclast Stimulating and Differentiating Factors in Human Cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louw, L. Acquired cholesteatoma: Summary of the cascade of molecular events. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2013, 127, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welkoborsky, H.J. Current concepts of the pathogenesis of acquired middle ear cholesteatoma. Laryngorhinootologie 2011, 90, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S.; Schilling, V.; Wollenberg, B.; Mack, B.; Nerlich, A. Localization of transforming growth factor-beta-expressing cells and comparison with major extracellular components in aural cholesteatoma. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1997, 106, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.A.; Nakata, S.; Sayed, R.H.; Ueda, H.; Badawy, B.S.; Nishimura, Y.; Kojima, T.; Iwata, N.; Ahmed, A.R.; Dahy, K.; et al. Pathogenesis and Bone Resorption in Acquired Cholesteatoma: Current Knowledge and Future Prospectives. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 9, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornhoffer, J.L.; Friedman, A.B.; Gluth, M.B. Management of acquired cholesteatoma in the pediatric population. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 21, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albino, A.P.; Kimmelman, C.P.; Parisier, S.C. Cholesteatoma: A molecular and cellular puzzle. Am. J. Otol. 1998, 19, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schulz, P.; Bujía, J.; Holly, A.; Shilling, V.; Kastenbauer, E. Possible autocrine growth stimulation of cholesteatoma epithelium by transforming growth factor alpha. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1993, 14, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhoff, H.; Dazert, S.; Gonzales, A.M.; Borkowski, G.; Park, S.Y.; Baird, A.; Hildmann, H.; Ryan, A.F. Angiogenesis and angiogenic growth factors in middle ear cholesteatoma. Am. J. Otol. 2000, 21, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.M.; Huang, C.; Abramson, M. Interleukin 1 causing bone destruction in middle ear cholesteatoma. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1990, 103, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruyama, T.; Furukawa, M.; Kusunoki, T.; Onoda, J.; Ikeda, K. Expression of IL-17 and Its Role in Bone Destruction in Human Middle Ear Cholesteatoma. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2010, 72, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xie, S.; Chen, X.; Rao, X.; Ren, H.; Hu, B.; Yin, T.; Xiang, Y.; Ren, J. Activation of the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in human middle ear cholesteatoma epithelium. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 709–715. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, M.A.; de Heer, E.; Ten Dijke, P.; Grote, J.J. Transforming growth factor beta and wound healing in human cholesteatoma. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Intermitted Otorrhea | TM Perforation | Otalgia | Hearing Impairment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 10% | 0% | 40% | 80% |
| CA | 53.80% | 69.20% | 76.92% | 53.84% |
| AA | 42.86% | 57.15% | 42.85% | 50% |
| Number of Patients | Congenital Form | Acquired Form (age < 16) | Acquired Form (age > 16) | |
| male | 29 | 8 | 10 | 11 |
| female | 8 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| mean age | 4.7 | 13.7 | 46.7 |
| Bone | Grading Score | Bone | Grading Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scutum | Intact = 0, Eroded = 1 | Sinus Plate | Intact = 0, Eroded = 1, Eroded with complications = 2 |
| Auditory ossicles | Intact = 0, One ossicle eroded = 1, ≥2 ossicles eroded = 2 | PCW | Intact = 0, Eroded without fistula = 1, Eroded with fistula = 2 |
| Tegmen | Intact = 0, Eroded = 1, Eroded with ICC = 2 | Mastoid | Free = 0, Eroded = 1, Abscess or fistula = 2 |
| Facial Canal | Intact = 0, Dehiscent = 1, facial palsy = 2 | Inner ear | Intact = 0, Erosion = 1, Fistula = 2 |
| Forms | Low Score (0–3) | Mid Score (3–6) | High Score (>6) |
| Acquired adult | 28.6% | 50% | 21.4% |
| Acquired child | 7.7% | 38.5% | 53.8% |
| Congenital | 70% | 20% | 10% |
| Optical Density (OD) | Skin | CC | AC | AA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF-C | 5.07 ± 1.59 | Matrix Peri-matrix | 76.46 ± 4.30 38.16 ± 1.88 | 81.21 ± 1.95 190.98 ± 11.91 | 78.65 ± 3.36 105.93 ± 4.11 |
| PDGFr | 7.76 ± 2.45 | Matrix Peri-matrix | 63.24 ± 3.58 37.34 ± 1.64 | 101.46 ± 5.21 227.51 ± 9.10 | 53.73 ± 1.75 94.97 ± 4.87 |
| TGF- β | 4.69 ± 0.52 | Matrix Peri-matrix | 27.06 ± 1.32 45.09 ± 5.63 | 79.08 ± 3.44 163.22 ± 9.40 | 61.17 ± 6.31 94.45 ± 3.04 |
| pSTAT3 | 17.64 ± 1.05 | Matrix Peri-matrix | 88.51 ± 5.97 26.31 ± 4.19 | 125.54 ± 4.88 37.86 ± 10.50 | 75.49 ± 2.72 18.34 ± 7.05 |
| IL-1β | 17.35 ± 1.55 | Matrix Peri-matrix | 38.41 ± 1.04 39.12 ± 0.93 | 36.14 ± 11.46 148.68 ± 4.07 | 39.55 ± 4.30 108.44 ± 9.47 |
| MATRIX | Skin/CC | Skin/AC | Skin/AA | CC/AC | CC/AA | AC/AA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF-C | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.31 | p = 0.693 | p = 0.474 |
| PDGFr | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.028 | p < 0.029 |
| TGF-β | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.022 |
| pSTAT3 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.063 | p < 0.001 |
| IL-1β | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.554 | p = 0.518 | p = 0.390 |
| PERI-MATRIX | Skin/CC | Skin/AC | Skin/AA | CC/AC | CC/AA | AC/AA |
| VEGF-C | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| PDGFr | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| TGF-β | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| pSTAT3 | p < 0.001 | p = 0.071 | p = 0.797 | p = 0.289 | p = 0.007 | p = 0.085 |
| IL-1β | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rolesi, R.; Paciello, F.; Paludetti, G.; De Corso, E.; Sergi, B.; Fetoni, A.R. Study of Angiogenic, Pro-Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Congenital and Acquired Cholesteatomas. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13081189
Rolesi R, Paciello F, Paludetti G, De Corso E, Sergi B, Fetoni AR. Study of Angiogenic, Pro-Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Congenital and Acquired Cholesteatomas. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(8):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13081189
Chicago/Turabian StyleRolesi, Rolando, Fabiola Paciello, Gaetano Paludetti, Eugenio De Corso, Bruno Sergi, and Anna Rita Fetoni. 2023. "Study of Angiogenic, Pro-Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Congenital and Acquired Cholesteatomas" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 8: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13081189
APA StyleRolesi, R., Paciello, F., Paludetti, G., De Corso, E., Sergi, B., & Fetoni, A. R. (2023). Study of Angiogenic, Pro-Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Congenital and Acquired Cholesteatomas. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(8), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13081189








